生态环境学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (2): 180-191.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2024.02.002
李霞1( ), 陈永昊1, 陈喆2,*(
), 陈永昊1, 陈喆2,*( ), 张国壮1, 唐梦雅1
), 张国壮1, 唐梦雅1
收稿日期:2023-12-01
出版日期:2024-02-18
发布日期:2024-04-03
通讯作者:
*陈喆。E-mail: 414409439@qq.com作者简介:李霞(1977年生),女,副教授,主要研究方向是地理信息技术及生态遥感。E-mail: lixia666@chd.edu.cn
基金资助:
LI Xia1( ), CHEN Yonghao1, CHEN Zhe2,*(
), CHEN Yonghao1, CHEN Zhe2,*( ), ZHANG Guozhuang1, TANG Mengya1
), ZHANG Guozhuang1, TANG Mengya1
Received:2023-12-01
Online:2024-02-18
Published:2024-04-03
摘要:
研究植被变化对区域生态修复具有重要意义。以中国沿海地区为例,基于归一化植被指数(NDVI)和降水、夜间灯光等自然和人为因子数据,运用Theil-Sen Median趋势分析+Mann-Kendall检验、最优参数地理探测器(OPGD)、相关分析和Hurst指数,多时空尺度探讨了中国沿海地区植被NDVI时空变化规律及其驱动力。结果表明:1)2001-2020年研究区植被状况较好,NDVI多年均值为0.762,具体到各分区,东北沿海的NDVI均值最高,其次是华南沿海,华东沿海和华北沿海;全区NDVI逐年变化率为0.019/10 a(P<0.01),不同分区的上升趋势从大到小为华南沿海、东北沿海、华北沿海和华东沿海,区域内植被状况不断改善,退耕还林还草和沿海防护林等生态工程效益不断显现;2)夜间灯光指数在全区各个因子中的解释力最大(q值为0.354),人为因素对NDVI的解释力明显大于自然因素,其对植被恢复产生了积极影响,并且随时间推移逐渐增强;3)两因子结合后的解释力大于单因子,表现为双因子增强和非线性增强。在全区范围内,影响最大的一对交互作用为土壤类型∩夜间灯光,其他分区则为日照时数∩夜间灯光(东北沿海地区),土壤类型∩夜间灯光(华北沿海和华东沿海地区),人口密度∩夜间灯光(华南沿海地区),自然因素和人类活动因素作用后影响力有了显著提升,但人类活动因素仍占据主导地位;4)Hurst指数均值为0.463,未来一段时间内,研究区内植被变化有66.3%的地区表现出一定的反持续性。研究结果有利于为中国沿海地区生态保护和高质量发展提供科学支撑。
中图分类号:
李霞, 陈永昊, 陈喆, 张国壮, 唐梦雅. 中国沿海地区植被NDVI时空变化及驱动力分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(2): 180-191.
LI Xia, CHEN Yonghao, CHEN Zhe, ZHANG Guozhuang, TANG Mengya. Analysis of Spatio-temporal Changes and Driving Vegetation NDVI in Coastal Areas of China[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2024, 33(2): 180-191.
| 气候因子 | 地表因子 | 人类活动因子 |
|---|---|---|
| 年降水量 (X1) | 高程 (X5) | GDP (X10) |
| 年均气温 (X2) | 坡度 (X6) | 人口密度 (X11) |
| 年均风速 (X3) | 地貌类型 (X7) | 夜间灯光 (X12) |
| 年日照时数 (X4) | 土壤类型 (X8) | 土地利用 (X13) |
| 植被类型 (X9) |
表1 中国沿海地区植被NDVI影响因子
Table 1 NDVI influencing factors of vegetation NDVI in coastal areas of China
| 气候因子 | 地表因子 | 人类活动因子 |
|---|---|---|
| 年降水量 (X1) | 高程 (X5) | GDP (X10) |
| 年均气温 (X2) | 坡度 (X6) | 人口密度 (X11) |
| 年均风速 (X3) | 地貌类型 (X7) | 夜间灯光 (X12) |
| 年日照时数 (X4) | 土壤类型 (X8) | 土地利用 (X13) |
| 植被类型 (X9) |
| 区域 | 单因子影响力排名 |
|---|---|
| 全区 | X12(0.354)>X10(0.311)>X13(0.310)>X8(0.225)>X11(0.210)> X9(0.191)>X7(0.178)>X6(0.170)>X5(0.169)>X3(0.110)>X1 (0.091)>X4(0.078)>X2(0.058) |
| 东北沿海 | X10(0.302)>X1(0.292)>X4(0.291)>X12(0.277)>X11(0.276)> X13(0.238)>X2(0.227)>X9(0.165)>X8(0.162)>X7(0.108)>X6 (0.104)>X3(0.086)>X5(0.078) |
| 华北沿海 | X8(0.292)>X13(0.237)>X1(0.220)>X10(0.170)>X12(0.164)> X3(0.151)>X9(0.146)>X4(0.130)>X7(0.114)>X11(0.112)>X6 (0.106)>X5(0.098)>X2(0.069) |
| 华东沿海 | X12(0.410)>X10(0.376)>X13(0.290)>X8(0.223)>X11(0.203)> X5(0.198)>X9(0.190)>X4(0.165)>X6(0.157)>X7(0.156)>X1 (0.155)>X3(0.110)>X2(0.067) |
| 华南沿海 | X12(0.540)>X5(0.493)>X10(0.483)>X13(0.432)>X11(0.428)>X7 (0.418)>X6(0.351)>X2(0.254)>X9(0.242)>X8(0.201)>X3(0.173)>X4(0.071)>X1(0.024) |
表2 中国沿海地区各分区单因子多年影响力排名
Table 2 Ranking of the long-term influence of single factors in different regions of coastal areas of China
| 区域 | 单因子影响力排名 |
|---|---|
| 全区 | X12(0.354)>X10(0.311)>X13(0.310)>X8(0.225)>X11(0.210)> X9(0.191)>X7(0.178)>X6(0.170)>X5(0.169)>X3(0.110)>X1 (0.091)>X4(0.078)>X2(0.058) |
| 东北沿海 | X10(0.302)>X1(0.292)>X4(0.291)>X12(0.277)>X11(0.276)> X13(0.238)>X2(0.227)>X9(0.165)>X8(0.162)>X7(0.108)>X6 (0.104)>X3(0.086)>X5(0.078) |
| 华北沿海 | X8(0.292)>X13(0.237)>X1(0.220)>X10(0.170)>X12(0.164)> X3(0.151)>X9(0.146)>X4(0.130)>X7(0.114)>X11(0.112)>X6 (0.106)>X5(0.098)>X2(0.069) |
| 华东沿海 | X12(0.410)>X10(0.376)>X13(0.290)>X8(0.223)>X11(0.203)> X5(0.198)>X9(0.190)>X4(0.165)>X6(0.157)>X7(0.156)>X1 (0.155)>X3(0.110)>X2(0.067) |
| 华南沿海 | X12(0.540)>X5(0.493)>X10(0.483)>X13(0.432)>X11(0.428)>X7 (0.418)>X6(0.351)>X2(0.254)>X9(0.242)>X8(0.201)>X3(0.173)>X4(0.071)>X1(0.024) |
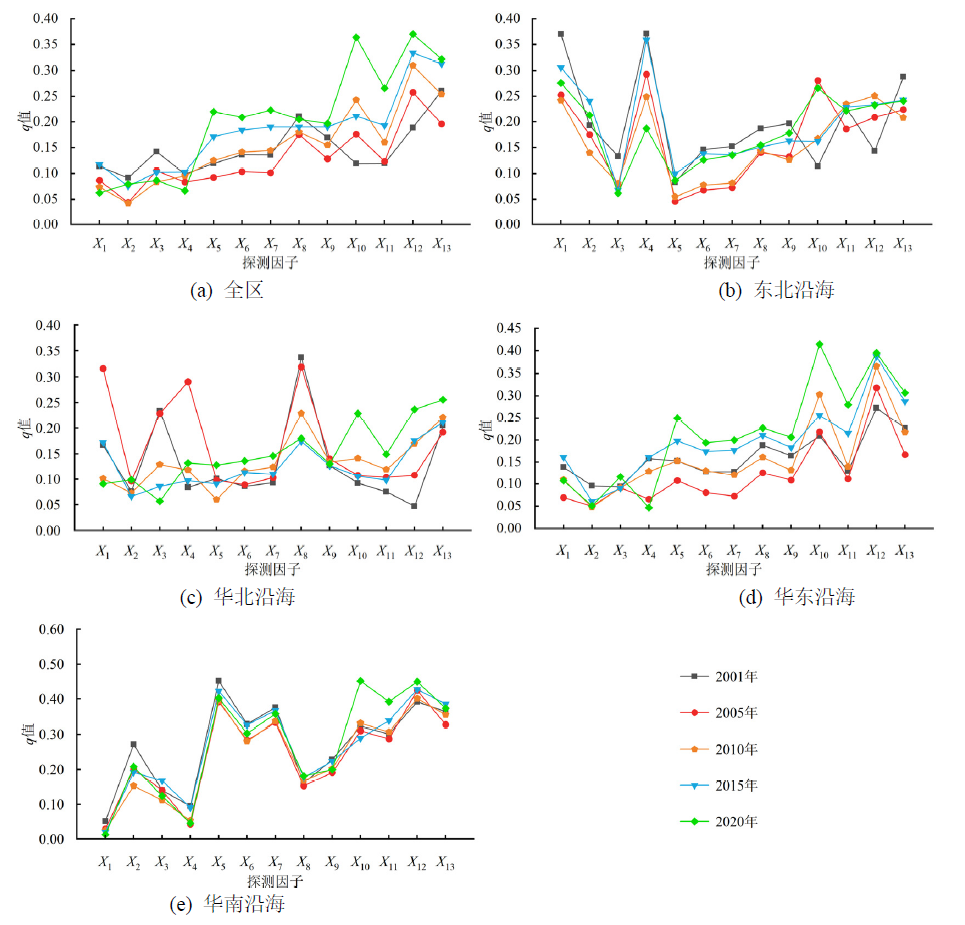
图5 2001—2020年中国沿海地区及各分区单因子q值变化 X1-X13分别代表年降水量、年均气温、年均风速、年日照时数、高程、坡度、地貌类型、土壤类型、植被类型、GDP、人口密度、夜间灯光、土地利用
Figure 5 Change of q value of single factor in coastal areas of China and subregions from 2001 to 2020
| 区域 | 交互因子 | q值 |
|---|---|---|
| 全区 | X8∩X12 | 0.540 |
| X12∩X13 | 0.512 | |
| X8∩X10 | 0.495 | |
| X10∩X13 | 0.479 | |
| 东北沿海 | X4∩X12* | 0.593 |
| X1∩X12 | 0.562 | |
| X4∩X10 | 0.550 | |
| X1∩X10* | 0.520 | |
| 华北沿海 | X8∩X12* | 0.481 |
| X8∩X13 | 0.470 | |
| X8∩X10* | 0.469 | |
| X8∩X11* | 0.449 | |
| 华东沿海 | X8∩X12 | 0.668 |
| X12∩X13 | 0.549 | |
| X9∩X12 | 0.539 | |
| X10∩X13 | 0.516 | |
| 华南沿海 | X11∩X12 | 0.668 |
| X5∩X12 | 0.667 | |
| X6∩X12 | 0.666 | |
| X7∩X12 | 0.662 |
表3 中国沿海地区各区域交互作用影响力前四位
Table 3 Coastal areas of China ranked the top four in terms of regional interaction influence
| 区域 | 交互因子 | q值 |
|---|---|---|
| 全区 | X8∩X12 | 0.540 |
| X12∩X13 | 0.512 | |
| X8∩X10 | 0.495 | |
| X10∩X13 | 0.479 | |
| 东北沿海 | X4∩X12* | 0.593 |
| X1∩X12 | 0.562 | |
| X4∩X10 | 0.550 | |
| X1∩X10* | 0.520 | |
| 华北沿海 | X8∩X12* | 0.481 |
| X8∩X13 | 0.470 | |
| X8∩X10* | 0.469 | |
| X8∩X11* | 0.449 | |
| 华东沿海 | X8∩X12 | 0.668 |
| X12∩X13 | 0.549 | |
| X9∩X12 | 0.539 | |
| X10∩X13 | 0.516 | |
| 华南沿海 | X11∩X12 | 0.668 |
| X5∩X12 | 0.667 | |
| X6∩X12 | 0.666 | |
| X7∩X12 | 0.662 |
| [1] |
CHEN B Z, XU G, COOPS N, et al., 2016. Satellite-observed changes in terrestrial vegetation growth trends across the Asia-Pacific region associated with land cover and climate from 1982 to 2011[J]. International Journal of Digital Earth, 9(11): 1055-1076.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
FENSHOLT R, PROUND S R, 2012. Evaluation of earth observation based global long term vegetation trends—Comparing GIMMS and MODIS global NDVI time series[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 119: 131-147.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
MENG Z Q, LIU M, GAO C C, et al., 2020. Greening and browning of the coastal areas in mainland China: Spatial heterogeneity, seasonal variation and its influential factors[J]. Ecological Indicators, 110: 105888.
DOI URL |
| [4] | SONG Y Z, WANG J F, GE Y, et al., 2020. An optimal parameters-based geographical detector model enhances geographic characteristics of explanatory variables for spatial heterogeneity analysis: Cases with different types of spatial data[J]. GIScience & Remote Sensing, 57(5): 593-610. |
| [5] |
YAN D H, XU T, GIRMA A, 2017. Regional correlation between precipitation and vegetation in the Huang-Huai-Hai river basin, China[J]. Water, 9(8): 557-567.
DOI URL |
| [6] | YAO J Q, ZHAO Y, CHEN Y N, et al., 2018. Multi-scale assessments of droughts: A case study in Xinjiang, China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 6(30): 444-452. |
| [7] |
VERBESSELT J, HYNDMAN R, 2010. Detecting trend and seasonal changes in satellite image time series[J]. Remote sensing of Environment, 114(1): 106-115.
DOI URL |
| [8] | 陈效逑, 王恒, 2009. 1982-2003年内蒙古植被带和植被覆盖度的时空变化[J]. 地理学报, 64(1): 84-94. |
|
CHEN X Q, WANG H, 2009. Spatial and temporal variations of vegetation belts and vegetation cover degrees in inner mongolia from 1982 to 2003[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 64(1): 84-94.
DOI |
|
| [9] | 陈雪萍, 赵学勇, 张晶, 等, 2022. 基于地理探测器的科尔沁沙地植被NDVI时空变化特征及其驱动因素[J]. 植物生态学报, 47(8): 1-12. |
|
CHEN X P, ZHAO X Y, ZHANG J, et al., 2022. Variation of NDVI spatio-temporal characteristics and its driving factors based on geodetector model in Horqin Sandy Land, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 47(8): 1-12.
DOI URL |
|
| [10] |
陈文裕, 夏丽华, 徐国良, 等, 2022. 2000-2020年珠江流域NDVI动态变化及影响因素研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 31(7): 1306-1316.
DOI |
| CHEN W Y, XIA L H, XU G L, et al., 2022. Dynamic variation of NDVI and its influencing factors in the pearl river basin from 2000 to 2020[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 31(7): 1306-1316. | |
| [11] |
曹子阳, 吴志峰, 匡耀求, 等, 2015. DMSP/OLS夜间灯光影像中国区域的校正及应用[J]. 地球信息科学学报, 17(9): 1092-1102.
DOI |
| CAO Z Y, WU Z F, KUANG Y Q, et al., 2015. Correction of DMSP/OLS night-time light images and its application in China[J]. Journal of Geo-information Science, 17(9): 1092-1102. | |
| [12] | 崔浩楠, 罗海江, 张学珍, 2021. 1982-2019年长江经济带植被覆盖变化的时空特征[J]. 生态学杂志, 40(8): 2517-2529. |
| CUI H N, LUO H J, ZHANG X Z. Temporal and spatial characteristics of green vegetation cover changes in the Yangtze river economic belt from 1982 to 2019[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 40(8): 2517-2529. | |
| [13] |
董玉祥, 徐茜, 杨忍, 等, 2017. 基于地理探测器的中国陆地热带北界探讨[J]. 地理学报, 72(1): 135-147.
DOI |
| DONG Y X, XU Q, YANG R, et al., 2017. Delineation of the northern border of the tropical zone of China's mainland using Geodetecto r[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 72(1): 135-147. | |
| [14] |
丁悦, 蔡建明, 任周鹏, 等, 2014. 基于地理探测器的国家级经济技术开发区经济增长率空间分异及影响因素[J]. 地理科学进展, 33(5): 657-666.
DOI |
|
DING Y, CAI J M, REN Z P, et al., 2014. Spatial disparities of economic growth rate of China's National-level ETDZs and their determinants based on geographical detector analysis[J]. Progress in Geography, 33(5): 657-666.
DOI |
|
| [15] | 耿庆玲, 陈晓青, 赫晓慧, 等, 2022. 中国不同植被类型归一化植被指数对气候变化和人类活动的响应[J]. 生态学报, 42(9): 3557-3568. |
| GENG Q L, CHEN X Q, HE X H, et al., 2022. Vegetation dynamics and its response to climate change and human based on different vegetation types in China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 42(9): 3557-3568. | |
| [16] | 国家统计局, 2022. 中国统计年鉴2022[M]. 北京: 中国统计出版社:36. |
| National Bureau of Statistics, 2022. China Statistical Yearbook 2022[M]. Beijing: China Statistics Press:36. | |
| [17] | 金岩松, 金凯, 王飞, 等, 2023. 气候变化和人类活动对东部沿海地区NDVI变化的影响分析[J]. 环境科学, 44(6): 3329-3342. |
| JIN Y S, JIN K, WANG F, et al., 2023. Impacts of climate change and human activities on NDVI change in eastern coastal areas of China[J]. Environmental Science, 44(6): 3329-3342. | |
| [18] |
李梦华, 韩颖娟, 赵慧, 等, 2022. 基于地理探测器的宁夏植被覆盖度时空变化特征及其驱动因子分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 31(7): 1317-1325.
DOI |
| LI M H, HAN Y J, ZHAO H, et al., 2022. Analysis on spatial-temporal variation characteristics and driving factors of fractional vegetation cover in ningxia based on geographical detector[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 31(7): 1317-1325. | |
| [19] |
李琛, 吴映梅, 高彬嫔, 等, 2022. 高原湖泊乡村聚落空间分异及驱动力探测——以环洱海地区为例[J]. 经济地理, 42(4): 220-229.
DOI |
| LI C, WU Y M, GAO B P, et al., 2022. Spatial differentiation and driving factors of rural settlement in Plateau Lake: A case study of the area around the Erhai[J]. Economic Geography, 42(4): 220-229. | |
| [20] |
李建国, 袁冯伟, 赵宴青, 等, 2020. 中国东部沿海地区暴雨对植被活动的影响[J]. 地理科学, 40(2): 324-334.
DOI |
|
LI J G, YUAN F W, ZHAO Y Q, et al., 2020. Effect of rainstorms on vegetation activities in eastern coastal area of China[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 40(2): 324-334
DOI |
|
| [21] | 李霞, 张国壮, 陈永昊, 等, 2022. 农牧交错带辽河流域2010-2019年植被覆盖变化及驱动因素分析[J]. 农业工程学报, 38(22): 63-72. |
| LI X, ZHANG G Z, CHEN Y H, et al., 2022. Vegetation cover change and driving factors in the agro-pastoral ecotone of Liaohe River Basin of China from 2010 to 2019[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 38(22): 63-72. | |
| [22] | 吕妍, 张黎, 闫慧敏, 等, 2018. 中国西南喀斯特地区植被变化时空特征及其成因[J]. 生态学报, 38(24): 8774-8786. |
| LÜ Y, ZHANG L, YAN H M, et al., 2018. Spatial and temporal patterns of changing vegetation and the influence of environmental factors in the karst region of southwest China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 38(24): 8774-8786. | |
| [23] | 吕勇, 修丽娜, 姚晓军, 2023. 2000-2020年湟水流域植被NDVI变化及其驱动力分析[J]. 水土保持学报, 37(4): 150-157. |
| LÜ Y, XIU L N, YAO X J, 2023. Vegetation NDVI change and driving force analysis in Huangshui watershed from 2000 to 2020[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 37(4): 150-157. | |
| [24] | 赖金林, 齐实, 廖瑞恩, 等, 2023. 2000-2019年西南高山峡谷区植被变化对气候变化和人类活动的响应[J]. 农业工程学报, 39(14): 1-9. |
| LAI J L, QI S, LIAO R E, et al., 2023. Vegetation change responses to climate change and human activities in southwest alpine canyon areas of China from 2000 to 2019[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 39(14): 1-9. | |
| [25] |
刘宇, 田济扬, 黄婷婷, 等, 2023. 长江流域NDVI变化及其驱动因素分析[J]. 地理科学, 43(6): 1022-1031.
DOI |
|
LIU Y, TIAN J Y, HUANG T T, et al., 2023. Analysis of NDVI changes and driving factors in the Yangtze River basin[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 43(6): 1022-1031.
DOI |
|
| [26] | 聂桐, 董国涛, 蒋晓辉, 等, 2023. 基于地理探测器的河南省植被NDVI时空变化及驱动力分析[J/OL]. 生态学杂志, [2023-03-27]. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/21.1148.Q.20230325.1823.016.html. |
| NIE T, DONG G H, JIANG X H, et al., 2023. Temporal and spatial variation and driving force analysis of NDVI in Henan province based on geodetector[J/OL]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, [2023-03-27]. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/21.1148.Q.20230325.1823.016.html. | |
| [27] | 庞鑫, 刘珺, 2023. 气候变化对亚洲地区植被NDVI变化的影响[J]. 自然资源遥感, 35(2): 295-305. |
| PANG X, LIU J, 2023. Effects of climate changes on the NDVI of vegetation in Asia[J]. Remote sensing for natural resources, 35(2): 295-305. | |
| [28] | 孙瑞, 张方敏, 翁升恒, 等, 2023. 2001-2021年中国NDVI时空格局变化及对气候的响应[J]. 中国环境科学, 43(10): 5519-5528. |
| SUN R, ZHANG F M, WENG S H, et al., 2023. Changes in the spatiotemporal pattern of NDVI in China from 2001 to 2021 and its response to climate[J]. China Environmental Science, 43(10): 5519-5528. | |
| [29] |
王劲峰, 徐成东, 2017. 地理探测器:原理与展望[J]. 地理学报, 72(1): 116-134.
DOI |
|
WANG J F, XU C D, 2017. Geodetector: Principle and prospective[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 72(1): 116-134.
DOI |
|
| [30] |
王晓利, 侯西勇, 2019. 1982-2014年中国沿海地区归一化植被指数(NDVI)变化及其对极端气候的响应[J]. 地理研究, 38(4): 807-821.
DOI |
|
WANG X L, HOU X Y, 2019. Variation of normalized difference vegetation index and its response to extreme climate in coastal China during 1982-2014[J]. Geographical Research, 38(4): 807-821.
DOI |
|
| [31] | 王强, 张勃, 戴声佩, 等, 2012. 三北防护林工程区植被覆盖变化与影响因子分析[J]. 中国环境科学, 32(7): 1302-1308. |
| WANG Q, ZHANG B, DAI S P, et al., 2012. Analysis of the vegetation cover change and its relationship with factors in the Three-North Shelter Forest Program[J]. China Environmental Science, 32(7): 1302-1308. | |
| [32] |
张志强, 刘欢, 左其亭, 等, 2021. 2000-2019年黄河流域植被覆盖度时空变化[J]. 资源科学, 43(4): 849-858.
DOI |
| ZHANG Z Q, LIU H, ZUO Q T, et al., 2021. Temporal and spatial changes of vegetation coverage in the yellow river basin from 2000 to 2019[J]. Resources Science, 43(4): 849-858. | |
| [33] |
张思源, 聂莹, 张海燕, 等, 2020. 基于地理探测器的内蒙古植被NDVI时空变化与驱动力分析[J]. 草地学报, 28(5): 1460-1472.
DOI |
|
ZHANG S Y, NIE Y, ZHANG H Y, et al., 2020. Spatiotemporal variation of vegetation NDVI and its driving forces in inner Mongolia based on geodetector[J]. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 28(5): 1460-1472.
DOI |
|
| [34] | 徐勇, 郑志威, 郭振东, 等, 2022. 2000-2020年长江流域植被NDVI动态变化及影响因素探测[J]. 环境科学, 43(7): 3730-3740. |
| XU Y, ZHENG Z W, GUO Z D, et al., 2022. Dynamic variation in vegetation cover and its influencing factor detection in the Yangtze river basin from 2000 to 2020[J]. Environmental Science, 43(7): 3730-3740. | |
| [35] | 徐建华, 2002. 现代地理学中的数学方法[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社:133. |
| XU J H, 2002. Mathematical methods in modern geography[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press:133. | |
| [36] | 张晨钰, 王伟, 黄莉, 等, 2023. 高度城镇化背景下粤港澳大湾区易涝点驱动力分析:以深圳市为例[J]. 水资源保护, 31(8): 1-19. |
| ZHANG C Y, WANG W, HUANG L, et al., 2023. Driving forces of waterlogging sites in Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao greater bay area in the context of high urbanization: Taking Shenzhen city as an example[J]. Water Resources Protection, 31(8): 1-19. | |
| [37] | 张若婧, 陈跃红, 张晓祥, 等, 2021. 基于参数最优地理探测器的江西省山洪灾害时空格局与驱动力研究[J]. 地理与地理信息科学, 37(4): 72-80. |
| ZHANG R J, CHEN Y H, ZHANG X X, et al., 2021. Spatial-temporal pattern and driving factors of flash flood disasters in Jiangxi province analyzed by optimal parameters-based geographical detector[J]. Geography and Geo-Information Science, 37(4): 72-80. | |
| [38] | 张华, 李明, 宋金岳, 等, 2021. 基于地理探测器的祁连山国家公园植被NDVI变化驱动因素分析[J]. 生态学杂志, 40(8): 2530-2540. |
| ZHANG H, LI M, SONG J Y, et al., 2021. Analysis of driving factors of vegetation NDVI change in Qilian Mountain National Park based on geographic detector[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology 40(8): 2530-2540. | |
| [39] | 中华人民共和国生态环境部, 2010. 2009年中国环境状况公报[R]. 北京: 中华人民共和国生态环境部. |
| Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People's Republic of China, 2010. 2009 China Environmental Status Bulletin[R]. Beijing: Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People's Republic of China. | |
| [40] | 中国气象局, 2015. 2014年中国气候公报[R]. 北京: 中国气象局. |
| China Meteorological Administration, 2015. 2014 China climate bulletin[R]. Beijing: China Meteorological Administration. | |
| [41] | 中华人民共和国自然资源部, 2022. 沿海行政区域分类与代码: HY/T 094—2022[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社: 1-2. |
| Ministry of Natural Resources, People's Republic of China, 2022. Coastal administrative areas classification and codes: HY/T 094—2022[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China: 1-2. |
| [1] | 古佳玮, 郭彩霞, 朱铧楠, 谭玉坤, 陈红跃. 广东丰溪省级自然保护区景观格局变化及其驱动力研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(2): 222-230. |
| [2] | 巫晨煜, 许帆帆, 魏士博, 樊晶晶, 刘观鹏, 王坤. 渭河流域地表植被覆盖对气候变化的响应研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 835-844. |
| [3] | 翁升恒, 张玉琴, 姜冬昕, 潘卫华, 李丽纯, 张方敏. 福建省森林植被NEP时空变化及影响因子分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 845-856. |
| [4] | 于菲, 曾海龙, 房怀阳, 付玲芳, 林澍, 董家豪. 典型感潮河网浮游藻类功能群时空变化特征及水质评价[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 756-765. |
| [5] | 李晖, 李必龙, 葛黎黎, 韩琛惠, 杨倩, 张岳军. 2000-2021年汾河流域植被时空演变特征及地形效应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 439-449. |
| [6] | 贾志峰, 刘鹏程, 刘宇, 吴博博, 陈丹姿, 张向飞. 气候变化和人类活动对松辽流域植被覆盖的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 1-10. |
| [7] | 孙梦鑫, 张岳, 辛宇, 钟鼎杰, 杨存建. 川西高原近20 a植被物候变化及其对气候变化的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(7): 1326-1339. |
| [8] | 陈文裕, 夏丽华, 徐国良, 余世钦, 陈行, 陈金凤. 2000—2020年珠江流域NDVI动态变化及影响因素研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(7): 1306-1316. |
| [9] | 李梦华, 韩颖娟, 赵慧, 王云霞. 基于地理探测器的宁夏植被覆盖度时空变化特征及其驱动因子分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(7): 1317-1325. |
| [10] | 曹晓云, 祝存兄, 陈国茜, 孙树娇, 赵慧芳, 朱文彬, 周秉荣. 2000—2021年柴达木盆地地表绿度变化及地形分异研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(6): 1080-1090. |
| [11] | 高思琦, 董国涛, 蒋晓辉, 聂桐, 郭欣伟, 党素珍, 李心宇, 李昊洋. 黄河源植被覆盖度变化及空间分布自然驱动力分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(3): 429-439. |
| [12] | 郝永佩, 宋晓伟, 赵文珺, 向发敏. 汾渭平原大气污染时空分布及相关因子分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(3): 512-523. |
| [13] | 杨媛媛, 佘志鹏, 宋进喜, 朱大为. 2000年以来浐灞河流域不同地貌区植被变化特征及影响因素研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(2): 224-230. |
| [14] | 石智宇, 王雅婷, 赵清, 张连蓬, 朱长明. 2001-2020年中国植被净初级生产力时空变化及其驱动机制分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(11): 2111-2123. |
| [15] | 付乐, 迟妍妍, 于洋, 张丽苹, 刘斯洋, 王夏晖, 许开鹏, 王晶晶, 张信. 2000—2020年黄河流域土地利用变化特征及影响因素分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(10): 1927-1938. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
