生态环境学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (2): 282-290.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2024.02.012
收稿日期:2023-10-31
出版日期:2024-02-18
发布日期:2024-04-03
作者简介:丛鑫(1976年生)女,教授,博士,研究方向为土壤环境化学和生态修复。E-mail: congxin1800@163.com
基金资助:
CONG Xin( ), CAO Ping, WANG Xiaobo
), CAO Ping, WANG Xiaobo
Received:2023-10-31
Online:2024-02-18
Published:2024-04-03
摘要:
以污染土壤中检出量较高的PCB118为目标污染物,采用银杏叶提取液绿色合成纳米铁材料(nZVI)、玉米秸秆制备生物炭(BC),将nZVI负载在BC表面合成生物炭负载纳米零价铁复合材料(BC-nZVI),利用制备的BC-nZVI复合材料催化活化过硫酸盐(PS)去除土壤中PCB118。主要探讨了在生物炭负载纳米零价铁活化过硫酸盐体系(BC-nZVI/PS)中复合材料BC-nZVI碳铁比及其投加量、PS浓度、pH值、温度等因素对PCB118去除速率的影响。结果表明,反应时间为24 h时,碳铁比为2꞉1时BC-nZVI反应体系对土壤中PCB118去除效果优于其他3种比例。实验条件下,随着BC-nZVI的投加量由0.002 g增加到0.500 g,PS浓度由0.05 mol·L−1增至0.35 mol·L−1,温度由15 ℃升高到45 ℃,土壤中PCB118的去除率分别增加了32.4%、10.6%及14.7%。随着溶液初始pH值由3升到9,土壤中PCB118的去除率降低了11.4%。单因素实验数据显示,在BC-nZVI的投加量为0.500 g,PS浓度为0.35 mol·L−1,pH值为3,温度为45 ℃的条件下,土壤中PCB118去除效果最佳。为分析不同因素及其交互作用对土壤中PCB118去除率的影响,采用Box-Behnken响应面法设计了三因素三水平试验,建立了PS浓度、温度和pH等3个变量的二次多项式回归模型,得到土壤中PCB118最佳去除条件为:PS浓度0.23 mol·L−1、pH 3.11、温度45 ℃。在此条件下,土壤中的PCB118在BC-nZVI/PS体系中去除率为71.6%。实验验证结果与模型预测值的相对偏差<5%,表明可使用此模型对BC-nZVI/PS体系中PCB118的去除率进行预测。该研究可为土壤中PCB118污染治理提供一些基础数据,为绿色环保修复土壤中有机污染物提供理论参考。
中图分类号:
丛鑫, 曹平, 王晓博. 生物炭负载纳米铁活化过硫酸盐去除土壤中的五氯联苯[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(2): 282-290.
CONG Xin, CAO Ping, WANG Xiaobo. Degradation of Pentachlorobiphenyl in Soil Using Persulfate Activated by Biochar-supported Nano Zero-valent Iron[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2024, 33(2): 282-290.
| 水平 | 实验因素 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| A: PS浓度/(mol·L−1) | B: 温度/℃ | C: pH | |
| −1 | 0.05 | 25 | 1 |
| 0 | 0.20 | 35 | 3 |
| 1 | 0.35 | 45 | 5 |
表1 响应面优化实验因素水平表
Table 1 The factors and levels of response surface optimization test
| 水平 | 实验因素 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| A: PS浓度/(mol·L−1) | B: 温度/℃ | C: pH | |
| −1 | 0.05 | 25 | 1 |
| 0 | 0.20 | 35 | 3 |
| 1 | 0.35 | 45 | 5 |
| 实验序号 | PS浓度/(mol·L−1) | 温度/℃ | pH | 去除率/% | 实验序号 | PS浓度/(mol·L−1) | 温度/℃ | pH | 去除率/% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.05 | 25 | 3 | 20.62 | 10 | 0.20 | 45 | 1 | 56.64 | |
| 2 | 0.35 | 25 | 3 | 45.79 | 11 | 0.20 | 25 | 5 | 38.61 | |
| 3 | 0.05 | 45 | 3 | 50.42 | 12 | 0.20 | 45 | 5 | 58.72 | |
| 4 | 0.35 | 45 | 3 | 61.81 | 13 | 0.20 | 35 | 3 | 59.68 | |
| 5 | 0.05 | 35 | 1 | 24.49 | 14 | 0.20 | 35 | 3 | 59.15 | |
| 6 | 0.35 | 35 | 1 | 36.23 | 15 | 0.20 | 35 | 3 | 58.32 | |
| 7 | 0.05 | 35 | 5 | 18.85 | 16 | 0.20 | 35 | 3 | 60.69 | |
| 8 | 0.35 | 35 | 5 | 46.78 | 17 | 0.20 | 35 | 3 | 60.33 | |
| 9 | 0.20 | 25 | 1 | 32.47 |
表2 响应面实验设计与结果
Table 2 Experiment design and results of response surface
| 实验序号 | PS浓度/(mol·L−1) | 温度/℃ | pH | 去除率/% | 实验序号 | PS浓度/(mol·L−1) | 温度/℃ | pH | 去除率/% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.05 | 25 | 3 | 20.62 | 10 | 0.20 | 45 | 1 | 56.64 | |
| 2 | 0.35 | 25 | 3 | 45.79 | 11 | 0.20 | 25 | 5 | 38.61 | |
| 3 | 0.05 | 45 | 3 | 50.42 | 12 | 0.20 | 45 | 5 | 58.72 | |
| 4 | 0.35 | 45 | 3 | 61.81 | 13 | 0.20 | 35 | 3 | 59.68 | |
| 5 | 0.05 | 35 | 1 | 24.49 | 14 | 0.20 | 35 | 3 | 59.15 | |
| 6 | 0.35 | 35 | 1 | 36.23 | 15 | 0.20 | 35 | 3 | 58.32 | |
| 7 | 0.05 | 35 | 5 | 18.85 | 16 | 0.20 | 35 | 3 | 60.69 | |
| 8 | 0.35 | 35 | 5 | 46.78 | 17 | 0.20 | 35 | 3 | 60.33 | |
| 9 | 0.20 | 25 | 1 | 32.47 |
| 方差来源 | 模型 | A | B | C | AB | AC | BC | 失拟项 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 平方和 | 3645.38 | 726.38 | 1014.75 | 21.55 | 47.47 | 65.53 | 4.12 | 2.87 |
| 自由度 | 9 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 |
| 均方 | 405.04 | 726.38 | 1014.75 | 21.55 | 47.47 | 65.53 | 4.12 | 0.9583 |
| F值 | 440.43 | 789.85 | 1103.42 | 23.43 | 51.62 | 71.25 | 4.48 | 1.08 |
| P值 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.0019 | 0.0002 | <0.0001 | 0.0721 | 0.4538 |
| 显著性 | 极显著 | 极显著 | 极显著 | 极显著 | 极显著 | 极显著 | 不显著 | 不显著 |
表3 回归模型方差分析
Table 3 The variance analysis of regression model
| 方差来源 | 模型 | A | B | C | AB | AC | BC | 失拟项 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 平方和 | 3645.38 | 726.38 | 1014.75 | 21.55 | 47.47 | 65.53 | 4.12 | 2.87 |
| 自由度 | 9 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 |
| 均方 | 405.04 | 726.38 | 1014.75 | 21.55 | 47.47 | 65.53 | 4.12 | 0.9583 |
| F值 | 440.43 | 789.85 | 1103.42 | 23.43 | 51.62 | 71.25 | 4.48 | 1.08 |
| P值 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.0019 | 0.0002 | <0.0001 | 0.0721 | 0.4538 |
| 显著性 | 极显著 | 极显著 | 极显著 | 极显著 | 极显著 | 极显著 | 不显著 | 不显著 |
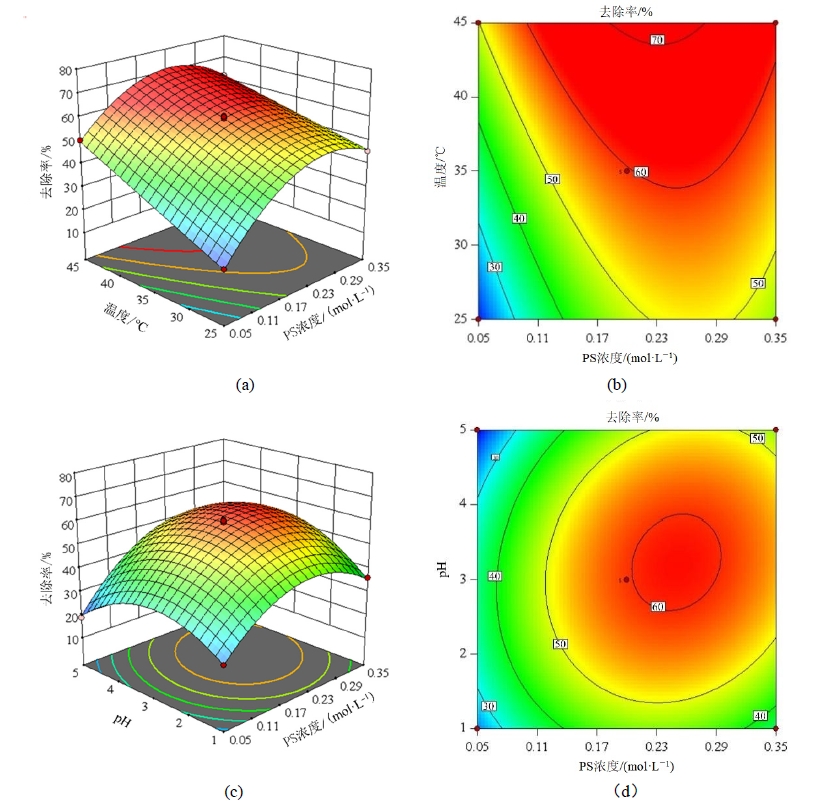
图6 反应温度、PS浓度与pH交互作用对PCB118去除率影响响应曲面及等高线图 左侧为响应面图,右侧为等高线图
Figure 6 Response surface and contour plot of the interaction of reaction temperature, PS concentration, and pH on the removal rate of PCB118
| [1] |
CHEN X Q, MURUGANANTHAN M, ZHANG Y R, 2016. Degradation of p-Nitrophenol by thermally activated persulfate in soil system[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 283: 1357-1365.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
DANISH M, GU X G, LU S G, et al., 2017. Efficient transformation of trichloroethylene activated through sodium percarbonate using heterogeneous zeolite supported nano zero valent iron-copper bimetallic composite[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 308: 396-407.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
DOMINGUEZ C M, RODRIGUEZ V, MONTERO E, et al., 2020. Abatement of dichloromethane using persulfate activated by alkali: A kinetic study[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 241: 116679.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
DONG H R, NING Q, LI L, et al., 2020. A comparative study on the activation of persulfate by bare and surface stabilized nanoscale zero-valent iron for the removal of sulfamethazine[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 230: 115869.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
DU J K, BAO J G, LU C H, et al., 2016. Reductive sequestration of chromate by hierarchical FeS@Fe(0) particles[J]. Water Research, 102: 73-81.
DOI PMID |
| [6] |
FU H C, MA S L, ZHAO P, et al., 2019. Activation of peroxymonosulfate by graphitized hierarchical porous biochar and MnFe2O4 magnetic nanoarchitecture for organic pollutants degradation: Structure dependence and mechanism[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 360: 157-170.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
GUANG Y H, MA J, LI X C, et al., 2011. Influence of pH on the formation of sulfate and hydroxyl radicals in the UV/peroxymonosulfate system[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 45(21): 9308-9314.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
GUO Y G, HUANG W L, CHEN B, et al., 2017. Removal of tetracycline from aqueous solution by MCM-41-zeolite A loaded nano zero valent iron: synthesis, characteristic, adsorption performance and mechanism[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 339: 22-32.
DOI PMID |
| [9] |
HUANG Y H, ZHANG T C, 2006. Reduction of nitrobenzene and formation of corrosion coatings in zerovalent iron systems[J]. Water Research, 40(16): 3075-3082.
DOI PMID |
| [10] |
JI Y F, FERRONATO C, SALVADOR A, et al., 2014. Degradation of ciprofloxacin and sulfamethoxazole by ferrous-activated persulfate: Implications for remediation of groundwater contaminated by antibiotics[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 472: 800-808.
DOI URL |
| [11] | KONG F L, WANG J R, HOU W H, et al., 2023. Influence of modified biochar supported sulfidation of nano-zero-valent-iron (S-nZVI/BC) on nitrate removal and greenhouse gas emission in constructed wetland[J]. Joumal of Environmental Sciences, 125: 568-581. |
| [12] | LE C, WU J H, LI P, et al., 2011. Decolorization of anthraquinone dye reactive blue 19 by the combination of persulfate and zero-valent iron[J]. Water Science & Technology, 64(3): 754-759. |
| [13] |
LI H H, ZHU F, HE S Y, 2019. The degradation of decabromodiphenyl ether in the e-waste site by biochar supported nanoscale zero-valent iron/ persulfate[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 183: 109540.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
NIE M H, YAN C X, LI M, et al., 2015. Degradation of chloramphenicol by persulfate activated by Fe2+ and zerovalent iron[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 279: 507-515.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
OH S Y, KIM H W, PARK J M, et al., 2009. Oxidation of polyvinyl alcohol by persulfate activated with heat, Fe2+, and zero-valent iron[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 168(1): 346-351.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
OUYANG D, YAN J C, QIAN L B, et al., 2017. Degradation of 1,4-dioxane by biochar supported nano magnetite particles activating persulfate[J]. Chemosphere, 184: 609-617.
DOI PMID |
| [17] |
PENG H J, ZHANG W, LIU L, et al., 2017. Degradation performance and mechanism of decabromodiphenyl ether (BDE209) by ferrous- activated persulfate in spiked soil[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 307: 750-755.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
SU H J, FANG Z Q, TSANG P E, et al., 2016. Stabilisation of nanoscale zero-valent iron with biochar for enhanced transport and in-situ remediation of hexavalent chromium in soil[J]. Environmental Pollution, 214: 94-100.
DOI PMID |
| [19] | WANG B, ZHU C, AI D, et al., 2021. Activation of persulfate by green nano-zero-valent iron-loaded biochar for the removal of p-nitrophenol: Performance, mechanism and variables effects[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 417(1): 26106. |
| [20] |
WENG X L, OWENS G, CHEN Z L, 2020. Synergetic adsorption and Fenton-like oxidation for simultaneous removal of ofloxacin and enrofloxacin using green synthesized Fe NPs[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 382: 122871.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
XIA X H, ZHU F Y, LI J N, et al., 2020. A Review Study on Sulfate- Radical-Based Advanced Oxidation Processes for Domestic/Industrial Wastewater Treatment: Degradation, Efficiency, and Mechanism[J]. Frontiers in Chemistry, 8: 592056.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
XU H B, ZHAO D Y, LI Y J, et al., 2014. Enhanced degradation of ortho-nitrochlorobenzene by the combined system of zero-valent iron reduction and persulfate oxidation in soil[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 21: 5132-5140.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
XU J, WANG X R, PAN F, et al., 2018. Synthesis of the mesoporous carbon-nano-zero-valent iron composite and activation of sulfite for removal of organic pollutants[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 353: 542-549.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
XUE H H, GAO S Y, ZHENG N, et al., 2019. Degradation of norfloxacin in aqueous solution with UV/peroxydisulfate[J]. Water Science and Technology, 79(12): 2387-2394.
DOI PMID |
| [25] |
YEN C H, CHEN K F, KAO C M, et al., 2011. Application of persulfate to remediate petroleum hydrocarbon-contaminated soil: Feasibility and comparison with common oxidants[J]. Journal of hazardous materials, 186(2-3): 2097-2012.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
ZHU F, WU Y Y, LIANG Y K et al., 2020. Degradation mechanism of norfloxacin in water using persulfate activated by BC@nZVI/Ni[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 389: 124276.
DOI URL |
| [27] | 昌盛, 白云松, 涂响, 等, 2022. 北江中上游地表水和沉积物中PAHs和PCBs污染特征和风险评估[J]. 环境科学, 43(12): 5534-5546. |
| CHANG S, BAI Y S, TU X, et al., 2022. Pollution characteristics and risk assessment of PAHs and PCBs in surface water and sediments in middle and upper reaches of Beijing River[J]. Environmental Science, 43(12): 5534-5546. | |
| [28] | 黄开友, 申英杰, 王晓岩, 等, 2020. 生物炭负载纳米零价铁制备及修复六价铬污染土壤技术研究进展[J]. 环境工程, 38(11): 203-210. |
| HUANG Y K, SHEN Y J, WANG X Y, et al., 2020. Review on preparation of bio-carbon loaded nano zero-valent iron and its application in remediating Cr(Ⅵ)-contaminated soil[J]. Environmental Engineering, 38(11): 203-210. | |
| [29] | 李丹琼, 2023. 生物炭负载纳米零价铁活化过硫酸盐降解水中菲的模拟研究[D]. 北京: 中国矿业大学. |
| LI D Q, 2022. Simulation study on degradation of phenanthrene in groundwater by persulfate activated with biochar-supported nano zero-valent iron[D]. Beijing: China University of Mining and Technology. | |
| [30] | 李璐玮, 祝方, 马少云, 等, 2017. 响应面分析法优化纳米零价铁铜双金属修复土壤浸提液中Cr(Ⅵ)[J]. 环境工程学报, 11(1): 608-612. |
| LI L W, ZHU F, MA S Y, et al., 2017. Optimization of remediation of Cr(Ⅵ) contaminated soil leachate by nano-zero valent iron/copper by response surface methodological analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 11(1): 608-612. | |
| [31] | 李永涛, 罗进, 岳东, 2017. 热活化过硫酸盐氧化修复柴油污染土壤[J]. 环境污染与防治, 39(10): 1143-1146. |
| LI Y T, LUO J, YUE D, 2017. Thermo activated persulfate oxidation for remediation of diesel oil contaminated soil[J]. Environmental Pollution and Control, 39(10):1143-1146. | |
| [32] | 刘勇, 2018. 桉树叶提取液绿色合成纳米铁材料及水中Cr(Ⅵ)的去除研究[D]. 福州: 福建师范大学. |
| LIU Y, 2018. Green synthesis of iron-based nanoparticles by eucalyptus leaf and used to remove Cr(Ⅵ) from aqueous solution[D]. Fuzhou: Fujian Normal University. | |
| [33] | 宁沁, 2020. 表面改性纳米零价铁在不同反应体系中去除有机污染物的效能与机制研究[D]. 长沙: 湖南大学. |
| NING Q, 2020. Efficiency and mechanisms of surface-modified nanoscale zero-valent iron for the removal of organic pollutants in different reaction systems[D]. Changsha: Hunan University. | |
| [34] | 宋艳, 林道辉, 2022. 过硫酸盐对电动-铁/碳复合材料联合修复多氯联苯污染土壤的强化作用[J]. 环境科学学报, 42(5): 435-443. |
| SONG Y, LIN D H, 2022. The enhancement of persulfate on the electrokinetic-iron/carbon composite co-remediation of PCBs- contaminated soil[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 42(5): 435-443. | |
| [35] | 宿程远, 李伟光, 刘兴哲, 等, 2013. 响应曲面法优化制备改性海泡石负载纳米铁材料的试验研究[J]. 环境科学学报, 33(4): 985-990. |
| SU C Y, LI W G, LIU X Z, et al., 2013. Optimal preparation conditions of sepiolite-supported nanoscale iron using response surface methodology[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 33(4): 985-990. | |
| [36] | 魏海江, 杨兴伦, 叶茂, 等, 2014. 活化过硫酸钠氧化法修复DDTs污染场地土壤研究[J]. 土壤, 46(3): 504-511. |
| WEI H J, YANG X L, YE M, et al., 2014. Application of activated persulfate oxidation method in degradating DDT in field contaminated soil[J]. Soils, 46(3): 504-511. | |
| [37] | 文勤亮, 张瀚文, 许海波, 等, 2014. 零价铁还原-过硫酸盐氧化联合降解土壤中对硝基氯苯的研究[J]. 南京农业大学学报, 37(6): 111-118. |
| WEN Q L, ZHANG H W, XU H B, et al., 2014. Degradation of p-nigtrochlorobenzene in soil by zero-valent iron activated persulfate[J]. Journal of Nanjing Agricultural University, 37(6): 111-118. | |
| [38] | 张羽, 高春阳, 陈昌照, 等, 2019. 零价铁活化过硫酸钠体系降解污染土壤中的多环芳烃[J]. 环境工程学报, 13(4): 955-962. |
| ZHANG Y, GAO C Y, CHEN C Z, et al., 2019. Degradation of PAHs in contaminated soil by zero valent iron activated sodium persulfate system[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 13(4): 955-962. | |
| [39] | 张志, 2010. 中国大气和土壤中多氯联苯空间分布特征及规律研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学. |
| ZHANG Z, 2010. Polychlorinated biphenyls in Chinese air and surface soil: Spatial distribution characteristics and their inherent causes[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology. |
| [1] | 李高帆, 徐文卓, 卫昊明, 晏再生, 尤佳, 江和龙, 黄娟. 三维多孔生物炭吸附剂的制备及其对菲的吸附行为[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(2): 261-271. |
| [2] | 赵维彬, 唐丽, 王松, 刘玲玲, 王树凤, 肖江, 陈光才. 两种生物炭对滨海盐碱土的改良效果[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 678-686. |
| [3] | 李卓轩, 彭自然, 何文辉, 卫瑞璐, 高琳茜. 羊粪炭对水体氮磷吸附条件的响应面优化及吸附机理研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(12): 2216-2227. |
| [4] | 赵丹丹, 李文健, 江丽霞, 单锐, 陈德珍, 袁浩然, 陈勇. 生物炭基光催化剂的制备及其降解废水中的有机污染物研究进展[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(11): 2019-2029. |
| [5] | 苏丹, 罗桥冰, 董昱杉, 杨彩霞, 王鑫. 混合型生物炭对寒冷地区PAHs污染土壤微生物修复的强化作用[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(11): 1942-1951. |
| [6] | 陈桂红. 硫和硅掺杂生物炭对镉污染土壤的修复研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(10): 1854-1860. |
| [7] | 游宏建, 张文文, 兰正芳, 马兰, 张宝娣, 穆晓坤, 李文慧, 曹云娥. 蚯蚓原位堆肥与生物炭对黄瓜根结线虫及根际微生物的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 99-109. |
| [8] | 李晓晖, 艾仙斌, 李亮, 王玺洋, 辛在军, 孙小艳. 新型改性稻壳生物炭材料对镉污染土壤钝化效果的研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(9): 1901-1908. |
| [9] | 房献宝, 张智钧, 赖阳晴, 叶脉, 刁增辉. 新型污泥生物炭对土壤重金属Cr和Cd的修复研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1647-1656. |
| [10] | 陶玲, 黄磊, 周怡蕾, 李中兴, 任珺. 污泥-凹凸棒石共热解生物炭对矿区土壤重金属生物有效性和环境风险的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1637-1646. |
| [11] | 钱莲文, 余甜甜, 梁旭军, 王义祥, 陈永山. 茶园土壤酸化改良中生物炭应用5 a后的稳定性研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(7): 1442-1447. |
| [12] | 张慧琦, 李子忠, 秦艳. 玉米秸秆生物炭用量对砂土孔隙和持水性的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(6): 1272-1277. |
| [13] | 邓晓, 武春媛, 杨桂生, 李怡, 李勤奋. 椰壳生物炭对海南滨海土壤的改良效果[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 723-731. |
| [14] | 程文远, 李法云, 吕建华, 吝美霞, 王玮. 碱改性向日葵秸秆生物炭对多环芳烃菲吸附特性研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 824-834. |
| [15] | 魏岚, 黄连喜, 李翔, 王泽煌, 陈伟盛, 黄庆, 黄玉芬, 刘忠珍. 生物炭基质可显著地促进香蕉幼苗生长[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 732-739. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
