生态环境学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (12): 2422-2430.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2022.12.017
任珺1,2,3,*( ), 潘佳璇1,2, 陶玲1,2,3, 仝云龙1,2, 王若安1,2, 孙新妮1,2
), 潘佳璇1,2, 陶玲1,2,3, 仝云龙1,2, 王若安1,2, 孙新妮1,2
收稿日期:2021-07-10
出版日期:2022-12-18
发布日期:2023-02-15
通讯作者:
*作者简介:任珺(1968年生),男,教授,博士,从事污染环境生态修复理论与技术研究。E-mail: renjun@mail.lzjtu.cn
基金资助:
REN Jun1,2,3,*( ), PAN Jiaxuan1,2, TAO Ling1,2,3, TONG Yunlong1,2, WANG Ruo’an1,2, SUN Xinni1,2
), PAN Jiaxuan1,2, TAO Ling1,2,3, TONG Yunlong1,2, WANG Ruo’an1,2, SUN Xinni1,2
Received:2021-07-10
Online:2022-12-18
Published:2023-02-15
摘要:
土壤重金属污染原位钝化修复技术主要通过钝化剂的溶解沉淀、离子交换吸附、氧化还原、有机络合等反应来降低土壤中重金属的生物有效性,在重金属污染修复中具有重要意义。为研究NaOH改性坡缕石对污染土壤中Cd的钝化作用,以坡缕石为原料,采用浸渍法,将NaOH与坡缕石按照不同质量比进行改性,并在人工配制的Cd污染土壤上进行钝化实验和盆栽实验,研究NaOH改性坡缕石对Cd污染土壤的钝化效果以及对玉米植株生长性状和玉米植株Cd富集的影响。研究结果显示:与对照相比,添加NaOH改性坡缕石能显著降低土壤中DTPA和TCLP提取有效态Cd含量,提高钝化效率,降低生态风险指数,其中添加NaOH与坡缕石质量比为1?2的改性材料,两种有效态Cd含量降幅最大,分别为22.37%和26.60%。添加NaOH改性坡缕石能有效地改善玉米植株的生长性状。与对照相比,添加质量比为1?2的改性材料后,玉米植株的茎长、根长、茎、根鲜质量和茎、根干质量分别增加了71.45%、65.21%、22.06%、44.44%、33.96%和50%,同时玉米植株茎和根对Cd的富集以及Cd在玉米植株体内的转运均有显著降低,其茎部Cd含量最大降幅为32.01%,根部Cd含量最大降幅为15.67%,转运系数最多可降至0.538,一定程度上有助于Cd固定在土壤和玉米植株的根中,减少其对植物和人体的毒害作用。玉米植株的茎生物量、根生物量与Cd的生物有效态均呈极显著负相关,玉米植株体内的富集系数、转运系数与生物有效态Cd均呈极显著正相关。由此可知,NaOH改性坡缕石在Cd污染土壤的修复工作中,具有较为广阔的应用前景。
中图分类号:
任珺, 潘佳璇, 陶玲, 仝云龙, 王若安, 孙新妮. 氢氧化钠改性坡缕石对Cd污染土壤的钝化修复效果[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(12): 2422-2430.
REN Jun, PAN Jiaxuan, TAO Ling, TONG Yunlong, WANG Ruo’an, SUN Xinni. Stabilization Remediation of Soil Polluted by Cd Using Palygorskite Modified by NaOH[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(12): 2422-2430.
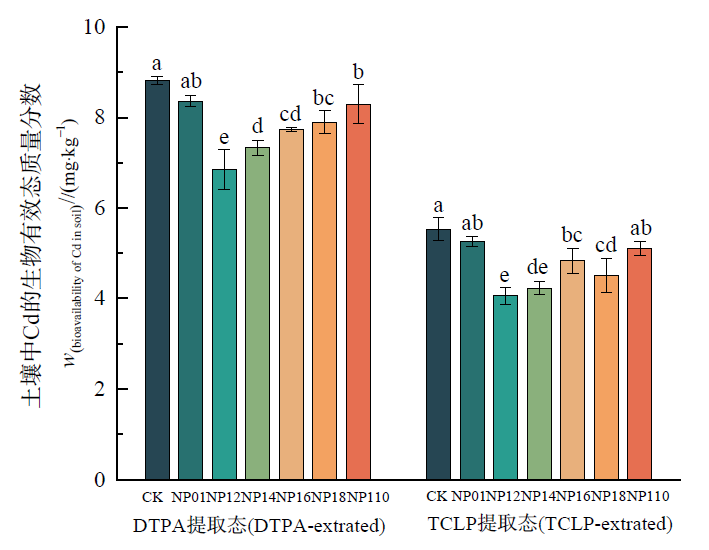
图1 NaOH改性坡缕石钝化土壤中Cd的生物有效态含量 不同小写字母表示处理之间差异显著(P<0.05)。下同
Figure 1 The stabilized with palygorskite modified by NaOH Different lowercase letters indicatesignificant differences between treatments (P<0.05). The same below
| 钝化剂 Stabilizer | 钝化效率Es/% | 生态风险指数Ier/% | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DTPA | TCLP | DTPA | TCLP | ||
| CK | 56.91 | 35.66 | |||
| NP01 | 5.18 | 4.77 | 53.96 | 33.96 | |
| NP12 | 22.37 | 26.60 | 44.18 | 26.18 | |
| NP14 | 16.91 | 21.41 | 47.29 | 27.30 | |
| NP16 | 12.38 | 12.61 | 49.86 | 31.17 | |
| NP18 | 10.47 | 18.32 | 50.95 | 29.13 | |
| NP110 | 6.00 | 7.56 | 53.49 | 32.97 | |
表1 NaOH改性坡缕石对土壤中Cd的钝化效率(Es)和生态风险指数(Ier)
Table 1 The stabilization efficiency and ecological risk index of Cd in soil stabilized with palygorskite modified by NaOH
| 钝化剂 Stabilizer | 钝化效率Es/% | 生态风险指数Ier/% | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DTPA | TCLP | DTPA | TCLP | ||
| CK | 56.91 | 35.66 | |||
| NP01 | 5.18 | 4.77 | 53.96 | 33.96 | |
| NP12 | 22.37 | 26.60 | 44.18 | 26.18 | |
| NP14 | 16.91 | 21.41 | 47.29 | 27.30 | |
| NP16 | 12.38 | 12.61 | 49.86 | 31.17 | |
| NP18 | 10.47 | 18.32 | 50.95 | 29.13 | |
| NP110 | 6.00 | 7.56 | 53.49 | 32.97 | |
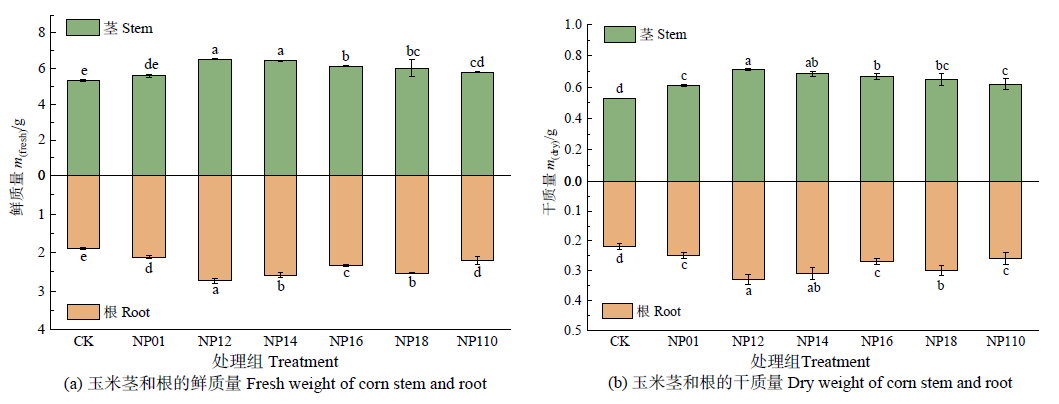
图3 NaOH改性坡缕石钝化土壤中种植玉米的茎和根的鲜质量和干质量
Figure 3 The fresh and dry weight of stem and root of corn planted in soils stabilized with palygorskite modified by NaOH
| 钝化剂 Stabilizer | 茎富集系数 Fbc shoot | 根富集系数 Fbc root | 转运系数 Ft |
|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 0.391±0.023a | 0.572±0.006a | 0.683±0.048a |
| NP01 | 0.343±0.030b | 0.526±0.002b | 0.652±0.054ab |
| NP12 | 0.260±0.007d | 0.483±0.002e | 0.538±0.015d |
| NP14 | 0.289±0.014c | 0.495±0.012d | 0.585±0.027cd |
| NP16 | 0.296±0.001c | 0.494±0.001d | 0.599±0.002bc |
| NP18 | 0.315±0.001bc | 0.509±0.001c | 0.620±0.001bc |
| NP110 | 0.326±0.011b | 0.513±0.001c | 0.636±0.022abc |
| F-value | 20.739*** | 91.179*** | 7.108*** |
表2 NaOH改性坡缕石钝化土壤中种植玉米的Cd生物富集系数(Fbc)和转运系数(Ft)
Table 2 The bioconcentration factor and transfer factor of Cd for corn planted in soils stabilized with palygorskite modified by NaOH
| 钝化剂 Stabilizer | 茎富集系数 Fbc shoot | 根富集系数 Fbc root | 转运系数 Ft |
|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 0.391±0.023a | 0.572±0.006a | 0.683±0.048a |
| NP01 | 0.343±0.030b | 0.526±0.002b | 0.652±0.054ab |
| NP12 | 0.260±0.007d | 0.483±0.002e | 0.538±0.015d |
| NP14 | 0.289±0.014c | 0.495±0.012d | 0.585±0.027cd |
| NP16 | 0.296±0.001c | 0.494±0.001d | 0.599±0.002bc |
| NP18 | 0.315±0.001bc | 0.509±0.001c | 0.620±0.001bc |
| NP110 | 0.326±0.011b | 0.513±0.001c | 0.636±0.022abc |
| F-value | 20.739*** | 91.179*** | 7.108*** |
| 项目 Items | 茎生物量 Biomass of stem | 根生物量 Biomass of root | 茎中Cd富集量 Cd in stem | 根中Cd富集量 Cd in root | 茎富集系数 Fbc shoot | 根富集系数 Fbc root | 转运系数 Ft |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DTPA | −0.875** | −0.850** | 0.912** | 0.825** | 0.900** | 0.826** | 0.872** |
| TCLP | −0.908** | −0.896** | 0.786** | 0.787** | 0.775** | 0.787** | 0.703** |
表3 NaOH改性坡缕石钝化土壤中Cd的生物有效态与玉米植株中Cd之间的相关系数
Table 3 The correlation coefficients between factors about Cd in maize plant and bioavailability of Cd in soils stabilized with palygorskite modified by NaOH
| 项目 Items | 茎生物量 Biomass of stem | 根生物量 Biomass of root | 茎中Cd富集量 Cd in stem | 根中Cd富集量 Cd in root | 茎富集系数 Fbc shoot | 根富集系数 Fbc root | 转运系数 Ft |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DTPA | −0.875** | −0.850** | 0.912** | 0.825** | 0.900** | 0.826** | 0.872** |
| TCLP | −0.908** | −0.896** | 0.786** | 0.787** | 0.775** | 0.787** | 0.703** |
| [1] | CHANG E E, CHIANG P C, LU P H, et al., 2001. Comparisons of metal leachability for various wastes by extraction and leaching methods[J]. Chemosphere (Oxford), 45(1): 91-99. |
| [2] |
CHEN T, ZHOU Z Y, XU S, et al., 2015. Adsorption behavior comparison of trivalent and hexavalent chromium on biochar derived from municipal sludge[J]. Bioresource Technology, 190: 388-394.
DOI PMID |
| [3] |
CHOPPALA G, BOLAN N, KUNHIKRISHNAN A, et al., 2016. Differential effect of biochar upon reduction-induced mobility and bioavailability of arsenate and chromate[J]. Chemosphere, 144: 374-381.
DOI PMID |
| [4] |
GENG H X, WANG L, 2019. Cadmium: Toxic effects on placental and embryonic development[J]. Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology, 67: 102-107.
DOI URL |
| [5] | GONZALO M A B, RAQUEL J, RITA P, et al., 2012. Heavy metals and trace elements in atmospheric fall-out: Their relationship with topsoil and wheat element composition[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 213-214: 447-456. |
| [6] |
HAJEB P, SLOTH J J, SHAKIBAZADEH S, et al., 2014. Toxic Elements in Food: Occurrence, Binding, and Reduction Approaches[J]. Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety, 13(4): 457-472.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
HUANG G Y, GAO R L, YOU J W, et al., 2019. Oxalic acid activated phosphate rock and bone meal to immobilize Cu and Pb in mine soils[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 174: 401-407.
DOI PMID |
| [8] |
HUANG R L, LIN Q T, ZHONG Q F, et al., 2020. Removal of Cd(II) and Pb(II) from aqueous solution by modified attapulgite clay[J]. Arabian Journal of Chemistry, 13(4): 4994-5008.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
LI X Z, HE C L, ZUO S X, et al., 2019. Photocatalytic nitrogen fixation over fluoride/attapulgite nanocomposite: Effect of upconversion and fluorine vacancy[J]. Solar Energy, 191: 251-262.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
MI X, REN J, TAO L, 2021. Stabilisation of heavy metals in soil using nanoscale zero-valent iron coated with palygorskite[J]. Chemistry in Ecology, 37(3): 234-251.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
MUHAMMAD F Q, MUHAMMAD Z U R, SHAFAQAT A, et al., 2017. Residual effects of monoammonium phosphate, gypsum and elemental sulfur on cadmium phytoavailability and translocation from soil to wheat in an effluent irrigated field[J]. Chemosphere, 174: 515-523.
DOI PMID |
| [12] |
SHARMA A, NAGPAL A K, 2018. Soil amendments: A tool to reduce heavy metal uptake in crops for production of safe food[J]. Reviews in Environmental Science and Bio/Technology, 17(1): 187-203.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
SHI L, GUO Z H, PENG C, et al., 2019. Immobilization of cadmium and improvement of bacterial community in contaminated soil following a continuous amendment with lime mixed with fertilizers: A four-season field experiment[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 171: 425-434.
DOI PMID |
| [14] |
TANG X, LI Q, WU M, et al., 2016. Review of remediation practices regarding cadmium-enriched farmland soil with particular reference to China[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 181: 646-662.
DOI PMID |
| [15] | WANG W B, WANG F F, KANG Y R, et al., 2015. Enhanced Adsorptive Removal of Methylene Blue from Aqueous Solution by Alkali-Activated Palygorskite[J]. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 226(3): 1-13. |
| [16] |
ZHANG D, DING A F, 2019. Effects of passivating agents on the availability of Cd and Pb and microbial community function in a contaminated acidic soil[J]. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 103(1): 98-105.
DOI PMID |
| [17] |
ZHANG M D, RAN R L, NAO W Q S, et al., 2019. Physiological effects of short-term copper stress on rape (Brassica napus L.) seedlings and the alleviation of copper stress by attapulgite clay in growth medium[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 171: 878-886.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
ZHANG Y, WANG W B, ZHANG J P, et al., 2015. A comparative study about adsorption of natural palygorskite for methylene blue[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 262: 390-398.
DOI URL |
| [19] | 陈展祥, 陈传胜, 陈卫平, 等, 2018. 凹凸棒石及其改性材料对土壤镉生物有效性的影响与机制[J]. 环境科学, 39(10): 4744-4751. |
| CHEN Z X, CHEN C S, CHEN W P, et al., 2018. Effect and mechanism of attapulgite and its modified materials on bioavailability of cadmium in soil[J]. Environmental Science, 39(10): 4744-4751. | |
| [20] | 邓新, 温璐璐, 迟鑫姝, 2010. 镉对人体健康危害及防治研究进展[J]. 中国医疗前沿, 5(10): 4-5. |
| DENG X, WEN L L, CHI X S, 2010. Cadmium hazards to human health and the prevention and treatment research[J]. National Medical Frontiers of China, 5(10): 4-5. | |
| [21] | 弓建泽, 张心然, 李志勇, 等, 2021. 有机肥施用和外源镉添加对土壤理化性质、油菜生长及其镉积累的影响[J]. 土壤通报, 52(3): 679-685. |
| GONG J Z, ZHANG X R, LI Z Y, et al., 2021. Effects of organic fertilizer combined with exogenous Cadmium addition on soil physical and chemical properties, rape growth and Cadmium accumulation[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 52(3): 679-685. | |
| [22] | 郝金才, 李柱, 吴龙华, 等, 2019. 铅镉高污染土壤的钝化材料筛选及其修复效果初探[J]. 土壤, 51(4): 752-759. |
| HAO J C, LI Z, WU L H, et al., 2019. Preliminary study on Cadmium and Lead stabilization in soil highly polluted with heavy metals using different stabilizing agents[J]. Soils, 51(4): 752-759. | |
| [23] | 纪艺凝, 徐应明, 王农, 等, 2019. 鱼骨粉对土壤Cd污染钝化修复效应及其理化性质的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 33(3): 312-319. |
| JI Y N, XU Y M, WANG N, et al., 2019. Effect of fish bone meal on immobilization remediation of Cacmium contaminated soil and its physiochemical properties[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 33(3): 312-319. | |
| [24] | 李龙凤, 2008. 改性凹凸棒粘土对水溶液中铜离子吸附性能的研究[J]. 淮北煤炭师范学院学报 (自然科学版), 29(4): 33-36. |
| LI L F, 2008. The study on the adsorption of copper ion on the modified attapugite clay[J]. Journal of Huaibei Coal Industry Teacher College (Natural Science), 29(4): 33-36. | |
| [25] | 李琳佳, 夏建国, 唐枭, 等, 2019. 海泡石对污染土壤中铅的钝化效果[J]. 生态环境学报, 28(5): 1013-1020. |
| LI L J, XIA J G, TANG X, et al., 2019. Immobilization of Pb in Contaminated Soil by Sepiolite[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 28(5): 1013-1020. | |
| [26] | 刘玉琳, 张友义, 妙凌云, 2001. 甘肃含碘凹凸棒石矿的发现及应用前景初探[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 20(4): 504-506. |
| LIU Y L, ZHANG Y Y, MIAO L Y, 2001. Discovery of iodic attapulgite deposits in gansu province and its preliminary application[J]. Acta Petrologica Et Mineralogica, 20(4): 504-506. | |
| [27] | 刘左军, 陈正宏, 袁惠君, 等, 2010. 凹凸棒石粘土对土壤团粒结构及小麦生长的影响[J]. 土壤通报, 41(1): 142-144. |
| LIU Z J, CHEN Z H, YUAN H J, et al., 2010. Effects of attapulgite clay on soil aggregate and wheat growth[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 41(1): 142-144. | |
| [28] | 吕本儒, 郭小伟, 李银光, 2017. 重金属污染土壤钝化修复效果化学评价方法研究进展[J]. 环境与可持续发展, 42(2): 73-76. |
| LÜ B R, GUO X W, LI Y G, 2017. Research progresses in chemical evaluation methods for passivating remediation effect of heavy metal contaminated soils[J]. Environment and Sustainable Development, 42(2): 73-76. | |
| [29] | 罗宁临, 李忠武, 黄梅, 等, 2020. 壳聚糖 (改性)-沸石对农田土壤重金属镉钝化技术研究[J]. 湖南大学学报 (自然科学版), 47(4): 132-140. |
| LUO N L, LI Z W, HUANG M, et al., 2020. Immobilizing cadmium in paddy soil by using modified chitosan-zeolite[J]. Journal of Hunan University (Natural Sciences), 47(4): 132-140. | |
| [30] | 马铁铮, 马友华, 徐露露, 等, 2013. 农田土壤重金属污染的农业生态修复技术[J]. 农业资源与环境学报, 30(5): 39-43. |
| MA T Z, MA Y H, XU L L, et al., 2013. Agro-ecological remediation technologies on heavy metal contamination in cropland soils[J]. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment, 30(5): 39-43. | |
| [31] | 冉洪珍, 郭朝晖, 肖细元, 等, 2019. 改良剂连续施用对农田水稻Cd吸收的影响[J]. 中国环境科学, 39(3): 1117-1123. |
| RAN H Z, GUO Z H, XIAO X Y, et al., 2019. Effects of continuous application of soil amendments on cadmium availability in paddy soil and uptake by rice[J]. China Environmental Science, 39(3): 1117-1123. | |
| [32] | 任珺, 刘丽莉, 陶玲, 等, 2013. 甘肃地区凹凸棒石的矿物组成分析[J]. 硅酸盐通报, 32(11): 2362-2365. |
| REN J, LIU L L, TAO L, et al., 2013. Mineral composition analysis of attapulgite from Gansu area[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 32(11): 2362-2365. | |
| [33] | 任静华, 廖启林, 范健, 等, 2017. 凹凸棒粘土对镉污染农田的原位钝化修复效果研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 26(12): 2161-2168. |
| REN J H, LIAO Q L, FAN J, et al., 2017. Effectof in-situ stabilizing remediation of Cd-polluted soil by attapulgite[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 26(12): 2161-2168. | |
| [34] | 陶玲, 管天成, 刘瑞珍, 等, 2021. 热改性坡缕石对土壤Cd污染的钝化修复研究[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 40(4): 782-790. |
| TAO L, GUAN T C, LIU R Z, et al., 2021. Stabilization remediation of cadmium contaminated soil by using heat-modified palygorskite[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 40(4): 782-790. | |
| [35] | 陶玲, 杨欣, 颜子皓, 等, 2018. 酸活化坡缕石制备重金属钝化材料的研究[J]. 非金属矿, 41(1): 11-14. |
| TAO L, YANG X, YAN Z H, et al., 2018. Study on the function of passivant for heavy metals with palygorskite modified by acid[J]. Non-Metallic Mines, 41(1): 11-14. | |
| [36] | 陶玲, 张倩, 张雪彬, 等, 2020. 凹凸棒石-污泥共热解生物炭对玉米苗期生长特性和重金属富集效应的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 39(7): 1512-1520. |
| TAO L, ZHANG Q, ZHANG X B, et al., 2020. Influence of biochar prepared by co-pyrolysis with attapulgite and sludge on maize growth and heavy metal accumulation[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 39(7): 1512-1520. | |
| [37] | 王金明, 易发成, 2006. 改性凹凸棒石表征及其对模拟核素Cs+的吸附研究[J]. 非金属矿, 29(2): 53-55. |
| WANG J M, YI F C, 2006. Study on characterization of modified attapulgite and its adsorption capacity on simulated nuclide Cs+[J]. Non-Metallic Mines, 29(2): 53-55. | |
| [38] | 武成辉, 李亮, 雷畅, 等, 2017. 硅酸盐钝化剂在土壤重金属污染修复中的研究与应用[J]. 土壤, 49(3): 446-452. |
| WU C H, LI L, LEI C, et al., 2017. Research and application of silicate passivation agent in remediation of heavy metal-contaminated soil: A review[J]. Soils, 49(3): 446-452. | |
| [39] | 徐奕, 李剑睿, 徐应明, 等, 2017. 膨润土钝化与不同水分灌溉联合处理对酸性稻田土镉污染修复效应及土壤特性的影响[J]. 环境化学, 36(5): 1026-1035. |
| XU Y, LI J R, XU Y M, et al., 2017. Effects of bentonite combined with different water management on immobilization remediation and soil properties of cadmium contaminated paddy soils[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 36(5): 1026-1035. | |
| [40] | 许振岚, 陈红, 2010. 城市污泥人工土壤中重金属生物有效性及综合毒性研究[J]. 浙江大学学报 (理学版), 37(3): 300-305. |
| XU Z L, CHEN H, 2010. Bioavailability and comprehensive toxicity of heavy metals in artificial soil composed of sewage sludge[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University (Science Edition), 37(3): 300-305. | |
| [41] | 殷飞, 王海娟, 李燕燕, 等, 2015. 不同钝化剂对重金属复合污染土壤的修复效应研究[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 34(3): 438-448. |
| YIN F, WANG H Y, LI Y Y, et al., 2015. Remediation of multiple heavy metal polluted soil using different immobilizing agents[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 34(3): 438-448. | |
| [42] | 张静静, 赵永芹, 王菲菲, 等, 2019. 膨润土、褐煤及其混合添加对铅污染土壤钝化修复效应研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 28(2): 395-402. |
| ZHANG J J, ZHAO Y Q, WANG F F, et al., 2019. Immobilization and remediation of Pb contaminated soil treated with bentonite, lignite and their mixed addition[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 28(2): 395-402. | |
| [43] | 张平萍, 陈雪刚, 程继鹏, 等, 2009. 水热条件下坡缕石在NaOH溶液中的行为及结构变化[J]. 无机化学学报, 25(9): 1545-1550. |
| ZHANG P P, CHEN X G, CHENG J P, et al., 2009. Behavior and structural transformation of palygorskite in NaOH solution under hydrothermal conditions[J]. Chinese Journal of Inorganic Chemistry, 25(9): 1545-1550. | |
| [44] | 章绍康, 弓晓峰, 申钊颖, 等, 2019. 改性凹凸棒土对土壤中Cd2+吸附解吸及钝化效果影响[J]. 环境工程, 37(3): 192-197. |
| ZHANG S K, GONG X F, SHEN Z Y, et al., 2019. Effect of modified attpulgite on the adsorption, desorption and immobilization of Cd2+ in soil[J]. Environmental Engineering, 37(3): 192-197. | |
| [45] | 周杰, 刘宁, 李云, 等, 1999. 凹凸棒石粘土的显微结构特征[J]. 硅酸盐通报, 18(6): 50-55. |
| ZHOU J, LIU N, LI Y, et al., 1999. Microscopic structure characteristics of attapulgite[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 18(6): 50-55. |
| [1] | 杜丹丹, 高瑞忠, 房丽晶, 谢龙梅. 旱区盐湖盆地土壤重金属空间变异及对土壤理化因子的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(6): 1123-1132. |
| [2] | 李传福, 朱桃川, 明玉飞, 杨宇轩, 高舒, 董智, 李永强, 焦树英. 有机肥与脱硫石膏对黄河三角洲盐碱地土壤团聚体及其有机碳组分的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 878-888. |
| [3] | 陈俊芳, 吴宪, 刘啸林, 刘娟, 杨佳绒, 刘宇. 不同土壤水分下元素化学计量对微生物多样性的塑造特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 898-909. |
| [4] | 董智今, 张呈春, 展秀丽, 张维福. 宁夏河东沙地生物土壤结皮及其下伏土壤养分的空间分布特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 910-919. |
| [5] | 周沁苑, 董全民, 王芳草, 刘玉祯, 冯斌, 杨晓霞, 俞旸, 张春平, 曹铨, 刘文亭. 放牧方式对高寒草地瑞香狼毒根际土壤团聚体及有机碳特征的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 660-667. |
| [6] | 潘昱伶, 璩向宁, 李琴, 王磊, 王筱平, 谭鹏, 崔庚, 安雨, 佟守正. 黄河宁夏段典型滩涂湿地土壤理化因子空间分布特征及其对微地形的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 668-677. |
| [7] | 赵维彬, 唐丽, 王松, 刘玲玲, 王树凤, 肖江, 陈光才. 两种生物炭对滨海盐碱土的改良效果[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 678-686. |
| [8] | 冯树娜, 吕家珑, 何海龙. KI淋洗对黄绵土汞污染的去除效果及土壤理化性状的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 776-783. |
| [9] | 陈敏毅, 朱航海, 佘伟铎, 尹光彩, 黄祖照, 杨巧玲. 珠三角某遗留造船厂场地土壤重金属人体健康风险评估及源解析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 794-804. |
| [10] | 张林, 齐实, 周飘, 伍冰晨, 张岱, 张岩. 北京山区针阔混交林地土壤有机碳含量的影响因素研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 450-458. |
| [11] | 秦浩, 李蒙爱, 高劲, 陈凯龙, 张殷波, 张峰. 芦芽山不同海拔灌丛土壤细菌群落组成和多样性研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 459-468. |
| [12] | 唐海明, 石丽红, 文丽, 程凯凯, 李超, 龙泽东, 肖志武, 李微艳, 郭勇. 长期施肥对双季稻田根际土壤氮素的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 492-499. |
| [13] | 刘抗旱, 郑刘根, 张理群, 丁丹, 单士锋. 复合型植物源活化剂强化蜈蚣草修复砷污染土壤的效应研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 635-642. |
| [14] | 樊慧琳, 张佳敏, 李欢, 王艳玲. 坡耕地稻田剖面磷的储存格局与流失风险研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(2): 283-291. |
| [15] | 宋孝帅, 丁武泉, 刘新敏, 李廷真. 离子特异性效应对紫色土孔隙状况的影响机制研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(2): 292-298. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
