生态环境学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (3): 460-468.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2024.03.014
刘楚天( ), 郭栋栋, 侯磊, 梁启斌, 王艳霞*, 施艳婷, 戚艳娥
), 郭栋栋, 侯磊, 梁启斌, 王艳霞*, 施艳婷, 戚艳娥
收稿日期:2024-01-30
出版日期:2024-03-18
发布日期:2024-05-08
通讯作者:
*王艳霞。作者简介:刘楚天(1995年生),男,硕士研究生,研究方向为重金属植物修复。E-mail: 752759936@qq.com
基金资助:
LIU Chutian( ), GUO Dongdong, HOU Lei, LIANG Qibin, WANG Yanxia*, SHI Yanting, QI Yane
), GUO Dongdong, HOU Lei, LIANG Qibin, WANG Yanxia*, SHI Yanting, QI Yane
Received:2024-01-30
Online:2024-03-18
Published:2024-05-08
摘要:
营养调控是强化植物修复效率的重要手段。滇杨(Populus yunnanensis)作为修复土壤镉(Cd)污染的重要候选树种,Cd耐受能力较强,但Cd积累量不高。以滇杨为研究对象,采用“3414”试验设计,开展氮(N)、磷(P)、钾(K)三因素四水平(0、100、200、400 mg∙kg−1)共15个处理的营养调控盆栽试验。通过肥料效应模型推算最佳施肥量、最大Cd积累量以及提升滇杨Cd积累量的最佳施肥方案。结果表明,施加N、P、K均能提升Cd胁迫下滇杨的生物量,提升比例为70.5%-132%,生物量随N、P和K浓度增加而呈现先增加后降低趋势,均在200 mg∙kg−1时达到最大值,施N对生物量的促进最显著。滇杨Cd积累量受N影响最大,其次为P,再次是K。无N处理(N0P0K0、N0P2K2)的Cd积累量最低,高N、高P处理(N2P4K2、N4P2K2)的Cd积累量最高。一元模型拟合结果显示,N以374.704 mg∙kg−1施加时可获得最大Cd积累量(2.168 mg∙pot−1),拟合方程为y= −0.0000090x2+0.0067x+0.92;二元模型拟合时,N、P分别按344.125、278.633 mg∙kg−1施加时Cd积累量较大,达到2.057 mg∙pot−1,拟合方程为y=0.091+0.0090x1+0.0028x2−0.000021x1x2−0.0000047x12+ 0.0000074x22;三元模型拟合时,N、P、K分别按468.911、46.774、305.529 mg∙kg−1施加时Cd积累量较大,拟合方程为y=0.81+0.0025x1−0.0015x2+0.0029x3+0.000012x1x2−0.0000065x2x3−0.000017x1x3+0.000011x22+0.0000015x32。结合实际最大处理(N4P2K2)与模型拟合结果,推荐基质营养背景下最佳施肥方案为:N 374.704 mg∙kg−1+P2O5 200.000 mg∙kg−1+K2O 200.000 mg∙kg−1。由冗余分析可知,滇杨Cd积累量与生物量、土壤速效N、速效P呈正相关,与pH、速效K呈负相关,说明营养调控可通过改变滇杨生物量以及土壤性质影响Cd积累。研究结果可为滇杨修复Cd污染土壤的应用实践提供科学依据。
中图分类号:
刘楚天, 郭栋栋, 侯磊, 梁启斌, 王艳霞, 施艳婷, 戚艳娥. 营养调控影响滇杨幼苗镉积累的效应模型分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(3): 460-468.
LIU Chutian, GUO Dongdong, HOU Lei, LIANG Qibin, WANG Yanxia, SHI Yanting, QI Yane. Analysis of the Effect Model for Nutrient Regulation on Cadmium Accumulation in Populus yunnanensis Seedlings[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2024, 33(3): 460-468.
| 编号 | 处理 | w(N)/(mg∙kg−1) | w(P2O5)/(mg∙kg−1) | w(K2O)/(mg∙kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | N0P0K0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 2 | N0P2K2 | 0 | 200 | 200 |
| 3 | N1P2K2 | 100 | 200 | 200 |
| 4 | N2P0K2 | 200 | 0 | 200 |
| 5 | N2P1K2 | 200 | 100 | 200 |
| 6 | N2P2K2 | 200 | 200 | 200 |
| 7 | N2P4K2 | 200 | 400 | 200 |
| 8 | N2P2K0 | 200 | 200 | 0 |
| 9 | N2P2K1 | 200 | 200 | 100 |
| 10 | N2P2K4 | 200 | 200 | 400 |
| 11 | N4P2K2 | 400 | 200 | 200 |
| 12 | N1P1K2 | 100 | 100 | 200 |
| 13 | N1P2K1 | 100 | 200 | 100 |
| 14 | N2P1K1 | 200 | 100 | 100 |
表1 试验设计
Table 1 Experimental design
| 编号 | 处理 | w(N)/(mg∙kg−1) | w(P2O5)/(mg∙kg−1) | w(K2O)/(mg∙kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | N0P0K0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 2 | N0P2K2 | 0 | 200 | 200 |
| 3 | N1P2K2 | 100 | 200 | 200 |
| 4 | N2P0K2 | 200 | 0 | 200 |
| 5 | N2P1K2 | 200 | 100 | 200 |
| 6 | N2P2K2 | 200 | 200 | 200 |
| 7 | N2P4K2 | 200 | 400 | 200 |
| 8 | N2P2K0 | 200 | 200 | 0 |
| 9 | N2P2K1 | 200 | 200 | 100 |
| 10 | N2P2K4 | 200 | 200 | 400 |
| 11 | N4P2K2 | 400 | 200 | 200 |
| 12 | N1P1K2 | 100 | 100 | 200 |
| 13 | N1P2K1 | 100 | 200 | 100 |
| 14 | N2P1K1 | 200 | 100 | 100 |
| 极差指标 | 因素 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | P | K | ||
| K0 | 5.251 | 8.026 | 8.492 | |
| K1 | 11.362 | 11.124 | 12.611 | |
| K2 | 41.252 | 38.232 | 39.186 | |
| K4 | 6.512 | 6.995 | 4.088 | |
| k0 | 0.875 | 1.338 | 1.415 | |
| k1 | 1.262 | 1.236 | 1.401 | |
| k2 | 1.719 | 1.593 | 1.633 | |
| k4 | 2.171 | 2.332 | 1.363 | |
| R | 1.295 | 1.096 | 0.270 | |
| 因素排序 | N>P>K | |||
| 最优方案 | N4P4K2 | |||
| 方差分析 | 0.001** | 0.001** | 0.027* | |
表2 Cd积累量的极差分析
Table 2 Range analyses of Cd accumulation
| 极差指标 | 因素 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | P | K | ||
| K0 | 5.251 | 8.026 | 8.492 | |
| K1 | 11.362 | 11.124 | 12.611 | |
| K2 | 41.252 | 38.232 | 39.186 | |
| K4 | 6.512 | 6.995 | 4.088 | |
| k0 | 0.875 | 1.338 | 1.415 | |
| k1 | 1.262 | 1.236 | 1.401 | |
| k2 | 1.719 | 1.593 | 1.633 | |
| k4 | 2.171 | 2.332 | 1.363 | |
| R | 1.295 | 1.096 | 0.270 | |
| 因素排序 | N>P>K | |||
| 最优方案 | N4P4K2 | |||
| 方差分析 | 0.001** | 0.001** | 0.027* | |
| 养分变量 | 方程 | r2 | F | F0.05 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | y= −0.000009x2+0.0067x+0.9189 | 0.834 | 22.542 | 0.000 |
| P | y=0.0000097x2−0.0023x+1.7238 | 0.570 | 5.960 | 0.022 |
| K | y= −0.0000031x2−0.00018x+1.9416 | 0.358 | 2.506 | 0.136 |
| NP | y=0.091+0.009x1+0.0028x2−0.000021x1x2−0.0000047x12+0.0000074x22 | 0.781 | 12.806 | 0.000 |
| PK | y=0.13+0.0073x1+0.0079x2−0.000048x1x2+0.0000097x12+0.00000032x22 | 0.580 | 4.970 | 0.005 |
| NK | y= −0.66+0.014x1+0.0089x2−0.000042x1x2−0.0000073x12−0.0000046x22 | 0.702 | 8.481 | 0.000 |
| NPK | y=0.81+0.0025x1−0.0015x2+0.0029x3+0.000012x1x2−0.0000065x2x3−0.000017x1x3−0.00000x12+ 0.000011x22+0.0000015x32 | 0.696 | 8.142 | 0.000 |
表3 养分因子(x)与滇杨Cd积累量(y)的回归方程
Table 3 Regression equations of nutrient factors (x) and Cd accumulation (y) in P. yunnanensis
| 养分变量 | 方程 | r2 | F | F0.05 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | y= −0.000009x2+0.0067x+0.9189 | 0.834 | 22.542 | 0.000 |
| P | y=0.0000097x2−0.0023x+1.7238 | 0.570 | 5.960 | 0.022 |
| K | y= −0.0000031x2−0.00018x+1.9416 | 0.358 | 2.506 | 0.136 |
| NP | y=0.091+0.009x1+0.0028x2−0.000021x1x2−0.0000047x12+0.0000074x22 | 0.781 | 12.806 | 0.000 |
| PK | y=0.13+0.0073x1+0.0079x2−0.000048x1x2+0.0000097x12+0.00000032x22 | 0.580 | 4.970 | 0.005 |
| NK | y= −0.66+0.014x1+0.0089x2−0.000042x1x2−0.0000073x12−0.0000046x22 | 0.702 | 8.481 | 0.000 |
| NPK | y=0.81+0.0025x1−0.0015x2+0.0029x3+0.000012x1x2−0.0000065x2x3−0.000017x1x3−0.00000x12+ 0.000011x22+0.0000015x32 | 0.696 | 8.142 | 0.000 |
| 养分变量 | 最大施肥量质量分数/(mg∙kg−1) | 最大Cd积累量/ (mg∙pot−1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | P | K | ||
| N | 374.704 | 2.168 | ||
| P | 无 | 无 | ||
| K | 无 | 无 | ||
| NP | 344.125 | 278.633 | 2.057 | |
| PK | 168.385 | 220.561 | 1.614 | |
| NK | 147.934 | 290.235 | 1.694 | |
| NPK | 468.911 | 46.774 | 305.529 | 1.812 |
表4 养分因子与滇杨Cd积累量的回归方程测算结果
Table 4 Results of regression equations of nutrient factors and Cd accumulation in P. yunnanensis
| 养分变量 | 最大施肥量质量分数/(mg∙kg−1) | 最大Cd积累量/ (mg∙pot−1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | P | K | ||
| N | 374.704 | 2.168 | ||
| P | 无 | 无 | ||
| K | 无 | 无 | ||
| NP | 344.125 | 278.633 | 2.057 | |
| PK | 168.385 | 220.561 | 1.614 | |
| NK | 147.934 | 290.235 | 1.694 | |
| NPK | 468.911 | 46.774 | 305.529 | 1.812 |
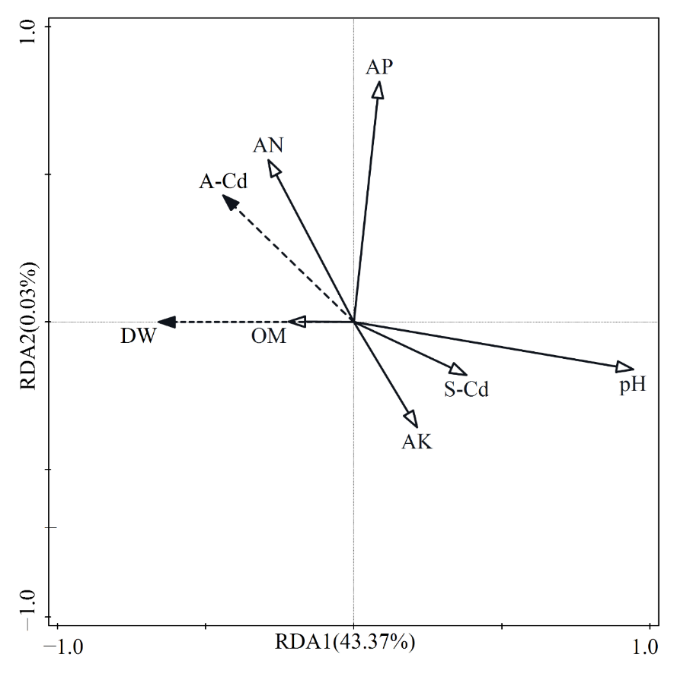
图6 滇杨Cd积累量和生物量与土壤理化性质的冗余分析 A-Cd:Cd积累量,DW:生物量,OM:有机质,AN:速效氮,AP:速效磷,AK:速效钾,pH:酸碱度,S-Cd:土壤镉
Figure 6 Redundancy analysis of Cd accumulation and biomass of P. yunnanensis with soil physico-chemical properties
| [1] |
ALI H, KHAN E, SAJAD M A, 2013. Phytoremediation of heavy metals—Concepts and applications[J]. Chemosphere, 91(7): 869-881.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
EVANGELOU M W H, EBEL M, SCHAEFFER A, 2007. Chelate assisted phytoextraction of heavy metals from soil. Effect, mechanism, toxicity, and fate of chelating agents[J]. Chemosphere, 68(6): 989-1003.
PMID |
| [3] | FAYIGA A O, MA L Q, RATHINASABAPATHI B, 2008. Effects of nutrients on arsenic accumulation by arsenic hyperaccumulator Pteris vittata L.[J]. Environmental & Experimental Botany, 62(3): 231-237. |
| [4] |
MAXTED A P, BLACK C R, WEST H M, et al., 2007. Phytoextraction of cadmium and zinc from arable soils amended with sewage sludge using Thlaspi caerulescens: Development of a predictive model[J]. Environmental Pollution, 150(3): 363-372.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
PENG S M, WU L R, SEYLER B C, et al., 2020. The combined effects of Cu and Pb on the sex-specific growth and physiology of the dioecious Populus yunnanensis[J]. Environmental Research, 184: 109276.
DOI URL |
| [6] | SUBHADRA A V, VYAS S J, 2007. Phytoremediation technology: A nature’s bliss[J]. Research Journal of Biotechnology, 2(3): 52-57. |
| [7] |
STROIA C, JOUANY M C, 2011. Nitrogen fertilization effects on grassland soil acidification: consequences on diffusive phosphorus ions[J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 75(1): 112-120.
DOI URL |
| [8] | ZIA A, BERG L V D, RIAZ M, et al., 2020. Nitrogen induced DOC and heavy metals leaching: Effects of nitrogen forms, deposition loads and liming[J]. Environmental Pollution, 265(Part B): 114981. |
| [9] | 白媛媛, 2020. 氮磷及其互作在蒿柳响应重金属镉胁迫中的作用[D]. 北京: 中国林业科学研究院: 32-34. |
| BAI Y Y, 2020. The role of nitrogen and phosphorus on Salix viminalis in response to cadmium[D]. Bejing: Chinese Academy of Forestry: 32-34. | |
| [10] | 鲍士旦, 2000. 土壤农化分析[M]. 3版. 北京: 中国农业出版社: 373-375. |
| BAO S D, 2000. Soil agrochemical analysis[M]. 3th Edition. Beijing: China Agriculture Press: 373-375. | |
| [11] | 陈同斌, 雷梅, 杨军, 等, 2014. 关于重金属污染土壤风险控制区划的研究与建议[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 29(3): 321-326. |
| CHEN T B, LEI M, YANG J, et al., 2014. Discussion on zoning of soil environmental risk control and remediation contaminated by heavy metals on regional scale[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, 29(3): 321-326. | |
| [12] | 邓小红, 姬拉拉, 王健健, 2020. 施氮对镉胁迫下山杨幼苗叶片氮磷钾吸收及镉积累量的影响[J]. 西北植物学报, 40(11): 1932-1939. |
| DONG X H, JI L L, WANG J J, 2020. Effect of nitrogen supplement on N, P, K uptake and cd accumulationin leaves of Populus davidiana under cadmium stress[J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 40(11): 1932-1939. | |
| [13] | 杜萌, 李丹丹, 杨军, 等, 2020. 不同氮肥类型及配施壳聚糖对八宝景天修复镉污染土壤的强化效果[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 26(9): 1714-1723. |
| DU M, LI D D, YANG J, et al., 2020. Study on different nitrogen forms and combined application of chitosan for enhancing phytoremediation of Cd-contaminated soil by Hylotelephium spectabile[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 26(9): 1714-1723. | |
| [14] | 冯子龙, 卢信, 张娜, 等, 2017. 农艺强化措施用于植物修复重金属污染土壤的研究进展[J]. 江苏农业科学, 45(2): 14-20. |
| FENG Z L, LU X, ZHANG N, et al., 2017. Research progress on agronomic intensification measures for phytoremediation of heavy metal contaminated soil[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Science, 45(2): 14-20. | |
| [15] | 郭俊娒, 杨俊兴, 杨军, 等, 2020. 田间条件下养分调控八宝景天Cd修复效率[J]. 环境科学, 41(9): 4226-4233. |
| GUO J M, YANG J X, YANG J, et al., 2020. Effect of nutrient regulation and control on Cd accumulation efficiency of Hylotelephium spectabile under field conditions[J]. Environmental Science, 41(9): 4226-4233. | |
| [16] | 刘金秀, 张松彦, 周建, 2023. 镉胁迫对刺槐幼苗生长与光合生理特性的影响[J]. 林业科学研究, 36(3): 168-178. |
| LIU J X, ZHANG S Y, ZHOU J, 2023. Effects of Cadmium stress on growth and photosynthetic physiological characteristics of Robinia pseudoacacia seedlings[J]. Forestry Research, 36(3): 168-178. | |
| [17] | 骆永明, 滕应, 2018. 我国土壤污染的区域差异与分区治理修复策略[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 33(2): 145-152. |
| LUO Y M, TENG Y, 2018. Regional difference in soil pollution and strategy of soil zonal governance and remediation in China[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, 33(2): 145-152. | |
| [18] | 李非里, 邵鲁泽, 吴兴飞, 等, 2021. 植物修复重金属强化技术和间套种研究进展[J]. 浙江工业大学学报, 49(3): 345-354. |
| LI F L, ZHAO L Z, WU X F, et al., 2021. Research progress of enhanced phytoremediation for heavy metals and intercropping technique[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University of Technology, 49(3): 345-354. | |
| [19] | 雷浩, 高陈晨, 陈良华, 等, 2021. 氮添加对美洲黑杨镉吸收、富集与分配的影响[J]. 四川农业大学学报, 39(5): 575-581. |
| LEI H, GAO C C, CHEN L H, et al., 2021. Effects of nitrogen application on cadmium absorption, enrichment and distribution in populus deltoides[J]. Journal of Sichuan Agricultural University, 39(5): 575-581. | |
| [20] | 吕亚敏, 杨京平, 赵杏, 等, 2015. 磷肥对茶园土壤中镉有效性及其生物累积的影响[J]. 浙江大学学报(理学版), 42(6): 726-731. |
| LÜ Y X, YANG J P, ZHAO X, et al., 2015. Effects of different hosphate fertilizers on the availability and bioaccumulation of Cadmium in the tea garden soil[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University (Science Edition), 42(6): 726-731. | |
| [21] | 申建波, 毛达如, 2011. 植物营养研究方法[M]. 3版. 北京: 中国农业大学出版社: 83-85. |
| SHEN J B, MAO D R, 2011. Methods of plant nutrition research[M]. 3th Edition. Beijing: China Agricultural University Press: 83-85. | |
| [22] | 帅祖苹, 刘汉燚, 崔浩, 等, 2022. 磷、锌和镉交互作用对小白菜生长和锌镉累积的影响[J]. 环境科学, 43(11): 5234-5243. |
| SHUAI Z P, LIU H Y, CUI H, et al., 2022. Effects of interaction of P, Zn and Cd on growth and accumulation of Zn and Cd in Brassica campestris L.[J]. Environmental Science, 43(11): 5234-5243. | |
| [23] | 谭长强, 何琴飞, 秦玉燕, 等, 2017. 施氮对镉胁迫下杂交相思树生长及镉吸收分配的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 23(5): 1326-1334. |
| TAN C Q, HE Q F, QIN Y Y, et al., 2017. Effect of nitrogen application on seedling growth and cadminm uptake and distribution in Acacia mangium×Acacia auriculiformis under cadmium stress[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 23(5): 1326-1334. | |
| [24] | 王雯雯, 叶如梦, 2020. 磷对旱柳生长特性及富集重金属Cd能力的影响[J]. 环境科学与技术, 43(S2): 79-86. |
| WANG W W, YE R M, 2020. The effects of phosphorus on the growth characteristics and Cd accumulation of Salix matsudana under Cd stress[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 43(S2): 79-86. | |
| [25] | 王晨骄, 2021. 氮、磷营养对植物修复土壤重金属污染的效应及经济效益分析[D]. 昆明: 云南师范大学: 30-31. |
| WANG C J, 2021. Effects of nitrogen and phosphorus on phytoremediation of soil heavy metal pollutionand its economic benefits[D]. Kunming: Yunnan Normal University: 30-31. | |
| [26] | 王艳霞, 郑武扬, 侯磊, 等, 2023. 滇杨幼苗对镉、锌胁迫的生理响应与耐受性研究[J]. 西南林业大学学报(自然科学), 43(6): 1-9. |
| WANG Y X, ZHENG W Y, HOU L, et al., 2023. Study on physiological response and tolerance of Populus yunnanensis seedlings with pertabations of Cadmium and Zinc[J]. Journal of Southwest Forestry University (Natural Sciences), 43(6): 1-9. | |
| [27] | 韦秀文, 姚斌, 刘慧文, 等, 2011. 重金属及有机物污染土壤的树木修复研究进展[J]. 林业科学, 47(5): 124-130. |
| WEI X W, YAO B, LIU H W, et al., 2011. Application of dendroremediation to the soil contaminated soil by heavy metals and organic pollutants[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 47(5): 124-130. | |
| [28] | 徐明岗, 曾希柏, 周世伟, 2014. 施肥与土壤重金属污染修复[M]. 北京: 科学出版社: 172-180. |
| XU M G, ZENG X B, ZHOU S W, 2014. Fertilization and remediation of soil heavy metal pollution[M]. Beijing: Science Press: 172-180. | |
| [29] | 郑武扬, 王艳霞, 郑雁方, 等, 2021. 镉、铅胁迫对滇杨 (Populus yunnanensis) 幼苗生长及其光合生理的影响[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 37(10): 1331-1340. |
| ZHENG W Y, WANG Y X, ZHENG Y F, et al., 2021. Effects of cadmium and lead stress on growth and photosynthetic physiology of Populus yunnanensis seedlings[J]. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 37(10): 1331-1340. | |
| [30] | 张昭昱, 文一, 刘伟江, 等, 2016. 四川省某铅锌矿尾矿库周边环境重金属污染特征[J]. 环境污染与防治, 38(6): 105-110. |
| ZHANG Z Y, WEN Y, LIU W J, et al., 2016. Polluted characteristics of heavy metals in surrounding environment near a Pb-Zn mine tailing in Sichuan Province[J]. Environmental Pollution & Control, 38(6): 105-110. | |
| [31] | 张德刚, 袁寒, 刘艳红, 2017. 云南锡矿尾矿库土壤肥力特征与重金属污染分析[J]. 西南农业学报, 30(5): 1158-1161. |
| ZHANG D G, YUAN H, LIU Y H, 2017. Analysis of soil heavy metal pollution and fertility properties in tintailings storehouse of Yunnan province[J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 30(5): 1158-1161. |
| [1] | 李振国, 郝星雨, 贺甜莲, 景蕊, 荣成, 顾承真, 郑新宇. 竹醋液对紫苏镉毒的缓解效应研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(7): 1313-1324. |
| [2] | 赵良侠, 高坤, 黄婷婷, 高也, 琚唐丹, 蒋秋阳, 金珩, 熊蕾, 汤在琳, 高灿红. 玉米籽粒高/低镉积累自交系不同生育期的镉累积特性研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 766-775. |
| [3] | 杨耀东, 陈玉梅, 涂鹏飞, 曾清如. 经济作物轮作模式下镉污染农田修复潜力[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 627-634. |
| [4] | 刘抗旱, 郑刘根, 张理群, 丁丹, 单士锋. 复合型植物源活化剂强化蜈蚣草修复砷污染土壤的效应研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 635-642. |
| [5] | 郝丽宇, 何苗苗, 汤家喜. 河流水体全氟化合物的污染现状及修复技术研究进展[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(12): 2115-2127. |
| [6] | 陈桂红. 硫和硅掺杂生物炭对镉污染土壤的修复研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(10): 1854-1860. |
| [7] | 魏岚, 黄连喜, 李翔, 王泽煌, 陈伟盛, 黄庆, 黄玉芬, 刘忠珍. 生物炭基质可显著地促进香蕉幼苗生长[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 732-739. |
| [8] | 伍德, 彭鸥, 刘玉玲, 张朴心, 尹雪斐, 黄薪铭, 铁柏清. 螯合剂及组配对伴矿景天修复两种镉污染土壤的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(12): 2414-2421. |
| [9] | 俞龙生, 李卫, 许铭宇, 林泽帆. 赤霉素浸种对2种矿区修复先锋植物种子萌发和幼苗生长的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(11): 2225-2233. |
| [10] | 丛超, 杨宁柯, 王海娟, 王宏镔. 吲哚乙酸和激动素配合施用提高蜈蚣草和龙葵对砷、镉富集的田间试验[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(6): 1299-1309. |
| [11] | 李富荣, 王琳清, 李文英, 吴志超, 王旭. 水芹对重金属的吸收累积及其应用研究进展[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(12): 2423-2430. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
