生态环境学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (6): 1141-1150.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2022.06.009
龚玲玄( ), 王丽丽*(
), 王丽丽*( ), 赵建宁, 刘红梅, 杨殿林, 张贵龙
), 赵建宁, 刘红梅, 杨殿林, 张贵龙
收稿日期:2021-12-16
出版日期:2022-06-18
发布日期:2022-07-29
通讯作者:
*E-mail: lili0229ok@126.com作者简介:龚玲玄(1999年生),女(壮族),硕士研究生,主要从事碳氮循环研究。E-mail: gong_lingxuan@163.com
基金资助:
GONG Lingxuan( ), WANG Lili*(
), WANG Lili*( ), ZHAO Jianning, LIU Hongmei, YANG Dianlin, ZHANG Guilong
), ZHAO Jianning, LIU Hongmei, YANG Dianlin, ZHANG Guilong
Received:2021-12-16
Online:2022-06-18
Published:2022-07-29
摘要:
覆盖作物作为重要的农业管理措施之一,可影响土壤有机碳的周转过程。茶是中国重要的经济作物,为探究不同覆盖作物模式下茶园土壤理化性质及土壤有机碳矿化动态,该研究自2019年选取茶园中清耕(C0)、黑麦草 (Lolium perenne L.)+白三叶 (Trifolium repens L.)(C1)、黑麦草+白三叶+早熟禾 (Poa annua L.)+红三叶 (Trifolium pretense L.)(C2)、黑麦草+白三叶+早熟禾+红三叶+紫羊茅 (Festuca rubra L.)+毛苕子 (Vicia villosa Roth.)+波斯菊 (Cosmos bipinnata Cav.)+百日草 (Zinnia elegans Jacq.)(C3)作为4种覆盖作物模式,测定其表层(0—30 cm)土壤理化性质并进行了为期471 d的矿化培养,使用一级动力学方程及指数加线性常数模型来探究土壤有机碳矿化特征。结果表明,覆盖作物能显著增加表层0—30 cm土壤中硝态氮、铵态氮、微生物量碳和微生物量氮的含量(P<0.05)。4种覆盖作物模式下,表层土壤有机碳矿化速率均随培养时间增加呈“先增后降”的变化模式,平均矿化速率为C1>C0>C2>C3。该研究发现覆盖作物种类越多,矿化速率变化越小,反应越“温和”。此外,随覆盖作物种类增加,表层土壤有机碳矿化作用增强,周转周期减小,但土壤惰性碳库含量随之增加,表明随覆盖作物多样性增加,土壤矿化作用增强,同时土壤碳的固存能力也在提高。该研究表明,在中国南方广泛种植的茶园中推广覆盖作物种植可增加表层土壤碳固持能力,对促进中国茶园土壤固碳功能具有重要意义。
中图分类号:
龚玲玄, 王丽丽, 赵建宁, 刘红梅, 杨殿林, 张贵龙. 不同覆盖作物模式对茶园土壤理化性质及有机碳矿化的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(6): 1141-1150.
GONG Lingxuan, WANG Lili, ZHAO Jianning, LIU Hongmei, YANG Dianlin, ZHANG Guilong. Effects of Different Cover Crop Patterns on Soil Physicochemical Properties and Organic Carbon Mineralization in Tea Gardens[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(6): 1141-1150.
| 覆盖模式 Cover model | 覆盖作物模式 Cover crops patterns |
|---|---|
| C0 | 清耕 |
| C1 | 黑麦草 (Lolium perenne L.); 白三叶 (Trifolium repens L.) |
| C2 | 黑麦草; 白三叶; 早熟禾 (Poa annua L.); 红三叶 (Trifolium pretense L.) |
| C3 | 黑麦草; 白三叶; 早熟禾; 红三叶; 紫羊茅 (Festuca rubra L.); 毛苕子 (Vicia villosa Roth.); 波斯菊 (Cosmos bipinnata Cav.); 百日草 (Zinnia elegans Jacq.) |
表1 试验期间不同覆盖作物模式
Table 1 Different crop coverage patterns during the experiment
| 覆盖模式 Cover model | 覆盖作物模式 Cover crops patterns |
|---|---|
| C0 | 清耕 |
| C1 | 黑麦草 (Lolium perenne L.); 白三叶 (Trifolium repens L.) |
| C2 | 黑麦草; 白三叶; 早熟禾 (Poa annua L.); 红三叶 (Trifolium pretense L.) |
| C3 | 黑麦草; 白三叶; 早熟禾; 红三叶; 紫羊茅 (Festuca rubra L.); 毛苕子 (Vicia villosa Roth.); 波斯菊 (Cosmos bipinnata Cav.); 百日草 (Zinnia elegans Jacq.) |
| 覆盖作物模式 Cover crop modes patterns | 含水率 Soil moisture/% | 铵态氮 w(NH4+-N)/(mg∙kg-1) | 硝态氮 w(NO3--N)/(mg∙kg-1) | 微生物量碳 (MBC) w(CO2-C)/(mg·kg-1) | 微生物量氮 (MBN) w(CO2-C)/(mg∙kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C0 | 12.76±0.20a | 5.47±0.03c | 15.38±0.33b | 101.40±4.52c | 18.08±0.51b |
| C1 | 12.34±0.36ab | 5.56±0.04c | 14.36±0.14c | 119.52±1.51b | 21.32±0.10a |
| C2 | 11.45±0.35bc | 6.33±0.02a | 17.58±0.39a | 140.63±2.47a | 20.42±0.84a |
| C3 | 11.07±0.41c | 5.94±0.15b | 15.63±0.29b | 106.73±2.09c | 16.73±0.58b |
表2 不同覆盖作物模式的土壤理化性质(±SE)
Table 2 Soil physical and chemical properties under different cover crop treatments (±SE)
| 覆盖作物模式 Cover crop modes patterns | 含水率 Soil moisture/% | 铵态氮 w(NH4+-N)/(mg∙kg-1) | 硝态氮 w(NO3--N)/(mg∙kg-1) | 微生物量碳 (MBC) w(CO2-C)/(mg·kg-1) | 微生物量氮 (MBN) w(CO2-C)/(mg∙kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C0 | 12.76±0.20a | 5.47±0.03c | 15.38±0.33b | 101.40±4.52c | 18.08±0.51b |
| C1 | 12.34±0.36ab | 5.56±0.04c | 14.36±0.14c | 119.52±1.51b | 21.32±0.10a |
| C2 | 11.45±0.35bc | 6.33±0.02a | 17.58±0.39a | 140.63±2.47a | 20.42±0.84a |
| C3 | 11.07±0.41c | 5.94±0.15b | 15.63±0.29b | 106.73±2.09c | 16.73±0.58b |
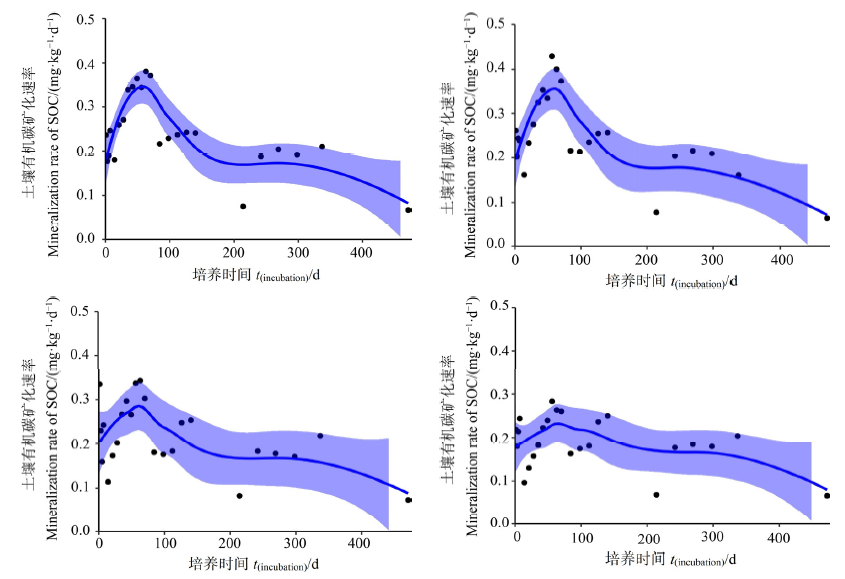
图5 4种模式Loess变化曲线,均采用最小二乘法计算 从左上至右下分别为C0、C1、C2、C3
Figure 5 Loess variation curves of the four modes, all calculated by the least square method From top left to bottom right are C0, C1, C2, C3
| 覆盖作物模式 Cover crop modes patterns | 线段A斜率 (×10-3) | 线段B (×10-3) |
|---|---|---|
| C0 | 3.4 | -0.61 |
| C1 | 2.80 | -0.65 |
| C2 | 1.00 | -0.44 |
| C3 | 0.95 | -0.31 |
表3 Loess变化曲线线性拟合斜率
Table 3 Linear fitting slope of Loess change curve
| 覆盖作物模式 Cover crop modes patterns | 线段A斜率 (×10-3) | 线段B (×10-3) |
|---|---|---|
| C0 | 3.4 | -0.61 |
| C1 | 2.80 | -0.65 |
| C2 | 1.00 | -0.44 |
| C3 | 0.95 | -0.31 |
| 覆盖作物模式 Cover crop models | 潜在矿化势CP/(mg∙kg-1) | 矿化常数(10-3/d) | (CP/k)×103 | r2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C0 | 2270.07±116.48 | 3.32±0.27 | 683.76 | 0.99 |
| C1 | 2290.19±112.07 | 3.35±0.26 | 683.64 | 0.99 |
| C2 | 2467.60±151.87 | 2.45±0.21 | 1007.18 | 0.99 |
| C3 | 2666.15±238.28 | 1.88±0.22 | 1418.16 | 0.99 |
表4 土壤有机碳矿化的一级动力学参数(±SE)
Table 4 Parameters of the first-order kinetics for the soil organic carbon mineralization (±SE)
| 覆盖作物模式 Cover crop models | 潜在矿化势CP/(mg∙kg-1) | 矿化常数(10-3/d) | (CP/k)×103 | r2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C0 | 2270.07±116.48 | 3.32±0.27 | 683.76 | 0.99 |
| C1 | 2290.19±112.07 | 3.35±0.26 | 683.64 | 0.99 |
| C2 | 2467.60±151.87 | 2.45±0.21 | 1007.18 | 0.99 |
| C3 | 2666.15±238.28 | 1.88±0.22 | 1418.16 | 0.99 |
| 覆盖作物模式 Cover crop models | CL/ (mg∙kg-1) | CR/ (mg∙kg-1) | kR (10-3/d) | r2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C0 | -15.956±18.961 | 2229.288±115.244 | 3.500±0.343 | 0.992 |
| C1 | -21.347±18.361 | 2239.969±106.265 | 3.590±0.328 | 0.993 |
| C2 | -11.054±14.302 | 2407.283±156.955 | 2.580±0.274 | 0.994 |
| C3 | -15.102±13.526 | 2525.511±229.135 | 2.070±0.279 | 0.994 |
表5 土壤有机碳矿化的指数加常数模型的拟合参数(±SE)
Table 5 Fitting parameters of exponential plus a constant model of soil organic carbon mineralization (±SE)
| 覆盖作物模式 Cover crop models | CL/ (mg∙kg-1) | CR/ (mg∙kg-1) | kR (10-3/d) | r2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C0 | -15.956±18.961 | 2229.288±115.244 | 3.500±0.343 | 0.992 |
| C1 | -21.347±18.361 | 2239.969±106.265 | 3.590±0.328 | 0.993 |
| C2 | -11.054±14.302 | 2407.283±156.955 | 2.580±0.274 | 0.994 |
| C3 | -15.102±13.526 | 2525.511±229.135 | 2.070±0.279 | 0.994 |
| 项目 Items | CP | k | CP/k | CL | kR | CR | 土壤含水率 Soil moisture | 微生物量碳 MBC | 微生物量氮 MBN | 铵态氮 NH4+-N |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k | -0.990** | |||||||||
| CP/k | 0.998** | -0.985* | ||||||||
| CL | 0.487 | -0.600 | 0.478 | |||||||
| kR | -0.982* | 0.998** | -0.976* | -0.643 | ||||||
| CR | 0.994** | -0.999** | 0.987* | 0.566 | -0.995** | |||||
| 土壤含水率 Soil moisture | -0.954* | 0.964* | -0.933 | -0.534 | 0.960* | -0.972* | ||||
| 微生物量碳 MBC | 0.063 | -0.148 | 0.001 | 0.422 | -0.173 | 0.155 | -0.353 | |||
| 微生物量氮 MBN | -0.562 | 0.535 | -0.614 | -0.282 | 0.529 | -0.513 | 0.298 | 0.698 | ||
| 铵态氮 NH4+-N | 0.639 | -0.723 | 0.598 | 0.800 | -0.748 | 0.717 | -0.806 | 0.762 | 0.073 | |
| 硝态氮 NO3--N | 0.395 | -0.517 | 0.368 | 0.958* | -0.561 | 0.490 | -0.525 | 0.664 | -0.001 | 0.889 |
表6 土壤有机碳矿化特征与土壤理化性质的相关性
Table 6 Correlation between soil organic carbon mineralization characteristics and soil physical and chemical properties
| 项目 Items | CP | k | CP/k | CL | kR | CR | 土壤含水率 Soil moisture | 微生物量碳 MBC | 微生物量氮 MBN | 铵态氮 NH4+-N |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k | -0.990** | |||||||||
| CP/k | 0.998** | -0.985* | ||||||||
| CL | 0.487 | -0.600 | 0.478 | |||||||
| kR | -0.982* | 0.998** | -0.976* | -0.643 | ||||||
| CR | 0.994** | -0.999** | 0.987* | 0.566 | -0.995** | |||||
| 土壤含水率 Soil moisture | -0.954* | 0.964* | -0.933 | -0.534 | 0.960* | -0.972* | ||||
| 微生物量碳 MBC | 0.063 | -0.148 | 0.001 | 0.422 | -0.173 | 0.155 | -0.353 | |||
| 微生物量氮 MBN | -0.562 | 0.535 | -0.614 | -0.282 | 0.529 | -0.513 | 0.298 | 0.698 | ||
| 铵态氮 NH4+-N | 0.639 | -0.723 | 0.598 | 0.800 | -0.748 | 0.717 | -0.806 | 0.762 | 0.073 | |
| 硝态氮 NO3--N | 0.395 | -0.517 | 0.368 | 0.958* | -0.561 | 0.490 | -0.525 | 0.664 | -0.001 | 0.889 |
| 试验地点 Test Location | 土壤类型 Soil type | 土层深度 Soil depth/ cm | 覆盖作物 Cover crops | 试验持续 时间(年) Test duration (year) | 土壤有机质 增加 Soil organic matter increase | 参考文献 References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 美国伊利诺伊州 Illinois, USA | 粉质粘壤土 Drummer silty clay loam | 0-50 | 白萝卜 (Raphanus sativus L. var. longipinnatus); 白萝卜+荞麦 (Fagopyrum esculentum L. Moench); 白萝卜+长柔毛野豌豆 (Vicia villosa Roth); 白萝卜+黑麦 (Secale cereale L.); 白萝卜+黑小麦 (Triticosecale) | 2 | NS | Acuña et al., |
| 巴西 Santo Antônio de Goiás Santo Antônio de Goiás. Brazil | 高岭土 Kaolinitic, thermic Typic Haplorthox | 0-20 | 大黍 (Panicum maximum); 刚果草(Brachiaria ruziziensis); 面包草 (Brachiaria brizantha); 御谷 (Pennisetum glaucum) | 3 | NS | Nascente et al., |
| 美国佛罗里达州 Florida, USA | 壤土 Loam soil (loamy-skeletal, carbonatic, hyperthermic Lithic Udorthents) | 0-10 | 菽麻 (Crotalaria juncea L.); 狗爪豆 (Mucuna pruriens var. utilis); 豇豆 (Vigna unguiculata L.); 高粱苏丹草 (Sorghum bicolor×S. bicolor var. sudanense (Piper) Stapf.) | 2 | NS | Wang et al., |
| 美国东兰辛 East Lansing, USA | 壤土 Loams | 0-25 | 黑麦 (Secale cereale L.) | 3 | NS | Fronning et al., |
| 美国田纳西州 Tennessee, USA | 砂壤土 Cumberland silt loam | 0-18 | 冬小麦 (Triticum aestivum) | 2 | 26% | Haruna, |
| 美国俄亥俄州 Ohio, USA | 砂壤土 Predominately (73%) Crosby silt loam | 0-15 | 燕麦 (Avena sativa L.)+ 冬黑麦 (Secale cereale L.); 多花黑麦草 (Lolium multiflorum L.) | 2 | 23% (POC) | Faé et al., |
| 加拿大不列颠哥伦比亚省 British Columbia, Canada | 粉质粘壤土 Westham silt clay loam | 0-20 | 春大麦 (Hordeum vulgare L.); 秋黑麦(Secale cereale L.); 多花黑麦草 (Lolium multiflorum Lam.) | 1 | 2.4 g∙kg-1 (P<0.05) | Liu et al., |
| 美国赫斯顿 Hesston, USA | 粉质壤土 Geary silt loam | 0-7.5 | 菽麻 (Crotalaria juncea L.) | 15 | 30% | Blanco-Canqu et al., |
| 大豆 (Glycine max (L.) Merr.) | 20% | |||||
| 挪威 Norway | 粘壤土 Clay loam soil | 0-20 | 意大利黑麦草 (Lolium multiflorum Lam. Var. Italicum); 白三叶(Trifolium repens L.) | 13 | NS | Yang et al., |
表7 覆盖作物对土壤有机碳影响的效果
Table 7 Effects of cover crops on soil organic carbon
| 试验地点 Test Location | 土壤类型 Soil type | 土层深度 Soil depth/ cm | 覆盖作物 Cover crops | 试验持续 时间(年) Test duration (year) | 土壤有机质 增加 Soil organic matter increase | 参考文献 References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 美国伊利诺伊州 Illinois, USA | 粉质粘壤土 Drummer silty clay loam | 0-50 | 白萝卜 (Raphanus sativus L. var. longipinnatus); 白萝卜+荞麦 (Fagopyrum esculentum L. Moench); 白萝卜+长柔毛野豌豆 (Vicia villosa Roth); 白萝卜+黑麦 (Secale cereale L.); 白萝卜+黑小麦 (Triticosecale) | 2 | NS | Acuña et al., |
| 巴西 Santo Antônio de Goiás Santo Antônio de Goiás. Brazil | 高岭土 Kaolinitic, thermic Typic Haplorthox | 0-20 | 大黍 (Panicum maximum); 刚果草(Brachiaria ruziziensis); 面包草 (Brachiaria brizantha); 御谷 (Pennisetum glaucum) | 3 | NS | Nascente et al., |
| 美国佛罗里达州 Florida, USA | 壤土 Loam soil (loamy-skeletal, carbonatic, hyperthermic Lithic Udorthents) | 0-10 | 菽麻 (Crotalaria juncea L.); 狗爪豆 (Mucuna pruriens var. utilis); 豇豆 (Vigna unguiculata L.); 高粱苏丹草 (Sorghum bicolor×S. bicolor var. sudanense (Piper) Stapf.) | 2 | NS | Wang et al., |
| 美国东兰辛 East Lansing, USA | 壤土 Loams | 0-25 | 黑麦 (Secale cereale L.) | 3 | NS | Fronning et al., |
| 美国田纳西州 Tennessee, USA | 砂壤土 Cumberland silt loam | 0-18 | 冬小麦 (Triticum aestivum) | 2 | 26% | Haruna, |
| 美国俄亥俄州 Ohio, USA | 砂壤土 Predominately (73%) Crosby silt loam | 0-15 | 燕麦 (Avena sativa L.)+ 冬黑麦 (Secale cereale L.); 多花黑麦草 (Lolium multiflorum L.) | 2 | 23% (POC) | Faé et al., |
| 加拿大不列颠哥伦比亚省 British Columbia, Canada | 粉质粘壤土 Westham silt clay loam | 0-20 | 春大麦 (Hordeum vulgare L.); 秋黑麦(Secale cereale L.); 多花黑麦草 (Lolium multiflorum Lam.) | 1 | 2.4 g∙kg-1 (P<0.05) | Liu et al., |
| 美国赫斯顿 Hesston, USA | 粉质壤土 Geary silt loam | 0-7.5 | 菽麻 (Crotalaria juncea L.) | 15 | 30% | Blanco-Canqu et al., |
| 大豆 (Glycine max (L.) Merr.) | 20% | |||||
| 挪威 Norway | 粘壤土 Clay loam soil | 0-20 | 意大利黑麦草 (Lolium multiflorum Lam. Var. Italicum); 白三叶(Trifolium repens L.) | 13 | NS | Yang et al., |
| [1] | ACUÑA J C M, VILLAMIL M B, 2014. Short-Term Effects of Cover Crops and Compaction on Soil Properties and Soybean Production in Illinois[J]. Agronomy Journal, 106(3): 860-870. |
| [2] | ALVAREZ R, ALVAREZ C R, 2020. Soil Organic Matter Pools and Their Associations with Carbon Mineralization Kinetics[J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 64(1): 184-189. |
| [3] | BLANCO-CANQUI H, MIKHA M M, PRESLEY D R et al., 2011. Addition of cover crops enhances no-till potential for improving soil physical properties[J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 75(4): 1471-1482. |
| [4] | BLANCO-CANQUI H, CLAASSEN M M, PRESLEY D R, 2012. Summer cover crops fix nitrogen, increase crop yield and improve soil-crop relationships[J]. Agronomy journal, 104(1): 137-147. |
| [5] | BOLINDER M A, CROTTY F, ELSEN A, et al., 2020. The effect of crop residues, cover crops, manures and nitrogen fertilization on soil organic carbon changes in agroecosystems: A synthesis of reviews[J]. Mitigation and Adaptation Strategies for Global Change, 25(6): 929-952. |
| [6] | BRUNNER W, FOCHT D D, 1984. Deterministic Three-Half-Order Kinetic Model for Microbial Degradation of Added Carbon Substrates in Soil[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 47(1): 167-172. |
| [7] | DE NOTARIS C, OLESEN J E, SØRENSEN P, et al., 2020. Input and mineralization of carbon and nitrogen in soil from legume-based cover crops[J]. Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems, 116(1):1-18. |
| [8] | ELLERT B H, BETTANY J R, 1988. Comparison of kinetic models for describing net sulfur and nitrogen mineralization[J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 52(6): 1692-1702. |
| [9] | FAÉ G S, SULC R M, BARKER D J, et al., 2009. Integrating winter annual forages into a no-till corn silage system[J]. Agronomy Journal, 101(5): 1286-1296. |
| [10] |
FAN F, VAN DER WERF W, MAKOWSKI D, et al., 2021. Cover crops promote primary crop yield in China: A meta-regression of factors affecting yield gain[J]. Field Crops Research, DOI: 10.1016/j.fcr.2021.108237.
DOI URL |
| [11] | FONTAINE S, MARIOTTI A, ABBADIE L, 2003. The priming effect of organic matter: a question of microbial competition?[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 35(6): 837-843. |
| [12] | FRONNING B E, THELEN K D, MIN D, 2008. Use of Manure, Compost, and Cover Crops to Supplant Crop Residue Carbon in Corn Stover Removed Cropping Systems[J]. Agronomy Journal, 100(6): 1703-1710. |
| [13] | GARCÍA-PALACIOS P, GATTINGER A, BRACHT-JØRGENSEN H, et al., 2017. Ecological intensification increases soil C stocks via changes in crop residue traits[C]// Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Proceedings of the Global Symposium on Soil Organic Carbon 2017. Rome, Italy: Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: 311-313. |
| [14] | HARUNA S I, 2019. Influence of winter wheat on soil thermal properties of a Paleudalf[J]. International Agrophysics, 33(3): 389-395. |
| [15] | HOUBA V J G, NOVOZAMSKY I, HUYBREGTS A W M, et al., 1986 Comparison of soil extractions by 0.01 M CaCl2, by EUF and by some conventional extraction procedures[J]. Plant and Soil, 96(3): 433-437. |
| [16] | HUBBARD R K, STRICKLAND T C, PHATAK S, et al., 2013. Effects of cover crop systems on soil physical properties and carbon/nitrogen relationships in the coastal plain of southeastern USA[J]. Soil and Tillage Research, 126: 276-283. |
| [17] | ISLAM N, WALLENDER W W, MITCHELL J, et al., 2006. A comprehensive experimental study with mathematical modeling to investigate the affects of cropping practices on water balance variables[J]. Agricultural Water Management, 82(1-2): 129-147. |
| [18] | ISMAIL I, BLEVINS R L, FRYE W W, 1994. Long-term no-tillage effects on soil properties and continuous corn yields[J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 58(1): 193-198. |
| [19] | JONES C A, 1984. Estimation of an active fraction of soil nitrogen[J]. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 15(1): 23-32. |
| [20] | KASPAR T C, PARKIN T B, JAYNES D B, et al., 2006. Examining changes in soil organic carbon with oat and rye cover crops using terrain covariates[J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 70(4): 1168-1177. |
| [21] | KIL B, LEE YOUB S, 1987 Allelopathic effects of Chrysanthemum morifolium on germination and growth of several herbaceous plants[J]. Journal of Chemical Ecology, 13(2): 299-308. |
| [22] | KUO S, SAINJU U M, JELLUM E J, 1997. Winter cover crop effects on soil organic carbon and carbohydrate in soil[J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 61(1): 145-152. |
| [23] | LAL R, 2003. Soil erosion and the global carbon budget[J]. Environment International, 29(4): 437-450. |
| [24] | LAL R, 2004a. Soil carbon sequestration impacts on global climate change and food security[J]. Science, 304(5677): 1623-1627. |
| [25] | LAL R, 2004b. Soil carbon sequestration to mitigate climate change[J]. Geoderma, 123(1): 1-22. |
| [26] | LEIFELD J, ZIMMERMANN M, FUHRER J, 2008. Simulating decomposition of labile soil organic carbon: Effects of pH[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 40(12): 2948-2951. |
| [27] |
LEUTHOLD S J, SALMERÓN M, WENDROTH O et al., 2021. Cover crops decrease maize yield variability in sloping landscapes through increased water during reproductive stages[J]. Field Crops Research, DOI: 10.1016/j.fcr.2021.108111.
DOI URL |
| [28] | LI F C, SØRENSEN P, LI X X, et al., 2020. Carbon and nitrogen mineralization differ between incorporated shoots and roots of legume versus non-legume based cover crops[J]. Plant and Soil, 446(1): 243-257. |
| [29] | LIU A, MA B L, BOMKE A A, 2005. Effects of cover crops on soil aggregate stability, total organic carbon, and polysaccharides[J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 69(6): 2041-2048. |
| [30] | LUGATO E, LAVALLEE J M, HADDIX M L, et al., 2021. Different climate sensitivity of particulate and mineral-associated soil organic matter[J]. Nature Geoscience, 14(5): 295-300. |
| [31] | MARINA W, LUCIE B, CAMILLE A, et al., 2017. Specific interactions leading to transgressive overyielding in cover crop mixtures[J]. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 241: 88-99. |
| [32] |
MCCLELLAND S C, PAUSTIAN K, WILLIAMS S, et al., 2021a. Modeling cover crop biomass production and related emissions to improve farm-scale decision-support tools[J]. Agricultural Systems, DOI: 10.1016/j.agsy.2021.103151.
DOI URL |
| [33] | MCCLELLAND S C, PAUSTIAN K, SCHIPANSKI M E, 2021b. Management of cover crops in temperate climates influences soil organic carbon stocks: A meta-analysis[J]. Ecological Applications, 31(3): e2278. |
| [34] | MEYER N, WELP G, RODIONOV A, et al., 2018. Nitrogen and phosphorus supply controls soil organic carbon mineralization in tropical topsoil and subsoil[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 119: 152-161. |
| [35] | NASCENTE A S, LI Y C, CRUSCIOL C A C, 2013. Cover crops and no-till effects on physical fractions of soil organic matter[J]. Soil and Tillage Research, 130: 52-57. |
| [36] | NOVARA A, MINACAPILLI M, SANTORO A, et al., 2019. Real cover crops contribution to soil organic carbon sequestration in sloping vineyard[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 652: 300-306. |
| [37] | OVALLE C, DEL POZO A, PEOPLES M B, et al., 2010. Estimating the contribution of nitrogen from legume cover crops to the nitrogen nutrition of grapevines using a 15N dilution technique[J]. Plant and Soil, 334(1): 247-259. |
| [38] | QI Z M, HELMERS M J, KALEITA A L, 2011. Soil water dynamics under various agricultural land covers on a subsurface drained field in north-central Iowa, USA[J]. Agricultural Water Management, 98(4): 665-674. |
| [39] | QUEMADA M, BARANSKI M, NOBEL-DE LANGE M, et al., 2013. Meta-analysis of strategies to control nitrate leaching in irrigated agricultural systems and their effects on crop yield[J]. Agriculture, ecosystems & environment, 174: 1-10. |
| [40] | RANELLS N N, WAGGER M G, 1997. Grass-Legume Bicultures as Winter Annual Cover Crops[J]. Agronomy Journal Agronomy Journal, 89(4): 659-665. |
| [41] | REDIN M, GUÉNON R, RECOUS S, et al., 2014. Carbon mineralization in soil of roots from twenty crop species, as affected by their chemical composition and botanical family[J]. Plant and Soil, 378(1): 205-214. |
| [42] | ROSOLEM C A, LI Y, GARCIA R A, 2016. Soil carbon as affected by cover crops under no-till under tropical climate[J]. Soil Use and Management, 32(4): 495-503. |
| [43] | SAINJU U M, SINGH B P, WHITEHEAD W F, 2002. Long-term effects of tillage, cover crops, and nitrogen fertilization on organic carbon and nitrogen concentrations in sandy loam soils in Georgia, USA[J]. Soil and Tillage Research, 63(3-4): 167-179. |
| [44] | SAINJU U M, SINGH B P, WHITEHEAD W F, et al., 2007. Accumulation and Crop Uptake of Soil Mineral Nitrogen as Influenced by Tillage, Cover Crops, and Nitrogen Fertilization[J]. Agronomy Journal, 99(3): 682-691. |
| [45] | SCHIPANSKI M E, BARBERCHECK M, DOUGLAS M R et al., 2014. A framework for evaluating ecosystem services provided by cover crops in agroecosystems[J]. Agricultural Systems, 125: 12-22. |
| [46] | SNAPP S S, SWINTON S M, LABARTA R, et al., 2005. Evaluating cover crops for benefits, costs and performance within cropping system niches[J]. Agronomy journal, 97(1): 322-332. |
| [47] | VÁZQUEZ N, PARDO A, SUSO M L, et al., 2005. A methodology for measuring drainage and nitrate leaching in unevenly irrigated vegetable crops[J]. Plant and Soil, 269(1): 297-308. |
| [48] | WANG Q R, KLASSEN W, LI Y C, et al., 2009. Cover crops and organic mulch to improve tomato yields and soil fertility[J]. Agronomy Journal, 101(2): 345-351. |
| [49] | WEINERT T L, PAN W L, MONEYMAKER M R, et al., 2002. Nitrogen recycling by nonleguminous winter cover crops to reduce leaching in potato rotations[J]. Agronomy Journal, 94(2): 365-372. |
| [50] | WU J, JOERGENSEN R G, POMMERENING B, et al., 1990. Measurement of soil microbial biomass C by fumigation-extraction-an automated procedure[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 22(8): 1167-1169. |
| [51] | YANG Z, SINGH B R, SITAULA B K, 2004. Fractions of organic carbon in soils under different crop rotations, cover crops and fertilization practices[J]. Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems, 70(2): 161-166. |
| [52] | YUNUSA I A M, NEWTON P J, 2003. Plants for amelioration of subsoil constraints and hydrological control: The primer-plant concept[J]. Plant and Soil, 257(2): 261-281. |
| [53] | 冯益民, 刘宵钰, 贺露颖, 等, 2018. 三种园林植物水浸提液对波斯菊化感作用的研究[J]. 科技通报, 34(4): 84-90. |
| FENG Y M, LIU X Y, HE L Y, et al., 2018. Three kinds of plants in water extraction of liquid on the allelopathy of calliopsis[J]. Bulletin of Science and Technology, 34(4): 84-90. | |
| [54] | 郭剑芬, 杨玉盛, 陈光水, 等, 2006. 森林凋落物分解研究进展[J]. 林业科学, 42(4): 93-100. |
| GUO J F, YANG Y S, CHEN G S, et al., 2006. A review on litter decomposition in forest ecosystem[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 42(4): 93-100. | |
| [55] | 郝存抗, 周蕊蕊, 鹿鸣, 等, 2020. 不同盐渍化程度下滨海盐渍土有机碳矿化规律[J]. 农业资源与环境学报, 37(1): 36-42. |
| HAO C K, ZHOU R R, LU M, et al., 2020. Soil organic carbon mineralization of coastal soils with different salinity levels[J]. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment, 37(1): 36-42. | |
| [56] | 李青梅, 张玲玲, 刘红梅, 等, 2020. 覆盖作物多样性对猕猴桃园土壤微生物群落功能的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 39(2): 351-359. |
| LI Q M, ZHANG L L, LIU H M, et al., 2020. Effects of cover crop diversity on soil microbial community functions in a kiwifruit orchard[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 39(2): 351-359. | |
| [57] | 李世玉, 2010. 中国茶园生态系统碳平衡研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学: Ⅲ-Ⅳ. |
| LI S Y, 2010. Carbon balance of tea plantation ecosystem in China[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University: Ⅲ-Ⅳ. | |
| [58] | 刘德燕, 宋长春, 王丽, 等, 2008. 外源氮输入对湿地土壤有机碳矿化及可溶性有机碳的影响[J]. 环境科学, 29(12): 3525-3530. |
| LIU D Y, SONG C C, WANG L, et al., 2008. Exogenous Nitrogen Enrichment Impact on the Carbon Mineralization and DOC of the Freshwater Marsh Soil[J]. Environmental Science, 29(12): 3525-3530. | |
| [59] | 刘晓冰, 宋春雨, HERBERT S J, 等, 2002. 覆盖作物的生态效应[J]. 应用生态学报, 13(3): 365-368. |
| LIU X B, SONG C Y, HERBERT S J, et al., 2002. Ecological effects of cover crops[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 13(3): 365-368. | |
| [60] | 刘义平, 2011. 新垦幼龄茶园套种经济绿肥的生态效应研究与应用[J]. 江西农业学报, 23(8): 17-18. |
| LIU Y P, 2011. Applied research on ecological effect of interplanting economic green manure in newly-reclaimed young tea plantation[J]. Acta Agriculturae Universitatis Jiangxiensis, 23(8): 17-18. | |
| [61] | 王明亮, 2020. 覆盖不同作物对茶园土壤理化性状及微生物与节肢动物多样性的影响[D]. 天津农学院: 天津农学院: Ⅰ-Ⅱ. |
| WANG M L, 2020b. Effects of mulching different crops on the physical and chemical properties of soil and diversity of microorganisms and arthropods in tea plantations[D]. Tianjin Agricultural University: Tianjin Agricultural University: Ⅰ-Ⅱ. | |
| [62] | 王明亮, 刘惠芬, 王丽丽, 等, 2020a. 不同覆盖作物模式对茶园土壤剖面物理性质的影响[J]. 天津师范大学学报 (自然科学版), 40(2): 56-62. |
| WANG M L, LIU H F, WANG L L, et al., 2020a. Effects of different cover crop patterns on physical properties of the soil profiles in tea garden[J]. Journal of Tianjin Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 40(2): 56-62. | |
| [63] | 王明亮, 刘惠芬, 王丽丽, 等, 2020b. 不同覆盖作物模式对茶园土壤微生物群落功能多样性的影响[J]. 农业资源与环境学报, 37(3): 332-339. |
| WANG M L, LIU H F, WANG L L, et al., 2020b. Effects of different cropping patterns on soil microbial community functional diversity in tea gardens[J]. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment, 37(3): 332-339. | |
| [64] | 汪洋, 杨殿林, 王丽丽, 等, 2020. 茶园多植物覆盖种植对土壤酶活性和有机碳矿化特征的影响[J]. 农业资源与环境学报, 37(3): 371-380. |
| WANG Y, YANG D L, WANG L L, et al., 2020. Effects of cover crops on soil enzyme activity and organic carbon mineralization in a plantation[J]. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment, 37(3): 371-380. | |
| [65] | 徐阳春, 沈其荣, 冉炜, 2002. 长期免耕与施用有机肥对土壤微生物生物量碳、氮、磷的影响[J]. 土壤学报, 39(1): 83-90. |
| XU Y C, SHEN Q R, RAN W, 2002. Effects of zero-tillage and application of manure on soil microbial biomass C, N, and P after sixteen years of cropping[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 39(1): 83-90. | |
| [66] | 杨阳, 刘秉儒, 2015. 荒漠草原不同植物根际与非根际土壤养分及微生物量分布特征[J]. 生态学报, 35(22): 7562-7570. |
| YANG Y, LIU B R, 2015. Distribution of soil nutrient and microbial biomass in rhizosphere versus nonrhizosphere area of different plant species in desertified steppe[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 35(22): 7562-7570. | |
| [67] | 叶菁, 王义祥, 王峰, 等, 2016. 豆科绿肥对茶园土壤有机碳矿化的模拟研究[J]. 茶叶学报, 57(3): 133-137. |
| YE Q, WANG Y X, WANG F, et al., 2016. Simulation study on organic carbon mineralization in soil of tea plantations with application of green legume fertilizer[J]. Acta Tea Sinica, 57(3): 133-137. | |
| [68] |
周丽霞, 丁明懋, 2007. 土壤微生物学特性对土壤健康的指示作用[J]. 生物多样性, 15(2): 162-171.
DOI |
| ZHOU L X, DING M M, 2007. Soil microbial characteristics as bioindicators of soil health[J]. Biodiversity Science, 15(2): 162-171. |
| [1] | 钱莲文, 余甜甜, 梁旭军, 王义祥, 陈永山. 茶园土壤酸化改良中生物炭应用5 a后的稳定性研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(7): 1442-1447. |
| [2] | 颜明娟, 陈贤玉, 曹榕彬, 林诚, 吴一群, 黄丁一, 吴海玲, 陈子聪. 福建典型白茶产区茶园土壤锰锌形态特征及其影响因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(5): 885-895. |
| [3] | 邢树文, 许佳敏, 黄彬, 高锦婷, 韩丽. 钨尾矿重金属污染对茶园土壤动物群落结构及多样性的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(9): 1903-1915. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
