生态环境学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (3): 439-449.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2023.03.002
李晖1( ), 李必龙1, 葛黎黎2,*(
), 李必龙1, 葛黎黎2,*( ), 韩琛惠1, 杨倩3, 张岳军4
), 韩琛惠1, 杨倩3, 张岳军4
收稿日期:2022-11-23
出版日期:2023-03-18
发布日期:2023-06-02
通讯作者:
*葛黎黎(1987年生),女,工程师,硕士,主要从事气象资料融合分析及质量控制。E-mail: gll_nuist@163.com作者简介:李晖(1986年生),男,工程师,硕士,主要从事气象服务与应用气象。E-mail: 313921251@qq.com
基金资助:
LI Hui1( ), LI Bilong1, GE Lili2,*(
), LI Bilong1, GE Lili2,*( ), HAN Chenhui1, YANG Qian3, ZHANG Yuejun4
), HAN Chenhui1, YANG Qian3, ZHANG Yuejun4
Received:2022-11-23
Online:2023-03-18
Published:2023-06-02
摘要:
运用NDVI数据在长时序上考虑不同地形绝对面积差异来评价汾河流域植被变化趋势的研究目前比较匮乏。为科学认识汾河流域植被变化及其地形效应,基于2000-2021年的MODIS NDVI数据并结合地形数据,采用线性趋势分析与地形差异修正的方法,分析了汾河流域植被的时空分布及演变特征,并探讨了其在海拔、坡向和坡度上的生长变化差异。结果表明,(1)近22年汾河流域植被NDVI呈流域中部低、外围高、低海拔盆地平川区小于高海拔山脉区的分布格局,随地形和土地覆盖类型变化规律性显著。2000-2021年汾河流域植被总体呈改善趋势,年际变化速率为0.07/(10 a),其中,63.24%的区域植被NDVI显著增加,33.78%的区域植被基本不变。(2)汾河流域植被NDVI分布和变化存在明显的地形效应,随着海拔递增,植被NDVI先减小后增大再减小,2200-2400 m海拔范围内NDVI最大;不同坡向的植被NDVI差异较小,但总体北坡大于南坡、东坡大于西坡,东北坡最大;随着坡度增加,植被NDVI阶梯式增大,20°-35°坡度范围内NDVI最大。(3)2000-2021年汾河流域不同地形的植被NDVI年际变化均呈改善趋势,但在海拔为800-1400 m、坡度为3°-8°的区域植被NDVI以显著增加为主;在海拔为600-800 m、坡度小于1°的平地区域植被NDVI年际增加速率较小,显著退化分布明显;在海拔为600-1000、1200-1400 m、坡度为1°-3°和8°-9°,由平地转为不同坡向的过渡区植被NDVI易出现波动,是生态治理注重和加强区。因此,在汾河流域植被保护及区域生态管理中应关注植被变化的地形效应。
中图分类号:
李晖, 李必龙, 葛黎黎, 韩琛惠, 杨倩, 张岳军. 2000-2021年汾河流域植被时空演变特征及地形效应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 439-449.
LI Hui, LI Bilong, GE Lili, HAN Chenhui, YANG Qian, ZHANG Yuejun. Temporal and Spatial Characteristics of Vegetation Evolution and Topographic Effects in Fenhe River Basin from 2000 to 2021[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(3): 439-449.
| 区域 | 平均年际变化速率/ (10-2∙a-1) | 面积比例/% | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 基本 不变 | 显著 增加 | 显著 减少 | 不显著 增加 | 不显著 减少 | ||
| 太原市 | 0.57 | 34.37 | 61.26 | 3.24 | 0.55 | 0.58 |
| 阳泉市 | 0.43 | 64.48 | 35.32 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.20 |
| 长治市 | 0.46 | 61.75 | 37.87 | 0.16 | 0.23 | 0.00 |
| 晋城市 | 0.58 | 42.72 | 57.13 | 0.05 | 0.10 | 0.00 |
| 晋中市 | 0.66 | 31.55 | 65.60 | 1.42 | 1.01 | 0.42 |
| 运城市 | 0.65 | 38.64 | 56.80 | 0.63 | 3.66 | 0.27 |
| 忻州市 | 0.73 | 26.78 | 72.39 | 0.12 | 0.63 | 0.08 |
| 临汾市 | 0.86 | 26.95 | 70.56 | 0.55 | 1.78 | 0.16 |
| 吕梁市 | 0.53 | 44.61 | 52.24 | 1.83 | 0.66 | 0.67 |
| 汾河流域 | 0.61 | 33.78 | 63.24 | 1.38 | 1.21 | 0.38 |
表1 2000-2021年汾河流域植被NDVI变化趋势及其显著性检验统计
Table 1 NDVI change trend and significance test statistics of vegetation in Fenhe River basin from 2000 to 2021
| 区域 | 平均年际变化速率/ (10-2∙a-1) | 面积比例/% | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 基本 不变 | 显著 增加 | 显著 减少 | 不显著 增加 | 不显著 减少 | ||
| 太原市 | 0.57 | 34.37 | 61.26 | 3.24 | 0.55 | 0.58 |
| 阳泉市 | 0.43 | 64.48 | 35.32 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.20 |
| 长治市 | 0.46 | 61.75 | 37.87 | 0.16 | 0.23 | 0.00 |
| 晋城市 | 0.58 | 42.72 | 57.13 | 0.05 | 0.10 | 0.00 |
| 晋中市 | 0.66 | 31.55 | 65.60 | 1.42 | 1.01 | 0.42 |
| 运城市 | 0.65 | 38.64 | 56.80 | 0.63 | 3.66 | 0.27 |
| 忻州市 | 0.73 | 26.78 | 72.39 | 0.12 | 0.63 | 0.08 |
| 临汾市 | 0.86 | 26.95 | 70.56 | 0.55 | 1.78 | 0.16 |
| 吕梁市 | 0.53 | 44.61 | 52.24 | 1.83 | 0.66 | 0.67 |
| 汾河流域 | 0.61 | 33.78 | 63.24 | 1.38 | 1.21 | 0.38 |
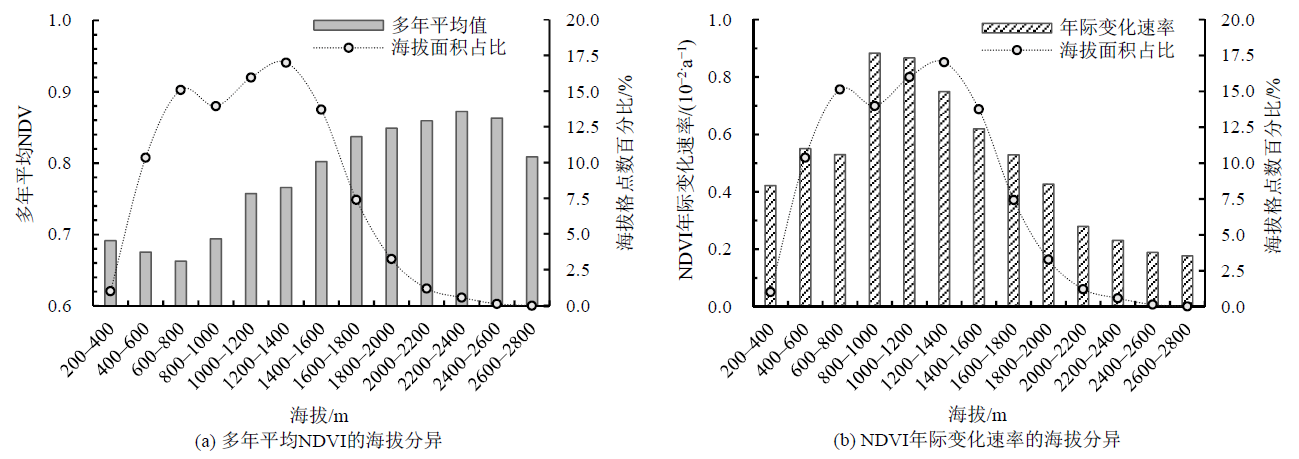
图6 汾河流域多年平均NDVI和NDVI年际变化速率的海拔分异
Figure 6 Elevation differences in the multi-year average NDVI and NDVI interannual rates of change in Fenhe River Basin
| [1] |
AFUYE G A, KALUMBA A M, ORIMOLOYE I R, 2021. Characterisation of vegetation response to climate change: A Review[J]. Sustainability, 13(13): 7265-7287.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
CALLIE B L, LYNN M R, YANG S, et al., 2020. Vegetation change as related to terrain factors at two glacier forefronts, Glacier National Park, Montana, U.S.A[J]. Journal of Mountain Science, 17(4): 1-15.
DOI |
| [3] |
CONG N, WANG T, NAN H J, et al., 2013. Changes in satellite-derived spring vegetation green-up date and its linkage to climate in China from 1982 to 2010: A Multimethod Analysis[J]. Global Change Biology, 19(3): 881-891.
DOI PMID |
| [4] |
LI H, ZHANG H Y, LI Q X, et al., 2021. Vegetation productivity dynamics in response to climate change and human activities under different topography and land cover in northeast China[J]. Remote Sensing, 13(5): 975.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
PARMESAN C, YOHE G, 2003. A globally coherent fingerprint of climate change impacts across natural systems[J]. Nature, 421(6918): 37-42.
DOI |
| [6] |
WU M M, HE H S, ZONG S W, et al., 2018. Topographic controls on vegetation changes in alpine tundra of the Changbai Mountains[J]. Forests, 9(12): 1-13.
DOI URL |
| [7] | 白建伟, 2019. 汾河流域近17年植被覆盖度时空特征变化研究[D]. 太原: 山西农业大学: 1-43. |
| BAI J W, 2019. Study on the temporal and spatial characteristics of vegetation coverage in the Fenhe River Basin in the past 17 years[D]. Taiyuan: Shanxi Agricultural University: 1-43. | |
| [8] | 白玛曲西, 普布多吉, 卓永, 等, 2022. 基于MODIS的横断山区植被时空演变特征及地形效应分析[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 39(1): 1-16. |
| BAI M Q X, PU B D J, ZHUO Y, et al., 2022. Analysis of temporal and spatial evolution characteristics and terrain effect of vegetation in Hengduan Mountains based on MODIS[J]. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 39(1): 1-16. | |
| [9] | 白鹏, 刘小莽, 2022. 汾河流域径流减少因素的定量解析[J]. 南水北调与水利科技, 20(5): 842-850. |
| BAI P, LIU X M, 2022. Quantitative analysis of runoff reduction factors in the Fenhe River Basin[J]. South-to-North Water Transfers and Water Science & Technology, 20(5): 842-850. | |
| [10] |
曹晓云, 祝存兄, 陈国茜, 等, 2022. 2000-2021年柴达木盆地地表绿度变化及地形分异研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 31(6): 1080-1090.
DOI |
| CAO X Y, ZHU C X, CHEN G Q, et al., 2022. Surface greenness change and topographic differentiation over Qaidam Basin from 2000 to 2021[J]. Ecology and Environment Sciences, 31(6): 1080-1090. | |
| [11] | 黄嘉佑, 李庆祥, 2015. 气象数据统计分析方法[M]. 北京: 气象出版社: 1-298. |
| HUANG J Y, LI Q X, 2015. Methods for statistical analysis of meteorological data[M]. Beijing: Meteorological Press: 1-298. | |
| [12] | 林菲, 池泽龙, 杨伟, 等, 2022. 1980-2020年汾河流域生态系统服务价值的时空变化[J]. 水土保持通报, 42(2): 322-329. |
| LIN F, CHI Z L, YANG W, et al., 2022. Spatial and temporal changes of ecosystem service value in Fenhe River Basin from 1980 to 2020[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 42(2): 322-329. | |
| [13] | 刘海龙, 王炜桥, 王跃飞, 等, 2021. 汾河流域生态敏感性综合评价及时空演变特征[J]. 生态学报, 41(10): 3952-3964. |
| LIU H L, WANG W Q, WANG Y F, et al., 2021. Comprehensive evaluation of ecological sensitivity and the characteristics of spatiotemporal variations in Fenhe River Basin[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 41(10): 3952-3964. | |
| [14] |
马士彬, 安裕伦, 杨广斌, 等, 2019. 不同地形梯度上的植被变化趋势及原因分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 28(5): 857-864.
DOI |
| MA S B, AN Y L, YANG G B, et al., 2019. The analysis of distribution characteristics and reasons of NDVI change trends along the terrain gradient[J]. Ecology and Environment Sciences, 28(5): 857-864. | |
| [15] | 苏迎庆, 张恩月, 刘源, 等, 2022. 汾河流域土地利用变化及生态环境效应[J]. 干旱区研究, 39(3): 968-977. |
| SU Y Q, ZHANG E Y, LIU Y, et al., 2022. Land-use change and ecological environment effects on Fenhe River Basin[J]. Arid Zone Research, 39(3): 968-977. | |
| [16] | 田惠文, 毕如田, 朱洪芬, 等, 2019. 汾河流域植被净初级生产力的驱动因素及梯度效应[J]. 生态学杂志, 38(10): 3066-3074. |
| TIAN H W, BI R T, ZHU H F, et al., 2019. Driving factors and gradient effect of net primary productivity in Fenhe River Basin[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 38(10): 3066-3074. | |
| [17] | 童晓伟, 王克林, 岳跃民, 等, 2014. 桂西北喀斯特区域植被变化趋势及其对气候和地形的响应[J]. 生态学报, 34(12): 3425-3434. |
| TONG X W, WANG K L, YUE Y M, et al., 2014. Trends in vegetation and their responses to climate and topography in northwest Guangxi[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 34(12): 3425-3434. | |
| [18] |
王瑞杰, 闫峰, 2020. 2000-2018年西北砒砂岩区植被覆盖度与地形效应[J]. 应用生态学报, 31(4): 1194-1202.
DOI |
| WANG R J, YAN F, 2020. Fractional vegetation cover and topographic effects in Pisha sandstone area of Northwest China in 2000-2018[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 31(4):1194-1202. | |
| [19] | 张会霞, 李永梅, 张娜, 2022. 汾河流域植被覆盖度时空特征与地形因子的关系[J]. 水土保持通报, 42(1):353-359. |
| ZHANG H X, LI Y M, ZHANG N, 2022. Relationship between temporal and spatial characteristics of vegetation coverage and topographic factors in Fenhe River Basin[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 42(1):353-359. | |
| [20] | 赵婷, 白红英, 邓晨晖, 等, 2019. 2000-2016年秦岭山地植被覆盖变化地形分异效应[J]. 生态学报, 39(12): 4499-4509. |
| ZHAO T, BAI H Y, DENG C H, et al., 2019. Topographic differentiation effect on vegetation cover in the Qinling Mountains from 2000 to 2016[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 39(12): 4499-4509. | |
| [21] |
朱林富, 谢世友, 杨华, 等, 2017. 基于MODIS EVI的重庆植被覆盖变化的地形效应[J]. 自然资源学报, 32(12): 2023-2033.
DOI |
| ZHU L F, XIE S Y, YANG H, et al., 2017. The response of dynamic change in vegetation coverage to topography in Chongqing based on MODIS EVI[J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 32(12): 2023-2033. | |
| [22] | 杜琦, 2018. 山西省汾河流域植被恢复对蒸散发的影响[J]. 人民珠江, 39(1): 10-12. |
| DU Q, 2018. Effects of vegetation restoration on evapotranspiration in Fenhe River Basin of Shanxi province[J]. Pearl River, 39(1): 10-12. | |
| [23] | 韩丽君, 李晶, 2017. 近10年汾河流域植被覆盖时空变化研究[J]. 山东农业大学学报(自然科学版), 48(6): 824-831. |
| HAN L J, LI J, 2017. Temporal and spatial variations of vegetational coverage in Fenhe River Basin during 10 Years[J]. Journal of Shandong Agricultural University (Natural Science Edition), 48(6): 824-831. | |
| [24] | 林兴贵, 2020. 汾河流域生态环境存在问题及生态修复总体思路探析[J]. 水利规划与设计(6): 32-34. |
| LIN X G, 2020. Analysis of the existing problems of the ecological environment in the Fenhe River Basin and the overall ideas of ecological restoration[J]. Water Resources Planning and Design (6): 32-34. | |
| [25] |
刘梁美子, 占车生, 胡实, 等, 2018. 黔桂喀斯特山区植被变化及其地形效应[J]. 地理研究, 37(12): 2433-2446.
DOI |
|
LIU L M Z, ZHAN C S, HU S, et al., 2018. Vegetation change and its topographic effects in the karst mountainous areas of Guizhou and Guangxi[J]. Geographical Research, 37(12): 2433-2446.
DOI |
|
| [26] |
潘霞, 汪季, 高永, 等, 2019. 基于MODIS数据的阿拉善盟植被指数变化的地形分异性[J]. 生态环境学报, 28(2): 226-234.
DOI |
| PAN X, WANG J, GAO Y, et al., 2019. Research on topographic differentiation of vegetation index based on MODIS in Alxa League[J]. Ecology and Environment Sciences, 28(2): 226-234. | |
| [27] | 王鹏, 魏信, 乔玉良, 2011. 多尺度下汾河流域生态环境质量评价与时序分析[J]. 遥感技术与应用, 26(6): 798-807. |
| WANG P, WEI X, QIAO Y L, 2011. Quality evaluation and time sequential analysis of eco-environment at multi-scales in Fen River Basin[J]. Remote Sensing Technology and Application, 26(6): 798-807. | |
| [28] | 王宇琛, 李松鸣, 王霄, 等, 2016. 汾河流域2001—2013年植被覆盖时空变化及其对气候因子的响应[J]. 山西农业科学, 44(5): 640-645. |
| WANG Y C, LI S M, WANG X, et al., 2016. Spatial and temporal dynamics of vegetation cover from 2001 to 2013 and its response to climatic[J]. Journal of Shanxi Agricultural Sciences, 44(5): 640-645. | |
| [29] | 银朵朵, 王艳慧, 2021. 温带大陆性半干旱季风气候区植被覆盖度时空变化及其地形分异研究[J]. 生态学报, 41(3): 1158-1167. |
| YIN D D, WANG Y H, 2021. Temporal and spatial changes of vegetation coverage and its topographic differentiation in temperate continental semi-arid monsoon climate region[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 41(3): 1158-1167. | |
| [30] | 张衡, 马义娟, 李乐乐, 等, 2022. 汾河流域植被NDVI的时空变化特征及其对气候因子的响应[J]. 海南师范大学学报(自然科学版), 35(3): 322-332. |
| ZHANG H, MA Y J, LI L L, et al., 2022. Spatial-temporal change characteristics of vegetation NDVI and response to climate factors in the Fenhe River Basin[J]. Journal of Hainan Normal University (Natural Science), 35(3): 322-332. | |
| [31] |
朱小聪, 2022. 汾河流域植被生产力时空变异特征分析[J]. 中国农学通报, 38(5): 86-93.
DOI |
|
ZHU X C, 2022. Spatial and temporal variation characteristics of vegetation productivity in Fen River Basin[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 38(5): 86-93.
DOI |
| [1] | 王雪梅, 杨雪峰, 赵枫, 安柏耸, 黄晓宇. 基于机器学习算法的干旱区绿洲地上生物量估算[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(6): 1007-1015. |
| [2] | 郝蕾, 翟涌光, 戚文超, 兰穹穹. 2001-2020年内蒙古植被碳源/碳汇时空动态及对气候因子的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 825-834. |
| [3] | 巫晨煜, 许帆帆, 魏士博, 樊晶晶, 刘观鹏, 王坤. 渭河流域地表植被覆盖对气候变化的响应研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 835-844. |
| [4] | 陈俊芳, 吴宪, 刘啸林, 刘娟, 杨佳绒, 刘宇. 不同土壤水分下元素化学计量对微生物多样性的塑造特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 898-909. |
| [5] | 何艳虎, 龚镇杰, 吴海彬, 蔡宴朋, 杨志峰, 陈晓宏. 粤港澳大湾区城市生态效率时空演变及影响因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 469-480. |
| [6] | 王嘉丽, 冯婧珂, 杨元征, 俎佳星, 蔡文华, 杨健. 南宁市主城区不透水面与热环境效应的空间关系研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 525-534. |
| [7] | 张鐥文, 杨冉, 侯文星, 王丽丽, 刘爽, 宋汉扬, 赵文吉, 李令军. 生态补水前后永定河两岸植被覆盖度变化及驱动力分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(2): 264-273. |
| [8] | 贾志峰, 刘鹏程, 刘宇, 吴博博, 陈丹姿, 张向飞. 气候变化和人类活动对松辽流域植被覆盖的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 1-10. |
| [9] | 郑晓豪, 陈颖彪, 郑子豪, 郭城, 黄卓男, 周泳诗. 湖北省生态系统服务价值动态变化及其影响因素演变[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 195-206. |
| [10] | 张立进, 杜虎, 曾馥平, 黄国勤, 宋敏, 宋同清. 喀斯特峰丛洼地植被恢复过程中生产力与多样性关系探讨[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 26-35. |
| [11] | 吴胜义, 王飞, 徐干君, 马浩, 党禹杰, 吴菲. 川西北高山峡谷区森林碳储量及空间分布研究--以四川洛须自然保护区为例[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(9): 1735-1744. |
| [12] | 秦艳培, 徐少君, 田耀武. 黄河流域河南段植被和土壤及其碳密度空间分异研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(9): 1745-1753. |
| [13] | 阮惠华, 许剑辉, 张菲菲. 2001—2020年粤港澳大湾区植被和地表温度时空变化研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1510-1520. |
| [14] | 齐月, 张强, 胡淑娟, 蔡迪花, 赵福年, 陈斐, 张凯, 王鹤龄, 王润元. 黄土高原地区气候变化及其对冬小麦生产潜力的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1521-1529. |
| [15] | 邓天乐, 谢立勇, 张凤哲, 赵洪亮, 蒋语童. CO2浓度升高条件下稗草与水稻生长空间竞争关系研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1566-1572. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
