生态环境学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (4): 679-687.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2022.04.005
陈瑶1,2( ), 李云红1,3, 邵英男1,3, 刘玉龙1,2, 刘延坤1,3,*(
), 李云红1,3, 邵英男1,3, 刘玉龙1,2, 刘延坤1,3,*( )
)
收稿日期:2022-02-11
出版日期:2022-04-18
发布日期:2022-06-22
通讯作者:
*刘延坤(1979年生),女,副研究员,博士,研究方向为森林生态。E-mail: liuyankun1979@126.com作者简介:陈瑶(1983年生),女,助理研究员,硕士,研究方向为森林生态。E-mail: chenyao198305@126.com
基金资助:
CHEN Yao1,2( ), LI Yunhong1,3, SHAO Yingnan1,3, LIU Yulong1,2, LIU Yankun1,3,*(
), LI Yunhong1,3, SHAO Yingnan1,3, LIU Yulong1,2, LIU Yankun1,3,*( )
)
Received:2022-02-11
Online:2022-04-18
Published:2022-06-22
摘要:
以湿生、中生、旱生的云杉Picea spp.-冷杉Abies spp.-红松Pinus koraiensis林(PLP)、椴树Tilia spp.-红松林(TPi)和蒙古栎Quercus mongolica-红松林(QP)为研究对象,分析3种林型之间植被物种多样性与土壤理化特征的差异,采用冗余分析的方法,探讨土壤理化特征对物种多样性的影响机制,以期为阔叶红松林的生物多样性保护和森林的可持续经营提供理论基础。结果表明,(1)研究区云杉-冷杉-红松林有40种,隶属于31科36属,椴树-红松林有49种,隶属于37科46属,蒙古栎-红松林有37种,隶属于21科25属,其中,椴树-红松林的物种结构组成丰富,蒙古栎-红松林物种组成结构最贫乏。(2)3种林型乔木层的丰富度指数、Shannon-Wiener 指数、Simpson优势度指数和Pielou均匀度指数之间差异显著,均以椴树-红松林的最高,显著高于其他两个林型。灌木层的丰富度指数、Shannon-Wiener指、Simpson优势度指数和Pielou均匀度指数之间差异不显著;草本层丰富度指数、Shannon-Wiener指数、Simpson优势度指数和Pielou均匀度指数之间差异显著,均呈现椴树-红松林最高,蒙古栎-红松林最低的分布。(3)3种林型土壤容重、含水量、全磷和全氮之间差异显著,土壤pH差异不显著。(4)冗余分析表明,土壤容重、全磷和含水量是显著影响乔木层、灌木层和草本层物种多样性的主要环境因子。小兴安岭阔叶红松林物种多样性与土壤理化特征具有相关性,调节土壤含水量、改善土壤通气性、补充土壤营养成分可促进林下植被生长发育,从而提高物种多样性。在生产经营中可以补充磷肥和抚育间伐等管理,保持良好的土壤性能,为更多物种的生存和发育提供良好的条件。
中图分类号:
陈瑶, 李云红, 邵英男, 刘玉龙, 刘延坤. 阔叶红松林物种多样性与土壤理化特征研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 679-687.
CHEN Yao, LI Yunhong, SHAO Yingnan, LIU Yulong, LIU Yankun. Study on Species Diversity and Soil Physical and Chemical Characteristics of Broad-leaved Pinus koraiensis Forest[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(4): 679-687.
| 林型 Forest type | 海拔 Altitude/m | 坡度 Slope/(°) | 坡位 Slope Position | 坡向 Aspect | 地形 Topography | 林分密度 Stand density/(plant∙hm-2) | 平均胸径DBH/cm | 生境 Habitat preference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PLP | 348±27 | 13±2 | 中坡 | 西南 | 山地 | 660 | 32.86±6.09 | 湿生 |
| TPi | 384±36 | 12±3 | 中坡 | 南 | 山地 | 500 | 33.71±1.74 | 中生 |
| QP | 478±2 | 20±2 | 上坡 | 南 | 山地 | 560 | 30.05±3.28 | 旱生 |
表1 样地概况
Table 1 General situation of the sample plot
| 林型 Forest type | 海拔 Altitude/m | 坡度 Slope/(°) | 坡位 Slope Position | 坡向 Aspect | 地形 Topography | 林分密度 Stand density/(plant∙hm-2) | 平均胸径DBH/cm | 生境 Habitat preference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PLP | 348±27 | 13±2 | 中坡 | 西南 | 山地 | 660 | 32.86±6.09 | 湿生 |
| TPi | 384±36 | 12±3 | 中坡 | 南 | 山地 | 500 | 33.71±1.74 | 中生 |
| QP | 478±2 | 20±2 | 上坡 | 南 | 山地 | 560 | 30.05±3.28 | 旱生 |
| 层次 Layer | 林型 Forest type | 科 Family | 属 Genus | 种 Species | 主要物种及其重要值 Main species and their important values | 和值 Sum values |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 乔木层 Arbors layer | PLP | 4 | 5 | 6 | 红松 (0.4005)+冷杉 (0.2171)+云杉 (0.0890)+椴树 (0.0683) Pinus koraiensis Sieb. et Zucc.+Abies nephrolepis (Trautv.) Maxim.+Picea spp.+Tilia spp. | 0.7704 |
| TPi | 7 | 8 | 11 | 红松 (0.6426)+椴树 (0.2068)+冷杉 (0.0623)+云杉 (0.0525) Pinus koraiensis Sieb. et Zucc.+Tilia spp.+Abies nephrolepis (Trautv.) Maxim.+Picea spp. | 0.9642 | |
| QP | 5 | 6 | 8 | 红松 (0.5708)+蒙古栎 (0.2900)+白桦 (0.0624)+枫桦 (0.0509) Pinus koraiensis Sieb. et Zucc.+Quercus mongolica Fisch. ex Ledeb.+Betula platyphylla Suk.+Betula costata Trautv | 0.9741 | |
| 灌木层 Shurb layer | PLP | 9 | 10 | 12 | 毛榛 (0.1429)+珍珠梅 (0.1029)+刺五加 (0.0952)+山刺玫 (0.0752) Corylus mandshurica Maxim.+Sorbaria sorbifolia (L.) A. Br+Acanthopanax senticosus (Rupr. Maxim.) Harms+Rosa davurica Pall. | 0.4162 |
| TPi | 8 | 9 | 9 | 瘤枝卫矛 (0.1538)+珍珠梅 (0.1338)+山梅花 (0.0769)+刺五加 (0.0679) Euonymus verrucosus Scop.+Sorbaria sorbifolia (L.) A. Br+Philadelphus incanus Koehne+Acanthopanax senticosus (Rupr. Maxim.) Harms | 0.4324 | |
| QP | 8 | 9 | 10 | 瘤枝卫矛 (0.2105)+胡枝子 (0.2005)+兴安杜鹃 (0.1579)+溲疏 (0.1053) Euonymus verrucosus Scop.+Lespedeza bicolor Turcz.+Rhododendron dauricum L.+Deutzia scabra Thunb. | 0.6742 | |
| 草本层 Herb layer | PLP | 18 | 21 | 22 | 金腰子 (0.1439)+新蹄盖蕨 (0.1364)+羊胡子苔草 (0.1136)+大穗苔草 (0.0716) Chrysosplenium serreanum H and.- Mazz.+Neoathyrium crenulatoserrulatum (Makino) Ching et Z. R. Wang+Eriophorum russeolum+Carex rhynchophysa C. A. Mey. | 0.4655 |
| TPi | 22 | 29 | 29 | 羊胡子苔草 (0.1377)+新蹄盖蕨 (0.1005)+宽叶山蒿 (0.0713)+金腰子 (0.0611) Carex callitrichos V. Krccz.in kom. FI+Neoathyrium crenulatoserrulatum (Makino) Ching et Z. R. Wang+Artemisia stolonifera (Maxim.) Komar.+Chrysosplenium serreanum H and.-Mazz. | 0.3706 | |
| QP | 8 | 10 | 19 | 羊胡子苔草 (0.4393)+舞鹤草 (0.0998)+东方草莓 (0.0967)+宽叶山蒿 (0.0764) Carex callitrichos V. Krccz.in kom. FI+Maianthemum bifolium (Linn.) F. W. Schmid+Fragaria orientalis Losinsk+Artemisia stolonifera (Maxim.) Komar | 0.7122 |
表2 不同林型主要植物组成及重要值
Table 2 Species composition and important values of main species of different forest type
| 层次 Layer | 林型 Forest type | 科 Family | 属 Genus | 种 Species | 主要物种及其重要值 Main species and their important values | 和值 Sum values |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 乔木层 Arbors layer | PLP | 4 | 5 | 6 | 红松 (0.4005)+冷杉 (0.2171)+云杉 (0.0890)+椴树 (0.0683) Pinus koraiensis Sieb. et Zucc.+Abies nephrolepis (Trautv.) Maxim.+Picea spp.+Tilia spp. | 0.7704 |
| TPi | 7 | 8 | 11 | 红松 (0.6426)+椴树 (0.2068)+冷杉 (0.0623)+云杉 (0.0525) Pinus koraiensis Sieb. et Zucc.+Tilia spp.+Abies nephrolepis (Trautv.) Maxim.+Picea spp. | 0.9642 | |
| QP | 5 | 6 | 8 | 红松 (0.5708)+蒙古栎 (0.2900)+白桦 (0.0624)+枫桦 (0.0509) Pinus koraiensis Sieb. et Zucc.+Quercus mongolica Fisch. ex Ledeb.+Betula platyphylla Suk.+Betula costata Trautv | 0.9741 | |
| 灌木层 Shurb layer | PLP | 9 | 10 | 12 | 毛榛 (0.1429)+珍珠梅 (0.1029)+刺五加 (0.0952)+山刺玫 (0.0752) Corylus mandshurica Maxim.+Sorbaria sorbifolia (L.) A. Br+Acanthopanax senticosus (Rupr. Maxim.) Harms+Rosa davurica Pall. | 0.4162 |
| TPi | 8 | 9 | 9 | 瘤枝卫矛 (0.1538)+珍珠梅 (0.1338)+山梅花 (0.0769)+刺五加 (0.0679) Euonymus verrucosus Scop.+Sorbaria sorbifolia (L.) A. Br+Philadelphus incanus Koehne+Acanthopanax senticosus (Rupr. Maxim.) Harms | 0.4324 | |
| QP | 8 | 9 | 10 | 瘤枝卫矛 (0.2105)+胡枝子 (0.2005)+兴安杜鹃 (0.1579)+溲疏 (0.1053) Euonymus verrucosus Scop.+Lespedeza bicolor Turcz.+Rhododendron dauricum L.+Deutzia scabra Thunb. | 0.6742 | |
| 草本层 Herb layer | PLP | 18 | 21 | 22 | 金腰子 (0.1439)+新蹄盖蕨 (0.1364)+羊胡子苔草 (0.1136)+大穗苔草 (0.0716) Chrysosplenium serreanum H and.- Mazz.+Neoathyrium crenulatoserrulatum (Makino) Ching et Z. R. Wang+Eriophorum russeolum+Carex rhynchophysa C. A. Mey. | 0.4655 |
| TPi | 22 | 29 | 29 | 羊胡子苔草 (0.1377)+新蹄盖蕨 (0.1005)+宽叶山蒿 (0.0713)+金腰子 (0.0611) Carex callitrichos V. Krccz.in kom. FI+Neoathyrium crenulatoserrulatum (Makino) Ching et Z. R. Wang+Artemisia stolonifera (Maxim.) Komar.+Chrysosplenium serreanum H and.-Mazz. | 0.3706 | |
| QP | 8 | 10 | 19 | 羊胡子苔草 (0.4393)+舞鹤草 (0.0998)+东方草莓 (0.0967)+宽叶山蒿 (0.0764) Carex callitrichos V. Krccz.in kom. FI+Maianthemum bifolium (Linn.) F. W. Schmid+Fragaria orientalis Losinsk+Artemisia stolonifera (Maxim.) Komar | 0.7122 |
| 土壤因子 Soil factors | 土层深度Soil depth/ cm | 林型Forest type | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PLP | TPi | QP | ||
| SBD/ (g∙cm-3) | 0‒10 | 0.85±0.05ABc | 0.62±0.05Bb | 1.10±0.06Aa |
| 10‒20 | 1.08±0.07Ab | 0.95±0.07Bab | 1.09±0.05Ba | |
| 20‒30 | 1.28±0.10Aa | 1.19±0.03Ba | 1.31±0.08Ba | |
| w(SWC)/ % | 0‒10 | 84.86±18.62Aa | 83.23±12.67Aa | 64.13±5.71Ba |
| 10‒20 | 69.37±19.88Aa | 40.50±2.66ABb | 24.54±2.69Ba | |
| 20‒30 | 33.47±5.38Ab | 34.04±2.96Ab | 18.84±2.64Aa | |
| pH | 0‒10 | 5.34±0.19Aa | 6.54±0.19Aa | 5.12±0.06Aa |
| 10‒20 | 5.29±0.09Aa | 6.52±0.22Aa | 5.16±0.05Aa | |
| 20‒30 | 5.74±0.13Aa | 6.62±0.19Aa | 5.47±0.08Aa | |
| w(TN)/ (g∙kg-1) | 0‒10 | 5.29±0.04Aa | 7.36±0.06Aa | 6.12±0.07Ba |
| 10‒20 | 2.91±0.06Ab | 3.52±0.02Ab | 3.36±0.03Bb | |
| 20‒30 | 1.47±0.04Ac | 2.46±0.03Ab | 1.89±0.03Ac | |
| w(TP)/ (g∙kg-1) | 0‒10 | 0.57±0.06Aa | 1.10±0.08Ba | 0.79±0.07Ab |
| 10‒20 | 0.54±0.06Ba | 0.73±4.00Aa | 0.71±0.06Bb | |
| 20‒30 | 0.53±0.06Ba | 0.62±0.08Aa | 0.66±0.03Aa | |
| w(OM)/ (g∙kg-1) | 0‒10 | 176.10±29.23Aa | 197.77±9.15Aa | 184.86±18.61Aa |
| 10‒20 | 84.26±13.95Ab | 102.02±8.90Ab | 83.36±6.09Ab | |
| 20‒30 | 46.89±6.19Ac | 72.22±8.09Ab | 62.6±8.84Ab | |
表3 不同林型土壤理化特征
Table 3 Physical and chemical characteristics of soil in different forest types
| 土壤因子 Soil factors | 土层深度Soil depth/ cm | 林型Forest type | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PLP | TPi | QP | ||
| SBD/ (g∙cm-3) | 0‒10 | 0.85±0.05ABc | 0.62±0.05Bb | 1.10±0.06Aa |
| 10‒20 | 1.08±0.07Ab | 0.95±0.07Bab | 1.09±0.05Ba | |
| 20‒30 | 1.28±0.10Aa | 1.19±0.03Ba | 1.31±0.08Ba | |
| w(SWC)/ % | 0‒10 | 84.86±18.62Aa | 83.23±12.67Aa | 64.13±5.71Ba |
| 10‒20 | 69.37±19.88Aa | 40.50±2.66ABb | 24.54±2.69Ba | |
| 20‒30 | 33.47±5.38Ab | 34.04±2.96Ab | 18.84±2.64Aa | |
| pH | 0‒10 | 5.34±0.19Aa | 6.54±0.19Aa | 5.12±0.06Aa |
| 10‒20 | 5.29±0.09Aa | 6.52±0.22Aa | 5.16±0.05Aa | |
| 20‒30 | 5.74±0.13Aa | 6.62±0.19Aa | 5.47±0.08Aa | |
| w(TN)/ (g∙kg-1) | 0‒10 | 5.29±0.04Aa | 7.36±0.06Aa | 6.12±0.07Ba |
| 10‒20 | 2.91±0.06Ab | 3.52±0.02Ab | 3.36±0.03Bb | |
| 20‒30 | 1.47±0.04Ac | 2.46±0.03Ab | 1.89±0.03Ac | |
| w(TP)/ (g∙kg-1) | 0‒10 | 0.57±0.06Aa | 1.10±0.08Ba | 0.79±0.07Ab |
| 10‒20 | 0.54±0.06Ba | 0.73±4.00Aa | 0.71±0.06Bb | |
| 20‒30 | 0.53±0.06Ba | 0.62±0.08Aa | 0.66±0.03Aa | |
| w(OM)/ (g∙kg-1) | 0‒10 | 176.10±29.23Aa | 197.77±9.15Aa | 184.86±18.61Aa |
| 10‒20 | 84.26±13.95Ab | 102.02±8.90Ab | 83.36±6.09Ab | |
| 20‒30 | 46.89±6.19Ac | 72.22±8.09Ab | 62.6±8.84Ab | |
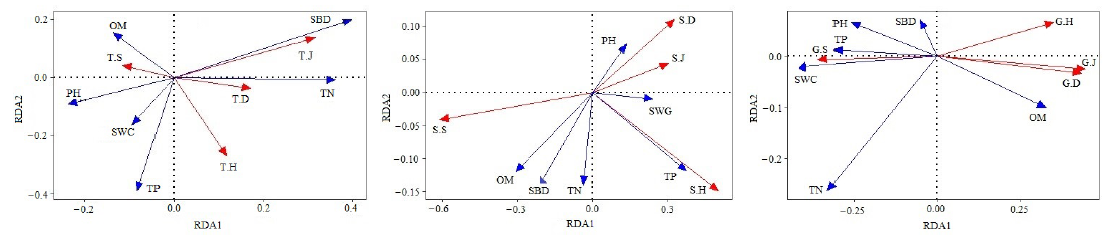
图2 乔木层、灌木层和草本层冗余分析RDA排序图 T.S:乔木层丰富度指数;T.H:乔木层多样性指数;T.D:乔木层优势度指数;T.J:乔木层均匀度指数;S.S:灌木层丰富度指数;S.H:灌木层多样性指数;S.D:灌木层优势度指数;S.J:灌木层均匀度指数;G.S:草本层丰富度指数;G.H:草本层多样性指数;G.D:草本层优势度指数;G.J:草本层均匀度指数;SWC:土壤含水率;SBD:土壤容重;pH:土壤;OM:有机质;TN:全氮;TP:全磷
Figure 2 Redundancy analysis (RDA) biplot of tree layer, shrub layer and herb layer T.S: Species richness index of tree layer; T.H: Shannon-Wiener diversity index of tree layer; T.D: Simpson dominance index of tree layer; T.J: Pielou evenness index of tree layer; S.S: Species richness index of shrub layer; S.H: Shannon-Wiener diversity index of shrublayer; S.D: Simpson dominance index of shrublayer; S.J: Pielou evenness index of shrub layer; G.S: Species richness index of grass layer; G.H: Shannon-Wiener diversity index of grass layer; G.D: Simpson dominance index of grass layer; G.J: Pielou evenness index of grass layer; SWC: Soil water content; SBD: Soil bulk density; pH: pH Soil pH; OM: Organic matter; TN: Total nitrogen; TP: Total phosphorus
| 环境 Environmental | 乔木层 Arbors layer | 灌木层 Shurb layer | 草本层 Herb layer | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RDA1 | RDA2 | F | P | RDA1 | RDA2 | F | P | RDA1 | RDA2 | F | P | |||
| SBD | 0.5335 | 0.2166 | 3.4 | 0.042 | -0.3084 | -0.0680 | 0.8 | 0.335 | -0.1746 | 0.0117 | 0.2 | 0.662 | ||
| SWC | -0.1023 | -0.2363 | 0.5 | 0.654 | 0.4816 | -0.0064 | 2.1 | 0.186 | -0.7414 | 0.0112 | 8.6 | 0.021 | ||
| PH | -0.3233 | -0.1117 | 0.9 | 0.459 | 0.2206 | 0.0247 | 0.4 | 0.561 | -0.4682 | 0.011 | 2.0 | 0.203 | ||
| TN | 0.4904 | 0.0240 | 2.2 | 0.141 | -0.0611 | -0.0545 | <0.1 | 0.875 | -0.6123 | -0.0464 | 4.2 | 0.076 | ||
| TP | -0.1039 | -0.4331 | 1.7 | 0.221 | 0.6107 | -0.0332 | 4.2 | 0.045 | -0.5226 | -0.0025 | 2.6 | 0.138 | ||
| OM | -0.1932 | 0.1294 | 0.4 | 0.675 | -0.4566 | -0.0418 | 1.9 | 0.214 | 0.6057 | -0.0194 | 4.1 | 0.096 | ||
| 特征值 Eigenvalues | 0.4525 | 0.2861 | 0.6241 | 0.0297 | 0.8827 | 0.0077 | ||||||||
| 累计解释变异 Explained variation | 45.25 | 73.86 | 62.41 | 65.39 | 88.27 | 89.04 | ||||||||
表4 冗余分析(RDA)排序及蒙特卡洛置换检验结果
Table 4 Results by Redundancy analysis (RDA) ordination with the first two axes and Monte Carlo permutation test
| 环境 Environmental | 乔木层 Arbors layer | 灌木层 Shurb layer | 草本层 Herb layer | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RDA1 | RDA2 | F | P | RDA1 | RDA2 | F | P | RDA1 | RDA2 | F | P | |||
| SBD | 0.5335 | 0.2166 | 3.4 | 0.042 | -0.3084 | -0.0680 | 0.8 | 0.335 | -0.1746 | 0.0117 | 0.2 | 0.662 | ||
| SWC | -0.1023 | -0.2363 | 0.5 | 0.654 | 0.4816 | -0.0064 | 2.1 | 0.186 | -0.7414 | 0.0112 | 8.6 | 0.021 | ||
| PH | -0.3233 | -0.1117 | 0.9 | 0.459 | 0.2206 | 0.0247 | 0.4 | 0.561 | -0.4682 | 0.011 | 2.0 | 0.203 | ||
| TN | 0.4904 | 0.0240 | 2.2 | 0.141 | -0.0611 | -0.0545 | <0.1 | 0.875 | -0.6123 | -0.0464 | 4.2 | 0.076 | ||
| TP | -0.1039 | -0.4331 | 1.7 | 0.221 | 0.6107 | -0.0332 | 4.2 | 0.045 | -0.5226 | -0.0025 | 2.6 | 0.138 | ||
| OM | -0.1932 | 0.1294 | 0.4 | 0.675 | -0.4566 | -0.0418 | 1.9 | 0.214 | 0.6057 | -0.0194 | 4.1 | 0.096 | ||
| 特征值 Eigenvalues | 0.4525 | 0.2861 | 0.6241 | 0.0297 | 0.8827 | 0.0077 | ||||||||
| 累计解释变异 Explained variation | 45.25 | 73.86 | 62.41 | 65.39 | 88.27 | 89.04 | ||||||||
| [1] | SIM-SIM M, LOPES T, RUAS S, et al., 2015. Does altitude shape molecular diversity and richness of bryophytes in Madeira's natural forest? Acase study with four bryophyte species at two altitudinal levels[J]. Plant Ecology and Evolution, 2148(2): 171-180. |
| [2] | 崔宁洁, 张丹桔, 刘洋, 等, 2014. 不同林龄马尾松人工林林下植物多样性与土壤理化性质[J]. 生态学杂志, 33(10): 2610-2617. |
| CUI N J, ZHANG D J, LIU Y, et al., 2014. Plant diversity and soil physicochemical properties under different aged Pinus massoniana plantations[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 33(10): 2610-2617. | |
| [3] | 董雪, 杜昕, 孙志虎, 等, 2020. 生境梯度影响下的天然红松种群空间格局与种内关联[J]. 生态学报, 40(15): 5239-5246. |
| DONG X, DU X, SUN Z H, et al., 2020. Spatial pattern and intraspecific association of natural Korean pine population under the influence of habitat gradient[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 40(15): 5239-5246. | |
| [4] | 冯健, 王骞春, 陆爱君, 等, 2021. 辽东山区落叶松-水曲柳混交林植物多样性和土壤特性研究[J]. 西北农林科技大学学报 (自然科学版), 49(6): 27-37. |
| FENG J, WANG Q C, LU A J, et al., 2021. Plant Diversity and soil characteristics of larch-manchurianssh mixed stand in eastern Liao ning[J]. Journal of Northwest & Funiversity, 49(6): 27-37. | |
| [5] | 郝凌颖, 2012. 紫金山不同坡位林分结构与生物多样性研究[D]. 南京: 南京林业大学: 1-41. |
| HAO L Y, 2012. Study on stand structure and biodiversity of different slope positions in Purple Mountain[D]. Nanjing: Journal of Nanjing Forestry University: 1-41. | |
| [6] | 侯红亚, 王立海, 2013. 小兴安岭阔叶红松林物种组成及主要种群的空间分布格局[J]. 应用生态学报, 24(11): 3043-3049. |
| HOU H Y, WANG L H, 2013. Species composition and main populations spatial distribution pattern in Korean pine broad- leaved forest in Xiaoxing’an Mountains of Northeast China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 24(11): 3043-3049. | |
| [7] | 黄润霞, 徐明锋, 刘婷, 等, 2020. 亚热带5种森林类型林下植物物种多样性及其环境解释[J]. 西南林业大学学报 (自然科学), 40(2): 53-62. |
| HUANG R X, XU M F, LIU T, et al., 2020. Environmental interpretation and species diversity of understory vegetation in 5 subtropical forest types[J]. Journal of Southwest forestry university, 40(2): 53-62. | |
| [8] | 李梦佳, 何中声, 江蓝, 等, 2021. 戴云山物种多样性与系统发育多样性海拔梯度分布格局及驱动因子[J]. 生态学报, 41(3): 1148-1157. |
| LI M J, HE Z S, JIANG L, et al., 2021. The elevation and factors driving the forest tree diversity and phylogenetic diversity on the south slope of Daiyun Mountain[J]. Acta Ecologica sinica, 41(3): 1148-1157. | |
| [9] | 李婷婷, 姬兰柱, 于大炮, 等, 2019. 东北阔叶红松林群落分类、排序及物种多样性比较[J]. 生态学报, 39(2): 620-628. |
| LI T T, JI L Z, YU D P, et al., 2019. Forest community classification,ordination,and comparison of species diversity in broadleaved-Korean pine mixed forests of Northeast China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 39(2): 620-628. | |
| [10] | 李文华, 2011. 东北天然林研究[M]. 北京: 气象出版社. |
| LI W H, 2011. Study on natural forest in northeast China[M]. Beijing: The meteorological press. | |
| [11] | 李瑛云, 宋森, 张艳波, 等, 2013. 阔叶红松林物种多样性变化对土壤性质的影响[J]. 森林工程, 29(4): 24-29. |
| LI Y Y, SONG S, ZHANG Y B, et al., 2013. Influence of Species Diversity on the Soil Properties of Broadleaved Korean Pine Forest[J]. Forest Engineering, 29(4): 24-29. | |
| [12] | 林丽, 代磊, 林泽北, 等, 2021. 黔中城市森林群落植物多样性及其与土壤理化性质的关系[J]. 生态环境学报, 30(11): 2130-2141. |
| LIN L, DAI L, LIN Z B, et al., 2021. Plant diversity and its relationship with soil physicochemical properties of urban forest communities in central Guizhou[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 30(11): 2130-2141. | |
| [13] | 刘道锟, 孙海龙, 甘秋妹, 等, 2016. 大兴安岭干旱阳坡不同植被退化阶段土壤理化性质与物种多样性研究[J]. 森林工程, 32(2): 1-6. |
| LIU D K, SUN H L, GAN Q M, et al., 2016. Soil physicochemical properties and plant species diversity of different vegetation degradation stages in arid sunny -slope of great Xing’an Mountains[J]. Forest Engineering, 32(2): 1-6. | |
| [14] | 刘少冲, 段文标, 冯静, 等, 2011. 林隙对小兴安岭阔叶红松林树种更新及物种多样性的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 22(6): 1381-1388. |
| LIU S C, DUAN W B, FENG J, et al., 2011. Effect sofforest gapontree species regeneration and diversity of mixed broadleaved Korean pineforestin Xiaoxing’an Mountains[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 22(6): 1381-1388. | |
| [15] | 娄淑兰, 刘目兴, 易军, 等, 2019. 三峡山地不同类型植被和坡位对土壤水文功能的影响[J]. 生态学报, 39(13): 4844-4854. |
| LOU S L, LIU M X, YI J, et al., 2019. Influence of vegetation coverage and topographic position on soil hydrological function in the hillslope of the three gorges area[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 39(13): 4844-4854. | |
| [16] | 骆丹, 王春胜, 刀保辉, 等, 2021. 云南德宏州西南桦天然林物种组成及多样性研究[J]. 林业科学研究, 34(5): 159-167. |
| LUO D, WANG C S, DAO B H, et al., 2021. Species Composition and Diversity of Betula alnoides Natural Forests at Dehong Prefecture, Yunnan Province[J]. Forest Research, 34(5): 159-167. | |
| [17] | 秦娟, 唐心红, 杨雪梅, 2013. 马尾松不同林型对土壤理化性质的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 22(4): 598-604. |
| QIN J, TANG X H, YANG X M, 2013. Effects of soil physical and chemical properties on different forest types of Pinus massoniana[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 22(4): 598-604. | |
| [18] | 舒韦维, 卢立华, 李华, 等, 2021. 林分密度对杉木人工林林下植被和土壤性质的影响[J]. 生态学报, 41(11): 4521-4530. |
| SHU W W, LU L H, LI H, et al., 2021. Effects of stand density on understory vegetation and soil properties of Cunninghamia lanceolata plantation[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 41(11): 4521-4530. | |
| [19] | 王冰, 张鹏杰, 张秋良, 2021. 不同林型兴安落叶松林土壤理化特征[J]. 西北林学院学报, 36(6): 65-71. |
| WANG B, ZHANG P J, ZHANG Q L, 2021. Soil physicochemical characteristics of Larix gmelinii Forest with different forest types[J]. Journal of Northwest Forestry University, 36(6): 65-71. | |
| [20] | 王梅, 2010. 陕北黄土高原油松人工林生物学特性与天然化发育评价[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学. |
| WANG M, 2010. Biological characteristics and evaluation of naturalized development of pinus tabulaeformis plantation in Some Random Place Somewhere of Shanbei[D]. Yangling: Journal of Northwest A & F University. | |
| [21] | 王媚臻, 齐锦秋, 魏丽萍, 等, 2018. 人为干扰对栲树次生林群落物种多样性和土壤理化性质的影响[J]. 热带亚热带植物学报, 26(4): 355-362. |
| WANG M Z, QI J Q, WEI L P, et al., 2018. Effect of Human disturbance on species diversity and soil physio-chemical properties of Castanopsis fargesii secondary forest[J]. Journal of Tropical and Subtropical Botany, 26(4): 355-362. | |
| [22] | 魏晨辉, 沈光, 裴忠雪, 等, 2015. 不同植物种植对松嫩平原盐碱地土壤理化性质与细根生长的影响[J]. 植物研究, 35(5): 759-764. |
| WEI C H, SHEN G, PEI Z X, et al., 2015. Effects of different plants cultivation on soil physical-chemical properties and fine root growth in saline-alkaline soil in Songnen Plain, northeastern China[J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 35(5): 759-764. | |
| [23] |
吴晓莆, 朱彪, 赵淑清, 等, 2004. 东北地区阔叶红松林的群落结构及其物种多样性比较[J]. 生物多样性, 12(1): 174-181.
DOI |
|
WU X P, ZHU B, ZHAO S Q, et al., 2004. Comparison of community structure and species diversity of mixed forests of deciduous broad-leaved tree and Korean pine in Northeast China[J]. Biodiversity Science, 12(1): 174-181.
DOI URL |
|
| [24] | 徐化成, 2001. 中国红松天然林[M]. 北京: 中国林业出版社. |
| XU H C, 2001. Natural Korean pine forest in China[M]. Beijing: China Forestry Publishing House. | |
| [25] | 杨京彪, 郭泺, 周萤, 等, 2015. 坡位对红松阔叶林物种多样性的影响[J]. 东北林业大学学报, 43(1): 28-31. |
| YANG J B, GUO S, ZHOU Y, et al., 2015. Effects of slope position on species diversity of broad-leaved Korea pine forest[J]. Journal of Northeast Forestry University, 43(1): 28-31. | |
| [26] | 杨晓惠, 林文树, 刘曦, 等, 2021. 小兴安岭典型阔叶红松林幼树的群落结构动态[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 41(12): 87-97. |
| YANG X H, LIN W S, LIU X, et al., 2021. The species-abundance distribution pattern of broad-leaved Korean pine forest in the Lesser Khingan mountains[J]. Journal of Central South University of Forestry & Technology, 40(12): 104-113, 133. | |
| [27] | 曾歆花, 张万军, 宋以刚, 等, 2013. 河北太行山低山丘陵区植被恢复过程中物种多样性与土壤养分变化[J]. 生态学杂志, 32(4): 852-858. |
| ZENG X H, ZHANG W J, SONG Y G, et al., 2013. Species diversity and soil nutrient dynamics along a chronosequence of vegetation restoration in Taihang Mountains hilly region, Hebei Province of North China[J]. Chinese Journal Ecology, 32(4): 852-858. | |
| [28] | 张林静, 岳明, 顾峰雪, 等, 2002. 新疆阜康绿洲荒漠过渡带植物群落物种多样性与土壤环境因子的耦合关系[J]. 应用生态学报, (06): 658-662. |
| ZHANG L J, YUE M, GU F X, et al., 2002. Coupling relationship between plant communities' species diversity and soil factors in ecotone between desert and oasis in Fukang, Xinjiang[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, (06): 658-662. | |
| [29] | 张玲, 张东来, 毛子军, 2017. 小兴安岭阔叶红松林不同演替系列土壤有机碳及各组分特征[J]. 林业科学, 53(9): 11-17. |
| ZHANG L, ZHANG D L, MAO Z J, 2017. Charicateristic of soil oranic carbon and its components in different successionalseries of broadleaved Korean pine forest in Xiaoxing’an Mountains[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 53(9): 11-17. | |
| [30] | 张沛健, 徐建民, 卢万鸿, 等, 2021. 雷州半岛不同林龄尾细桉林植物多样性和土壤理化性质分析[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 41(9): 96-105. |
| ZHANG P J, XU J M, LU W H, et al., 2021. Plant diversity and soil physicochemical properties under different aged Eucalyptus urophylla×Eucalyptus tereticornis plantations in Leizhou Peninsula[J]. Journal of Central South University of Forestry & Technology, 41(9): 96-105. | |
| [31] | 张荣, 李婷婷, 金锁, 等, 2020. 人为干扰对蒙顶山木荷次生林物种多样性及土壤理化性质的影响[J]. 浙江农林大学学报, 37(5): 867-875. |
| ZHANG R, LI T T, JIN S, et al., 2020. Effects of human disturbance on species diversity and soil physiochemical properties of Schimasuperba community in Mengding Mountain[J]. Journal of Zhejiang A & F University, 37(5): 867-875. | |
| [32] | 张筱, 陈义堂, 杨秋菊, 等, 2022. 不同地形100年生杉木人工林土壤理化性质及林下植被多样性差异分析[J]. 西南林业大学学报 (自然科学), 42(1): 1-11. |
| ZHANG X, CHEN Y T, YANG Q J, et al., 2022. Differences of soil physicochemical properties and undergrowth vegetation diversity of 100 year old chinese fir plantations in different terrain[J]. Journal of Southwest Forestry University (Natural Sciences), 42(1): 1-11. | |
| [33] | 张勇强, 李智超, 厚凌宇, 等, 2020. 林分密度对杉木人工林下物种多样性和土壤养分的影响[J]. 土壤学报, 57(1): 239-250. |
| ZHANG Y Q, LI Z C, HOU L Y, et al., 2020. Effects of stand density on understory species diversity and soil nutrients in Chinese fir plantation[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 57(1): 239-250. | |
| [34] | 赵一臣, 张鑫, 张君卿, 2019. 原始阔叶红松林土壤微生物特征研究[J]. 林业资源管理, (3): 132-138. |
| ZHAO Y C, ZHANG X, ZHANG J Q, 2019. Study on soil microbial characteristics of primitive broad-leaved Korean pine forest[J]. Forest Resources Management, (3): 132-138. | |
| [35] | 郑鸾, 龙翠玲, 2020. 茂兰喀斯特森林不同地形植物多样性与土壤理化特征研究[J]. 广西植物, 40(6): 792-801. |
| ZHENG L, LONG C L, 2020. Differences of plant diversity and soil physicochemical properties in Maolan karst forest under different topographic conditions[J]. Guihaia, 40(6): 792-801. | |
| [36] | 周润惠, 苏天成, 喻静, 等, 2022. 碧峰峡常绿阔叶林不同群落物种多样性和土壤理化性质[J]. 生态学杂志, 41(1): 1-8. |
| ZHOU R H, SU T C, YU J, et al., 2022. Species diversity and soil physicochemical properties of different communities in Bifengxia evergreen broad-leaved forest[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 41(1): 1-8. | |
| [37] | 周晓果, 2016. 林下植物功能群丧失对桉树人工林土壤生态系统多功能性的影响[D]. 南宁: 广西大学: 1-169. |
| ZHOU X G, 2016. Effects of understory plant functional groups loss on soil ecosystem multifunctionlity in Eucalyptus plantations[D]. Nanning: Guangxi University: 1-169. |
| [1] | 杜丹丹, 高瑞忠, 房丽晶, 谢龙梅. 旱区盐湖盆地土壤重金属空间变异及对土壤理化因子的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(6): 1123-1132. |
| [2] | 李善家, 王兴敏, 刘海锋, 孙梦格, 雷雨昕. 河西走廊荒漠植物多样性及其对环境因子的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 429-438. |
| [3] | 张立进, 杜虎, 曾馥平, 黄国勤, 宋敏, 宋同清. 喀斯特峰丛洼地植被恢复过程中生产力与多样性关系探讨[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 26-35. |
| [4] | 马辉英, 李昕竹, 马鑫钰, 贡璐. 新疆天山北麓中段不同植被类型下土壤有机碳组分特征及其影响因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(6): 1124-1131. |
| [5] | 冯凌, 喻理飞, 王阳, 张丽敏, 赵庆, 李方兵. 喀斯特地区植被不同恢复阶段功能冗余和功能多样性对群落稳定性的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 670-678. |
| [6] | 胡靓达, 周海菊, 黄永珍, 姚贤宇, 叶绍明, 喻素芳. 不同杉木林分类型植物多样性及其土壤碳氮关系的研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(3): 451-459. |
| [7] | 玄锦, 李祖婵, 邹诚, 秦子博, 吴雅华, 黄柳菁. 江心洲景观类型和格局对植物多样性的多尺度影响——以闽江流域福州段为例[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(12): 2320-2330. |
| [8] | 韩鑫, 袁春阳, 李济宏, 洪宗文, 刘宣, 杜婷, 李晗, 游成铭, 谭波, 朱鹏, 徐振锋. 树种和土层对土壤无机氮的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(11): 2143-2151. |
| [9] | 洪文君, 莫罗坚, 张浩. 华南地区马占相思人工林不同改造模式对林分结构的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(7): 1360-1367. |
| [10] | 何斌, 李青, 陈群利, 李望军, 游萍. 黔西北黄杉群落物种多样性的海拔梯度格局[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(6): 1111-1120. |
| [11] | 潘红丽, 李慧超, 余志祥, 蔡蕾, 李旭华, 刘兴良. 攀枝花市入侵植物马缨丹群落的物种组成与多样性研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(6): 1177-1182. |
| [12] | 黄成, 吴月颖, 吉恒宽, 陈丽铭, 李倍莹, 符传良, 李建宏, 吴蔚东, 吴治澎. 海南典型水稻土厌氧铁还原特征对DOM分子特性的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(5): 957-967. |
| [13] | 姜倪皓, 张诗函. 楚雄市西郊云南松林下草本优势种种间联结及环境解释[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(11): 2109-2120. |
| [14] | 张洋洋, 周清慧, 许骄阳, 魏鸣, 陈继豪, 何伟, 王鹏程, 晏召贵. 林龄对马尾松人工林林下植物与土壤种子库多样性的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(11): 2121-2129. |
| [15] | 林丽, 代磊, 林泽北, 吴际通, 颜伟, 王志杰. 黔中城市森林群落植物多样性及其与土壤理化性质的关系[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(11): 2130-2141. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
