生态环境学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (1): 129-138.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2023.01.014
收稿日期:2022-07-18
出版日期:2023-01-18
发布日期:2023-04-06
通讯作者:
*童银栋(1986年生),男,教授,博士,研究方向为水体富营养化与有毒物耦合生态风险。E-mail: yindongtong@tju.edu.cn基金资助:
TONG Yindong*( ), HUANG Lanlan, YANG Ning, ZHANG Yiyan, LI Zipeng, SHAO Bo
), HUANG Lanlan, YANG Ning, ZHANG Yiyan, LI Zipeng, SHAO Bo
Received:2022-07-18
Online:2023-01-18
Published:2023-04-06
摘要:
由于气候变暖和氮磷等外源营养物输入居高不下,全球许多水体中蓝藻水华(CyanoHABs)事件频繁发生,甚至在一些水质已经恢复的区域出现了反弹。部分水华蓝藻(如铜绿微囊藻Microcystis aeruginosa、念珠藻Nostoc等)会产生微囊藻毒素(Microcystins,MCs),危害人体和水生态健康。利用Web of Science数据库调研了全球不同地区324个湖库(共1291条数据)和15条河流(共96条数据)中MCs质量浓度;同时调查水温、pH、氨氮、硝酸盐氮、氮磷比等信息。结果表明,49.8%调查水体中胞外MCs质量浓度低于世界卫生组织标准(1 μg·L-1)。相关性分析表明,水体中ΣMCs质量浓度与硝酸盐氮、氨氮、氮磷比等水环境因子指标存在显著相关性。基于美国环保署水生物毒性数据库,利用风险商法评估了MC-LR水生态风险,研究表明,17.5%调查水体具有较低风险(0.1<RQ≤1),10.2%水体中具有中风险(1<RQ≤10),1.5%水体具有较高的风险(RQ>10)。在MCs毒害作用机制方面,应加强MCs对生物体已有疾病(如炎症、糖原动态平衡障碍)的作用机理研究以及MCs对线粒体的影响研究,并进一步研究MCs对PP1/2A酶的亚基蛋白影响机理。
中图分类号:
童银栋, 黄兰兰, 杨宁, 张奕妍, 李子芃, 邵波. 全球水体微囊藻毒素分布特征及其潜在环境风险分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 129-138.
TONG Yindong, HUANG Lanlan, YANG Ning, ZHANG Yiyan, LI Zipeng, SHAO Bo. Distribution Characteristics and Potential Environmental Risk Analysis of Microcystins in Global Water Bodies[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(1): 129-138.
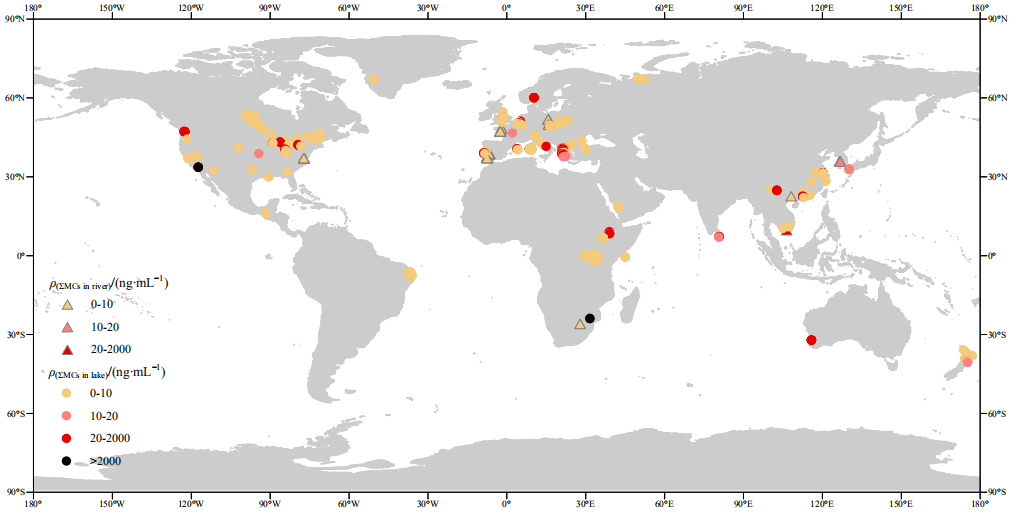
图2 全球不同国家地区水体ΣMCs质量浓度分布特征
Figure 2 Concentration and distribution characteristics of ΣMCs in water bodies of different countries and regions around the world
| 分类 | 物种 | MCs类型 | 暴露方式 | LC50/ (mg·L-1) | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 植物 | 金鱼藻C eratophyllum demersum | MC-LR | 静水暴露 | 5.00 | Pflugmacher, |
| 少根紫萍 Spirodela oligorrhiza | MC-LR | 静水暴露 | 0.52 | (吕志伟, | |
| 浮游植物 | 浮丝藻 Planktothrix rubescens | MC-LR | 静水暴露 | 8.60 | EPA毒性数据库 |
| 无脊椎动物 | 丰年虾 Artemia salina | MC-LR | 静水暴露 | 0.85-4.58 | EPA毒性数据库 (Romanowska-Duda et al., |
| 大旋口虫 Spirostomum ambiguum | MC-LR | 静水暴露 | 19.40 | (Tarczynska et al., | |
| 蚤草属 Daphnia pulicaria | MC-LR | 静水暴露 | 21.40 | (DeMott et al., | |
| 透明溞 Daphnia hyalma | MC-LR | 静水暴露 | 11.60 | (DeMott et al., | |
| 蚤状溞 Daphnia pulex | MC-LR | 静水暴露 | 9.60 | (DeMott et al., | |
| 镖水蚤 Diaptomus birgei | MC-LR | 静水暴露 | 0.73 | (DeMott et al., | |
| 真宽水蚤 Eurytemora affinis | MC-LR | 静水暴露 | 0.27 | (Reinikainen et al., | |
| 多刺裸腹溞 Moina macrocopa | MC-LR | 静水暴露 | 1.65 | (Yasuno et al., | |
| 二纹蜉蝣 Hexagenia sp. hatchlings | MC-LR | 静水暴露 | 1.11 | (Smith et al., | |
| 大型溞 Daphnia magna | MC-LR | 静水暴露 | 20.30 | (Chen et al., | |
| 埃及伊蚊 Aedes aegypti | MC-LR | 静水暴露 | 14.90 | (Kiviranta et al., | |
| 原足虫 Kalliapseudes schubartii | MC-LR | 静水暴露 | 1440.00 | (Montagnolli et al., | |
| 圣保罗对虾 Farfantepenaeus paulensis | MC-LR | 静水暴露 | 2960.00 | (吕志伟, | |
| 圣保罗对虾后期幼体 Farfantepenaeus paulensis postlarvae | MC-LR | 静水暴露 | 2.25 | (Salomon et al., | |
| 萼花臂轮虫 Brachionus calyciflorus | MC-LR | 静水暴露 | 0.06 | EPA毒性数据库 | |
| 梨形四膜虫 Tetrahymena pyriformis | MC-LR | 静水暴露 | 252.00 | (Romanowska-Duda et al., | |
| 同形溞 Daphnia similis | MC-LR | 静水暴露 | 667.50 | (Herrera et al., | |
| 光滑溞 Daphnia laevis | MC-LR | 静水暴露 | 295.25 | (Herrera et al., | |
| 微型裸腹溞 Moina micrura | MC-LR | 静水暴露 | 985.25 | (Herrera et al., | |
| 贻贝 Lampsilis siliquoidea | MC-LR | 静水暴露 | 0.13 | EPA毒性数据库 | |
| 脊椎动物 | 成年泥鳅 Misguruns mizolepis juvenile | MC-LR | 静水暴露 | 0.59 | (Liu et al., |
| 幼体泥鳅 Misguruns mizolepis larvae | MC-LR | 静水暴露 | 0.16 | (Liu et al., | |
| 胚胎泥鳅 Misguruns mizolepis embryo | MC-LR | 静水暴露 | 0.24 | (Liu et al., |
表1 不同类型水生生物MC-LR毒性阈值
Table 1 Toxicity thresholds of MC-LR in different aquatic organisms
| 分类 | 物种 | MCs类型 | 暴露方式 | LC50/ (mg·L-1) | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 植物 | 金鱼藻C eratophyllum demersum | MC-LR | 静水暴露 | 5.00 | Pflugmacher, |
| 少根紫萍 Spirodela oligorrhiza | MC-LR | 静水暴露 | 0.52 | (吕志伟, | |
| 浮游植物 | 浮丝藻 Planktothrix rubescens | MC-LR | 静水暴露 | 8.60 | EPA毒性数据库 |
| 无脊椎动物 | 丰年虾 Artemia salina | MC-LR | 静水暴露 | 0.85-4.58 | EPA毒性数据库 (Romanowska-Duda et al., |
| 大旋口虫 Spirostomum ambiguum | MC-LR | 静水暴露 | 19.40 | (Tarczynska et al., | |
| 蚤草属 Daphnia pulicaria | MC-LR | 静水暴露 | 21.40 | (DeMott et al., | |
| 透明溞 Daphnia hyalma | MC-LR | 静水暴露 | 11.60 | (DeMott et al., | |
| 蚤状溞 Daphnia pulex | MC-LR | 静水暴露 | 9.60 | (DeMott et al., | |
| 镖水蚤 Diaptomus birgei | MC-LR | 静水暴露 | 0.73 | (DeMott et al., | |
| 真宽水蚤 Eurytemora affinis | MC-LR | 静水暴露 | 0.27 | (Reinikainen et al., | |
| 多刺裸腹溞 Moina macrocopa | MC-LR | 静水暴露 | 1.65 | (Yasuno et al., | |
| 二纹蜉蝣 Hexagenia sp. hatchlings | MC-LR | 静水暴露 | 1.11 | (Smith et al., | |
| 大型溞 Daphnia magna | MC-LR | 静水暴露 | 20.30 | (Chen et al., | |
| 埃及伊蚊 Aedes aegypti | MC-LR | 静水暴露 | 14.90 | (Kiviranta et al., | |
| 原足虫 Kalliapseudes schubartii | MC-LR | 静水暴露 | 1440.00 | (Montagnolli et al., | |
| 圣保罗对虾 Farfantepenaeus paulensis | MC-LR | 静水暴露 | 2960.00 | (吕志伟, | |
| 圣保罗对虾后期幼体 Farfantepenaeus paulensis postlarvae | MC-LR | 静水暴露 | 2.25 | (Salomon et al., | |
| 萼花臂轮虫 Brachionus calyciflorus | MC-LR | 静水暴露 | 0.06 | EPA毒性数据库 | |
| 梨形四膜虫 Tetrahymena pyriformis | MC-LR | 静水暴露 | 252.00 | (Romanowska-Duda et al., | |
| 同形溞 Daphnia similis | MC-LR | 静水暴露 | 667.50 | (Herrera et al., | |
| 光滑溞 Daphnia laevis | MC-LR | 静水暴露 | 295.25 | (Herrera et al., | |
| 微型裸腹溞 Moina micrura | MC-LR | 静水暴露 | 985.25 | (Herrera et al., | |
| 贻贝 Lampsilis siliquoidea | MC-LR | 静水暴露 | 0.13 | EPA毒性数据库 | |
| 脊椎动物 | 成年泥鳅 Misguruns mizolepis juvenile | MC-LR | 静水暴露 | 0.59 | (Liu et al., |
| 幼体泥鳅 Misguruns mizolepis larvae | MC-LR | 静水暴露 | 0.16 | (Liu et al., | |
| 胚胎泥鳅 Misguruns mizolepis embryo | MC-LR | 静水暴露 | 0.24 | (Liu et al., |
| 计算结果 | 湖库 | 河流 | MCs指导值 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 范围 | 平均值 | 中值 | 范围 | 平均值 | 中值 | ||||||
| ρ(MEC)/(μg·L-1) | 0-471.45 | 11.27 | 0.31 | 0.05-97 | 10.64 | 0.53 | 0.8 | 1 | 1.3 | 10 | |
| RQ | 0-38.55 | 0.92 | 0.03 | <7.93 | 0.87 | 0.04 | 0.07 | 0.08 | 0.11 | 0.82 | |
表2 河流与湖库MC-LR的RQ值
Table 2 RQ values of MC-LR of lakes, reservoirs and rivers
| 计算结果 | 湖库 | 河流 | MCs指导值 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 范围 | 平均值 | 中值 | 范围 | 平均值 | 中值 | ||||||
| ρ(MEC)/(μg·L-1) | 0-471.45 | 11.27 | 0.31 | 0.05-97 | 10.64 | 0.53 | 0.8 | 1 | 1.3 | 10 | |
| RQ | 0-38.55 | 0.92 | 0.03 | <7.93 | 0.87 | 0.04 | 0.07 | 0.08 | 0.11 | 0.82 | |
| [1] |
ADAMSKI M, WOŁOWSKI K, KAMINSKI A, et al., 2020. Cyanotoxin cylindrospermopsin producers and the catalytic decomposition process: A review[J]. Harmful Algae, 98: 101894.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
ARMAH A D L C, MARIA G A, ANASTASIA H, et al., 2011. Can we effectively degrade microcystins? - Implications on human health[J]. Anti-Cancer Agents in Medicinal Chemistry, 11(1): 19-37.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
BU Q W, CAO Y B, YU G, et al., 2020. Identifying targets of potential concern by a screening level ecological risk assessment of human use pharmaceuticals in China[J]. Chemosphere, 246: 125818.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
CHEN L, GIESY J P, ADAMOVSKY O, et al., 2021. Challenges of using blooms of Microcystis spp. in animal feeds: A comprehensive review of nutritional, toxicological and microbial health evaluation[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 764: 142319.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
CHEN W, SONG L, OU D, et al., 2005. Chronic toxicity and responses of several important enzymes in Daphnia magna on exposure to sublethal microcystin-LR[J]. Environmental Toxicology, 20(3): 323-330.
DOI PMID |
| [6] | CHORUS I, 1999. Toxic Cyanobacteria in Water - A guide to their public health consequences, monitoring and management[M]. Britain: St Edmundsbury Press: 141. |
| [7] | CHORUS I, WELKER M, 2021. Toxic cyanobacteria in water: a guide to their public health consequences, monitoring and management[M]. Second Edition. London: CRC Press: 21. |
| [8] |
DAVIS T W, BERRY D L, BOYER G L, et al., 2009. The effects of temperature and nutrients on the growth and dynamics of toxic and non-toxic strains of Microcystis during cyanobacteria blooms[J]. Harmful Algae, 8(5): 715-725.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
DELANEY J M, WILKINS R M, 1995. Toxicity of microcystin-LR, isolated from Microcystis aeruginosa, against various insect species[J]. Toxicon, 33(6): 771-778.
PMID |
| [10] |
DEMOTT W R, ZHANG Q-X, CARMICHAEL W W, 1991. Effects of toxic cyanobacteria and purified toxins on the survival and feeding of a copepod and three species of Daphnia[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 36(7): 1346-1357.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
DIETRICH D, HOEGER S, 2005. Guidance values for microcystins in water and cyanobacterial supplement products (blue-green algal supplements): a reasonable or misguided approach?[J]. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology, 203(3): 273-289.
DOI PMID |
| [12] |
DONALD M A, PATRICIA M G, JOANN M B, et al., 2002. Harmful algal blooms and eutrophication: nutrient sources, composition, and consequences[J]. Estuaries, 25(4): 704-726.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
DU B B, LIU G F, KE M J, et al., 2019. Proteomic analysis of the hepatotoxicity of Microcystis aeruginosa in adult zebrafish (Danio rerio) and its potential mechanisms[J]. Environmental Pollution, 254(Part A): 113019.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
DUAN H T, MA R H, XU X F, et al., 2009. Two-decade reconstruction of algal blooms in China’s Lake Taihu[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 43(10): 3522-3528.
DOI URL |
| [15] | GLIBERT P M, HEIL C A, MADDEN C J, et al., 2021. Dissolved organic nutrients at the interface of fresh and marine waters: flow regime changes, biogeochemical cascades and picocyanobacterial blooms—the example of Florida Bay, USA[J]. Biogeochemistry, (1): 1-27. |
| [16] |
GRAHAM J L, JONES J R, JONES S B, et al., 2004. Environmental factors influencing microcystin distribution and concentration in the Midwestern United States[J]. Water Research, 38(20): 4395-4404.
PMID |
| [17] |
GUO W, JIANG R, LI J, et al., 2020. Acute toxicity of 4 algal toxins on 5 common fishes of the pearl river estuary[J]. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 467(1): 012131.
DOI |
| [18] |
HANSEN J D, LOFTIN K A, LAUGHREY Z, et al., 2021. Neither microcystin, nor nodularin, nor cylindrospermopsin directly interact with human toll-like receptors[J]. Chemosphere, 274: 129623.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
HERRERA N A, ECHEVERRI L F, FERRÃO-FILHO A S, 2015. Effects of phytoplankton extracts containing the toxin microcystin-LR on the survival and reproduction of cladocerans[J]. Toxicon, 95: 38-45.
DOI PMID |
| [20] |
HOWARD M D A, KUDELA R M, HAYASHI K, et al., 2021. Multiple co-occurring and persistently detected cyanotoxins and associated cyanobacteria in adjacent California lakes[J]. Toxicon, 192: 1-14.
DOI PMID |
| [21] |
HUANG P, CHEN K L, MA T F, et al., 2020. The effects of short-term treatment of microcystin-LR on the insulin pathway in both the HL7702 cell line and livers of mice[J]. Environmental Toxicology, 35(7): 727-737.
DOI PMID |
| [22] |
JAKOBI C, RINEHART K L, CODD G A, et al., 1996. Occurrence of toxic water blooms containing microcystins in a German Lake over a three year period[J]. Systematic and Applied Microbiology, 19(2): 249-254.
DOI URL |
| [23] | KAEBERNICK M, NEILAN BA, BORNER T, et al., 2000. Light and the transcriptional response of the microcystin biosynthesis gene cluster[J]. Applied & Environmental Microbiology, 66(8): 3387-3392. |
| [24] |
KAMEYAMA K, SUGIURA N, ISODA H, et al., 2002. Effect of nitrate and phosphate concentration on production of microcystins by Microcystis viridis NIES 102[J]. Aquatic Ecosystem Health and Management, 5(4): 443-449.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
KIVIRANTA J, NAMIKOSHI M, SIVONEN K, et al., 1992. Structure determination and toxicity of a new microcystin from Microcystis aeruginosa strain 205[J]. Toxicon, 30(9): 1093-1098.
PMID |
| [26] |
KLEINKAUF H, VON DöHREN H, 1990. Nonribosomal biosynthesis of peptide antibiotics[J]. European Journal of Biochemistry, 192(1): 1-15.
PMID |
| [27] |
KOTAK B G, LAM K Y, PREPAS E E, et al., 2000. Role of chemical and physical variables in regulating microcystin-LR concentration in phytoplankton of eutrophic lakes[J]. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, 57(8): 1584-1593.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
KRAUSFELDT L E, FARMER A T, CASTRO H F, et al., 2020. Nitrogen flux into metabolites and microcystins changes in response to different nitrogen sources in Microcystis aeruginosa NIES-843[J]. Environmental Microbiology, 22(6): 2419-2431.
DOI PMID |
| [29] |
LI H Y, XIE P, LI G Y, et al., 2009. In vivo study on the effects of microcystin extracts on the expression profiles of proto-oncogenes (c-fos, c-jun and c-myc) in liver, kidney and testis of male Wistar rats injected i.v. with toxins[J]. Toxicon, 53(1): 169-175.
DOI PMID |
| [30] |
LIN W, GUO H H, WANG L K, et al., 2020. Waterborne microcystin-LR exposure induced chronic inflammatory response via MyD88- dependent toll-like receptor signaling pathway in male zebrafish[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 702: 134969.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
LIU J C, ZHOU X H, SHI H C, 2018. An optical biosensor-based quantification of the microcystin synthetase a gene: Early warning of toxic cyanobacterial blooming[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 90(3): 2362-2368.
DOI PMID |
| [32] |
LIU Y D, SONG L R, LI X Y, et al., 2002. The toxic effects of microcystin-LR on embryo-larval and juvenile development of loach, Misguruns mizolepis Gunthe[J]. Toxicon, 40(4): 395-399.
DOI PMID |
| [33] |
MA J G, FENG Y Y, LIU Y, et al., 2016. PUMA and survivin are involved in the apoptosis of HepG2 cells induced by microcystin-LR via mitochondria-mediated pathway[J]. Chemosphere, 157: 241-249.
DOI PMID |
| [34] |
MACKINTOSH C, BEATTIE K A, KLUMPP S, et al., 1990. Cyanobacterial microcystin-LR is a potent and specific inhibitor of protein phosphatases 1 and 2A from both mammals and higher plants[J]. FEBS Letters, 264(2): 187-192.
DOI PMID |
| [35] |
MASANGO M G, MYBURGH J G, LABUSCHAGNE L, et al., 2010. Assessment of microcystis bloom toxicity associated with wildlife mortality in the kruger national park, south africa[J]. Journal of Wildlife Diseases, 46(1): 95-102.
PMID |
| [36] |
METCALF J S, LINDSAY J, BEATTIE K A, et al., 2002. Toxicity of cylindrospermopsin to the brine shrimp Artemia salina: comparisons with protein synthesis inhibitors and microcystins[J]. Toxicon, 40(8): 1115-1120.
DOI PMID |
| [37] | MONTAGNOLLI W, ZAMBONI A, LUVIZOTTO-SANTOS R, et al., 2004. Acute effects of Microcystis aeruginosa from the patos lagoon estuary, Southern Brazil, on the Microcrustacean kalliapseudes schubartii (Crustacea: Tanaidacea)[J]. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 46(4): 463-469. |
| [38] |
PAERL H W, HALL N S, CALANDRINO E S, 2011. Controlling harmful cyanobacterial blooms in a world experiencing anthropogenic and climatic-induced change[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 409(10): 1739-1745.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
PAPADIMITRIOU T, KATSIAPI M, VLACHOPOULOS K, et al., 2018. Cyanotoxins as the “common suspects” for the Dalmatian pelican (Pelecanus crispus) deaths in a Mediterranean reconstructed reservoir[J]. Environmental Pollution, 234: 779-787.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
PFLUGMACHER S, 2002. Possible allelopathic effects of cyanotoxins, with reference to microcystin-LR, in aquatic ecosystems[J]. Environmental Toxicology, 17(4): 407-413.
DOI PMID |
| [41] |
PLAAS H E, PAERL H W, 2021. Toxic cyanobacteria: a growing threat to water and air quality[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 55(1): 44-64.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
PREECE E P, MOORE B C, HARDY F J, 2015. Transfer of microcystin from freshwater lakes to Puget Sound, WA and toxin accumulation in marine mussels (Mytilus trossulus)[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 122: 98-105.
DOI PMID |
| [43] |
REINIKAINEN M, LINDVALL F, MERILUOTO J, et al., 2002. Effects of dissolved cyanobacterial toxins on the survival and egg hatching of estuarine calanoid copepods[J]. Marine Biology, 140(3): 577-583.
DOI URL |
| [44] |
ROMANOWSKA-DUDA Z, TARCZYŃSKA M, 2002. The influence of microcystin-LR and hepatotoxic cyanobacterial extract on the water plant Spirodela oligorrhiza[J]. Environmental Toxicology, 17(5): 434-440.
DOI URL |
| [45] | SALOMON P S, YUNES J S, PARISE M, et al., 2017. Toxicidade de um extrato de Microcystis aeruginosa da lagoa dos patos sobre camundongos e sua alterações sobre o tecido hepático[J]. VITTALLE- Revista De Ciências Da Saúde, 8(1): 23-32. |
| [46] |
SMITH J L, BOYER G L, MILLS E, et al., 2008. Toxicity of microcystin-LR, a cyanobacterial toxin, to multiple life stages of the burrowing mayfly, Hexagenia, and possible implications for recruitment[J]. Environmental Toxicology, 23(4): 499-506.
DOI PMID |
| [47] |
TAN C K, ISHIZAKA J, MATSUMURA S, et al., 2006. Seasonal variability of SeaWiFS chlorophyll a in the Malacca Straits in relation to Asian monsoon[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 26(2): 168-178.
DOI URL |
| [48] |
TANABE Y, SANO T, KASAI F, et al., 2009. Recombination, cryptic clades and neutral molecular divergence of the microcystin synthetase (mcy) genes of toxic cyanobacterium microcystis aeruginosa[J]. BMC Evolutionary Biology, 9(1): 115.
DOI URL |
| [49] |
TARCZYNSKA M, NALECZ-JAWECKI G, ROMANOWSKA-DUDA Z, et al., 2001. Tests for the toxicity assessment of cyanobacterial bloom samples[J]. Environmental Toxicology, 16(5): 383-390.
DOI PMID |
| [50] |
TILLETT D, DITTMANN E, ERHARD M, et al., 2000. Structural organization of microcystin biosynthesis in Microcystis aeruginosa PCC7806: an integrated peptide-polyketide synthetase system[J]. Chemistry & Biology, 7(10): 753-764.
DOI URL |
| [51] |
TONG Y D, WANG M Z, PENUELAS J, et al., 2020. Improvement in municipal wastewater treatment alters lake nitrogen to phosphorus ratios in populated regions[J]. Proceedings of The National Academy of Sciences of The United States of America, 117(21): 11566-11572.
DOI PMID |
| [52] |
WALLS J T, WYATT K H, DOLL J C, et al., 2018. Hot and toxic: Temperature regulates microcystin release from cyanobacteria[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 610-611: 786-795.
DOI URL |
| [53] |
WANG H J, XU C, LIU Y, et al., 2021. From unusual suspect to serial killer: Cyanotoxins boosted by climate change may jeopardize megafauna[J]. The Innovation, 2(2): 100092.
DOI URL |
| [54] | WANG J, CHEN Y B, CHEN Z P, et al., 2018b. Microcystin-leucine arginine inhibits gonadotropin-releasing hormone synthesis in mice hypothalamus[J]. Ecotoxicology & Environmental Safety, 163: 391-399. |
| [55] |
WANG S L, LI J S, ZHANG B, et al., 2018a. Trophic state assessment of global inland waters using a MODIS-derived Forel-Ule index[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 217: 444-460.
DOI URL |
| [56] |
WANG Z K, LI G Y, WU Q, et al., 2019. Microcystin-LR exposure induced nephrotoxicity by triggering apoptosis in female zebrafish[J]. Chemosphere, 214: 598-605.
DOI PMID |
| [57] |
WYNNE T, STUMPF R, 2015. Spatial and temporal patterns in the seasonal distribution of toxic cyanobacteria in western Lake Erie from 2002-2014[J]. Toxins, 7(5): 1649-1663.
DOI PMID |
| [58] | YASUNO M, SUGAYA Y, 1991. Toxicities of microcystis-viridis and the isolated hepatotoxic polypeptides on cladocerans[J], International Association of Theoretical and Applied Limnology-Proceedings, 24(4): 2622-2626. |
| [59] |
ZANCHETT G, OLIVEIRA E C, 2013. Cyanobacteria and cyanotoxins: from impacts on aquatic ecosystems and human health to anticarcinogenic effects[J]. Toxins, 5(10): 1896-1917.
DOI PMID |
| [60] |
ŽEGURA B, LAH T T, FILIPIČ M, 2004. The role of reactive oxygen species in microcystin-LR-induced DNA damage[J]. Toxicology, 200(1): 59-68.
DOI PMID |
| [61] |
ZHANG S Y, DU X S, LIU H H, et al., 2021. The latest advances in the reproductive toxicity of microcystin-LR[J]. Environmental Research, 192: 110254.
DOI URL |
| [62] | 陈秦, 2017. 浮丝藻中微囊藻毒素基因的检测技术及在环境中变异研究[D]. 陕西: 西北农林科技大学:12-13. |
| CHEN Q, 2017. Detection technology of microcystin gene in Pseudomonas and study on variation in the environment[D]. Shaanxi: Northwest Agriculture And Forestry University of Science and Technology:12-13. | |
| [63] | 杜怡闻, 2020. 溶解性有机质光化学特性及光敏活性中间体对藻毒素的光异构化研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆大学:76-77. |
| DU Y W, 2020. Photochemical properties of dissolved organic matter and photoisomerization of algal toxins by photoactive intermediates[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing University:76-77. | |
| [64] | 贺云, 陈艺生, 任岚, 等, 2021. 微囊藻毒素-LR对小鼠原代肝细胞线粒体功能的影响[J]. 中国实验动物学报, 29(6): 816-822. |
| HE Y, CHEN Y S, REN L, et al., 2021. Effects of microcystin-LR on mitochondrial function of mouse primary hepatocytes[J]. Acta Laboratorium Animalis Scientia Sinica, 29(6): 816-822. | |
| [65] | 李效宇, 宋立荣, 刘永定, 1999. 微囊藻毒素的产生、检测和毒理学研究[J]. 水生生物学报 (5): 7. |
| LI X Y, SONG L R, LIU Y D, 1999. Production, detection and toxicology of microcystins[J]. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica (5): 7. | |
| [66] | 梁佳, 曹明明, 2010. 微囊藻毒素的研究进展[J]. 地下水, 32(2): 133-135. |
| LIANG J, CAO M M, 2010. Research progress of microcystins[J]. Ground Water, 32(2): 133-135. | |
| [67] | 吕志伟, 2015. 海河干流上游段水体富营养化及微囊藻毒素的生态风险评价[D]. 天津: 天津大学:37. |
| LÜ Z W, 2015. Eutrophication and ecological risk assessment of microcystins in the upper reaches of the main stream of the Haihe River[D]. Tianjin: Tianjin University: 37. | |
| [68] | 生态环境部, 2021. 《2020年中国生态环境状况公报》发布[R]. 电力科技与环保, 37(3): 38. |
| Ministry of Ecology and Environment, 2021. 2020 Bulletin on the state of China’s ecological environment[R]. Electric Power Environmental Protection, 37(3): 38. | |
| [69] | 史红星, 曲久辉, 刘会娟, 等, 2008. 微囊藻毒素产生过程中氮素作用的同位素示踪研究[J]. 科学通报, 53(4): 407-412. |
| SHI H X, QU J H, LIU H J, et al., 2008. Isotope tracing of the role of nitrogen in the production of microcystins[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 53(4): 407-412. | |
| [70] | 舒为群, 2020. 蓝藻毒素污染与健康[M]. 武汉: 湖北科学技术出版社:22-23. |
| SHU W Q, 2020. Cyanobacterial toxin pollution and health[M]. Wuhan: Hubei Science and Technology Press:22-23. | |
| [71] | 宋瑞霞, 刘征涛, 沈萍萍, 2004. 太湖微囊藻毒素对细胞染色体及DNA损伤效应[J]. 中国公共卫生, 20(12): 1446-1447. |
| SONG R X, LIU Z T, SHEN P P, 2004. Effects of Taihu Lake microcystins on cell chromosome and DNA damage[J]. Chinese Journal of Public Health, 20(12): 1446-1447. | |
| [72] | 王蓓蕾, 2016. 微囊藻毒素-LR对人喉癌细胞Hep2蛋白磷酸酶2A的抑制作用及产生的细胞学影响[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学: 43-52. |
| WANG B L, 2016. Inhibitory effect of microcystin-LR on human laryngeal carcinoma cells Hep2 protein phosphatase 2A and its cytological effect[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University: 43-52. | |
| [73] | 王菲, 廖静, 茅丹俊, 等, 2017. 中国典型河湖水体铅的水生生物安全基准与生态风险评价[J]. 生态毒理学报, 12(3): 434-445. |
| WANG F, LIAO J, MAO D J, et al., 2017. Aquatic biosafety benchmark and ecological risk assessment of lead in typical rivers and lakes in China[J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicolog, 12(3): 434-445. | |
| [74] | 魏代春, 苏婧, 王骥, 等, 2013. 微囊藻毒素分布及与理化因子关系的研究进展[J]. 环境科学与技术 (S2): 7. |
| WEI D C, SU J, WANG J, et al, 2013. Research progress on the distribution of microcystins and their relationship with physical and chemical factors[J]. Environmental Science and Technology (S2): 7. | |
| [75] | 张会敏, 2010. 产微囊藻毒素藻株的PCR检测方法的研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨大学: 12-14. |
| ZHANG H M, 2010. Study on PCR detection method of microcystin-producing algal strains[D]. Harbin: Harbin University: 12-14. | |
| [76] | 张默, 2014. 陶然亭湖微囊藻毒素时间分布特征、成因及降解技术研究[D]. 大连: 大连海洋大学: 38. |
| ZHANG M, 2014. Research on the time distribution characteristics, genesis and degradation technology of microcystins in Taoranting Lake[D]. Dalian: Dalian Ocean University: 38. | |
| [77] | 张奕妍, 黄兰兰, 王夕予, 等, 2022. 噬藻体对蓝藻种群密度的调控及其对水体中物质循环的影响[J]. 湖泊科学, 34(2): 376-390. |
|
ZHANG Y Y, HUANG L L, WANG X Y, et al., 2022. The regulation of cyanobacterial population density by algae and its effect on the material cycle in water[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 34(2): 376-390.
DOI URL |
|
| [78] | 周文珊, 2012. 微囊藻毒素对鱼和哺乳动物红细胞致毒效应及对哺乳动物造血机能影响的研究[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学: 5. |
| ZHOU W S, 2012. Study on the toxic effect of microcystin on erythrocytes and hematopoietic function of fish and mammals[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University: 5. | |
| [79] | 朱光灿, 吕锡武, 王超, 2003. 微囊藻毒素的产生及其影响因子[J]. 污染防治技术 (Z2): 132-136, 145. |
| ZHU G C, LÜ X W, WANG C, 2003. Production of microcystins and its influencing factors[J]. Pollution Control Technology (Z2): 132-136, 145. | |
| [80] | 朱小奕, 2017. 水生态的物种敏感性风险评价方法改进及应用[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学: 18-19. |
| ZHU X Y, 2017. Improvement and application of species sensitivity risk assessment method in water ecology[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University: 18-19. |
| [1] | 王家一, 孙亭亭, 沙润钰, 谌婷红, 邢冉, 秦伯强, 施文卿. 富营养化湖泊蓝藻打捞减污降碳效果模拟研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(6): 1108-1114. |
| [2] | 王铁铮, 瞿心悦, 刘春香, 李有志. 东江湖水质时空变化规律及其与流域土地利用的关系[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 722-732. |
| [3] | 于菲, 曾海龙, 房怀阳, 付玲芳, 林澍, 董家豪. 典型感潮河网浮游藻类功能群时空变化特征及水质评价[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 756-765. |
| [4] | 杨秋, 曹英杰, 张宇, 陈建耀, 王诗忠, 田帝. 闭坑铅锌矿区地下水-矿坑水水化学特征及成因分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(2): 361-371. |
| [5] | 李海燕, 杨小琴, 简美鹏, 张晓然. 城市水体中微塑料的来源、赋存及其生态风险研究进展[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(2): 407-420. |
| [6] | 张丽聪, 肖凯, 张鹏, 李海龙, 王俊坚, 李镇扬, 王芬芳, 徐华林, 郭跃华. 淤泥质潮滩重金属和溶解性有机质的潮汐变化特征及其环境影响评价[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(11): 2169-2179. |
| [7] | 王海鹤, 孙媛媛, 张帅, 徐小蓉, 商成梅, 黎春想. 贵阳市集中式饮用水源地重金属污染特征及健康风险评价[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(10): 2039-2047. |
| [8] | 刘畅, 罗艳丽, 刘晨通, 郑玉红, 晁博, 董乐乐. 奎屯河下游区域地下水和农田土壤砷的空间分布特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(10): 2070-2078. |
| [9] | 王钊, 张曼胤, 胡宇坤, 刘魏魏, 张苗苗. 盐度对典型滨海湿地沉积物汞甲基化的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(9): 1876-1884. |
| [10] | 陈小弯, 田华川, 常军军, 陈礼强, 舒兴权, 冯秀祥. 杞麓湖中河河口表流湿地净化河道污染水的效果及其微生物群落特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(9): 1865-1875. |
| [11] | 吴昊平, 秦红杰, 贺斌, 尤毅, 陈金峰, 邹春萍, 杨思雨, 郝贝贝. 基于碳中和的农业面源污染治理模式发展态势刍议[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(9): 1919-1926. |
| [12] | 房献宝, 张智钧, 赖阳晴, 叶脉, 刁增辉. 新型污泥生物炭对土壤重金属Cr和Cd的修复研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1647-1656. |
| [13] | 陶玲, 黄磊, 周怡蕾, 李中兴, 任珺. 污泥-凹凸棒石共热解生物炭对矿区土壤重金属生物有效性和环境风险的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1637-1646. |
| [14] | 樊珂宇, 高原, 赖子尼, 曾艳艺, 刘乾甫, 李海燕, 麦永湛, 杨婉玲, 魏敬欣, 孙金辉, 王超. 珠三角河网鱼类微塑料污染特征研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1590-1598. |
| [15] | 王默雷, 李智慧, 陈来国, 郭送军, 刘明, 王硕, 陆海涛. 城市垃圾焚烧厂烟气及周边土壤中多溴联苯醚的污染特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1582-1589. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
