生态环境学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (4): 548-559.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2024.04.006
李多美1( ), 孔涛1,*, 陈曦1, 高明夫2, 高熙梣1, 曾泽宇1, 保佳慧3
), 孔涛1,*, 陈曦1, 高明夫2, 高熙梣1, 曾泽宇1, 保佳慧3
收稿日期:2023-11-28
出版日期:2024-04-18
发布日期:2024-05-31
通讯作者:
*孔涛。作者简介:李多美(1996年生),女,硕士研究生,生态修复理论与技术研究。E-mail: duomeili1996@hotmail.com
基金资助:
LI Duomei1( ), KONG Tao1,*, CHEN Xi1, GAO Mingfu2, GAO Xichen1, ZENG Zeyu1, BAO Jiahui3
), KONG Tao1,*, CHEN Xi1, GAO Mingfu2, GAO Xichen1, ZENG Zeyu1, BAO Jiahui3
Received:2023-11-28
Online:2024-04-18
Published:2024-05-31
摘要:
古龙酸母液(RAE)是工业上通过二步发酵法生产维生素C过程中产生的废液,胶质芽胞杆菌(Bacillus mucilaginosus)是解钾细菌,二者在改善土壤质量、提升土壤肥力和促进植物生长方面具有重要意义。使用RAE与胶质芽胞杆菌的混合液作为古龙酸母液混制肥(RB),设RB施加量为0%(CK)、0.5%、1.0%的3个处理,并设置草席覆盖和未覆盖处理,开展田间小区试验,对紫花苜蓿(Medicago sativa)和披碱草(Elymus dahuricus)的生长、生理指标、土壤养分指标及相关关系进行分析。结果表明,相同覆盖处理下,RB总体上显著提高了牧草的生长和生理指标,表现为1.0%>0.5%>CK,在1.0% RB处理下,紫花苜蓿的地上生物量平均提高了112%,披碱草平均提高了80.1%。相同RB施加量处理,覆盖处理的牧草总体上发芽率、发芽势、株高、地上生物量和根系发育显著高于未覆盖处理,紫花苜蓿和披碱草发芽率平均提高164%和194%,地上生物量平均提高64.3%和24.9%。相同覆盖处理下,土壤有机碳和速效养分含量均随RB处理有效提高,1.0%RB将土壤有机碳和速效钾分别显著提高了33.1%和105%。相同RB施加量下,覆盖处理能提高土壤的有机碳含量,平均提高了2.75%。双因素方差分析表明RB和草席覆盖措施对牧草的生长、生理指标和土壤养分含量具有显著的交互影响。冗余分析和Pearson相关性分析表明影响牧草生长生理指标的环境因子主要为有机碳、铵态氮、有效磷、速效钾,建议采用1.0% RB与草席覆盖联用来改良新疆旱区土壤促进牧草生长。研究结果为古龙酸母液、胶质芽胞杆菌资源化利用和新疆旱区土地资源开发提供了科学依据。
中图分类号:
李多美, 孔涛, 陈曦, 高明夫, 高熙梣, 曾泽宇, 保佳慧. 古龙酸母液混制肥和草席覆盖措施对新疆旱区牧草生长和土壤养分含量的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(4): 548-559.
LI Duomei, KONG Tao, CHEN Xi, GAO Mingfu, GAO Xichen, ZENG Zeyu, BAO Jiahui. Effects of Residue after Evaporation Mixed Fertilizer and Grass Mat Mulching Measures on the Growth and Soil Nutrient Content of Pasture Grasses in the Dry Zone of Xinjiang[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2024, 33(4): 548-559.
| 处理方式 | 处理组别 | 施加量 | 简写 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 紫花苜蓿 (Medicago sativa)+草席覆盖 | ZF | 0% (CK) | CKZF |
| 紫花苜蓿 (Medicago sativa)+草席覆盖 | ZF | 0.5% | 0.5% ZF |
| 紫花苜蓿 (Medicago sativa)+草席覆盖 | ZF | 1.0% | 1.0% ZF |
| 紫花苜蓿 (Medicago sativa) 无覆盖 | ZW | 0% (CK) | CKZW |
| 紫花苜蓿 (Medicago sativa) 无覆盖 | ZW | 0.5% | 0.5% ZW |
| 紫花苜蓿 (Medicago sativa) 无覆盖 | ZW | 1.0% | 1.0% ZW |
| 披碱草 (Elymus dahuricus)+草席覆盖 | PF | 0% (CK) | CKPF |
| 披碱草 (Elymus dahuricus)+草席覆盖 | PF | 0.5% | 0.5% PF |
| 披碱草 (Elymus dahuricus)+草席覆盖 | PF | 1.0% | 1.0% PF |
| 披碱草 (Elymus dahuricus) 无覆盖 | PW | 0% (CK) | CKPW |
| 披碱草 (Elymus dahuricus) 无覆盖 | PW | 0.5% | 0.5% PW |
| 披碱草 (Elymus dahuricus) 无覆盖 | PW | 1.0% | 1.0% PW |
表1 实验处理组别
Table 1 Experimental treatment groups
| 处理方式 | 处理组别 | 施加量 | 简写 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 紫花苜蓿 (Medicago sativa)+草席覆盖 | ZF | 0% (CK) | CKZF |
| 紫花苜蓿 (Medicago sativa)+草席覆盖 | ZF | 0.5% | 0.5% ZF |
| 紫花苜蓿 (Medicago sativa)+草席覆盖 | ZF | 1.0% | 1.0% ZF |
| 紫花苜蓿 (Medicago sativa) 无覆盖 | ZW | 0% (CK) | CKZW |
| 紫花苜蓿 (Medicago sativa) 无覆盖 | ZW | 0.5% | 0.5% ZW |
| 紫花苜蓿 (Medicago sativa) 无覆盖 | ZW | 1.0% | 1.0% ZW |
| 披碱草 (Elymus dahuricus)+草席覆盖 | PF | 0% (CK) | CKPF |
| 披碱草 (Elymus dahuricus)+草席覆盖 | PF | 0.5% | 0.5% PF |
| 披碱草 (Elymus dahuricus)+草席覆盖 | PF | 1.0% | 1.0% PF |
| 披碱草 (Elymus dahuricus) 无覆盖 | PW | 0% (CK) | CKPW |
| 披碱草 (Elymus dahuricus) 无覆盖 | PW | 0.5% | 0.5% PW |
| 披碱草 (Elymus dahuricus) 无覆盖 | PW | 1.0% | 1.0% PW |
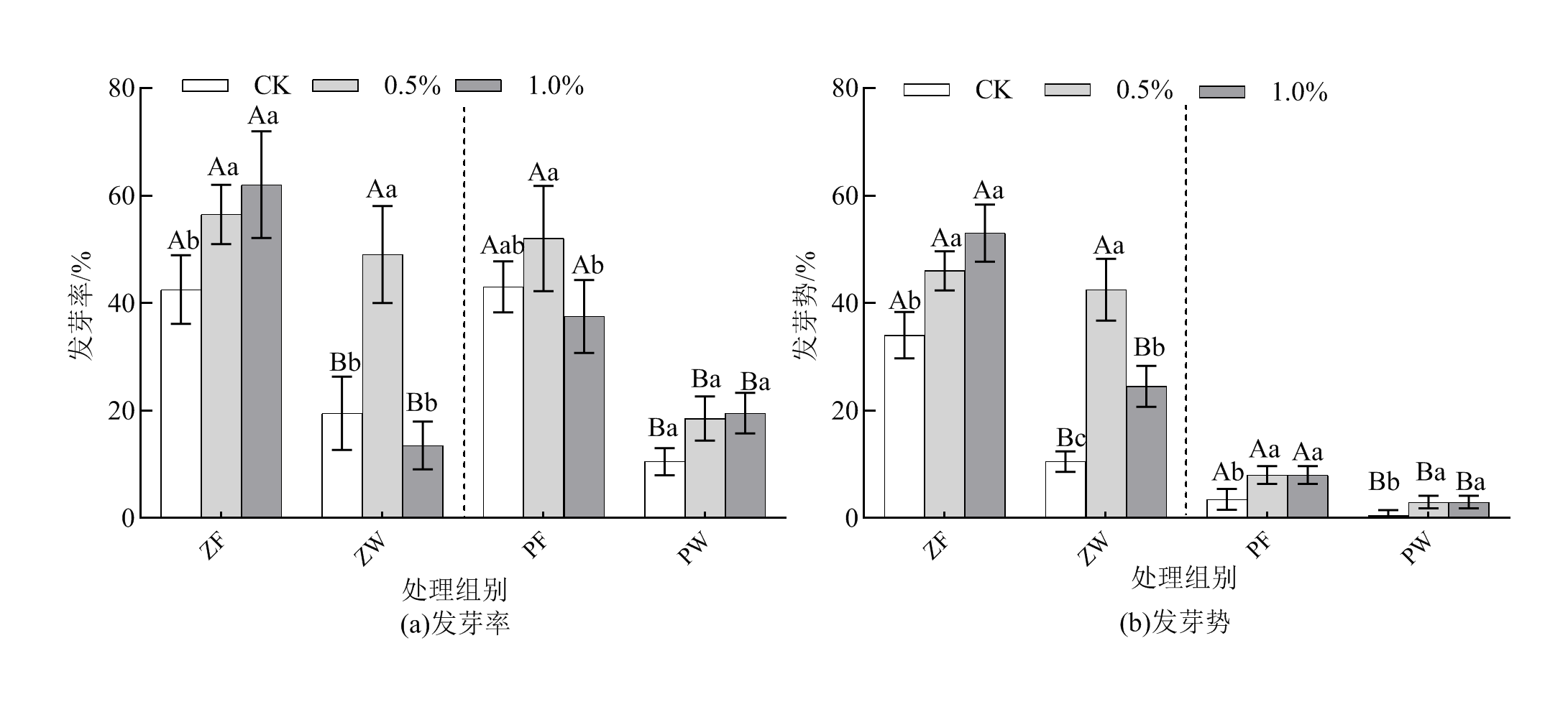
图2 RB和草席覆盖处理下的牧草发芽率和发芽势 不同小写字母表示同一草席覆盖措施处理(覆盖和未覆盖)下不同施加量的RB之间存在显著差异,不同大写字母表示同一RB处理下不同草席覆盖措施处理之间存在显著差异(p<0.05),n=3;紫花苜蓿和披碱草以虚线分隔开。下同
Figure 2 Forage germination and germination potential under RB and mat cover treatments
| 影响因素 | 发芽率 | 发芽势 | 株高 | 地上生物量 | Ca | Cb | Cab | Ccar | L-抗坏血酸 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 覆盖 | 204.38*** | 151.77*** | 171.50*** | 66.19*** | 0.15 | 13.91** | 0.56 | 0.01 | 1.38 |
| 施加量 | 16.55*** | 262.18*** | 105.99*** | 125.48*** | 10.29*** | 9.36*** | 14.96*** | 10.31*** | 57.14*** |
| 覆盖×施加量 | 9.34*** | 25.37*** | 12.00*** | 12.56*** | 1.38 | 4.71* | 0.99 | 5.58** | 1.78 |
表2 RB的施加量和覆盖措施对牧草发芽、生长及生理指标影响的双因素方差分析
Table 2 Two-factor analysis of variance (ANOVA) of the effects of RB application and mulching measures on forage seedling germination, growth and physiological indices
| 影响因素 | 发芽率 | 发芽势 | 株高 | 地上生物量 | Ca | Cb | Cab | Ccar | L-抗坏血酸 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 覆盖 | 204.38*** | 151.77*** | 171.50*** | 66.19*** | 0.15 | 13.91** | 0.56 | 0.01 | 1.38 |
| 施加量 | 16.55*** | 262.18*** | 105.99*** | 125.48*** | 10.29*** | 9.36*** | 14.96*** | 10.31*** | 57.14*** |
| 覆盖×施加量 | 9.34*** | 25.37*** | 12.00*** | 12.56*** | 1.38 | 4.71* | 0.99 | 5.58** | 1.78 |
| 影响因素 | 总根长 | 根平均直径 | 根体积 | 根表面积 | 根投影面积 | 根尖数 | 有机碳 | 硝态氮 | 铵态氮 | 有效磷 | 速效钾 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 覆盖 | 40.96***1) | 2.29 | 15.73**2) | 30.99*** | 27.27*** | 14.98** | 1.33 | 0.81 | 0.02 | 2.87 | 0.90 |
| 施加量 | 36.31*** | 18.07*** | 94.25*** | 90.23*** | 79.41*** | 11.10*** | 18.81*** | 5.27** | 6.92*** | 14.26*** | 6.44** |
| 覆盖×施加量 | 12.03*** | 1.67 | 4.25** | 10.46*** | 9.21*** | 14.04*** | 2.29*3) | 1.48 | 10.94*** | 5.30** | 0.99 |
表3 RB的施加量和覆盖措施对牧草根系发育和土壤养分含量影响的双因素方差分析
Table 3 Two-way ANOVA of the effects of RB application and mulching practices on forage root development and soil nutrient content
| 影响因素 | 总根长 | 根平均直径 | 根体积 | 根表面积 | 根投影面积 | 根尖数 | 有机碳 | 硝态氮 | 铵态氮 | 有效磷 | 速效钾 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 覆盖 | 40.96***1) | 2.29 | 15.73**2) | 30.99*** | 27.27*** | 14.98** | 1.33 | 0.81 | 0.02 | 2.87 | 0.90 |
| 施加量 | 36.31*** | 18.07*** | 94.25*** | 90.23*** | 79.41*** | 11.10*** | 18.81*** | 5.27** | 6.92*** | 14.26*** | 6.44** |
| 覆盖×施加量 | 12.03*** | 1.67 | 4.25** | 10.46*** | 9.21*** | 14.04*** | 2.29*3) | 1.48 | 10.94*** | 5.30** | 0.99 |
| 环境参数 | 叶绿素a | 叶绿素b | 总叶绿素 | 类胡萝卜素 | 总根长 | 根体积 | 根尖数 | L-抗坏血酸 | 株高 | 地上生物量 | 发芽率 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 有机碳 | 0.190 | 0.066 | 0.174 | 0.399* | 0.211 | 0.266 | 0.029 | 0.010 | 0.060 | 0.420* | 0.359* |
| 铵态氮 | -0.551** 1) | -0.302 | -0.580** | -0.444** | 0.190 | 0.210 | 0.050 | 0.239 | -0.460** | 0.328 | 0.137 |
| 硝态氮 | -0.142 | -0.191 | -0.186 | -0.022 | -0.010 | 0.126 | -0.157 | 0.298 | -0.195 | -0.008 | -0.033 |
| 有效磷 | 0.517** | 0.421* 2) | 0.573** | 0.017 | -0.240 | -0.228 | 0.120 | -0.439** | 0.410* | -0.433** | -0.374* |
| 速效钾 | 0.516** | 0.164 | 0.533** | 0.276 | -0.265 | -0.233 | 0.023 | -0.319 | 0.471** | -0.404* | -0.328 |
表4 土壤养分含量与牧草生长生理指标的相关系数
Table 4 Correlation coefficient between soil nutrient content and forage growth physiological indexes
| 环境参数 | 叶绿素a | 叶绿素b | 总叶绿素 | 类胡萝卜素 | 总根长 | 根体积 | 根尖数 | L-抗坏血酸 | 株高 | 地上生物量 | 发芽率 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 有机碳 | 0.190 | 0.066 | 0.174 | 0.399* | 0.211 | 0.266 | 0.029 | 0.010 | 0.060 | 0.420* | 0.359* |
| 铵态氮 | -0.551** 1) | -0.302 | -0.580** | -0.444** | 0.190 | 0.210 | 0.050 | 0.239 | -0.460** | 0.328 | 0.137 |
| 硝态氮 | -0.142 | -0.191 | -0.186 | -0.022 | -0.010 | 0.126 | -0.157 | 0.298 | -0.195 | -0.008 | -0.033 |
| 有效磷 | 0.517** | 0.421* 2) | 0.573** | 0.017 | -0.240 | -0.228 | 0.120 | -0.439** | 0.410* | -0.433** | -0.374* |
| 速效钾 | 0.516** | 0.164 | 0.533** | 0.276 | -0.265 | -0.233 | 0.023 | -0.319 | 0.471** | -0.404* | -0.328 |
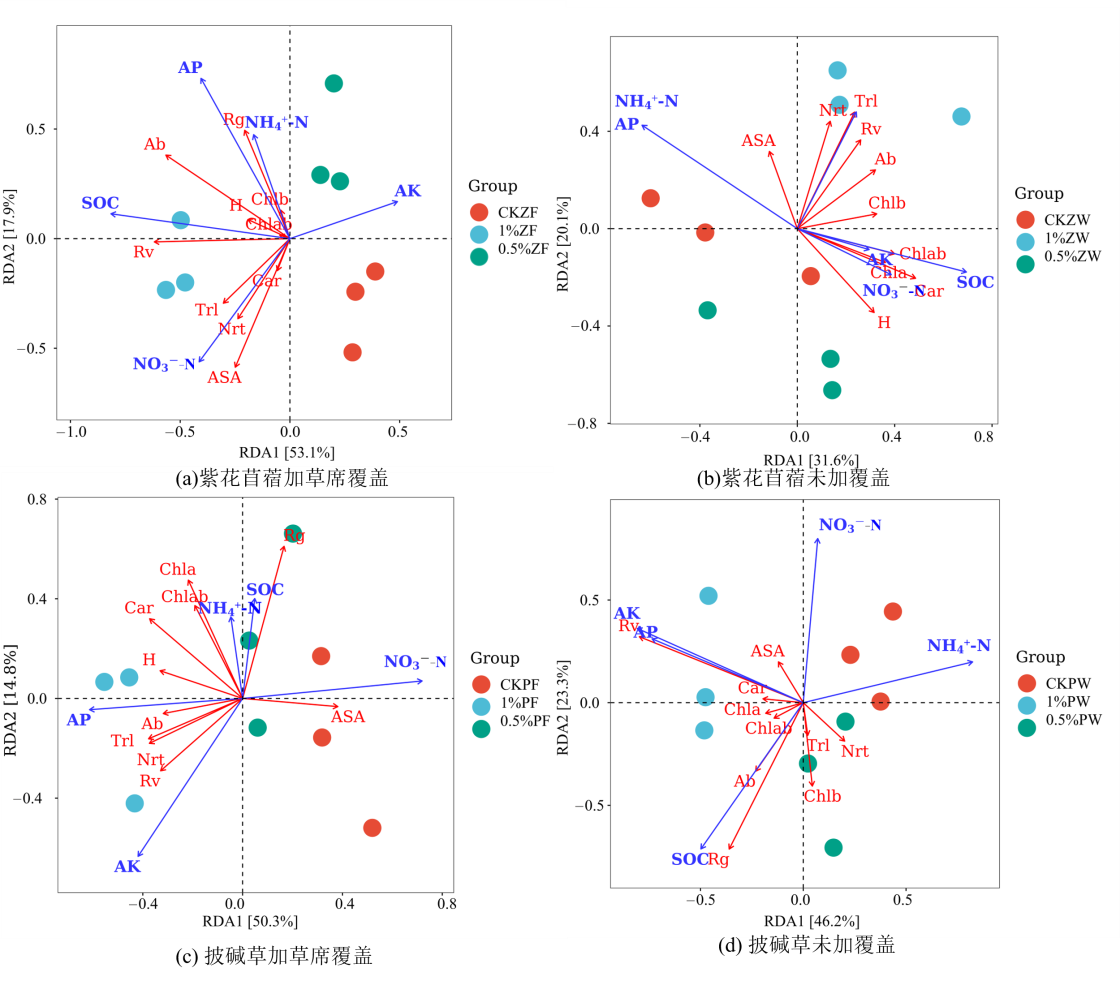
图8 牧草生长生理指标与环境因子的冗余分析 图中ASA表示L-抗坏血酸;Trl表示总根长;Rv表示根体积;Nrt表示根尖数;Chla表示叶绿素a;Chlb表示叶绿素b;Chlab表示总叶绿素;Car表示类胡萝卜素;H表示株高;Ab表示地上生物量;Rg表示发芽;NO3--N表示硝态氮;NH4+-N表示铵态氮
Figure 8 Redundancy analysis of plant physiological indicators and environmental factors
| [1] | CHEN Y P, REKHA P D, ARUN A B, et al., 2006. Phosphate solubilizing bacteria from subtropical soil and their tricalcium phosphate solubilizing abilities[J]. Applied Soil Ecology, 34(1): 33-41. |
| [2] | CHEN S, LIAN B, LIU C Q, 2008. Effect of Bacillus mucilaginosus on weathering of phosphorite and a preliminary analysis of bacterial proteins[J]. Chinese Journal of Geochemistry, 27: 209-216 |
| [3] | GAO M F, SUN H, SHI M J, et al., 2021. 2-Keto-L-gulonic acid improved the salt stress resistance of non-heading chinese cabbage by increasing L-ascorbic acid accumulation[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 12: 697184. |
| [4] | HEI J Y, WANG S, HE X H, 2023. Effects of exogenous organic acids on the growth, edaphic factors, soil extracellular enzymes, and microbiomes predict continuous cropping obstacles of Panax notoginseng from the forest understorey[J]. Plant and Soil, DOI:10.1007/s11104-023-06044-0. |
| [5] |
KONG T, XU H, WANG Z Y, et al., 2014. Effect of a residue after evaporation from industrial vitamin C fermentation on chemical and microbial properties of alkali-saline soil[J]. Pakistan journal of pharmaceutical sciences, 27(4 Suppl): 1069-1074.
PMID |
| [6] | LICHTENTHALER H K, 1987. Chlorophylls and carotenoids: Pigments of photosynthetic biomembranes[M]// Methods in enzymology. Academic Press, 148: 350-382. |
| [7] | SABIR M, HANAFI M M, ZIA-UR-REHMANe M, et al., 2014. Comparison of low-molecular-weight organic acids and ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid to enhance phytoextraction of heavy metals by maize[J]. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 45(1): 42-52. |
| [8] | SHAO P, LIANG C, RUBERT-NASON K, et al., 2019. Secondary successional forests undergo tightly-coupled changes in soil microbial community structure and soil organic matter[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 128: 56-65. |
| [9] | TYAGI S, VERMA P C, SINGH K, et al., 2020. Molecular characterization of ascorbate peroxidase (APX) and APX-related (APX-R) genes in Triticum aestivum L.[J]. Genomics, 112(6): 4208-4223. |
| [10] | WANG B, SUN H, YANG W C, et al., 2022. Potential utilization of vitamin C industrial effluents in agriculture: oil fertility and bacterial community composition[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 851(Part 2): 158253. |
| [11] |
ZHANG W, ZHOU Q P, CHEN Y J, et al., 2021. Comparison of production performance and forage quality of ten introduced oat varieties in Hulunbuir, China[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 30(12): 129-142.
DOI |
| [12] | ZHAO Y F, WANG X, CHEN F, et al., 2023. Soil organic matter enhances aboveground biomass in alpine grassland under drought[J]. Geoderma, 433: 116430. |
| [13] | 鲍士旦, 2000. 土壤农化分析[M]. 第3版. 北京: 中国农业出版社. |
| BAO S D, 2000. Soil agrochemical analysis[M]. Third Edition. Beijing: China Agriculture Press. | |
| [14] | 葛小艺, 2023. 维C工业废母液对不结球白菜氮素利用及品质的影响[J/OL]. 沈阳: 生态学杂志, 1-10 [2024-3-14]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/21.1148.Q.20230508.1729.006.html . |
| GE X Y, 2023. Effect of vitamin C industrial waste mother liquor on nitrogen utilization and quality of Brassica rapa L.[J/OL]. Shenyang: Chinese Journal of Ecology, 1-10 [2024-3-14]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/21.1148.Q.20230508.1729.006.html . | |
| [15] |
高熙梣, 孔涛, 李华孙, 等, 2023. 古龙酸母液、木霉菌与活性污泥配施对矸石山黑麦草生理特性及土壤微生物性质的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 32(9): 1709-1718.
DOI |
| GAO X C, KONG T, LI H S, et al., 2023. Effect of combined application residue after evaporation, Trichoderma longibrachiatum and activated sludge on physiological characteristics of perennial ryegrass and soil microbial properties in gangue hill[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 32(9): 1709-1718. | |
| [16] | 胡立峰, 胡春胜, 安忠民, 等, 2005. 不同土壤耕作法对作物产量及土壤硝态氮淋失的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 19(6): 186-189. |
| HU L F, HU C S, AN Z M, et al., 2005. Effect of different soil tillage practices on crop yield and soil nitrate-nitrogen leaching[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 19(6): 186-189. | |
| [17] | 韩晓, 高明夫, 徐慧, 2023. 维生素C工业废弃液对新疆盐碱土中棉花种子萌发的影响[J]. 江苏农业科学, 51(17): 105-111. |
| HAN X, GAO M F, XU H, 2023. Impact of vitamin C industrial waste liquid on Gossypium hirsutum seed germination in saline-alkali soil in Xinjiang area[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 51(17): 105-111. | |
| [18] | 孔涛, 孟凡浩, 关飞, 等, 2015. 古龙酸母液对盐碱土壤微生物数量和酶活性的影响[J]. 环境化学, 34(11): 2053-2058. |
| KONG T, MENG F H, GUAN F, et al., 2015. Effect of colognic acid mother liquor on microbial abundance and enzyme activity in saline-alkali soil[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 34(11): 2053-2058. | |
| [19] | 孔涛, 李勃, 李志能, 等, 2016. 古龙酸母液和北虫草废弃培养基混制有机肥对设施蔬菜和土壤肥力的影响[J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 53(6): 56-61. |
| KONG T, LI B, LI Z N, et al., 2016. Effect of the ecological organic fertilizer made from residue after evaporation and Chinese caterpillar fungus wastes on greenhouse vegetable and soil fertility[J]. Soil and Fertilizer in China, 53(6): 56-61. | |
| [20] | 孔涛, 任曦玥, 张宇航, 等, 2021. 胶质芽孢杆菌与苜蓿根瘤菌双接种对排土场紫花苜蓿生长和土壤性质的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 35(4): 321-326. |
| KONG T, REN X Y, ZHANG Y H, et al., 2021. Effect of dual inoculant of Paenibacillus mucilaginosus and Rhizobium meliloti on Medicago sativa growth and soil properties of dumping in mining area[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 35(4): 321-326. | |
| [21] |
雷海英, 赵青松, 杨潇, 等, 2020. 苦参根际高效固氮菌的分离及复合菌肥对幼苗的促生效应[J]. 生物技术通报, 36(9): 157-166.
DOI |
| LEI H Y, ZHAO Q S, YANG X, et al., 2020. Isolation of efficient nitrogen-fixing Bacteria from the rhizosphere of aophora flavescens and the growth-promoting effect of compound microbial fertilizer on seedlings[J]. Biotechnology Bulletin, 36(9): 157-166. | |
| [22] | 刘五星, 徐旭士, 杨启银, 等, 2004. 胶质芽孢杆菌对土壤矿物的分解作用及机理研究[J]. 土壤, 47(5): 547-550. |
| LIU W X, XU X S, YANG Q Y, et al., 2004. Mechanisms of Bacillus mucilaginosus decomposing soil minerals[J]. Soils, 47(5): 547-550. | |
| [23] | 马树庆, 王琪, 吕厚荃, 等, 2012. 水分和温度对春玉米出苗速度和出苗率的影响[J]. 生态学报, 32(11): 3378-3385. |
| MA S Q, WANG Q, LÜ H Q, et al., 2012. Impact of water and temperature on spring Zea mays emergence speed and emergence rate[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 32(11): 3378-3385. | |
| [24] | 倪子怡, 许海, 詹旭, 等, 2024. 东南丘陵山区深水水库两种浮床植物脱氮效率对比研究[J]. 湖泊科学, 36(1): 123-136. |
| NI Z Y, XU H, ZHAN X, et al., 2024. Comparative research on nitrogen removal efficiency of two floating bed plants in deep reservoir of southeast hilly region[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 36(1): 123-136. | |
| [25] | 任曦玥, 2022. 芽孢杆菌与根瘤菌双接种对矿区排土场复垦效果的研究[D]. 阜新: 辽宁工程技术大学: 1-78. |
| REN X Y, 2022. Study on the effect of double inoculation of Bacillus and Rhizobium on the reclamation of dump in mining area[D]. Fuxin: Liaoning Technical University: 1-78. | |
| [26] | 宋歌, 孙波, 教剑英, 2007. 测定土壤硝态氮的紫外分光光度法与其他方法的比较[J]. 土壤学报, 44(2): 288-293. |
| SONG G, SUN B, JIAO J Y, 2007. Comparison of between ultraviolet spectrophotometry and other methods in determination of soil nitrate-N[J]. Journal of Soil Science, 44(2): 288-293. | |
| [27] | 宋金凤, 崔晓阳, 2008. 森林土壤中低分子有机酸研究进展[J]. 林业科学, 44(6): 118-124. |
| SONG J F, CUI X Y, 2008. Research progress on low molecular weight organic acids in forest soil[J]. Journal of Forestry Science, 44(6): 118-124. | |
| [28] | 孙亚钦, 叶盛嘉, 范国安, 等, 2022. 麦田土壤解磷细菌的筛选及其解磷能力研究[J]. 西北农业学报, 31(3): 379-387. |
| SUN Y Q, YE S J, FAN G A, et al., 2022. Isolation and phosphate solubilizing capability of phosphate-solubilizing bacteria in a wheat field[J]. Northwest Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 31(3): 379-387. | |
| [29] | 王艳玲, 何园球, 李成亮, 2007. 柠檬酸对红壤磷的持续活化效应及其活化机理的探讨[J]. 土壤学报, 44(1): 130-136. |
| WANG Y L, HE Y Q, LI C L, 2007. Persistent activating effect of citric acid on phosphorus in red soil and its mechanism[J]. Journal of Soil Science, 44(1): 130-136. | |
| [30] | 王轶夫, 孙玉军, 郭孝玉, 2013. 基于BP神经网络的马尾松立木生物量模型研究[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 35(2): 17-21. |
| WANG Y F, SUN Y J, GUO X Y, 2013. Single-tree biomass modeling of Pinus massoniana based on BP neural network[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 35(2): 17-21. | |
| [31] |
王亚文, 史慧芳, 张鹏, 等, 2021. 微生物菌肥在设施蔬菜生产中的研究进展[J]. 农学学报, 11(11): 27-32.
DOI |
|
WANG Y W, SHI H F, ZHANG P, et al., 2021. Research progress of microbial fertilizer in facility vegetable production[J]. Journal of Agriculture, 11(11): 27-32.
DOI |
|
| [32] |
王传旗, 刘文辉, 张永超, 等, 2021. 野生垂穗披碱草成苗期间的耐旱性研究[J]. 草业学报, 30(9): 76-85.
DOI |
| WANG C Q, LIU W H, ZHANG Y C, et al., 2021. Drought tolerance of wild Elymus nutans during germination and seedling establishment[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 30(9): 76-85. | |
| [33] | 王慧敏, 李明昊, 李云, 等, 2023. 谷子品种(系)萌发期耐盐碱性鉴定及评价[J]. 作物杂志, 39(2): 57-66. |
| WANG H M, LI M H, LI Y, et al., 2023. Identification and evaluation of salt-alkali tolerance of foxtail millet cultivars (lines) at germination stage[J]. Crops, 39(2): 57-66. | |
| [34] | 徐慧, 杨伟超, 李嘉文, 2021. 维生素C第二步混菌发酵技术研究新进展[J]. 微生物学杂志, 41(2): 1-9. |
| XU H, YANG W C, LI J W, 2021. New progress in the research of vitamin C second-step mixed fermentation technology[J]. Chinese Journal of Microbiology, 41(2): 1-9. | |
| [35] | 尹国丽, 贠旭疆, 师尚礼, 等, 2010. 半干旱区沟垄集雨种植对紫花苜蓿出苗及草产量的影响[J]. 甘肃农业大学学报, 45(1): 111-115. |
| YIN G L, YI X J, SHI S L, et al., 2010. Effects of furrow ridge rainfall harvesting planting on Medicago sativa seedling emergence and grass yield in semi-arid region[J]. Journal of Gansu Agricultural University, 45(1): 111-115. | |
| [36] | 杨晓帆, 梁家慧, 于文英, 等 2022. 促生荧光假单胞菌对桃树根区土壤环境和植株生长的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 28(8): 1494-1508. |
| YANG X F, LIANG J H, YU W Y, et al., 2022. Effect of pseudomonas fluorescens on rhizospheric soil quality and growth of peach (Prunus persica L. Batsch)[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 28(8): 1494-1508. | |
| [37] | 杨振亚, 周本智, 周燕, 等, 2018. PEG模拟干旱对毛竹种子萌发及生长生理特性的影响[J]. 林业科学研究, 31(6): 47-54. |
| YANG Z Y, ZHOU B Z, ZHOU Y, et al., 2018. Effects of drought stress simulated by PEG on seed germination and growth physiological characteristics of Phyllostachys edulis[J]. Forest Research, 31(6): 47-54. | |
| [38] | 张志忠, 孙志浩, 陈文辉, 等, 2013. 有机酸类化感物质对甜瓜的化感效应[J]. 生态学报, 33(15): 4591-4598. |
| ZHANG Z Z, SUN Z H, CHEN W H, et al., 2013. Allelopathic effects of organic acid allelochemicals on melon[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 33(15): 4591-4598. | |
| [39] | 庄正, 李艳娟, 刘青青, 等, 2017. 外源低分子有机酸对杉木种子萌发及幼苗抗氧化特性的影响[J]. 江西农业大学学报, 39(2): 302-311. |
| ZHUANG Z, LI Y J, LIU Q Q, et al., 2017. Effects of exogenous low molecular weight organic acids on seed germination and antioxidant characteristics of seedlings of chinese Cunninghamia lanceolata[J]. Journal of Jiangxi Agricultural University, 39(2): 302-311. | |
| [40] |
赵鹏志, 陈祥伟, 杨小燕, 等, 2018. 低分子有机酸对东北黑土酶活性与养分关系的影响[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 42(1): 105-112.
DOI |
| ZHAO P Z, CHEN X W, YANG X Y, et al., 2018. Effect of low molecular weight organic acids on enzyme activity and nutrient relationship in black soil in northeast china[J]. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Science Edition), 42(1): 105-112. | |
| [41] | 郑宁, 2023. 基于环境因子变化的区域植被叶绿素研究[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古工业大学: 1-137. |
| ZHENG N, 2023. A study on regional vegetation chlorophyll based on changes in environmental factors[D]. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia University of Technology: 1-137. |
| [1] | 高熙梣, 孔涛, 李华孙, 李多美, 张加良. 古龙酸母液、木霉菌与活性污泥配施对矸石山黑麦草生理特性及土壤微生物性质的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(9): 1709-1718. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
