生态环境学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (12): 2320-2330.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2022.12.006
玄锦( ), 李祖婵, 邹诚, 秦子博, 吴雅华, 黄柳菁(
), 李祖婵, 邹诚, 秦子博, 吴雅华, 黄柳菁( )
)
收稿日期:2022-08-27
出版日期:2022-12-18
发布日期:2023-02-15
通讯作者:
*黄柳菁(1985年生),女,副教授,博士,硕士研究生导师,研究方向为植物群落和生物多样性保护和评价。E-mail: huanglj@fafu.edu.cn作者简介:玄锦(1998年生),女,硕士研究生,研究方向为风景园林生态学。E-mail: 1434097279@qq.com
基金资助:
XUAN Jin( ), LI Zuchan, ZOU Cheng, QIN Zibo, WU Yahua, HUANG Liujing(
), LI Zuchan, ZOU Cheng, QIN Zibo, WU Yahua, HUANG Liujing( )
)
Received:2022-08-27
Online:2022-12-18
Published:2023-02-15
摘要:
研究不同尺度下江心洲景观格局对植物多样性的影响对江心洲植被保护与开发建设具有应用价值和实际意义。以闽江流域福州段5个江心洲为研究对象,对江心洲内共23个植物样地进行群落调查,同时基于研究区2020年高清遥感数据,在ArcGIS软件支持下,以植物样地为中心,建立6个(100、200、300、400、500、600 m)不同尺度的缓冲区,应用Fragstats软件计算各缓冲区在景观水平和类型水平上的景观格局指数。在此基础上应用Canoco软件对不同尺度下景观格局指数与植物多样性指数进行冗余分析(RDA),筛选出对植物多样性影响最显著的景观格局指数。结果表明,(1)类型水平上,农田面积和形状对植物多样性有较大影响。其中,农田面积在200—500 m尺度对3个植物多样性有明显抑制作用,相关系数为?0.489— ?0.757。(2)在景观水平上,形状指数FRAC_MN、SHAPE_MN在所有尺度上均与植物多样性呈显著负相关,相关系数为?0.3289— ?0.641,在400 m尺度下FRAC_MN和SHAPE_MN可以更好地指示江心洲的植物多样性;破碎度指数IJI在100—500 m尺度下与植物多样性呈负相关,相关系数为?0.4149— ?0.126;连通性指数在100—600 m尺度对植物多样性有较小且不稳定的影响。因此,在对江心洲的保护和建设中,需要在考虑尺度效应的同时优化景观格局以保护的植物多样性。
中图分类号:
玄锦, 李祖婵, 邹诚, 秦子博, 吴雅华, 黄柳菁. 江心洲景观类型和格局对植物多样性的多尺度影响——以闽江流域福州段为例[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(12): 2320-2330.
XUAN Jin, LI Zuchan, ZOU Cheng, QIN Zibo, WU Yahua, HUANG Liujing. Multi-scale Effects of Central Bar Landscape Class and Pattern on Plant Diversity in Minjiang River: The Case of Minjiang River Basin (Fuzhou Section) Planning[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(12): 2320-2330.
| 类型 Type | 指数缩写 Index abbreviation | 数量 Number | 选取指数 Selected metric | 含义 Index meaning |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 形状指数 Shape metrics | LSI | 1 | LSI | 景观形状指数 |
| SHAPE | 3 | SHAPE_MN、SHAPE_AM、SHAPE_CV | 形状指数 | |
| PARA | 3 | PARA_MN、PARA_AM、PARA_CV | 周长面积比 | |
| FRAC | 3 | FRAC_MN、FRAC_AM、FRAC_CV | 分维度指数 | |
| CIRCLE | 3 | CIRCLE_MN、CIRCLE_AM、CIRCLE_CV | 相关外接圆 | |
| 面积指数 Area metrics | AREA | 3 | AREA_MN、AREA_AM、AREA_CV | 斑块面积 |
| 连通性指数 Connectivity metrics | PROX | 3 | PROX_MN、PROX_AM、PROX_CV | 邻近度指数 |
| CONTIG | 3 | CONTIG_MN、CONTIG_AM、CONTIG_CV | 邻近指数 | |
| 破碎度指数 Fragmentation metrics | GYRATE | 3 | GYRATE_MN、GYRATE_AM、GYRATE_CV | 回旋半径 |
| IJI | 1 | IJI | 散布与并列指数 | |
| DIVISION | 1 | DIVISION | 景观分割指数 | |
| COHESION | 1 | COHESION | 聚集度指数 | |
| 总计 Total | 28 |
表1 本研究选取的景观格局指数
Table 1 Selected landscape pattern metrics in the study
| 类型 Type | 指数缩写 Index abbreviation | 数量 Number | 选取指数 Selected metric | 含义 Index meaning |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 形状指数 Shape metrics | LSI | 1 | LSI | 景观形状指数 |
| SHAPE | 3 | SHAPE_MN、SHAPE_AM、SHAPE_CV | 形状指数 | |
| PARA | 3 | PARA_MN、PARA_AM、PARA_CV | 周长面积比 | |
| FRAC | 3 | FRAC_MN、FRAC_AM、FRAC_CV | 分维度指数 | |
| CIRCLE | 3 | CIRCLE_MN、CIRCLE_AM、CIRCLE_CV | 相关外接圆 | |
| 面积指数 Area metrics | AREA | 3 | AREA_MN、AREA_AM、AREA_CV | 斑块面积 |
| 连通性指数 Connectivity metrics | PROX | 3 | PROX_MN、PROX_AM、PROX_CV | 邻近度指数 |
| CONTIG | 3 | CONTIG_MN、CONTIG_AM、CONTIG_CV | 邻近指数 | |
| 破碎度指数 Fragmentation metrics | GYRATE | 3 | GYRATE_MN、GYRATE_AM、GYRATE_CV | 回旋半径 |
| IJI | 1 | IJI | 散布与并列指数 | |
| DIVISION | 1 | DIVISION | 景观分割指数 | |
| COHESION | 1 | COHESION | 聚集度指数 | |
| 总计 Total | 28 |
| 样地 Sample Site | 多样性指数 Diversity Index | 样地 Sample Site | 多样性指数 Diversity Index | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D | H | J | D | H | J | ||
| 1 | 0.8007 | 1.971 | 0.7469 | 13 | 0.8253 | 2.054 | 0.7782 |
| 2 | 0.4889 | 1.249 | 0.4614 | 14 | 0.8953 | 2.453 | 0.8331 |
| 3 | 0.8833 | 2.358 | 0.7521 | 15 | 0.7515 | 1.746 | 0.7027 |
| 4 | 0.8482 | 2.305 | 0.7694 | 16 | 0.8665 | 2.496 | 0.8076 |
| 5 | 0.8566 | 2.21 | 0.8374 | 17 | 0.7822 | 1.916 | 0.7468 |
| 6 | 0.8722 | 2.338 | 0.7941 | 18 | 0.7993 | 1.935 | 0.7785 |
| 7 | 0.8992 | 2.46 | 0.851 | 19 | 0.6824 | 1.265 | 0.7858 |
| 8 | 0.7564 | 1.735 | 0.7897 | 20 | 0.3272 | 0.6659 | 0.4803 |
| 9 | 0.7684 | 1.797 | 0.7493 | 21 | 0.7119 | 1.748 | 0.7033 |
| 10 | 0.8442 | 2.06 | 0.803 | 22 | 0.6759 | 1.629 | 0.6555 |
| 11 | 0.7465 | 1.774 | 0.714 | 23 | 0.8471 | 2.078 | 0.8364 |
| 12 | 0.656 | 1.305 | 0.7285 | ||||
表2 各样地植物多样性指数
Table 2 Plant diversity index of each sample sitet
| 样地 Sample Site | 多样性指数 Diversity Index | 样地 Sample Site | 多样性指数 Diversity Index | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D | H | J | D | H | J | ||
| 1 | 0.8007 | 1.971 | 0.7469 | 13 | 0.8253 | 2.054 | 0.7782 |
| 2 | 0.4889 | 1.249 | 0.4614 | 14 | 0.8953 | 2.453 | 0.8331 |
| 3 | 0.8833 | 2.358 | 0.7521 | 15 | 0.7515 | 1.746 | 0.7027 |
| 4 | 0.8482 | 2.305 | 0.7694 | 16 | 0.8665 | 2.496 | 0.8076 |
| 5 | 0.8566 | 2.21 | 0.8374 | 17 | 0.7822 | 1.916 | 0.7468 |
| 6 | 0.8722 | 2.338 | 0.7941 | 18 | 0.7993 | 1.935 | 0.7785 |
| 7 | 0.8992 | 2.46 | 0.851 | 19 | 0.6824 | 1.265 | 0.7858 |
| 8 | 0.7564 | 1.735 | 0.7897 | 20 | 0.3272 | 0.6659 | 0.4803 |
| 9 | 0.7684 | 1.797 | 0.7493 | 21 | 0.7119 | 1.748 | 0.7033 |
| 10 | 0.8442 | 2.06 | 0.803 | 22 | 0.6759 | 1.629 | 0.6555 |
| 11 | 0.7465 | 1.774 | 0.714 | 23 | 0.8471 | 2.078 | 0.8364 |
| 12 | 0.656 | 1.305 | 0.7285 | ||||
| 土地利用类型 Land use type | 林地 Forestland | 草地 Grassland | 未利用地 Unused land | 农田 Agricultural land | 建筑用地 Building land | 水体 Water | 合计 Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 面积 Area/hm2 | 157.55 | 47.32 | 31.78 | 6.53 | 0.69 | 0.45 | 244.33 |
| 占比 Proportion/% | 64.49 | 19.37 | 13.01 | 2.67 | 0.28 | 0.18 | 100 |
表3 江心洲景观类型面积占比
Table 3 Proportion of landscape type area in Jiangxinzhou
| 土地利用类型 Land use type | 林地 Forestland | 草地 Grassland | 未利用地 Unused land | 农田 Agricultural land | 建筑用地 Building land | 水体 Water | 合计 Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 面积 Area/hm2 | 157.55 | 47.32 | 31.78 | 6.53 | 0.69 | 0.45 | 244.33 |
| 占比 Proportion/% | 64.49 | 19.37 | 13.01 | 2.67 | 0.28 | 0.18 | 100 |
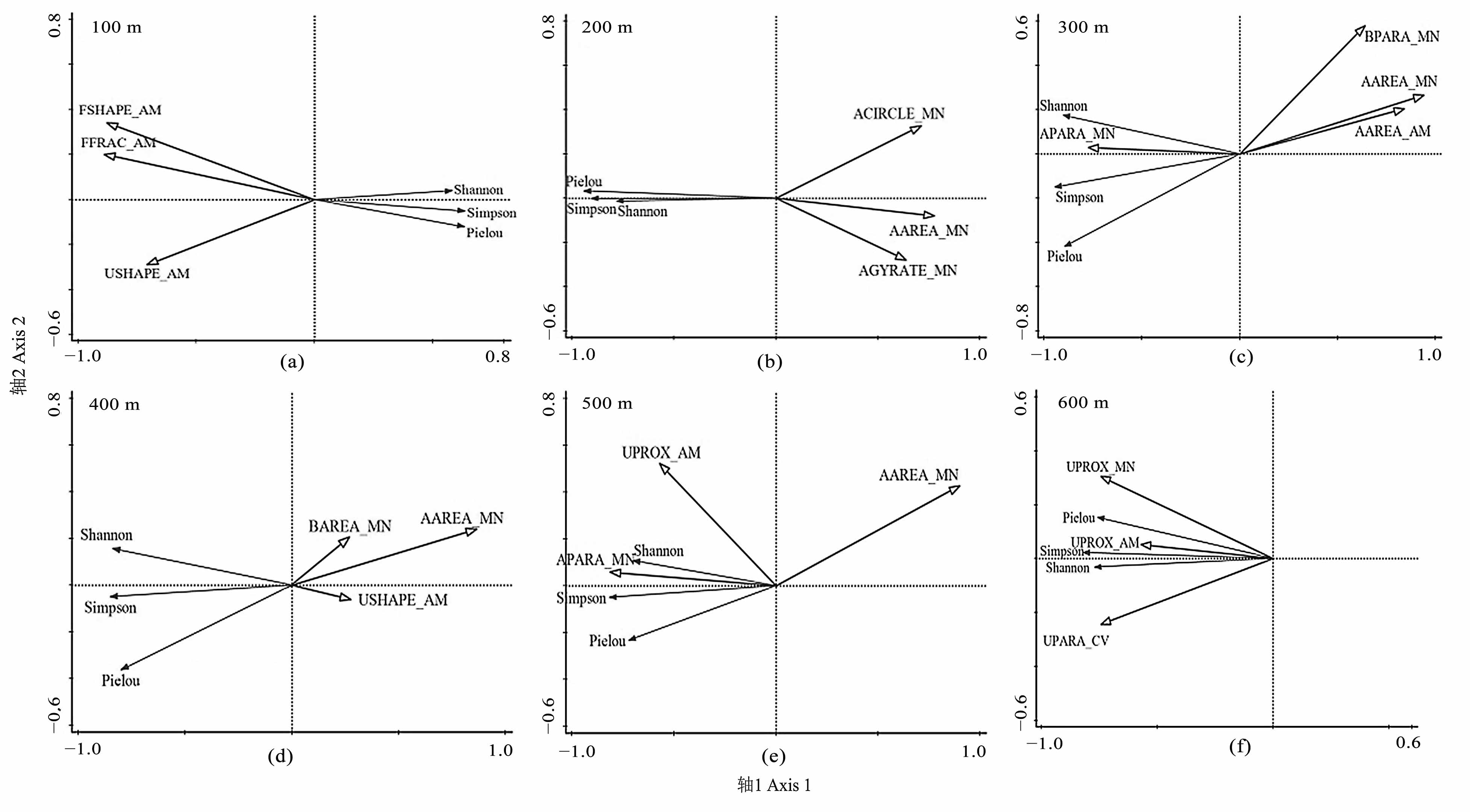
图3 不同尺度下类型水平指数与植物物种多样性的冗余分析 指数前缀A、B、F、U分别表示农田、建筑、林地、未利用地
Figure 3 RDA between landscape-class leve metrics and plant species in six spatial scales Prefixes A, B, F, and U represent farmland, building land, forestland, and unused land, respectively
| 尺度 Scale | 指数 Index | 相关系数 Correlation coefficients | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D | H | P | |||
| 100 m | FSHAPE_AM | −0.600* | −0.529* | −0.606** | |
| FFRAC_AM | −0.604** | −0.545* | −0.591** | ||
| USHAPE_AM | −0.637* | −0.601* | −0.575** | ||
| 200 m | ACIECLE_MN | −0.641* | −0.557* | −0.663* | |
| AAREA_MN | −0.697** | −0.601* | −0.735** | ||
| AGYRATE_MN | −0.569* | −0.491 | −0.612* | ||
| 300 m | BPARA_MN | −0.701* | −0.508* | −0.775** | |
| AAREA_MN | −0.740** | −0.569* | −0.757** | ||
| AAREA_AM | −0.268 | −0.156 | −0.299 | ||
| APARA_MN | 0.639** | 0.545** | 0.571* | ||
| 400 m | AAREA_MN | −0.491* | −0.489** | −0.644** | |
| BAREA_MN | −0.387 | −0.457 | −0.353 | ||
| USHAPE_AM | −0.458* | −0.324* | −0.583** | ||
| 500 m | AAREA_MN | −0.752** | −0.573* | −0.745** | |
| UPROX_AM | 0.451* | 0.474* | 0.450* | ||
| APARA_MN | 0.670** | 0.557* | 0.548* | ||
| 600 m | UPROX_MN | 0.575** | 0.542** | 0.617** | |
| UPARA_CV | 0.511* | 0.577** | 0.501* | ||
| UPROX_AM | 0.442* | 0.431* | 0.447* | ||
表4 不同尺度下类型水平指数对植物物种多样性影响的相关系数
Table 4 Correlation coefficients between landscape-class leve metrics and plant species in six spatial scales
| 尺度 Scale | 指数 Index | 相关系数 Correlation coefficients | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D | H | P | |||
| 100 m | FSHAPE_AM | −0.600* | −0.529* | −0.606** | |
| FFRAC_AM | −0.604** | −0.545* | −0.591** | ||
| USHAPE_AM | −0.637* | −0.601* | −0.575** | ||
| 200 m | ACIECLE_MN | −0.641* | −0.557* | −0.663* | |
| AAREA_MN | −0.697** | −0.601* | −0.735** | ||
| AGYRATE_MN | −0.569* | −0.491 | −0.612* | ||
| 300 m | BPARA_MN | −0.701* | −0.508* | −0.775** | |
| AAREA_MN | −0.740** | −0.569* | −0.757** | ||
| AAREA_AM | −0.268 | −0.156 | −0.299 | ||
| APARA_MN | 0.639** | 0.545** | 0.571* | ||
| 400 m | AAREA_MN | −0.491* | −0.489** | −0.644** | |
| BAREA_MN | −0.387 | −0.457 | −0.353 | ||
| USHAPE_AM | −0.458* | −0.324* | −0.583** | ||
| 500 m | AAREA_MN | −0.752** | −0.573* | −0.745** | |
| UPROX_AM | 0.451* | 0.474* | 0.450* | ||
| APARA_MN | 0.670** | 0.557* | 0.548* | ||
| 600 m | UPROX_MN | 0.575** | 0.542** | 0.617** | |
| UPARA_CV | 0.511* | 0.577** | 0.501* | ||
| UPROX_AM | 0.442* | 0.431* | 0.447* | ||
| 景观指数 Landscape index | 多样性指数 Diversity Index | 相关系数 Correlation coefficients | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 m | 200 m | 300 m | 400 m | 500 m | 600 m | ||
| FRAC_MN | D | −0.458* | −0.361* | −0.463* | −0.609** | −0.462* | −0.473* |
| H | −0.465* | −0.328* | −0.424* | −0.576** | −0.423* | −0.419* | |
| J | −0.459* | −0.341* | −0.551** | −0.637** | −0.550** | ||
| SHAPE_MN | D | −0.551** | −0.356* | −0.557** | −0.660** | −0.541** | −0.577** |
| H | −0.556** | −0.339* | −0.521* | −0.557** | −0.507* | −0.544** | |
| J | −0.519* | −0.409** | −0.559** | −0.641** | −0.543** | −0.476* | |
| SHAPE_AM | D | — | — | — | — | — | −0.216 |
| H | — | — | — | — | — | −0.223 | |
| J | — | — | — | — | — | −0.097 | |
| PARA_MN | D | — | — | — | 0.464* | 0.399* | 0.562** |
| H | — | — | — | 0.334 | 0.424* | 0.580** | |
| J | — | — | — | 0.477* | 0.297 | 0.363 | |
| PARA_AM | D | −0.283* | — | — | — | — | −0.217 |
| H | −0.299* | — | — | — | — | −0.226 | |
| J | −0.228 | — | — | — | — | −0.136 | |
| LSI | D | −0.285* | — | — | — | — | — |
| H | −0.251 | — | — | — | — | — | |
| J | −0.189 | — | — | — | — | — | |
| CIRCLE_AM | D | — | — | — | −0.270 | — | — |
| H | — | — | — | −0.174 | — | — | |
| J | — | — | — | −0.252 | — | — | |
| CIRCLE_MN | D | — | — | −0.461* | — | −0.463* | — |
| H | — | — | −0.452* | — | −0.447* | — | |
| J | — | — | −0.522* | — | −0.502* | — | |
| CIRCLE_CV | D | 0.520* | — | — | — | — | — |
| H | 0.554* | — | — | — | — | — | |
| J | 0.533* | — | — | — | — | — | |
| CONTIG_AM | D | 0.064 | — | — | — | — | 0.179 |
| H | 0.071 | — | — | — | — | 0.198 | |
| J | 0.070 | — | — | — | — | 0.102 | |
| CONTIG_CV | D | — | — | — | 0.432* | — | — |
| H | — | — | — | 0.276 | — | — | |
| J | — | — | — | 0.483** | — | — | |
| CONTIG_MN | D | — | — | — | — | — | |
| H | — | — | — | — | — | ||
| J | — | — | — | — | — | ||
| PROX_CV | D | — | 0.077 | — | — | — | — |
| H | — | 0.043 | — | — | — | — | |
| J | — | 0.218 | — | — | — | — | |
| GYRATE_CV | D | — | — | — | 0.555** | — | 0.518* |
| H | — | — | — | 0.493* | — | 0.521* | |
| J | — | — | — | 0.495* | — | 0.363 | |
| IJI | D | −0.414* | −0.268 | −0.339* | −0.373 | −0.314 | — |
| H | −0.395* | −0.275* | −0.369* | −0.440* | −0.345* | — | |
| J | −0.268 | −0.270 | −0.225 | −0.126 | −0.168 | — | |
表5 主要景观指数的Pearson双变量分析
Table 5 Pearson’s correlation coefficients of of major landscape indices
| 景观指数 Landscape index | 多样性指数 Diversity Index | 相关系数 Correlation coefficients | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 m | 200 m | 300 m | 400 m | 500 m | 600 m | ||
| FRAC_MN | D | −0.458* | −0.361* | −0.463* | −0.609** | −0.462* | −0.473* |
| H | −0.465* | −0.328* | −0.424* | −0.576** | −0.423* | −0.419* | |
| J | −0.459* | −0.341* | −0.551** | −0.637** | −0.550** | ||
| SHAPE_MN | D | −0.551** | −0.356* | −0.557** | −0.660** | −0.541** | −0.577** |
| H | −0.556** | −0.339* | −0.521* | −0.557** | −0.507* | −0.544** | |
| J | −0.519* | −0.409** | −0.559** | −0.641** | −0.543** | −0.476* | |
| SHAPE_AM | D | — | — | — | — | — | −0.216 |
| H | — | — | — | — | — | −0.223 | |
| J | — | — | — | — | — | −0.097 | |
| PARA_MN | D | — | — | — | 0.464* | 0.399* | 0.562** |
| H | — | — | — | 0.334 | 0.424* | 0.580** | |
| J | — | — | — | 0.477* | 0.297 | 0.363 | |
| PARA_AM | D | −0.283* | — | — | — | — | −0.217 |
| H | −0.299* | — | — | — | — | −0.226 | |
| J | −0.228 | — | — | — | — | −0.136 | |
| LSI | D | −0.285* | — | — | — | — | — |
| H | −0.251 | — | — | — | — | — | |
| J | −0.189 | — | — | — | — | — | |
| CIRCLE_AM | D | — | — | — | −0.270 | — | — |
| H | — | — | — | −0.174 | — | — | |
| J | — | — | — | −0.252 | — | — | |
| CIRCLE_MN | D | — | — | −0.461* | — | −0.463* | — |
| H | — | — | −0.452* | — | −0.447* | — | |
| J | — | — | −0.522* | — | −0.502* | — | |
| CIRCLE_CV | D | 0.520* | — | — | — | — | — |
| H | 0.554* | — | — | — | — | — | |
| J | 0.533* | — | — | — | — | — | |
| CONTIG_AM | D | 0.064 | — | — | — | — | 0.179 |
| H | 0.071 | — | — | — | — | 0.198 | |
| J | 0.070 | — | — | — | — | 0.102 | |
| CONTIG_CV | D | — | — | — | 0.432* | — | — |
| H | — | — | — | 0.276 | — | — | |
| J | — | — | — | 0.483** | — | — | |
| CONTIG_MN | D | — | — | — | — | — | |
| H | — | — | — | — | — | ||
| J | — | — | — | — | — | ||
| PROX_CV | D | — | 0.077 | — | — | — | — |
| H | — | 0.043 | — | — | — | — | |
| J | — | 0.218 | — | — | — | — | |
| GYRATE_CV | D | — | — | — | 0.555** | — | 0.518* |
| H | — | — | — | 0.493* | — | 0.521* | |
| J | — | — | — | 0.495* | — | 0.363 | |
| IJI | D | −0.414* | −0.268 | −0.339* | −0.373 | −0.314 | — |
| H | −0.395* | −0.275* | −0.369* | −0.440* | −0.345* | — | |
| J | −0.268 | −0.270 | −0.225 | −0.126 | −0.168 | — | |
| [1] |
AGGEMYR E, COUSINS S A O, 2012. Landscape structure and land use history influence changes in island plant composition after 100 years[J]. Journal of Biogeography, 39(9): 1645-1656.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
AMICI V, ROCCHINI D, FILIBECK G, et al., 2015. Landscape structure effects on forest plant diversity at local scale: Exploring the role of spatial extent[J]. Ecological Complexity, 21: 44-52.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
DAVID L C, 2005. Principles of planning and establishment of buffer zones[J]. Ecological Engineering, 24(5): 433-439
DOI URL |
| [4] |
HIGGINS S, MAHON M, MCDONAGH J, 2012. Interdisciplinary interpretations and applications of the concept of scale in landscape research[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 113: 137-145.
DOI PMID |
| [5] |
HONNAY O, PIESSENS K, LANDUYT W V, et al., 2003. Satellite based land use and landscape complexity indices as predictors for regional plant species diversity[J]. Landscape and Urban Planning, 63(4): 241-250.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
HUBBLE T C T, DOCKER B B, RUTHERFURD I D, 2009. The role of riparian trees in maintaining riverbank stability: A review of Australian experience and practice[J]. Ecological Engineering, 36(3): 292-304.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
ISABELLE B, DAMIEN G, CÉDRIC D, et al., 2014. Anticipating the spatio-temporal response of plant diversity and vegetation structure to climate and land use change in a protected area[J]. Ecography, 37(12): 1230-1239.
PMID |
| [8] |
KRAUSS J, KLEIN A MARIA, DEWENTER S I, et al., 2004. Effects of habitat area, isolation,and landscape diversity on plant species richness of calcareous grasslands[J]. Biodiversity and Conservation, 13(8): 1427-1439.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
LUIS J H, 2005. Relationships between landscape patterns and species richness of trees, shrubs and vines in a tropical forest[J]. Plant Ecology, 179(1): 53-65.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
MENDEZ T, MOISES, ZERMENO H, et al., 2014. Effect of land use on the structure and diversity of riparian vegetation in the Duero river watershed in Michoacan, Mexico[J]. Plant Ecology, 215(3): 285-296.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
MONTEIRO A T, FAVA F, GONÇALVES J, et al., 2013. Landscape context determinants to plant diversityin the permanent meadows of Southern European Alps[J]. Biodiversity and Conservation, 22(4): 937-958.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
MOSER D, ZECHMEISTER H G, PLUTZAR C, et al., 2002. Landscape patch shape complexity as an effective measure for plant species richness in rural landscapes[J]. Landscape Ecology, 17(7): 657-669.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
MÕISJA K, UUEMAA E, OJA T, 2016. Integrating small-scale landscape elements into land use/cover: The impact on landscape metrics’ values[J]. Ecological Indicators, 67: 714-722.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
POGGIO S L, CHANETON E J, GHERSA C M, 2010. Landscape complexity differentially affects alpha, beta, and gamma diversities of plants occurring in fencerows and crop fields[J]. Biological Conservation, 143(11): 2477-2486.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
RAMALHO C E, LALIBERTÉ E E, POOT P, et al., 2018. Effects of fragmentation on the plant functional composition and diversity of remnant woodlands in a young and rapidly expanding city[J]. Journal of Vegetation Science, 29(2): 285-296.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
REITALU T, PURSCHKE O, JOHANSSON, et al., 2012. Responses of grassland species richness to local and landscape factors depend on spatial scale and habitat specialization[J]. Journal of Vegetation Science, 23(1): 41-51.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
SCHINDLER S, WEHRDEN H, POIRAZIDIS K, et al., 2013. Multiscale performance of landscape metrics as indicators of species richness of plants, insects and vertebrates[J]. Ecological Indicators, 31: 41-48.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
SCHMIDT K J, POPPENDIECK H, JENSEN K, 2014. Effects of urban structure on plant species richness in a large European city[J]. Urban Ecosystems, 17(2): 427-444.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
TSCHARNTKE T, TYLIANAKIS J M, RAND T A, et al., 2012. Landscape moderation of biodiversity patterns and processes-eight hypotheses[J]. Biological reviews of the Cambridge Philosophical Society, 87(3): 661-685.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
TULLOCH A I T, BARNES M D, RINGMA J, et al., 2016. Understanding the importance of small patches of habitat for conservation[J]. Journal of Applied Ecology, 53(2): 418-429.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
WALZ U, 2015. Indicators to monitor the structural diversity of landscapes[J]. Ecological Modelling, 295: 88-106.
DOI URL |
| [22] | YANG J Y, LUO X Y, LU S R, et al., 2021. Effects of compositional and configurational heterogeneity of the urban matrix on the species richness of woody plants in urban remnant forest patches[J]. Landscape Ecology: 619-632. |
| [23] |
ZBIGNIEW D, STEFANIA L, 1988. Species richness of small woodlands on the western Carpathian Foothills[J]. Vegetatio, 76(1-2): 15-27.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
ZHANG D, WANG W J, ZHENG H F, et al., 2017. Effects of urbanization intensity on forest structural-taxonomic attributes, landscape patterns and their associations in Changchun, Northeast China: Implications for urban green infrastructure planning[J]. Ecological Indicators, 80: 286-296.
DOI URL |
| [25] | ZHANG J X, LI H, ZHANG X F, et al., 2020. Sensitivity evaluation of soil erosion based on land use types: A case study of Minjiang River Basin[J]. Journal of Intellgent & Fuzzy Systems, 38(5): 5697-5705. |
| [26] | 陈丽慧, 肖静文, 冯晶红, 等, 2022. 干湿环境对河岸带硝化及反硝化潜力的影响[J/OL]. 中国农村水利水电: http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/42.1419.TV.20220408.1433.027.html. |
| CHEN L H, XIAO J W, FENG J H, et al., 2022. Effect of dry and flooding environment on nitrification and denitrification potential in riparian zone[J/OL]. China Rural Water and Hydropower: http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/42.1419.TV.20220408.1433.027.html. | |
| [27] | 董翠芳, 梁国付, 丁圣彦, 等, 2014. 不同干扰背景下景观指数与物种多样性的多尺度效应——以巩义市为例[J]. 生态学报, 34(12): 3444-3451. |
| DONG C F, LIANG G F, DING S Y, et al., 2014. Multi-scale effects for landscape metrics and species diversity under the different disturbance: A case study of Gongyi City[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 34(12): 3444-3451. | |
| [28] | 范敏, 彭羽, 王庆慧, 等, 2018. 景观格局与植物多样性的关系及其空间尺度效应——以浑善达克沙地为例[J]. 生态学报, 38(7): 2450-2461. |
| FAN M, PENG Y, WANG Q H, et al., 2018. Correlations between landscape pattern and plant diversity at multiple spatial scales: a case study of Hunshandak Sandland[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 38(7): 2450-2461. | |
| [29] | 侯朝伟, 孙西艳, 刘永亮, 等, 2020. 烟台近海浮游动物优势种空间生态位研究[J]. 生态学报, 40(16): 5822-5833. |
| HOU C W, SUN X Y, LIU Y L, et al., 2020. Spatial niches of dominant zooplankton species in the Yantai offshore waters[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 40(16): 5822-5833. | |
| [30] | 李羽翎, 张广奇, 杨婷婷, 等, 2022. 茂兰喀斯特森林林窗下木本植物多样性及其驱动力[J]. 生态学杂志, 41(3): 444-453. |
| LI Y L, ZHANG G Q, YANG T T, et al., 2022. Woody species diversity in forest gaps and its driving forces in Maolan karst forest[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 41(3): 444-453. | |
| [31] |
李祖政, 尤海梅, 王梓懿, 2018. 徐州城市景观格局对绿地植物多样性的多尺度影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 29(6): 1813-1821.
DOI |
| LI Z Z, YOU H M, WANG Z Y, 2018. Multi-scale effects of urban landscape pattern on plant diversity in Xuzhou City, Jiangsu Province, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 29(6): 1813-1821. | |
| [32] | 刘梅冰, 2006. 闽江下游河道水动力水质动态模拟[D]. 福州:福建师范大学:11-15. |
| LIU M B, 2006. Hydrodynamic and water quality modeling for the lower reaches of Minjiang River[D]. Fuzhou:Fujian Normal University: 11-15. | |
| [33] | 卢洋, 2016. 漓江江心洲植被演替及其修复机制研究[D]. 北京:北京林业大学: 8-25. |
| LU Y, 2016. Research on vegetation succession and restoration mechanism of the central bars in Lijiang River[D]. Beijing:Beijing Forestry University: 8-25. | |
| [34] | 马宇龙, 林志垒, 2017. 基于面向对象和CART决策树方法的遥感影像湿地变化检测研究——以龙祥岛地区为例[J]. 福建师范大学学报 (自然科学版), 33(6): 69-80. |
| MA Y L, LIN Z L, 2017. Wetland change detection based on object-oriented and CART Decision tree method: A case study of wetlands in Longxiang Island[J]. Journal of Fujian Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 33(6): 69-80. | |
| [35] | 彭建, 王仰麟, 张源, 等, 2006. 土地利用分类对景观格局指数的影响[J]. 地理学报, 61(2): 157-168. |
|
PENG J, WANG Y L, ZHANG Y, et al., 2006. Research on the influence of land use classification on landscape metrics[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 61(2): 157-168.
DOI |
|
| [36] | 彭羽, 范敏, 卿凤婷, 等, 2016. 景观格局对植物多样性影响研究进展[J]. 生态环境学报, 25(6): 1061-1068. |
| PENG Y, FAN M, QING F T, et al., 2016. Study progresses on effects of landscape metrics on plant diversity[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 25(6): 1061-1068. | |
| [37] |
彭羽, 王玟涛, 卢奕曈, 等, 2020. 城市化景观格局对本土植物多样性的多尺度影响——以北京市顺义区为例[J]. 应用生态学报, 31(12): 4058-4066.
DOI |
|
PENG Y, WANG W T, LU Y T, et al., 2020. Multiscale influences of urbanized landscape metrics on the diversity of indigenous plant species: A case study in Shunyi District of Beijing, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 31(12): 4058-4066.
DOI |
|
| [38] | 王萌, 2019. 上海市植物多样性空间分布格局及其影响因素[D]. 上海:华东师范大学:77-94. |
| WANG M, 2019. The spatial pattern of urban plant diversity and its influencing factors in Shanghai, China[D]. Shanghai:East China Normal University:77-94. | |
| [39] | 魏雯, 李哲惠, 黄贞珍, 2018. 城市河岸带土地利用和景观格局演变研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 27(11): 2127-2133. |
| WEI W, LI Z H, HUANG Z Z, 2018. Study on the evolution of land use and landscape patterns in urban riparian zones[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 27(11): 2127-2133. | |
| [40] | 魏志洪, 2020. 不同频率洪水作用下闽江下游采砂规划对河道演变的影响[J]. 水资源开发与管理 (7): 49-54. |
| WEI Z H, 2020. Influence of sand excavation planning on river channel evolution in lower Minjiang River under different frequencies of floods[J]. Water Resources Development and Management (7): 49-54. | |
| [41] | 尹久娜, 闫帅, 何颖焕, 等, 2019. 福州乌龙江浦上岛生态问题及修复策略建议[J]. 南方园艺, 30(6): 57-63. |
| YIN J N, YAN S, HE Y H, et al., 2019. Ecological problems and restoration strategies of Pushang Island in Wulong River of Fuzhou[J]. Southern Horticulture, 30(6): 57-63. |
| [1] | 杜丹丹, 高瑞忠, 房丽晶, 谢龙梅. 旱区盐湖盆地土壤重金属空间变异及对土壤理化因子的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(6): 1123-1132. |
| [2] | 张钧韦, 夏圣洁, 陈慧儒, 刘艳红. 山西中部城市群景观格局演变对其热环境的影响研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 943-955. |
| [3] | 李阳, 侯志勇, 陈薇, 于晓英, 谢永宏, 黄鑫, 谭佩阳, 李继承, 黎尚林, 杨辉. 大围山高山湿地植物多样性与区系组成研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 643-650. |
| [4] | 李善家, 王兴敏, 刘海锋, 孙梦格, 雷雨昕. 河西走廊荒漠植物多样性及其对环境因子的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 429-438. |
| [5] | 王哲, 田胜尼, 张永梅, 张和禹, 周忠泽. 巢湖派河口滩涂植物群落特征研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(9): 1823-1831. |
| [6] | 王礼霄, 刘晋仙, 柴宝峰. 华北亚高山土壤细菌群落及氮循环对退耕还草的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1537-1546. |
| [7] | 王晨茜, 张琼锐, 张若琪, 孙学超, 徐颂军. 广东省珠江流域景观格局对水质净化服务的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(7): 1425-1433. |
| [8] | 张博文, 秦娟, 任忠明, 陈子齐, 姚舜佳, 刘烨, 宋炎玉. 坡向对北亚热带区马尾松纯林及不同针阔混交林型林下植物多样性的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(6): 1091-1100. |
| [9] | 马辉英, 李昕竹, 马鑫钰, 贡璐. 新疆天山北麓中段不同植被类型下土壤有机碳组分特征及其影响因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(6): 1124-1131. |
| [10] | 段文军, 李达, 李冲. 5种不同林龄尾巨桉人工林林下植物多样性及其影响因素分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(5): 857-864. |
| [11] | 陈瑶, 李云红, 邵英男, 刘玉龙, 刘延坤. 阔叶红松林物种多样性与土壤理化特征研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 679-687. |
| [12] | 胡靓达, 周海菊, 黄永珍, 姚贤宇, 叶绍明, 喻素芳. 不同杉木林分类型植物多样性及其土壤碳氮关系的研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(3): 451-459. |
| [13] | 韩鑫, 袁春阳, 李济宏, 洪宗文, 刘宣, 杜婷, 李晗, 游成铭, 谭波, 朱鹏, 徐振锋. 树种和土层对土壤无机氮的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(11): 2143-2151. |
| [14] | 陈双双, 朱宁华, 周光益, 袁星明, 尚海, 王迤翾. 不同等级石漠化环境下人工乔木林的植被与土壤物理特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(1): 52-61. |
| [15] | 边振兴, 张宇飞, 果晓玉, 林琳, 于淼. 低山丘陵区农业景观格局对害虫-捕食性天敌食物网的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(1): 79-88. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
