生态环境学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (5): 989-1000.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2023.05.016
寇祝1,2( ), 卿纯1,2, 袁昌果1,2, 李平1,2,*(
), 卿纯1,2, 袁昌果1,2, 李平1,2,*( )
)
收稿日期:2023-02-27
出版日期:2023-05-18
发布日期:2023-08-09
通讯作者:
*李平(1975年生),女,研究员,主要从事与环境地质成因的砷、硫、铁循环密切相关的微生物群落结构和功能及其生物地球化学方面的研究。E-mail: pli@cug.edu.cn作者简介:寇祝(1997年生),女,硕士研究生,主要从事环境微生物方面的研究。E-mail: kouzhu_kz@163.com
基金资助:
KOU Zhu1,2( ), QING Chun1,2, YUAN Changguo1,2, LI Ping1,2,*(
), QING Chun1,2, YUAN Changguo1,2, LI Ping1,2,*( )
)
Received:2023-02-27
Online:2023-05-18
Published:2023-08-09
摘要:
热泉中存在大量的硫氧化菌,而西藏东北部丰富的热泉资源中硫氧化菌的相关研究较少。为探究西藏东北部热泉水中不同类型硫氧化菌(Sulfur-Oxidizing Bacteria,SOB)的多样性、群落结构及其分布特征,采集西藏东北部5个地热区总共13个热泉的地球化学及微生物样品,构建硫氧化基因dsrA和soxB的功能基因克隆文库、qPCR定量分析dsrA和soxB基因丰度,结合水化参数对比分析热泉水中dsrA型SOB和soxB型SOB的群落结构及其分布特征的差异。结果表明,西藏东北部热泉水中的硫氧化菌主要为β变形菌纲(Betaproteobacteria)、α变形菌纲(Alphaproteobacteria)、γ变形菌纲(Gammaproteobacteria)和嗜氢菌纲(Hydrogenophilalia),其中dsrA型SOB和soxB型SOB的优势类群在纲水平上均为Betaproteobacteria,但目水平上则存在差异,即soxB型SOB优势菌目为亚硝化单胞菌目(Nitrosomonadales)(30.0%-91.7%);dsrA型SOB优势菌目为红环菌目(Rhodocyclales)(33.3%-96.0%)。冗余分析(redundancy analysis,RDA)表明,SO42-、S2-、HCO3-、pH、温度等是影响硫氧化菌群落分布的关键环境因子。soxB基因相对丰度主要与SO42-浓度、氧化还原电位(Oxidation-Reduction Potential,ORP)以及S2-浓度相关,dsrA基因相对丰度受总砷(AsT)浓度和HCO3-浓度影响较大。这些结果表明,soxB基因型SOB主要分布于偏氧化环境,而dsrA基因型SOB主要分布于砷浓度、碱度相对偏高的热泉。该研究进一步完善了关于西藏热泉水环境中SOB多样性和分布规律的认识,促进了对热泉硫的生物地球化学循环的理解。
中图分类号:
寇祝, 卿纯, 袁昌果, 李平. 西藏东北部热泉水中硫氧化菌的多样性及分布特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 989-1000.
KOU Zhu, QING Chun, YUAN Changguo, LI Ping. Diversity and Distribution of Sulfur Oxidizing Bacteria in Hot Springs of Northeast Tibet, China[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(5): 989-1000.
| 采样点 | 温度 t/℃ | pH | 氧化还原电位 ORP/mV | ρ(五价砷As5+)/ (µg·L-1) | ρ(总砷AsT)/ (µg·L-1) | ρ(硫酸根SO42-)/ (mg·L-1) | ρ(硫离子S2-)/ (mg·L-1) | ρ(总铁FeT)/ (mg·L-1) | ρ(碳酸氢根HCO3-)/ (mg·L-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DB1 | 56.0±0.1e1) | 7.19±0.10g | -253.4±0.3g | 8331.27±2.02b | 8331.27±2.02b | 615.1±1.5c | 1.92±0.03e | 0.010±0.006h | 2221.08±1.35a |
| DB41 | 69.8±0.2a | 7.27±0.15e | -301.0±0.4j | 9298.58±1.08a | 9298.58±1.08a | 643.3±0.9a | 1.55±0.04j | 0.057±0.025g | ND |
| DB45 | 37.7±0.1i | 8.37±0.01a | -105.8±0.5b | 2891.80±1.15f | 2891.80±1.15g | 455.6±2.1h | 1.52±0.01k | ND2) | 1763.48±1.95c |
| DB5 | 51.4±0.1f | 7.21±0.15fg | -157.5±0.8e | 1279.50±1.37h | 6053.57±1.10d | 557.3±1.4f | 2.00±0.03d | 0.186±0.002e | 1434.05±1.11d |
| DB6 | 50.2±0.1g | 7.01±0.01j | -307.3±0.5k | 7415.97±1.54c | 7415.97±1.54c | 604.2±0.9d | 1.76±0.02g | 0.144±0.002f | 1385.16±1.83e |
| DB7 | 36.7±0.2j | 7.35±0.02d | -126.6±0.3d | 2331.15±1.06g | 2331.15±1.06h | 536.1±1.8g | 1.62±0.02i | 0.495±0.003c | 2105.17±1.33b |
| DB8 | 28.5±0.2l | 8.01±0.01b | -109.9±0.3c | 4211.16±2.22d | 4211.16±2.22e | 578.1±1.4e | 1.67±0.03h | 0.200±0.002d | 1113.62±1.99h |
| DB10 | 35.0±0.1k | 7.05±0.04i | -229.5±0.4f | 3445.68±0.97e | 3445.68±0.97f | 47.7±1.0l | 2.08±0.02c | 0.144±0.003f | 1354.56±1.93f |
| ZM1 | 69.2±0.1b | 7.11±0.03h | -301.3±0.4j | 24.57±2.32k | 29.27±2.33l | 54.4±1.1k | 2.56±0.02a | 0.495±0.003c | 1113.60±1.71h |
| ZM2 | 61.0±0.0d | 7.66±0.03c | -277.3±0.8h | ND | ND | 31.7±1.2m | 2.16±0.03b | 0.200±0.001d | 988.50±2.28j |
| BDW | 38.2±0.1h | 6.59±0.01k | -45.5±0.3a | 0.00±0.00l | 43.17±2.08k | 620.7±1.3b | 0.80±0.04l | 3.315±0.003b | 1025.11±1.55i |
| QS | 66.0±0.0c | 7.23±0.01f | -282.5±0.4i | 235.89±2.00j | 235.89±2.00j | 125.4±1.5i | 1.82±0.02f | 0.183±0.002e | 1189.93±0.87g |
| GN | 25.0±0.1m | 7.07±0.01i | ND | 346.66±1.51i | 346.66±1.51i | 109.6±1.8j | ND | 4.294±0.005a | ND |
表1 采样点主要地球化学参数
Table 1 Main geochemical parameters of hot spring water in Tibet
| 采样点 | 温度 t/℃ | pH | 氧化还原电位 ORP/mV | ρ(五价砷As5+)/ (µg·L-1) | ρ(总砷AsT)/ (µg·L-1) | ρ(硫酸根SO42-)/ (mg·L-1) | ρ(硫离子S2-)/ (mg·L-1) | ρ(总铁FeT)/ (mg·L-1) | ρ(碳酸氢根HCO3-)/ (mg·L-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DB1 | 56.0±0.1e1) | 7.19±0.10g | -253.4±0.3g | 8331.27±2.02b | 8331.27±2.02b | 615.1±1.5c | 1.92±0.03e | 0.010±0.006h | 2221.08±1.35a |
| DB41 | 69.8±0.2a | 7.27±0.15e | -301.0±0.4j | 9298.58±1.08a | 9298.58±1.08a | 643.3±0.9a | 1.55±0.04j | 0.057±0.025g | ND |
| DB45 | 37.7±0.1i | 8.37±0.01a | -105.8±0.5b | 2891.80±1.15f | 2891.80±1.15g | 455.6±2.1h | 1.52±0.01k | ND2) | 1763.48±1.95c |
| DB5 | 51.4±0.1f | 7.21±0.15fg | -157.5±0.8e | 1279.50±1.37h | 6053.57±1.10d | 557.3±1.4f | 2.00±0.03d | 0.186±0.002e | 1434.05±1.11d |
| DB6 | 50.2±0.1g | 7.01±0.01j | -307.3±0.5k | 7415.97±1.54c | 7415.97±1.54c | 604.2±0.9d | 1.76±0.02g | 0.144±0.002f | 1385.16±1.83e |
| DB7 | 36.7±0.2j | 7.35±0.02d | -126.6±0.3d | 2331.15±1.06g | 2331.15±1.06h | 536.1±1.8g | 1.62±0.02i | 0.495±0.003c | 2105.17±1.33b |
| DB8 | 28.5±0.2l | 8.01±0.01b | -109.9±0.3c | 4211.16±2.22d | 4211.16±2.22e | 578.1±1.4e | 1.67±0.03h | 0.200±0.002d | 1113.62±1.99h |
| DB10 | 35.0±0.1k | 7.05±0.04i | -229.5±0.4f | 3445.68±0.97e | 3445.68±0.97f | 47.7±1.0l | 2.08±0.02c | 0.144±0.003f | 1354.56±1.93f |
| ZM1 | 69.2±0.1b | 7.11±0.03h | -301.3±0.4j | 24.57±2.32k | 29.27±2.33l | 54.4±1.1k | 2.56±0.02a | 0.495±0.003c | 1113.60±1.71h |
| ZM2 | 61.0±0.0d | 7.66±0.03c | -277.3±0.8h | ND | ND | 31.7±1.2m | 2.16±0.03b | 0.200±0.001d | 988.50±2.28j |
| BDW | 38.2±0.1h | 6.59±0.01k | -45.5±0.3a | 0.00±0.00l | 43.17±2.08k | 620.7±1.3b | 0.80±0.04l | 3.315±0.003b | 1025.11±1.55i |
| QS | 66.0±0.0c | 7.23±0.01f | -282.5±0.4i | 235.89±2.00j | 235.89±2.00j | 125.4±1.5i | 1.82±0.02f | 0.183±0.002e | 1189.93±0.87g |
| GN | 25.0±0.1m | 7.07±0.01i | ND | 346.66±1.51i | 346.66±1.51i | 109.6±1.8j | ND | 4.294±0.005a | ND |
| 采样点 | 序列数 | OTU数 | 覆盖度/ % | Chao 1 指数 | Shannon指数 | Simpson_ 1-D指数 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DB1 | 25 | 4 | 96 | 4 | 1.4 | 0.5 |
| DB45 | 16 | 5 | 94 | 5 | 2.1 | 0.7 |
| DB5 | 23 | 5 | 96 | 5 | 2.0 | 0.7 |
| DB6 | 25 | 3 | 96 | 3 | 1.0 | 0.4 |
| DB7 | 22 | 6 | 95 | 6 | 2.4 | 0.8 |
| DB8 | 17 | 4 | 100 | 4 | 1.9 | 0.7 |
| DB10 | 29 | 4 | 93 | 5 | 1.2 | 0.5 |
| BDW | 23 | 4 | 95 | 4 | 1.2 | 0.4 |
| QS | 27 | 5 | 92 | 6 | 1.6 | 0.6 |
| GN | 20 | 7 | 95 | 7 | 2.6 | 0.8 |
表2 硫氧化基因dsrA克隆文库的多样性指数
Table 2 Diversity indices of dsrA gene clone libraries
| 采样点 | 序列数 | OTU数 | 覆盖度/ % | Chao 1 指数 | Shannon指数 | Simpson_ 1-D指数 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DB1 | 25 | 4 | 96 | 4 | 1.4 | 0.5 |
| DB45 | 16 | 5 | 94 | 5 | 2.1 | 0.7 |
| DB5 | 23 | 5 | 96 | 5 | 2.0 | 0.7 |
| DB6 | 25 | 3 | 96 | 3 | 1.0 | 0.4 |
| DB7 | 22 | 6 | 95 | 6 | 2.4 | 0.8 |
| DB8 | 17 | 4 | 100 | 4 | 1.9 | 0.7 |
| DB10 | 29 | 4 | 93 | 5 | 1.2 | 0.5 |
| BDW | 23 | 4 | 95 | 4 | 1.2 | 0.4 |
| QS | 27 | 5 | 92 | 6 | 1.6 | 0.6 |
| GN | 20 | 7 | 95 | 7 | 2.6 | 0.8 |
| 采样点 | 序列数 | OTU数 | 覆盖度/ % | Chao 1指数 | Shannon指数 | Simpson_ 1-D指数 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DB1 | 20 | 3 | 95 | 3.0 | 1.1 | 0.4 |
| DB41 | 41 | 8 | 95 | 12.0 | 2.9 | 0.8 |
| DB5 | 41 | 5 | 97 | 5.5 | 1.9 | 0.7 |
| DB6 | 40 | 8 | 95 | 9.0 | 2.3 | 0.7 |
| DB7 | 37 | 7 | 94 | 8.0 | 2.2 | 0.7 |
| DB8 | 28 | 9 | 93 | 10.0 | 2.9 | 0.8 |
| DB10 | 38 | 6 | 95 | 7.0 | 1.6 | 0.5 |
| ZM1 | 25 | 7 | 92 | 6.5 | 2.2 | 0.7 |
| ZM2 | 24 | 4 | 92 | 5.0 | 0.9 | 0.3 |
| BDW | 20 | 4 | 95 | 4.5 | 1.5 | 0.6 |
表3 硫氧化基因soxB克隆文库的多样性指数
Table 3 Diversity indices of soxB gene clone libraries
| 采样点 | 序列数 | OTU数 | 覆盖度/ % | Chao 1指数 | Shannon指数 | Simpson_ 1-D指数 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DB1 | 20 | 3 | 95 | 3.0 | 1.1 | 0.4 |
| DB41 | 41 | 8 | 95 | 12.0 | 2.9 | 0.8 |
| DB5 | 41 | 5 | 97 | 5.5 | 1.9 | 0.7 |
| DB6 | 40 | 8 | 95 | 9.0 | 2.3 | 0.7 |
| DB7 | 37 | 7 | 94 | 8.0 | 2.2 | 0.7 |
| DB8 | 28 | 9 | 93 | 10.0 | 2.9 | 0.8 |
| DB10 | 38 | 6 | 95 | 7.0 | 1.6 | 0.5 |
| ZM1 | 25 | 7 | 92 | 6.5 | 2.2 | 0.7 |
| ZM2 | 24 | 4 | 92 | 5.0 | 0.9 | 0.3 |
| BDW | 20 | 4 | 95 | 4.5 | 1.5 | 0.6 |
| 环境 因子 | Chao1指数 | Shannon指数 | Simpson_1-D指数 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| r | P | r | P | r | P | |||
| pH | 0.244 | 0.497 | 0.591 | 0.072 | 0.642 | 0.045 | ||
| ORP | 0.280 | 0.432 | 0.289 | 0.418 | 0.327 | 0.356 | ||
| As5+ | -0.476 | 0.165 | -0.154 | 0.671 | -0.099 | 0.786 | ||
| T | -0.500 | 0.141 | -0.474 | 0.166 | -0.543 | 0.105 | ||
| AsT | -0.530 | 0.115 | -0.098 | 0.787 | -0.105 | 0.773 | ||
| SO42- | -0.854 | 0.002 | -0.455 | 0.186 | -0.451 | 0.191 | ||
| S2- | -0.177 | 0.625 | -0.302 | 0.397 | -0.358 | 0.310 | ||
| FeT | 0.468 | 0.173 | 0.457 | 0.184 | 0.433 | 0.211 | ||
| HCO3- | -0.146 | 0.687 | 0.068 | 0.853 | 0.012 | 0.973 | ||
表4 环境因子与dsrA基因α多样性指数相关性分析
Table 4 Correlation analysis between environmental factors and alpha diversity index of dsrA
| 环境 因子 | Chao1指数 | Shannon指数 | Simpson_1-D指数 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| r | P | r | P | r | P | |||
| pH | 0.244 | 0.497 | 0.591 | 0.072 | 0.642 | 0.045 | ||
| ORP | 0.280 | 0.432 | 0.289 | 0.418 | 0.327 | 0.356 | ||
| As5+ | -0.476 | 0.165 | -0.154 | 0.671 | -0.099 | 0.786 | ||
| T | -0.500 | 0.141 | -0.474 | 0.166 | -0.543 | 0.105 | ||
| AsT | -0.530 | 0.115 | -0.098 | 0.787 | -0.105 | 0.773 | ||
| SO42- | -0.854 | 0.002 | -0.455 | 0.186 | -0.451 | 0.191 | ||
| S2- | -0.177 | 0.625 | -0.302 | 0.397 | -0.358 | 0.310 | ||
| FeT | 0.468 | 0.173 | 0.457 | 0.184 | 0.433 | 0.211 | ||
| HCO3- | -0.146 | 0.687 | 0.068 | 0.853 | 0.012 | 0.973 | ||

图3 基于Neighbor-joining方法构建的soxB基因氨基酸序列系统发育树 蓝色的序列号表示本研究达巴(DB)热泉soxB基因OTU,紫色的序列号表示卓玛(ZM)热泉soxB基因OTU,黄色的序列号表示滨达微(BDW)热泉soxB基因OTU,括号中的数值代表各OTU序列的个数
Figure 3 Neighbor-joining tree showing the phylogenetic relationships of the deduced soxB amino acid sequences translated from the soxB gene OTU clone sequences
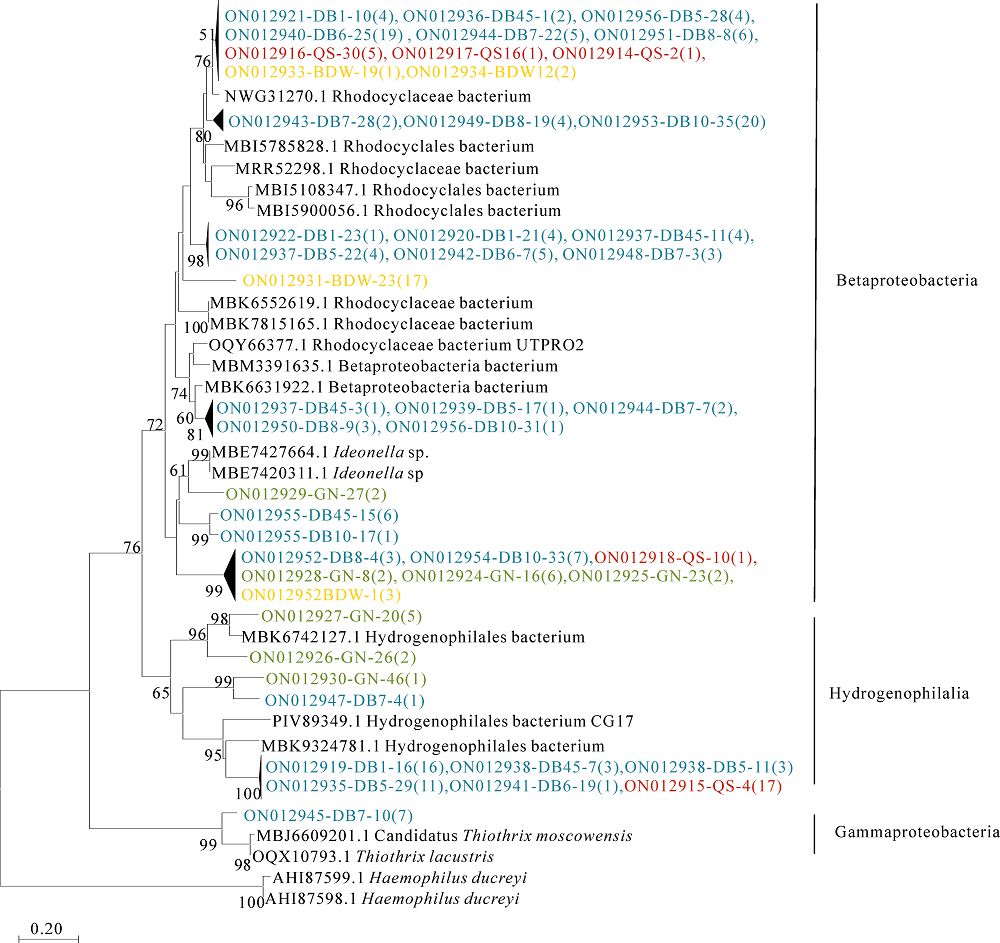
图4 基于Neighbor-joining方法构建的dsrA基因氨基酸序列系统发育树 蓝色的序列号表示本研究达巴(DB)热泉dsrA基因OTU,红色的序列号表示却色(QS)热泉dsrA基因OTU,黄色的序列号表示滨达微(BDW)热泉dsrA基因OTU,绿色的序列号表示嘎弄(GN)热泉dsrA基因OUT,括号中的数值代表各OTU序列的个数
Figure 4 Neighbor-joining tree showing the phylogenetic relationships of the deduced dsrA amino acid sequences translated from the dsrA gene OTU clone sequences
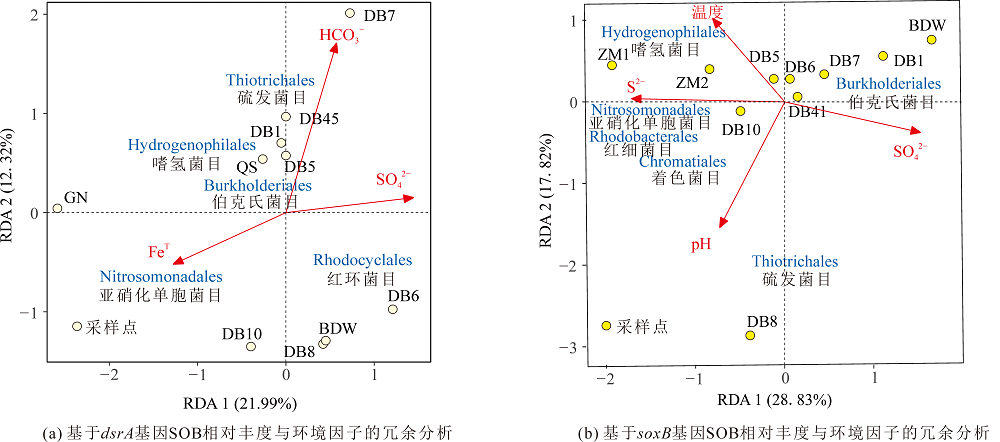
图5 基于各样点dsrA基因(a)与soxB基因(b)的SOB相对丰度与环境因子的相关性分析 图中蓝色字体代表本研究热泉中硫氧化菌。箭头的长度表示该环境因子与样本分布间相关程度的大小,连线越长,相关性越大,反之越小。箭头与样点或微生物之间的夹角表示相关性,锐角表示成正相关关系,钝角则表示成负相关关系
Figure 5 Correlation analysis of SOB relative abundance and environmental factors based on dsrA gene (a) and soxB gene (b)
| 样点 名称 | soxB基因拷贝数/ (copies·mL-1) | dsrA基因拷贝数/ (copies·mL-1) | 16S rRNA基因拷贝数/ (copies·mL-1) | soxB基因相对丰度/ % | dsrA基因相对丰度/ % | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| soxB | SD | dsrA | SD | 16S2) | SD | soxB/16S | dsrA/16S | ||||
| DB1 | 4.53E+04 | 1.16E+04 | 2.24E+05 | 2.83E+03 | 7.41E+05 | 4.22E+05 | 6.12 | 30.25 | |||
| DB41 | 3.62E+03 | 7.85E+02 | ND | ND | 2.31E+05 | 4.88E+04 | 1.57 | ND | |||
| DB45 | ND1) | ND | 2.18E+02 | 1.48E+02 | 9.69E+02 | 6.36E+00 | ND | 22.50 | |||
| DB5 | 2.14E+05 | 3.61E+03 | 8.42E+04 | 3.99E+03 | 4.66E+06 | 2.51E+05 | 4.59 | 1.80 | |||
| DB6 | 3.72E+03 | 1.12E+03 | 2.07E+04 | 1.59E+03 | 2.50E+05 | 7.35E+04 | 1.49 | 8.28 | |||
| DB7 | 1.37E+05 | 3.17E+04 | 6.55E+04 | 7.06E+03 | 3.43E+06 | 4.24E+04 | 4.00 | 1.91 | |||
| DB8 | 4.89E+04 | 1.07E+04 | 1.36E+04 | 1.46E+03 | 2.23E+06 | 1.06E+05 | 2.19 | 0.61 | |||
| DB10 | 3.31E+04 | 2.25E+03 | 1.69E+04 | 2.19E+03 | 1.84E+06 | 3.25E+05 | 1.80 | 0.92 | |||
| ZM1 | 1.77E+03 | 5.02E+02 | ND | ND | 5.33E+05 | 3.61E+04 | 0.33 | ND | |||
| ZM2 | 2.00E+03 | 2.28E+02 | ND | ND | 5.17E+05 | 6.79E+04 | 0.39 | ND | |||
| BDW | 7.88E+05 | 2.05E+04 | 9.76E+04 | 0.00E+00 | 6.68E+06 | 2.83E+04 | 11.80 | 1.46 | |||
| QS | ND | ND | 2.00E+04 | 5.40E+03 | 2.35E+06 | 3.82E+05 | ND | 0.85 | |||
| GN | ND | ND | 4.38E+03 | 1.63E+02 | 1.95E+05 | 1.02E+05 | ND | 2.24 | |||
表5 各样点中soxB 基因、dsrA基因、细菌 16S rRNA 基因拷贝数及比例
Table 5 Abundance and proportion of total bacterial 16S rRNA, soxB and dsrA genes as determined by qPCR
| 样点 名称 | soxB基因拷贝数/ (copies·mL-1) | dsrA基因拷贝数/ (copies·mL-1) | 16S rRNA基因拷贝数/ (copies·mL-1) | soxB基因相对丰度/ % | dsrA基因相对丰度/ % | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| soxB | SD | dsrA | SD | 16S2) | SD | soxB/16S | dsrA/16S | ||||
| DB1 | 4.53E+04 | 1.16E+04 | 2.24E+05 | 2.83E+03 | 7.41E+05 | 4.22E+05 | 6.12 | 30.25 | |||
| DB41 | 3.62E+03 | 7.85E+02 | ND | ND | 2.31E+05 | 4.88E+04 | 1.57 | ND | |||
| DB45 | ND1) | ND | 2.18E+02 | 1.48E+02 | 9.69E+02 | 6.36E+00 | ND | 22.50 | |||
| DB5 | 2.14E+05 | 3.61E+03 | 8.42E+04 | 3.99E+03 | 4.66E+06 | 2.51E+05 | 4.59 | 1.80 | |||
| DB6 | 3.72E+03 | 1.12E+03 | 2.07E+04 | 1.59E+03 | 2.50E+05 | 7.35E+04 | 1.49 | 8.28 | |||
| DB7 | 1.37E+05 | 3.17E+04 | 6.55E+04 | 7.06E+03 | 3.43E+06 | 4.24E+04 | 4.00 | 1.91 | |||
| DB8 | 4.89E+04 | 1.07E+04 | 1.36E+04 | 1.46E+03 | 2.23E+06 | 1.06E+05 | 2.19 | 0.61 | |||
| DB10 | 3.31E+04 | 2.25E+03 | 1.69E+04 | 2.19E+03 | 1.84E+06 | 3.25E+05 | 1.80 | 0.92 | |||
| ZM1 | 1.77E+03 | 5.02E+02 | ND | ND | 5.33E+05 | 3.61E+04 | 0.33 | ND | |||
| ZM2 | 2.00E+03 | 2.28E+02 | ND | ND | 5.17E+05 | 6.79E+04 | 0.39 | ND | |||
| BDW | 7.88E+05 | 2.05E+04 | 9.76E+04 | 0.00E+00 | 6.68E+06 | 2.83E+04 | 11.80 | 1.46 | |||
| QS | ND | ND | 2.00E+04 | 5.40E+03 | 2.35E+06 | 3.82E+05 | ND | 0.85 | |||
| GN | ND | ND | 4.38E+03 | 1.63E+02 | 1.95E+05 | 1.02E+05 | ND | 2.24 | |||
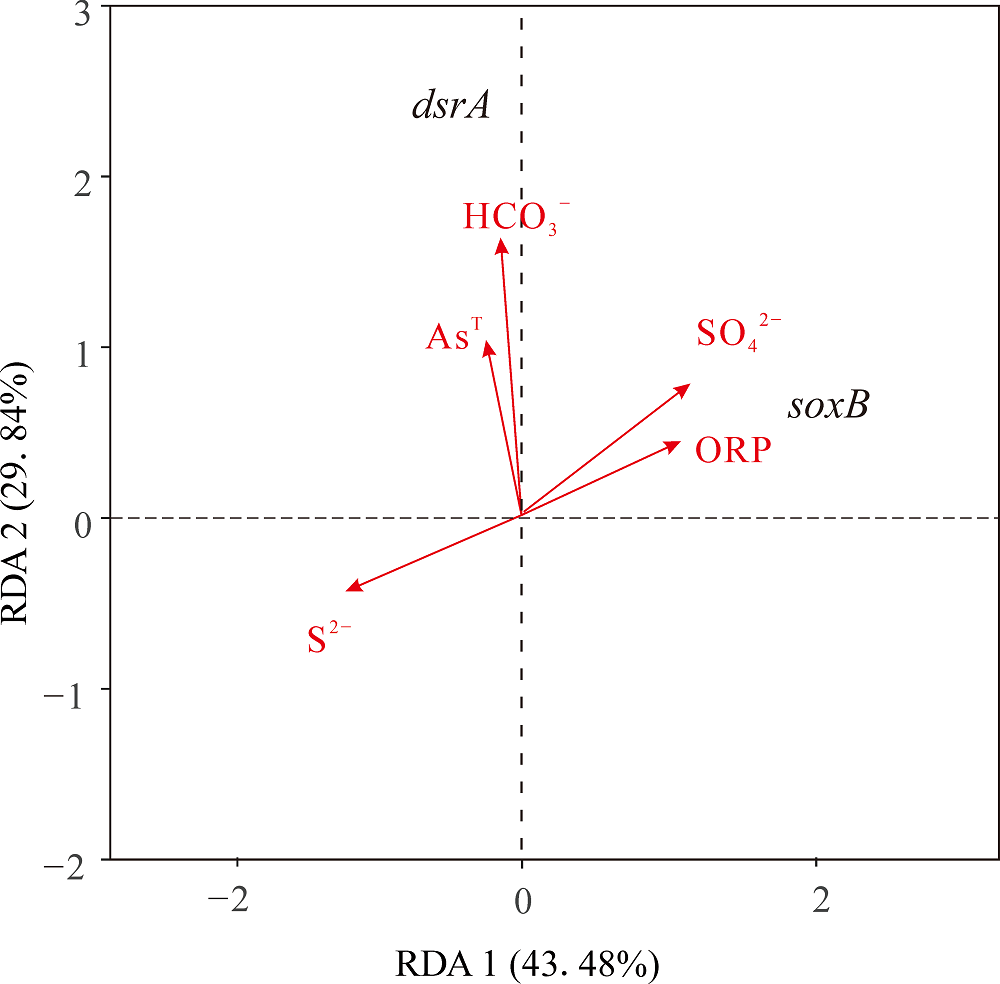
图7 soxB与dsrA基因相对丰度与环境因子的RDA分析 图中dsrA表示dsrA基因相对丰度,soxB表示soxB基因相对丰度。箭头的长度表示该环境因子与基因相对丰度相关程度的大小,连线越长,相关性越大,反之越小。箭头与基因相对丰度之间的夹角表示相关性,锐角表示成正相关关系,钝角则表示成负相关关系
Figure 7 RDA analysis of relative abundance of soxB and dsrA genes and environmental factors
| [1] |
ABUSAM A, AL-SALMAIN F, MYDLARCZYK A, 2019. Seasonal variations of the growth of filamentous bacteria in Kuwait’s wastewater treatment plants[J]. Desalination and Water Treatment, 176: 370-374.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
ALONSO-SÁEZ L, MORÁN X A G, GONZÁLEZ J M, 2020. Transcriptional patterns of biogeochemically relevant marker genes by temperate marine bacteria[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 11: 465.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
CASTELÁN-SÁNCHEZ H G, MEZA-RODRIGUEZ P M, CARRILLO E, et al., 2020. The microbial composition in circumneutral thermal springs from Chignahuapan, Puebla, Mexico reveals the presence of particular sulfur-oxidizing bacterial and viral communities[J]. Microorganisms, 8(11): 1677.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
CHEN Y, MI T Z, LIU Y T, et al., 2020. Microbial community composition and function in sediments from the Pearl River Mouth Basin[J]. Journal of Ocean University of China, 19(4): 941-953.
DOI |
| [5] | CHERNITSYNA S M, KHALZOV I A, POGODAEVA T V, et al., 2020. Distribution and morphology of colorless sulfur bacterium of the genus Thiothrix in water reservoirs of Baikal Rift Zone[J]. Limnology and Freshwater Biology, 4(4): 976-978. |
| [6] | GAO S X, HE Q L, WANG H Y, 2019. Research on the aerobic granular sludge under alkalinity in sequencing batch reactors: removal efficiency, metagenomic and key microbes[J]. Bioresource Technology, 296: 122280. |
| [7] | GUO L, WANG G C, SHENG Y Z, et al., 2021. Hydrogeochemical constraints shape hot spring microbial community compositions: evidence from acidic, moderate-temperature springs and alkaline, high-temperature springs, south-western Yunnan geothermal areas, China[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Biogeosciences, 126(3): e2020JG005868-1-e2020JG005868-19. |
| [8] |
GUO Q H, PLANER-FRIEDRICH B P, LIU M L, et al., 2019. Magmatic fluid input explaining the geochemical anomaly of very high arsenic in some southern Tibetan geothermal waters[J]. Chemical Geology, 513: 32-43.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
GUPTA S, PLUGGE C M, KLOK J B M, et al., 2022. Comparative analysis of microbial communities from different full-scale haloalkaline biodesulfurization systems[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 106(4): 1759-1776.
DOI PMID |
| [10] | HOU W G, WANG S, DONG H L, et al., 2013. A comprehensive census of microbial diversity in hot springs of Tengchong, Yunnan province China using 16S rRNA gene pyrosequencing[J]. PloS One, 8(1): 1-15. |
| [11] |
JAFFER Y D, PURUSHOTHAMAN C S, KUMAR H S, et al., 2019. A combined approach of 16S rRNA and a functional marker gene, soxB to reveal the diversity of sulphur-oxidising bacteria in thermal springs[J]. Archives of Microbiology, 201(5) :951-967.
DOI |
| [12] | JIANG Z, LI P, JIANG D W, et al., 2016. Microbial community structure and arsenic biogeochemistry in an acid vapor-formed spring in Tengchong geothermal area, China[J]. PloS One, 11(1): 1-16. |
| [13] | KOJIMA H, WATANABE T, IWATA T, et al., 2014. Identification of major planktonic sulfur oxidizers in stratified freshwater lake[J]. PLoS One, 9(4): e93877. |
| [14] |
KUBO K, KNITTEL K, AMANN R, et al., 2011. Sulfur-metabolizing bacterial populations in microbial mats of the Nakabusa hot spring, Japan[J]. Systematic and Applied Microbiology, 34(4): 293-302.
DOI PMID |
| [15] |
LI P, JIANG Z, WANG Y H, et al., 2017. Analysis of the functional gene structure and metabolic potential of microbial community in high arsenic groundwater[J]. Water Research, 123: 268-276.
DOI PMID |
| [16] | LU G S, LAROWE D E, AMEND J P, 2021. Bioenergetic potentials in terrestrial, shallow-sea and deep-sea hydrothermal systems[J]. Chemical Geology, 583: 120449. |
| [17] |
LUO J F, TAN X Q, LIU K X, et al., 2018. Survey of sulfur-oxidizing bacterial community in the Pearl River water using soxB, sqr, and dsrA as Molecular Biomarkers[J]. 3 Biotech, 8(1): 1-12.
DOI URL |
| [18] | MA L, WU G, YANG J, et al., 2021. Distribution of hydrogen-producing bacteria in Tibetan hot springs, China[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 12: 1-12. |
| [19] |
PANDEY S K, NARAYAN K D, BANDYOPADHYAY S, et al., 2009. Thiosulfate oxidation by Comamonas sp s23 isolated from a sulfur spring[J]. Current Microbiology, 58(5): 516-521.
DOI URL |
| [20] | QING C, NICOL A, LI P, et al., 2023. Different sulfide to arsenic ratios driving arsenic speciation and microbial community interactions in two alkaline hot springs[J]. Environmental Research, 218: 115033. |
| [21] |
SHU W S, HUANG L N, 2022. Microbial diversity in extreme environments[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 20(4): 219-235.
DOI |
| [22] |
SKIRNISDOTTIR S, HREGGVIDSSON G O, HJÖRLEIFSDOTTIR S, et al., 2000. Influence of sulfide and temperature on species composition and community structure of hot spring microbial mats[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 66(7): 2835-2841.
DOI PMID |
| [23] |
SOROKIN D Y, TOUROVA T P, KUZNETSOV B B, et al., 2000. Roseinatronobacter thiooxidans gen. nov., sp, nov., a new alkaliphilic aerobic bacteriochlorophylla-containing bacterium isolated from a soda lake[J]. Microbiology, 69(1): 75-82.
DOI URL |
| [24] | TAKEDA M, KAMAGATA Y, GHIROSE W C, et al., 2002. Caldimonas manganoxidans gen. nov., sp nov., a poly(3-hydroxybutyrate)-degrading, manganese-oxidizing thermophile[J]. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 52(3): 895-900. |
| [25] |
TOUROVA T P, SLOBODOVA N V, BUMAZHKIN B K., et al., 2013. Analysis of community composition of sulfur-oxidizing bacteria in hypersaline and soda lakes using soxB as a functional molecular marker[J]. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 84(2): 280-289.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
VIOLLIER E, INGLETT P W, HUNTER K, et al., 2000. The ferrozine method revisited: Fe(II)/Fe(III) determination in natural waters[J]. Applied geochemistry, 15(6): 785-790.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
WANG L, YU M, LIU Y, et al., 2018. Comparative analyses of the bacterial community of hydrothermal deposits and seafloor sediments across Okinawa Trough[J]. Journal of Marine Systems, 180: 162-172.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
WANG R, LIN J Q, LIU X M, et al., 2019. Sulfur oxidation in the acidophilic autotrophic Acidithiobacillus spp[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 9: 3290.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
WANG Y H, LI P, JIANG Z, et al., 2018. Diversity and abundance of arsenic methylating microorganisms in high arsenic groundwater from Hetao Plain of Inner Mongolia, China[J]. Ecotoxicology, 27(8): 1047-1057.
DOI PMID |
| [30] |
WANG Y X., LI P, GUO Q H., et al., 2018. Environmental biogeochemistry of high arsenic geothermal fluids[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 97: 81-92.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
WATANABE T, KOJIMA H, SHINOHARA A, et al., 2016. Sulfurirhabdus autotrophica gen. nov., sp nov., isolated from a freshwater lake[J]. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 66(1): 113-117.
DOI URL |
| [32] | WU B, LIU F F, FANG W W, et al., 2021. Microbial sulfur metabolism and environmental implications[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 778(12-13): 146085. |
| [33] |
YANG J, JIANG H C, DONG H L, et al., 2013. Abundance and diversity of sulfur-oxidizing bacteria along a salinity gradient in four Qinghai-Tibetan lakes, China[J]. Geomicrobiology Journal, 30(9): 851-860.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
ZECCHIN S, COLOMBO M, CAVALCA L, 2019. Exposure to different arsenic species drives the establishment of iron and sulfur-oxidizing bacteria on rice root iron plaques[J]. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 35(8): 1-12.
DOI |
| [35] |
ZHANG D R, XIA J L, NIE ZH Y, et al., 2019. Mechanism by which ferric iron promotes the bioleaching of arsenopyrite by the moderate thermophile Sulfobacillus Thermosulfidooxidans [J]. Process Biochem, 81: 11-21.
DOI URL |
| [36] | ZHAO Z Q, SUN C, LI Y, et al., 2020. Driving microbial sulfur cycle for phenol degradation coupled with Cr(VI) reduction via Fe(III)/Fe(II) transformation[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 393: 124801. |
| [37] | ZHOU L, WANG D W, ZHANG S L, et al., 2020. Functional microorganisms involved in the sulfur and nitrogen metabolism in production water from a high-temperature offshore petroleum reservoir[J]. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 154: 105057. |
| [38] | 刘阳, 姜丽晶, 邵宗泽, 2018. 硫氧化细菌的种类及硫氧化途径的研究进展[J]. 微生物学报, 58(2): 191-201. |
| LIU Y, JIANG L J, SHAO Z Z, 2018. Advances in sulfur-oxidizing bacterial taxa and their sulfur oxidation pathways[J]. Acta Microbiologica Sinica, 58(2): 191-201. | |
| [39] | 吕苑苑, 郑绵平, 赵平, 等, 2014. 滇藏地热带地热水硼同位素地球化学过程及其物源示踪[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 44(9): 1968-1979. |
| LÜ Y Y, ZHENG M P, ZHAO P, et al., 2014. Geochemical processes and origin of boron isotopes in geothermal water in the Yunnan-Tibet geothermal zone[J]. Science China: Earth Sciences, 44(9): 1968-1979. | |
| [40] | 韩天赐, 2018. 西藏曲才热泉的细菌多样性及栖热菌属比较基因组学[D]. 昆明: 云南大学. |
| HAN T C, 2018. Bacterial diversity of Qucai hot springs in Tibet & comparative genomics of the genus Thermus[D]. Kunming: Yunnan University. | |
| [41] | 姜舟, 2016. 腾冲地热区砷的环境生物地球化学研究[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学(武汉). |
| JIANG Z, 2016. Environmental biogeochemistry of arsenic in Tengchong geothermal area, china[D] Wuhan: China University of Geosciences (Wuhan). | |
| [42] | 邵博, 2019. 微氧强化自养-异养联合反硝化处理含不同硫氮比废水的效能研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学. |
| SHAO B, 2019. Research on mitigating adverseimpact of varying sulfide to nitrateratio on the integrated autotrophicand heterotrophic denitrification process via microaerobic condition[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology. | |
| [43] | 王尚, 2015. 滇藏热泉微生物群落分布及其控制因素研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学 (北京). |
| WANG S, 2015. The distribution patterns and environmental constraints of microbial community in hot springs in Western China[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing). | |
| [44] | 杨磊, 张爽, 刘涛, 等, 2020. 五大连池东焦得布山硫氧化细菌多样性及其与环境因子的关系[J]. 黑龙江八一农垦大学学报, 32(5): 77-82. |
| YANG L, ZHANG S, LIU T, et al., 2020. Sulfur-oxidizing bacteria diversity in Dongjiao-debu Volcanoes located in Wudalianchi[J]. Journal of Heilongjiang Bayi Agricultural University, 32(5): 77-82. | |
| [45] | 张玉, 米铁柱, 甄毓, 等, 2018. 海洋沉积物中硫酸盐还原菌和硫氧化菌群落分析方法的比较[J]. 环境科学, 39(1): 438-449. |
| ZHANG Y, MI T Z, ZHEN Y, et al., 2018. Analysis of sulfate-reducing and sulfur-oxidizing prokaryote community structures in marine sediments with different sequencing technologies[J]. Environmental Science, 39(1): 438-449. | |
| [46] | 甄莉, 吴耿, 杨渐, 等, 2019. 西藏热泉沉积物的硫氧化细菌多样性及其影响因素[J]. 微生物学报, 59(6): 1089-1104. |
| ZHEN L, WU G, YANG J, et al., 2019. Distribution and diversity of sulfur-oxidizing bacteriain the surface sediments of Tibetan hot springs[J]. Acta Microbiologica Sinica, 59(6): 1089-1104. |
| [1] | 侯晖, 颜培轩, 谢沁宓, 赵宏亮, 庞丹波, 陈林, 李学斌, 胡杨, 梁咏亮, 倪细炉. 贺兰山蒙古扁桃灌丛根际土壤AM真菌群落多样性特征研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 857-865. |
| [2] | 姜永伟, 丁振军, 袁俊斌, 张峥, 李杨, 问青春, 王业耀, 金小伟. 辽宁省主要河流底栖动物群落结构及水质评价研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 969-979. |
| [3] | 王云, 郑西来, 曹敏, 李磊, 宋晓冉, 林晓宇, 郭凯. 滨海含水层咸-淡水过渡带反硝化性能与控制因素研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 980-988. |
| [4] | 胡芳, 刘聚涛, 温春云, 韩柳, 文慧. 抚河流域浮游植物群落结构特征及其水生态状况评价[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 744-755. |
| [5] | 于菲, 曾海龙, 房怀阳, 付玲芳, 林澍, 董家豪. 典型感潮河网浮游藻类功能群时空变化特征及水质评价[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 756-765. |
| [6] | 李善家, 王兴敏, 刘海锋, 孙梦格, 雷雨昕. 河西走廊荒漠植物多样性及其对环境因子的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 429-438. |
| [7] | 王礼霄, 刘晋仙, 柴宝峰. 华北亚高山土壤细菌群落及氮循环对退耕还草的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1537-1546. |
| [8] | 姜倪皓, 张世浩, 张诗函. 哀牢山紫茎泽兰入侵群落主要物种种间联结及环境解释[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(7): 1370-1382. |
| [9] | 王英成, 姚世庭, 金鑫, 俞文政, 芦光新, 王军邦. 三江源区高寒退化草甸土壤细菌多样性的对比研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 695-703. |
| [10] | 刘红梅, 海香, 安克锐, 张海芳, 王慧, 张艳军, 王丽丽, 张贵龙, 杨殿林. 不同施肥措施对华北潮土区玉米田土壤固碳细菌群落结构多样性的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 715-722. |
| [11] | 夏开, 邓鹏飞, 马锐豪, 王斐, 温正宇, 徐小牛. 马尾松次生林转换为湿地松和杉木林对土壤细菌群落结构和多样性的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(3): 460-469. |
| [12] | 宋秀丽, 黄瑞龙, 柯彩杰, 黄蔚, 章武, 陶波. 不同种植方式对连作土壤细菌群落结构和多样性的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(3): 487-496. |
| [13] | 薛文凯, 朱攀, 德吉, 郭小芳. 纳木措水体可培养丝状真菌优势种的时空特征研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(12): 2331-2340. |
| [14] | 李聪, 吕晶花, 陆梅, 杨志东, 刘攀, 任玉连, 杜凡. 滇东南亚热带土壤细菌群落对植被垂直带变化的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(10): 1971-1983. |
| [15] | 白海锋, 王怡睿, 宋进喜, 孔飞鹤, 张雪仙, 李琦. 渭河浮游生物群落结构特征及其与环境因子的关系[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(1): 117-130. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
