生态环境学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (8): 1192-1202.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2024.08.004
吴艺1,2( ), 毛旭锋1,2,*(
), 毛旭锋1,2,*( ), 刘泽碧1,2, 夏亮1,2, 金鑫1,2, 唐文家3, 于红妍4, 杜凯1,2
), 刘泽碧1,2, 夏亮1,2, 金鑫1,2, 唐文家3, 于红妍4, 杜凯1,2
收稿日期:2024-06-28
出版日期:2024-08-18
发布日期:2024-09-25
通讯作者:
*毛旭锋。E-mail: maoxufeng@yeah.net作者简介:吴艺(1994年生),男,博士研究生,主要研究方向为湿地生态过程。E-mail: mambawu@yeah.net
基金资助:
WU Yi1,2( ), MAO Xufeng1,2,*(
), MAO Xufeng1,2,*( ), LIU Zebi1,2, XIA Liang1,2, JIN Xin1,2, TANG Wenjia3, YU Hongyan4, DU Kai1,2
), LIU Zebi1,2, XIA Liang1,2, JIN Xin1,2, TANG Wenjia3, YU Hongyan4, DU Kai1,2
Received:2024-06-28
Online:2024-08-18
Published:2024-09-25
摘要:
甲烷氧化菌(Methanotrophs)是一类可以利用甲烷(CH4)作为唯一碳源和能源的细菌,在生态系统碳循环过程中起着重要的作用。为探究黄河上游梯级水库沉积物甲烷氧化菌的群落组成、基因丰度及其影响因素,以黄河上游大河家至龙羊峡段的10座梯级水库为研究对象,通过甲烷氧化菌功能基因(pmoA)高通量测序和实时荧光定量PCR研究黄河上游不同水文期(枯水期、丰水期)和不同库龄(高库龄、低库龄)梯级水库沉积物中甲烷氧化菌的群落组成和基因丰度,利用“rdacca.hp”包及FAPROTAX功能预测分析甲烷氧化菌的影响因素和生态功能。结果表明,1)黄河上游梯级水库沉积物相对丰度排名前3的甲烷氧化菌属分别为甲基孢囊菌属(Methylocystis,22.70%)、甲基杆菌属(Methylobacter,19.00%)和甲基暖菌属(Methylocaldum,7.17%);甲烷氧化菌α多样性和β多样性均表现为丰水期高于枯水期(p<0.05),二者在不同库龄之间差异性不显著(p>0.05)。2)甲烷氧化菌的pmoA基因丰度在枯水期(1.47×105 copies·g−1)显著低于丰水期(9.08×105 copies·g−1)(p<0.05);空间上,枯水期呈现从上游(3.92×105 copies·g−1)到下游(0.50×105 copies·g−1)减少的趋势,丰水期呈现为从上游(5.37×105 copies·g−1)到下游(26.52×105 copies·g−1)增加的趋势。3)水体总有机碳(19.31%)、总氮(16.40%)、沉积物温度(13.03%)和pH(10.40%)是影响甲烷氧化菌群落组成的重要环境因素;甲烷氧化、甲基营养化、烃降解和化能异养是甲烷氧化菌的主要生态功能。梯级水库的建设影响了沉积物甲烷氧化菌群落演替的时空模式。研究结果可为黄河上游梯级水库CH4生物减排提供一定的参考。
中图分类号:
吴艺, 毛旭锋, 刘泽碧, 夏亮, 金鑫, 唐文家, 于红妍, 杜凯. 黄河上游梯级水库沉积物甲烷氧化菌丰度和群落结构特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(8): 1192-1202.
WU Yi, MAO Xufeng, LIU Zebi, XIA Liang, JIN Xin, TANG Wenjia, YU Hongyan, DU Kai. Abundance and Community Structure of Methanotrophs in the Sediment of Cascade Reservoirs in the Upper Yellow River[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2024, 33(8): 1192-1202.
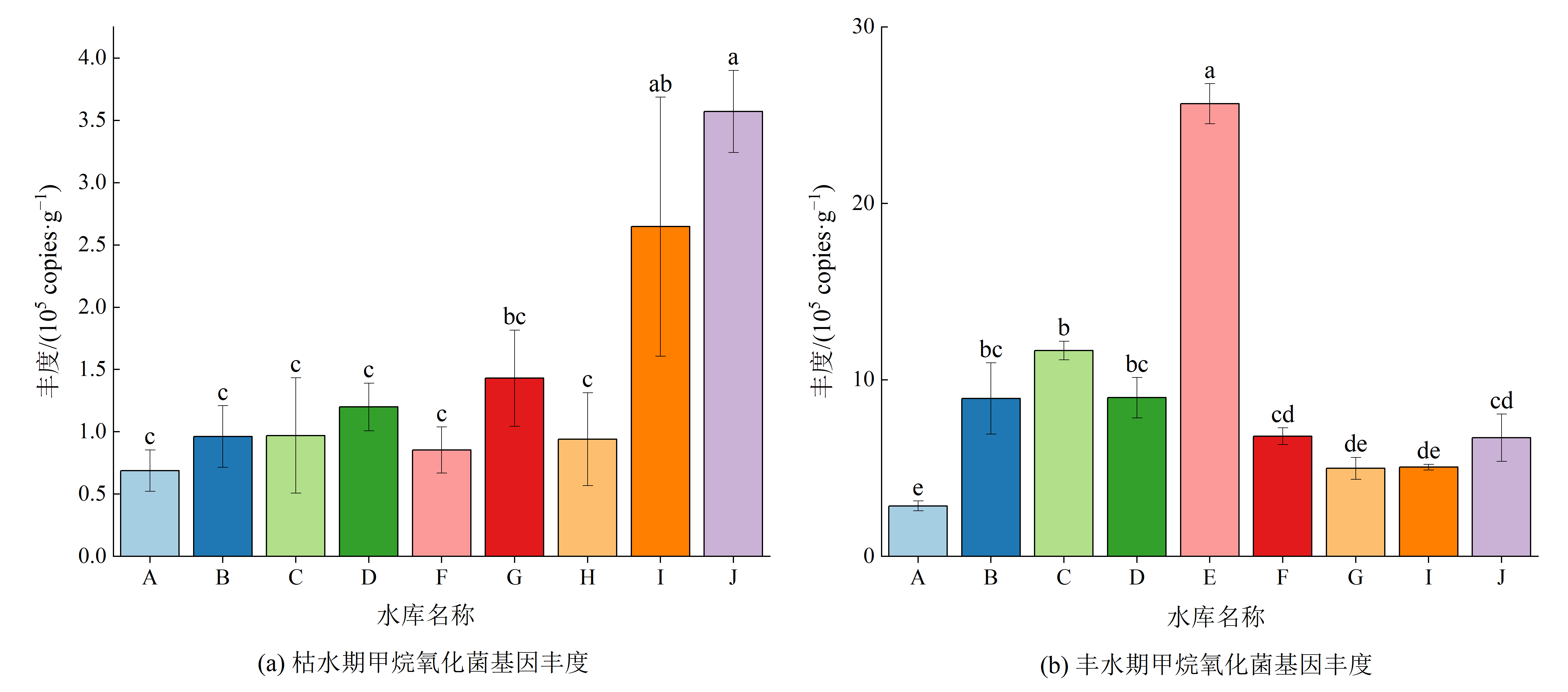
图5 黄河上游梯级水库沉积物pmoA基因丰度 图中不同小写字母代表差异显著(p<0.05),误差棒代表标准差
Figure 5 Abundance of the pmoA gene in sediments of cascade reservoirs in the upper Yellow River
| [1] | CHEN H, PENG C, ZHU Q, et al., 2015. Methane emissions from rice paddies, natural wetlands and lakes in China[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press: 155-194. |
| [2] | CHEN Z B, ZHOU Z Y, PENG X, et al., 2013. Effects of wet and dry seasons on the aquatic bacterial community structure of the Three Gorges Reservoir[J]. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 29(5): 841-853. |
| [3] | CHOWDHURY T R, DICK R P, 2013. Ecology of aerobic methanotrophs in controlling methane fluxes from wetlands[J]. Applied Soil Ecology, 65(Part B): 8-22. |
| [4] |
COSTELLO A M, LIDSTROM M E, 1999. Molecular characterization of functional and phylogenetic genes from natural populations of methanotrophs in lake sediments[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 65(11): 5066-5074.
PMID |
| [5] | DENG Y C, CUI X Y, LÜ K C, et al., 2013. Aerobic methanotroph diversity in R iganqiao peatlands on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau[J]. Environmental Microbiology Reports, 5(4): 566-574. |
| [6] |
DENG Y C, LIU Y Q, DUMONT M G, et al., 2017. Salinity affects the composition of the aerobic methanotroph community in Alkaline Lake sediments from the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Microbial Ecology, 73(1): 101-110.
DOI PMID |
| [7] |
DUMESTRE J F, GUEZENNEC J, GALY-LACAUX C, et al., 1999. Influence of light intensity on methanotrophic bacterial activity in Petit Saut Reservoir, French Guiana[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 65(2): 534-539
PMID |
| [8] |
DUMONT M G, POMMERENKE B, CASPER P, et al., 2011. DNA-, rRNA- and mRNA-based stable isotope probing of aerobic methanotrophs in lake sediment.[J]. Environmental Microbiology, 13(5): 1153-1167.
DOI PMID |
| [9] | HARRISON J, PRAIRIE Y, MERCIER B S, et al., 2021. Year‐2020 global distribution and pathways of reservoir methane and carbon dioxide emissions according to the greenhouse gas from reservoirs (G‐res) model[J]. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 35(6): e2020GB006888. |
| [10] | HIROMI K, TAKAHIRO S, NORIHISA M, et al., 2022. Environmental factors affecting the community of methane-oxidizing bacteria[J]. Microbes and Environments, 37(1): ME21074. |
| [11] | HØJ L, OLSEN R A, TORSVIK V L, 2008. Effects of temperature on the diversity and community structure of known methanogenic groups and other archaea in high Arctic peat[J]. The ISME Journal, 2(1): 37-48. |
| [12] | IVANOV M V, RUSANOV I I, PIMENOV N V, et al., 2001. Microbial processes of the carbon and sulfur cycles in Lake Mogil'noe[J]. Microbiology, 70: 583-593. |
| [13] | JI Y, FERNANDEZ S A, KLOSE M, et al., 2015. Functional and structural responses of methanogenic microbial communities in Uruguayan soils to intermittent drainage[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 89: 238-247. |
| [14] | KIP N, VAN W J F, PAN Y, et al., 2010. Global prevalence of methane oxidation by symbiotic bacteria in peat-moss ecosystems[J]. Nature Geoscience, 3(9): 617-621. |
| [15] | KNIEF C, 2015. Diversity and habitat preferences of cultivated and uncultivated aerobic methanotrophic bacteria evaluated based on pmoA as molecular marker[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 15(6): 1346. |
| [16] | LI S N, JI X H, CHEN C, et al., 2021. Effects of increasing lime application rates on microbial diversity and community structure in paddy soils[J]. Applied Soil Ecology, 161: 103837. |
| [17] | PENG H J, CHI J S, YAO H, et al., 2021. Methane emissions offset net carbon dioxide uptake from an alpine peatland on the Eastern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 126(19): e2021JD034671. |
| [18] | ROSENTRETER J A, BORGES A V, DEEMER B R, et al., 2021. Half of global methane emissions come from highly variable aquatic ecosystem sources[J]. Nature Geoscience, 14: 225-230 |
| [19] | SAUNOIS M, STAVERT A, POULTER B I, et al., 2016. The global methane budget 2000-2017[J]. Earth System Science Data, 12(3): 1561-1623 |
| [20] | SHEN L D, TIAN M H, CHENG H X, et al., 2020. Different responses of nitrite- and nitrate-dependent anaerobic methanotrophs to increasing nitrogen loading in a freshwater reservoir[J]. Environmental Pollution, 263(Part A): 114623. |
| [21] | SMITH G J, ANGLE J C, SOLDEN L M, et al., 2018. Members of the genus methylobacter are inferred to account for the majority of aerobic methane oxidation in oxic soils from a freshwater wetland[J]. mBio, 9(6): e00815-18. |
| [22] | SOUED C, HARRISON J A, MERCIER B S, et al., 2022. Reservoir CO2 and CH4 emissions and their climate impact over the period 1900-2060[J]. Nature Geoscience, 15(9): 700-705. |
| [23] | WANG J, JUN J Y, LIU D, et al., 2016. Research progresses on methanogenesis pathway and methanogens in coastal wetlands[J]. The Journal of Applied Ecology, 27(3): 993-1001. |
| [24] |
WHITTENBURY R, DAVIES S L, DAVEY J F, et al., 1970. Exospores and cysts formed by methane-utilizing bacteria[J]. Journal of General Microbiology, 61(2): 219-226.
PMID |
| [25] | WU B, TIAN J Q, BAI C M, et al., 2013. The biogeography of fungal communities in wetland sediments along the Changjiang River and other sites in China[J]. The ISME Journal, 7(7): 1299-1309. |
| [26] | WU H B, WANG X X, GANJURJAV H, et al., 2020. Effects of increased precipitation combined with nitrogen addition and increased temperature on methane fluxes in alpine meadows of the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 705: 135818. |
| [27] | YANG Y Y, CHEN J F, TONG T L, et al., 2019. Eutrophication influences methanotrophic activity, abundance and community structure in freshwater lakes[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 662: 863-872. |
| [28] | YANG Y Y, ZHAO Q, CUI Y H, et al., 2015. Spatio-temporal variation of sediment methanotrophic microorganisms in a large eutrophic lake[J]. Microbial Ecology, 71: 9-17. |
| [29] |
YUN J L, ZHUANG G Q, MA A Z, et al., 2012. Community structure, abundance, and activity of methanotrophs in the Zoige wetland of the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Microbial Ecology, 63(4): 835-843.
DOI PMID |
| [30] | ZHANG K, LIU Y H, CHEN Q, et al., 2018. Effect of submerged plant species on CH4 flux and methanogenic community dynamics in a full-scale constructed wetland[J]. Ecological Engineering, 115: 96-104. |
| [31] |
ZHANG Q Q, ZHAO J, WANG G J, et al., 2024. Differences of bacterioplankton communities between the source and upstream regions of the Yangtze River: microbial structure, co-occurrence pattern, and environmental influencing factors[J]. Brazilian Journal of Microbiology, 55(1): 571-586.
DOI PMID |
| [32] | ZHAO B L, ZENG Q H, WANG J H, et al., 2024. Impact of cascade reservoirs on nutrients transported downstream and regulation method based on hydraulic retention time[J]. Water Research, 252: 121187. |
| [33] | ZHAO J, CAI Y F, JIA Z J, 2020. The pH-based ecological coherence of active canonical methanotrophs in paddy soils[J]. Biogeosciences, 17(6): 1451-1462. |
| [34] | 白文广, 2010. 温室气体CH4卫星遥感监测初步研究[D]. 北京: 中国气象科学研究院: 5-10. |
| BAI W G, 2010. Preliminary study of satellite remote sensing of greenhouse gases methane[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Meteorological Sciences: 5-10. | |
| [35] | 丁维新, 蔡祖聪, 2003. 温度对甲烷产生和氧化的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 14(4): 604-608. |
| DING W X, CAI Z C, 2003. Effect of temperature on methane production and oxidation in soils[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 14(4): 604-608. | |
| [36] | 郭家宏, 范熠, 张西美, 2022. 温度对不同生态系统土壤甲烷氧化过程和甲烷氧化细菌的影响[J]. 中国农业气象, 43(6): 427-439. |
| GUO J H, FAN Y, ZHANG X M, 2022. Effect of temperature on soil methane oxidation and methanotrophs in different ecosystems[J]. Chinese Journal of Agrometeorology, 43(6): 427-439. | |
| [37] | 毛羽丰, 何蕊序, 李宏, 等, 2024. 三峡水库支流甲烷排放研究进展[J]. 湖泊科学, 36(1): 17-33. |
| MAO Y F, HE R X, LI H, et al., 2024. Research progress on methane emissions from tributaries of the three gorges reservoir[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 36(1): 17-33. | |
| [38] | 李宏恩, 马桂珍, 王芳, 等, 2021. 2000-2018年中国水库溃坝规律分析与对策[J]. 水利水运工程学报 (5): 101-111. |
| LI H E, MA G Z, WANG F, et al., 2021. Analysis of dam failure trend of China from 2000 to 2018 and improvement suggestions[J]. Hydro-Science and Engineering (5): 101-111. | |
| [39] | 李馨怡, 王北辰, 熊雄, 等, 2023. 青海湖岸带土壤与沉积物的地化特征与细菌群落对水位上升的响应[J]. 微生物学报, 63(6): 2312-2329. |
| LI X Y, WANG B C, XIONG X, et al., 2023. Response of geochemistry and bacterial communities to water-level rise in the soil and sediment of the coastal zone in Qinghai Lake[J]. Acta Microbiologica Sinica, 63(6): 2312-2329. | |
| [40] | 刘丹, 王烜, 李春晖, 等, 2019. 水文连通性对湖泊生态环境影响的研究进展[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 28(7): 1702-1715. |
| LIU D, WANG X, LI C H, et al., 2019. Eco-environmental effects of hydrological connectivity on lakes: A review[J]. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 28(7): 1702-1715. | |
| [41] | 刘洋, 陈永娟, 王晓燕, 等, 2018. 人类活动对河流沉积物中反硝化厌氧甲烷氧化菌群落特征的影响[J]. 环境科学, 39(8): 3677-3688. |
| LIU Y, CHEN Y J, WANG X Y, et al., 2018. Influences of anthropogenic activities on the community structure of N-DAMO bacteria in the north canal[J]. Environmental Science, 39(8): 3677-3688. | |
| [42] |
吕伟涛, 胡夏嵩, 刘昌义, 等, 2024. 黄河上游龙羊峡至积石峡段流域植被对气候变化的响应[J]. 草地学报, 32(6): 1923-1935.
DOI |
| LÜ W T, HU X S, LIU C Y, et al., 2024. Response of vegetation to climate change along the Longyang Gorge and jishi Gorge in the upper Yellow River[J]. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 32(6): 1923-1935. | |
| [43] |
孟华旦尚, 薛曌, 郭小芳, 等, 2023. 西藏纳木错沿岸表层水体浮游细菌群落结构及生态功能预测[J]. 冰川冻土, 45(1): 254-266.
DOI |
| MENG H D S, XUE Z, GUO X F, et al., 2023. Structure of bacterioplanktonic community and ecological function prediction in coastal surface water of Nam Co lake, Tibet[J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 45(1): 254-266. | |
| [44] | 聂明, 2020. 气候变暖下水圈甲烷排放及其微生物学机制[J]. 微生物学报, 60(9): 1821-1833. |
| NEI M, 2020. Hydrospheric methane emission and its microbiological mechanisms under climate warming[J]. Acta Microbiologica Sinica, 60(9): 1821-1833. | |
| [45] | 沈李东, 金靖昊, 刘心, 2022. 内陆湿地与水体甲烷厌氧氧化功能微生物研究进展[J]. 生态学报, 42(9): 3842-3855. |
| SHEN L D, JIN J H, LIU X, 2022. Research progress on anaerobic methanotrophs in inland wetlands and freshwater aquatic systems[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 42(9): 3842-3855. | |
| [46] | 孙志禹, 陈永柏, 李翀, 等, 2020. 中国水库温室气体研究 (2009-2019): 回顾与展望[J]. 水利学报, 51(3): 253-267. |
| SUN Z Y, CHEN Y B, LI C, et al., 2020. Research of reservoir greenhouse gas emissions in China (2009-2019): Review and outlook[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 51(3): 253-267. | |
| [47] | 唐千, 薛校风, 王惠, 等, 2018. 湖泊生态系统产甲烷与甲烷氧化微生物研究进展[J]. 湖泊科学, 30(3): 597-610. |
| TANG Q, XIE X F, WANG H, et al., 2018. New knowledge of methanogens and methanotrophs in lake ecosystems[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 30(3): 597-610. | |
| [48] | 夏品华, 林陶, 2021. 云贵高原典型湖滨湿地好氧甲烷氧化细菌群落结构和数量的时空动态[J]. 生态学报, 41(12): 4776-4785. |
| XIA P H, LIN T, 2021. Spatio-temporal variation in the abundance and structure of aerobic methane-oxidizing bacteria in the littoral wetland, Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau lake[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 41(12): 4776-4785. | |
| [49] | 尤本胜, 马书占, 耿梦蝶, 等, 2023. 太湖水体和沉积物细菌群落分布格局及其驱动因素[J]. 湖泊科学, 35(5): 1774-1787. |
| YOU B S, MA S Z, GENG M D, et al., 2023. Distribution patterns and driving factors of bacterial communities in water and sediment of Lake Taihu[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 35(5): 1774-1787. | |
| [50] | 张佩, 王晓锋, 袁兴中, 2020. 中国淡水生态系统甲烷排放基本特征及研究进展[J]. 中国环境科学, 40(8): 3567-3579. |
| ZHANG P, WANG X F, YUAN X Z, 2020. General characteristics and research progress of methane emissions from freshwater ecosystems in China[J]. China Environmental Science, 40(8): 3567-3579. | |
| [51] | 赵若男, 艾佳, 李彦澄, 等, 2024. 贵州阿哈湖水库沉积物中甲烷氧化菌分布与功能[J]. 微生物学报, 64(3): 809-825. |
| ZHAO R N, AI J, LI Y C, et al., 2024. Distribution and functions of methanotrophs in the sediments of Aha Lake Reservoir, Guizhou Province[J]. Acta Microbiologica Sinica, 64(3): 809-825. | |
| [52] | 赵瑞欣, 周保, 李滨, 2013. 黄河上游龙羊峡至积石峡段巨型滑坡OSL测年[J]. 地质通报, 32(12): 1943-1951. |
| ZHAO R X, ZHOU B, LI B, 2013. The application of optical stimulate luminescence dating to the study of clustered landslides activity[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 32(12): 1943-1951. |
| [1] | 李璇, 王路茗, 闫春妮, 黄娟. 金属氧化物与非金属氧化物纳米颗粒暴露下人工湿地微生物群落的响应差异[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(7): 1089-1095. |
| [2] | 李成阳, 梁志辉, 李臻明, 蔡敏, 许瑞瑶, 陈秀宇, 丁佳音, 许秋云, 彭飞. 长江源区北麓河流域退化高寒草甸植物群落特征和土壤特性[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(7): 1063-1071. |
| [3] | 刘泽碧, 毛旭锋, 吴艺, 宋秀华, 于红妍, 金鑫, 杜凯, 谢顺邦. 海湖湿地水体蓝藻水华期浮游生物群落特征及其影响因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(6): 946-957. |
| [4] | 夏凡, 韩怡蒙, 周剑兴, 谢丹妮. 氮和硫在人为扰动的青藏高原高寒森林中的分布特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(5): 689-698. |
| [5] | 闫兴蕊, 龚平, 王小萍, 商立海, 李一农, 毛飞剑, 牛学锐, 张勃. 三江源地区土壤和牧草中的有机氯污染物:分布、来源和生态风险[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(3): 428-438. |
| [6] | 丁昊, 李长鑫, 丁静, 兰昊. n-damo细菌在不同生态环境中的遗传多样性和潜在功能研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(2): 202-211. |
| [7] | 陈懂懂, 霍莉莉, 赵亮, 陈昕, 舒敏, 贺福全, 张煜坤, 张莉, 李奇. 青海高寒草地水热因子对土壤微生物生物量碳、氮空间变异的贡献——基于增强回归树模型[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(7): 1207-1217. |
| [8] | 陈丽娟, 周文君, 易艳芸, 宋清海, 张一平, 梁乃申, 鲁志云, 温韩东, MOHD Zeeshan, 沙丽清. 云南哀牢山亚热带常绿阔叶林土壤CH4通量特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(5): 949-960. |
| [9] | 张涵, 唐常源, 禤映雪, 江涛, 黄品怡, 杨秋, 曹英杰. 珠江口红树林土壤甲烷和二氧化碳通量特征及其影响因素研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(5): 939-948. |
| [10] | 李成伟, 刘章勇, 龚松玲, 杨伟, 李绍秋, 朱波. 稻作模式改变对稻田CH4和N2O排放的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(5): 961-968. |
| [11] | 杨冲, 王春燕, 王文颖, 毛旭峰, 周华坤, 陈哲, 索南吉, 靳磊, 马华清. 青藏高原黄河源区高寒草地土壤营养特征变化及质量评价[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(5): 896-908. |
| [12] | 贾晨波, 郭洋, 马成莲, 苏建宇, 徐春燕. 宁杞1号枸杞健康株与根腐病患病株的土壤微生物群落和功能差异[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(9): 1831-1841. |
| [13] | 党慧慧, 刘超, 伍翥嵘, 王圆媛, 胡正华, 李琪, 陈书涛. 不同播期粳稻稻田甲烷排放及综合效益研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(7): 1436-1446. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
