生态环境学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (7): 1090-1099.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2025.07.009
蔡敏1( ), 周丽1,*(
), 周丽1,*( ), 张旭1,2, 崔娜欣1, 庞思1, 邹国燕1, 袁泉1, 黄伟伟1, 赵志勇3
), 张旭1,2, 崔娜欣1, 庞思1, 邹国燕1, 袁泉1, 黄伟伟1, 赵志勇3
收稿日期:2024-11-09
出版日期:2025-07-18
发布日期:2025-07-11
通讯作者:
*E-mail: 作者简介:蔡敏(1991年生),男,助理研究员,硕士,主要从事水环境治理研究。E-mail: caiminjay@foxmail.com
基金资助:
CAI Min1( ), ZHOU Li1,*(
), ZHOU Li1,*( ), ZHANG Xu1,2, CUI Naxin1, PANG Si1, ZOU Guoyan1, YUAN Quan1, HUANG Weiwei1, ZHAO Zhiyong3
), ZHANG Xu1,2, CUI Naxin1, PANG Si1, ZOU Guoyan1, YUAN Quan1, HUANG Weiwei1, ZHAO Zhiyong3
Received:2024-11-09
Online:2025-07-18
Published:2025-07-11
摘要:
水产养殖水体中的浮游植物群落结构及其功能组成是养殖生态系统的关键组成部分。在上海市金山区某生态养殖农场开展了一项为期40 d的实验,旨在评估植物提取液对水产养殖水体中浮游植物群落演替的影响。所使用的植物提取液主要为中草药提取物,中草药包括穿心莲(Andrographis paniculata)、赶黄草(Penthorum chinense)、香兰草(Vanilla planifolia)、虎咬癀(Mollugo lotoides)和对叶草(Cynanchum hancockianum)。实验中,植物提取液与池塘水的体积比例设定为1꞉(1.20×104-1.44×104)。在实验期间,定期监测水质参数,并运用宏基因组学技术分析植物提取液对环境因子及浮游植物群落结构与功能的影响。结果显示,植物提取液有效降低了水体中叶绿素a、氮营养盐及有机物的浓度,并促进了浮游植物群落由蓝藻门向硅藻门进行演替。此外,植物提取液还降低了浮游植物的代谢功能,增强了与遗传信息处理相关的功能。蓝藻丰度与pH、叶绿素a、总磷及化学需氧量呈正相关,而与溶解氧和氮营养盐呈负相关;反之,硅藻对环境因子的响应与蓝藻相反。研究结果为植物提取液在水产养殖领域针对浮游植物群落调控的潜在应用提供了重要见解。
中图分类号:
蔡敏, 周丽, 张旭, 崔娜欣, 庞思, 邹国燕, 袁泉, 黄伟伟, 赵志勇. 植物提取液对养殖水体浮游植物群落结构和功能的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2025, 34(7): 1090-1099.
CAI Min, ZHOU Li, ZHANG Xu, CUI Naxin, PANG Si, ZOU Guoyan, YUAN Quan, HUANG Weiwei, ZHAO Zhiyong. Effects of Plant Extracts on Phytoplankton Community Structure and Function in Aquaculture Water[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2025, 34(7): 1090-1099.
| 水体基本理化指标 | 处理 | 时间/d | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | ||
| 水温(WT)/℃ | CK | 24.50±0.36 | 26.37±0.15 | 31.37±0.15 | 29.47±0.06 | 26.47±0.12 |
| T | 24.60±0.50 | 26.53±0.12 | 31.50±0.36 | 29.30±0.35 | 26.27±0.15 | |
| pH | CK | 8.42±0.44 | 7.06±0.12 | 7.72±0.12 | 7.44±0.33 | 7.00±0.24 |
| T | 8.25±0.32 | 7.39±0.08 | 7.83±0.10 | 7.87±0.06 | 7.52±0.06 | |
| 溶解氧(DO)质量浓度/ (mg·L−1) | CK | 7.53±0.04 | 8.13±0.06 | 7.52±0.08 | 7.58±0.09 | 7.69±0.02 |
| T | 7.59±0.05 | 7.72±0.04 | 7.56±0.04 | 7.54±0.05 | 7.83±0.03 | |
| 电导率/(µS·cm−1) | CK | 447.00±2.65 | 577.33±0.58 | 559.33±7.09 | 547.00±7.21 | 554.00±6.08 |
| T | 442.00±5.29 | 540.67±0.58 | 535.67±5.03 | 530.00±0.00 | 541.33±0.58 | |
表1 养殖池塘水体基本理化指标
Table 1 Physicochemical parameters in the water bodies of the culture ponds
| 水体基本理化指标 | 处理 | 时间/d | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | ||
| 水温(WT)/℃ | CK | 24.50±0.36 | 26.37±0.15 | 31.37±0.15 | 29.47±0.06 | 26.47±0.12 |
| T | 24.60±0.50 | 26.53±0.12 | 31.50±0.36 | 29.30±0.35 | 26.27±0.15 | |
| pH | CK | 8.42±0.44 | 7.06±0.12 | 7.72±0.12 | 7.44±0.33 | 7.00±0.24 |
| T | 8.25±0.32 | 7.39±0.08 | 7.83±0.10 | 7.87±0.06 | 7.52±0.06 | |
| 溶解氧(DO)质量浓度/ (mg·L−1) | CK | 7.53±0.04 | 8.13±0.06 | 7.52±0.08 | 7.58±0.09 | 7.69±0.02 |
| T | 7.59±0.05 | 7.72±0.04 | 7.56±0.04 | 7.54±0.05 | 7.83±0.03 | |
| 电导率/(µS·cm−1) | CK | 447.00±2.65 | 577.33±0.58 | 559.33±7.09 | 547.00±7.21 | 554.00±6.08 |
| T | 442.00±5.29 | 540.67±0.58 | 535.67±5.03 | 530.00±0.00 | 541.33±0.58 | |
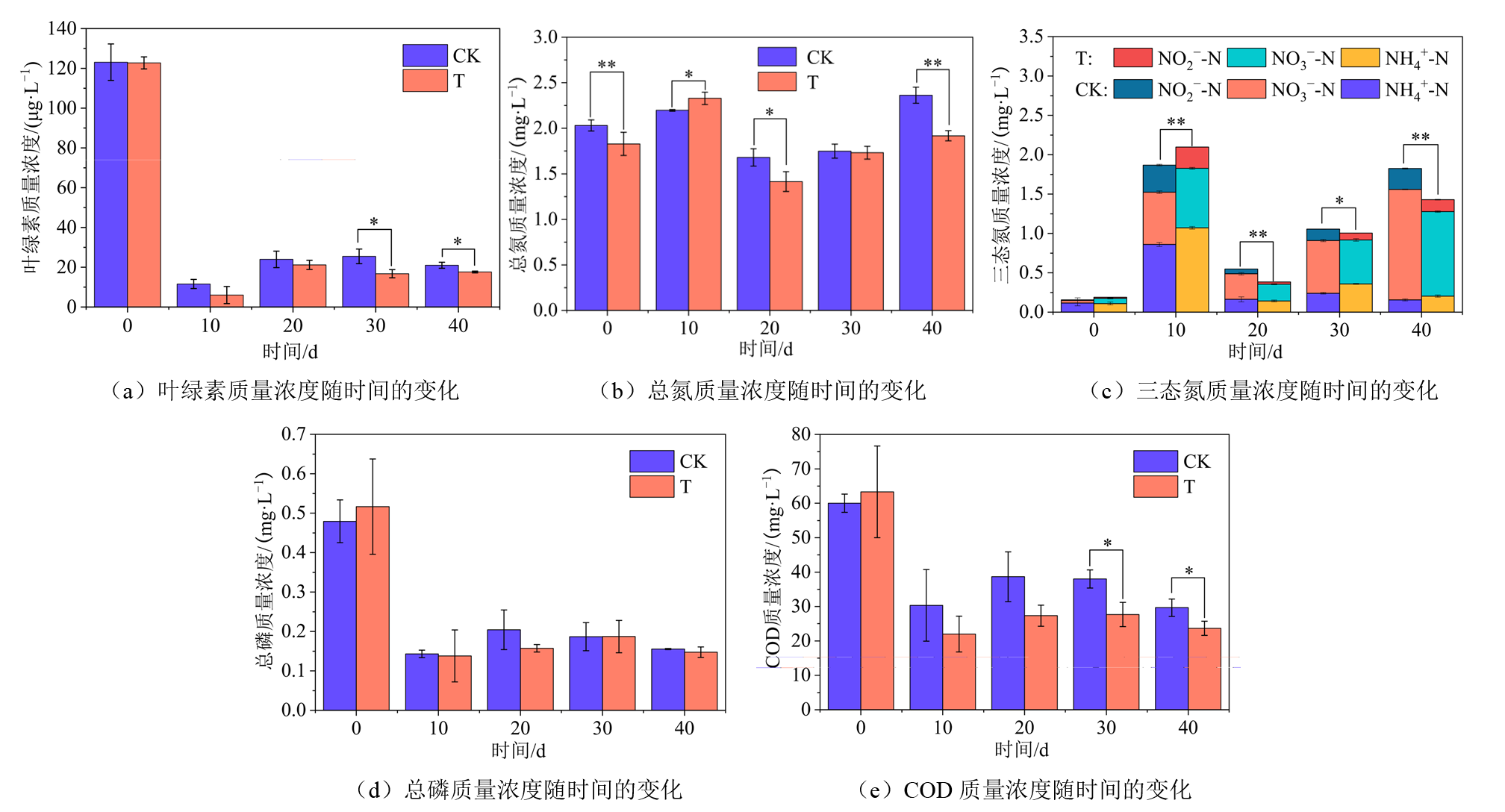
图1 养殖水体中各理化指标质量浓度随时间的变化 图中“*”表示p<0.05,“**”表示p<0.01。下同
Figure 1 Temporal variations of mass concentration of physicochemical parameters in aquaculture water
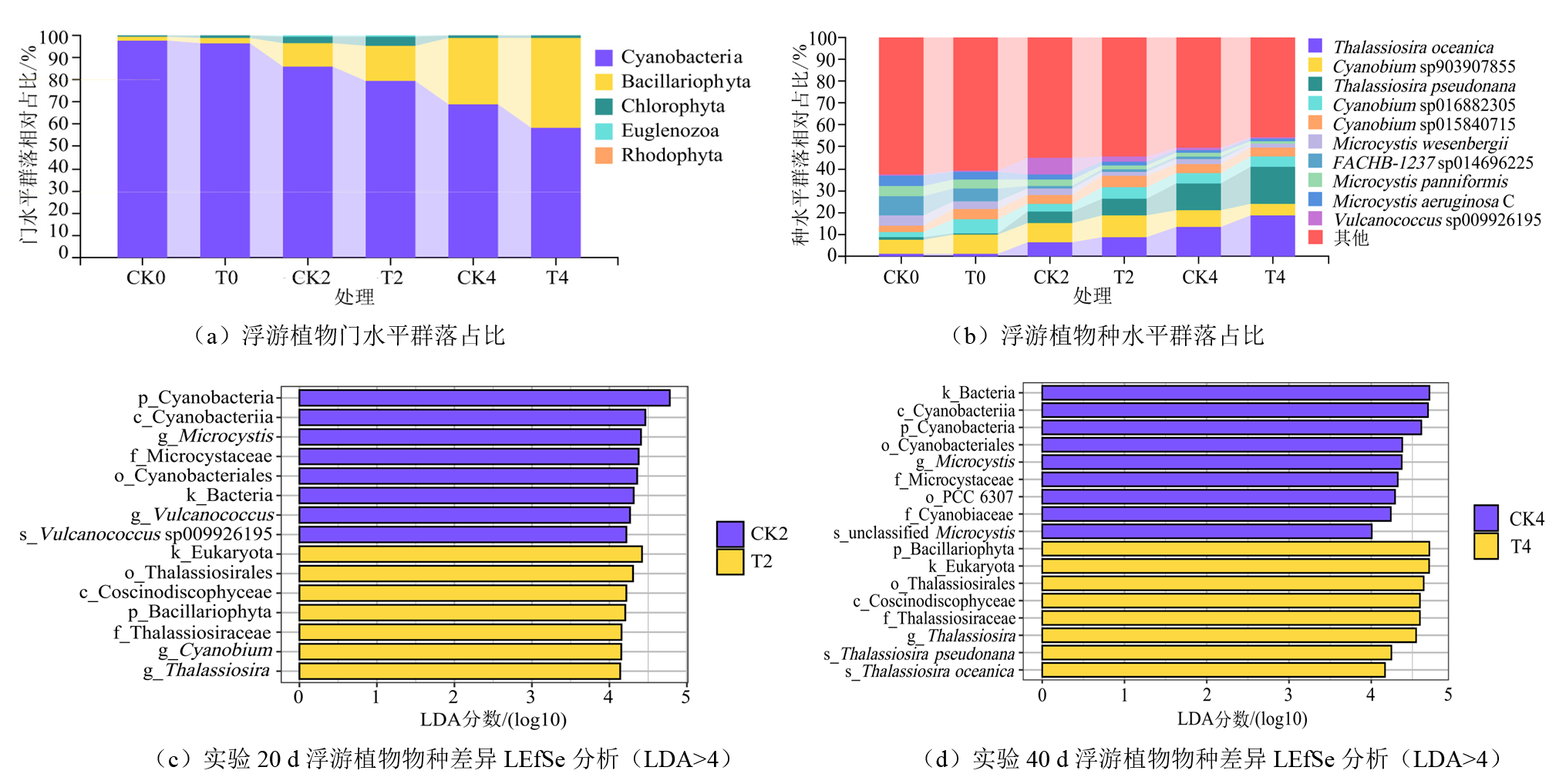
图2 养殖水体中浮游植物门和种水平群落占比及实验20 d和40 d的浮游植物物种差异LEfSe分析 图中前缀k代表界(kindom),p代表门(phylum),c代表纲(class),o代表目(order),f代表科(family),g代表属(genus),s代表种(species)
Figure 2 The composition of phytoplankton communities at the phylum and species level and LEfSe analysis of species differences at 20 and 40 days in the aquaculture water

图3 养殖水体中浮游植物代谢功能的KEGG通路及门水平物种贡献度分析 前缀L1、L2和L3代表KEGG代谢通路数据库中的三级分类体系
Figure 3 KEGG pathway and phylum-level species contribution analysis of metabolic functions in phytoplankton from aquaculture water
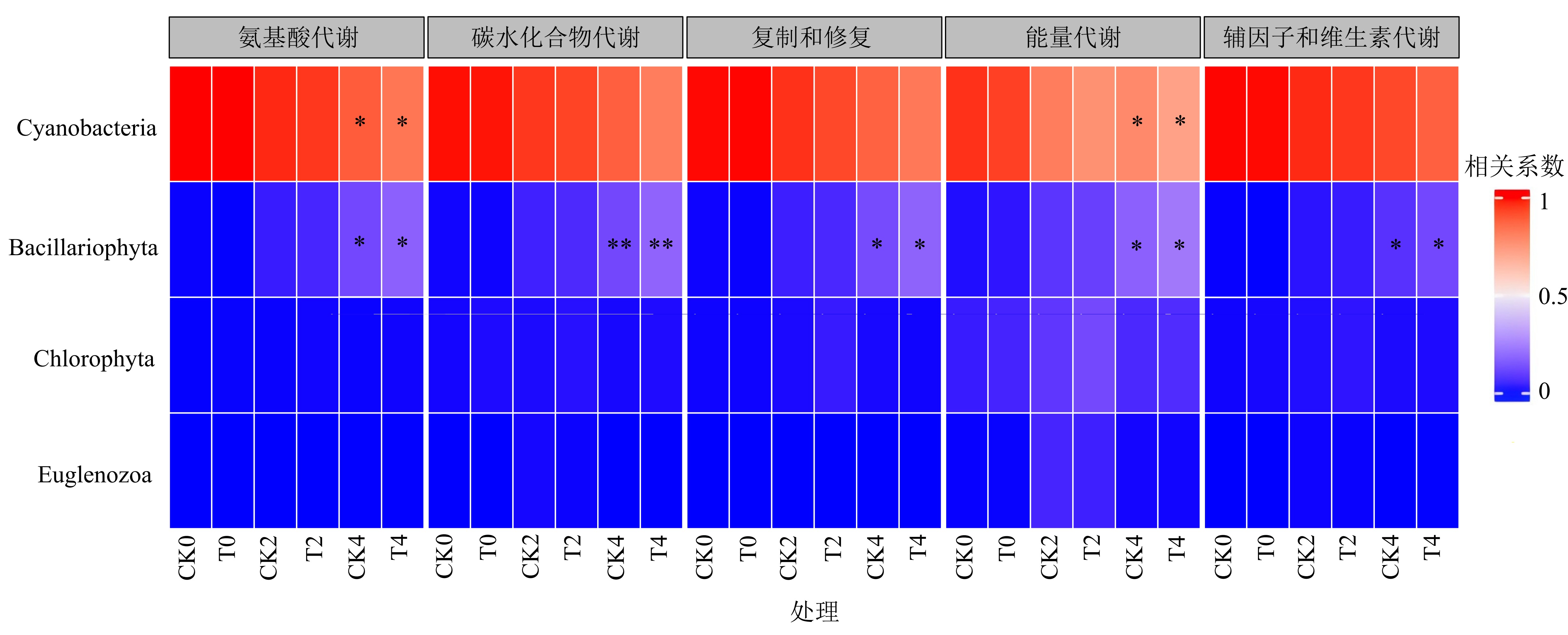
图4 KEGG代谢通路L2分类水平上功能(排名前5)的门水平的物种贡献度热图
Figure 4 Heatmap of phylum-level microbial contributions to the top 5 functional categories in KEGG metabolic pathways at L2 classification level
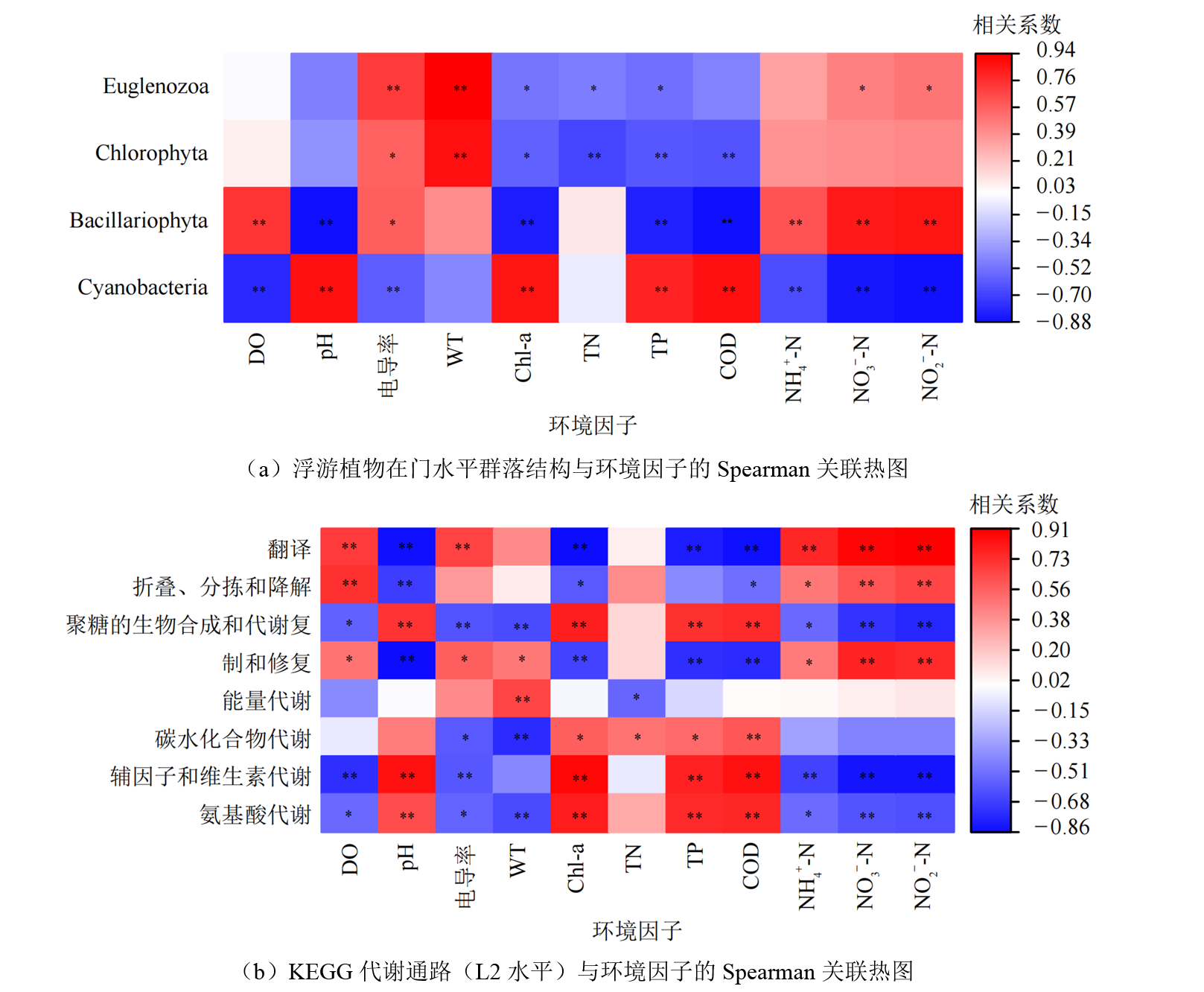
图5 浮游植物在门水平群落结构和KEGG代谢通路(L2水平)与环境因子的Spearman关联热图分析
Figure 5 Spearman correlation heatmap analysis of phytoplankton community structure at the phylum level and KEGG metabolic pathways at L2 level with environmental factors
| [1] |
AGRAWAL S, ACHARYA D, ADHOLEYA A, et al., 2017. Nonribosomal peptides from marine microbes and their antimicrobial and anticancer potential[J]. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 8: 828.
DOI PMID |
| [2] |
BAEK S H, SON M, KIM Y O, et al., 2019. Can algicide (the thiazolidinedione derivative TD49) truly contribute to the restoration of microbial communities?[J]. Environmental Research, 173: 517-527.
DOI PMID |
| [3] | CHEN L F, WANG Y, SHI L L, et al., 2019. Identification of allelochemicals from pomegranate peel and their effects on Microcystis aeruginosa growth[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 26(22): 22389-22399. |
| [4] | DE VARGAS C, AUDIC S, HENRY N, et al., 2015. Eukaryotic plankton diversity in the sunlit ocean[J]. Science, 348(6237): 1261605. |
| [5] | DOWNING T G, MEYER C, GEHRINGER M M, et al., 2005. Microcystin content of Microcystis aeruginosa is modulated by nitrogen uptake rate relative to specific growth rate or carbon fixation rate[J]. Environmental Toxicology, 20(3): 257-262. |
| [6] | EL-BILAWY E H, AL-MANSORI A N A, ALOTIBI F O, et al., 2022. Antiviral and antifungal of Ulva fasciata extract: HPLC analysis of polyphenolic compounds[J]. Sustainability, 14(19): 12799. |
| [7] | FAYED W M A, KHALIL R H, SALLAM G R, et al., 2019. Estimating the effective level of Yucca schidigera extract for improvement of the survival, haematological parameters, immunological responses and Water quality of European seabass juveniles (dicentrarchus labrax)[J]. Aquaculture Reports, 15: 100208. |
| [8] |
GUARDIA T, ROTELLI A E, JUAREZ A O, et al., 2001. Anti-inflammatory properties of plant flavonoids. Effects of rutin, quercetin and hesperidin on adjuvant arthritis in rat[J]. Farmaco, 56(9): 683-687.
DOI PMID |
| [9] | HALSEY K H, JONES B M., 2015. Phytoplankton strategies for photosynthetic energy allocation[J]. Annual Review of Marine Science, 7(1): 265-297. |
| [10] | SANTONJA M, LE ROUZIC B, THIÉBAU G, 2018. Seasonal dependence and functional implications of macrophyte-phytoplankton allelopathic interactions[J]. Freshwater Biology, 63(9): 1161-1172. |
| [11] | YI Y L, LEI Y, YIN Y B, et al., 2012. The antialgal activity of 40 medicinal plants against Microcystis aeruginosa[J]. Journal of Applied Physiology, 24(4): 847-856. |
| [12] | ZHAO G P, HONG Y, LI L H, et al., 2022. Selection and characterization of plant-derived alkaloids with strong antialgal inhibition: Growth inhibition selectivity and inhibitory mechanism[J]. Harmful Algae, 117: 102272. |
| [13] | ZHOU L R, BI Y H, JIANG L H, et al., 2012. Effect of black wattle (Acacia mearnsii) Extract on blue‐Green algal bloom control and plankton structure optimization: A Field Mesocosm Experiment[J]. Water Environment Research, 84(12): 2133-2142. |
| [14] |
ZHOU L, HOU L L, HU Y Y, et al., 2010. Effects of wattle extract on Microcystic aeruginosa growth and the simulated mini fresh water ecosystem-Web of Science Core Collection[J]. Journal of Environmental Biology, 31(6): 1023-1030.
PMID |
| [15] | 曹雪, 孙佳, 杨质楠, 等, 2023. 中草药在水产动物养殖中的研究进展[J]. 饲料研究, 46(24): 133-137. |
| CAO X, SUN J, YANG Z N, et al., 2023. Research progress of Chinese herbal medicine in aquaculture[J]. Feed Research, 46(24): 133-137. | |
| [16] | 陈静, 盖建军, 王晶晶, 等, 2023. 青鱼生态养殖池塘浮游生物群落结构初探[J]. 水产养殖, 44(12): 26-30. |
| CHEN J, GAI J J, WANG J J, et al., 2023. Preliminary study on plankton community structure in ecological aquaculture pond of black carp Hypophthalmichthys molitrix[J]. Journal of Aquaculture, 44(12): 26-30. | |
| [17] | 侯德昌, 张莹莹, 魏文志, 2022. 不同中华鳖养殖模式浮游植物功能群特征及水环境评价[J]. 安徽农业科学, 50(9): 96-99. |
| HOU D C, ZHANG Y Y, WEI W Z, 2022. Phytoplankton community structure and water environment evaluation in different culture modes of Pelodiscus sinensis[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 50(9): 96-99. | |
| [18] | 李宗岩, 尹业师, 2023. 植物提取物抗菌剂耐药性研究进展[J]. 湖南科技学院学报, 44(5): 6-9. |
| LI Z Y, YIN Y S, 2023. Research progress on antimicrobial resistance of plant extracts[J]. Journal of Hunan University of Science and Technology, 44(5): 6-9. | |
| [19] | 刘克奉, 2013. 不同中草药对水体主要理化因子的调控作用[J]. 河北渔业 (11): 10-12, 66. |
| LIU K F, 2013. Regulation effect of different Chinese herbs on main physicochemical factors in water body[J]. Hebei Fisheries (11): 10-12, 66. | |
| [20] | 刘荣军, 梁佳, 赵露, 等, 2023. 植物提取物在水产养殖中的应用[J]. 水产养殖, 44(1): 57-58. |
| LIU R J, LIANG J, ZHAO L, et al., 2023. Application of plant extracts in aquaculture[J]. Journal of Aquaculture, 44(1): 57-58. | |
| [21] | 毛梦哲, 2017. 硅藻定向培育对池塘水质和浮游植物的影响[D]. 上海: 上海海洋大学: 3-4. |
| MAO M Z, 2017. The effects of the oriented cultivation of Bacillariophyta on the water quality and phytoplankton in culture pond[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Ocean University: 3-4. | |
| [22] | 蒲炜佳, 董世鹏, 张东旭, 等, 2022. 三疣梭子蟹池塘综合养殖系统浮游植物群落结构及其与环境因子的关系[J]. 中国水产科学, 29(4): 549-561. |
| PU W J, DONF S P, ZHANG D X, et al., 2022. Community structure of phytoplankton and their relationships with environmental factors within an integrated pond aquaculture system of Portunus trituberculatus[J]. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 29(4): 549-561. | |
| [23] | 钱福根, 闵婕, 钱韧, 2018. 采用植物提取液治理污染河道的试验——以常熟地区水系为例[J]. 净水技术, 37(7): 114-118. |
| QIAN F G, MIN J, QIAN R, 2018. Experiment of applying plant extracts for polluted river remediation: An example of Changshu river system[J]. Water Purification Technology, 37(7): 114-118. | |
| [24] | 钱福根, 闵婕, 钱韧, 等, 2020. 植物提取液治理水产养殖尾水的工程实践[J]. 净水技术, 39(2): 140-145. |
| QIAN F G, MIN J, QIAN R, et al., 2020. Engineering practice of plant extract for aquaculture tail water treatment[J]. Water Purification Technology, 39(2): 140-145. | |
| [25] | 乔玲, 常志强, 李健, 等, 2022. 基于形态学和高通量测序的海水池塘生态养殖系统中浮游植物多样性比较[J]. 渔业科学进展, 43(2): 32-43. |
| QIAO L, CHANG Z Q, LI J, et al., 2022. Comparison of phytoplankton community diversity in the ecological aquaculture system of a marine pond using morphological analysis and high-throughput sequencing[J]. Progress in Fishery Sciences, 43(2): 32-43. | |
| [26] | 魏复盛, 2002. 水和废水监测分析方法[M]. 第4版. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社: 180-183. |
| WEI F S, 2002. Methods for monitoring and analysis of water and wastewater[M]. The fourth edition. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press: 180-183. | |
| [27] | 卫鹏, 毕相东, 戴伟, 等, 2022. 淡水养殖池塘微型和超微型浮游植物的群落结构组成[J]. 大连海洋大学学报, 37(1): 113-119. |
| WEI P, BI X D, DAI W, et al., 2022. Community structure composition of nanophytoplankton and picophytoplankton in freshwater culture ponds[J]. Journal of Dalian Fisheries University, 37(1): 113-119. | |
| [28] | 韦毓, 翁旭东, 于瑾, 等, 2024. 不同养殖模式对鲫鱼 (Carassius auratus) 营养品质及特征风味的影响研究[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 55(1): 243-252. |
| WEI Y, WENG X D, YU J, et al., 2024. Study on the effects of different culture modes on the nutritional quality and characteristic flavor of Carassius auratus[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 55(1): 243-252. | |
| [29] | 吴天浩, 刘劲松, 邓建明, 等, 2019. 大型过水性湖泊——洪泽湖浮游植物群落结构及其水质生物评价[J]. 湖泊科学, 31(2): 440-448. |
| WU T H, LIU J S, LIU J M, et al., 2019. Community structure of phytoplankton and bioassessment of water quality in a large water-carrying lake, Lake Hongze[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 31(2): 440-448. | |
| [30] | 吴振斌, 2016. 大型水生植物对藻类的化感作用[M]. 北京: 科学出版社: 1-8. |
| WU Z B, 2016. Allelopathic effects of large aquatic plants on algae[M]. Beijing: Science Press: 1-8. | |
| [31] | 徐洪凯, 2018. 东海浮游植物藻华爆发期的动态宏蛋白质组学研究[D]. 北京: 中国科学院大学: 4-5. |
| XU H K, 2018. Dynamic metaproteomic study of phytoplankton blooms in the east China sea[D]. Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences: 4-5. | |
| [32] | 徐沙, 2019. 基于宏基因组技术探究甲藻水华生消过程中微生物群落特征及功能代谢变化[D]. 重庆: 西南大学: 49-51. |
| XU S, 2019. Microbial community characteristics and functional metabolic changes during the progress of Dinoflagellates blooming based on Metagenomic technology[D]. Chongqing: Southwest University: 49-51. | |
| [33] | 许歆, 2018. 秦皇岛近海浮游植物群落结构变化及其组学研究[D]. 青岛: 中国科学院大学(中国科学院海洋研究所): 5-6. |
| XU X, 2018. Study on the changes in community structure of phytoplankton and its omic research in the coastal waters of Qinhuangdao[D]. Qingdao: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Institute of Oceanology): 5-6. | |
| [34] | 杨航, 杨志刚, 周俊宇, 等, 2017. 植物提取物在水产养殖中的应用[J]. 饲料研究 (22): 30-33, 38. |
| YANG H, YANG Z G, ZHOU J Y, et al., 2017. Application of plant extracts in aquaculture[J]. Feed Research (22): 30-33, 38. | |
| [35] | 王储, 2022. Luteovulum azotoformans与Chlorella vulgaris联用对鲫鱼的益生作用及养殖水质净化能力研究[D]. 北京: 北京林业大学: 2-3. |
| WANG C, 2022. Study on probiotic effect of Luteovulum azotoformans and Chlorella vulgaris on Crucian carp and its water purification ability[D]. Beijing: Beijing Forestry University: 2-3. | |
| [36] | 张瑞芳, 2023. 养殖池塘蓝藻丰度及影响其竞争优势形成的因素研究[D]. 陕西: 西北农林科技大学: 17-19. |
| ZHANG R F, 2023. Abundance of Cyanobacteria in aquaculture ponds and competitive predominance of blue-green algae with different environmental factors[D]. Shaanxi: Northwest Agriculture & Forestry University: 17-19. | |
| [37] | 赵文, 2015. 水生生物学[M]. 第2版. 北京: 中国农业出版社: 1-3. |
| ZHAO W, 2015. Hydrobiology[M]. The second edition. Beijing: China Agriculture Press: 1-3. | |
| [38] | 中华人民共和国生态环境部, 1989. 渔业水质标准: GB 11607—1989[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社: 1-6. |
| Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China, 1989. Water Quality Standards for Fisheries: GB 11607—1989[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press: 1-6. | |
| [39] | 中华人民共和国生态环境部,国家市场监督管理总局, 2002. 地表水环境质量标准: GB 3838—2002[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社: 1-12. |
| Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China, State Administration for Market Regulation, 2002. Environmental Quality Standards for Surface Water: GB 3838—2002[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press: 1-12. | |
| [40] | 邹国燕, 蔡敏, 周丽, 等, 2022. 一种用于猪舍除臭的方法: 中国, ZL202110276293.6[P]. 2022-03-08 [2024-11-09]. https://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/patent/ChhQYXRlbnROZXdTMjAyNTAzMTgwODIxNTASE0NOMjAyMTEwMjc2MjkzLjZfc3EaCGdldTdiM2No. |
| ZOU G Y, CAI M, ZHOU L, et al., 2022. A method for pig house deodorization: China, ZL202110276293.6[P]. 2022-03-08 [2024-11-09]. https://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/patent/ChhQYXRlbnROZXdTMjAyNTAzMTgwODIxNTASE0NOMjAyMTEwMjc2MjkzLjZfc3EaCGdldTdiM2No. |
| [1] | 李彦林, 陈杨洋, 杨霜溶, 刘菊梅. 植物根系分泌的有机酸对土壤碳氮矿化的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(9): 1362-1371. |
| [2] | 潘家响, 朱明飞, 秦念慈, 肖晶, 刘晨, 李秋华. 贵州高原车田河浮游植物功能群时空特征及水环境质量评价[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(6): 935-945. |
| [3] | 刘泽碧, 毛旭锋, 吴艺, 宋秀华, 于红妍, 金鑫, 杜凯, 谢顺邦. 海湖湿地水体蓝藻水华期浮游生物群落特征及其影响因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(6): 946-957. |
| [4] | 黄倩, 朱时应, 李天顺, 李明燕, 索南措, 普布. 西藏热振国家森林公园土壤原生动物群落沿海拔分布格局及其与环境因子的关联特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(4): 499-508. |
| [5] | 丛鑫, 曹平, 王晓博. 生物炭负载纳米铁活化过硫酸盐去除土壤中的五氯联苯[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(2): 282-290. |
| [6] | 马媛, 田路露, 吕杰, 柳沛, 张旭, 李二阳, 张清航. 天山北坡雪岭云杉森林土壤微生物群落及影响因素研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(1): 1-11. |
| [7] | 姜永伟, 丁振军, 袁俊斌, 张峥, 李杨, 问青春, 王业耀, 金小伟. 辽宁省主要河流底栖动物群落结构及水质评价研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 969-979. |
| [8] | 寇祝, 卿纯, 袁昌果, 李平. 西藏东北部热泉水中硫氧化菌的多样性及分布特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 989-1000. |
| [9] | 胡芳, 刘聚涛, 温春云, 韩柳, 文慧. 抚河流域浮游植物群落结构特征及其水生态状况评价[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 744-755. |
| [10] | 李善家, 王兴敏, 刘海锋, 孙梦格, 雷雨昕. 河西走廊荒漠植物多样性及其对环境因子的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 429-438. |
| [11] | 周佳诚, 宋志斌, 苗芃, 谭路, 唐涛. 柳江不同河网位置大型底栖动物群落特征及其影响因子差异比较研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(10): 1794-1801. |
| [12] | 姜倪皓, 张世浩, 张诗函. 哀牢山紫茎泽兰入侵群落主要物种种间联结及环境解释[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(7): 1370-1382. |
| [13] | 夏开, 邓鹏飞, 马锐豪, 王斐, 温正宇, 徐小牛. 马尾松次生林转换为湿地松和杉木林对土壤细菌群落结构和多样性的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(3): 460-469. |
| [14] | 薛文凯, 朱攀, 德吉, 郭小芳. 纳木措水体可培养丝状真菌优势种的时空特征研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(12): 2331-2340. |
| [15] | 李聪, 吕晶花, 陆梅, 杨志东, 刘攀, 任玉连, 杜凡. 滇东南亚热带土壤细菌群落对植被垂直带变化的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(10): 1971-1983. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
