生态环境学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (8): 1182-1191.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2024.08.003
收稿日期:2024-04-22
出版日期:2024-08-18
发布日期:2024-09-25
通讯作者:
*翟水晶。E-mail: zhaisj@fjnu.edu.cn作者简介:王文静(1999年生),女,硕士研究生,主要研究方向为湿地生态系统硅的循环。E-mail: wwj17662426185@163.com
基金资助:
WANG Wenjing1,2,3( ), ZHAI Shuijing1,*(
), ZHAI Shuijing1,*( ), WANG Sai1,2,3
), WANG Sai1,2,3
Received:2024-04-22
Online:2024-08-18
Published:2024-09-25
摘要:
湿地土壤是硅的重要储库,在控制其生物地球化学循环中发挥着重要作用。于2019年10月采集闽江下游沿岸湿地0-60 cm柱状土壤分析全硅、有效硅和生物硅的沿程分布特征。结果表明:闽江下游沿岸湿地土壤中全硅含量介于128-247 mg·g−1之间,生物硅含量介于30.8-40.5 mg·g−1之间,在由陆及海方向上均呈现先降后升的趋势;有效硅含量介于104-541 μg·g−1之间,在由陆及海方向上呈现“W”型波动上升趋势。在剖面上,土壤有效硅含量随土层深度增加呈现降低趋势且变化显著(p<0.001),而土壤全硅和生物硅含量随深度无明显变化。土壤理化性质、植被是影响闽江下游湿地土壤硅分布的主要因素,相关分析表明,土壤全硅含量与pH(p<0.010)、砂粒(p<0.050)呈正相关关系,与粉粒(p<0.050)、含水率(p<0.010)呈负相关关系。土壤有效硅含量与黏粒(p<0.010)、EC(p<0.010)、粉粒(p<0.010)呈正相关关系,与砂粒呈极显著负相关关系(p<0.010)。土壤生物硅含量与黏粒(p<0.050)、粉粒(p<0.050)呈正相关关系,与砂粒(p<0.050)呈负相关关系。此外,植被类型和生物量对闽江下游湿地土壤各形态硅的沿程分布也有一定的影响。该研究揭示了闽江下游湿地土壤硅的空间分布及影响因素,研究结果可为认识硅在湿地生态系统中的生物地球化学循环过程及机制提供重要的理论基础。
中图分类号:
王文静, 翟水晶, 王赛. 闽江下游湿地土壤硅的沿程分布特征及影响因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(8): 1182-1191.
WANG Wenjing, ZHAI Shuijing, WANG Sai. Distribution Characteristics of Silicon and Its Influencing Factors in the Wetland Soils along the Minjiang River Downstream[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2024, 33(8): 1182-1191.
| 样点 | pH | 含水率/% | 黏粒质量分数/% | 粉粒质量分数/% | 砂粒质量分数/% | EC/(mS·cm−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 6.91±0.34ab | 29.7±7.04c | 9.69±1.36b | 17.5±3.60a | 72.8±4.65d | 0.07±0.02c |
| S2 | 5.71±0.11d | 50.1±2.01a | 8.32±0.81b | 32.1±4.81c | 59.5±5.33d | 0.06±0.02c |
| S3 | 6.42±0.06c | 45.3±2.12ab | 9.08±1.41b | 45.1±4.49b | 45.9±5.79c | 0.17 ±0.01c |
| S4 | 5.97±0.07d | 43.4±1.04b | 14.7±1.18a | 60.2±3.01a | 25.1±4.05b | 1.63±0.29b |
| S5 | 7.18±0.26a | 42.2±1.08b | 5.14±2.99c | 17.3±9.71c | 77.5±12.7a | 3.95±1.27a |
| S6 | 6.69±0.23bc | 43.7±0.10ab | 13.1±1.73a | 64.2±2.73a | 22.8±3.38a | 4.36±0.64a |
表1 闽江下游各样点的土壤理化特征
Table 1 Soil physical and chemical properties in the wetland of the Minjiang River downstream
| 样点 | pH | 含水率/% | 黏粒质量分数/% | 粉粒质量分数/% | 砂粒质量分数/% | EC/(mS·cm−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 6.91±0.34ab | 29.7±7.04c | 9.69±1.36b | 17.5±3.60a | 72.8±4.65d | 0.07±0.02c |
| S2 | 5.71±0.11d | 50.1±2.01a | 8.32±0.81b | 32.1±4.81c | 59.5±5.33d | 0.06±0.02c |
| S3 | 6.42±0.06c | 45.3±2.12ab | 9.08±1.41b | 45.1±4.49b | 45.9±5.79c | 0.17 ±0.01c |
| S4 | 5.97±0.07d | 43.4±1.04b | 14.7±1.18a | 60.2±3.01a | 25.1±4.05b | 1.63±0.29b |
| S5 | 7.18±0.26a | 42.2±1.08b | 5.14±2.99c | 17.3±9.71c | 77.5±12.7a | 3.95±1.27a |
| S6 | 6.69±0.23bc | 43.7±0.10ab | 13.1±1.73a | 64.2±2.73a | 22.8±3.38a | 4.36±0.64a |
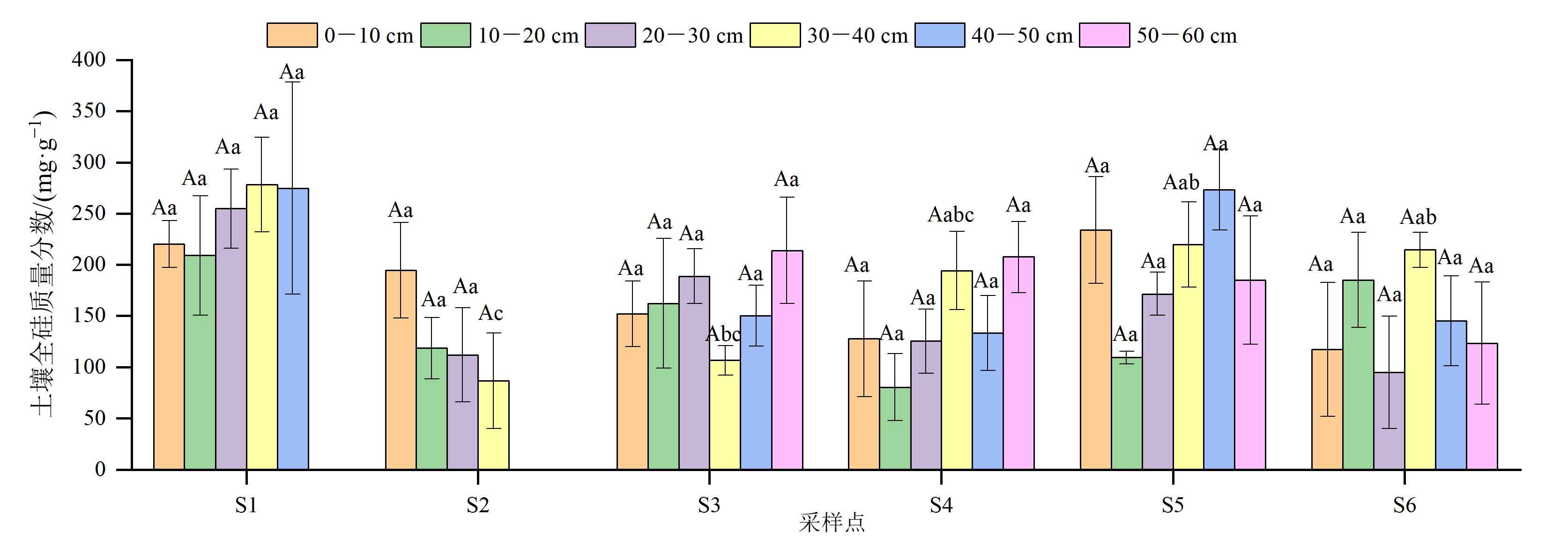
图2 闽江下游湿地土壤全硅质量分数变化特征 样本重复数n=3;误差棒代表SE;不同大写字母表示同一样点不同深度之间存在差异显著,p<0.001;不同小写字母表示同一土层不同样点之间存在差异显著,p<0.001。下同
Figure 2 Variation characteristics of TSi mass fraction in the wetland of the Minjiang River downstream
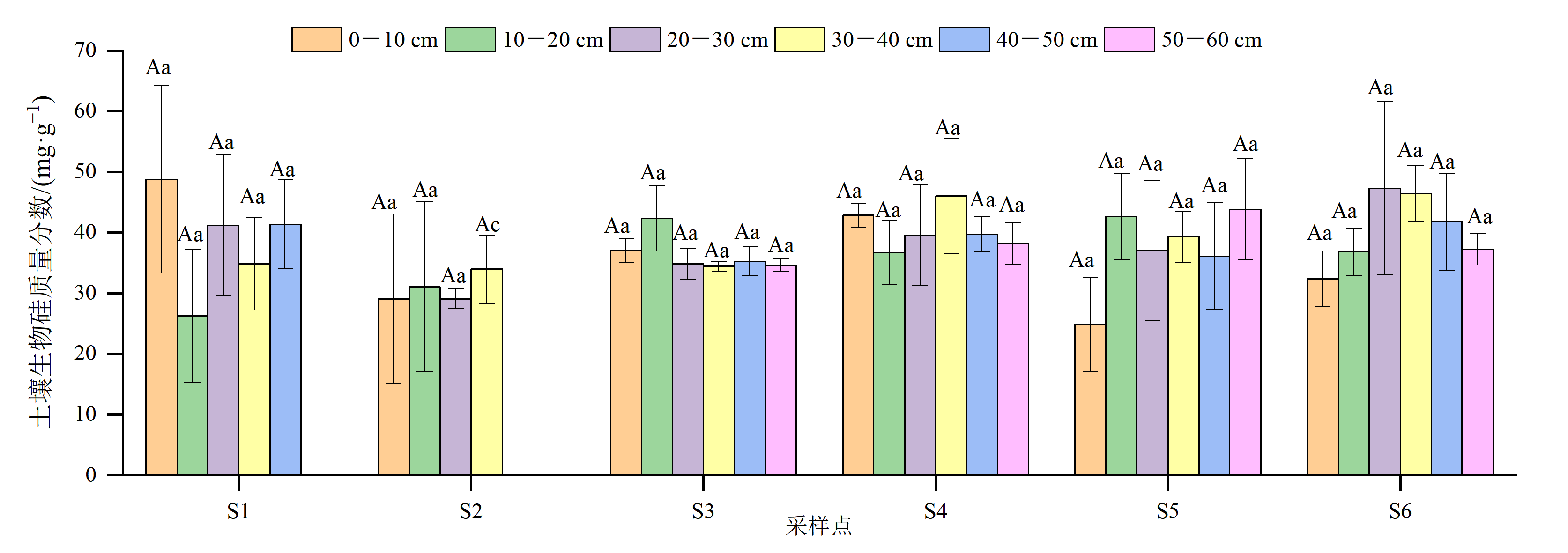
图4 闽江下游湿地土壤生物硅质量分数变化特征 样本重复数n=3;误差棒代表SE;不同大写字母表示同一样点不同深度之间差异显著,p<0.001;不同小写字母表示同一土层不同样点之间存在差异显著,p<0.001
Figure 4 Characteristics of BSi mass fraction variation in the wetland of the Minjiang River downstream
| 指标 | pH | EC | 含水率 | 黏粒 | 粉粒 | 砂粒 | 植物生物硅 | 地下生物量 | 地上生物量 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 全硅 | 0.32** 1) | −0.08 | −0.26** | −0.19 | −0.31* 2) | 0.30* | 0.01 | −0.03 | −0.28 |
| 有效硅 | 0.11 | 0.51** | 0.18 | 0.39** | 0.63** | −0.61** | −0.22 | 0.59** | 0.47* |
| 生物硅 | 0.08 | 0.18 | −0.01 | 0.26* | 0.24* | −0.25* | 0.46 | −0.22 | 0.29 |
表2 闽江下游湿地土壤不同硅含量与环境因子之间的相关关系
Table 2 Correlation between different silicon content and environmental factors in soil in the wetland of the Minjiang River downstream
| 指标 | pH | EC | 含水率 | 黏粒 | 粉粒 | 砂粒 | 植物生物硅 | 地下生物量 | 地上生物量 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 全硅 | 0.32** 1) | −0.08 | −0.26** | −0.19 | −0.31* 2) | 0.30* | 0.01 | −0.03 | −0.28 |
| 有效硅 | 0.11 | 0.51** | 0.18 | 0.39** | 0.63** | −0.61** | −0.22 | 0.59** | 0.47* |
| 生物硅 | 0.08 | 0.18 | −0.01 | 0.26* | 0.24* | −0.25* | 0.46 | −0.22 | 0.29 |
| 成分 | 初始特征值 | 环境 因子 | 主成分 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 特征值 | 贡献率/ % | 累积贡献率/ % | Z1 | Z2 | Z3 | ||
| 1 | 3.25 | 54.2 | 54.2 | pH | −0.61 | 0.73 | −0.04 |
| 2 | 1.44 | 24.0 | 78.2 | EC | 0.18 | 0.87 | 0.39 |
| 3 | 1.02 | 16.9 | 95.1 | 含水率 | 0.47 | −0.29 | 0.82 |
| 4 | 0.20 | 3.27 | 98.3 | 黏粒 | 0.86 | 0.15 | −0.43 |
| 5 | 0.10 | 1.67 | 100.0 | 粉粒 | 0.97 | 0.15 | −0.02 |
| 6 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 100.0 | 砂粒 | −0.98 | −0.16 | 0.09 |
表3 闽江下游湿地土壤硅的特征值及主成分矩阵
Table 3 Characteristic values and principal component matrix of soil silicon in the wetland of the Minjiang River downstream
| 成分 | 初始特征值 | 环境 因子 | 主成分 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 特征值 | 贡献率/ % | 累积贡献率/ % | Z1 | Z2 | Z3 | ||
| 1 | 3.25 | 54.2 | 54.2 | pH | −0.61 | 0.73 | −0.04 |
| 2 | 1.44 | 24.0 | 78.2 | EC | 0.18 | 0.87 | 0.39 |
| 3 | 1.02 | 16.9 | 95.1 | 含水率 | 0.47 | −0.29 | 0.82 |
| 4 | 0.20 | 3.27 | 98.3 | 黏粒 | 0.86 | 0.15 | −0.43 |
| 5 | 0.10 | 1.67 | 100.0 | 粉粒 | 0.97 | 0.15 | −0.02 |
| 6 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 100.0 | 砂粒 | −0.98 | −0.16 | 0.09 |
| [1] | ALEXANDRE A, MEUNIER J D, COLIN F, et al., 1997. Plant impact on the biogeochemical cycle of silicon and related weathering processes[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 61(3): 677-682. |
| [2] | BERNARDEZ P, FRANCES G, PREGO R, 2006. Benthic-pelagic coupling and postdepositional processes as revealed by the distribution of opal in sediments: The case of the Ría de Vigo (NW Iberian Peninsula)[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 68(1-2): 271-281. |
| [3] | BILLEN G, LANCELOT C, MEYBECK M, et al., 1991. N, P and Si retention along the aquatic continuum from land to ocean[J]. Ocean Margin Processes in Global Change, 1: 19-44. |
| [4] |
CAUBET M, CORNU S, SABY N P, et al., 2020. Agriculture increases the bioavailability of silicon, a beneficial element for crop, in temperate soils[J]. Scientific Reports, 10(1): 19999-19999.
DOI PMID |
| [5] | CHRISTINA L, DE L R, MARK A, et al., 2000. A first look at the distribution of the stable isotopes of silicon in natural waters[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 64(14): 2467-2477. |
| [6] | CORNELIS J T, TITEUX H, RANGER J, et al., 2011. Identification and distribution of the readily soluble silicon pool in a temperate forest soil below three distinct tree species[J]. Plant and Soil, 342(1): 369-378. |
| [7] | EPSTEIN E, 1999. Silicon[J]. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 50(1): 641-664. |
| [8] | HAYNES R J, BELAEVA O N, KINGSTON G, 2013. Evaluation of industrial wastes as sources of fertilizer silicon using chemical extractions and plant uptake[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Soil Science, 176(2): 238-248. |
| [9] |
HOU L J, LIU M, YANG Y, et al., 2010. Biogenic silica in intertidal marsh plants and associated sediments of the Yangtze Estuary[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 22(3): 374-380.
PMID |
| [10] | LANNING F C, ELEUTERIUS L N, 1985. Silica and ash in tissues of some plants growing in the coastal area of Mississippi[J]. Annals of Botany, 56(2): 157-172. |
| [11] | LI Z M, MEUMIER J D, DELVAUXB, 2022. Aggregation reduces the release of bioavailable silicon from allophane and phytolith[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 325: 87-105. |
| [12] | LI Z M, UNZUE B D, CORNELIS J T, et al., 2019. Effects of phytolithic rice-straw biochar, soil buffering capacity and pH on silicon bioavailability[J]. Plant and Soil, 438(1): 187-203. |
| [13] | MA J F, TAKAHSHI E, 2002. Soil, fertilizer and plant silicon research in Japan[M]. Amsterdam: Elsevier: 63-106. |
| [14] | MEUNIER J D, CORNU S, KELLER C, et al., 2002. The role of silicon in the supply of terrestrial ecosystem services[J]. Environmental Chemistry Letters, 20(3): 2109-2121. |
| [15] | MEUNIER J D, SANDHYA K, PRAKASH N B, et al., 2018. pH as a proxy for estimating plant available Si? A case study in rice fields in Karnataka (South India)[J]. Plant and Soil, 432(1): 143-155. |
| [16] |
MITANIN, MA J F, 2005. Uptake system of silicon in different plant species[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 56(414): 1255-1261.
DOI PMID |
| [17] | MORTLOCK R A, FROELICH P N, 1989. A simple method for the rapid determination of biogenic opal in pelagic marine sediments[J]. Deep Sea Research Part A. Oceanographic Research Papers, 36(9): 1415-1426. |
| [18] | NORRIS A R, HACKNEY C T, 1999. Silica content of a mesohaline tidal marsh in north Carolina, Estuarine[J]. Coastal and Shelf Science, 49(4): 597-605. |
| [19] | PAUL J, TREGUER, CHRISTINA L, et al., 2013. The world ocean silica cycle[J]. Annual Review of Marine Science, 5(1): 477-501. |
| [20] | RICHARD J H, 2017. The nature of biogenic Si and its potential role in Si supply in agricultural soils[J]. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 245: 100-111. |
| [21] |
SCHELSKE C L, STOERMER E F, 1971. Eutrophication, silica depletion, and predicted changes in algal quality in Lake Michigan[J]. Science, 173(3995): 423-424.
DOI PMID |
| [22] | SHAKOOR S A, BHAT M, MIR S, 2014. Phytoliths in plants: A review[J]. Research and Reviews: Journal of Botanical Sciences, 3: 10-24. |
| [23] | SOCRATIS L, PHILIPPE V C, THILO B, 2008. Dissolution of biogenic silica from land to ocean: role of salinity and pH[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 53(4): 1614-1621. |
| [24] | SOMMER M, KACZOREK D, KUZYAKOV Y, et al., 2006. Silicon pools and fluxes in soils and landscapes: A review[J]. Plant Nutrition and Soil Science, 169(4): 310-329. |
| [25] | STRUYF, ERIC, DANIEL J, et al., 2009. Silica: An essential nutrient in wetland biogeochemistry[J]. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment, 7(2): 88-94. |
| [26] | STRUYF E, VAN D S, GRIBSHOLT B, et al., 2007. Phragmites australis and silica cycling in tidal wetlands[J]. Aquatic Botany, 87(2): 134-140. |
| [27] | STRUYF E, VAN D S, GRIBSHOLT B, et al., 2005. Biogenic silica in tidal freshwater marsh sediments and vegetation (Schelde estuary, Belgium)[J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 303: 51-60. |
| [28] | STRUYF E, CARL-MAGUNS M, CHRISTOPH H, et al., 2010. An enormous amorphous silica stock in boreal wetlands[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 115(G4): G04008. |
| [29] | TORN M S, TRUMBORE S E, CHADWICK O A, et al., 1997. Mineral control of soil organic carbon storage and turnover[J]. Nature, 389(6647): 170-173. |
| [30] | TRÉGUER P, NELSON D M, VAN B A, et al., 1995. The Silica Balance in the World Ocean: A Reestimate[J]. Science, 268(5209): 376-79. |
| [31] | TUBANA B S, BABU T, DATNOFF L E, 2016. A review of silicon in soils and plants and its role in US agriculture: History and future perspectives[J]. Soil Science, 181(9-10): 393-411. |
| [32] | TURNER B F, WHITE A F, BRANTLEY S L, 2010. Effects of temperature on silicate weathering: Solute fluxes and chemical weathering in a temperate rain forest watershed, Jamieson Creek, British Columbia[J]. Chemical Geology, 269(1-2): 62-78. |
| [33] | VAN C P, QIU L, 1997. Biogenic silica dissolution in sediments of the Southern Ocean. II. Kinetics[J]. Deep Sea Research Part II: Topical Studies in Oceanography, 44(5): 1109-1128. |
| [34] | WEISS A, AMANN T, HARTMANN J, 2013. Silica dynamics of tidal marshes in the inner Elbe Estuary, Germany[J]. Silicon, 5(1): 75-89. |
| [35] | XIA S P, SONG Z L, FAN Y R, et al., 2023. Spatial distribution patterns and controls of bioavailable silicon in coastal wetlands of China[J]. Plant Soil, 493(1-2): 187-205. |
| [36] | YANG S L, HAO Q, LIU H Y, et al., 2019. Impact of grassland degradation on the distribution and bioavailability of soil silicon: Implications for the Si cycle in grasslands[J]. Science of Total Environment, 657: 811-818. |
| [37] | ZHANG L L, CHEN M H, XIANG R, et al., 2009. Distribution of biogenic silica content in surface sediments from the southern South China Sea and its environmental significance[J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 11(1): 43-52. |
| [38] | ZHAO X W, ZHANG X D, LI Z, et al., 2023. Silicon fractionations at the margin of a coastal wetland and its response to sea level rise[J]. Geoderma, 269: 62-78. |
| [39] | 鲍士旦, 2008. 土壤农化分析[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社: 235-236. |
| BAO S D, 2008. Soil and agricultural chemistry analysis[M]. Beijing: China Agriculture Press: 235-236. | |
| [40] | 陈敏建, 王立群, 丰华丽, 等, 2008. 湿地生态水文结构理论与分析[J]. 生态学报, 28(6): 2887-2893. |
| CHEN M J, WANG L Q, FENG H L, et al., 2008. Theory and analysis of wetlands’ eco-hydrological configuration[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 28(6): 2887-2893. | |
| [41] | 高会, 2018. 闽江河口湿地植物-土壤系统硅素的分配特征研究[D]. 福州: 福建师范大学: 40-47. |
| GAO H, 2018. Distribution characteristics of silica in plant-soil systems in the wetland of Min River estuary[D]. Fuzhou: Fujian Normal University: 40-47. | |
| [42] |
侯贯云, 翟水晶, 乐晓青, 等, 2017. 潮汐对闽江口感潮湿地孔隙水及土壤中硅、氮浓度的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 28(1): 337-344.
DOI |
| HOU G Y, ZHAI S J, LE X Q, et al., 2017. Influences of tide on silicon and nitrogen contents in soil and porewater in the Minjiang River estuary, Southeast China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 28(1): 337-344. | |
| [43] | 黄镇国, 1996. 中国南方红色风化壳[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社: 1-56. |
| HUANG Z G, 1996. Red weathered crust in southern China[M]. Beijing: Chinese Ocean Press: 1-56. | |
| [44] | 贾国涛, 顾会战, 许自成, 等, 2016. 作物硅素营养研究进展[J]. 山东农业科学, 48(5): 153-158. |
| JIA G T, GU H Z, XU Z C, et al., 2016. Research progress on silica nutrition in crops[J]. Shandong Agricultural Sciences, 48(5): 153-158. | |
| [45] | 李家书, 谢振翅, 胡定金, 等, 1997. 湖北省土壤有效硅含量分布[J]. 热带亚热带土壤科学, 6(3): 176-181. |
| LI J S, XIE Z C, HU D J, et al., 1997. Study on soil available silicon content and Si fertilizer application in Hubei[J]. Tropical and Subtropical Soil Science, 6(3): 176-181. | |
| [46] | 李亚瑾, 2021. 闽江福州段湿地沉积物重金属分布特征及其生态风险评估[D]. 福州: 福建师范大学: 10-14. |
| LI Y J, 2021. Spatial distribution and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in marsh sediments in Fuzhou reaches of the Min River[D]. Fuzhou: Fujian Normal University: 10-14. | |
| [47] | 李自民, 宋照亮, 李蓓蕾, 2013. 白洋淀芦苇湿地生态系统中植硅体的产生和积累研究[J]. 土壤学报, 50(3): 632-636. |
| LI Z M, SONG Z L, LI P L, 2013. Generation and accumulation of phytoliths in Baiyangdian reed wetland ecosystems[J]. Acta Pedological Sinica, 50(3): 632-636. | |
| [48] | 渠悦, 马涛, 胡月明, 等, 2021. 从化区农田耕层土壤有效硅空间分布及影响因素[J]. 农业资源与环境学报, 38(6): 989-998. |
| LIAN Y, MA T, HU Y M, et al., 2021. Spatial distribution and influencing factors of soil available silicon in farmland cultivated layers in Conghua district[J]. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment, 38(6): 989-998. | |
| [49] | 刘丽君, 黄张婷, 孟赐福, 等, 2021. 中国不同生态系统土壤硅的研究进展[J]. 土壤学报, 58(1): 31-41. |
| LIU L J, HUANG Z T, MENG C F, et al., 2021. Research progress on soil silicon in different ecosystems in China[J]. Acta Pedological Sinica, 58(1): 31-41. | |
| [50] | 刘鸣达, 张玉龙, 2001. 水稻土硅素肥力的研究现状与展望[J]. 土壤通报, 32(4): 187-192. |
| LIU M D, ZHANG Y L, 2001. Advance in the study of silicon fertility in paddy fields[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 32(4): 187-192. | |
| [51] | 刘森, 冉祥滨, 车宏, 等, 2014. 黄河口湿地土壤中生物硅的分布与植硅体的形态特征[J]. 土壤, 46(5): 886-893. |
| LIU S, RAN X B, CHE H, et al., 2014. Distribution of biogenic silica and composition of phytolith in the Yellow River estuary wetland[J]. Soils, 46(5): 886-893. | |
| [52] | 马朝红, 杨利, 胡时友, 2009. 土壤供硅能力与硅肥应用研究进展[J]. 湖北农业科学, 48(4): 987-989. |
| MA C H, YANG L, HU S Y, 2009. Silicon supplying ability of soil and advances of silicon fertilizer research[J]. Hubei Agricultural Sciences, 48(4): 987-989. | |
| [53] | 米慧珊, 2016. 闽江河口湿地典型植物群落与交错带SiO2分布特征及植硅体固碳潜力研究[D]. 福州: 福建师范大学: 15-30. |
| MI H S, 2016. Distribution characteristics of SiO2 and the potential of phytolith sequestration carbon in typical plant communities and ecotones in the Min River Estuary[D]. Fuzhou: Fujian Normal University: 15-30. | |
| [54] | 邱思婷, 米慧珊, 高会, 等, 2020. 闽江河口湿地不同植被带土壤全硅的含量及分布特征[J]. 生态学报, 40(22): 8306-8314. |
| QIU S T, MI H S, GAO H, et al., 2020. Total silicon content and distribution characteristics of wetland soil in different vegetation zones in the Min River estuary[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 40(22): 8306-8314. | |
| [55] | 冉祥滨, 车宏, 臧家业, 等, 2015. 黄河流域硅的组成与输出[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 45(7): 982-993. |
| RAN X B, CHE H, ZANG J Y, et al., 2015. Variability in the composition and export of silica in the Huanghe River Basin[J]. Science China Press, 45(7): 982-993. | |
| [56] | 王赛, 翟水晶, 邱思婷, 等, 2022. 闽江下游湿地植物硅素空间分布特征及其影响因素[J]. 亚热带资源与环境学报, 17(1): 58-63. |
| WANG S, ZHAI S J, QIU S T, et al., 2022. Spatial distribution characteristics of plant silicon in wetlands downstream of Min River[J]. Journal of Subtropical Resources and Environment, 17(1): 58-63. | |
| [57] | 王仕海, 张崇德, 杨文钢, 等, 2022. 六盘水市烟田土壤有效硅含量与空间分布特征[J]. 土壤, 54(5): 945-949. |
| WANG S H, ZHANG C D, YANG W G, et al., 2022. Contents and spatial distribution of soil available silicon of tobacco fields in Liupanshui city[J]. Soils, 54(5): 945-949. | |
| [58] | 王生全, 谢宵斐, 侯晨涛, 等, 2009. 煤矸石制作硅肥技术试验研究[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 37(6): 43-46. |
| WANG S Q, XIE X F, HOU J T, et al., 2009. Technology for producing silicon fertilizer from coal gangue[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 37(6): 43-46. | |
| [59] | 汪秀芳, 叶文, 陈圣宾, 等, 2007. 漳江流域沿岸植物叶片中Si元素含量的变化[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 29(6): 47-52. |
| WANG X F, YE W, CHEN S B, et al., 2007. Changes of Si concentration in leaves of plants along the Zhangjiang River Watershed, southeastern China[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 29(6): 47-52. | |
| [60] | 魏朝富, 杨剑虹, 高明, 等, 1997. 紫色水稻土硅有效性的研究[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 3(3): 229-236. |
| WEI C F, YANG J H, GAO M, et al., 1997. Study on available of silicon in paddy soils from purple soil[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 3(3): 229-236. | |
| [61] | 杨雅杰, 1995. 用镍坩埚碱溶消化测定水稻植株硅的方法[J]. 生物技术, 5(3): 42-44. |
| YANG Y J, 1995. Separation、characterization、immobilization of photobacteria in PVA vectors and application of it in cleaning water of fish pool[J]. Biotechnology, 5(3): 42-44. | |
| [62] | 臧家业, 王昊, 刘军, 等, 2020. 生物硅组成及对硅循环影响的研究进展[J]. 海洋科学进展, 38(1): 11-20. |
| ZANG J Y, WANG H, LIU J, et al., 2020. The research progress in biogenic silica composition and its impactions on silica cycle[J]. Advances in Marine Sciences, 38(1): 11-20. | |
| [63] | 翟水晶, 薛丽丽, 2016. 闽江口潮滩湿地不同植被带土壤及间隙水中硅的分布特征[J]. 生态学报, 36(21): 6766-6776. |
| ZHAI S J, XUE L L, 2016. Changes in the distribution of silica in the porewaters and sediments of the intertidal zone with different plant communities in the Min River Estuary[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 36(21): 6766-6776. | |
| [64] | 张林海, 曾从盛, 仝川, 2008. 闽江河口湿地芦苇和互花米草生物量季节动态研究[J]. 亚热带资源与环境学报, 3(2): 25-33. |
| ZHANG L H, ZENG C S, TONG C, 2008. Study on biomass dynamics of phragmites australis and spartina alterniflora in the wetlands of Minjiang River Estuary[J]. Journal of Subtropical Resources and Environment, 3(2): 25-33. | |
| [65] | 张晓东, 2016. 中国东部森林土壤中植硅体积累和硅形态分布研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江农林大学: 29-37. |
| ZHANG X D, 2016. Research on phytolith accumulation and noncrystalline silicon distribution of forest soils in East China[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang A & F University: 29-37. | |
| [66] | 张兴梅, 张之一, 殷奎生, 等, 1996. 土壤有效硅含量及其与土壤理化性状的相关研究[J]. 黑龙江八一农垦大学学报, 8(4): 42-45. |
| ZHANG X M, ZHANG Z Y, YIN K S, et al., 1996. Study on the available silicon content and the relationship between it and the properties of physics and chemistry of soils[J]. Journal of Heilongjiang august first land Reclamation University, 8(4): 42-45. | |
| [67] | 赵烨, 李天杰, 1995. 南极乔治王岛菲尔德斯半岛土壤矿物化学风化特征分析[J]. 南极研究(中文版), 7(2): 21-27. |
| ZHAO Y, LI T J, 1995. Analysis of the chemical weathering characteristics of soil minerals on fields peninsula of King George Island, Antarctica[J]. Antarctic Research (Chinese edition), 7(2): 21-27. | |
| [68] | 郑德祥, 钟兆全, 龚直文, 等, 2005. 闽江流域生态安全问题及建议[J]. 北华大学学报(自然科学版), 6(5): 445-448. |
| ZHENG D X, ZHONG Z Q, GONG Z W, et al., 2005. The problems of ecological security in Minjiang River basin and suggestion[J]. Journal of Beihua University (Natural Science), 6(5): 445-448. |
| [1] | 范贝贝, 丁帅, 张田田, 张帅, 魏露露, 陈清. 周期性淹水-落干和施用秸秆对白云石改良棕壤磷素流失风险的模拟研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(8): 1203-1213. |
| [2] | 庞波, 海香, 张海芳, 张艳军, 王慧, 刘红梅, 杨殿林. 藜芦扩散对山地草甸草地植被特征和土壤理化性质的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(8): 1174-1181. |
| [3] | 欧阳美凤, 尹宇莹, 张金谌, 刘清霖, 谢意南, 方平. 洞庭湖典型水域重金属含量的空间分布与来源解析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(8): 1269-1278. |
| [4] | 林于蓝, 陈厚朴, 于文豪, 王宝英, 张杨, 张金波, 蔡祖聪, 赵军. 强还原处理对土壤中常见抗生素及其抗性基因的影响研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(7): 1107-1116. |
| [5] | 张京磊, 王国良, 吴波, 贾春林, 张进红, 周圆, 马冰. 滨海盐碱地苜蓿-小黑麦轮作对土壤细菌和真菌群落多样性与网络结构的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(7): 1048-1062. |
| [6] | 李璇, 王路茗, 闫春妮, 黄娟. 金属氧化物与非金属氧化物纳米颗粒暴露下人工湿地微生物群落的响应差异[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(7): 1089-1095. |
| [7] | 蒋云峰, 严婷, 刘俊男, 马丙增, 王海萌, 窦笑萌. 黑土区农田中型土壤动物群落对免耕玉米秸秆覆盖频率的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(5): 699-707. |
| [8] | 吴文伟, 沈城, 沙晨燕, 林匡飞, 吴健, 谢雨晴, 周璇. 城市工业地块土壤重金属污染风险评价与源解析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(5): 791-801. |
| [9] | 李多美, 孔涛, 陈曦, 高明夫, 高熙梣, 曾泽宇, 保佳慧. 古龙酸母液混制肥和草席覆盖措施对新疆旱区牧草生长和土壤养分含量的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(4): 548-559. |
| [10] | 黄倩, 朱时应, 李天顺, 李明燕, 索南措, 普布. 西藏热振国家森林公园土壤原生动物群落沿海拔分布格局及其与环境因子的关联特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(4): 499-508. |
| [11] | 卫玺玺, 晁鑫艳, 郑景明, 唐可欣, 万龙, 周金星. 贺兰山东、西侧典型植物群落物种多样性差异及其影响因子[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(4): 520-530. |
| [12] | 陈弘杰, 廖洪凯, 龙健, 赵雨鑫, 湛凯翔, 冉泰山, 杨国梅. 强还原土壤灭菌对土壤原生生物群落的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(4): 539-547. |
| [13] | 何杰, 李宗明, 杨正宇, 沈健林, 刘国平, 吴金水. 牛粪化肥配施对双季稻田CH4和N2O排放的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(4): 573-584. |
| [14] | 何艺, 秦欣欣, 张翔, 孙楠, 杨雅淋, 连军锋. 微塑料断面分布的不均一性——以赣江水域赣州段为例[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(4): 626-632. |
| [15] | 刘楚天, 郭栋栋, 侯磊, 梁启斌, 王艳霞, 施艳婷, 戚艳娥. 营养调控影响滇杨幼苗镉积累的效应模型分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(3): 460-468. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
