生态环境学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (7): 1306-1316.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2022.07.003
陈文裕1,2( ), 夏丽华1,2,*(
), 夏丽华1,2,*( ), 徐国良1,2, 余世钦1,2, 陈行1,2, 陈金凤1,2
), 徐国良1,2, 余世钦1,2, 陈行1,2, 陈金凤1,2
收稿日期:2022-03-07
出版日期:2022-07-18
发布日期:2022-08-31
通讯作者:
*夏丽华(1964年生),女,教授,主要研究方向是海岸带土地利用变化与景观生态等。E-mail: xialihua@gzhu.edu.cn作者简介:陈文裕(1996年生),男,硕士研究生,主要研究方向为GIS空间分析与遥感应用。E-mail: 2112001050@e.gzhu.edu.cn
基金资助:
CHEN Wenyu1,2( ), XIA Lihua1,2,*(
), XIA Lihua1,2,*( ), XU Guoliang1,2, YU Shiqin1,2, CHEN Hang1,2, CHEN Jinfeng1,2
), XU Guoliang1,2, YU Shiqin1,2, CHEN Hang1,2, CHEN Jinfeng1,2
Received:2022-03-07
Online:2022-07-18
Published:2022-08-31
摘要:
研究植被的时空变化趋势及其对自然和人为因素的响应机制,对区域的植被恢复和生态保护具有重要意义。以珠江流域为例,基于Theil-Sen Median斜率估计和Mann-Kendall显著性检验探究NDVI时空演化特征,通过相关分析揭示NDVI与气候因素和人为因素的相关性,并使用地理探测器探究珠江流域NDVI空间分异的主要影响因素。结果表明,(1)2000—2020年珠江流域NDVI整体呈上升趋势,2000—2004年、2005—2009年和2014—2018年是NDVI快速增长的3个时期;4个子流域NDVI变化趋势均以增长为主,但不同子流域内NDVI的空间分布和增长速率存在差异,东江流域的NDVI均值最高,北江流域的NDVI上升速率最高,而珠江三角洲流域的NDVI均值最低且增长速率较低。(2)在研究时段内,珠江流域的林地面积有所减少,建设用地面积显著增加。由其他土地覆盖类型转换为林地、草地和耕地的区域内,NDVI呈上升趋势的面积占比分别为95.37%、85.31%和90.75%;而在转换为建设用地的区域内,NDVI则以下降趋势为主,土地覆盖类型的转换对NDVI变化的影响存在差异。(3)NDVI与平均气温和降水量均以正相关为主,表明在珠江流域气候因素对NDVI的影响以正向促进作用为主;NDVI与夜间灯光强度以正相关为主,与人口密度则是以负相关为主;NDVI与人为因素呈显著正相关的区域主要分布于珠三角城市群以及各大城市的外围地区,呈负相关的区域主要分布于珠三角城市群以及各大城市的城区。(4)从单一因子来看,土地覆盖类型、人口密度和夜间灯光强度对NDVI空间分异的解释力度较高;影响因子交互作用结果均表现为双因子增强和非线性增强;在不同子流域中,土地覆盖∩夜间灯光强度和土地覆盖∩人口密度的解释力均较高。研究结果可为制定珠江流域植被资源管理方案提供依据。
中图分类号:
陈文裕, 夏丽华, 徐国良, 余世钦, 陈行, 陈金凤. 2000—2020年珠江流域NDVI动态变化及影响因素研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(7): 1306-1316.
CHEN Wenyu, XIA Lihua, XU Guoliang, YU Shiqin, CHEN Hang, CHEN Jinfeng. Dynamic Variation of NDVI and Its Influencing Factors in the Pearl River Basin from 2000 to 2020[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(7): 1306-1316.
| 判断依据 Judgment basis | 交互作用类型 Interaction type |
|---|---|
| q(X1∩X2)<Min(q(X1), q(X2)) | 非线性减弱 |
| Min(q(X1), q(X2)) <q(X1∩X2)<Max(q(X1), q(X2)) | 单因子非线性减弱 |
| q(X1∩X2)>Max(q(X1), q(X2)) | 双因子增强 |
| q(X1∩X2)=q(X1)+q(X2) | 独立 |
| q(X1∩X2)>q(X1)+q(X2) | 非线性增强 |
表1 双因子交互作用结果类型
Table 1 Types of two-factor interaction result
| 判断依据 Judgment basis | 交互作用类型 Interaction type |
|---|---|
| q(X1∩X2)<Min(q(X1), q(X2)) | 非线性减弱 |
| Min(q(X1), q(X2)) <q(X1∩X2)<Max(q(X1), q(X2)) | 单因子非线性减弱 |
| q(X1∩X2)>Max(q(X1), q(X2)) | 双因子增强 |
| q(X1∩X2)=q(X1)+q(X2) | 独立 |
| q(X1∩X2)>q(X1)+q(X2) | 非线性增强 |
| 土地覆盖类型 Land cover type | 2000年 Year 2000 | 2010年 Year 2010 | 2020年 Year 2020 | 2000—2010年 Year 2000‒2010 | 2010—2020年 Year 2010‒2020 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 面积 Area/km2 | 面积占比 Area ratio/% | 面积 Area/km2 | 面积占比 Area ratio/% | 面积 Area/km2 | 面积占比 Area ratio/% | 变化 Change/km2 | 变化 Change/km2 | |||||
| 耕地 Cropland | 1166312 | 26.46 | 117836 | 26.73 | 113177 | 25.68 | 1204 | -4659 | ||||
| 林地 Forest | 264369 | 59.98 | 259521 | 58.88 | 254982 | 57.85 | -4848 | -4539 | ||||
| 草地 Grass | 44160 | 10.02 | 46775 | 10.61 | 45352 | 10.29 | 2615 | -1423 | ||||
| 水体 Water | 8527 | 1.93 | 8535 | 1.94 | 9758 | 2.21 | 8 | 1223 | ||||
| 建设用地 Construction land | 7059 | 1.60 | 8088 | 1.83 | 17479 | 3.97 | 1029 | 9391 | ||||
| 裸地 Bare land | 26 | 0.01 | 19 | 0.01 | 26 | 0.01 | -7 | 7 | ||||
表2 珠江流域2000、2010和2020年土地覆盖变化情况
Table 2 Land cover transformation in the Pearl River basin in 2000, 2010 and 2020
| 土地覆盖类型 Land cover type | 2000年 Year 2000 | 2010年 Year 2010 | 2020年 Year 2020 | 2000—2010年 Year 2000‒2010 | 2010—2020年 Year 2010‒2020 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 面积 Area/km2 | 面积占比 Area ratio/% | 面积 Area/km2 | 面积占比 Area ratio/% | 面积 Area/km2 | 面积占比 Area ratio/% | 变化 Change/km2 | 变化 Change/km2 | |||||
| 耕地 Cropland | 1166312 | 26.46 | 117836 | 26.73 | 113177 | 25.68 | 1204 | -4659 | ||||
| 林地 Forest | 264369 | 59.98 | 259521 | 58.88 | 254982 | 57.85 | -4848 | -4539 | ||||
| 草地 Grass | 44160 | 10.02 | 46775 | 10.61 | 45352 | 10.29 | 2615 | -1423 | ||||
| 水体 Water | 8527 | 1.93 | 8535 | 1.94 | 9758 | 2.21 | 8 | 1223 | ||||
| 建设用地 Construction land | 7059 | 1.60 | 8088 | 1.83 | 17479 | 3.97 | 1029 | 9391 | ||||
| 裸地 Bare land | 26 | 0.01 | 19 | 0.01 | 26 | 0.01 | -7 | 7 | ||||
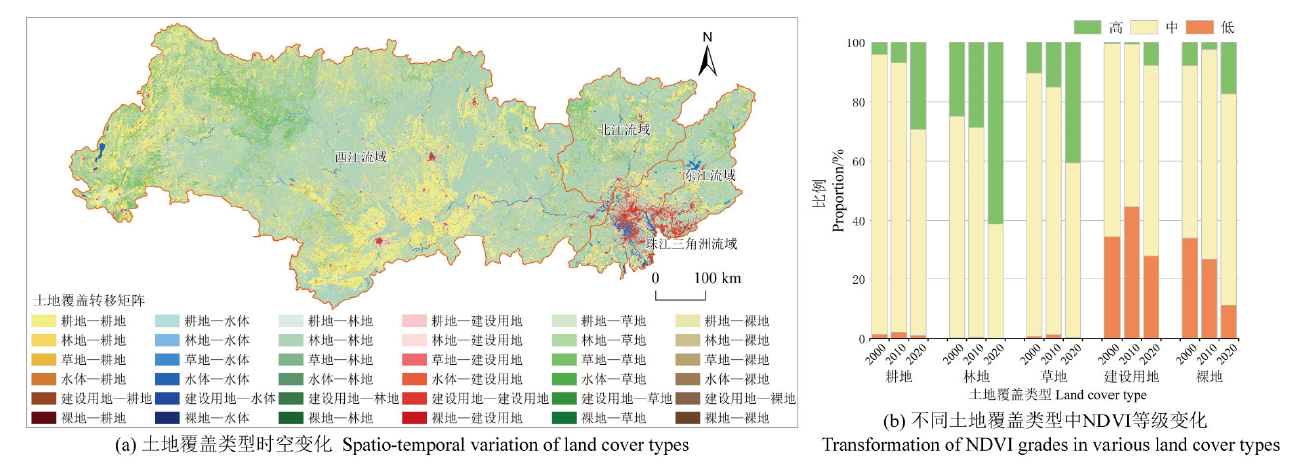
图4 2000—2020年珠江流域土地覆盖类型转变和各种土地覆盖类型中NDVI等级变化图
Figure 4 Transformation of land cover and NDVI grades in various land cover types in the Pearl River basin from 2000 to 2020
| 地区 Region | 海拔 Altitude | 坡度 Slope | 坡向 Aspect | 降水量 Precipitation | 平均气温 Temperature | 土地覆盖 Land cover | 土壤类型 Soil type | 夜间灯光强度 Nighttime light intensity | 人口密度 Population density |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 东江流域 Dongjiang River basin | 0.43* | 0.29* | 0.04 | 0.28* | 0.47* | 0.51* | 0.21* | 0.50* | 0.48* |
| 西江流域 Xijiang River basin | 0.2* | 0.12* | 0.01 | 0.13* | 0.10* | 0.29* | 0.08* | 0.22* | 0.28* |
| 北江流域 Beijiang River basin | 0.26* | 0.18* | 0.01 | 0.24* | 0.15* | 0.37* | 0.15* | 0.34* | 0.40* |
| 珠江三角洲流域 Pearl River Delta basin | 0.59* | 0.32* | 0.01 | 0.41* | 0.46* | 0.59* | 0.43* | 0.64* | 0.59* |
表3 珠江流域内4个子流域单元影响因素q值
Table 3 The q values of influencing factors of four sub-basin units in the Pearl River basin
| 地区 Region | 海拔 Altitude | 坡度 Slope | 坡向 Aspect | 降水量 Precipitation | 平均气温 Temperature | 土地覆盖 Land cover | 土壤类型 Soil type | 夜间灯光强度 Nighttime light intensity | 人口密度 Population density |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 东江流域 Dongjiang River basin | 0.43* | 0.29* | 0.04 | 0.28* | 0.47* | 0.51* | 0.21* | 0.50* | 0.48* |
| 西江流域 Xijiang River basin | 0.2* | 0.12* | 0.01 | 0.13* | 0.10* | 0.29* | 0.08* | 0.22* | 0.28* |
| 北江流域 Beijiang River basin | 0.26* | 0.18* | 0.01 | 0.24* | 0.15* | 0.37* | 0.15* | 0.34* | 0.40* |
| 珠江三角洲流域 Pearl River Delta basin | 0.59* | 0.32* | 0.01 | 0.41* | 0.46* | 0.59* | 0.43* | 0.64* | 0.59* |
| [1] |
CHEN T, XIA J, ZOU L, et al., 2020. Quantifying the influences of natural factors and human activities on NDVI changes in the Hanjiang River basin, China[J]. Remote Sensing, 12(22): 1-21.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
CHEN Z Q, YU B L, YANG C S, et al., 2021. An extended time series (2000-2018) of global NPP-VIIRS-like nighttime light data from a cross-sensor calibration[J]. Earth System Science Data, 13(3): 889-906.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
LI Y, YE H P, GAO X, et al., 2021. Spatiotemporal patterns of urbanization in the three most developed urban agglomerations in China based on continuous nighttime light data (2000-2018)[J]. Remote Sensing, 13(12): 2245.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
PEI F S, ZHOU Y, XIA Y, 2021. Application of normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) for the detection of extreme precipitation change[J]. Forests, 12(5): 594.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
PENG S Z, DING Y X, LIU W Z, et al., 2019. 1 km monthly temperature and precipitation dataset for China from 1901 to 2017 [J]. Earth System Science Data, 11(4): 1931-1946.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
QI G Z, BAI H Y, ZHAO T, et al., 2021. Sensitivity and areal differentiation of vegetation responses to hydrothermal dynamics on the northern and southern slopes of the Qinling Mountains in Shaanxi province[J]. Journal of Geographical Sciences, 31(6): 785-801.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
XUE F, LIU J, DONG G T, et al., 2021. Spatial-temporal variation of NDVI and its responses to precipitation in the upper of Heihe from 2000 to 2019 [J]. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 783(1): 012148.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
陈颖彪, 郑子豪, 吴志峰, 等, 2019. 夜间灯光遥感数据应用综述和展望[J]. 地理科学进展, 38(2): 205-223.
DOI |
| CHEN Y B, ZHENG Z H, WU Z F, et al., 2019. Review and prospect of application of nighttime light remote sensing data[J]. Progress in Geography, 38(2): 205-223. | |
| [9] | 宫兆宁, 陆丽, 金点点, 等, 2021. 土地利用/覆被变化扎龙湿地蒸散发量及生态需水量的遥感估算[J]. 生态学报, 41(9): 3572-3587. |
| GONG Z N, LU L, JIN D D, et al., 2021. Remote sensing estimation of evapotranspiration and ecological water demand in Zhalong wetland under land use/cover change[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 41(9): 3572-3587. | |
| [10] | 黄栋, 李鹏, 董南, 2021. 近20 a环渤海地区GS_NDVI时空分异及其对气候变化和LUCC的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 30(12): 2275-2284. |
| HUANG D, LI P, DONG N, 2021. Spatial-temporal differentiation of GS_NDVI in recent 20 years and its responses to climate change and LUCC in the Bohai Coastal region[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 30(12): 2275-2284. | |
| [11] | 吉珍霞, 裴婷婷, 陈英, 等, 2021. 黄土高原植被物候变化及其对季节性气候变化的响应[J]. 生态学报, 41(16): 6600-6612. |
| JI Z X, PEI T T, CHEN Y, et al., 2021. Vegetation phenology change and its response to seasonal climate changes on the Loess Plateau[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 41(16): 6600-6612. | |
| [12] | 贾路, 于坤霞, 徐国策, 等, 2021. 基于耦合协调度的黄土高原地区NDVI与降水关系的变异诊断[J]. 生态学报, 41(18): 7357-7366. |
| JIA L, YU K X, XU G C, et al., 2021. Diagnosis of the relationship between NDVI and precipitation based on the coupling coordination degree[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 41(18): 7357-7366. | |
| [13] |
金凯, 王飞, 韩剑桥, 等, 2020. 1982-2015年中国气候变化和人类活动对植被NDVI变化的影响[J]. 地理学报, 75(5): 961-974.
DOI |
|
JIN K, WANG F, HAN J Q, et al., 2020. Contribution of climatic change and human activities to vegetation NDVI change over China during 1982-2015 [J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 75(5): 961-974.
DOI |
|
| [14] |
李建国, 袁冯伟, 赵宴青, 等, 2020. 中国东部沿海地区暴雨对植被活动的影响[J]. 地理科学, 40(2): 324-334.
DOI |
| LI J G, YUAN F W, ZHAO Y Q, et al., 2020. Effect of rainstorms on vegetation activities in eastern coastal area of China[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 40(2): 324-334. | |
| [15] |
李茂华, 都金康, 李皖彤, 等, 2020. 1982-2015年全球植被变化及其与温度和降水的关系[J]. 地理科学, 40(5): 823-832.
DOI |
| LI M H, DU J K, LI W T, et al., 2020. Global vegetation change and its relationship with precipitation and temperature based on GLASS-LAI in 1982-2015 [J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 40(5): 823-832. | |
| [16] | 李茜铭, 郑伯红, 熊羽军, 2021. 基于夜间灯光遥感数据的环洞庭湖生态经济区城市群时空扩展[J]. 经济地理, 41(2): 92-102. |
|
LI Q M, ZHENG B H, XIONG Y J, 2021. Spatio-temporal expansion of the Dongting Lake Eco-economic zone urban agglomeration based on nighttime light remote sensing data[J]. Economic Geography, 41(2): 92-102.
DOI URL |
|
| [17] |
李双双, 张玉凤, 汪成博, 等, 2021. 气候变化和生态建设对秦岭-淮河南北植被动态的影响[J]. 地理科学进展, 40(6): 1026-1036.
DOI |
| LI S S, ZHANG Y F, WANG C B, et al., 2021. Coupling effects of climate change and ecological restoration on vegetation dynamics in the Qinling-Huaihe region[J]. Progress in Geography, 40(6): 1026-1036. | |
| [18] |
林依雪, 李艳忠, 余文君, 等, 2020. 植被恢复工程对黄河中游12个典型流域水热平衡的影响研究[J]. 地理研究, 39(11): 2593-2606.
DOI |
| LIN Y X, LI Y Z, YU W J, et al., 2020. Quantitative assessment of the impact of the vegetation restoration project on water-energy balance in 12 typical basins of the middle Yellow River[J]. Geographical Research, 39(11): 2593-2606. | |
| [19] |
刘梁美子, 占车生, 胡实, 等, 2019. 黔桂喀斯特山区年NDVI变化的影响因素研究[J]. 地理科学进展, 38(11): 1783-1792.
DOI |
| LIU L M Z, ZHAN C S, HU S, et al., 2019. Impact factors of annual NDVI change in karst mountain areas of Guizhou and Guangxi provinces[J]. Geographical Research, 38(11): 1783-1792. | |
| [20] |
齐贵增, 白红英, 赵婷, 等, 2021. 秦岭陕西段南北坡植被对干湿变化响应敏感性及空间差异[J]. 地理学报, 76(1): 44-56.
DOI |
| QI G Z, BAI H Y, ZHAO T, et al., 2021. Sensitivity and areal differentiation of vegetation responses to hydrothermal dynamics on the southern and northern slopes of the Qinling Mountains in Shaanxi province[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 76(1): 44-56. | |
| [21] |
邵亚婷, 王卷乐, 严欣荣, 2021. 蒙古国植被物候特征及其对地理要素的响应[J]. 地理研究, 40(11): 3029-3045.
DOI |
| SHAO Y T, WANG J L, YAN X R, 2021. The phenological characteristics of Mongolian vegetation and its response to geographical elements[J]. Geographical Research, 40(11): 3029-3045. | |
| [22] | 沈洁, 2021. 中国城市集中的度量及其空间分异特征--基于DMSP-OLS夜间灯光数据[J]. 经济地理, 41(5): 46-56. |
| SHEN J, 2021. The measurement of urban concentration in China and the study of its spatial differentiation characteristics: Based on DMSP-OLS nighttime light data[J]. Economic Geography, 41(5): 46-56. | |
| [23] |
孙倩倩, 刘超, 郑蓓君, 2021. 基于ICEEMDAN方法的黄土高原植被覆盖变化及其对气候变化的响应[J]. 应用生态学报, 32(6): 2129-2137.
DOI |
| SUN Q Q, LIU C, ZHENG B J, 2021. Vegetation cover change and its response to climate change on the Loess Plateau, Northwest China based on ICEEMDAN method[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 32(6): 2129-2137. | |
| [24] |
孙锐, 陈少辉, 苏红波, 2019. 2000-2016年黄土高原不同土地覆盖类型植被NDVI时空变化[J]. 地理科学进展, 38(8): 1248-1258.
DOI |
| SUN R, CHEN S H, SU H B, 2019. Spatiotemporal variations of NDVI of different land cover types on the Loess Plateau from 2000 to 2016 [J]. Progress in Geography, 38(8): 1248-1258. | |
| [25] |
孙锐, 陈少辉, 苏红波, 2020. 黄土高原不同生态类型NDVI时空变化及其对气候变化响应[J]. 地理研究, 39(5): 1200-1214.
DOI |
| SUN R, CHEN S H, SU H B, 2020. Spatiotemporal variation of NDVI in different ecotypes on the Loess Plateau and its response to climate change[J]. Geographical Research, 39(5): 1200-1214. | |
| [26] | 孙爽, 李令军, 赵文吉, 等, 2019. 京津冀大气污染变化规律及其与植被指数相关性分析[J]. 环境科学, 40(4): 1585-1593. |
| SUN S, LI L J, ZHAO W J, et al., 2019. Variation in pollutant concentrations and correlation analysis with the vegetation index in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei[J]. Environmental Science, 40(4): 1585-1593. | |
| [27] | 田智慧, 任祖光, 魏海涛, 2022. 2000-2020年黄河流域植被时空演化驱动机制[J]. 环境科学, 43(2): 743-751. |
|
TIAN Z H, REN Z G, WEI H T, 2022. Driving mechanism of the spatiotemporal evolution of vegetation in the Yellow River basin from 2000 to 2020 [J]. Environmental Science, 43(2): 743-751.
DOI URL |
|
| [28] |
王劲峰, 徐成东, 2017. 地理探测器:原理与展望[J]. 地理学报, 72(1): 116-134.
DOI |
| WANG J F, XU C D, 2017. Geodetector: Principle and prospective[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 72(1): 116-134. | |
| [29] | 王银霞, 施平, 曾丽丽, 等, 2011. 1982-1999年珠江流域归一化植被指数与降水年际变化分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 30(4): 44-50. |
| WANG Y X, SHI P, ZENG L L, et al., 2011. Interannual variation of vegetation and precipitation in Pearl River basin during 1982-1999 [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 30(4): 44-50. | |
| [30] | 王兆礼, 陈晓宏, 李艳, 2006. 珠江流域植被覆盖时空变化分析[J]. 生态科学, 25(4): 303-307, 311. |
| WANG Z L, CHEN X H, LI Y, 2006. Spatio-temporal changes of NDVI in the Pearl River basin[J]. Ecologic Science, 25(4): 303-307, 311. | |
| [31] | 邢愿, 贺中华, 2021. 基于NDVI的贵州省植被覆盖时空特征分析[J]. 华南师范大学学报 (自然科学版), 53(2): 84-95. |
| XING Y, HE Z H, 2021. An NDVI-based analysis of the temporal and spatial characteristics of vegetation coverage in Guizhou province[J]. Journal of South China Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 53(2): 84-95. | |
| [32] | 徐勇, 黄雯婷, 窦世卿, 等, 2022. 2000-2020年西南地区植被NDVI对气候变化和人类活动响应特征[J]. 环境科学, 43(6): 3230-3240. |
| XU Y, HUANG W T, DOU S Q, et al., 2022. Responding mechanism of vegetation cover to climate change and human activities in southwest China from 2000 to 2020 [J]. Environmental Science, 43(6): 3230-3240. | |
| [33] | 杨玉莲, 杨昆, 罗毅, 等, 2021. 1998-2016中国八大经济区植被覆盖对PM2.5浓度时空分布的影响[J]. 环境科学, 42(11): 5100-5108. |
| YANG Y L, YANG K, LUO Y, et al., 2021. Effect of vegetation coverage on the temporal and spatial distribution of PM2.5 concentration in China’s Eight Major Economic Regions from 1998 to 2016 [J]. Environmental Science, 42(11): 5100-5108. | |
| [34] | 易扬, 胡昕利, 史明昌, 等, 2021. 基于MODIS NDVI的长江中游区域植被动态及与气候因子的关系[J]. 生态学报, 41(19): 7796-7807. |
| YI Y, HU X L, SHI M C, et al., 2021. Vegetation dynamics and its relationship with climate factors in the middle reaches of the Yangtze River based on MODIS NDVI[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 41(19): 7796-7807. | |
| [35] | 袁倩颖, 马彩虹, 文琦, 等, 2021. 六盘山贫困区生长季植被覆盖变化及其对水热条件的响应[J]. 国土资源遥感, 33(2): 220-227. |
| YUAN Q Y, MA C H, WEN Q, et al., 2021. Vegetation cover change and its response to water and heat conditions in the growing season in Liupanshan poverty-stricken area[J]. Remote Sensing for Land and Resources, 33(2): 220-227. | |
| [36] | 岳辉, 刘英, 2019. 近15 a陕西省植被时空变化与影响因素分析[J]. 干旱区地理, 42(2): 314-323. |
| YUE H, LIU Y, 2019. Vegetation spatiotemporal variation and its driving factors of Shaanxi province in recent 15 years[J]. Arid Land Geography, 42(2): 314-323. | |
| [37] | 张翀, 白子怡, 李学梅, 等, 2021. 2001-2018年黄土高原植被覆盖人为影响时空演变及归因分析[J]. 干旱区地理, 44(1): 188-196. |
| ZHANG C, BAI Z Y, LI X M, et al., 2021. Spatio-temporal evolution and attribution analysis of human effects of vegetation cover on the Loess Plateau from 2001 to 2018 [J]. Arid Land Geography, 44(1): 188-196. | |
| [38] |
张华, 徐存刚, 王浩, 2020. 2001-2018年西北地区植被变化对气象干旱的响应[J]. 地理科学, 40(6): 1029-1038.
DOI |
| ZHANG H, XU C G, WANG H, 2020. Response of vegetation change to Meteorological drought in northwest China from 2001 to 2018 [J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 40(6): 1029-1038. | |
| [39] | 张静, 杜加强, 盛芝露, 等, 2021. 1982-2015年黄河流域植被NDVI时空变化及影响因素分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 30(5): 929-937. |
| ZHANG J, DU J Q, SHENG Z L, et al., 2021. Spatio-temporal changes of vegetation cover and their influencing factors in the Yellow River basin from 1982 to 2015 [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 30(5): 929-937. | |
| [40] |
张琍, 李斌, 阳文静, 等, 2021. 基于时序遥感的庐山自然保护区植被分类及其变化分析[J]. 地理科学进展, 40(4): 703-712.
DOI |
|
ZHANG L, LI B, YANG W J, et al., 2021. Forest vegetation classification and its variation in Lushan Nature Reserve using Proba-V vegetation products[J]. Progress in Geography, 40(4): 703-712.
DOI |
|
| [41] | 张鹏骞, 胡理乐, 白加德, 2021. 京津冀地区近20年NDVI时空变化特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 30(1): 29-36. |
| ZHANG P Q, HU L L, BAI J D, 2021. Spatio-temporal variation of NDVI in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region in the past 20 years[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 30(1): 29-36. | |
| [42] | 张思源, 聂莹, 张海燕, 等, 2020. 基于地理探测器的内蒙古植被NDVI时空变化与驱动力分析[J]. 草地学报, 28(5): 1460-1472. |
| ZHANG S Y, NIE Y, ZHANG H Y, et al., 2020. Spatiotemporal variation of vegetation NDVI and its driving forces in inner Mongolia based on Geodetector[J]. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 28(5): 1460-1472. | |
| [43] | 赵伟, 高博, 卢清, 等, 2021. 2006-2019年珠三角地区臭氧污染趋势[J]. 环境科学, 42(1): 97-105. |
| ZHAO W, GAO B, LU Q, et al., 2021. Ozone pollution trend in the Pearl River Delta region during 2006-2019 [J]. Environmental Science, 42(1): 97-105. |
| [1] | 王琳, 卫伟. 黄土高原典型县域生态系统服务变化特征及驱动因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(6): 1140-1148. |
| [2] | 巫晨煜, 许帆帆, 魏士博, 樊晶晶, 刘观鹏, 王坤. 渭河流域地表植被覆盖对气候变化的响应研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 835-844. |
| [3] | 王超, 杨倩楠, 张池, 刘同旭, 张晓龙, 陈静, 刘科学. 丹霞山不同土地利用方式土壤磷组分特征及其有效性[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 889-897. |
| [4] | 李建辉, 党争, 陈琳. 黄河几字弯都市圈PM2.5时空特征及影响因素分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 697-705. |
| [5] | 李晖, 李必龙, 葛黎黎, 韩琛惠, 杨倩, 张岳军. 2000-2021年汾河流域植被时空演变特征及地形效应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 439-449. |
| [6] | 张林, 齐实, 周飘, 伍冰晨, 张岱, 张岩. 北京山区针阔混交林地土壤有机碳含量的影响因素研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 450-458. |
| [7] | 何艳虎, 龚镇杰, 吴海彬, 蔡宴朋, 杨志峰, 陈晓宏. 粤港澳大湾区城市生态效率时空演变及影响因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 469-480. |
| [8] | 王嘉丽, 冯婧珂, 杨元征, 俎佳星, 蔡文华, 杨健. 南宁市主城区不透水面与热环境效应的空间关系研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 525-534. |
| [9] | 郝金虎, 韦玮, 李胜男, 马牧源, 李肖夏, 杨洪国, 姜琦宇, 柴沛东. 基于GEE平台的京津冀长时序水体时空格局及其影响因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 556-566. |
| [10] | 王成武, 罗俊杰, 唐鸿湖. 基于InVEST模型的太行山沿线地区生态系统碳储量时空分异驱动力分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(2): 215-225. |
| [11] | 张莉, 李铖, 谭皓泽, 韦家怡, 程炯, 彭桂香. 广州典型城市林地对大气颗粒物的削减效应及影响因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(2): 341-350. |
| [12] | 贾志峰, 刘鹏程, 刘宇, 吴博博, 陈丹姿, 张向飞. 气候变化和人类活动对松辽流域植被覆盖的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 1-10. |
| [13] | 付蓉, 武新梅, 陈斌. 城市地表温度空间分异及驱动因子差异性分析——以合肥市为例[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 110-122. |
| [14] | 郑晓豪, 陈颖彪, 郑子豪, 郭城, 黄卓男, 周泳诗. 湖北省生态系统服务价值动态变化及其影响因素演变[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 195-206. |
| [15] | 袁林江, 李梦博, 冷钢, 钟冰冰, 夏大朋, 王景华. 厌氧环境下硫酸盐还原与氨氧化的协同作用[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 207-214. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
