生态环境学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (9): 1823-1831.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2022.09.012
王哲1( ), 田胜尼1,*(
), 田胜尼1,*( ), 张永梅1, 张和禹1, 周忠泽2
), 张永梅1, 张和禹1, 周忠泽2
收稿日期:2022-02-22
出版日期:2022-09-18
发布日期:2022-11-07
通讯作者:
*田胜尼(1971年生),男,副教授,博士,研究方向为植物生态学。E-mail: tiansn@ahau.edu.cn作者简介:王哲(1998年生),女,硕士研究生,研究方向为湿地生态学。E-mail: 1726263315@qq.com
基金资助:
WANG Zhe1( ), TIAN Shengni1,*(
), TIAN Shengni1,*( ), ZHANG Yongmei1, ZHANG Heyu1, ZHOU Zhongze2
), ZHANG Yongmei1, ZHANG Heyu1, ZHOU Zhongze2
Received:2022-02-22
Online:2022-09-18
Published:2022-11-07
摘要:
巢湖水鸟主要集中分布在派河口滩涂区域,这与河口滩涂栖息地生境和植物群落结构存在一定关系。采用样地调查法和样方法研究了巢湖派河口滩涂植物物种组成、区系特征和群落特征,为巢湖水鸟等生物多样性保护提供依据。派河口滩涂维管植物植物多样性丰富,达64科171属233种,其中禾本科、菊科、豆科、莎草科和蓼科为优势科。派河口滩涂维管植物在科、属的区系组成上存在显著差异。在科的水平上,世界分布占较大比重(53.13%),其次为泛热带分布(23.44%)。从科的总体结构上看,热带区系和温带区系分别占26.56%和18.75%。在属的水平上,所占比重较大的为北温带分布(22.81%),其次为世界分布(21.05%)。从属的总体结构上看,热带区系和温带区系分别占28.07%和49.12%。春季植物群丛主要为羊蹄(Rumex japonicus)、扁秆荆三棱(Bolboschoenus planiculmis)、芦苇(Phragmites australis)等10个群丛。其中羊蹄群丛Shannon-Wiener多样性指数最高,达2.025;扁秆荆三棱群丛Shannon-Wiener多样性指数最低,为0.199。扁秆荆三棱群丛Simpson优势度指数最高,达0.925;羊蹄群丛Simpson优势度指数最低,为0.168。植物多样性指数与土壤含水量、有机质、pH、全钾、全氮含量呈负相关。巢湖派河口滩涂植物多样性丰富,优势物种以生活史短、具地下根状茎、球茎和挺水的生态对策方式适应巢湖季节水位变化。多样的植物群落和独特的异质性湿地空间为水鸟提供了重要的食物资源和栖息场所,是派河口滩涂水鸟种类和数量于环巢湖湖滨带集中分布的主要原因。
中图分类号:
王哲, 田胜尼, 张永梅, 张和禹, 周忠泽. 巢湖派河口滩涂植物群落特征研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(9): 1823-1831.
WANG Zhe, TIAN Shengni, ZHANG Yongmei, ZHANG Heyu, ZHOU Zhongze. Study on the Plant Community Characteristics of the Estuary of Pai River in Chaohu Lake[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(9): 1823-1831.
| 科名 Family name | 属数 Genera | 比例 Ratio/% | 种数 Species | 占比 Ratio/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 禾本科 Poaceae | 23 | 13.45 | 30 | 12.88 |
| 菊科 Asteraceae | 22 | 12.87 | 29 | 12.45 |
| 豆科 Fabaceae | 12 | 7.02 | 19 | 8.15 |
| 莎草科 Cyperaceae | 6 | 3.51 | 12 | 5.15 |
| 蓼科 Polygonaceae | 2 | 1.17 | 11 | 4.72 |
| 蔷薇科 Rosaceae | 7 | 4.10 | 9 | 3.86 |
| 十字花科 Brassicaceae | 5 | 2.92 | 9 | 3.86 |
| 伞形科 Umbelliferae | 6 | 3.51 | 6 | 2.58 |
| 石竹科 Caryophyllaceae | 4 | 2.34 | 5 | 2.15 |
| 玄参科 Scrophulariaceae | 2 | 1.17 | 5 | 2.15 |
表1 派河口滩涂植物排名前十的属、种情况
Table 1 The top ten genera and species of plants at the lake beaches of Pai River estuary
| 科名 Family name | 属数 Genera | 比例 Ratio/% | 种数 Species | 占比 Ratio/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 禾本科 Poaceae | 23 | 13.45 | 30 | 12.88 |
| 菊科 Asteraceae | 22 | 12.87 | 29 | 12.45 |
| 豆科 Fabaceae | 12 | 7.02 | 19 | 8.15 |
| 莎草科 Cyperaceae | 6 | 3.51 | 12 | 5.15 |
| 蓼科 Polygonaceae | 2 | 1.17 | 11 | 4.72 |
| 蔷薇科 Rosaceae | 7 | 4.10 | 9 | 3.86 |
| 十字花科 Brassicaceae | 5 | 2.92 | 9 | 3.86 |
| 伞形科 Umbelliferae | 6 | 3.51 | 6 | 2.58 |
| 石竹科 Caryophyllaceae | 4 | 2.34 | 5 | 2.15 |
| 玄参科 Scrophulariaceae | 2 | 1.17 | 5 | 2.15 |
| 区系组 Flora | 分布区类型 Areal-types | 科数 Families | 比例 Ratio/% | 属数 Genera | 比例 Ratio/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 世界分布 Cosmopolitan | 世界分布 | 34 | 53.13 | 36 | 21.05 |
| 热带区系成分 Tropic | 泛热带分布 | 15 | 23.44 | 28 | 16.37 |
| 热带亚洲和热带美洲间断分布 | 1 | 1.56 | 3 | 1.75 | |
| 旧世界热带分布 | 1 | 1.56 | 6 | 3.51 | |
| 热带亚洲至热带大洋洲分布 | 0 | 0.00 | 4 | 2.34 | |
| 热带亚洲至热带非洲分布 | 0 | 0.00 | 2 | 1.17 | |
| 热带亚洲分布 | 0 | 0.00 | 5 | 2.92 | |
| 温带区系成分 Temperate | 北温带分布 | 10 | 15.63 | 39 | 22.81 |
| 东亚和北美洲间断分布 | 1 | 1.56 | 11 | 6.43 | |
| 旧世界温带分布 | 1 | 1.56 | 17 | 9.94 | |
| 温带亚洲分布 | 0 | 0.00 | 2 | 1.17 | |
| 地中海区、西亚至中亚分布 | 0 | 0.00 | 4 | 2.34 | |
| 东亚分布 | 0 | 0.00 | 11 | 6.43 | |
| 中国特有 Endemic to China | 中国特有分布 | 1 | 1.56 | 3 | 1.75 |
| 总计 | 64 | 100.00 | 171 | 100.00 |
表2 巢湖派河口滩涂植物科、属的分布区类型
Table 2 Distribution area types of plants at the lake beaches of Pai River estuary
| 区系组 Flora | 分布区类型 Areal-types | 科数 Families | 比例 Ratio/% | 属数 Genera | 比例 Ratio/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 世界分布 Cosmopolitan | 世界分布 | 34 | 53.13 | 36 | 21.05 |
| 热带区系成分 Tropic | 泛热带分布 | 15 | 23.44 | 28 | 16.37 |
| 热带亚洲和热带美洲间断分布 | 1 | 1.56 | 3 | 1.75 | |
| 旧世界热带分布 | 1 | 1.56 | 6 | 3.51 | |
| 热带亚洲至热带大洋洲分布 | 0 | 0.00 | 4 | 2.34 | |
| 热带亚洲至热带非洲分布 | 0 | 0.00 | 2 | 1.17 | |
| 热带亚洲分布 | 0 | 0.00 | 5 | 2.92 | |
| 温带区系成分 Temperate | 北温带分布 | 10 | 15.63 | 39 | 22.81 |
| 东亚和北美洲间断分布 | 1 | 1.56 | 11 | 6.43 | |
| 旧世界温带分布 | 1 | 1.56 | 17 | 9.94 | |
| 温带亚洲分布 | 0 | 0.00 | 2 | 1.17 | |
| 地中海区、西亚至中亚分布 | 0 | 0.00 | 4 | 2.34 | |
| 东亚分布 | 0 | 0.00 | 11 | 6.43 | |
| 中国特有 Endemic to China | 中国特有分布 | 1 | 1.56 | 3 | 1.75 |
| 总计 | 64 | 100.00 | 171 | 100.00 |
| 群落编号 Communities | 植物群丛 Associations | 样方号 Quadrat number | 分布区域 Distributional area | 丰富度R Richness | 总盖度 Coverage/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | 小苜蓿+救荒野豌豆群丛 | 1、2、4、5、13、14、29 | LA | 9 | 80-90 |
| II | 荠菜+球序卷耳群丛 | 3、6、8、10、17、18 | LA | 8 | 60-75 |
| III | 齿果酸模群丛 | 31、32、35、39 | LBA | 13 | 70-80 |
| IV | 羊蹄群丛 | 36、37、38 | LBA | 12 | 80-90 |
| V | 芦苇群丛 | 56、58、66、69、70 | LBA | 6 | 55-65 |
| VI | 菵草+陌上菅群丛 | 41、44 | LBA | 8 | 80-85 |
| VII | 菵草+沼生蔊菜群丛 | 39、43 | LBA | 6 | 65-75 |
| VIII | 菵草群丛 | 42、45、49 | SWA | 8 | 70-85 |
| IX | 看麦娘群丛 | 46、47、48 | SWA | 7 | 65-75 |
| X | 扁秆荆三棱群丛 | 57、60、61、64、65 | SWA | 4 | 90-100 |
表3 典型群落分布特征
Table 3 Distribution characteristics of typical communities
| 群落编号 Communities | 植物群丛 Associations | 样方号 Quadrat number | 分布区域 Distributional area | 丰富度R Richness | 总盖度 Coverage/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | 小苜蓿+救荒野豌豆群丛 | 1、2、4、5、13、14、29 | LA | 9 | 80-90 |
| II | 荠菜+球序卷耳群丛 | 3、6、8、10、17、18 | LA | 8 | 60-75 |
| III | 齿果酸模群丛 | 31、32、35、39 | LBA | 13 | 70-80 |
| IV | 羊蹄群丛 | 36、37、38 | LBA | 12 | 80-90 |
| V | 芦苇群丛 | 56、58、66、69、70 | LBA | 6 | 55-65 |
| VI | 菵草+陌上菅群丛 | 41、44 | LBA | 8 | 80-85 |
| VII | 菵草+沼生蔊菜群丛 | 39、43 | LBA | 6 | 65-75 |
| VIII | 菵草群丛 | 42、45、49 | SWA | 8 | 70-85 |
| IX | 看麦娘群丛 | 46、47、48 | SWA | 7 | 65-75 |
| X | 扁秆荆三棱群丛 | 57、60、61、64、65 | SWA | 4 | 90-100 |
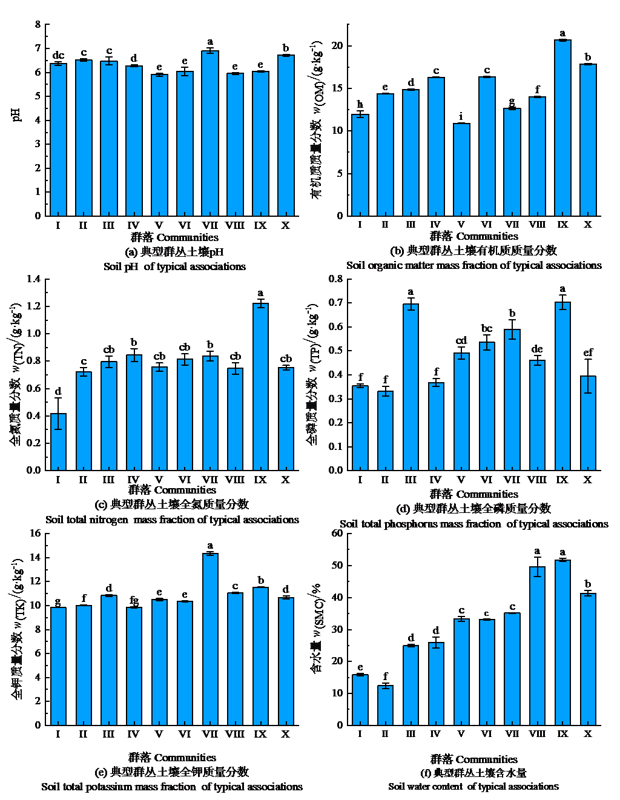
图3 典型群落土壤理化性质分布图 图中字母表示不同典型群丛各土壤理化性质间差异显著性(P<0.05),n=3
Figure 3 Distribution diagram of soil physical and chemical properties of typical communities Letters indicate the significance of difference of soil physical and chemical properties between different typical associations (P<0.05), n=3
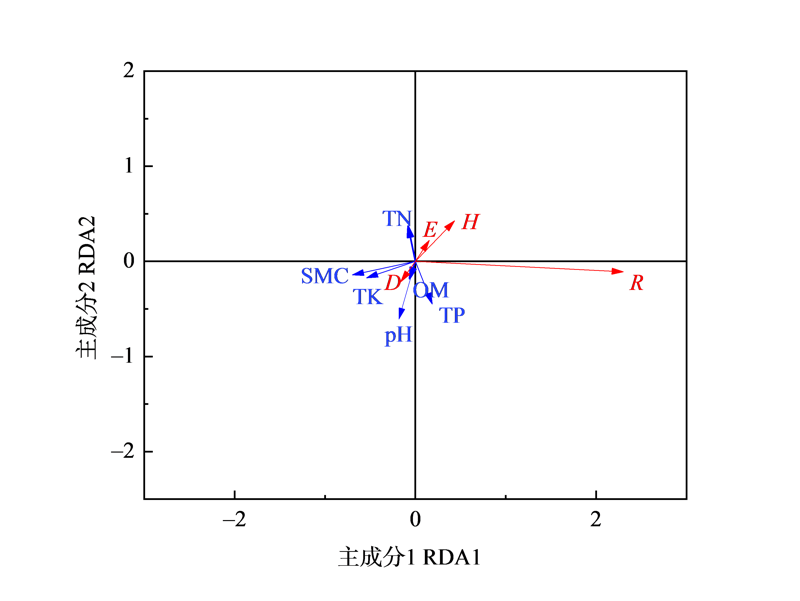
图4 植物多样性与土壤环境因子的冗余分析(RDA)图 TP:总磷;TN:总氮;TK:全钾;pH:土壤酸碱度;OM:有机质;SMC:土壤含水量;D:Simpson优势度指数;H:Shannon-Wiener多样性指数;E:Pielou均匀度指数;R:Patrick丰富度指数
Figure 4 Redundancy analysis (RDA) diagram of plant diversity and soil environmental factors TP: total phosphorus; TN: total nitrogen; TK: total potassium; pH: soil pH; OM: organic matter; SMC: soil moisture content; D: Simpson index; H: Shannon-Wiener index; E: Pielou index; R: Patrick index
| [1] |
LI Q N, LIANG Y H, MU D, et al., 2021. Diversity of plant resources in Qunli National Urban Wetland Park in Harbin, China[J]. Journal of Resources and Ecology, 12(6): 822-828.
DOI |
| [2] |
SHAO K Q, YAO X, WU Z S, et al., 2021. The bacterial community composition and its environmental drivers in the rivers around eutrophic Chaohu Lake, China[J]. BMC Microbiology, 21(1): 179.
DOI PMID |
| [3] |
ZHANG X K, LIU X Q, WANG H Z, 2015. Effects of water level fluctuations on lakeshore vegetation of three subtropical floodplain lakes, China[J]. Hydrobiologia, 747(1): 43-52.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
ZHANG Y L, JEPPESEN E, LIU X H, et al., 2017. Global loss of aquatic vegetation in lakes[J]. Earth-science Reviews, 173: 259-265.
DOI URL |
| [5] | 陈军林, 周立志, 许仁鑫, 等, 2010. 巢湖湖岸带鸟类多样性的初步研究[J]. 动物学杂志, 45(3): 139-147. |
| CHEN J L, ZHOU L Z, XU R X, et al., 2010. A preliminary study on bird diversity in shore habitats of Chaohu Lake[J]. Chinese Journal of Zoology, 45(3): 139-147. | |
| [6] | 陈艳, 黄涛, 2021. 引江济淮工程派河口复线船闸建设规模[J]. 水运工程 (11): 105-110, 191. |
| CHEN Y, HUANG T, 2021. Construction scale of Paihe second-line ship lock of the Yangtze-to-Huaihe water diversion project[J]. Port & Waterway Engineering (11): 105-110, 191. | |
| [7] | 邓超, 卢文, 金杰, 等, 2016. 巢湖烔炀湿地植物群落调查研究与多样性分析[J]. 安徽农学通报, 22(17): 26-28, 48. |
| DENG C, LU W, JIN J, et al., 2016. Investigation and diversity analysis of plant community in Chaohu Tongyang Wetland[J]. Anhui Agricultural Science Bulletin, 22(17): 26-28, 48. | |
| [8] | 丁疆华, 温琰茂, 舒强, 等, 1999. 鄱阳湖湿地保护与可持续发展[J]. 环境与开发, 14(3): 42-44. |
| DING J H, WEN Y M, SHU Q, et al., 1999. Conservation and sustainable development of Poyang Lake Wetland[J]. Environment and Exploitation, 14(3): 42-44. | |
| [9] | 高吉喜, 叶春, 杜娟, 等, 1997. 水生植物对面源污水净化效率研究[J]. 中国环境科学, 17(3): 56-60. |
| GAO J X, YE C, DU J, et al., 1997. Study of removing ability of macrophytes to N, P in run-off[J]. China Environmental Science, 17(3): 56-60. | |
| [10] | 管佳佳, 2021. 引江济淮引江济巢段交叉河道水文分析[J]. 安徽农学通报, 27(20): 139-140. |
| GUAN J J, 2021. Hydrologic analysis of the intersecting channel of the Yangtze-to-Huaihe water diversion project[J]. Anhui Agricultural Science Bulletin, 27(20): 139-140. | |
| [11] | 郭二辉, 樊子豪, 张瑞香, 等, 2021. 河岸带生态系统植被与土壤对水文变化的响应研究进展[J]. 生态学报, 41(23): 1-10. |
|
GUO E H, FAN Z H, ZHANG R X, et al., 2021. Research progresses on the response of vegetation and soil to hydrological changes in riparian ecosystem[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 41(23): 1-10.
DOI URL |
|
| [12] | 侯志勇, 谢永宏, 高大立, 等, 2016. 洞庭湖湿地典型植物群落生活型构成及其环境影响因子[J]. 应用与环境生物学报, 22(6): 993-999. |
| HOU Z Y, XIE Y H, GAO D L, 2016. The life form and environment factors of typical plant communities in the Dongting Lake wetlands[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied & Environmental Biology, 22(6): 993-999. | |
| [13] | 胡玲玲, 朱仁果, 付建平, 2014. 鄱阳湖湿地植物群落分布对水位变化的响应[J]. 江西化工, (4): 39-42. |
| HU L L, ZHU R G, FU J P, 2014. The distribution of phytobiocoenose on Poyang Lake wetlands response to water level changes[J]. Jiangxi Chemical Industry, (4): 39-42. | |
| [14] | 黄晓敏, 杨盛昌, 彭建, 等, 2019. 派河流域滨岸带植物群落物种多样性和群落相似性分析及滨岸缓冲带模型构建[J]. 环境工程, 37(12): 55-59. |
| HUANG X M, YANG S C, PENG J, et al., 2019. Analysis of species diversity and community similarity of plant communities in riparian zone of the paihe River: Constructing the model of riparian buffer strips[J]. Environmental Engineering, 37(12): 55-59. | |
| [15] | 黄永杰, 刘登义, 王友保, 等, 2006. 八种水生植物对重金属富集能力的比较研究[J]. 生态学杂志, 25(5): 541-545. |
| HUANG Y J, LIU D Y, WANG Y B, et al., 2006. Heavy metals accumulation by hydrophytes[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 25(5): 541-545. | |
| [16] | 简尊吉, 马凡强, 郭泉水, 等, 2017. 三峡水库峡谷地貌区消落带优势植物种群生态位[J]. 生态学杂志, 36(2): 328-334. |
| JIAN Z J, MA F Q, GUO Q S, et al., 2017. Niche of dominant plant populations in the water level fluctuation zone of canyon landform area of the Three Gorges Reservoir[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 36(2): 328-334. | |
| [17] | 姜倪皓, 张诗函, 2021. 楚雄市西郊云南松林下草本优势种种间联结及环境解释[J]. 生态环境学报, 30(11): 2109-2120. |
| JIANG N H, ZHANG S H, 2021. Interspecific association and environmental interpretation of dominant herbaceous species in Pinus yunnanensis Forest in the western suburbs of Chuxiong City[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 30(11): 2109-2120. | |
| [18] | 蒋政权, 洪剑明, 胡东, 2004. 北京市杨镇湿地植物群落多样性及优势种重要值的研究[J]. 湿地科学, 2(3): 213-219. |
| JIANG Z Q, HONG J M, HU D, 2004. Plant diversity and seasonal variation of key value of dominant species in Yangzhen wetland[J]. Wetland science, 2(3): 213-219. | |
| [19] | 孔维静, 夏会娟, 张远, 等, 2015. 辽河保护区及其支流河岸草本植物群落数量分析[J]. 应用与环境生物学报, 21(5): 904-911. |
| KONG W J, XIA H J, ZHANG Y, et al., 2015. Quantitative analysis of riparian herbaceous community in Liaohe River conservation area and its tributaries[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied & Environmental Biology, 21(5): 904-911. | |
| [20] | 雷昆, 张明祥, 2005. 中国的湿地资源及其保护建议[J]. 湿地科学, 3(2): 81-86. |
| LEI K, ZHANG M X, 2005. The wetland resources in China and the conservation advices[J]. Wetland science, 3(2): 81-86. | |
| [21] | 李如忠, 丁丰, 2009. 巢湖主要入湖河口湿地植被生态学特征分析--以派河和十五里河为例[J]. 安徽建筑工业学院学报 (自然科学版), 17(1): 80-84. |
| LI R Z, DING F, 2009. Mainly estuarine wetland vegetation analysis of ecological characteristics of the rivers into the Chaohu Lake: As pai River and Shiwuli River for an example[J]. Journal of Anhui Institute of Architecture & Industry, 17(1): 80-84. | |
| [22] | 李雅, 于秀波, 刘宇, 等, 2018. 湿地植物功能性状对水文过程的响应研究进展[J]. 生态学杂志, 37(3): 952-959. |
| LI Y, YU X B, LIU Y, et al., 2018. Response of wetland plant functional traits to hydrological processes: A review[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 37(3): 952-959. | |
| [23] | 李英杰, 许秋瑾, 金相灿, 等, 2004. 湖泊水生植被恢复物种选择及群落配置分析[J]. 环境污染治理技术与设备, 5(8): 23-26. |
| LI Y J, XU Q J, JIN X C, et al., 2004. Analyses on species selection and community collocation of macrophyte in lake restoration[J]. Techniques and Equipment for Environmental Pollution Control, 5(8): 23-26. | |
| [24] | 卢心固, 1984. 巢湖水生植被調查[J]. 安徽农学院学报 (2): 95-102. |
| LU X G, 1984. Investigation of aquatic vegetation in Chaohu Lake[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural College (2): 95-102. | |
| [25] | 马克平, 1993. 试论生物多样性的概念[J]. 生物多样性, 1(1): 20-22. |
|
MA K P, 1993. On the concept of biodiversity[J]. Biodiversity Science, 1(1): 20-22.
DOI URL |
|
| [26] | 马小伟, 胡东, 华振铃, 等, 2008. 土壤水分、盐分对野鸭湖湿地植物群落演替的影响[J]. 首都师范大学学报 (自然科学版), 29(1): 50-54. |
| MA X W, HU D, HUA Z L, et al., 2008. Affects of soil moisture and salinity on the plant community succession in Yeyahu Lake Wetland[J]. Journal of Capital Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 29(1): 50-54. | |
| [27] | 倪受东, 李萌, 刘枫, 等, 2016. 安徽环巢湖流域药用植物资源调查[J]. 现代中药研究与实践, 30(1): 13-16, 25. |
| NI S D, LI M, LIU F, et al., 2016. Investigation on resources of medicinal plant in Anhui Chaohu basin[J]. Modern Chinese Materia Medica Research & Practice, 30(1): 13-16, 25. | |
| [28] | 潘云芬, 徐庆, 程元启, 等, 2008. 安徽升金湖自然保护区湿地草本种子植物区系研究[J]. 湿地科学, 6(2): 304-309. |
| PAN Y F, XU Q, CHENG Y Q, et al., 2008. Herbaceous seed elora of wetlands in Shengjin Lake nature reserve of Anhui Province[J]. Wetland science, 6(2): 304-309. | |
| [29] | 任璘婧, 李秀珍, 李希之, 等, 2014. 长江口滩涂湿地景观变化对典型水鸟生境适宜性的影响[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 23(10): 1367-1374. |
| REN L J, LI X Z, LI X Z, et al., 2014. Effect of landscape changes on the habitat suitability for typical waterbirds at the Yangtze estuary[J]. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 23(10): 1367-1374. | |
| [30] | 任艳芹, 陈开宁, 2011. 巢湖沉水植物现状 (2010年) 及其与环境因子的关系[J]. 湖泊科学, 23(3): 409-416. |
|
REN Y Q, CHEN K N, 2011. Status of submerged macrophytes and its relationship with environmental factors in Lake Chaohu, 2010[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 23(3): 409-416.
DOI URL |
|
| [31] | 茹辉军, 刘学勤, 黄向荣, 等, 2008. 大型通江湖泊洞庭湖的鱼类物种多样性及其时空变化[J]. 湖泊科学, 20(1): 93-99. |
|
RU H J, LIU X Q, HUANG X R, et al., 2008. Diversity of fish species and its spatio-temporal variations in Lake Dongting, a large Yangtze-connected lake[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 20(1): 93-99.
DOI URL |
|
| [32] | 王圣瑞, 年跃刚, 侯文华, 等, 2004. 人工湿地植物的选择[J]. 湖泊科学, 16(1): 91-96. |
|
WANG S R, NIAN Y G, HOU W H, et al., 2004. Macrophyte selection in artificial wetland[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 16(1): 91-96.
DOI URL |
|
| [33] | 韦翠珍, 张佳宝, 周凌云, 2011. 沿黄河下游湖泊湿地植物群落演替及其多样性研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 20(1): 30-36. |
| WEI C Z, ZHANG J B, ZHOU L Y, 2011. Plant community succession and species diversity of lakeshore wetlands along the lower Yellow River[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 20(1): 30-36. | |
| [34] | 吴海龙, 顾长明, 2017. 安徽鸟类图志[M]. 芜湖: 安徽师范大学出版社. |
| WU H L, GU C M, 2017. Bird atlas of Anhui province[M]. Wuhu: Anhui Normal University Press. | |
| [35] | 吴征镒, 1991. 中国种子植物属的分布区类型[J]. 云南植物研究, 13(S4): 1-139. |
| WU Z Y, 1991. The areal-types of Chinese genera of seed plants[J]. Acta Botanica Yunnanica, 13(S4): 1-139. | |
| [36] | 吴征镒, 周浙昆, 李德株, 等, 2003. 世界种子植物科的分布区类型系统[J]. 云南植物研究, 25(3): 245-257. |
| WU Z Y, ZHOU Z K, LI D S, et al., 2003. The areal-types of the world families of seed plants[J]. Acta Botanica Yunnanica, 25(3): 245-257. | |
| [37] | 肖德荣, 田昆, 张利权, 2008. 滇西北高原纳帕海湿地植物多样性与土壤肥力的关系[J]. 生态学报, 28(7): 3116-3124. |
| XIAO D R, TIAN K, ZHANG L Q, 2008. Relationship between plant diversity and soil fertility in Napahai wetland of Northwestern Yunnan Plateau[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 28(7): 3116-3124. | |
| [38] | 杨李, 董斌, 汪庆, 等, 2015. 安徽升金湖国家级自然保护区水鸟生境适宜性变化[J]. 湖泊科学, 27(6): 1027-1034. |
|
YANG L, DONG B, WANG Q, et al., 2015. Habitat suitability change of water birds in Shengjinhu National Nature Reserve, Anhui Province[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 27(6): 1027-1034.
DOI URL |
|
| [39] | 杨娇, 厉恩华, 蔡晓斌, 等, 2014. 湿地植物对水位变化的响应研究进展[J]. 湿地科学, 12(6): 807-813. |
| YANG J, LI E H, CAI X B, et al., 2014. Research progress in response of plants in wetlands to water level change[J]. Wetland science, 12(6): 807-813. | |
| [40] | 殷福才, 张之源, 2003. 巢湖富营养化研究进展[J]. 湖泊科学, 15(4): 377-384. |
|
YIN F C, ZHANG Z Y, 2003. Survey of Chaohu Lake eutrophication research[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 15(4): 377-384.
DOI URL |
|
| [41] | 余婷, 2022. 引江济淮派河截导污尾水净化湿地设计研究[J]. 水利规划与设计, (2): 119-124. |
| YU T, 2022. Study on the design of wetland for the purification of sewage tail water from the Paihe River of the Yangtze-to-Huaihe water diversion project[J]. Water Resources Planning and Design, (2): 119-124. | |
| [42] | 张萌, 倪乐意, 徐军, 等, 2013. 鄱阳湖草滩湿地植物群落响应水位变化的周年动态特征分析[J]. 环境科学研究, 26(10): 1057-1063. |
| ZHANG M, NI L Y, XU J, et al., 2013. Annual dynamics of the wetland plants community in Poyang Lake in response to water-level variations[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 26(10): 1057-1063. | |
| [43] | 朱昊彧, 张浏, 隗岚琳, 2021. 派河岸边带湿地水力停留时间扩增估算[J]. 安徽农业科学, 49(10): 190-193. |
| ZHU H Y, ZHANG L, WEI L L, 2021. Amplification estimation of hydraulic retention time in Pai River riparian zones with wetlands[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 49(10): 190-193. | |
| [44] | 张黎明, 皇甫超河, 远勇帅, 等, 2021. 升金湖消落带植被特征及与土壤特性的关系[J]. 草业科学, 38(1): 52-62. |
| ZHANG L M, HUANGFU C H, YUAN Y S, et al., 2021. The correlations between vegetation composition and soil characteristics in the riparian zone of Shengjin Lake[J]. Pratacultural Science, 38(1): 52-62. | |
| [45] | 张笑辰, 金斌松, 陈家宽, 等, 2014. 鄱阳湖四种水鸟的栖息地利用与水深和食物的关系[J]. 动物学杂志, 49(5): 657-665. |
| ZHANG X C, JIN B S, CHEN J K, et al., 2014. Relationship between habitat use of four waterbird species and water depth and food resource in Poyang Lake[J]. Chinese Journal of Zoology, 49(5): 657-665. |
| [1] | 何斌, 李青, 陈群利, 李望军, 游萍. 黔西北黄杉群落物种多样性的海拔梯度格局[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(6): 1111-1120. |
| [2] | 张晓龙, 周继华, 来利明, 郑元润. 黑河下游胡杨群落多样性沿河岸距离的变化特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(10): 1952-1960. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
