生态环境学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (4): 573-584.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2024.04.008
何杰1,2,3( ), 李宗明2,3, 杨正宇2,3, 沈健林2,3,*(
), 李宗明2,3, 杨正宇2,3, 沈健林2,3,*( ), 刘国平1,*(
), 刘国平1,*( ), 吴金水2,3
), 吴金水2,3
收稿日期:2024-03-06
出版日期:2024-04-18
发布日期:2024-05-31
通讯作者:
刘国平,E-mail: guoping.liu@yangtzeu.edu.cn作者简介:何杰(1999年生),女,硕士研究生,主要研究方向为农田温室气体减排。E-mail: 2547079771@qq.com
基金资助:
HE Jie1,2,3( ), LI Zongming2,3, YANG Zhengyu2,3, SHEN Jianlin2,3,*(
), LI Zongming2,3, YANG Zhengyu2,3, SHEN Jianlin2,3,*( ), LIU Guoping1,*(
), LIU Guoping1,*( ), WU Jinshui2,3
), WU Jinshui2,3
Received:2024-03-06
Online:2024-04-18
Published:2024-05-31
摘要:
畜禽粪便有机肥替代化肥是实现农田化肥减施和养分循环利用的重要措施。以湖南典型红壤双季稻田系统为研究对象,采用静态箱-气相色谱法结合土壤理化和生物学性质测定,研究了水稻生长季基肥配施牛粪条件下CH4和N2O的排放特征及其主要影响因素。结果表明,与常规施用化肥处理相比,牛粪化肥配施显著影响CH4和N2O累积排放量。具体而言,两个稻季生长期内牛粪替代50%化学氮肥处理(CM)的CH4累积排放量较常规氮肥处理(CON)显著提高43.2%;而CM处理N2O累积排放量较CON处理显著降低45.2%。同时CM处理显著增加了土壤有机碳、土壤总氮、土壤可溶性有机碳、土壤铵态氮和硝态氮质量分数和土壤pH,但显著降低了土壤Eh。受土壤性质改变的影响,早晚稻季土壤中甲烷产生功能基因、甲烷氧化功能基因的基因拷贝数平均分别显著增加79.1%、13.0%;同时完全氨氧化细菌amoA功能基因、反硝化nirS功能基因、反硝化nosZ功能基因的基因拷贝数平均分别显著增加35.8%、50.8%、7.1%,但反硝化nirK功能基因和反硝化nosZⅡ功能基因的基因拷贝数平均分别显著降低了46.5%和17.5%。通过冗余分析发现,土壤有机碳和土壤总氮质量分数对CH4平均排放通量、甲烷产生功能基因拷贝数、甲烷氧化功能基因拷贝数的影响作用最大。另外土壤有机碳、土壤铵态氮和土壤总氮质量分数对N2O平均排放通量、完全氨氧化细菌amoA功能基因拷贝数、反硝化nirS功能基因拷贝数、反硝化nosZ功能基因拷贝数、反硝化nirK功能基因和反硝化nosZⅡ功能基因的基因拷贝数的影响作用最大。考虑CH4和N2O的总的温室效应,与CON处理相比CM处理的温室气体排放(以CO2计)显著增加了41.0%。综上所述,稻田有机无机肥配施改变土壤理化和生物学性质而增加了温室气体排放,需要在稻田温室效应评估中加以考虑。
中图分类号:
何杰, 李宗明, 杨正宇, 沈健林, 刘国平, 吴金水. 牛粪化肥配施对双季稻田CH4和N2O排放的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(4): 573-584.
HE Jie, LI Zongming, YANG Zhengyu, SHEN Jianlin, LIU Guoping, WU Jinshui. Effects of Combined Application of Cow Manure and Chemical Fertilizer on CH4 and N2O Emissions in Paddy Fields with Double-Rice Cropping[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2024, 33(4): 573-584.
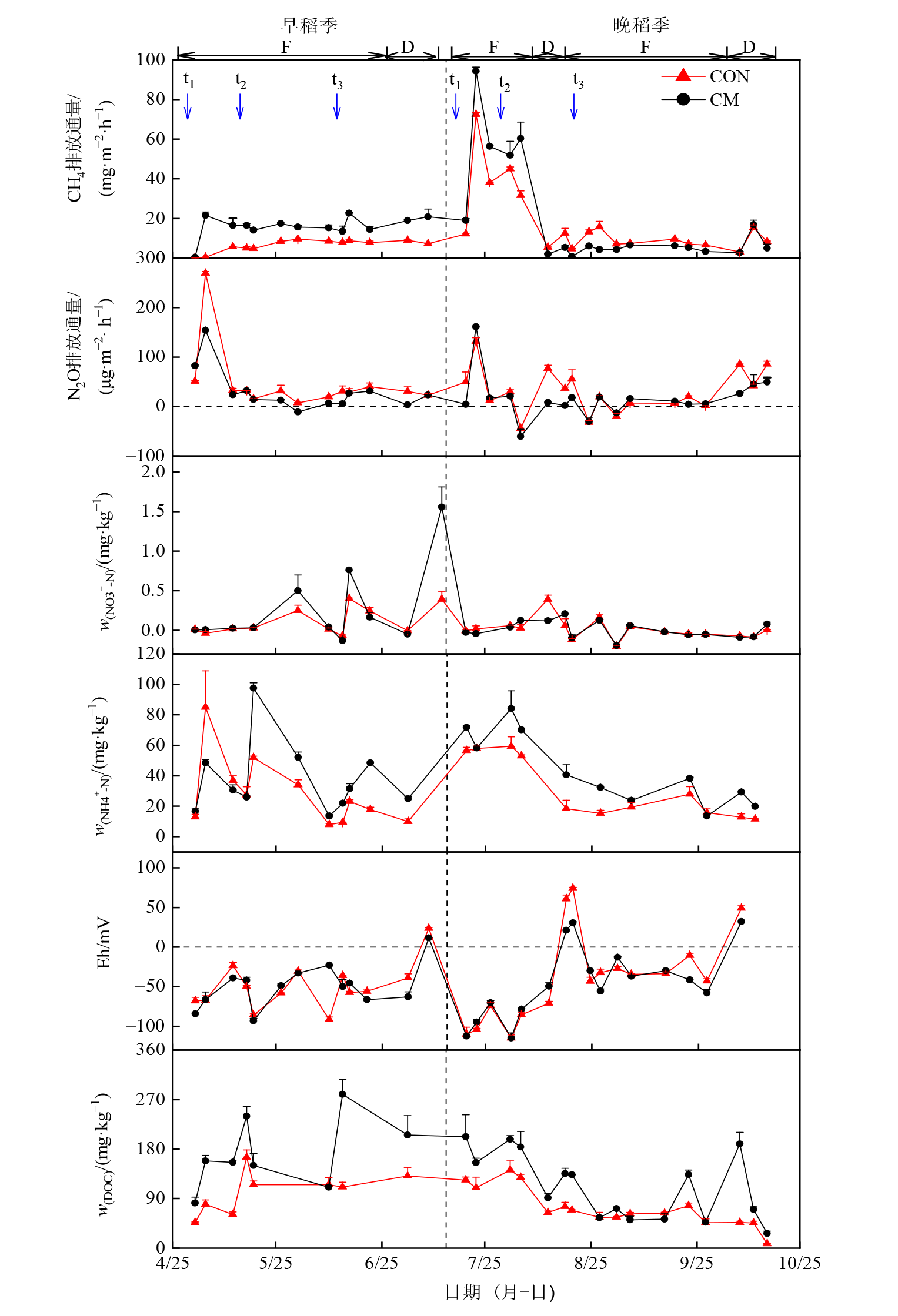
图1 CH4和N2O排放通量及土壤Eh?NH4+-N?NO3--N和DOC质量分数的变化动态 1)F:淹水;2)D:晒田;3)t1:基肥;4)t2:分蘖肥;5)t3:穗肥;6)由上到下依次为图(a)、(b)、(c)、(d)、(e)、(f)
Figure 1 Dynamics of CH4 and N2O emission fluxes, soil Eh, NH4+-N, NO3--N and DOC contents
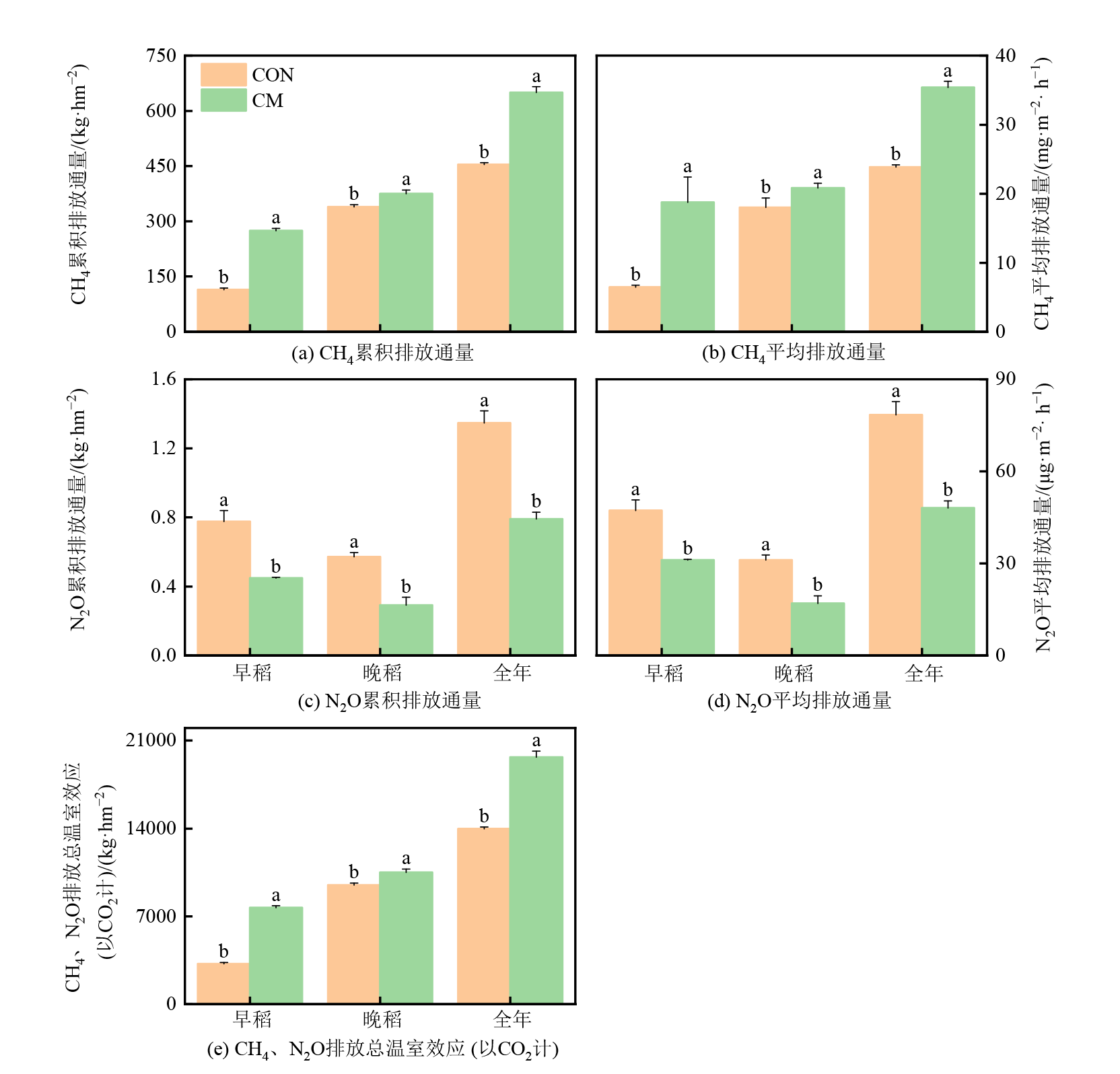
图2 CH4、N2O累积排放量、平均排放通量和总温室效应(以CO2计) 图中不同小写字母表示差异显著(p<0.05)。下同
Figure 2 Cumulative CH4, N2O emissions, average emission fluxes and total greenhouse effect (in CO2)
| 项目 | CON | CM |
|---|---|---|
| w(SOC)/(g·kg-1) | 19.0±0.198b | 31.5±0.430a |
| w(TN)/(g·kg-1) | 1.83±0.037b | 2.86±0.110a |
| w(NH4+-N)/(mg·kg-1) | 30.8±0.597b | 40.7±0.606a |
| w(NO3-N)/(mg·kg-1) | 0.061±0.002b | 0.136±0.005a |
| w(DOC)/(mg·kg-1) | 90.3±1.948b | 142.5±4.62a |
| pH | 5.21±0.012b | 5.57±0.003a |
| Eh/(mV) | -43.4±0.897a | -46.7±0.368b |
| 早稻季产量/(t·hm-2) | 4.37±0.277a | 4.21±0.047a |
| 晚稻季产量/(t·hm-2) | 6.56±0.277a | 6.79±0.147a |
| 全年产量/(t·hm-2) | 10.9±0.309a | 11.0±0.130a |
表1 土壤理化性质和稻季产量变化
Table 1 Changes of soil physical and chemical properties and rice yield during rice season
| 项目 | CON | CM |
|---|---|---|
| w(SOC)/(g·kg-1) | 19.0±0.198b | 31.5±0.430a |
| w(TN)/(g·kg-1) | 1.83±0.037b | 2.86±0.110a |
| w(NH4+-N)/(mg·kg-1) | 30.8±0.597b | 40.7±0.606a |
| w(NO3-N)/(mg·kg-1) | 0.061±0.002b | 0.136±0.005a |
| w(DOC)/(mg·kg-1) | 90.3±1.948b | 142.5±4.62a |
| pH | 5.21±0.012b | 5.57±0.003a |
| Eh/(mV) | -43.4±0.897a | -46.7±0.368b |
| 早稻季产量/(t·hm-2) | 4.37±0.277a | 4.21±0.047a |
| 晚稻季产量/(t·hm-2) | 6.56±0.277a | 6.79±0.147a |
| 全年产量/(t·hm-2) | 10.9±0.309a | 11.0±0.130a |
| 拷贝数(以干计)/g-1 | CON | CM |
|---|---|---|
| 甲烷产生基因 (mcrA) | 7.33×108±2.80×107b | 1.31×109±3.53×106a |
| 甲烷氧化基因 (pmoA) | 1.41×109±3.45×107b | 1.60×109±5.31×107a |
| 氨氧化古菌amoA 功能基因 (AOA) | 6.44×107± 5.08×106a | 5.98×107± 4.96×106a |
| 氨氧化细菌amoA 功能基因 (AOB) | 3.70×105± 4.17×103a | 3.61×105± 2.69×104a |
| 完全氨氧化菌amoA 功能基因 (CMX) | 4.96×107± 1.05×106b | 6.73×107± 1.99×106a |
| 反硝化功能基因nirK基因 | 2.05×109±4.89×107a | 1.10×109±2.64×107b |
| 反硝化功能基因nirS基因 | 3.47×109±8.03×107b | 5.24×109±7.87×107a |
| 反硝化功能基因nosZ基因 | 2.04×109±4.21×107b | 2.18×109±2.01×107a |
| 反硝化功能基因nosZⅡ基因 | 1.74×109±2.58×107a | 1.44×109±8.77×107b |
表2 CH4和N2O排放相关功能基因拷贝数均值
Table 2 Mean copy number of CH4 and N2O emission related functional genes
| 拷贝数(以干计)/g-1 | CON | CM |
|---|---|---|
| 甲烷产生基因 (mcrA) | 7.33×108±2.80×107b | 1.31×109±3.53×106a |
| 甲烷氧化基因 (pmoA) | 1.41×109±3.45×107b | 1.60×109±5.31×107a |
| 氨氧化古菌amoA 功能基因 (AOA) | 6.44×107± 5.08×106a | 5.98×107± 4.96×106a |
| 氨氧化细菌amoA 功能基因 (AOB) | 3.70×105± 4.17×103a | 3.61×105± 2.69×104a |
| 完全氨氧化菌amoA 功能基因 (CMX) | 4.96×107± 1.05×106b | 6.73×107± 1.99×106a |
| 反硝化功能基因nirK基因 | 2.05×109±4.89×107a | 1.10×109±2.64×107b |
| 反硝化功能基因nirS基因 | 3.47×109±8.03×107b | 5.24×109±7.87×107a |
| 反硝化功能基因nosZ基因 | 2.04×109±4.21×107b | 2.18×109±2.01×107a |
| 反硝化功能基因nosZⅡ基因 | 1.74×109±2.58×107a | 1.44×109±8.77×107b |
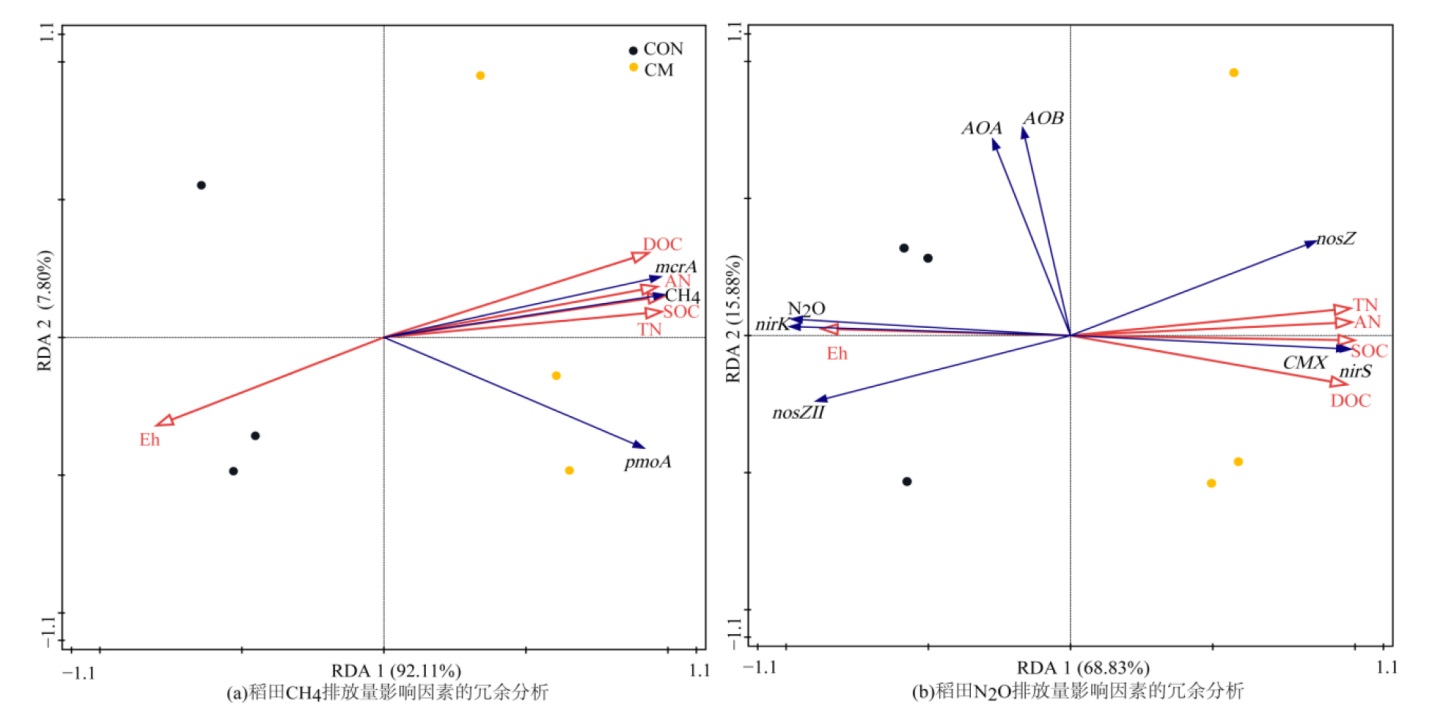
图6 CH4?N2O平均排放通量及其相关微生物功能基因拷贝数与土壤理化性质的冗余分析 1)CH4:甲烷平均排放通量;2)AN:土壤铵态氮质量分数;3)SOC:土壤有机碳质量分数;4)TN:土壤总氮质量分数;Eh.氧化还原电位;5)mcrA:产甲烷功能基因拷贝数;6)pmoA:甲烷氧化功能基因拷贝数;7)AOA:氨氧化古菌amoA基因拷贝数;8)AOB:氨氧化细菌amoA基因拷贝数;9)CMX:完全氨氧化细菌amoA基因拷贝数;10)nirK:反硝化功能基因nirK拷贝数;11)nirS:反硝化功能基因nirS拷贝数;12)nosZ:反硝化功能基因nosZ拷贝数;13)nosZⅡ:反硝化功能基因nosZⅡ拷贝数
Figure 6 Redundancy analysis of average emission fluxes of CH4 and N2O, copy number of related microbial functional genes and basic physicochemical properties of soil
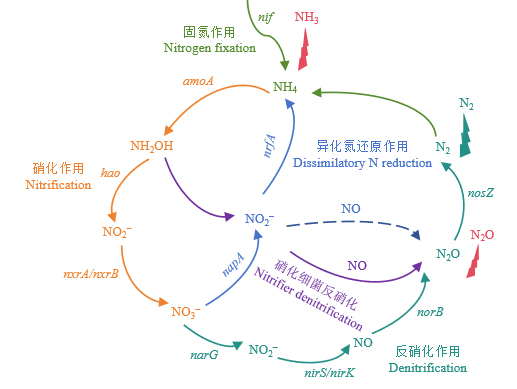
图7 微生物介导土壤中氮素循环的主要过程(Klimasmith et al.,2022) 不同颜色箭头表示不同的氮素循环过程,箭头上标记基因表示该周转过程中关键酶的标记功能基因
Figure 7 Main processes of microbial mediation in soil nitrogen cycling
| [1] | AMBUS P, ZECHMEISTER-BOLTENSTERN S, BUTTERBACH-BAHL K, 2006. Sources of nitrous oxide emitted from European forest soils[J]. Biogeosciences, 3(2): 135-145. |
| [2] | CHEN X P, CUI Z L, FAN M S, et al., 2014. Producing more grain with lower environmental costs[J]. Nature, 514(7523): 486-489. |
| [3] | JIA X C, YANG Q L, DONG S T, et al., 2020. Using manure for improving nitrogen fertilization and maize yield[J]. Experimental Agriculture, 56(6): 901-914. |
| [4] | KLEMEDTSSON B K K W, 2009. Strong pH influence on N2O and CH4 fluxes from forested organic soils[J]. European Journal of Soil Science, 60(3): 311-320. |
| [5] |
KLIMASMITH I M, KENT A D, 2022. Micromanaging the nitrogen cycle in agroecosystems[J]. Trends in Microbiology, 30(11): 1045-1055.
DOI PMID |
| [6] | KÖGEL-KNABNER I, AMELUNG W, CAO Z, et al., 2010. Biogeochemistry of paddy soils[J]. Geoderma, 157(1): 1-14. |
| [7] | MEIJIDE A, GRUENING C, GODED I, et al., 2016. Water management reduces greenhouse gas emissions in a Mediterranean rice paddy field[J]. Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment, 238: 168-178. |
| [8] | WANG C, LI Z M, SHEN J L, et al., 2023. Biochar amendment increases the abundance and alters the community composition of diazotrophs in a double rice cropping system[J]. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 59(80): 873-886. |
| [9] | WASSMANN R, NEUE H U, LANTIN R S, et al., 2001. Characterization of methane emissions from rice fields in Asia I. Comparison among field sites in five countries[J]. Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems, 91(8): 1-12. |
| [10] |
XIA L L, CAO L, YANG Y, et al., 2023. Integrated biochar solutions can achieve carbon-neutral staple crop production[J]. Nature Food, 4(3): 236-246
DOI PMID |
| [11] | XIA L L, KEE S L, YAN X Y, et al., 2017. How does recycling of livestock manure in agroecosystems affect crop productivity, reactive nitrogen losses, and soil carbon balance?[J]. Environmental Science Technology, 51(13): 7450-7457. |
| [12] | XING G X, ZHU Z L, 2000. An assessment of N loss from agricultural fields to the environment in China[J]. Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems, 57(1): 67-73. |
| [13] | YAN X Y, CAI Z C, WANG S W, et al., 2011. Direct measurement of soil organic carbon content change in the croplands of China[J]. Global Change Biology, 17(3): 1487-1496. |
| [14] | ZHU E Y, DENG J S, WANG H Q, et al., 2019. Identify the optimization strategy of nitrogen fertilization level based on trade-off analysis between rice production and greenhouse gas emission[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 239: 1-11. |
| [15] | 蔡祖聪, 徐华, 马静, 2009. 稻田生态系统CH4和N2O排放[M]. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学出版社: 153-158. |
| CAI Z C, XU H, MA J, 2009. CH4 and N2O emissions from paddy ecosystems[M]. Hefei: Press of University of Science and Technology of China: 153-158. | |
| [16] | 曹金留, 任立涛, 汪国好, 等, 2000. 爽水性稻田甲烷排放特点[J]. 农业环境保护, 19(1): 10-14. |
| CAO J L, REN L T, WANG G H, et al., 2000. Methane emission characteristics of water-borne paddy fields[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 19(1): 10-14. | |
| [17] | 成臣, 曾勇军, 杨秀霞, 等, 2015. 不同耕作方式对稻田净增温潜势和温室气体强度的影响[J]. 环境科学学报, 35(6): 1887-1895. |
| CHENG C, ZENG Y J, YANG X X, et al., 2015. Effect of different tillage methods on net global warming potential and greenhouse gas intensity in double rice cropping systems[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 35(6): 1887-1895. | |
| [18] | 樊代佳, 2020. 氮肥深施对免耕稻田土壤有机质特性、甲烷排放及微生物群落的影响机制[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学. |
| FAN D J, 2020. Effects of nitrogen fertilizer deep placement on organic matter properties, methane emissions and microbial communities in no tillage paddy soil[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University. | |
| [19] | 范紫月, 齐晓波, 曾麟岚, 等, 2022. 中国农业系统近40年温室气体排放核算[J]. 生态学报, 42(23): 9470-9482. |
| FAN Z Y, QI X B, ZENG L L, et al., 2022. Accounting of greenhouse gas emissions in the Chinese agricultural system from 1980 to 2020[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 42(23): 9470-9482. | |
| [20] | 龚伟, 颜晓元, 王景燕, 2011. 长期施肥对土壤肥力的影响[J]. 土壤, 43(3): 336-342. |
| GONG W, YAN X Y, WANG J Y, 2011. Effect of long-term fertilization on soil fertility[J]. Soils, 43(3): 336-342. | |
| [21] | 郭时金, 付石军, 张志美, 等, 2013. 规模化养殖场废弃物无害化处理及资源化利用现状研究[J]. 家禽科学 (11): 42-47. |
| GUO S J, FU S J, ZHANG Z M, et al., 2013. Progress on the harmless treatment and resource utilization of waste from large-scale farms[J]. China Poultry Science (11): 42-47. | |
| [22] | 郭智, 周炜, 陈留根, 等, 2013. 施用猪粪有机肥对稻麦两熟农田稻季养分径流流失的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 27(6): 21-27. |
| GUO Z, ZHOU W, CHEN L G, et al., 2013. Effect of pig manure application on surface runoff losses of soil nitrogen and phosphorus during the paddy season in intensive rice-wheat rotation field[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 27(6): 21-27. | |
| [23] | 韩燕云, 吴永红, 李丹, 等, 2023. 微生物介导的稻田水土界面温室气体排放及其农事减排措施研究进展[J]. 环境科学研究, 36(12): 2369-2381. |
| HAN Y Y, WU Y H, LI D, et al., 2023. Advancements in research on microbe-mediated greenhouse gas emissions at the rice paddy soil-water Interface and agricultural mitigation strategies[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 36(12): 2369-2381. | |
| [24] | 何美霞, 段鹏鹏, 李德军, 2023. 土壤氧化亚氮产生路径及其研究方法进展[J]. 生态学杂志, 42(6): 1497-1508. |
|
HE M X, DUAN P P, LI D J, 2023. Review on the pathways of soil nitrous oxide production and its research methods[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 42(6): 1497-1508.
DOI |
|
| [25] | 黄耀, 孙文娟, 2006. 近20年来中国大陆农田表土有机碳含量的变化趋势[J]. 科学通报, 51(7): 750-763. |
| HUANG Y, SUN W J, 2006. Changes of topsoil organic carbon content in China in the last 20 years[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 51(7): 750-763. | |
| [26] | 林海波, 夏忠敏, 陈海燕, 2017. 有机、无机肥料配施研究进展与展望[J]. 耕作与栽培 (4): 67-69. |
| LIN H B, XIA Z M, CHEN H Y, 2017. Advances and prospects of rational application of organic ang chemical fertilizers[J]. Tillage and Cultivation (4): 67-69. | |
| [27] | 罗澜, 2022. 长期施肥对土壤可溶性有机碳生物降解及矿物质含量的影响[D]. 郑州: 河南农业大学. |
| LUO L, 2022. Effects of long-term fertilization on dissolved organic carbon biodegradation and mineral content[D]. Zhengzhou: Henam Agricultural University. | |
| [28] | 吕凤莲, 杨学云, 赵冉, 等, 2022. 静态箱/气相色谱法监测农田温室气体排放研究[J]. 实验技术与管理, 39(9): 15-24. |
| LÜ F L, YANG X Y, ZHAO R, et al., 2022. Study on static chamber/gas chromatography method for monitoring greenhouse gas emission in field ecosystem[J]. Experimental Technology and Management, 39(9): 15-24. | |
| [29] | 马静, 徐华, 蔡祖聪, 2010. 施肥对稻田甲烷排放的影响[J]. 土壤, 42(2): 153-163. |
| MA J, XU H, CAI Z C, 2010. Effects of fertilization on methane emissions in paddy fields[J]. Soils, 42(2): 153-163. | |
| [30] | 马宁宁, 李天来, 武春成, 等, 2010. 长期施肥对设施菜田土壤酶活性及土壤理化性状的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 21(7): 1766-1771. |
| MA N N, LI T L, WU C C, et al., 2010. Effects of long-term fertilization on soil enzyme activities and soil physical and chemical properties in protected vegetable fields[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 21(7): 1766-1771. | |
| [31] |
苗茜, 黄琼, 朱小莉, 等, 2020. 有机肥等氮替代化肥对稻田CH4和N2O排放的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 29(4): 740-747.
DOI |
| MIAO Q, HUANG Q, ZHU X L, et al., 2020. Effects of partial organic substitution for chemical fertilizer on CH4 and N2O emissions in paddy field[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 29(4): 740-747. | |
| [32] |
宁川川, 王建武, 蔡昆争, 2016. 有机肥对土壤肥力和土壤环境质量的影响研究进展[J]. 生态环境学报, 25(1): 175-181.
DOI |
| NING C C, WANG J W, CAI K Z, et al., 2016. The effects of organic fertilizers on soil fertility and soil environmental quality: A review[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 25(1): 175-181. | |
| [33] | 且天真, 武迪, 张德健, 等, 2023. 不同年限施用有机肥对土壤理化性质的影响[J]. 安徽农业科学, 51(12): 135-141, 170. |
| QIE T Z, WU D, ZHANG D J, et al., 2023. Effects of different years of application of organic fertilizer on physical and chemical properties of soil[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 51(12): 135-141, 170. | |
| [34] | 石生伟, 李玉娥, 李明德, 等, 2011. 不同施肥处理下双季稻田CH4和N2O排放的全年观测研究[J]. 大气科学, 35(4): 707-720. |
| SHI S W, LI Y E, LI M D, et al., 2011. Annual CH4 and N2O emissions from double rice cropping systems under various fertilizer regimes in Hunan Province, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences, 35(4): 707-720. | |
| [35] | 宋伟凤, 2022. 有机肥替代化肥对稻田土理化性质、微生物群落结构以及水稻产量的影响[D]. 泰安: 山东农业大学. |
| SONG W F, 2022. Effects substitute chemical fertilizers with organic fertilizers on soil physicochemical parameters, microbial community composition rice yield in paddy field[D]. Tai’an: Shandong Agricultural University. | |
| [36] | 唐海明, 肖小平, 孙继民, 等, 2014. 种植不同冬季作物对稻田甲烷、氧化亚氮排放和土壤微生物的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 23(5): 736-742. |
| TANG H M, XIAO X P, SUN J M, et al., 2014. Effects of different winter covering crops cultivation on methane and nitrous oxide emission fluxes and soil microorganism in double-cropping paddy field[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 23(5): 736-742. | |
| [37] | 田伟, 伍延正, 汤水荣, 等, 2019. 不同施肥模式对热区晚稻水田CH4和N2O排放的影响[J]. 环境科学, 40(5): 2426-2434. |
| TIAN W, WU Y Z, TANG S R, et al., 2019. Effects of different fertilization modes on greenhouse gas emission characteristics of paddy fields in hot areas[J]. Environmental Science, 40(5): 2426-2434. | |
| [38] | 王成己, 潘根兴, 田有国, 2009. 保护性耕作下农田表土有机碳含量变化特征分析—基于中国农业生态系统长期试验资料[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 28(12): 2464-2475. |
| WANG C J, PAN G X, TIAN Y G, 2009. Characteristics of cropland topsoil organic carbon dynamics under different conservation tillage treatments based on long-term agro-ecosystem experiments across mainland China[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 28(12): 2464-2475. | |
| [39] | 王聪, 沈健林, 郑亮, 等, 2014. 猪粪化肥配施对双季稻田CH4和N2O排放及其全球增温潜势的影响[J]. 环境科学, 35(8): 3120-3127. |
| WANG C, SHEN J L, ZHENG L, et al., 2014. Effects of combined applications of pig manure and chemical fertilizers on CH4 and N2O emissions and their global warming potentials in paddy fields with double-rice cropping[J]. Environmental Science, 35(8): 3120-3127. | |
| [40] | 王迎红, 2005. 陆地生态系统温室气体排放观测方法研究、应用及结果比对分析[D]. 北京: 中国科学院研究生院(大气物理研究所). |
| WANG Y H, 2005, Research on observation methods, application and comparison of results of greenhouse gas emissions in terrestrial ecosystems[D]. Beijing: Institute of Atmospheric, Chinese Academy of Sciences. | |
| [41] | 吴乐知, 蔡祖聪, 2007. 基于长期试验资料对中国农田表土有机碳含量变化的估算[J]. 生态环境, 16(6): 1768-1774. |
| WU L Z, CAI Z C, 2007. Estimation of organic carbon content change in farmland topsoil in China based on long-term experimental data[J]. Ecology and Environment, 16(6): 1768-1774. | |
| [42] | 闫鹏, 张靖, 沈健林, 等, 2023. 有机无机肥配施对设施菜地N2O排放和NH3挥发的影响[J]. 农业现代化研究, 44(4): 701-711. |
| YAN P, ZHANG J, SHEN J L, et al., 2023. Effects of combined application of organic and chemical fertilizers on N2O emission and NH3 volatilization in protected vegetable soils[J]. Research of Agricultural Modernization, 44(4): 701-711. | |
| [43] | 于飞, 施卫明, 2015. 近10年中国大陆主要粮食作物氮肥利用率分析[J]. 土壤学报, 52(6): 1311-1324. |
| YU F, SHI W M, 2015. Nitrogen use efficiencies of major grain crops in China in recent 10 years[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 52(6): 1311-1324. | |
| [44] |
余锋, 李思宇, 邱园园, 等, 2022. 稻田甲烷排放的微生物学机理及节水栽培对甲烷排放的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 36(1): 1-12.
DOI |
|
YU F, LI S Y, QIU Y Y, et al., 2022. Microbiological mechanism of methane emission in paddy field and influence of water-saving cultivation on methane emission[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 36(1): 1-12.
DOI |
|
| [45] | 张广斌, 马静, 徐华, 等, 2011. 稻田甲烷产生途径研究进展[J]. 土壤, 43(1): 6-11. |
| ZHANG G B, MA J, XU H, et al., 2011. Research progress on methane production pathways in paddy fields[J]. Soil, 43(1): 6-11. | |
| [46] | 张英, 武淑霞, 雷秋良, 等, 2022. 不同类型粪肥还田对土壤酶活性及微生物群落的影响[J]. 土壤, 54(6): 1175-1184. |
| ZHANG Y, WU S X, LEI Q L, et al., 2022. Effects of different manures on soil enzyme activity and microbial community[J]. Soil, 54(6): 1175-1184. | |
| [47] | 朱志成, 钟民正, 侯磊, 等, 2024. 整县推进畜禽粪污资源化利用项目温室气体减排量评估方法[J]. 环境工程技术学报, 14(1): 25-32. |
| ZHU Z C, ZHONG M Z, HOU L, et al., 2024. Evaluation on greenhouse gas emission reduction of the whole county's promotion project of livestock and poultry manure resource utilization[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology, 14(1): 25-32. |
| [1] | 丁昊, 李长鑫, 丁静, 兰昊. n-damo细菌在不同生态环境中的遗传多样性和潜在功能研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(2): 202-211. |
| [2] | 马媛, 田路露, 吕杰, 柳沛, 张旭, 李二阳, 张清航. 天山北坡雪岭云杉森林土壤微生物群落及影响因素研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(1): 1-11. |
| [3] | 袁茜, 傅开道, 陶雨晨, 张年, 杨丽莎. 澜沧江(云南段)水-气界面氧化亚氮释放通量时空分布特征及其影响因素研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(1): 54-61. |
| [4] | 苗敬杰, 张开, 孟钰博, 王乃加, 李海楠, 郭康军, 张君, 高西宁, 王立为. 覆膜垄作对旱地雨养马铃薯田N2O排放的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(1): 62-71. |
| [5] | 唐志伟, 翁颖, 朱夏童, 蔡洪梅, 代雯慈, 王捧娜, 郑宝强, 李金才, 陈翔. 秸秆还田下中国农田土壤微生物生物量碳变化及其影响因素的Meta分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(9): 1552-1562. |
| [6] | 李航, 陈金平, 丁兆华, 舒洋, 魏江生, 赵鹏武, 周梅, 王宇轩, 梁驰昊, 张轶超. 火干扰对兴安落叶松林土壤氮组分及土壤中氮循环功能基因的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(9): 1563-1573. |
| [7] | 梁鑫, 韩亚峰, 郑柯, 王旭刚, 陈志怀, 杜鹃. 磁铁矿对稻田土壤碳矿化的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(9): 1615-1622. |
| [8] | 刘晗, 王萍, 孙鲁沅, 秦文婧, 陈晓芬, 陈金, 周国朋, 梁婷, 刘佳, 李燕丽. 种植冬绿肥对红壤幼龄橘园土壤微生物量碳、氮和酶活的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(9): 1623-1631. |
| [9] | 陈懂懂, 霍莉莉, 赵亮, 陈昕, 舒敏, 贺福全, 张煜坤, 张莉, 李奇. 青海高寒草地水热因子对土壤微生物生物量碳、氮空间变异的贡献——基于增强回归树模型[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(7): 1207-1217. |
| [10] | 宫亮, 金丹丹, 牛世伟, 王娜, 邹晓锦, 张鑫, 隋世江, 解占军, 韩瑛祚. 辽宁省水稻田固碳减排潜力分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(7): 1226-1236. |
| [11] | 朱忆雯, 尹丹, 胡敏, 杜衍红, 洪泽彬, 程宽, 于焕云. 稻田土壤氮循环与砷形态转化耦合的研究进展[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(7): 1344-1354. |
| [12] | 刘紫薇, 葛继稳, 王月环, 杨诗雨, 姚东, 谢金林. 大九湖泥炭湿地甲烷通量变异特征及影响因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 706-714. |
| [13] | 唐海明, 石丽红, 文丽, 程凯凯, 李超, 龙泽东, 肖志武, 李微艳, 郭勇. 长期施肥对双季稻田根际土壤氮素的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 492-499. |
| [14] | 秦佳琪, 肖指柔, 明安刚, 朱豪, 滕金倩, 梁泽丽, 陶怡, 覃林. 针阔人工混交林及其纯林对土壤微生物碳循环功能基因丰度的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(10): 1719-1731. |
| [15] | 李威闻, 黄金权, 齐瑜洁, 刘小岚, 刘纪根, 毛治超, 高绣纺. 土壤侵蚀条件下土壤微生物生物量碳含量变化及其影响因素的Meta分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 47-55. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
