生态环境学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (6): 1124-1131.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2022.06.007
马辉英1,2,3( ), 李昕竹1,2,3, 马鑫钰1,2,3, 贡璐1,2,3,*(
), 李昕竹1,2,3, 马鑫钰1,2,3, 贡璐1,2,3,*( )
)
收稿日期:2022-01-22
出版日期:2022-06-18
发布日期:2022-07-29
通讯作者:
*贡璐(1978年生),女,教授,博士,主要从事干旱区生态环境研究。E-mail: gonglu721@163.com作者简介:马辉英(1980年生),女(回族),讲师,主要研究方向为干旱区生态环境。E-mail: dreampie@163.com
基金资助:
MA Huiying1,2,3( ), LI Xinzhu1,2,3, MA Xinyu1,2,3, GONG Lu1,2,3,*(
), LI Xinzhu1,2,3, MA Xinyu1,2,3, GONG Lu1,2,3,*( )
)
Received:2022-01-22
Online:2022-06-18
Published:2022-07-29
摘要:
土壤有机碳受植被类型干扰影响,其含量变化会呈现一定变化,深刻影响森林物质循环过程,从而对植被产生反馈影响。该研究以新疆天山中段云杉林、灌丛地、草地3种植被类型下的土壤为研究对象,分析土壤有机碳组分包括总有机碳、可溶性有机碳轻组分有机碳和微生物量碳的质量分数特征,并研究这3种植被的土壤有机碳及其组分质量分数的差异性。结果表明,(1)不同植被类型下土壤有机碳、可溶性有机碳、轻组分有机碳和微生物生物量碳质量分数均具有一定差异。总体趋势表现为云杉林>灌丛地>草地,w(SOC)在云杉林达到峰值(120.68 g∙kg-1),并且土壤表层有机碳组分质量分数高于下层(P<0.05)。(2)冗余分析表明总有机碳、可溶性有机碳、轻组分有机碳和微生物量碳之间均呈正相关关系且具有相同的变化趋势。土壤环境因子对土壤有机碳组分影响的重要性由大到小依次为土壤电导率、土壤pH值、土壤容重、土壤含水量(解释量依次为87.7%,79.4%,67.9%,35.8%),并且4种环境因子对土壤有机碳组分征的影响均为极显著(P<0.01)。探讨有机碳组分质量分数与其环境因子的相关关系,为评估天山森林土壤固碳效应提供科学根据。
中图分类号:
马辉英, 李昕竹, 马鑫钰, 贡璐. 新疆天山北麓中段不同植被类型下土壤有机碳组分特征及其影响因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(6): 1124-1131.
MA Huiying, LI Xinzhu, MA Xinyu, GONG Lu. Characteristics and Driving Factors of Soil Organic Carbon Fractions under Different Vegetation Types of the mid-Northern Piedmont of the Tianshan Mountains, Xinjiang[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(6): 1124-1131.
| 植被类型 Vegetational form | 土壤类型 Soil type | 土层 Soil layer/cm | 样地描述 Sample Site Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 云杉林 Spruce forest | 灰褐色森林土 | 0-10 10-20 | 以雪岭云杉(Picea schrenkiana)为主,林下分布少量植物 |
| 灌丛地 Grinding ground | 灰褐色森林土 | 0-10 10-20 | 黑果小檗(Berberis heteropoda)、红果小檗(Berberis nummularia)、天山花楸(Sorbus tianschanica)等 |
| 草地 Grassplot | 灰褐色森林土 | 0-10 10-20 | 绣线菊(Spiraea hypericifolia)、天山羽衣草(Alchemilla tianschanica)、羊角芹(Aegopodium podagraria)等 |
表1 不同植被类型样地基本情况
Table 1 Basic information of sample sites of different vegetation types
| 植被类型 Vegetational form | 土壤类型 Soil type | 土层 Soil layer/cm | 样地描述 Sample Site Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 云杉林 Spruce forest | 灰褐色森林土 | 0-10 10-20 | 以雪岭云杉(Picea schrenkiana)为主,林下分布少量植物 |
| 灌丛地 Grinding ground | 灰褐色森林土 | 0-10 10-20 | 黑果小檗(Berberis heteropoda)、红果小檗(Berberis nummularia)、天山花楸(Sorbus tianschanica)等 |
| 草地 Grassplot | 灰褐色森林土 | 0-10 10-20 | 绣线菊(Spiraea hypericifolia)、天山羽衣草(Alchemilla tianschanica)、羊角芹(Aegopodium podagraria)等 |
| 参数 Parameter | 植被类型 Vegetation Types | 均值 Mean | 标准差 Standard deviation | 极差 Range | 最小值Minimum | 最大值Maximum | 偏度 Skewness | 变异系数 Coefficient of variation/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| w(SOC)/ (g∙kg-1) | 云杉林 | 115.66 | 6.15 | 15.41 | 109.11 | 124.52 | 0.38 | 18.81 |
| 灌丛 | 84.85 | 6.13 | 15.05 | 79.21 | 94.26 | 0.76 | 13.83 | |
| 草地 | 76.27 | 4.81 | 12.70 | 69.54 | 82.24 | -0.24 | 15.87 | |
| w(DOC)/ (g∙kg-1) | 云杉林 | 4.03 | 0.07 | 0.19 | 3.93 | 4.12 | -0.32 | 60.39 |
| 灌丛 | 3.99 | 0.09 | 0.22 | 3.88 | 4.10 | -0.03 | 44.69 | |
| 草地 | 3.90 | 0.07 | 0.18 | 3.83 | 4.01 | 0.81 | 58.71 | |
| w(LFOC)/ (g∙kg-1) | 云杉林 | 9.93 | 0.60 | 1.59 | 9.04 | 10.63 | -0.31 | 16.60 |
| 灌丛 | 8.92 | 0.69 | 1.61 | 8.23 | 9.84 | 0.28 | 12.88 | |
| 草地 | 7.80 | 0.59 | 1.51 | 7.07 | 8.58 | -0.08 | 13.23 | |
| w(MBC)/ (mg∙kg-1) | 云杉林 | 315.06 | 8.50 | 20.21 | 304.13 | 324.34 | -0.53 | 37.05 |
| 灌丛 | 293.68 | 10.21 | 27.95 | 276.39 | 304.34 | -0.97 | 28.76 | |
| 草地 | 273.06 | 9.56 | 23.34 | 260.89 | 284.23 | -0.17 | 28.56 |
表2 不同植被类型下土壤有机碳及其组分质量分数的统计学分析
Table 2 Descriptive statistical analysis of soil organic carbon fractions in different vegetation types
| 参数 Parameter | 植被类型 Vegetation Types | 均值 Mean | 标准差 Standard deviation | 极差 Range | 最小值Minimum | 最大值Maximum | 偏度 Skewness | 变异系数 Coefficient of variation/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| w(SOC)/ (g∙kg-1) | 云杉林 | 115.66 | 6.15 | 15.41 | 109.11 | 124.52 | 0.38 | 18.81 |
| 灌丛 | 84.85 | 6.13 | 15.05 | 79.21 | 94.26 | 0.76 | 13.83 | |
| 草地 | 76.27 | 4.81 | 12.70 | 69.54 | 82.24 | -0.24 | 15.87 | |
| w(DOC)/ (g∙kg-1) | 云杉林 | 4.03 | 0.07 | 0.19 | 3.93 | 4.12 | -0.32 | 60.39 |
| 灌丛 | 3.99 | 0.09 | 0.22 | 3.88 | 4.10 | -0.03 | 44.69 | |
| 草地 | 3.90 | 0.07 | 0.18 | 3.83 | 4.01 | 0.81 | 58.71 | |
| w(LFOC)/ (g∙kg-1) | 云杉林 | 9.93 | 0.60 | 1.59 | 9.04 | 10.63 | -0.31 | 16.60 |
| 灌丛 | 8.92 | 0.69 | 1.61 | 8.23 | 9.84 | 0.28 | 12.88 | |
| 草地 | 7.80 | 0.59 | 1.51 | 7.07 | 8.58 | -0.08 | 13.23 | |
| w(MBC)/ (mg∙kg-1) | 云杉林 | 315.06 | 8.50 | 20.21 | 304.13 | 324.34 | -0.53 | 37.05 |
| 灌丛 | 293.68 | 10.21 | 27.95 | 276.39 | 304.34 | -0.97 | 28.76 | |
| 草地 | 273.06 | 9.56 | 23.34 | 260.89 | 284.23 | -0.17 | 28.56 |
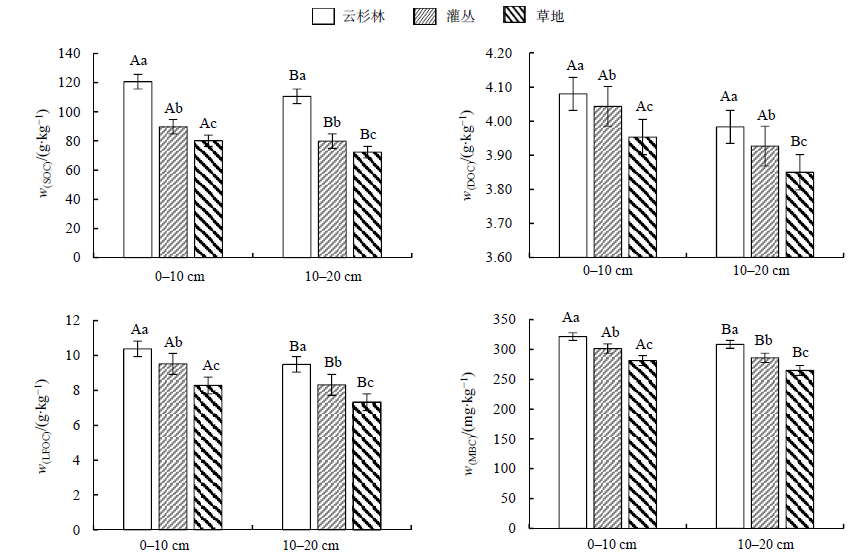
图1 不同植被类型下土壤有机碳组分质量分数 SOC:有机碳;DOC:可溶性有机碳;LFOC:轻组分有机碳;MBC:微生物生物量碳。不同大写字母表示同一植被类型不同土层之间有机碳组分的显著性差异(P<0.05);不同小写字母表示同一土层不同植被类型之间有机碳组分的显著性差异(P<0.05)
Figure 1 Soil organic carbon components under different vegetation types Different capital letters indicate the significant difference of organic carbon components in different soil layers of the same vegetation type (P<0.05); Different lowercase letters indicate the significant difference of organic carbon components between different vegetation types in the same soil layer (P<0.05)
| 源Source | 因变量 Dependent variable | 平方和 Sum of Squares | df | 均方 Mean square | F | Sig. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 土层深度 Soil depth | SOC | 384.014 | 1 | 384.014 | 49.427 | <0.001** |
| DOC | 0.050 | 1 | 0.050 | 20.659 | <0.001** | |
| LFOC | 4.651 | 1 | 4.651 | 50.989 | <0.001** | |
| MBC | 1018.810 | 1 | 1018.810 | 44.411 | <0.001** | |
| 植被类型 Vegetational form | SOC | 5148.741 | 2 | 2574.371 | 331.354 | <0.001** |
| DOC | 0.052 | 2 | 0.026 | 10.722 | 0.001** | |
| LFOC | 13.709 | 2 | 6.854 | 75.141 | <0.001** | |
| MBC | 5291.743 | 2 | 2645.871 | 115.337 | <0.001** |
表3 土层深度和植被类型对土壤有机碳组分的协同效应分析
Table 3 Analysis of synergistic effects of soil depth and vegetation type on soil organic carbon components
| 源Source | 因变量 Dependent variable | 平方和 Sum of Squares | df | 均方 Mean square | F | Sig. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 土层深度 Soil depth | SOC | 384.014 | 1 | 384.014 | 49.427 | <0.001** |
| DOC | 0.050 | 1 | 0.050 | 20.659 | <0.001** | |
| LFOC | 4.651 | 1 | 4.651 | 50.989 | <0.001** | |
| MBC | 1018.810 | 1 | 1018.810 | 44.411 | <0.001** | |
| 植被类型 Vegetational form | SOC | 5148.741 | 2 | 2574.371 | 331.354 | <0.001** |
| DOC | 0.052 | 2 | 0.026 | 10.722 | 0.001** | |
| LFOC | 13.709 | 2 | 6.854 | 75.141 | <0.001** | |
| MBC | 5291.743 | 2 | 2645.871 | 115.337 | <0.001** |
| 指标 Index | 土壤有机碳 Soil organic carbon | 土壤可溶性有机碳 Soil-soluble organic carbon | 土壤轻组分有机碳 Soil light components of organic carbon | 土壤微生物生物量碳 Soil microbial biomass of carbon | 含水量 Moisture content | pH值 pH value | 电导率 Conductivity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 土壤有机碳 Soil organic carbon | 1 | ||||||
| 土壤可溶性有机碳 Soil-soluble organic carbon | 0.476 | 1 | |||||
| 土壤轻组分有机碳 Soil light components of organic carbon | 0.769* | -0.823* | 1 | ||||
| 土壤微生物生物量碳 Soil microbial biomass of carbon | 0.357 | 0.797** | -0.762* | 1 | |||
| 含水量 Moisture content | 0.289 | 0.740* | 0.431 | 0.688* | 1 | ||
| pH值 pH value | -0.122 | -0.293 | 0.269 | -0.185 | -0.288 | 1 | |
| 电导率 Conductivity | 0.227 | 0.097 | -0.206 | 0.198 | 0.361 | 0.287 | 1 |
表4 各植被类型土壤表层有机碳及其组分质量分数与土壤环境因子的关系
Table 4 Relationship between the content of surface organic carbon and its components in soils of various vegetation types and soil environmental factors
| 指标 Index | 土壤有机碳 Soil organic carbon | 土壤可溶性有机碳 Soil-soluble organic carbon | 土壤轻组分有机碳 Soil light components of organic carbon | 土壤微生物生物量碳 Soil microbial biomass of carbon | 含水量 Moisture content | pH值 pH value | 电导率 Conductivity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 土壤有机碳 Soil organic carbon | 1 | ||||||
| 土壤可溶性有机碳 Soil-soluble organic carbon | 0.476 | 1 | |||||
| 土壤轻组分有机碳 Soil light components of organic carbon | 0.769* | -0.823* | 1 | ||||
| 土壤微生物生物量碳 Soil microbial biomass of carbon | 0.357 | 0.797** | -0.762* | 1 | |||
| 含水量 Moisture content | 0.289 | 0.740* | 0.431 | 0.688* | 1 | ||
| pH值 pH value | -0.122 | -0.293 | 0.269 | -0.185 | -0.288 | 1 | |
| 电导率 Conductivity | 0.227 | 0.097 | -0.206 | 0.198 | 0.361 | 0.287 | 1 |
| 排序轴 Axes | Ⅰ | Ⅱ | Ⅲ | Ⅳ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 土壤有机碳组分含量解释量 Explained variation of soil organic carbon fractions content/% | 0.896 | 0.015 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| 土壤有机碳组分含量与环境因子相关性 Correlations between soil organic carbon fractions content and their environmental factors | 0.970 | 0.622 | 0.232 | 0.086 |
| 土壤有机碳组分含量累积解释量 Cumulative explained variation of soil organic carbon fractions content/% | 89.6 | 91.1 | 91.1 | 91.1 |
| 土壤有机碳组分含量--环境因子关系累积解释量 Cumulative explained variation of relations between soil organic carbon fractions content and their environmental factors/% | 98.4 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
| 总特征值 Sum of all eigenvalues | 1.000 | |||
| 典范特征值 Sum of all canonical eigenvalues | 0.743 |
表5 土壤有机碳组分质量分数的变化解释变量冗余分析
Table 5 RDA of Soil organic carbon fractions content
| 排序轴 Axes | Ⅰ | Ⅱ | Ⅲ | Ⅳ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 土壤有机碳组分含量解释量 Explained variation of soil organic carbon fractions content/% | 0.896 | 0.015 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| 土壤有机碳组分含量与环境因子相关性 Correlations between soil organic carbon fractions content and their environmental factors | 0.970 | 0.622 | 0.232 | 0.086 |
| 土壤有机碳组分含量累积解释量 Cumulative explained variation of soil organic carbon fractions content/% | 89.6 | 91.1 | 91.1 | 91.1 |
| 土壤有机碳组分含量--环境因子关系累积解释量 Cumulative explained variation of relations between soil organic carbon fractions content and their environmental factors/% | 98.4 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
| 总特征值 Sum of all eigenvalues | 1.000 | |||
| 典范特征值 Sum of all canonical eigenvalues | 0.743 |
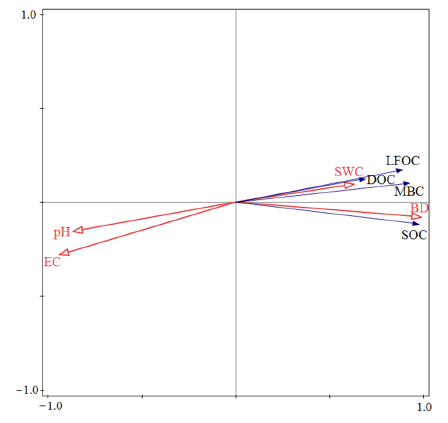
图2 土壤有机碳组分质量分数与环境因子关系的冗余分析二维排序图 SWC:土壤含水量;EC:土壤电导率;pH:土壤pH值;SOC:有机碳;DOC:可溶性有机碳;LFOC:轻组分有机碳;MBC:微生物生物量碳;BD:土壤容重
Figure 2 Bidimensional ordering chart of the RDA of relationships of soil organic carbon fractions content with their environmental factors SWC: soil moisture; EC: soil electrical conductivity; pH: Soil pH; SOC: organic carbon; DOC: soluble organic carbon; LFOC: light fraction organic carbon; MBC: microbial biomass carbon;BD:soil bulk density
| 土壤环境因子 Soil environmental factors | 重要性 排序 Importance sequencing | 土壤环境因子 所占解释量 Explained variation of soil environmental factors/% | F | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 土壤电导率 Soil conductivity | 1 | 87.7 | 113.9 | 0.002 |
| 土壤容重 Soil bulk density | 2 | 79.4 | 61.62 | 0.002 |
| 土壤pH值 Soil pH | 3 | 67.9 | 33.828 | 0.002 |
| 土壤含水量 Soil moisture content | 4 | 35.8 | 8.937 | 0.008 |
表6 土壤环境因子解释的重要性排序和显著性检验的结果
Table 6 Importance sequencing and Duncan test of soil environmental factors
| 土壤环境因子 Soil environmental factors | 重要性 排序 Importance sequencing | 土壤环境因子 所占解释量 Explained variation of soil environmental factors/% | F | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 土壤电导率 Soil conductivity | 1 | 87.7 | 113.9 | 0.002 |
| 土壤容重 Soil bulk density | 2 | 79.4 | 61.62 | 0.002 |
| 土壤pH值 Soil pH | 3 | 67.9 | 33.828 | 0.002 |
| 土壤含水量 Soil moisture content | 4 | 35.8 | 8.937 | 0.008 |
| [1] | AMEND A S, MATULICH K L, MARTINY J B H, 2015. Nitrogen addition, not initial phylogenetic diversity, increases litter decomposition by fungal communities[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 6(109): 1-10. |
| [2] | BOWDEN R D, DEEM L, PLANTE A F, et al., 2014. Litter input controls on soil carbon in a temperate deciduous forest[J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 78(S1): 66-75. |
| [3] | DAVIDSON E A, JANSSENS I A, 2006. Temperature sensitivity of soil carbon decomposition and feedbacks to climate change[J]. Nature, 440(7081): 165-173. |
| [4] | FERNÁNDEZ R, BELMONTE V, QUIROGA A, et al., 2021. Land-use change affects soil hydro-physical properties in Mollisols of semiarid Central Argentina[J]. Geoderma Regional, 25: e00394. |
| [5] | HANSON P J, EDWARDS N T, GARTEN C T, et al., 2000. Separating root and soil microbial contributions to soil respiration: A review of methods and observations[J]. Biogeochemistry, 48(1): 115-146. |
| [6] | JANZEN H H, CAMPBELL C A, BRANDT S A, et al., 1992. Light-fraction organic matter in soils from long-term crop rotations[J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 56(6): 1799-1806. |
| [7] | JONESDL, WILLETT V B, 2006, Experimental evaluation of methods to quantify dissolved organic nitrogen (DON) and dissolved organic carbon (DOC) in soil[J]. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 38(5): 991-999. |
| [8] | JOBBAGY E G, JACKSON R B, 2000. The vertical distribution of soil organic carbon and its relation to climate and vegetation[J]. Ecology Application, 10(2): 423-436. |
| [9] | LAL R, 2004. Soil carbon sequestration impacts on global climate change and food security[J]. Science, 304(5677): 1623-1627. |
| [10] | LEWIS S L, 2006. Tropical forests and the changing earth system[J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 361(1465): 195-210. |
| [11] | PISANI O, FREY S D, SIMPSON A J, et al., 2015. Soil warming and nitrogen deposition alter soil organic matter composition at the molecular-level[J]. Biogeochemistry, 123(3): 391-409. |
| [12] | SOLLINS P, HOMANN P, CALDWELL B A, 1996. Stabilization and destabilization of soil organic matter: Mechanisms and controls[J]. Geoderma, 74(1-2): 65-105. |
| [13] | WANG C G, LI H X, SUN X X, et al., 2021. Responses of soil microbial biomass and enzyme activities to natural restoration of reclaimed temperate marshes after abandonment[J]. Frontiers in Environmental Science, 9: 1-12. |
| [14] | WANG S Q, HUANG M, SHAO X M, et al., 2004. Vertical distribution of soil organic carbon in China[J]. Environmental Management, 33: 200-209. |
| [15] | WEI X R, SHAO M G, GALE W, et al., 2014. Global pattern of soil carbon losses due to the conversion of forests to agricultural land[J]. Scientific Reports, 4(4): 4062. |
| [16] | 鲍士旦, 2000. 土壤农化分析[M]. 第3版. 北京: 中国农业出版社: 14-111. |
| BAO S D, 2000. Soil agrochemical analysis[M]. 3rd edition. Beijing: China Agriculture Press: 14-111. | |
| [17] | 陈心桐, 徐天乐, 李雪静, 等, 2019. 中国北方自然生态系统土壤有机碳含量及其影响因素[J]. 生态学杂志, 38(4): 1133-1140. |
| CHEN X T, XU T L, LI X J, et al., 2019. Soil organic carbon content and its influencing factors in natural ecosystems in northern China[J]. Journal of Chemical Ecology, 38(4): 1133-1140. | |
| [18] | 楚珺尧, 王晶苑, 王绍强, 2014. 中亚热带典型人工针叶林土壤溶解性有机碳浓度变化特征研究[J]. 自然资源学报, 29(8): 1403-1410. |
| CHU J Y, WANG J Y, WANG S Q, 2014. Characteristics of soil dissolved organic carbon concentration in a typical subtropical coniferous forest[J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 29(8): 1403-1410. | |
| [19] | 国家林业局, 1999. 森林土壤有机质的测定及碳氮比的计算: LY/T 1237-1999[S]. 北京: 国家林业局. |
| State Forestry Administration, 1999. Determination of organic matter in forest soil and calculation of carbon-nitrogen ratio: LY/T 1237-1999[S]. Beijing: State Forestry Administration | |
| [20] | 侯翠翠, 宋长春, 李英臣, 等, 2011. 不同水分条件下小叶章湿地表土有机碳及活性有机碳组分季节动态[J]. 环境科学, 32(1): 290-297. |
| HOU C C, SONG C C, LI Y C, et al., 2011. Seasonal dynamics of topsoil organic carbon and active organic carbon components under different water conditions[J]. Environmental Science, 32(1): 290-297. | |
| [21] | 胡尧, 李懿, 侯雨乐, 2018. 岷江流域不同土地利用方式对土壤有机碳组分及酶活性的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 27(9): 1617-1624. |
| HU Y, LI Y, HOU Y L, 2018. The Variation of soil organic carbon fractions and soil enzyme activity of different land use types in Minjiang River Valley[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 27(9): 1617-1624. | |
| [22] | 胡宗达, 刘世荣, 刘兴良, 等, 2020. 川西亚高山3种天然次生林土壤有机碳氮组分特征[J]. 林业科学, 56(11): 1-11. |
| HU Z D, LIU S R, LIU X L, et al., 2020. Soil organic carbon and nitrogen components of three natural secondary forests in subalpine region of western Sichuan[J]. Forestry Science, 56(11): 1-11. | |
| [23] | 黄桥明, 吕茂奎, 聂阳意, 等, 2020. 武夷山不同海拔森林表层土壤轻组有机质特征[J]. 生态学报, 40(17): 6215-6222. |
| HUANG Q M, LÜ M K, NIE Y Y, et al., 2020. Characteristics of light organic matter in forest surface soil at different elevations in Wuyi Mountain[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 40(17): 6215-6222. | |
| [24] | 姜培坤, 徐秋芳, 周国模, 等, 2007. 石灰岩荒山造林后土壤养分与活性碳含量的变化[J]. 林业科学, 43(z1): 39-42. |
| JIANG P K, XU Q F, ZHOU G M, et al., 2007. Changes of soil nutrients and active carbon content after afforestation on barren limestone mountain[J]. Forestry Science, 43(z1): 39-42. | |
| [25] | 刘光崧, 蒋能慧, 张连第, 等, 1996. 土壤理化分析与土壤剖面描述[M]. 北京: 中国北京标准出版社: 166-167. |
| LIUG S, JIANG N H, ZHANG L D, et al., 1996. Soil physical and chemical analysis and soil profile description[M]. Beijing: Beijing standard press, China: 166-167. | |
| [26] | 苗娟, 周传艳, 李世杰, 等, 2014. 不同林龄云南松林土壤有机碳和全氮积累特征[J]. 应用生态学报, 25(3): 625-631. |
| MIAO J, ZHOU C Y, Ll S J, et al., 2014. Accumulation of soil organic carbon and total nitrogen in Pinus yunnanensis forests at different age stages[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 25(3): 625-631. | |
| [27] | 倪惠菁, 苏文会, 范少辉, 等, 2019. 养分输入方式对森林生态系统土壤养分循环的影响研究进展[J]. 生态学杂志, 38(3): 863-872. |
| NI H J, SU W H, FAN S H, et al., 2019. Research progress on effects of nutrient input patterns on soil nutrient cycling in forest ecosystems[J]. Journal of Chemical Ecology, 38(3): 863-872. | |
| [28] | 盛茂银, 刘洋, 熊康宁, 2013. 中国南方喀斯特石漠化演替过程中土壤理化性质的响应[J]. 生态学报, 33(19): 6303-6313. |
| SHENG M Y, LIU Y, XIONG K N, 2013. Responses of soil physicochemical properties to karst rocky desertification in southern China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 33(19): 6303-6313. | |
| [29] | 王浩, 陈永金, 刘加珍, 等, 2022. 黄河三角洲新生湿地3种柽柳灌丛对土壤有机碳空间分布的影响研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 31(1): 9-16. |
| WANG H, CHEN Y J, LIU J Z, et al., 2022. Effects of three types tamarix shrubs communities on spatial distribution of soil organic carbon in the new wetland of the Yellow River Delta[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 31(1): 9-16. | |
| [30] | 王慧杰, 常顺利, 张毓涛, 等, 2017. 天山雪岭云杉林土壤有机碳密度空间分异及其与森林发育的关系[J]. 山地学报, 35(3): 300-307. |
| WANG H J, CHANG S L, ZHANG Y T, et al., 2017. Spatial variation of soil organic carbon density and its relationship with forest development in Picea oleracea forest in The Tianshan Mountains[J]. Journal of Mountain, 35(3): 300-307. | |
| [31] | 武小钢, 郭晋平, 田旭平, 等, 2014. 芦芽山土壤有机碳和全氮沿海拔梯度变化规律[J]. 生态环境学报, 23(1): 50-57. |
| WU X G, GUO J P, TIAN X P, et al., 2014. Distribution characteristics of soil organic carbon and total nitrogen along elevation gradients in Luya Mountain[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 23(1): 50-57. | |
| [32] | 习丹, 旷远文, 2019. 广州城郊森林公园常绿阔叶林土壤有机碳及组分特征[J]. 生态科学, 38(1): 226-232. |
| XI D, KUANG Y W, 2019. Characteristics of soil organic carbon and its components in an evergreen broad-leaved forest in Guangzhou suburban Forest Park[J]. Ecological Science, 38(1): 226-232. | |
| [33] | 向成华, 栾军伟, 骆宗诗, 等, 2010. 川西沿海拔梯度典型植被类型土壤活性有机碳分布[J]. 生态学报, 30(4): 1025-1034. |
| XIANG C H, LUAN J W, LUO Z S, et al., 2010. Labile soil organic carbon distribution on influenced by vegetation types along an elevation gradient in west Sichuan China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 30(4): 1025-1034. | |
| [34] | 肖烨, 黄志刚, 武海涛, 等, 2015. 三江平原不同湿地类型土壤活性有机碳组分及含量差异[J]. 生态学报, 35(23): 7625-7633. |
| XIAO Y, HUANG Z G, WU H T, et al., 2015. Differences of soil active organic carbon components and contents among different wetland types in Sanjiang Plain[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 35(23): 7625-7633. | |
| [35] | 徐广平, 李艳琼, 沈育伊, 等, 2019. 桂林会仙喀斯特湿地水位梯度下不同植物群落土壤有机碳及其组分特征[J]. 环境科学, 40(3): 1491-1503. |
| XU G P, LI Y Q, SHEN Y Y, et al., 2019. Soil organic carbon and its components in different plant communities under water level gradient in Huixian Karst wetland of Guilin[J]. Environmental Science, 40(3): 1491-1503. | |
| [36] | 余健, 房莉, 卞正富, 等, 2014. 土壤碳库构成研究进展[J]. 生态学报, 34(17): 4829-4838. |
| YU J, FANG L, BIAN Z F, et al., 2014. Advances in soil carbon pool composition[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 34(17): 4829-4838. | |
| [37] | 张梦歌, 石兆勇, 杨梅, 等, 2020. 热带山地雨林土壤球囊霉素的分布特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 29(3): 457-463. |
| ZHANG M G, SHI Z Y, YANG M, et al., 2020. Elevational Distribution of Glomalin-rated Soil Proteins in ATropical Montane Rain Forest[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 29(3): 457-463. | |
| [38] | 张莎莎, 李爱琴, 王会荣, 等, 2020. 不同海拔杉木人工林土壤碳氮磷生态化学计量特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 29(1): 97-104. |
| ZHANG S S, LI A Q, WANG H R, et al., 2020. Ecological stoichiometry of soil carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus in cunninghamia lanceolata plantation across an elevation gradient[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 29(1): 97-104. | |
| [39] | 张勇, 史学正, 赵永存, 等, 2008. 滇黔桂地区土壤有机碳储量与影响因素研究[J]. 环境科学, 29(8): 2314-2319. |
| ZHANG Y, SHI X Z, ZHAO Y C, et al., 2008. Study on soil organic carbon storage and influencing factors in Dian-Qian-gui region[J]. Environmental Science, 29(8): 2314-2319. | |
| [40] | 祖元刚, 李冉, 王文杰, 等, 2011. 我国东北土壤有机碳、无机碳含量与土壤理化性质的相关性[J]. 生态学报, 31(18): 5207-5216. |
| ZU Y G, LI R, WANG W J, et al., 2011. Correlation between soil organic carbon and inorganic carbon content and soil physical and chemical properties in northeast China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 31(18): 5207-5216. |
| [1] | 杜丹丹, 高瑞忠, 房丽晶, 谢龙梅. 旱区盐湖盆地土壤重金属空间变异及对土壤理化因子的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(6): 1123-1132. |
| [2] | 李传福, 朱桃川, 明玉飞, 杨宇轩, 高舒, 董智, 李永强, 焦树英. 有机肥与脱硫石膏对黄河三角洲盐碱地土壤团聚体及其有机碳组分的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 878-888. |
| [3] | 李善家, 王兴敏, 刘海锋, 孙梦格, 雷雨昕. 河西走廊荒漠植物多样性及其对环境因子的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 429-438. |
| [4] | 张林, 齐实, 周飘, 伍冰晨, 张岱, 张岩. 北京山区针阔混交林地土壤有机碳含量的影响因素研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 450-458. |
| [5] | 张怀成, 韩红, 王在峰, 韩立钊, 刘克, 张桂芹, 范晶, 魏小锋. 济南市城市扬尘的微观形貌和化学组分特征分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 545-555. |
| [6] | 肖国举, 李秀静, 郭占强, 胡延斌, 王静. 贺兰山东麓土壤有机碳对玉米生长发育及水分利用的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(9): 1754-1764. |
| [7] | 韩翠, 康扬眉, 余海龙, 李冰, 黄菊莹. 荒漠草原凋落物分解过程中降水量对土壤酶活性的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(9): 1802-1812. |
| [8] | 陈乐, 卫伟. 西北旱区典型流域土地利用与生境质量的时空演变特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(9): 1909-1918. |
| [9] | 王超, 杨倩楠, 张池, 李祥东, 陈静, 张晓龙, 陈金洁, 刘科学. 东南湿润区典型丹霞地貌土壤有机碳组分及其敏感性研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(6): 1132-1140. |
| [10] | 龚玲玄, 王丽丽, 赵建宁, 刘红梅, 杨殿林, 张贵龙. 不同覆盖作物模式对茶园土壤理化性质及有机碳矿化的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(6): 1141-1150. |
| [11] | 雷俊, 张健, 赵福年, 齐月, 张秀云, 李强, 尚军林. 春小麦开花期光合参数对土壤水分和温度变化的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(6): 1151-1159. |
| [12] | 杜雪, 王海燕, 邹佳何, 孟海, 赵晗, 崔雪, 董齐琪. 长白山北坡云冷杉阔叶混交林土壤有机碳分布特征及其影响因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 663-669. |
| [13] | 陈瑶, 李云红, 邵英男, 刘玉龙, 刘延坤. 阔叶红松林物种多样性与土壤理化特征研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 679-687. |
| [14] | 胡靓达, 周海菊, 黄永珍, 姚贤宇, 叶绍明, 喻素芳. 不同杉木林分类型植物多样性及其土壤碳氮关系的研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(3): 451-459. |
| [15] | 玄锦, 李祖婵, 邹诚, 秦子博, 吴雅华, 黄柳菁. 江心洲景观类型和格局对植物多样性的多尺度影响——以闽江流域福州段为例[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(12): 2320-2330. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
