生态环境学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (5): 857-864.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2022.05.001
• 研究论文 •
下一篇
收稿日期:2022-04-05
出版日期:2022-05-18
发布日期:2022-07-12
作者简介:段文军(1977年生),男,教授,博士,博士研究生导师,主要研究方向为生态恢复、生态旅游。E-mail: duanwenjunagr@163.com
基金资助:
DUAN Wenjun( ), LI Da, LI Chong
), LI Da, LI Chong
Received:2022-04-05
Online:2022-05-18
Published:2022-07-12
摘要:
尾巨桉(Eucalyptus urophylla×E. grandis)是中国南方人工林的典型树种,尾巨桉人工林林下植物多样性及影响因素是决定其生态恢复和自然化改造的重要基础。为探明不同林龄尾巨桉人工林林下植物多样性变化趋势及影响因素,选择广西贵港市1—5 a及以上尾巨桉人工林进行林下植物多样性和环境因子调查,运用双向指示种分析(TWINSPAN)和除趋势对应分析(DCA)对林下植物群落进行对比,通过典范对应分析(CCA)来分析影响植物多样性的主要环境因子。结果表明:(1)不同林龄尾巨桉人工林林植物多样性随林龄呈现先上升或下降的趋势,林龄3—4 a的林下植物生物多样性最高;(2)尾巨桉人工林林下植物群落呈现从以禾本科植物(Poaceae)和铁芒萁(Dicranopteris linearis)为代表的阳生耐旱草本植物群落—桃金娘(Rhodomyrtus tomentosa)、野牡丹(Melastoma candidum)为代表的阳生耐旱灌木群落—米碎花(Eurya chinensis)、白背叶(Mallotus apelta)、梅叶冬青(Ilex asprella)等为代表的中生灌木群落—三叉苦(Evodia lepta)、鸭脚木(Schefflera octophylla)等为代表的耐荫灌木群落的演替趋势;(3)林下透光率和土壤水分是尾巨桉人工林林下植物多样性的主要影响因素,土壤容量、土壤有机质含量等为次要影响因素。尾巨桉人工林的近自然化改造和生态恢复的最重要限制因素是林下透光率,只要适当间伐,人工构建一些林窗,将为乡土植物定居创造良好条件。
中图分类号:
段文军, 李达, 李冲. 5种不同林龄尾巨桉人工林林下植物多样性及其影响因素分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(5): 857-864.
DUAN Wenjun, LI Da, LI Chong. Comparison and Determinant Factors Analysis of Understory Plant Diversity of 5 different Ages Eucalyptus urophylla×E. grandis Plantation[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(5): 857-864.
| 样方号 Plot code | 坡度 Slope/ (°) | 海拔 Altitude/m | 坡向 Aspect/ (°) | 林龄 age/ a | 抚育措施 Tending Measures |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| p1-8 | 15 | 119-125 | NE (48°) | 1 | 萌牙更新、不炼山、 施一次底肥 |
| p9-16 | 13 | 155-165 | NE (51°) | 2 | 萌牙更新、不炼山、不除草、10月间砍一次桉苗、每年施一次肥 |
| p17-24 | 13 | 162-172 | NE (49°) | 3 | 萌牙更新、不炼山、不除草、每年10—11月间砍一次桉苗、每年施一次肥 |
| p25-32 | 14 | 144-169 | NE (48°) | 4 | 萌牙更新、不炼山、不除草、前3年每年10—11月间砍一次桉苗、每年施一次肥 |
| p33-40 | 14 | 141-147 | NE (49°) | ≥5 | 萌牙更新、不炼山、不除草、前3年每年10—11月间砍一次桉苗、每年施一次肥 |
表1 尾巨桉人工林样地概况
Table 1 General situation of Eucalyptus urophylla×E. grandis plantation plots
| 样方号 Plot code | 坡度 Slope/ (°) | 海拔 Altitude/m | 坡向 Aspect/ (°) | 林龄 age/ a | 抚育措施 Tending Measures |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| p1-8 | 15 | 119-125 | NE (48°) | 1 | 萌牙更新、不炼山、 施一次底肥 |
| p9-16 | 13 | 155-165 | NE (51°) | 2 | 萌牙更新、不炼山、不除草、10月间砍一次桉苗、每年施一次肥 |
| p17-24 | 13 | 162-172 | NE (49°) | 3 | 萌牙更新、不炼山、不除草、每年10—11月间砍一次桉苗、每年施一次肥 |
| p25-32 | 14 | 144-169 | NE (48°) | 4 | 萌牙更新、不炼山、不除草、前3年每年10—11月间砍一次桉苗、每年施一次肥 |
| p33-40 | 14 | 141-147 | NE (49°) | ≥5 | 萌牙更新、不炼山、不除草、前3年每年10—11月间砍一次桉苗、每年施一次肥 |
| 序号 Code | 中文名 Chinese name | 拉丁名 Scientific name | 科 Family | 备注 Note |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| s1 | 铁芒萁 | Dicranopteris linearis | 里白科 | 草本 |
| s2 | 海金沙 | Lygodium japonicum | 海金沙科 | 草本 |
| s3 | 白茅 | Imperata cylindrica | 禾本科 | 草本 |
| s4 | 南方露珠草 | Circaea mollis | 柳叶菜科 | 草本 |
| s5 | 乌毛蕨 | Blechnum orientale | 乌毛蕨科 | 草本 |
| s6 | 凤尾蕨 | Pteris cretica | 凤尾蕨科 | 草本 |
| s7 | 铁线蕨 | Adiantum capillus-veneris | 铁线蕨科 | 草本 |
| s8 | 扇叶铁线蕨 | Adiantum flabellulatum | 铁线蕨科 | 草本 |
| s9 | 地稔 | Melastoma dodecandrum | 野牡丹科 | 草本 |
| s10 | 五节芒 | Miscanthus floridulus | 禾本科 | 草本 |
| s11 | 狗尾草 | Setaria viridis | 禾本科 | 草本 |
| s12 | 野菊 | Chrysanthemum indicum | 菊科 | 草本 |
| s13 | 沿阶草 | Ophiopogon bodinieri | 百合科 | 草本 |
| s14 | 弓果黍 | Cyrtococcum patens | 禾本科 | 草本 |
| s15 | 鬼针草 | Bidens pilosa | 菊科 | 草本 |
| s16 | 火炭母草 | Polygonum chiensis | 蓼科 | 草本 |
| s17 | 芒草 | Miscanthus sinensis | 禾本科 | 草本 |
| s18 | 纤毛鸭嘴草 | Ischaemum indicum | 禾本科 | 草本 |
| s19 | 铺地蜈蚣 | Lycopodium cernuum | 石松科 | 草本 |
| s20 | 淡竹叶 | Lophatherum gracile | 禾本科 | 草本 |
| s21 | 山菅兰 | Dianella ensifolia | 百合科 | 草本 |
| s22 | 两耳草 | Paspalum conjugatum | 禾本科 | 草本 |
| 序号 Code | 中文名 Chinese name | 拉丁名 Scientific name | 科 Family | 备注 Note |
| s23 | 类芦 | Neyraudia neyraudiana | 禾本科 | 草本 |
| s24 | 地桃花 | Urena lobata | 锦葵科 | 草本 |
| s25 | 假地豆 | Desmodium heterocarpon | 是豆科 | 灌木 |
| s26 | 菝葜 | Smilax china | 百合科 | 藤本 |
| s27 | 酸藤子 | Embelia laeta | 紫金牛科 | 攀援灌木 |
| s28 | 粗叶悬钩子 | Rubus alceaefolius | 蔷薇科 | 攀援灌木 |
| s29 | 玉叶金花 | Mussaenda pubescens | 茜草科 | 攀援灌木 |
| s30 | 鬼灯笼 | Clerodendron fortunatum | 无患子科 | 藤本 |
| s31 | 假鹰爪 | Desmos chinensis | 番荔枝科 | 灌木 |
| s32 | 九节 | Psychotria rubra | 茜草科 | 灌木或 小乔木 |
| s33 | 米碎花 | Eurya chinensis | 山茶科 | 灌木 |
| s34 | 野牡丹 | Melastoma candidum | 野牡丹科 | 灌木 |
| s35 | 了哥王 | Wikstroemia indica | 瑞香科 | 灌木 |
| s36 | 五指毛桃 | Ficus hirta | 桑科 | 灌木或 小乔木 |
| s37 | 毛果算盘子 | Glochidion eriocarpum | 大戟科 | 灌木 |
| s38 | 白背叶 | Mallotus apelta | 大戟科 | 灌木或 小乔木 |
| s39 | 山苍子 | Litsea cubeba | 樟科 | 灌木或 小乔木 |
| s40 | 豺皮樟 | Litsea rotundifolia | 樟科 | 灌木或 小乔木 |
| s41 | 黄栀子 | Gardenia sootepensis | 茜草科 | 灌木 |
| s42 | 桃金娘 | Rhodomyrtus tomentosa | 桃金娘科 | 灌木 |
| s43 | 岗松 | Baeckea frutescens | 桃金娘科 | 灌木 |
| s44 | 三叉苦 | Evodia lepta | 芸香科 | 灌木或 小乔木 |
| s45 | 光叶山黄麻 | Trema cannabina | 榆科 | 灌木或 小乔木 |
| s46 | 鸭脚木 | Schefflera octophylla | 五加科 | 灌木 |
| s47 | 梅叶冬青 | Ilex asprella | 冬青科 | 灌木 |
| s48 | 马尾松 | Pinus massoniana | 松科 | 乔木 |
| s49 | 粗叶榕 | Ficus hirta | 桑科 | 灌木或 小乔木 |
| s50 | 山茶 | Camellia japonica | 山茶科 | 灌木或 小乔木 |
| s51 | 盐肤木 | Rhus chinensis | 漆树科 | 灌木或 小乔木 |
| s52 | 大叶樟 | Cinnamomum Camphora | 樟科 | 乔木 |
| s53 | 山乌桕 | Triadica cochinchinensis | 大戟科 | 乔木 |
| s54 | 木姜子 | Litsea pungens | 樟科 | 小乔木 |
| s55 | 黄樟 | Cinnamomum parthenoxylon | 樟科 | 乔木 |
表2 尾巨桉人工林样地林下植物种类统计
Table 2 Code number and scientific name of 55 plant species in Eucalyptus urophylla×E. grandis plantation plots
| 序号 Code | 中文名 Chinese name | 拉丁名 Scientific name | 科 Family | 备注 Note |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| s1 | 铁芒萁 | Dicranopteris linearis | 里白科 | 草本 |
| s2 | 海金沙 | Lygodium japonicum | 海金沙科 | 草本 |
| s3 | 白茅 | Imperata cylindrica | 禾本科 | 草本 |
| s4 | 南方露珠草 | Circaea mollis | 柳叶菜科 | 草本 |
| s5 | 乌毛蕨 | Blechnum orientale | 乌毛蕨科 | 草本 |
| s6 | 凤尾蕨 | Pteris cretica | 凤尾蕨科 | 草本 |
| s7 | 铁线蕨 | Adiantum capillus-veneris | 铁线蕨科 | 草本 |
| s8 | 扇叶铁线蕨 | Adiantum flabellulatum | 铁线蕨科 | 草本 |
| s9 | 地稔 | Melastoma dodecandrum | 野牡丹科 | 草本 |
| s10 | 五节芒 | Miscanthus floridulus | 禾本科 | 草本 |
| s11 | 狗尾草 | Setaria viridis | 禾本科 | 草本 |
| s12 | 野菊 | Chrysanthemum indicum | 菊科 | 草本 |
| s13 | 沿阶草 | Ophiopogon bodinieri | 百合科 | 草本 |
| s14 | 弓果黍 | Cyrtococcum patens | 禾本科 | 草本 |
| s15 | 鬼针草 | Bidens pilosa | 菊科 | 草本 |
| s16 | 火炭母草 | Polygonum chiensis | 蓼科 | 草本 |
| s17 | 芒草 | Miscanthus sinensis | 禾本科 | 草本 |
| s18 | 纤毛鸭嘴草 | Ischaemum indicum | 禾本科 | 草本 |
| s19 | 铺地蜈蚣 | Lycopodium cernuum | 石松科 | 草本 |
| s20 | 淡竹叶 | Lophatherum gracile | 禾本科 | 草本 |
| s21 | 山菅兰 | Dianella ensifolia | 百合科 | 草本 |
| s22 | 两耳草 | Paspalum conjugatum | 禾本科 | 草本 |
| 序号 Code | 中文名 Chinese name | 拉丁名 Scientific name | 科 Family | 备注 Note |
| s23 | 类芦 | Neyraudia neyraudiana | 禾本科 | 草本 |
| s24 | 地桃花 | Urena lobata | 锦葵科 | 草本 |
| s25 | 假地豆 | Desmodium heterocarpon | 是豆科 | 灌木 |
| s26 | 菝葜 | Smilax china | 百合科 | 藤本 |
| s27 | 酸藤子 | Embelia laeta | 紫金牛科 | 攀援灌木 |
| s28 | 粗叶悬钩子 | Rubus alceaefolius | 蔷薇科 | 攀援灌木 |
| s29 | 玉叶金花 | Mussaenda pubescens | 茜草科 | 攀援灌木 |
| s30 | 鬼灯笼 | Clerodendron fortunatum | 无患子科 | 藤本 |
| s31 | 假鹰爪 | Desmos chinensis | 番荔枝科 | 灌木 |
| s32 | 九节 | Psychotria rubra | 茜草科 | 灌木或 小乔木 |
| s33 | 米碎花 | Eurya chinensis | 山茶科 | 灌木 |
| s34 | 野牡丹 | Melastoma candidum | 野牡丹科 | 灌木 |
| s35 | 了哥王 | Wikstroemia indica | 瑞香科 | 灌木 |
| s36 | 五指毛桃 | Ficus hirta | 桑科 | 灌木或 小乔木 |
| s37 | 毛果算盘子 | Glochidion eriocarpum | 大戟科 | 灌木 |
| s38 | 白背叶 | Mallotus apelta | 大戟科 | 灌木或 小乔木 |
| s39 | 山苍子 | Litsea cubeba | 樟科 | 灌木或 小乔木 |
| s40 | 豺皮樟 | Litsea rotundifolia | 樟科 | 灌木或 小乔木 |
| s41 | 黄栀子 | Gardenia sootepensis | 茜草科 | 灌木 |
| s42 | 桃金娘 | Rhodomyrtus tomentosa | 桃金娘科 | 灌木 |
| s43 | 岗松 | Baeckea frutescens | 桃金娘科 | 灌木 |
| s44 | 三叉苦 | Evodia lepta | 芸香科 | 灌木或 小乔木 |
| s45 | 光叶山黄麻 | Trema cannabina | 榆科 | 灌木或 小乔木 |
| s46 | 鸭脚木 | Schefflera octophylla | 五加科 | 灌木 |
| s47 | 梅叶冬青 | Ilex asprella | 冬青科 | 灌木 |
| s48 | 马尾松 | Pinus massoniana | 松科 | 乔木 |
| s49 | 粗叶榕 | Ficus hirta | 桑科 | 灌木或 小乔木 |
| s50 | 山茶 | Camellia japonica | 山茶科 | 灌木或 小乔木 |
| s51 | 盐肤木 | Rhus chinensis | 漆树科 | 灌木或 小乔木 |
| s52 | 大叶樟 | Cinnamomum Camphora | 樟科 | 乔木 |
| s53 | 山乌桕 | Triadica cochinchinensis | 大戟科 | 乔木 |
| s54 | 木姜子 | Litsea pungens | 樟科 | 小乔木 |
| s55 | 黄樟 | Cinnamomum parthenoxylon | 樟科 | 乔木 |
| 样方号 Plot code | 植物种数 Number of plant | 植物种类 Plant species | 优势种 Dominant species |
|---|---|---|---|
| p1-8 | 21 | s1铁芒萁; s3白茅; s9地稔; s10五节芒; s11狗尾草; s12野菊; s14弓果黍; s15鬼针草; s17芒草; s18纤毛鸭嘴草; s19铺地蜈蚣; s22两耳草; s23类芦; s24地桃花; s27菝葜; s33米碎花; s42桃金娘; s43岗松; s45光叶山黄麻; s47梅叶冬青; s51盐肤木 | s1铁芒萁; s3白茅; s10五节芒 |
| p9-16 | 31 | s1铁芒萁; s3白茅; s9地稔; s11狗尾草; s12野菊; s14弓果黍; s15鬼针草; s17芒草; s18纤毛鸭嘴草; s19铺地蜈蚣; s22两耳草; s23类芦; s24地桃花; s25假地豆; s26菝葜; s28粗叶悬钩子; s29玉叶金花; s30鬼灯笼; s33米碎花; s34野牡丹; s37了哥王; s36五指毛桃; s39白背叶; s41山苍子; s42桃金娘; s43岗松; s45光叶山黄麻; s47梅叶冬青; s50马尾松; s51粗叶榕; s51盐肤木 | s42桃金娘; s34野牡丹; s1铁芒萁 |
| p17-24 | 30 | s1铁芒萁; s2海金沙; s4南方露珠草; s5乌毛蕨; s6凤尾蕨; s15鬼针草; s16火炭母草; s17芒草; s20淡竹叶; s26菝葜; s28粗叶悬钩子; s29玉叶金花; s30鬼灯笼; s31假鹰爪; s33米碎花; s34野牡丹; s35了哥王; s36五指毛桃; s37毛果算盘子; s38白背叶; s39山苍子; s42桃金娘; s45光叶山黄麻; s47梅叶冬青; s48马尾松; s49粗叶榕; s51盐肤木; s52大叶樟; s55山乌桕; s56木姜子 | s33米碎花; s38白背叶; s47梅叶冬青 |
| p25-32 | 26 | s2海金沙; s4南方露珠草; s5乌毛蕨; s6凤尾蕨; s7铁线蕨; s8扇叶铁线蕨; s13沿阶草; s16火炭母草; s20淡竹叶; s27酸藤子; s29玉叶金花; s33米碎花; s35了哥王; s36五指毛桃; s38白背叶; s39山苍子; s40豺皮樟; s41黄栀子; s44三叉苦; s46鸭脚木; s49粗叶榕; s50山茶; s52大叶樟; s53山乌桕; s54木姜子; s55黄樟 | s44三叉苦; s38白背叶; s4海金沙 |
| p33-40 | 16 | s2海金沙; s4南方露珠草; s5乌毛蕨; s6凤尾蕨; s7铁线蕨; s8扇叶铁线蕨; s13沿阶草; s20淡竹叶; s21山菅兰; s32九节; s36五指毛桃; s41黄栀子; s44三叉苦; s46鸭脚木; s50山茶; s52大叶樟 | s44三叉苦; s46鸭脚木; s4海金沙 |
表3 5种龄级尾巨桉人工林林下植物种类对比
Table 3 Comparison of understory plant species of 5 ages Eucalyptus urophylla×E. grandis Plantation
| 样方号 Plot code | 植物种数 Number of plant | 植物种类 Plant species | 优势种 Dominant species |
|---|---|---|---|
| p1-8 | 21 | s1铁芒萁; s3白茅; s9地稔; s10五节芒; s11狗尾草; s12野菊; s14弓果黍; s15鬼针草; s17芒草; s18纤毛鸭嘴草; s19铺地蜈蚣; s22两耳草; s23类芦; s24地桃花; s27菝葜; s33米碎花; s42桃金娘; s43岗松; s45光叶山黄麻; s47梅叶冬青; s51盐肤木 | s1铁芒萁; s3白茅; s10五节芒 |
| p9-16 | 31 | s1铁芒萁; s3白茅; s9地稔; s11狗尾草; s12野菊; s14弓果黍; s15鬼针草; s17芒草; s18纤毛鸭嘴草; s19铺地蜈蚣; s22两耳草; s23类芦; s24地桃花; s25假地豆; s26菝葜; s28粗叶悬钩子; s29玉叶金花; s30鬼灯笼; s33米碎花; s34野牡丹; s37了哥王; s36五指毛桃; s39白背叶; s41山苍子; s42桃金娘; s43岗松; s45光叶山黄麻; s47梅叶冬青; s50马尾松; s51粗叶榕; s51盐肤木 | s42桃金娘; s34野牡丹; s1铁芒萁 |
| p17-24 | 30 | s1铁芒萁; s2海金沙; s4南方露珠草; s5乌毛蕨; s6凤尾蕨; s15鬼针草; s16火炭母草; s17芒草; s20淡竹叶; s26菝葜; s28粗叶悬钩子; s29玉叶金花; s30鬼灯笼; s31假鹰爪; s33米碎花; s34野牡丹; s35了哥王; s36五指毛桃; s37毛果算盘子; s38白背叶; s39山苍子; s42桃金娘; s45光叶山黄麻; s47梅叶冬青; s48马尾松; s49粗叶榕; s51盐肤木; s52大叶樟; s55山乌桕; s56木姜子 | s33米碎花; s38白背叶; s47梅叶冬青 |
| p25-32 | 26 | s2海金沙; s4南方露珠草; s5乌毛蕨; s6凤尾蕨; s7铁线蕨; s8扇叶铁线蕨; s13沿阶草; s16火炭母草; s20淡竹叶; s27酸藤子; s29玉叶金花; s33米碎花; s35了哥王; s36五指毛桃; s38白背叶; s39山苍子; s40豺皮樟; s41黄栀子; s44三叉苦; s46鸭脚木; s49粗叶榕; s50山茶; s52大叶樟; s53山乌桕; s54木姜子; s55黄樟 | s44三叉苦; s38白背叶; s4海金沙 |
| p33-40 | 16 | s2海金沙; s4南方露珠草; s5乌毛蕨; s6凤尾蕨; s7铁线蕨; s8扇叶铁线蕨; s13沿阶草; s20淡竹叶; s21山菅兰; s32九节; s36五指毛桃; s41黄栀子; s44三叉苦; s46鸭脚木; s50山茶; s52大叶樟 | s44三叉苦; s46鸭脚木; s4海金沙 |
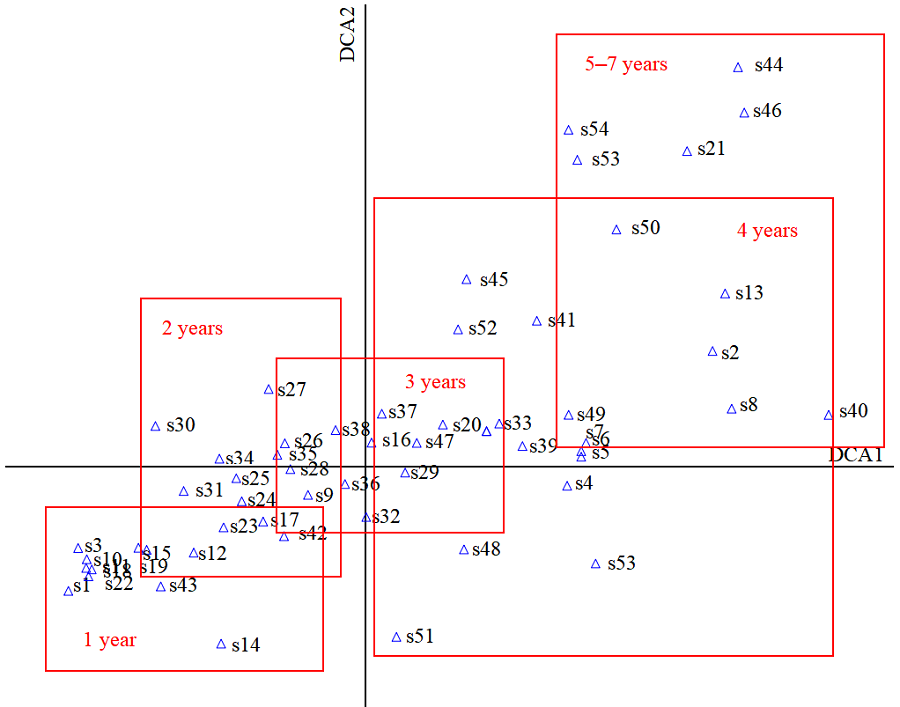
图2 5种林龄尾巨桉人工林林下植物种DCA分析 s+数字对应不同植物种类
Figure 2 DCA diagram of 55 understory species of 5 ages Eucalyptus urophylla×E. grandis plantation s+number is the species code
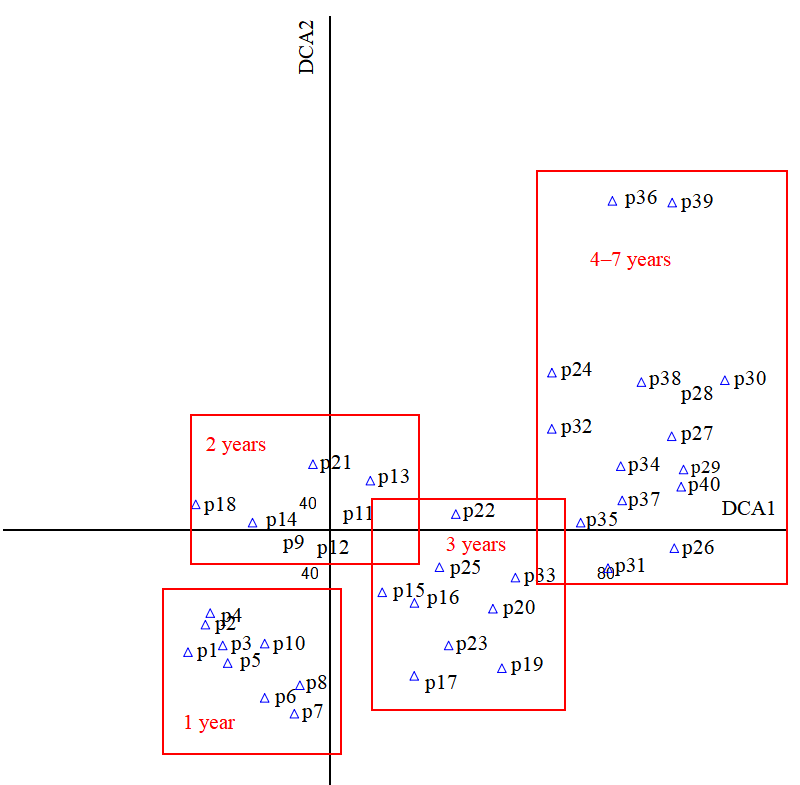
图3 5种林龄尾巨桉人工林40个样方的DCA分析 p+数字对应不同样方
Figure 3 DCA diagram of 40 plots of 5 ages Eucalyptus urophylla×E. grandis plantation p+number represent different plots
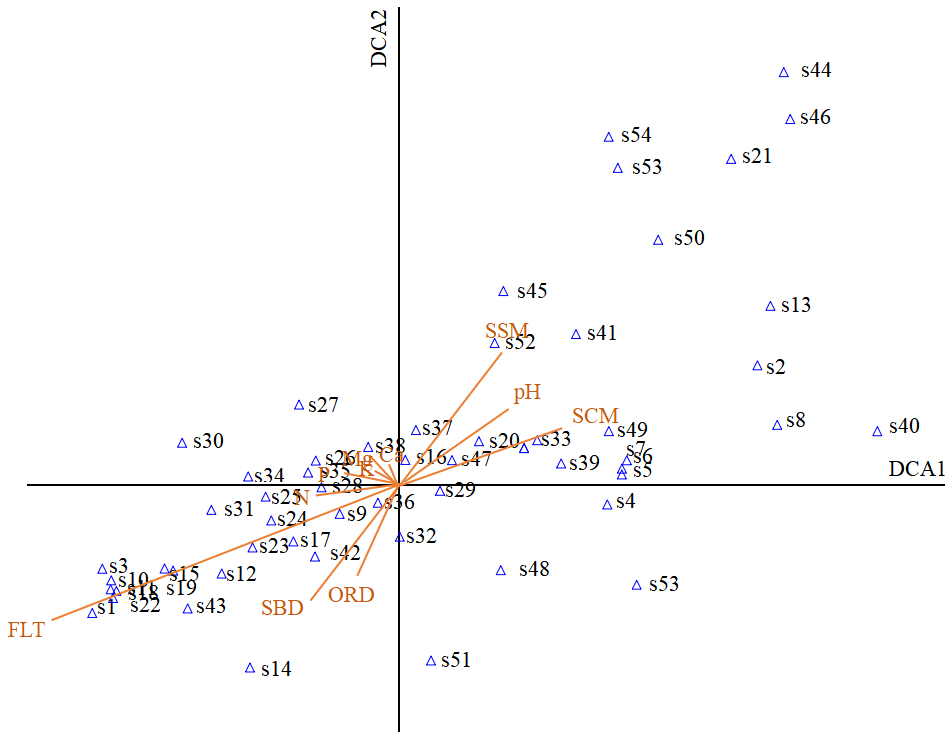
图4 5种林龄尾巨桉人工林55个林下植物和11个环境因子的CCA分析 FLT:林下透光率;ORD:土壤有机质含量;SBD:土壤容重;SCM土壤饱和含水量;SSM:土壤毛管含水量;N:水解N;P:速效P;K交换性K;Ca:交换性Ca;Mg: 交换性Mg
Figure 4 CCA diagram of 55 understory species and 11 environmental factors of 5 ages Eucalyptus urophylla×E. grandis plantation FLT, understory light transmittance; ORD, soil organic matter; SBD, soil bulk density; SSM, soil saturation moisture; SCM, soil capillary moisture; N, hydrolyzed nitrogen; P, available phosphorus; K, exchanged kalium
| [1] |
ARCHIBALD R D, 2011. Managing small remnants of native forest to increase biodiversity within plantation landscapes in the south west of Western Australia[J]. Forest Ecology and Management, 261(7): 1254-1264.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
GERBER J F, 2011. Conflicts over industrial tree plantations in the South: Who, how and why?[J]. Global Environmental Change, 21(1): 165-176.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
SEBASTIEN, 1999. Seed shadows, survival and recruitment: How simple mechanisms lead to dynamics of plantation recruitment curves[J]. Oikos, 86(2): 320-330.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
WANG J, HUI D F, REN H, et al., 2013. Effects of understory vegetation and litter on plant nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), N꞉P ratio and their relationships with growth rate of indigenous seedlings in subtropical plantations[J]. Plos One, 8(12): e84130.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
WANG J, REN H, YANG L, et al., 2009. Establishment and early growth of introduced indigenous tree species in typical plantations and shrubland in South China[J]. Forest Ecology and Management, 258(7): 1293-1300.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
YANG L, CHEN Y Q, HUANG Y H, et al., 2016. Effects of shrub islands created by Rhodomyrtus tomentosa (AITON) Hassk. on the growth, chlorophyll fluorescence, and chloroplast ultrastructure of pine seedlings in degrade land of South China[J]. Land Degradation & Development, 27: 729-737.
DOI URL |
| [7] | 成向荣, 徐金良, 刘佳, 等, 2014. 间伐对杉木人工林林下植被多样性及其营养元素现存量影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 23(1): 30-34. |
| CHENG X R, XU J L, LIU J, et al., 2014. Effect of thinning on understory vegetation diversity and its nutrient stocks in Cunninghamia lanceolata plantation[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 23(1): 30-34. | |
| [8] | 韩富任, 冯亚磊, 冯金朝, 2016. 桉树人工林生物多样性及可持续发展[J]. 南方农业, 10(21): 124-125. |
| HAN F R, FENG Y L, FENG J C, 2016. Biodiversity and sustainable development of eucalyptus plantation[J]. Southern Agriculture, 10(21): 124-125. | |
| [9] | 郝建锋, 王德艺, 唐永彬, 等, 2014. 人为干扰对江油地区马尾松人工林群落结构和物种多样性的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 23(5): 729-735. |
| HAO J F, WANG D Y, TANG Y B, et al., 2014. Effects of human disturbance on species diversity of Pinus massoniana plantation in Jiangyou district, Sichuan province[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 23(5): 729-735. | |
| [10] | 李东海, 杨小波, 邓运武, 等, 2006. 桉树人工林林下植被、地面覆盖物与土壤物理性质的关系[J]. 生态学杂志, 25(6): 607-611. |
| LI D H, YANG X B, DENG Y W, et al., 2006. Soil physical properties under effects of Eucalyptus understory vegetation and litter[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 25(6): 1607-611. | |
| [11] | 刘光崧, 1996. 土壤理化分析和剖面描述[M]. 北京: 中国标准出版社. |
| LIU G S, 1996. Soil physicochemical analysis and soil profile description[M]. Beijing: China Standard Press. | |
| [12] | 马倩, 周晓果, 梁宏温, 等, 2017. 不同经营措施对桉树人工林植物多样性的影响[J]. 广西科学, 24(2): 182-187, 195. |
| MA Q, ZHOU X G, LIANG H W, et al., 2017. Effects of different management measures on plant diversity in Eucalyptus plantations[J]. Guangxi Sciences, 24(2):182-187, 195. | |
| [13] | 聂鑫, 章文波, 薛丽霞, 2017. 广西速生桉种植的空间分布及生态特征[J]. 北京师范大学学报 (自然科学版), 53(2): 215-221. |
| NIE X, ZHANG W B, XUE L X, 2017. Spatial distribution and ecological characteristics of fast-growing Eucalyptus plantations in Guangxi[J]. Journal of Beijing Normal University (Natural Science), 53(2): 215-221. | |
| [14] | 欧建德, 吴志庄, 罗宁, 2016. 林窗大小对杉木林内南方红豆杉生长与形质的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 27(10): 3098-3104. |
| OU J D, WU Z Z, LUO N, 2016. Effects of forest gap size on the growth and form quality of Taxus wallichiana var. mairei in Cunninghamia lanceolata forests[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 27(10): 3098-3104. | |
| [15] | 庞圣江, 张培, 贾宏炎, 等, 2020. 不同造林模式对桉树人工林林下植物物种多样性的影响[J]. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 48(9): 44-52. |
| PANG S J, ZHANG P, JIA H Y, et al., 2020. Effects of different afforestation modes on diveristy of undergrowth plants in Eucalyptus plantations[J]. Journal of Northwest A & F University (Natural Science Edition), 48(9): 44-52. | |
| [16] | 王克林, 岳跃民, 马祖陆, 等, 2016. 喀斯特峰丛洼地石漠化治理与生态服务提升技术研究[J]. 生态学报, 36(22): 7098-7102. |
| WANG K L, YUE Y M, MA Z L, et al., 2016. Research and demonstration on technologies for rocky desertification treatment and ecosystem services enhancement in karst peak-cluster depression regions[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 36(22): 7098-7102. | |
| [17] | 王敏, 周润惠, 余飞燕, 等, 2021. 不同林龄桉树人工林林下物种多样性和生物量的动态变化[J]. 植物研究, 41(4): 496-505. |
| WANG M, ZHOU R H, YU F Y, et al., 2021. Dynamic changes of undergrowth species diversity and biomass of Eucalyptus robusta plantations at different ages[J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 41(4): 496-505. | |
| [18] | 魏天兴, 陈致富, 赵健, 等, 2012. 低效低质人工林优化改造后林下植被多样性研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 21(5): 800-806. |
| WEI T X, CHEN Z, ZHAO J, et al., 2012. Understory biodiversity of managed plantation stands from the inefficient and inferior forests[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 21(5): 800-806. | |
| [19] | 温远光, 刘世荣, 陈放, 等, 2005. 桉树工业人工林植物物种多样性及动态研究[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 27(4): 17-22. |
| WEN Y G, LIU S R, CHEN F, et al., 2005. Plant diversity and dynamics in industrial plantations of eucalyptus[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 27(4): 17-22. | |
| [20] | 温远光, 严宇航, 陶彦良, 等, 2018. 不同林地清理和培肥措施对桉树人工林植物多样性的影响[J]. 广西科学, 25(2): 117-127. |
| WEN Y G, YAN Y H, TAO Y L, et al., 2018. Effect of different ground clearance and fertilizing treatments on plant diversity of Eucalyptus plantations in subtropical China[J]. Guangxi Sciences, 25(2): 117-127. | |
| [21] | 温远光, 周晓果, 朱宏光, 等, 2019. 桉树生态营林的理论探索与实践[J]. 广西科学, 26(2): 159-175, 252. |
| WEN Y G, ZHOU X G, ZHU H G, et al., 2019. Theoretical Exploration and Practices of Ecological Management in Eucalyptus Plantations[J]. Guangxi Sciences, 26(2): 159-175, 252. | |
| [22] | 徐馨, 王法明, 邹碧, 等, 2013. 不同林龄木麻黄人工林生物多样性与土壤养分状况研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 22(9): 1514-1522. |
| XU X, WANG F M, ZOU B, et al., 2013. Biodiversity and soil nutrient research of Casuarina equisetifolia plantation at different stand ages[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 22(9): 1514-1522. | |
| [23] | 尤业明, 陈永康, 朱宏光, 等, 2019. 桉树人工林更新方式对林下植物功能群的影响[J]. 广西植物, 39(1): 126-135. |
| YOU Y M, CHEN Y K, ZHU H G, et al., 2019. Effects of different regeneration modes on understory plant functional group in Eucalyptus plantations[J]. Guihaia, 39(1): 126-135. | |
| [24] | 于洋洋, 廖博一, 程飞, 等, 2018. 不同抚育措施对尾巨桉人工林生长动态及其林下植被多样性的影响[J]. 西南林业大学学报, 38(5): 58-64. |
| YU Y Y, LIAO B Y, CHENG F, et al., 2018. Effects of different tending measures on growth dynamics of Eucalyptus urophylla×Eucalyptus grandis plantation and variation of vegetation diversity under forest[J]. Journal of Southwest Forestry University, 38(5): 58-64. | |
| [25] | 张静美, 2018. 桉树工业原料林林下植物多样性与土壤养分关系[J]. 甘肃科技纵横, 47(10): 15-17, 45. |
| ZHANG J M, 2018. Relationship between understory plant diversity and soil nutrients in eucalyptus industrial raw materials forest[J]. Gansu Science and Technology, 47(10): 15-17, 45. | |
| [26] | 张培, 赵志刚, 贾宏炎, 等, 2021. 林窗面积对桉树林分内格木生长、形态及生物量分配的影响[J]. 西北农林科技大学学报 (自然科学版), 49(5): 40-46, 55. |
| ZHANG P, ZHAO Z G, JIA H Y, 2021. Effects of gap size on growth, morphology and biomass distribution of Erythrophleum fordii in Eucalyptus Plantation[J]. Journal of Northwest A & F University (Natural Science Edition), 49(5): 40-46, 55. | |
| [27] | 张洋洋, 周清慧, 许骄阳, 等, 2021. 林龄对马尾松人工林林下植物与土壤种子库多样性的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 30(11): 2121-2129. |
| ZHANG Y Y, ZHOU Q H, XU J Y, et al., 2021. Effects of forest ages on the diversity of understory plants and soil seed bank of Pinus massoniana plantations[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 30(11): 2121-2129. | |
| [28] | 中国科学院土壤研究所, 1978. 土壤理化分析[M]. 上海: 上海科学技术出版社. |
| Institute of Soil Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), 1978. Soil Physical and Chemical Analysis[M]. Shanghai: Shanghai Technology Press, of China. | |
| [29] | 周润惠, 唐永彬, 王敏, 等, 2021. 威远不同年龄桉树人工林林下物种多样性和土壤理化性质[J]. 应用与环境生物学报, 27(3): 742-748. |
| ZHOU R H, TANG Y B, WANG M, et al., 2021. Species diversity and soil physicochemical properties at Eucalyptus robusta plantations of different ages in Weiyuan[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology, 27(3): 742-748. | |
| [30] | 朱育锋, 肖智华, 彭晚霞, 等, 2018. 广西不同龄级桉树人工林植物多样性和群落结构动态变化特征[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 38(12): 38-44. |
| ZHU Y F, XIAO Z H, PENG W X, et al., 2018. Dynamics of plant diversity and community structure of Eucalyptus plantation at different ages class in Guangxi[J]. Journal of Central South University of Forestry & Technology, 38(12): 38-44. | |
| [31] | 朱宇林, 唐庆兰, 张照远, 等, 2012. 不同类型桉树人工林土壤种子库特征研究[J]. 热带作物学报, 33(3): 572-577. |
| ZHU Y L, TANG Q L, ZHANG Z Y, et al., 2016. Characteristics of Soil Seed Banks in Different Eucalyptus urophylla×E. grandis Forest Types Chinese[J]. Journal of Tropical Crops, 33(3): 572-577. |
| [1] | 王超, 杨倩楠, 张池, 刘同旭, 张晓龙, 陈静, 刘科学. 丹霞山不同土地利用方式土壤磷组分特征及其有效性[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 889-897. |
| [2] | 李建辉, 党争, 陈琳. 黄河几字弯都市圈PM2.5时空特征及影响因素分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 697-705. |
| [3] | 张林, 齐实, 周飘, 伍冰晨, 张岱, 张岩. 北京山区针阔混交林地土壤有机碳含量的影响因素研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 450-458. |
| [4] | 何艳虎, 龚镇杰, 吴海彬, 蔡宴朋, 杨志峰, 陈晓宏. 粤港澳大湾区城市生态效率时空演变及影响因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 469-480. |
| [5] | 郝金虎, 韦玮, 李胜男, 马牧源, 李肖夏, 杨洪国, 姜琦宇, 柴沛东. 基于GEE平台的京津冀长时序水体时空格局及其影响因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 556-566. |
| [6] | 周世强, Vanessa HULL, 张晋东, 刘巅, 谢浩, 黄金燕, 张和民. 野生大熊猫与放牧家畜利用生境的特征比较[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(2): 309-319. |
| [7] | 张莉, 李铖, 谭皓泽, 韦家怡, 程炯, 彭桂香. 广州典型城市林地对大气颗粒物的削减效应及影响因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(2): 341-350. |
| [8] | 郑晓豪, 陈颖彪, 郑子豪, 郭城, 黄卓男, 周泳诗. 湖北省生态系统服务价值动态变化及其影响因素演变[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 195-206. |
| [9] | 袁林江, 李梦博, 冷钢, 钟冰冰, 夏大朋, 王景华. 厌氧环境下硫酸盐还原与氨氧化的协同作用[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 207-214. |
| [10] | 刘希林, 卓瑞娜. 崩岗崩积体坡面初始产流时间影响因素及其临界阈值[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 36-46. |
| [11] | 李威闻, 黄金权, 齐瑜洁, 刘小岚, 刘纪根, 毛治超, 高绣纺. 土壤侵蚀条件下土壤微生物生物量碳含量变化及其影响因素的Meta分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 47-55. |
| [12] | 李萍, 白小明, 陈鑫, 李娟霞, 冉福, 陈辉, 杨小妮, 康瑞卿. 白三叶入侵对禾本科草坪土壤特性和植物群落的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 70-79. |
| [13] | 苏泳松, 宋松, 陈叶, 叶子强, 钟润菲, 王昭尧. 珠江三角洲人类活动净氮输入时空特征及其影响因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1599-1609. |
| [14] | 陈文裕, 夏丽华, 徐国良, 余世钦, 陈行, 陈金凤. 2000—2020年珠江流域NDVI动态变化及影响因素研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(7): 1306-1316. |
| [15] | 王占永, 陈昕, 胡喜生, 何红弟, 蔡铭, 彭仲仁. 植物屏障影响路边大气颗粒物分布机理及研究方法的进展[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(5): 1047-1058. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
