生态环境学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (7): 1185-1195.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2023.07.002
李惠梅1,2( ), 李荣杰1, 晏旭昇1, 武非非1, 高泽兵1,*(
), 李荣杰1, 晏旭昇1, 武非非1, 高泽兵1,*( ), 谭永忠2
), 谭永忠2
收稿日期:2023-04-23
出版日期:2023-07-18
发布日期:2023-09-27
通讯作者:
* 高泽兵。E-mail: 2008011@qhmu.edu.cn作者简介:李惠梅(1980年生),女,教授,博士,研究方向为国家公园、生态系统服务与福祉。E-mail: 22995670qq.com
基金资助:
LI Huimei1,2( ), LI Rongjie1, YAN Xusheng1, WU Feifei1, GAO Zebing1,*(
), LI Rongjie1, YAN Xusheng1, WU Feifei1, GAO Zebing1,*( ), TAN Yongzhong2
), TAN Yongzhong2
Received:2023-04-23
Online:2023-07-18
Published:2023-09-27
摘要:
将生态风险结合生态重要性区域进行生态功能分区,是缓解人类活动与生态保护矛盾的重要手段。气候变化和旅游对青海湖流域产生了生态风险的威胁,借助GIS空间技术,在生态系统服务的重要性和敏感性评价基础上,遵循压力点-暴露框架,基于压力-状态-响应模型评估了青海湖流域的生态风险,进行生态功能分区并提出管控建议。结果表明:(1)流域生态风险空间分布格局两级分化明显,高风险面积为7.77×103 km2,占流域面积的26.4%,集中在环青海湖地区及刚察县城;低风险区面积为12.7×103 km2,占流域面积的43.1%,主要是流域的水体及草地覆盖区;(2)流域生态系统服务重要性空间格局具有异质性,高值区面积为7.77×103 km2,占流域面积的26.4%,主要包括水体、湖泊、山林和高寒草地覆盖度高的生态区;低值区主要是环湖地区、高海拔地区和城镇扩张明显地区;(3)国家公园的功能区划不仅要考虑生态保护,还要考虑居民的生产生活需求和社区发展的需要,采用功能分区优化以充分体现“生态保护优先和高质量发展”。将高度重要区和高风险区整合为生态红线区,以最大程度保持区域内生态系统的原真性和完整性;将低/中风险区和轻度/中等重要区化为优先开发区,高风险区和较重要区的叠加为生态开发区,是未来国家公园运营过程中的生态畜牧业和生态旅游业发展区;剩余区域规划为保护发展过渡区,是未来的缓冲空间。该分区方案旨在尝试缓解生态保护与发展的矛盾,以有助于推动青海湖国家公园建设,为自然保护地的生态功能区规划提供了新思路,也为区域可持续发展提供科学参考。
中图分类号:
李惠梅, 李荣杰, 晏旭昇, 武非非, 高泽兵, 谭永忠. 青海湖流域生态风险评价及生态功能分区研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(7): 1185-1195.
LI Huimei, LI Rongjie, YAN Xusheng, WU Feifei, GAO Zebing, TAN Yongzhong. The Ecological Function Zoning of Qinghai Lake Basin Based on Ecological Risk Assessment[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(7): 1185-1195.
| 数据 | 格式 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| 土地利用数据 | 矢量 | 国家青藏高原科学数据中心数据 ( |
| 高程模型 | 栅格 | 地理空间数据云 ( |
| 归一化植被指数 | 栅格 | 中国科学院资源环境科学与数据中心 ( |
| 净生产力数据 | 栅格 | 用DEM数据使用CASA光能利用率模型数据计算得到 |
| 土壤数据 | 栅格 | 土壤类型和质地等数据来自世界土壤数据库 ( |
| 气象数据 | 栅格 | 中国气象数据网 ( |
| 自然保护地 | 矢量 | 青海省自然资源管理部门, 包括自然保护区、湿地公园等 |
| 基础地理数据 | 矢量 | 国家基础地理信息中心 ( |
表1 数据来源及数据库
Table 1 Data sources and databases
| 数据 | 格式 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| 土地利用数据 | 矢量 | 国家青藏高原科学数据中心数据 ( |
| 高程模型 | 栅格 | 地理空间数据云 ( |
| 归一化植被指数 | 栅格 | 中国科学院资源环境科学与数据中心 ( |
| 净生产力数据 | 栅格 | 用DEM数据使用CASA光能利用率模型数据计算得到 |
| 土壤数据 | 栅格 | 土壤类型和质地等数据来自世界土壤数据库 ( |
| 气象数据 | 栅格 | 中国气象数据网 ( |
| 自然保护地 | 矢量 | 青海省自然资源管理部门, 包括自然保护区、湿地公园等 |
| 基础地理数据 | 矢量 | 国家基础地理信息中心 ( |
| 评价因子 | 敏感性等级 | 权重 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 低 | 轻度 | 一般 | 较高 | 高 | ||
| 植被覆盖度 | >0.75 | 0.65-0.75 | 0.50-0.65 | 0.35-0.50 | ≤0.35 | 0.30 |
| 高程/m | ≤500 | 500-1000 | 1000-1500 | 1500-2000 | >2000 | 0.20 |
| 坡度/(°) | ≤5 | 5-10 | 10-15 | 15-25 | >25 | 0.25 |
| 土地利用类型 | 林地 | 水域 | 草地 | 耕地 | 其他 | 0.10 |
| 土壤侵蚀 强度 | 微侵蚀 | 轻度 侵蚀 | 中度 侵蚀 | 强烈 侵蚀 | 极强烈侵蚀 | 0.15 |
表2 青海湖流域生态环境敏感性评价因子及权重
Table 2 Evaluation Factors and Weights of Eco-environmental Sensitivity in Qinghai Lake Basin
| 评价因子 | 敏感性等级 | 权重 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 低 | 轻度 | 一般 | 较高 | 高 | ||
| 植被覆盖度 | >0.75 | 0.65-0.75 | 0.50-0.65 | 0.35-0.50 | ≤0.35 | 0.30 |
| 高程/m | ≤500 | 500-1000 | 1000-1500 | 1500-2000 | >2000 | 0.20 |
| 坡度/(°) | ≤5 | 5-10 | 10-15 | 15-25 | >25 | 0.25 |
| 土地利用类型 | 林地 | 水域 | 草地 | 耕地 | 其他 | 0.10 |
| 土壤侵蚀 强度 | 微侵蚀 | 轻度 侵蚀 | 中度 侵蚀 | 强烈 侵蚀 | 极强烈侵蚀 | 0.15 |
| 目标层 | 一级指标 | 二级指标 | 三级指标 | 权重 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 生态风险评价 指标体系 | 生态系统压力A1 (0.35) | 游憩压力B1 (0.65) | 旅游人次C1, 旅游收入C2 | 0.58, 0.42 |
| 气候压力B2 (0.35) | 年均气温C3, 年均降水C4 | 0.40, 0.60 | ||
| 生态系统状态A2 (0.40) | 生态系统状态B3 | 植被覆盖度C5, 生态系统服务重要度C6, 生态系统服务敏感性C7 | 0.20, 0.55, 0.45 | |
| 生态保护与建设措施 响应A3 (0.25) | 生态保护与建设B4 (0.25), 荒漠化治理B5 (0.50), 湿地保护与恢复B6 (0.25) | 生态管护资金C8, 封山/沙育林金额C9, 退耕还林补贴C10, 湿地保护补助C11 | 0.25, 0.35, 0.15, 0.25 |
表3 青海湖流域生态风险评价指标及权重
Table 3 Evaluation index and weight of ecological risk in Qinghai Lake Basin
| 目标层 | 一级指标 | 二级指标 | 三级指标 | 权重 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 生态风险评价 指标体系 | 生态系统压力A1 (0.35) | 游憩压力B1 (0.65) | 旅游人次C1, 旅游收入C2 | 0.58, 0.42 |
| 气候压力B2 (0.35) | 年均气温C3, 年均降水C4 | 0.40, 0.60 | ||
| 生态系统状态A2 (0.40) | 生态系统状态B3 | 植被覆盖度C5, 生态系统服务重要度C6, 生态系统服务敏感性C7 | 0.20, 0.55, 0.45 | |
| 生态保护与建设措施 响应A3 (0.25) | 生态保护与建设B4 (0.25), 荒漠化治理B5 (0.50), 湿地保护与恢复B6 (0.25) | 生态管护资金C8, 封山/沙育林金额C9, 退耕还林补贴C10, 湿地保护补助C11 | 0.25, 0.35, 0.15, 0.25 |
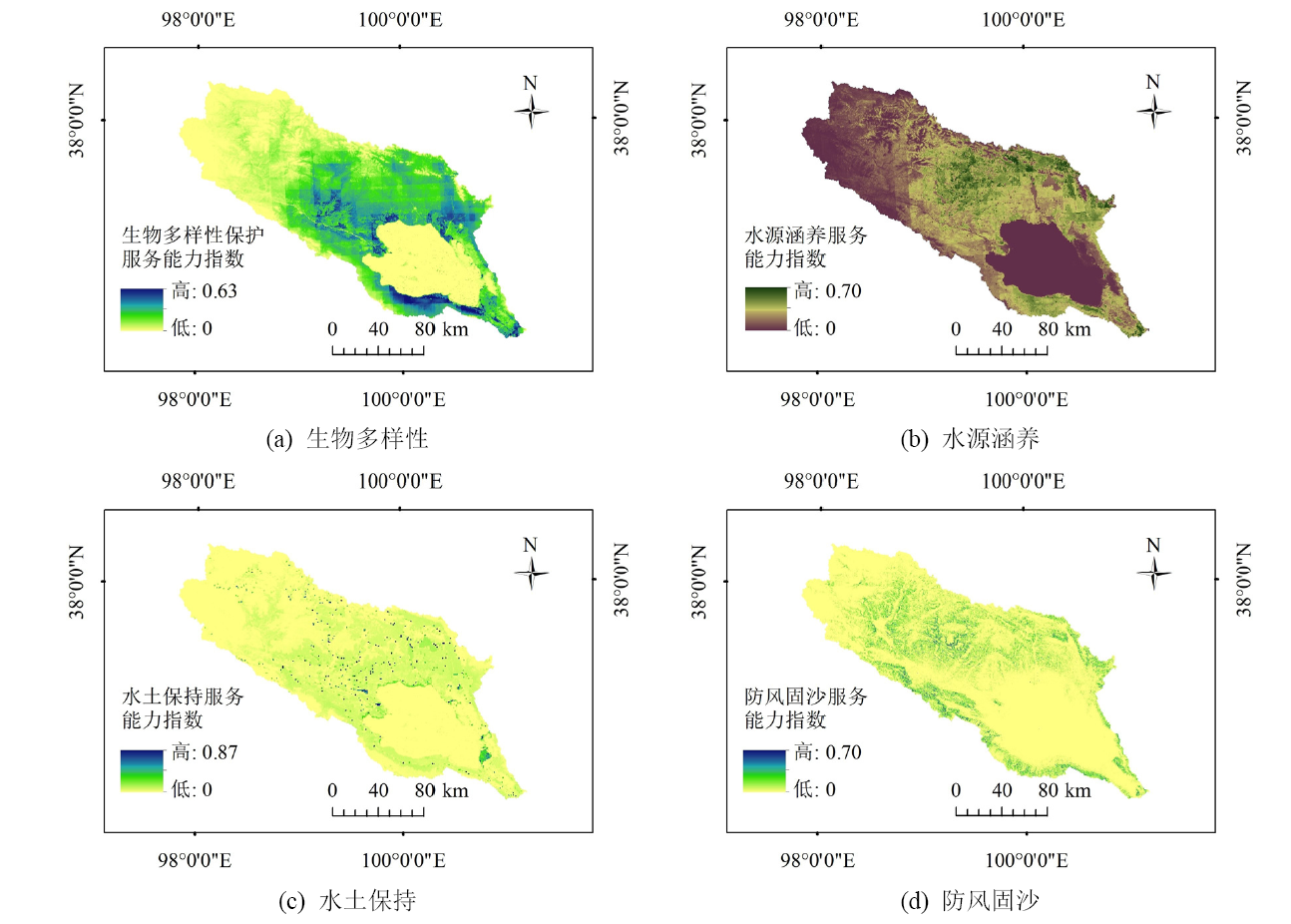
图3 青海湖流域防风固沙、水源涵养、水土保持、生物多样性生态系统服务重要性
Figure 3 The importance of ecosystem services, importance (windbreak and sand fixation, water conservation, soil and water conservation, biodiversity) in the Qinghai Lake Basin
| 重要性 | 生态系统服务重要性面积和比例 | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 水源涵养 | 水土保持 | 防风固沙 | 生物多样性维持 | 生态系统服务 | |||||||||||
| 面积/103 km2 | 比例/% | 面积/103 km2 | 比例/% | 面积/103 km2 | 比例/% | 面积/103 km2 | 比例/% | 面积/103 km2 | 比例/% | ||||||
| 弱 | 1 | 10.6 | 35.9 | 16.0 | 54.2 | 21.4 | 72.5 | 12.8 | 43.6 | 9.77 | 33.2 | ||||
| 一般 | 2 | 6.27 | 21.3 | 13.0 | 44.0 | 5.72 | 19.4 | 4.38 | 14.9 | 4.52 | 15.3 | ||||
| 中等 | 3 | 5.71 | 19.4 | 0.346 | 1.17 | 1.78 | 6.03 | 5.88 | 20.2 | 6.15 | 20.9 | ||||
| 次重要 | 4 | 4.79 | 16.2 | 0.179 | 0.606 | 0.532 | 1.78 | 4.53 | 15.4 | 6.61 | 22.4 | ||||
| 最重要 | 5 | 2.13 | 7.19 | 0 | 0 | 0.0856 | 0.290 | 1.79 | 6.09 | 2.41 | 8.18 | ||||
表4 青海湖流域生态系统服务重要性分区面积比例
Table 4 The zoning area and proportion ratio of ecosystem services’s importance in the Qinghai Lake Basin
| 重要性 | 生态系统服务重要性面积和比例 | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 水源涵养 | 水土保持 | 防风固沙 | 生物多样性维持 | 生态系统服务 | |||||||||||
| 面积/103 km2 | 比例/% | 面积/103 km2 | 比例/% | 面积/103 km2 | 比例/% | 面积/103 km2 | 比例/% | 面积/103 km2 | 比例/% | ||||||
| 弱 | 1 | 10.6 | 35.9 | 16.0 | 54.2 | 21.4 | 72.5 | 12.8 | 43.6 | 9.77 | 33.2 | ||||
| 一般 | 2 | 6.27 | 21.3 | 13.0 | 44.0 | 5.72 | 19.4 | 4.38 | 14.9 | 4.52 | 15.3 | ||||
| 中等 | 3 | 5.71 | 19.4 | 0.346 | 1.17 | 1.78 | 6.03 | 5.88 | 20.2 | 6.15 | 20.9 | ||||
| 次重要 | 4 | 4.79 | 16.2 | 0.179 | 0.606 | 0.532 | 1.78 | 4.53 | 15.4 | 6.61 | 22.4 | ||||
| 最重要 | 5 | 2.13 | 7.19 | 0 | 0 | 0.0856 | 0.290 | 1.79 | 6.09 | 2.41 | 8.18 | ||||
| 分级 | 敏感性 | 植被 | 土地利用 | 土壤 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 面积/103 km2 | 比例/% | 面积/103 km2 | 比例/% | 面积/103 km2 | 比例/% | 面积/103 km2 | 比例/% | ||||
| 低敏感 | 7.28 | 24.7 | 4.83 | 5.57 | 0.93 | 3.13 | 10.0 | 33.7 | |||
| 轻度敏感 | 6.45 | 21.9 | 8.05 | 9.29 | 6.40 | 21.6 | 4.51 | 15.2 | |||
| 一般敏感 | 7.41 | 25.1 | 63.3 | 73.1 | 18.8 | 63.4 | 9.87 | 33.3 | |||
| 较高敏感 | 5.88 | 19.9 | 6.14 | 7.08 | 0.36 | 1.21 | 4.56 | 15.4 | |||
| 高敏感 | 2.49 | 8.44 | 4.32 | 4.98 | 3.18 | 10.7 | 0.738 | 2.45 | |||
表5 青海湖流域生态敏感性分级
Table 5 Grading of ecological sensitivity in Qinghai Lake Watershed
| 分级 | 敏感性 | 植被 | 土地利用 | 土壤 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 面积/103 km2 | 比例/% | 面积/103 km2 | 比例/% | 面积/103 km2 | 比例/% | 面积/103 km2 | 比例/% | ||||
| 低敏感 | 7.28 | 24.7 | 4.83 | 5.57 | 0.93 | 3.13 | 10.0 | 33.7 | |||
| 轻度敏感 | 6.45 | 21.9 | 8.05 | 9.29 | 6.40 | 21.6 | 4.51 | 15.2 | |||
| 一般敏感 | 7.41 | 25.1 | 63.3 | 73.1 | 18.8 | 63.4 | 9.87 | 33.3 | |||
| 较高敏感 | 5.88 | 19.9 | 6.14 | 7.08 | 0.36 | 1.21 | 4.56 | 15.4 | |||
| 高敏感 | 2.49 | 8.44 | 4.32 | 4.98 | 3.18 | 10.7 | 0.738 | 2.45 | |||
| 生态风险 | 低 | 较低 | 中等 | 较高 | 高 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 面积/103 km2 | 6.39 | 6.31 | 5.35 | 3.60 | 7.77 |
| 比例/% | 21.7 | 21.4 | 18.2 | 12.2 | 26.4 |
表6 青海湖流域生态风险分级
Table 6 Grading of ecological risks in the Qinghai Lake Basin
| 生态风险 | 低 | 较低 | 中等 | 较高 | 高 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 面积/103 km2 | 6.39 | 6.31 | 5.35 | 3.60 | 7.77 |
| 比例/% | 21.7 | 21.4 | 18.2 | 12.2 | 26.4 |
| [1] |
CIRONE P A, DUNCAN P B, 2000. Integrating human health and ecological concerns in risk assessment[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 78(1-3): 1-17.
DOI URL |
| [2] | FENG Y, LI G, LI J, et al., 2021. Community stewardship of China’s national parks[J]. Science, 374(6565): 268-269. |
| [3] |
GALIC N, SCHMOLKE A, FORBES V, et al., 2012. The role of ecological models in linking ecological risk assessment to ecosystem services in agroecosystems[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 415(2): 93-100.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
XUE J, LI Z X, FENG Q, et al., 2023. Construction of ecological conservation pattern based on ecosystem services of Three River Headwaters, Western China[J]. Global Ecology and Conservation, 44(4): e02491.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
JIN G, SHI X, HE D W, et al., 2020. Designing a spatial pattern to rebalance the orientation of development and protection in Wuhan[J]. Journal of Geographical Sciences, 30(4): 569-582.
DOI |
| [6] |
JOHNSON C N, BALMFORD A, BROOK B W, et al., 2017. Biodiversity losses and conservation responses in the Anthropocene[J]. Science, 356(6335): 270-275.
DOI PMID |
| [7] |
JONES K R, VENTER O, FULLER R A, et al., 2018. One-third of global protected land is under intense human pressure[J]. Science, 360(6390): 788-791.
DOI PMID |
| [8] |
TAN L, LUO W, YANG B, et al., 2023. Evaluation of landscape ecological risk in key ecological functional zone of South-to-North Water Diversion Project, China[J]. Ecological Indicators, 147(8): 109934.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
LI Y F, SHI Y L, QURESHI S, et al., 2014. Applying the concept of spatial resilience to socio-ecological systems in the urban wetland interface[J]. Ecological Indicators, 42(7): 135-146.
DOI URL |
| [10] | LIU C X, LI Y C, YANG H, et al., 2011. RS and GIS-based assessment for eco-environmental sensitivity of the Three Gorges Reservoir Area of Chongqing[J]. Acta Geograhica Sinica, 66(5): 631-642. |
| [11] |
LIU H M, GAO J X, LIU X, et al., 2020. Monitoring and assessment of the ecosystem services value in the national key ecological function zones[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 40(6): 1-12.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
LIU Y, 2022. Study on the zoning of Northeast China Tiger and Leopard National Park[J]. International Journal of Geoheritage and Parks, 10(1): 113-123.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
PAN F J, SONG M J, WAN Q, et al., 2022. A conservation planning framework for China’s national key ecological function area based on ecological risk assessment[J]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 194(2): 74.
DOI |
| [14] |
PORRAS L P, VAZQUEZ L B, SARMIENTO-AGUILAR R, et al., 2016. Influence of human activities on some medium and large-sized mammals’ richness and abundance in the Lacandon rainforest[J]. Journal for Nature Conservation, 34(6): 75-81.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
PERRODIN Y, BOILLOT C, ANGERVILLE R, et al., 2011. Ecological risk assessment of urban and industrial systems: A review[J]. Science of the total environment, 409(24): 5162-5176.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
VILLARREAL-ROSAS J, SONTER L J, RUNTING R K, et al., 2020. Advancing systematic conservation planning for ecosystem services[J]. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 35(12): 1129-1139.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
WANG Q, YU H, ZHONG L S, et al., 2023. Optimising the relationship between ecological protection and human development through functional zoning[J]. Biological Conservation, 281(5): 110001.
DOI URL |
| [18] | WU C Z, YANG H N, ZHANG Y Q, et al., 2017. Behaviour analysis based funcation zoning model for National Park in China: Taking Dashanbao National Park in Yunnan Province as an example[J]. Environmental Protection, 45(14): 21-27. |
| [19] |
JIN X X, WEI L Y, WANG Y, et al., 2021. Construction of ecological security pattern based on the importance of ecosystem service functions and ecological sensitivity assessment: A case study in Fengxian county of Jiangsu province, China[J]. Environment, Development and Sustainability, 23(1): 563-590.
DOI |
| [20] | 曹玉红, 陈晨, 张大鹏, 等, 2019. 皖江城市带土地利用变化的生态风险格局演化研究[J]. 生态学报, 39(13): 4773-4781. |
| CAO Y H, CHEN C, ZHANG D P, et al., 2019. Study on the evolution of ecological risk pattern of land use change in Wanjiang urban belt[J]. Journal of Ecology, 39(13): 4773-4781. | |
| [21] |
陈峰, 李红波, 张安录, 2019. 基于生态系统服务的中国陆地生态风险评价[J]. 地理学报, 74(3): 432-445.
DOI |
| CHEN F, LI H B, ZHANG A L, 2019. Land ecological risk assessment in China based on ecosystem services[J]. Journal of Geography, 74(3): 432-445. | |
| [22] | 陈利顶, 周伟奇, 韩立建, 等, 2016. 京津冀城市群地区生态安全格局构建与保障对策[J]. 生态学报, 36(22): 7125-7129. |
| CHEN L D, ZHOU W Q, HAN L J, et al., 2016. Construction of ecological security pattern in the Jing-Jin-Ji and countermeasures for protection[J]. Journal of Ecology, 36(22): 7125-7129. | |
| [23] | 陈晓琴, 2012. 青海湖流域生态环境敏感性评价研究[D]. 西宁: 青海师范大学:31-33. |
| CHEN X Q, 2012. Study on ecological environment sensitivity assessment of Qinghai Lake basin[D]. Xining: Qinghai Normal University:31-33. | |
| [24] |
丁振民, 姚顺波, 2019. 区域生态敏感性评估的理论框架与模型设计——以陕西省为例[J]. 地理研究, 38(8): 2085-2098.
DOI |
| DING Z M, YAO S B, 2019. Theoretical framework and model design for regional ecological sensitivity assessment: A case study of Shaanxi province[J]. Geographic Research, 38(8): 2085-2098. | |
| [25] | 董玉红, 刘世梁, 王军, 等, 2017. 基于景观格局的土地整理风险与固碳功能评价[J]. 农业工程学报, 33(7): 246-253. |
| DONG Y H, LIU S L, WANG J, et al., 2017. Assessment of risk and carbon sequestration function of Land consolidation based on landscape pattern[J] Journal of Agricultural Engineering, 33(7): 246-253. | |
| [26] |
方莹, 王静, 黄隆杨, 等, 2020. 基于生态安全格局的国土空间生态保护修复关键区域诊断与识别——以烟台市为例[J]. 自然资源学报, 35(1): 190-203.
DOI |
|
FANG Y, WANG J, HUANG L Y, et al., 2020. Diagnosis and identification of key areas for land space ecological protection and restoration based on ecological security pattern: Taking Yantai City as an example[J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 35(1): 190-203.
DOI |
|
| [27] | 国家林业和草原局, 2020. 国家公园总体规划技术规范: GB/T 39736-2020[S]. 北京: 中国国家标准化管理委员会: 8-9. |
| National Forestry and Grassland Administration, 2020. Technical Specifications for Overall Planning of National Parks: GB/T 39736-2020[S]. Beijing: Standardization Administration of China: 8-9. | |
| [28] | 韩艳莉, 2021. 气候与景观格局变化对青海湖流域生态系统服务的影响[D]. 西宁: 青海师范大学:54-56. |
| HAN Y L, 2021. Impact of climate and landscape pattern changes on ecosystem services in the Qinghai Lake basin[D]. Xining: Qinghai Normal University:54-56. | |
| [29] | 环境保护部, 国家发展和改革委员会, 2017. 生态保护红线划定指南[EB/OL]. [2017-08-18]. https://www.mee.gov.cn/gkml/hbb/bgt/201707/W020170728397753220005. |
| Ministry of Environmental Protection, National Development and Reform Commission, 2017. Guidelines for delineating ecological protection red lines [EB/OL] [2017-08-18]. https://www.mee.gov.cn/gkml/hbb/bgt/201707/W020170728397753220005.pdf. | |
| [30] | 黄心怡, 赵小敏, 郭熙, 等, 2020. 基于生态系统服务功能和生态敏感性的自然生态空间管制分区研究[J]. 生态学报, 40(3): 1065-1076. |
| HUANG X Y, ZHAO X M, GUO X, et al., 2020. A study on natural ecological spatial regulation zoning based on ecosystem service functions and ecological sensitivity[J]. Journal of Ecology, 40(3): 1065-1076. | |
| [31] | 景永才, 陈利顶, 孙然好, 2018. 基于生态系统服务供需的城市群生态安全格局构建框架[J]. 生态学报, 38(12): 4121-4131. |
| JING Y C, CHEN L D, SUN R H, 2018. Framework for constructing the ecological security pattern of urban agglomeration based on the supply and demand of ecosystem services[J]. Journal of Ecology, 38(12): 4121-4131. | |
| [32] | 康鹏, 陈卫平, 王美娥, 2016. 基于生态系统服务的生态风险评价研究进展[J]. 生态学报, 36(5): 1192-1203. |
| KANG P, CHEN W P, WANG M E, 2016. Research progress on ecological risk assessment based on ecosystem services[J]. Journal of Ecology, 36(5): 1192-1203. | |
| [33] | 李永格, 李宗省, 冯起, 等, 2019. 基于生态红线划定的祁连山生态保护性开发研究[J]. 生态学报, 39(7): 2343-2352. |
| LI Y G, LI Z S, FENG Q, et al., 2019. Research on ecological protective development of Qilian Mountains based on ecological red line delimitation[J]. Journal of Ecology, 39(7): 2343-2352. | |
| [34] | 刘世梁, 侯笑云, 张月秋, 等, 2017. 基于生态系统服务的土地整治生态风险评价与管控建议[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 33(3): 193-200. |
| LIU S L, HOU X Y, ZHANG Y Q, et al., 2017. Ecological risk assessment and control suggestions for land remediation based on ecosystem services[J] Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 33(3): 193-200. | |
| [35] |
刘焱序, 王仰麟, 彭建, 等, 2015. 基于生态适应性循环三维框架的城市景观生态风险评价[J]. 地理学报, 70(7): 1052-1067.
DOI |
| LIU Y X, WANG Y L, PENG J, et al., 2015. Urban landscape ecological risk assessment based on the three-dimensional framework of ecological adaptability cycle[J]. Journal of Geography, 70(7): 1052-1067. | |
| [36] | 邱胜荣, 张希明, 白玲, 等, 2022. 中国自然保护地规划制度构建研究[J]. 世界林业研究, 35(2):76-81. |
| QIU S R, ZHANG X M, BAI L, et al., 2022. Construction of China’s natural protected area planning system[J]. World Forestry Research, 35(2): 76-81. | |
| [37] | 税伟, 杜勇, 王亚楠, 等, 2019. 闽三角城市群生态系统服务权衡的时空动态与情景模拟[J]. 生态学报, 39(14): 5188-5197. |
| SHUI W, DU Y, WANG Y N, et al., 2019. The spatiotemporal dynamics and scenario simulation of ecosystem service balance in the Fujian Delta urban agglomeration[J]. Journal of Ecology, 39(14): 5188-5197. | |
| [38] | 苏冲, 董建权, 马志刚, 等, 2019. 基于生态安全格局的山水林田湖草生态保护修复优先区识别——以四川省华蓥山区为例[J]. 生态学报, 39(23): 8948-8956. |
| SU C, DONG J Q, MA Z G, et al., 2019. Identification of priority areas for ecological protection and restoration of mountains, rivers, forests, fields, lakes, and grasslands based on ecological security patterns: A case study of Huaying Mountain Area in Sichuan Province[J]. Journal of Ecology, 39(23): 8948-8956. | |
| [39] | 王浩, 马星, 杜勇, 2021. 基于生态系统服务重要性和生态敏感性的广东省生态安全格局构建[J]. 生态学报, 41(5): 1705-1715. |
| WANG H, MA X, DU Y, 2021. Construction of an Ecological Security Pattern in Guangdong Province Based on the Importance and Sensitivity of Ecosystem Services[J]. Journal of Ecology, 41(5): 1705-1715. | |
| [40] | 王秀明, 赵鹏, 龙颖贤, 等, 2022. 基于生态安全格局的粤港澳地区陆域空间生态保护修复重点区域识别[J]. 生态学报, 42(2): 450-461. |
| WANG X M, ZHAO P, LONG Y X, et al., 2022. Identification of key areas for land spatial ecological protection and restoration in the Guangdong Hong Kong Macao region based on ecological security patterns[J]. Journal of Ecology, 42(2): 450-461. | |
| [41] | 熊善高, 秦昌波, 于雷, 等, 2018. 基于生态系统服务功能和生态敏感性的生态空间划定研究——以南宁市为例[J]. 生态学报, 38(22): 1-13. |
|
XIONG S G, QIN C B, YU L, et al., 2018. Research on delineation of ecological space based on ecosystem service function and ecological sensitivity: Taking Nanning city as an example[J]. Journal of Ecology, 38(22): 1-13.
DOI URL |
|
| [42] | 杨姗姗, 邹长新, 沈渭寿, 等, 2016. 基于生态红线划分的生态安全格局构建——以江西省为例[J]. 生态学杂志, 35(1): 250-258. |
| YANG S S, ZOU C X, SHEN W S, et al., 2016. Construction of ecological security pattern based on ecological red line division: A case study of Jiangxi Province[J]. Journal of Ecology, 35(1): 250-258. | |
| [43] |
杨天荣, 匡文慧, 刘卫东, 等, 2017. 基于生态安全格局的关中城市群生态空间结构优化布局[J]. 地理研究, 36(3): 441-452.
DOI |
| YANG T R, KUANG W H, LIU W D, et al., 2017. Optimization of ecological spatial structure in Guanzhong urban agglomeration based on ecological security pattern[J]. Geography Research, 36(3): 441-452. | |
| [44] | 张豆, 渠丽萍, 张桀滈, 2019. 基于生态供需视角的生态安全格局构建与优化——以长三角地区为例[J]. 生态学报, 39(20): 7525-7537. |
| ZHANG D, QU L P, ZHANG J Z, 2019. Construction and optimization of ecological security pattern from the perspective of ecological supply and demand: A case study of the Yangtze River Delta Region[J] Journal of Ecology, 39(20): 7525-7537. | |
| [45] |
张学斌, 石培基, 罗君, 等, 2014. 基于景观格局的干旱内陆河流域生态风险分析: 以石羊河流域为例[J]. 自然资源学报, 29(3): 410-419.
DOI |
| ZHANG X B, SHI P J, LUO J, et al., 2014. Ecological risk analysis of arid inland river basin based on landscape pattern: Taking Shiyang River basin as an example[J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 29(3): 410-419. |
| [1] | 张平江, 党国锋. 基于MCR模型与蚁群算法的洮河流域生态安全格局构建[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 481-491. |
| [2] | 童银栋, 黄兰兰, 杨宁, 张奕妍, 李子芃, 邵波. 全球水体微囊藻毒素分布特征及其潜在环境风险分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 129-138. |
| [3] | 李秀华, 赵玲, 滕应, 骆永明, 黄标, 刘冲, 刘本乐, 赵其国. 贵州汞矿区周边农田土壤汞镉复合污染特征空间分布及风险评估[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1629-1636. |
| [4] | 吉冰静, 刘艺, 吴杨, 高淑涛, 曾祥英, 于志强. 长江口及邻近东海沉积物中多环芳烃和含氧多环芳烃的分布特征、来源及生态风险[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(7): 1400-1408. |
| [5] | 彭红丽, 谭海霞, 王颖, 魏建梅, 冯阳. 不同种植模式下土壤重金属形态分布差异与生态风险评价[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(6): 1235-1243. |
| [6] | 朱立安, 张会化, 程炯, 李婷, 林梓, 李俊杰. 珠江三角洲林业用地土壤重金属潜在生态风险格局分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(6): 1253-1262. |
| [7] | 施建飞, 靳正忠, 周智彬, 王鑫. 额尔齐斯河流域典型尾矿库区周边土壤重金属污染评价[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(5): 1015-1023. |
| [8] | 张云, 舒抒, 罗鑫, 钟琴, 邹华. 水环境中糖皮质激素的环境行为及生态风险研究进展[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(2): 400-408. |
| [9] | 任珺, 潘佳璇, 陶玲, 仝云龙, 王若安, 孙新妮. 氢氧化钠改性坡缕石对Cd污染土壤的钝化修复效果[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(12): 2422-2430. |
| [10] | 谢洁芬, 章家恩, 危晖, 刘自强, 陈璇. 土壤中微塑料复合污染研究进展与展望[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(12): 2431-2440. |
| [11] | 谢邵文, 郭晓淞, 杨芬, 黄强, 陈曼佳, 魏兴琥, 刘承帅. 广州市城市公园土壤重金属累积特征、形态分布及其生态风险[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(11): 2206-2215. |
| [12] | 刘志坚, 董元华, 张琇, 卿成实. 卫宁平原农用地土壤重金属污染特征与生态风险研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(11): 2216-2224. |
| [13] | 王飞, 赵颖. 太原市污灌区农田土壤中多环芳烃污染特征及生态风险评价[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(1): 160-169. |
| [14] | 汪进, 韩智勇, 冯燕, 周若昕, 王双超. 成都市工业区绿地土壤重金属形态分布特征及生态风险评价[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(9): 1923-1932. |
| [15] | 他维媛, 康桢, 孟昭君, 金盛华, 杨幸, 郭龙飞, 赵东旭, 张馨. 秦岭典型停产关闭锌冶炼企业场地土壤重金属污染特征研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(7): 1513-1521. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
