生态环境学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (3): 451-459.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2022.03.003
胡靓达( ), 周海菊, 黄永珍, 姚贤宇, 叶绍明, 喻素芳*(
), 周海菊, 黄永珍, 姚贤宇, 叶绍明, 喻素芳*( )
)
收稿日期:2021-09-07
出版日期:2022-03-18
发布日期:2022-05-25
通讯作者:
*喻素芳,E-mail: yusufang@gxu.edu.cn作者简介:胡靓达(1996 年生),女,硕士研究生,研究方向为森林经理。E-mail: 1397442176@qq.com
基金资助:
HU Jingda( ), ZHOU Haiju, HUANG Yongzhen, YAO Xianyu, YE Shaoming, YU Sufang*(
), ZHOU Haiju, HUANG Yongzhen, YAO Xianyu, YE Shaoming, YU Sufang*( )
)
Received:2021-09-07
Online:2022-03-18
Published:2022-05-25
摘要:
探讨不同杉木混交林类型的林分植物多样性及土壤碳氮特征,为科学经营杉木人工林提供理论依据。以中国林业科学研究院热带林业实验中心的27年生的杉木(Cunninghamia lanceolate)×红锥(Castanopsis hystrix)混交林(MCC)、杉木×大叶栎(Quercus griffithii)混交林(MCQ)及杉木纯林(PCL)为试验对象,采用群落调查法分析3种林分乔木层、灌木层、草本层以及整个群落的植物多样性和土壤碳氮含量差异及其之间的相关性。结果表明,3种杉木林分类型中,整个群落植物多样性表现为MCQ>MCC>PCL,混交林乔木层植物多样性显著高于PCL(P<0.05),灌木层和草本层无显著差异(P>0.05)。MCQ土壤有机碳含量显著高于PCL,但氮含量、碳氮比在3种林分中无显著差异。相关性分析结果显示,乔木层仅Shannon-Wiener指数与土壤有机碳含量呈显著正相关;土壤有机碳、全氮含量与碳氮比与灌木层植物多样性指数呈一定的相关性,与草本层无显著相关性;群落植物多样性指数与土壤有机碳、全氮含量及碳氮比无显著关系。杉木与红锥、大叶栎混交提高了植物多样性,且杉木与大叶栎混交显著提高了土壤有机碳含量,更有利于改善杉木人工林土壤质量。
中图分类号:
胡靓达, 周海菊, 黄永珍, 姚贤宇, 叶绍明, 喻素芳. 不同杉木林分类型植物多样性及其土壤碳氮关系的研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(3): 451-459.
HU Jingda, ZHOU Haiju, HUANG Yongzhen, YAO Xianyu, YE Shaoming, YU Sufang. A Study on Plant Species Diversity and Soil Carbon and Nitrogen in Different Cunninghamia lanceolata Stand Types[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(3): 451-459.
| 林分 类型 Stand type | 样地 编号 Number | 坡位 Slope position | 坡度 Slope/ (°) | 坡向 Aspect | 胸径 Diameter at breast height/cm | 树高 Tree height/m | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 杉木 C. lanceolata | 红锥 C. hystrix | 大叶栎 Q. griffithii | 杉木 C. lanceolata | 红锥 C. hystrix | 大叶栎 Q. griffithii | ||||||
| MCC | 1 | 上 | 52 | 西偏南 | 23.94±5.70a | 12.26±4.62a | — | 19.86±1.02c | 12.84±5.57a | — | |
| 2 | 中 | 46 | 西偏南 | 23.31±3.70a | 11.65±3.07a | — | 21.71±0.90a | 14.43±3.59a | — | ||
| 3 | 下 | 39 | 西偏南 | 25.11±4.36a | 13.55±4.37a | — | 21.06±1.06b | 14.41±5.03a | — | ||
| MCQ | 4 | 上 | 50 | 西偏南 | 21.83±5.12a | — | 16.51±7.10a | 19.42±4.65a | — | 12.58±6.39b | |
| 5 | 中 | 40 | 西偏南 | 16.55±10.34b | — | 19.54±6.73a | 14.33±7.10b | — | 18.78±3.11a | ||
| 6 | 下 | 36 | 西偏南 | 25.54±3.54a | — | 17.69±8.37a | 21.44±1.08a | — | 14.77±5.23b | ||
| PCL | 7 | 上 | 53 | 西偏南 | 17.57±8.81a | — | — | 16.13±7.07a | — | — | |
| 8 | 中 | 45 | 西偏南 | 15.86±7.70a | — | — | 15.63±6.58a | — | — | ||
| 9 | 下 | 38 | 西偏南 | 17.14±6.71a | — | — | 17.01±5.85a | — | — | ||
表1 不同类型林分样地基本情况
Table 1 Basic situation of different stand types on the ground
| 林分 类型 Stand type | 样地 编号 Number | 坡位 Slope position | 坡度 Slope/ (°) | 坡向 Aspect | 胸径 Diameter at breast height/cm | 树高 Tree height/m | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 杉木 C. lanceolata | 红锥 C. hystrix | 大叶栎 Q. griffithii | 杉木 C. lanceolata | 红锥 C. hystrix | 大叶栎 Q. griffithii | ||||||
| MCC | 1 | 上 | 52 | 西偏南 | 23.94±5.70a | 12.26±4.62a | — | 19.86±1.02c | 12.84±5.57a | — | |
| 2 | 中 | 46 | 西偏南 | 23.31±3.70a | 11.65±3.07a | — | 21.71±0.90a | 14.43±3.59a | — | ||
| 3 | 下 | 39 | 西偏南 | 25.11±4.36a | 13.55±4.37a | — | 21.06±1.06b | 14.41±5.03a | — | ||
| MCQ | 4 | 上 | 50 | 西偏南 | 21.83±5.12a | — | 16.51±7.10a | 19.42±4.65a | — | 12.58±6.39b | |
| 5 | 中 | 40 | 西偏南 | 16.55±10.34b | — | 19.54±6.73a | 14.33±7.10b | — | 18.78±3.11a | ||
| 6 | 下 | 36 | 西偏南 | 25.54±3.54a | — | 17.69±8.37a | 21.44±1.08a | — | 14.77±5.23b | ||
| PCL | 7 | 上 | 53 | 西偏南 | 17.57±8.81a | — | — | 16.13±7.07a | — | — | |
| 8 | 中 | 45 | 西偏南 | 15.86±7.70a | — | — | 15.63±6.58a | — | — | ||
| 9 | 下 | 38 | 西偏南 | 17.14±6.71a | — | — | 17.01±5.85a | — | — | ||
| 层次 Layer | PCL | MCC | MCQ | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 植物名称 Plants | 重要值 Important value/% | 植物名称 Plants | 重要值 Important value/% | 植物名称 Plants | 重要值 Important value/% | |||
| 乔木层 Tree layer | 杉木 Cunninghamia lanceolate | 60.49 | 杉木 | 42.81 | 杉木 | 36.72 | ||
| 黄毛榕 Ficus esquiroliana | 5.36 | 红锥 Castanopsis hystrix | 21.21 | 大叶栎 Quercus griffithii | 23.72 | |||
| 毛黄肉楠 Actinodaphne pilosa | 5.35 | 香梓楠 Michelia hedyosperma | 14.97 | 格木 Erythrophleum fordii | 7.44 | |||
| 水东哥 Saurauia tristyla | 4.06 | 中平树 Macaranga denticulata | 7.12 | 三桠苦 | 6.08 | |||
| 鹅掌柴 Schefflera octophylla | 3.10 | 银合欢 Leucaena leucocephala | 3.21 | 黄毛榕 | 5.03 | |||
| 米老排 Mytilaria laosensis | 2.77 | 潺槁木姜子 Litsea glutinosa | 3.05 | 红锥 | 5.01 | |||
| 三桠苦 Evodia lepta | 2.64 | 水东哥 | 2.80 | 中平树 | 3.47 | |||
| 大青 Clerodendrum cyrtophyllum | 2.35 | 华润楠 Machilus chinensis | 2.84 | |||||
| 簕欓花椒 Zanthoxylum avicennae | 2.07 | 水东哥 | 2.83 | |||||
| 灌木层 Shurb layer | 倒卵叶紫麻 Oreocnide obovata | 15.62 | 三桠苦 | 17.1 | 大管 | 27.53 | ||
| 水东哥 | 13.16 | 杜茎山 | 16.68 | 水东哥 | 9.44 | |||
| 九节 Psychotria rubra | 10.12 | 潺槁木姜子 | 8.66 | 三桠苦 | 7.00 | |||
| 杜茎山 Maesa japonica | 7.57 | 粗叶榕 | 6.76 | 大叶栎 | 6.31 | |||
| 三桠苦 | 6.38 | 香梓楠 | 6.10 | 大青 | 6.22 | |||
| 亮叶猴耳环 Archidendron lucidum | 5.88 | 野牡丹 Melastoma candidum | 5.23 | 格木 | 4.84 | |||
| 绒毛山胡椒 Lindera nacusua | 5.78 | 九节 | 4.56 | 中平树 | 4.65 | |||
| 大管 Micromelum falcatum | 5.42 | 红锥 | 3.61 | 粗叶榕 | 3.74 | |||
| 粗叶榕 Ficus hirta | 4.93 | 柏拉木 | 3.56 | 水锦树 Wendlandia uvariifolia | 2.66 | |||
| 大青 | 4.08 | 水同木 Ficus fistulosa | 2.67 | 九节 | 2.64 | |||
| 南方荚蒾 Viburnum fordiae | 3.68 | 润楠 Machilus pingii | 2.58 | 倒卵叶紫麻 | 2.54 | |||
| 柏拉木 Blastuscochinchinensis | 3.49 | 倒卵叶紫麻 | 2.54 | 斑鸠菊 Vernonia esculenta | 2.29 | |||
| 红紫珠 Callicarpa rubella | 3.18 | 鹅掌柴 | 2.21 | 粗糠柴 | 2.16 | |||
| 黄毛榕 | 3.14 | |||||||
| 粗糠柴 Mallotus philippensis | 2.34 | |||||||
| 草本层 Herbal layer | 金毛狗 Cibotiumbarometz | 31.61 | 金毛狗 | 22.89 | 乌毛蕨 | 39.85 | ||
| 霹雳薹草 Carex perakensis | 21.40 | 乌毛蕨 | 11.94 | 半边旗 | 28.00 | |||
| 华南毛蕨 Cyclosorus parasiticus | 10.53 | 团叶陵齿蕨 | 10.37 | 扇叶铁线蕨 | 14.08 | |||
| 黄腺羽蕨 Pleocnemia winitii | 9.83 | 三羽新月蕨 | 9.97 | 淡竹叶 | 4.82 | |||
| 乌毛蕨 Blechnum orientale | 7.11 | 淡竹叶 | 9.74 | 华南毛蕨 | 3.98 | |||
| 团叶陵齿蕨 Lindasea orbiculata | 6.56 | 半边旗 Pteris semipinnata | 8.58 | 粽叶芦 Thysanolaena maxima | 4.82 | |||
| 三羽新月蕨 Pronephrium triphyllum | 4.51 | 扇叶铁线蕨 Adiantum flabellulatum | 7.35 | 芒萁 Dicranopteris dichotoma | 4.45 | |||
| 福建观音座莲 Angiopteris fokiensis | 2.76 | 华南毛蕨 | 5.67 | |||||
| 淡竹叶 Lophatherum gracile | 2.54 | 边缘鳞盖蕨 Microlepia marginata | 3.20 | |||||
| 霹雳薹草 | 3.20 | |||||||
| 长柄山姜Alpinia kwangsiensis | 2.62 | |||||||
表2 不同林分类型物种组成及重要值
Table 2 Species composition and important value of plants in different stand types
| 层次 Layer | PCL | MCC | MCQ | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 植物名称 Plants | 重要值 Important value/% | 植物名称 Plants | 重要值 Important value/% | 植物名称 Plants | 重要值 Important value/% | |||
| 乔木层 Tree layer | 杉木 Cunninghamia lanceolate | 60.49 | 杉木 | 42.81 | 杉木 | 36.72 | ||
| 黄毛榕 Ficus esquiroliana | 5.36 | 红锥 Castanopsis hystrix | 21.21 | 大叶栎 Quercus griffithii | 23.72 | |||
| 毛黄肉楠 Actinodaphne pilosa | 5.35 | 香梓楠 Michelia hedyosperma | 14.97 | 格木 Erythrophleum fordii | 7.44 | |||
| 水东哥 Saurauia tristyla | 4.06 | 中平树 Macaranga denticulata | 7.12 | 三桠苦 | 6.08 | |||
| 鹅掌柴 Schefflera octophylla | 3.10 | 银合欢 Leucaena leucocephala | 3.21 | 黄毛榕 | 5.03 | |||
| 米老排 Mytilaria laosensis | 2.77 | 潺槁木姜子 Litsea glutinosa | 3.05 | 红锥 | 5.01 | |||
| 三桠苦 Evodia lepta | 2.64 | 水东哥 | 2.80 | 中平树 | 3.47 | |||
| 大青 Clerodendrum cyrtophyllum | 2.35 | 华润楠 Machilus chinensis | 2.84 | |||||
| 簕欓花椒 Zanthoxylum avicennae | 2.07 | 水东哥 | 2.83 | |||||
| 灌木层 Shurb layer | 倒卵叶紫麻 Oreocnide obovata | 15.62 | 三桠苦 | 17.1 | 大管 | 27.53 | ||
| 水东哥 | 13.16 | 杜茎山 | 16.68 | 水东哥 | 9.44 | |||
| 九节 Psychotria rubra | 10.12 | 潺槁木姜子 | 8.66 | 三桠苦 | 7.00 | |||
| 杜茎山 Maesa japonica | 7.57 | 粗叶榕 | 6.76 | 大叶栎 | 6.31 | |||
| 三桠苦 | 6.38 | 香梓楠 | 6.10 | 大青 | 6.22 | |||
| 亮叶猴耳环 Archidendron lucidum | 5.88 | 野牡丹 Melastoma candidum | 5.23 | 格木 | 4.84 | |||
| 绒毛山胡椒 Lindera nacusua | 5.78 | 九节 | 4.56 | 中平树 | 4.65 | |||
| 大管 Micromelum falcatum | 5.42 | 红锥 | 3.61 | 粗叶榕 | 3.74 | |||
| 粗叶榕 Ficus hirta | 4.93 | 柏拉木 | 3.56 | 水锦树 Wendlandia uvariifolia | 2.66 | |||
| 大青 | 4.08 | 水同木 Ficus fistulosa | 2.67 | 九节 | 2.64 | |||
| 南方荚蒾 Viburnum fordiae | 3.68 | 润楠 Machilus pingii | 2.58 | 倒卵叶紫麻 | 2.54 | |||
| 柏拉木 Blastuscochinchinensis | 3.49 | 倒卵叶紫麻 | 2.54 | 斑鸠菊 Vernonia esculenta | 2.29 | |||
| 红紫珠 Callicarpa rubella | 3.18 | 鹅掌柴 | 2.21 | 粗糠柴 | 2.16 | |||
| 黄毛榕 | 3.14 | |||||||
| 粗糠柴 Mallotus philippensis | 2.34 | |||||||
| 草本层 Herbal layer | 金毛狗 Cibotiumbarometz | 31.61 | 金毛狗 | 22.89 | 乌毛蕨 | 39.85 | ||
| 霹雳薹草 Carex perakensis | 21.40 | 乌毛蕨 | 11.94 | 半边旗 | 28.00 | |||
| 华南毛蕨 Cyclosorus parasiticus | 10.53 | 团叶陵齿蕨 | 10.37 | 扇叶铁线蕨 | 14.08 | |||
| 黄腺羽蕨 Pleocnemia winitii | 9.83 | 三羽新月蕨 | 9.97 | 淡竹叶 | 4.82 | |||
| 乌毛蕨 Blechnum orientale | 7.11 | 淡竹叶 | 9.74 | 华南毛蕨 | 3.98 | |||
| 团叶陵齿蕨 Lindasea orbiculata | 6.56 | 半边旗 Pteris semipinnata | 8.58 | 粽叶芦 Thysanolaena maxima | 4.82 | |||
| 三羽新月蕨 Pronephrium triphyllum | 4.51 | 扇叶铁线蕨 Adiantum flabellulatum | 7.35 | 芒萁 Dicranopteris dichotoma | 4.45 | |||
| 福建观音座莲 Angiopteris fokiensis | 2.76 | 华南毛蕨 | 5.67 | |||||
| 淡竹叶 Lophatherum gracile | 2.54 | 边缘鳞盖蕨 Microlepia marginata | 3.20 | |||||
| 霹雳薹草 | 3.20 | |||||||
| 长柄山姜Alpinia kwangsiensis | 2.62 | |||||||
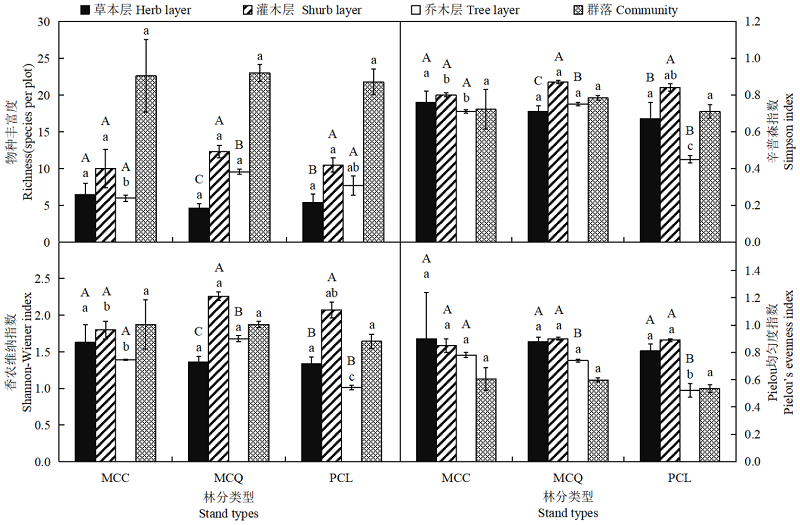
图1 不同林分类型植物多样性指数比较图中不同小写字母表示同一层次不同林分类型间存在显著差异,P<0.05,不同大写字母表示同一林分类型不同层次间存在显著差异
Figure 1 Comparative study on the indexes of plant species diversity in different forest types Different lowercase letters in the figure indicate that there are significant differences among different stand types at the same level, P<0.05, and different uppercase letters indicate that there are significant differences among different levels of the same stand type
| 层次 Layer | 植物多样性指数 Plant species diversity index | 土壤 有机碳 SOC | 土壤全氮 TN | 碳氮比 C/N |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 乔木 Tree | 丰富度指数 | 0.46 | 0.51 | -0.40 |
| 香浓维纳指数 | 0.74* | 0.51 | -0.21 | |
| 辛普森指数 | 0.53 | 0.31 | -0.06 | |
| Pielou均匀度指数 | 0.38 | 0.16 | 0.03 | |
| 灌木 Shurb | 丰富度指数 | 0.26 | 0.66 | -0.75* |
| 香浓维纳指数 | 0.63 | 0.89** | -0.81** | |
| 辛普森指数 | 0.70* | 0.80** | -0.66 | |
| Pielou均匀度指数 | 0.41 | -0.01 | 0.30 | |
| 草本 Herbal | 丰富度指数 | -0.35 | -0.03 | -0.17 |
| 香浓维纳指数 | -0.24 | 0.09 | -0.23 | |
| 辛普森指数 | -0.10 | 0.16 | -0.23 | |
| Pielou均匀度指数 | 0.10 | 0.20 | -0.16 | |
| 群落 Community | 丰富度指数 | 0.01 | -0.28 | 0.41 |
| 香浓维纳指数 | -0.04 | 0.09 | -0.12 | |
| 辛普森指数 | 0.09 | 0.16 | -0.14 | |
| Pielou均匀度指数 | -0.05 | 0.19 | -0.26 |
表3 植物多样性指数与土壤碳氮含量相关分析
Table 3 Correlation analysis between plant species diversity indices of tree and chemical properties
| 层次 Layer | 植物多样性指数 Plant species diversity index | 土壤 有机碳 SOC | 土壤全氮 TN | 碳氮比 C/N |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 乔木 Tree | 丰富度指数 | 0.46 | 0.51 | -0.40 |
| 香浓维纳指数 | 0.74* | 0.51 | -0.21 | |
| 辛普森指数 | 0.53 | 0.31 | -0.06 | |
| Pielou均匀度指数 | 0.38 | 0.16 | 0.03 | |
| 灌木 Shurb | 丰富度指数 | 0.26 | 0.66 | -0.75* |
| 香浓维纳指数 | 0.63 | 0.89** | -0.81** | |
| 辛普森指数 | 0.70* | 0.80** | -0.66 | |
| Pielou均匀度指数 | 0.41 | -0.01 | 0.30 | |
| 草本 Herbal | 丰富度指数 | -0.35 | -0.03 | -0.17 |
| 香浓维纳指数 | -0.24 | 0.09 | -0.23 | |
| 辛普森指数 | -0.10 | 0.16 | -0.23 | |
| Pielou均匀度指数 | 0.10 | 0.20 | -0.16 | |
| 群落 Community | 丰富度指数 | 0.01 | -0.28 | 0.41 |
| 香浓维纳指数 | -0.04 | 0.09 | -0.12 | |
| 辛普森指数 | 0.09 | 0.16 | -0.14 | |
| Pielou均匀度指数 | -0.05 | 0.19 | -0.26 |
| [1] |
CHIANUCCI F, MINARI E, FARDUSI M J, et al., 2016. Relationships between overstory and understory structure and diversity in semi-natural mixed floodplain forests at Bosco Fontana (Italy)[J]. Iforest-Biogeosciences and Forestry, 9(6): 919-926.
DOI URL |
| [2] | GANUZA A, ALMENDROS G, 2003. Organic carbon storage in soils of the Basque Country (Spain): the effect of climate, vegetation type and edaphic variables[J]. Biology & Fertility of Soils, 37(3): 154-162. |
| [3] |
JACTEL H, GRITTI E S, DRÖSSLER L, et al., 2018. Positive biodiversity-productivity relationships in forests: Climate matters[J]. Biology Letters, DOI: 10.1098/rsbl.2017.0747.
DOI |
| [4] |
KOOIJMAN A M, WEILER H A, CUSELL C, et al., 2019. Litter quality and microtopography as key drivers to topsoil properties and understorey plant diversity in ancient broadleaved forests on decalcified marl[J]. Science of The Total Environment, DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.05.285.
DOI |
| [5] | MAGURRAN A E, 1998. Ecological Diversity and Its Measurement[M]. New Jersey: Princeton University Press. |
| [6] |
NAEEM S, LI S, 1997. Biodiversity enhances ecosystem reliability[J]. Nature, 390(6659): 507-509.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
YAO X Y, LI Y F, LIAO L N, et al., 2019. Enhancement of nutrient absorption and interspecific nitrogen transfer in a Eucalyptus urophylla×eucalyptus grandis and Dalbergia odorifera mixed plantation[J]. Forest Ecology and Management, DOI: 10.1016/j.foreco.2019.117465.
DOI |
| [8] | 曹小玉, 李际平, 杨静, 等, 2019. 不同龄组杉木林土壤碳、氮、磷的生态化学计量特征[J]. 土壤, 51(2): 290-296. |
| CAO X Y, LI J P, YANG J, et al., 2019. Stoichiometric characteristics of soil C, N, and P of different age-group of Chinese fir plantation[J]. Soils, 51(2): 290-296. | |
| [9] | 程瑞梅, 肖文发, 王晓荣, 等, 2010. 三峡库区植被不同演替阶段的土壤养分特征[J]. 林业科学, 46(9): 1-6. |
| CHENG R M, XIAO W F, WANG X R, et al., 2010. Soil nutrient characteristics in different vegetation successional stages of Three Gorges Reservoir Area[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 46(9): 1-6. | |
| [10] | 董云中, 王永亮, 张建杰, 等, 2014. 晋西北黄土高原丘陵区不同土地利用方式下土壤碳氮储量[J]. 应用生态学报, 25(4): 955-960. |
| DONG Y Z, WANG Y L, ZHANG J J, et al., 2014. Soil carbon and nitrogen storage under different land use patterns in the some random place somewhere hilly area of northwestern Shanxi[J]. Journal of Applied Ecology, 25(4): 955-960. | |
| [11] | 冯健, 王骞春, 陆爱君, 等, 2021. 辽东山区落叶松-水曲柳混交林植物多样性和土壤特性研究[J]. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 49(6): 27-37. |
| FENG J, WANG Q C, LU A J, et al., 2021. Plant diversity and soil characteristics of larch-manchurian ashmixed stand in eastern Liaoning[J]. Journal of Northwest A & F University (Natural Science Edition), 49(6): 27-37. | |
| [12] | 高贤明, 马克平, 陈灵芝, 2001. 暖温带若干落叶阔叶林群落物种多样性及其与群落动态的关系[J]. 植物生态学报, 25(3): 283-290. |
| GAO X M, MA K P, CHEN L Z, 2001. Species diversity of some deciduous broad-road-leaved forests in the warm-temperate zone and its relations to community stability[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 25(3): 283-290. | |
| [13] | 郭冬艳, 2013. 退化草地的生态化学计量学研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学. |
| GUO D Y, 2013. Research on ecological stoichiometry of degraded grassland[D]. Changchun: Jilin University. | |
| [14] | 郭家新, 2008. 杉木火力楠混交林与杉木纯林土壤碳氮库研究[J]. 福建林业科技, 35(2): 5-9, 29. |
| GUO J X, 2008. Comparison of soil organic carbon and nitrogen pool between mixed and pure forests of Chinese fir[J]. Journal of Fujian Forestry Science and Technology, 35(2): 5-9, 29. | |
| [15] | 黄冬梅, 2017. 杉木纯林与混交林林下植物多样性比较[J]. 安徽农业科学, 45(1): 13-16. |
| HUANG D M, 2017. Comparison of undergrowth plant diversity of pure and mixed Chinese fir plantations[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 45(1): 13-16. | |
| [16] | 黄宇, 冯宗炜, 汪思龙, 等, 2005. 杉木、火力楠纯林及其混交林生态系统C、N贮量[J]. 生态学报, 25(12): 3146-3154. |
| HUANG Y, FENG Z W, WANG S L, et al., 2005. C and N stocks under three plantation forest ecosystems of Chinese-fir, Michelia macclurei and their mixture[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 25(12): 3146-3154. | |
| [17] | 姜俊, 刘宪钊, 贾宏炎, 等, 2019. 杉木人工林近自然化改造对林下植被多样性和土壤理化性质的影响[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 41(5): 170-177. |
| JIANG J, LIU X Z, JIA H Y, et al., 2019. Effects of stand density on understory species diversity and soil physicochemical properties after close-to-nature transformation management of Chinese fir plantation[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 41(5): 170-177. | |
| [18] | 康永祥, 康博文, 刘建军, 等, 2010. 陕北黄土高原文冠果群落结构及物种多样性[J]. 生态学报, 30(16): 4328-4339. |
| KANG Y X, KANG B W, LIU J J, et al., 2010. Structure and species diversity of Xanthoceras sorbifolia community in the Loess Plateau of North Shaanxi[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 30(16): 4328-4339. | |
| [19] | 李海霞, 姜涛, 吴江, 等, 2010. 红松、刺楸人工针阔混交林物种多样性研究[J]. 防护林科技 (3): 25-26, 41. |
| LI H X, JIANG T, WU J, et al., 2010. Species diversity of conifer-hardwood plantation of Pinus koraiensis & Kalopanax septemlobus[J]. Protection Forest Science and Technology (3): 25-26, 41. | |
| [20] | 李萌, 陈永康, 徐浩成, 等, 2020. 不同间伐强度对南亚热带杉木人工林林下植物功能群的影响[J]. 生态学报, 40(14): 4985-4993. |
| LI M, CHEN Y K, XU H C, et al., 2020. Effects of different thinning intensities on undergrowth plant functional groups in subtropical Cunninghamia lanceolata plantations[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 40(14): 4985-4993. | |
| [21] | 李勇, 2016. 混交比例对杉木木荷混交林生物量及碳储量的影响[J]. 林业勘察设计, 36(3): 37-40. |
| LI Y, 2016. Effects of mixing proportion on biomass and carbon storage of mixed forest of Schima Superba and Cunninghamia lanceolate [J]. Forestry Prospect and Design, 36(3): 37-40. | |
| [22] | 刘俊杰, 吕倩, 沈逸, 等, 2021. 目标树初期经营对杉木人工林林下植物多样性和土壤理化性质的影响[J]. 应用与环境生物学报, 27(2): 408-415. |
| LIU J J, LÜ Q, SHEN Y, et al., 2021. Early effects of target tree management on plant diversity and soil physicochemical properties in a Cunninghamia lanceolata plantation[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology, 27(2): 408-415. | |
| [23] | 刘林馨, 王健, 杨晓杰, 等, 2018. 大兴安岭不同森林群落植被多样性对土壤有机碳密度的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 27(9): 1610-1616. |
| LIU L X, WANG J, YANG X J, et al., 2018. Forest plant community and soil organic carbon density in Da Xing'an mountains[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 27(9): 1610-1616. | |
| [24] | 刘世荣, 杨予静, 王晖, 2018. 中国人工林经营发展战略与对策: 从追求木材产量的单一目标经营转向提升生态系统服务质量和效益的多目标经营[J]. 生态学报, 38(1): 1-10. |
|
LU S R, YANG Y J, WANG H, 2018. Development strategy and management countermeasures of planted forests in China: transforming from timber-centered single objective management towards multi-purpose management for enhancing quality and benefits of ecosystem services[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 38(1): 1-10.
DOI URL |
|
| [25] | 刘雨晖, 2018. 杉木细叶青冈混交林生物量及林下植物多样性[J]. 亚热带农业研究, 14(2): 104-109. |
| LIU Y H, 2018. Biomass and underst canopy plant diversity of mixed forest of Chinese fir (Cunninghamia lanceolata) and Cyclobalanopsis gracils[J]. Subtropical Agriculture Research, 14(2): 104-109. | |
| [26] | 卢立华, 贾宏炎, 何日明, 等, 2008. 南亚热带6种人工林凋落物的初步研究[J]. 林业科学研究, 21(3): 346-352. |
| LU L H, JIA H Y, HE R M, et al., 2008. Preliminary study on litter falls of six kinds of plantations in the tropical south Asia[J]. Forest Research, 21(3): 346-352. | |
| [27] | 鲁如坤, 2000. 土壤农业化学分析方法[M]. 北京: 中国农业科技出版社. |
| LU R K, 2000. Methods of soil agricultural chemical analysis[M]. Beijing: China Agricultural Science and Technology Press. | |
| [28] | 明安刚, 2017. 南亚热带针叶人工林近自然化改造过程中群落结构与碳动态研究[D]. 北京: 中国林业科学研究院. |
| MING A G, 2017. Community structure and carbon dynamics during close-to- nature transformation in south subtropical conifer plantation[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Forestry. | |
| [29] | 庞圣江, 张培, 贾宏炎, 等, 2020. 不同造林模式对桉树人工林林下植物物种多样性的影响[J]. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 48(9): 44-52. |
| PANG S J, ZHANG P, JIA H Y, et al., 2020. Effects of different afforestation modes on diversity of undergrowth plants in Eucalyptus Plantations[J]. Journal of Northwest A & F University (Natural Science Edition), 48(9): 44-52. | |
| [30] | 石亮, 张日升, 2021. 樟子松人工林混交改造后土壤养分综合评价[J]. 林业资源管理 (1): 132-139. |
| SHI L, ZHANG R S, 2021. Comprehensive evaluation of soil nutrient after mixed transformation of Pinus Sylvestris Var. Mongolica plantation[J]. Forest Resources Management (1): 132-139. | |
| [31] | 舒韦维, 卢立华, 李华, 等, 2021. 林分密度对杉木人工林林下植被和土壤性质的影响[J]. 生态学报, 41(11): 4521-4530. |
| SHU W W, LU L H, LI H, et al., 2021. Effects of stand density on undergrowth vegetation and soil properties of Cunninghamia lanceolata plantation[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 41(11): 4521-4530. | |
| [32] | 孙浩, 赖祁华, 刘晓勇, 等, 2020. 赣南地区生态公益林5种森林类型土壤有机碳特征[J]. 南方林业科学, 48(6): 45-48, 63. |
| SUN H, LAI Q H, LIU X Y, et al., 2020. Characteristics of soil organic carbon for five typical ecological forest in southern Jiangxi Province[J]. South China Forestry Science, 48(6): 45-48, 63. | |
| [33] | 唐学君, 肖舜祯, 王伟峰, 等, 2019. 中亚热带典型杉阔混交林碳储量分配特征[J]. 地域研究与开发, 38(4): 111-114, 121. |
| TANG X J, XIAO S Z, WANG W F, et al., 2019. Carbon storage and its allocation characteristics of typical Chinese fir and broad-leaved mixed forests in mid-subtropical areas[J]. Areal Research and Development, 38(4): 111-114, 121. | |
| [34] | 王春香, 2014. 晋西黄土区人工林下植物多样性与土壤养分研究[D]. 北京: 北京林业大学. |
| WANG C X, 2014. Study on the plant species diversity and soil nutrients of artificial forests in Loess Plateau of Western Shanxi Province[D]. Beijing: Beijing Forestry University. | |
| [35] | 王光州, 贾吉玉, 张俊伶, 2021. 植物-土壤反馈理论及其在自然和农田生态系统中的应用研究进展[J/OL]. 生态学报, 41(23): 1-14[2021-11-15]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.2031.Q.20210723.1224.044.html. |
|
WANG G Z, JIA J Y, ZHANG J L, 2021. Plant soil feedback theory and its application and prospects in natural and agricultual ecosystems[J/OL]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 41(23): 1-14[2021-11-15]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.2031. Q. 20210723. 1224. 044. html.
DOI URL |
|
| [36] | 王青天, 2014. 杉木混交林近自然经营效果研究[J]. 西北林学院学报, 29(1): 95-99. |
| WANG Q T, 2014. Effectiveness study on the close-to-nature management for mixed forest of Chinese fir[J]. Journal of Northwest Forestry University, 29(1): 95-99. | |
| [37] | 王玉杰, 李绍才, 缪宁, 等, 2020. 四川盆周山地5种典型林分的植物多样性分析[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 40(7): 89-98. |
| WANG Y J, LI S C, MIAO N, et al., 2020. Analysis of plant diversity of five typical forests in mountain areas around Sichuan basin[J]. Journal of Central South University of Forestry & Technology, 40(7): 89-98. | |
| [38] | 肖石红, 高常军, 蔡坚, 等, 2018. 南亚热带杉木和红锥林及其混交林的土壤肥力[J]. 森林与环境学报, 38(2): 142-148. |
| XIAO S H, GAO C J, CAI J, et al., 2018. Soil fertility of pure and mixed forest of Cunninghamia lanceolata and Castanopsis hystrix in south subtropical area[J]. Journal of Forest and Environment, 38(2): 142-148. | |
| [39] | 谢君毅, 蔡斌, 张惠光, 等, 2021. 碳输入方式对森林土壤活性氮库及氮循环的影响研究进展[J/OL]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版):1-16[2021-06-18].http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/32.1161.S.20210525.1858.008.html. |
| XIE J Y, CAI B, ZHANG H G, et al., 2021. Resposes of forest soil nitrogen pool and nitrogen cycle to the changes of carbon input[J/OL]. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition): 1-16 [2021-06-18].http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/32.1161.S.20210525.1858.008.html. | |
| [40] | 徐海东, 苑海静, 熊静, 等, 2020. 杉阔异龄复层林对土壤团聚体稳定性和有机碳及养分储量的影响[J]. 林业科学研究, 33(3): 107-115. |
| XU H D, YUAN H J, XIONG J, et al., 2020. Effects of uneven-aged Cunninghamia lanceolata and evergreen broadleaved mixed plantations on soil aggregate stability and soil organic carbon and nutrients stocks[J]. Forest Rearch, 33(3): 107-115. | |
| [41] | 杨玉盛, 谢锦升, 王义祥, 等, 2003. 杉木观光木混交林C库与C吸存[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 25(5): 10-14. |
| YANG Y S, XIE J S, WANG Y X, et al., 2003. Carbon stock and carbon sequestration in mixed forest of Cunninghamia lanceolata and Tsoongiodendron odorum[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 25(5): 10-14. | |
| [42] | 叶绍明, 温远光, 杨梅, 等, 2010. 连栽桉树人工林生产力和植物多样性及其相关性分析[J]. 西北植物学报, 30(7): 1458-1467. |
| YE S M, WEN Y G, YANG M, et al., 2010. Correlation analysis on productivity and plant diversity of Eucalyptus plantations under successive rotation[J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 30(7): 1458-1467. | |
| [43] | 余轩, 王兴, 吴婷, 等, 2021. 荒漠草原植物多样性恢复与土壤生境的关系[J/OL]. 生态学报, 41(21):1-9[2021-11-11].http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.2031.Q.20210705.1452.010.html. |
|
YU X, WANG X, WU T, et al., 2021. Relationship between restoration of plant diversity and soil habitat in desert steppe[J/OL]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 41(21): 1-9 [2021-11-11].http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.2031.Q.20210705.1452.010.html.
DOI URL |
|
| [44] | 张涵丹, 康希睿, 邵文豪, 等, 2021. 不同类型杉木人工林林下草本植物多样性特征[J]. 生态学报, 41(6): 2118-2128. |
| ZHANG H D, KANG X R, SHAO W H, et al., 2021. Characteristics of herbaceous plant biodiversity in Cunninghamia lanceolate plantations with different community structures[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 41(6): 2118-2128. | |
| [45] | 张莉, 2019. 闽北山地杉木-厚朴混交林生长状况及土壤理化性质研究[J]. 防护林科技 (6): 29-30, 44. |
| ZHANG L, 2019. Growth and soil physical-chemical character of mixed forest of Cunninghamia lanceolata and Magnolia officinalis in Fujian North Mountain[J]. Protection Forest Science and Technology (6): 29-30, 44. | |
| [46] | 赵耀, 王百田, 2018. 晋西黄土区不同林地植物多样性研究[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 40(9): 45-54. |
| ZHAO Y, WANG B T, 2018. Plant diversity of different forestland in the loess region of western Shanxi Province, northern China[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 40(9): 45-54. | |
| [47] | 甄倩, 王百田, 赵耀, 等, 2020. 基于土壤理化性质和植物多样性的晋西黄土区人工林质量评价[J]. 中国水土保持科学, 18(4): 12-20. |
| ZHEN Q, WANG B T, ZHAO Y, 2020. Evaluation of plantation quality based on soil physico-chemical properties and plant diversity in the loess area of western Shanxi province[J]. Science of Soil and Water Conservation, 18(4): 12-20. | |
| [48] | 周霆, 盛炜彤, 2008. 关于我国人工林可持续问题[J]. 世界林业研究, 21(3): 49-53. |
| ZHOU T, SHENG W T, 2008. On the plantation sustainability in China[J]. World Forestry Research, 21(3): 49-53. | |
| [49] | 吴迪, 湛斌, 闫新利, 等, 2017. 紫金山栓皮栎枫香混交林群落结构与物种多样性[J]. 安徽农业大学学报, 44(1): 50-54. |
| WU D, ZHAN B, YAN X L, et al., 2017. Plant diversity in a mixed plantation of Quercus variabilis and Liquidambar Formosana in Ziinshan mountain[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural University, 44(1): 50-54. |
| [1] | 李阳, 侯志勇, 陈薇, 于晓英, 谢永宏, 黄鑫, 谭佩阳, 李继承, 黎尚林, 杨辉. 大围山高山湿地植物多样性与区系组成研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 643-650. |
| [2] | 张林, 齐实, 周飘, 伍冰晨, 张岱, 张岩. 北京山区针阔混交林地土壤有机碳含量的影响因素研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 450-458. |
| [3] | 肖国举, 李秀静, 郭占强, 胡延斌, 王静. 贺兰山东麓土壤有机碳对玉米生长发育及水分利用的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(9): 1754-1764. |
| [4] | 王哲, 田胜尼, 张永梅, 张和禹, 周忠泽. 巢湖派河口滩涂植物群落特征研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(9): 1823-1831. |
| [5] | 王礼霄, 刘晋仙, 柴宝峰. 华北亚高山土壤细菌群落及氮循环对退耕还草的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1537-1546. |
| [6] | 张博文, 秦娟, 任忠明, 陈子齐, 姚舜佳, 刘烨, 宋炎玉. 坡向对北亚热带区马尾松纯林及不同针阔混交林型林下植物多样性的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(6): 1091-1100. |
| [7] | 马辉英, 李昕竹, 马鑫钰, 贡璐. 新疆天山北麓中段不同植被类型下土壤有机碳组分特征及其影响因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(6): 1124-1131. |
| [8] | 龚玲玄, 王丽丽, 赵建宁, 刘红梅, 杨殿林, 张贵龙. 不同覆盖作物模式对茶园土壤理化性质及有机碳矿化的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(6): 1141-1150. |
| [9] | 段文军, 李达, 李冲. 5种不同林龄尾巨桉人工林林下植物多样性及其影响因素分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(5): 857-864. |
| [10] | 杜雪, 王海燕, 邹佳何, 孟海, 赵晗, 崔雪, 董齐琪. 长白山北坡云冷杉阔叶混交林土壤有机碳分布特征及其影响因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 663-669. |
| [11] | 陈瑶, 李云红, 邵英男, 刘玉龙, 刘延坤. 阔叶红松林物种多样性与土壤理化特征研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 679-687. |
| [12] | 宋瑞朋, 杨起帆, 郑智恒, 习丹. 3种林下植被类型对杉木人工林土壤有机碳及其组分特征的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(12): 2283-2291. |
| [13] | 高歌, 葛晓改, 周君刚, 周本智, 李正才, 杨南. 施氮和干旱对杉木和青冈幼苗生物量及根系形态的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(12): 2292-2301. |
| [14] | 玄锦, 李祖婵, 邹诚, 秦子博, 吴雅华, 黄柳菁. 江心洲景观类型和格局对植物多样性的多尺度影响——以闽江流域福州段为例[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(12): 2320-2330. |
| [15] | 陈双双, 朱宁华, 周光益, 袁星明, 尚海, 王迤翾. 不同等级石漠化环境下人工乔木林的植被与土壤物理特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(1): 52-61. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
