生态环境学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (8): 1203-1213.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2024.08.005
范贝贝1,2( ), 丁帅1(
), 丁帅1( ), 张田田1, 张帅1,3, 魏露露1, 陈清1,*(
), 张田田1, 张帅1,3, 魏露露1, 陈清1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2024-04-09
出版日期:2024-08-18
发布日期:2024-09-25
通讯作者:
*陈清。E-mail: qchen@cau.edu.cn作者简介:范贝贝(1997年生),男,助理工程师,从事土壤改良和废弃物资源化利用。E-mail: jiubeifan@issas.ac.cn †这些作者对这项工作的贡献相等:丁帅(1996年生),男,博士研究生,从事农业面源污染控制与修复。E-mail: ds19961018@qq.com
基金资助:
FAN Beibie1,2( ), DING Shuai1(
), DING Shuai1( ), ZHANG Tiantian1, ZHANG Shuai1,3, WEI Lulu1, CHEN Qing1,*(
), ZHANG Tiantian1, ZHANG Shuai1,3, WEI Lulu1, CHEN Qing1,*( )
)
Received:2024-04-09
Online:2024-08-18
Published:2024-09-25
摘要:
农田土壤磷累积及潜在的磷素流失风险在中国受到广泛的关注。施用白云石是降低土壤磷流失风险的有效措施之一,但常见农田管理措施(秸秆还田、交替灌溉以及它们的组合措施等)如何影响白云石改良后土壤的磷素流失风险及其相关机制目前还不清楚。采用培养试验,探究施用秸秆、周期性淹水-落干、周期性淹水-落干和施用秸秆联合处理对白云石改良土壤活性磷含量、磷吸附/解吸特性、连续浸提磷组分和土壤理化性质的影响。结果表明:与仅施用白云石的对照(CK)相比,施用秸秆(S)和周期性淹水-落干处理(FW)使土壤不稳定磷(CaCl2-P)分别增加62.3%和15.9%;并同时降低土壤磷最大吸附容量(6.26%-12.5%)和NaHCO3-Pi(6.97%-19.2%)。秸秆本身含有的磷和易解吸态磷(NaHCO3-Pi)的释放分别是上述处理土壤活性磷增加的主要原因。周期性淹水-落干和施用秸秆联合处理(FWS)使土壤CaCl2-P和Bray-P分别降低43.4%和23.2%。这一处理也显著提高了土壤非晶质铁质量分数(21.6%),增强土壤对磷的吸附,并抑制吸附态磷的解吸,进而降低土壤活性磷质量分数。此外,周期性淹水-落干和施用秸秆联合处理也显著提高了土壤Fe2+(423%)和铁活化度(18.8%),促进了土壤Fe/Al-P向稳定态磷转化,使HCl-P增加26.9%。土壤磷吸附能力的提高、非晶质铁对活性磷的固定和稳定态磷(HCl-P)质量分数的增加是周期性淹水-落干和施用秸秆联合处理中磷流失风险降低的重要原因。结构方程模型表明,土壤非晶质铁和有机质是影响磷素流失的关键因素。研究表明,适当的淹水-落干措施配合秸秆还田能增强白云石改良土壤中磷素的固持,降低磷素流失风险,可为胶东半岛高磷土壤的管理提供科学依据。
中图分类号:
范贝贝, 丁帅, 张田田, 张帅, 魏露露, 陈清. 周期性淹水-落干和施用秸秆对白云石改良棕壤磷素流失风险的模拟研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(8): 1203-1213.
FAN Beibie, DING Shuai, ZHANG Tiantian, ZHANG Shuai, WEI Lulu, CHEN Qing. Simulation Study on Phosphorus Loss Risk with Periodic Flooding-Drying and Straw Incorporation in a Dolomite-Amended Brown Soil[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2024, 33(8): 1203-1213.
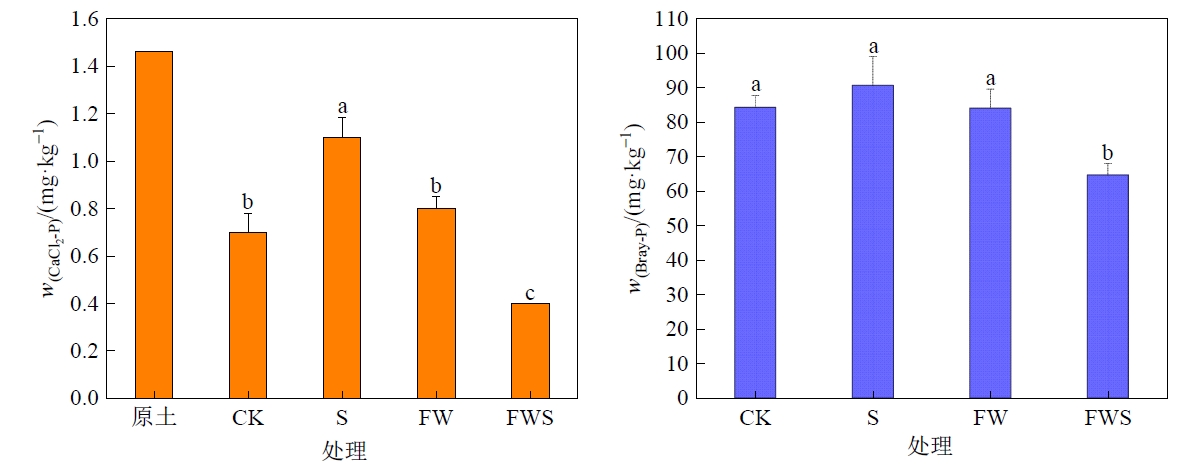
图1 不同处理下土壤CaCl2-P和Bray-P的质量分数 图中不同小写字母表示不同处理之间差异显著(p<0.05),下同
Figure 1 Mass fraction of CaCl2-P and Bray-P after soil incubation under different treatments
| 处理 | w(H2O-Pi)/ (mg∙kg−1) | w(NaHCO3-Pi)/ (mg∙kg−1) | w(NaOH-Pi)/ (mg∙kg−1) | w(HCl-P)/ (mg∙kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 35.0a | 172a | 144a | 48.6b |
| S | 37.6a | 160a | 133a | 48.6b |
| FW | 32.6a | 139b | 130a | 47.4b |
| FWS | 30.7a | 171a | 122b | 61.7a |
表1 不同处理下土壤无机磷组分变化特征
Table 1 Change characteristics of soil phosphorus fractions under different treatments
| 处理 | w(H2O-Pi)/ (mg∙kg−1) | w(NaHCO3-Pi)/ (mg∙kg−1) | w(NaOH-Pi)/ (mg∙kg−1) | w(HCl-P)/ (mg∙kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 35.0a | 172a | 144a | 48.6b |
| S | 37.6a | 160a | 133a | 48.6b |
| FW | 32.6a | 139b | 130a | 47.4b |
| FWS | 30.7a | 171a | 122b | 61.7a |
| 处理 | Langmuir | Freundlich | Liner | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qmax/(mg∙kg−1) | Kl/(L∙mg−1) | Q(PBC)/(L∙kg−1) | r2 | w(DPS)/% | Kf | 1/n | r2 | 解吸率/% | r2 | |||
| CK | 431 | 0.083 | 47.7 | 0.994 | 11.8 | 52.1 | 0.536 | 0.989 | 20.7 | 0.992 | ||
| S | 377 | 0.074 | 27.9 | 0.985 | 13.8 | 45.8 | 0.513 | 0.995 | 26.6 | 0.981 | ||
| FW | 404 | 0.088 | 35.6 | 0.960 | 12.7 | 58.8 | 0.471 | 0.964 | 22.8 | 0.992 | ||
| FWS | 438 | 0.122 | 54.3 | 0.985 | 11.6 | 74.8 | 0.465 | 0.987 | 17.9 | 0.975 | ||
表2 不同处理下土壤对磷的吸附等温线拟合参数和解吸特征
Table 2 Fitting parameters and phosphorus adsorption and desorption isotherm under different treatments
| 处理 | Langmuir | Freundlich | Liner | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qmax/(mg∙kg−1) | Kl/(L∙mg−1) | Q(PBC)/(L∙kg−1) | r2 | w(DPS)/% | Kf | 1/n | r2 | 解吸率/% | r2 | |||
| CK | 431 | 0.083 | 47.7 | 0.994 | 11.8 | 52.1 | 0.536 | 0.989 | 20.7 | 0.992 | ||
| S | 377 | 0.074 | 27.9 | 0.985 | 13.8 | 45.8 | 0.513 | 0.995 | 26.6 | 0.981 | ||
| FW | 404 | 0.088 | 35.6 | 0.960 | 12.7 | 58.8 | 0.471 | 0.964 | 22.8 | 0.992 | ||
| FWS | 438 | 0.122 | 54.3 | 0.985 | 11.6 | 74.8 | 0.465 | 0.987 | 17.9 | 0.975 | ||
| 处理 | pH | 电导率/(μS∙cm−1) | w(SOM)/(g∙kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 5.78b | 269.3a | 25.3bc |
| S | 6.10a | 204.3b | 26.8b |
| FW | 6.10a | 204.7b | 22.4c |
| FWS | 6.10a | 154.3c | 36.1a |
表3 不同处理下的土壤理化性质
Table 3 Soil physical and chemical properties under different treatments
| 处理 | pH | 电导率/(μS∙cm−1) | w(SOM)/(g∙kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 5.78b | 269.3a | 25.3bc |
| S | 6.10a | 204.3b | 26.8b |
| FW | 6.10a | 204.7b | 22.4c |
| FWS | 6.10a | 154.3c | 36.1a |
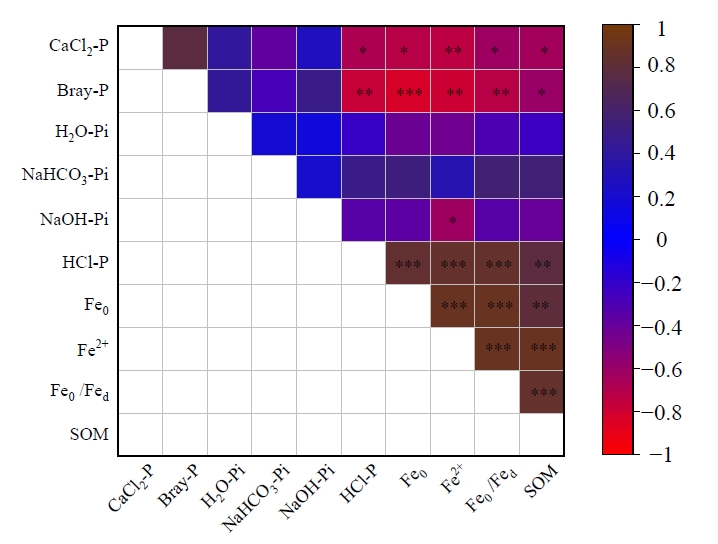
图4 土壤活性磷质量分数与磷组分和土壤理化性质的相关性关系 Feo:非晶质铁;Fe2+:二价铁离子;Feo/Fed:铁活化度。*表示在p<0.05水平下的显著差异,**表示在p<0.01水平下的显著差异,***表示在p<0.001水平下的显著差异
Figure 4 Correlation between soil phosphorus availability, phosphorus components and soil physicochemical properties
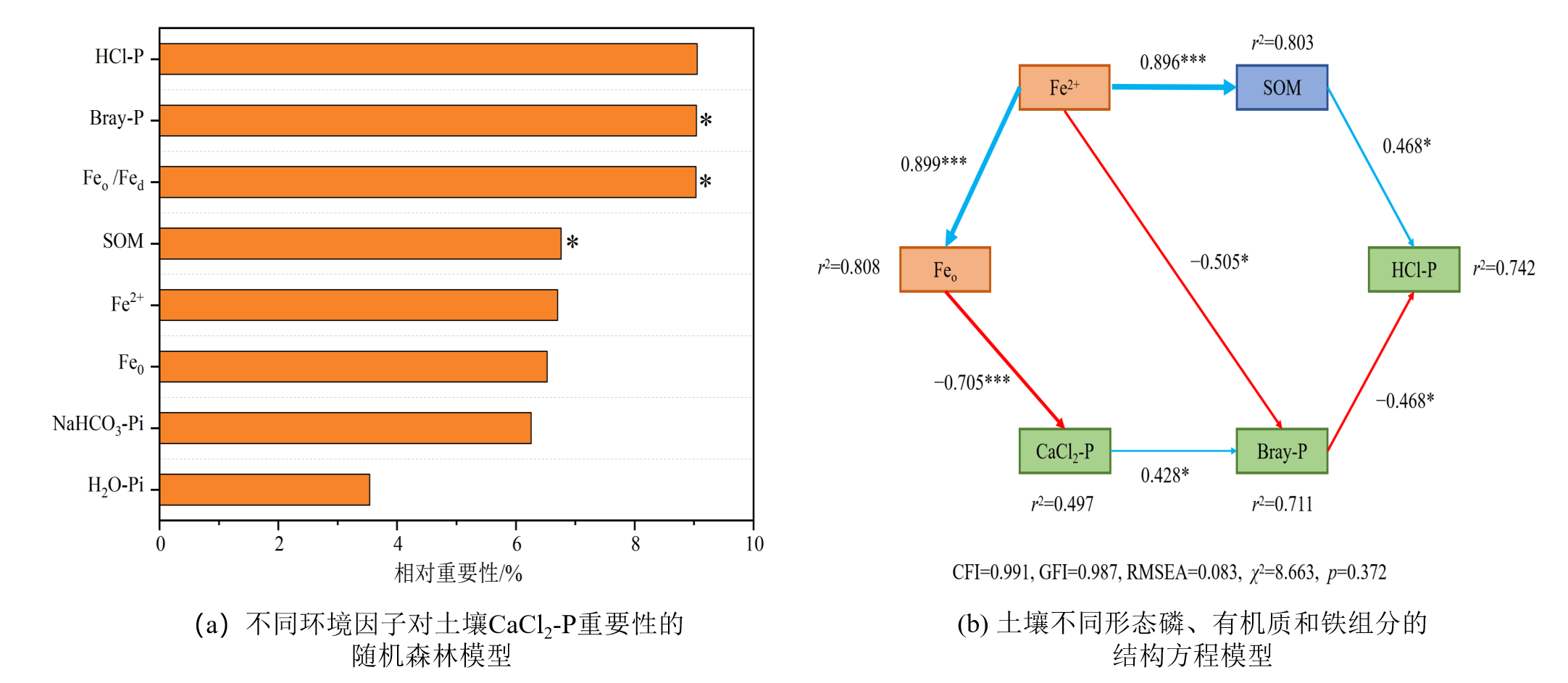
图5 不同环境因子对土壤CaCl2-P变化的重要性模型分析 Feo:非晶质铁;Fe2+:二价铁离子;Feo/Fed:铁活化度。*表示在p<0.05水平下的显著差异.
Figure 5 Model analysis of the importance of different environmental factors to the changes of soil CaCl2-P changes
| [1] | ATTANAYAKE C P, DHARMAKEERTHI R S, KUMARAMAGE D, et al., 2022. Flooding‐induced inorganic phosphorus transformations in two soils, with and without gypsum amendment[J]. Journal of Environmental Quality, 51(1): 90-100. |
| [2] | DING S, ZHANG T T, FAN B B, et al., 2023. Enhanced phosphorus fixation in red mud-amended acidic soil subjected to periodic flooding-drying and straw incorporation[J]. Environmental Research, 229: 115960. |
| [3] | ESLAMIAN F, QI Z, TATE M J, et al., 2018. Phosphorus loss mitigation in leachate and surface runoff from clay loam soil using four lime-based materials[J]. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 229: 1-13. |
| [4] | FAN B Q, DING J H, FENTON O, et al., 2022. Investigation of differential levels of phosphorus fixation in dolomite and calcium carbonate amended red soil[J]. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 102(2): 740-749. |
| [5] | FAN B Q, DING J H, FENTON O, et al., 2020. Understanding phosphate sorption characteristics of mineral amendments in relation to stabilizing high legacy P calcareous soil[J]. Environmental Pollution, 261: 114175. |
| [6] | FAN B Q, WANG J, FENTON O, et al., 2019. Strategic differences in phosphorus stabilization by alum and dolomite amendments in calcareous and red soils[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 26(5): 4842-4854. |
| [7] | GARCIA-SANCHEZ M, BERTRAND I, BARAKAT A, et al., 2023. Improved rock phosphate dissolution from organic acids is driven by nitrate assimilation of bacteria isolated from nitrate and CaCO3-rich soil[J]. Plos One, 18(3): e0283437. |
| [8] | GERKE J, 2015. The acquisition of phosphate by higher plants: Effect of carboxylate release by the roots. A critical review[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Soil Science, 178(3): 351-364. |
| [9] | JAVOT H, PUMPLIN N, HARRISON M J, 2007. Phosphate in the arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis: Transport properties and regulatory roles[J]. Plant, Cell & Environment, 3(3): 310-322. |
| [10] | JOHNSON S E, LOEPPERT R H, 2006. Role of organic acids in phosphate mobilization from iron oxide[J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 70(1): 222-234. |
| [11] | KIANPOOR Y, HUANG B, HU W, et al., 2021. Environmental soil quality and vegetable safety under current greenhouse vegetable production management in China[J]. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 307: 107230. |
| [12] | KONG F X, ZHANG X T, ZHU Y H, et al., 2022. Alternate wetting and drying irrigation reduces P availability in paddy soil irrespective of straw incorporation[J]. Agronomy, 12(7): 1718. |
| [13] | LI Y P, WANG J, SHAO M A, 2022. Earthworm inoculation and straw return decrease the phosphorus adsorption capacity of soils in the loess region, China[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 312: 114921. |
| [14] | LUO G W, SUN B, LI L, et al., 2019. Understanding how long-term organic amendments increase soil phosphatase activities: Insight into phoD- and phoC-harboring functional microbial populations[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 139: 107632. |
| [15] | MARANGUIT D, GUILLAUMET, KUZYAKOV Y, 2017. Effects of flooding on phosphorus and iron mobilization in highly weathered soils under different land-use types: Short-term effects and mechanisms[J]. Catena, 158: 161-170. |
| [16] | MATSUI H, MAHOWALD N M, MOTEKI N, et al., 2018. Anthropogenic combustion iron as a complex climate forcer[J]. Nature Communications, 9(1): 1593. |
| [17] | PENG Y T, ZHANG T T, TANG B B, et al., 2022. Interception of fertile soil phosphorus leaching with immobilization materials: Recent progresses, opportunities, and challenges[J]. Chemosphere, 308(Part 2): 136337. |
| [18] |
PIOL M N, PARICOTO M, SARALEGUI A B, et al., 2019. Dolomite used in phosphate water treatment: desorption processes, recovery, reuse and final disposition[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 237: 359-364.
DOI PMID |
| [19] | PRIYANKA A, ANITA P, 2019. Phosphate solubilization potential of endophytic fungi isolated from Taxus wallichiana Zucc. Roots[J]. Rhizosphere, 9: 2-9. |
| [20] | RAFAELl R, FERNANDEZ-MARCOS M L, COCCO S, et al., 2018. Assessment of potential nutrient release from phosphate rock and dolostone for application in acid soils[J]. Pedosphere, 28(1): 44-58. |
| [21] | SUN K N, WEN D, YANG N, et al., 2019. Heavy metal and soil nutrient accumulation and ecological risk assessment of vegetable fields in representative facilities in Shandong Province, China[J]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 191(4): 240. |
| [22] |
SUN Q, HU Y J, CHEN X B, et al., 2021. Flooding and straw returning regulates the partitioning of soil phosphorus fractions and phod-harboring bacterial community in paddy soils[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 105(24): 9343-9357.
DOI PMID |
| [23] | WARRINNIER R, BOSSUYT S, RESSEDUIER C, et al., 2020. Anaerobic respiration in the unsaturated zone of agricultural soil mobilizes phosphorus and manganese[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 54(8): 4922-4931. |
| [24] | WEI Z M, ZUO H D, LI J, et al., 2021. Insight into the mechanisms of insoluble phosphate transformation driven by the interactions of compound microbes during composting[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 28(25): 32844-32855. |
| [25] | XU N, CHEN M, ZHOU K R, et al., 2014. Retention of phosphorus on calcite and dolomite: Speciation and modeling[J]. Rsc Advances, 4(66): 35205. |
| [26] | YANG Y G, HE Z L, YANG X, et al., 2013. Dolomite phosphate rock (Dpr) application in acidic sandy soil in reducing leaching of phosphorus and heavy metals-a column leaching study[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 20(6): 3843-3851. |
| [27] | ZOU L L, LIU Y S, WANG Y S, et al., 2020. Assessment and analysis of agricultural non-point source pollution loads in China: 1978-2017[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 263: 110400. |
| [28] | 鲍士旦, 2000. 土壤农化分析[M]. 3版. 北京: 中国农业出版社. |
| BAO S D, 2000. Agrochemical analysis of the soil[M]. Version 3. Beijing: China Agricultural Press. | |
| [29] | 蔡振国, 2020. 淹水-落干条件下红壤中磷与铁的形态转化及其耦合机制[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学. |
| CAI Z G, 2020. Speciation transformation and coupling mechanism of phosphorus and iron in red soil under flooding-drying condition[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University. | |
| [30] | 崔宸阳, 2022. 干湿交替环境南方酸性土壤磷、铁形态转化及其耦合机理[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学. |
| CUI C Y, 2022. Transformation and coupling mechanism of phosphorus and iron during wet-dry rotation in acidic soils in Southern China[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University. | |
| [31] | 崔宸阳, 严玉鹏, 王小明, 等, 2022. 华中地区水旱轮作酸性土磷、铁形态转化及机理[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 41(9): 1993-2003. |
| CUI C Y, YAN Y P, WANG X M, et al., 2022. Speciation transformation and mechanism of phosphorus and iron in acid soils in paddy-upland rotation in central China[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 41(9): 1993-2003. | |
| [32] | 丁佳惠, 王祺, 樊秉乾, 等, 2020. 乙二胺四乙酸和柠檬酸活化石灰性土壤磷素的潜力评估[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 26(2): 362-369. |
| DING J H, WANG Q, FAN B Q, et al., 2020. Activation potential of soil legacy phosphorus by EDTA and citric acid evaluated with consecutive extraction method in the calcareous soil[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 26(2): 362-369. | |
| [33] | 甘国渝, 金慧芳, 李燕丽, 等, 2023. 秸秆及其生物炭添加对土壤Olsen-P及磷素组分的影响[J]. 灌溉排水学报, 42(5): 43-51. |
| GAN G Y, JIN H F, LI Y L, et al., 2023. Effects of straw incorporation and biochar amendment on Olsen-P and phosphorus fraction in soil[J]. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage, 42(5): 43-51. | |
| [34] | 亢龙飞, 2023. 稻田水分变化和有机碳添加对土壤磷转化及水稻生长的影响[D]. 石河子: 石河子大学. |
| KANG L F, 2023. Effects of soil moisture alteration and organic carbon addition on phosphorus transformation and rice growthcharacteristics in paddy soils[D]. Shihezi: Shihezi University. | |
| [35] | 梁俭, 李珊, 刘晓凤, 等, 2022. 生物炭对土壤磷淹水释放及吸附特性的影响[J]. 江西农业学报, 34(12): 72-78. |
| LIANG J, LI S, LIU X F, et al., 2022. Effects of biochar on phosphorus release and adsorption characteristics from submerged soil[J]. Acta Agriculturae Jiangxi, 34(12): 72-78. | |
| [36] | 龙方莉, 2022. 秸秆还田对稻田土壤磷循环微生物及关键功能基因的影响[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学. |
| LONG F L, 2022. Effects of straw returning on phosphorus cycling microorganisms and key functional genes in paddy soil[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University. | |
| [37] | 何梦欣, 2022. 淹水条件下秸秆还田后磷的迁移与转化特征[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学. |
| HE M X, 2022. Characteristics of phosphorus migration and transformation after straw returning under flooding condition[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University. | |
| [38] |
任文畅, 王沛芳, 钱进, 等, 2015. 干湿交替对土壤磷素迁移转化影响的研究综述[J]. 长江科学院院报, 32(5): 41-47.
DOI |
| REN W C, WANG P F, QIAN J, et al., 2015. Review of the effect of drying-rewetting alternation on the transportation and transformation of soil phosphorus[J]. Journal of Yangtze River Scientific Research Institute, 32(5): 41-47. | |
| [39] | 王辉, 王清洲, 付庆灵, 等, 2023. 秸秆还田深度对稻田土壤磷生物有效性的影响[J]. 中国土壤与肥料 (8): 33-41. |
| WANG H, WANG Q Z, FU Q L, et al., 2023. Effects of straw returning depth on soil phosphorus bioavailability in paddy fields[J]. Soils and Fertilizers Sciences in China (8): 33-41. | |
| [40] | 王旭刚, 孙丽蓉, 马林娟, 等, 2018. 黄河中下游湿地土壤铁还原氧化过程的温度敏感性[J]. 土壤学报, 55(2): 380-389. |
| WANG X, SUN L R, MA L J, et al., 2018. Temperature sensitivity of soil iron reduction oxidation process in wetlands in the middle and lower reaches of the Yellow River[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 55(2): 380-389. | |
| [41] | 温芳悦, 张羽, 陈尚才, 等, 2024. 秸秆还田对黑土中磷素吸附特性及释放风险研究[J]. 中国环境科学, 1-13. [2024-07-25]. https://doi.org/10.19674/j.cnki.issn1000-6923.20240023.005. |
| WEN F Y, ZHANG Y, CHEN S C, et al., 2024. Characterization of phosphorus adsorption and risk of phosphorus release from black soil by returning straw to the field[J]. China Environmental Science, 1-13. [2024-07-25]. https://doi.org/10.19674/j.cnki.issn1000-6923.20240023.005. | |
| [42] | 夏建国, 仲雨猛, 曹晓霞, 2011. 干湿交替条件下土壤磷释放及其与土壤性质的关系[J]. 水土保持学报, 25(4): 237-242, 248. |
| XIA J G, ZHONG Y M, CAO X X, 2011. Relation between phosphorous release and soil character with alternative dry-wet conditions[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 25(4): 237-242, 248. | |
| [43] | 颜晓, 卢志红, 魏宗强, 等, 2019. 几种典型酸性旱地土壤磷吸附的关键影响因素[J]. 中国土壤与肥料 (3): 1-7. |
| YAN X, LU Z H, WEN Z Q, et al., 2019. Key factors influencing phosphorus sorption for several acid upland soils[J]. Soils and Fertilizers Sciences in China (3): 1-7. | |
| [44] | 颜双双, 2021. 寒地水稻秸秆还田对土壤碳磷组分与微生物影响效应的研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 东北农业大学. |
| YAN S S, 2021. Effects of rice straw return on soil organic carbon fractions, phosphorus fractions and microbial community in cold region[D]. Harbin: Northeast Agricultural University. | |
| [45] | 杨娇, 信秀丽, 钟新月, 等, 2023. 长期不同施肥对潮土磷素吸附特征的影响[J]. 土壤学报, 60(4): 1047-1057. |
| YANG J, XIN X L, ZHONG X Y, et al., 2023. Effects of long-term fertilization on phosphorus adsorption characteristics of fluvo-aquic soils[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 60(4): 1047-1057. | |
| [46] | 杨昆仑, 杨守军, 辛秀琛, 2012. 玉米秸秆还田对土壤中磷有效性的影响[J]. 安徽农业科学, 40(28): 13782-13783, 13806. |
| YANG K L, YANG S J, XIN X C, 2012. Effect of maize straw returning to soil on phosphorus availability[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 40(28): 13782-13783, 13806. | |
| [47] |
冶赓康, 俄胜哲, 陈政宇, 等, 2023. 土壤中磷的存在形态及分级方法研究进展[J]. 中国农学通报, 39(1): 96-102.
DOI |
|
YE G K, E S Z, CHEN Z Y, et al., 2023. The forms and classification methods of phosphorus in soil: Research progress[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 39(1): 96-102.
DOI |
|
| [48] | 尹贵明, 樊秉乾, 王洪媛, 等, 2024. 设施土壤磷素固持材料的选择与应用研究进展[J]. 农业资源与环境, 41(4): 868-879. |
| YIN G M, FAN B Q, WANG H Y, et al., 2024. Selection and application of phosphorus retention materials in protected vegetable field soils[J]. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment, 41(4): 868-879. | |
| [49] | 张凤华, 廖文华, 刘建玲, 2009. 连续过量施磷和有机肥的产量效应及环境风险评价[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 15(6): 1280-1287. |
| ZHANG F H, LIAO W H, LIU J L, 2009. Applications of phosphorus and organic fertilizers on yields of vegetables and their environmental impacts[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 15(6): 1280-1287. | |
| [50] | 张焕菊, 王贵嵩, 高进华, 等, 2022. 山东省设施蔬菜土壤酸碱性、有机质及中微量元素含量调查与评价[J]. 江苏农业科学, 50(4): 211-215. |
| ZHANG H J, WANG G S, GAO J H, et al., 2022. Investigation and evaluation of soil acidity, alkalinity, organic matter and trace elements in facility vegatables in Shangdong Province[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 50(4): 211-215. | |
| [51] | 张颖, 赵庚星, 王卓然, 等, 2018. 山东棕壤耕地地力评价及其特征分析[J]. 农业资源与环境学报, 35(4): 359-366. |
| ZHANG Y, ZHAO G X, WANG Z R, et al., 2018. Fertility evaluation and characteristics analysis of brown soil cultivated land in Shandong Province[J]. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment, 35(4): 359-366. | |
| [52] |
赵媛媛, 靳嘉雯, 陈硕, 等, 2023. 碳氮投入对4种不同土地利用方式土壤磷含量及胞外酶活性的影响[J]. 华北农学报, 38(3): 139-147.
DOI |
|
ZHAO Y Y, JIN J W, CHEN S, et al., 2023. Effects of carbon and nitrogen input on organic phosphorus and extracellular enzyme activities in four different land use soils[J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica, 38(3): 139-147.
DOI |
|
| [53] | 周驰, 李阳, 曹秀云, 等, 2012. 风干和淹水过程对巢湖流域土壤和沉积物磷吸附行为的影响[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 21(S2): 10-17. |
| ZHOU C, LI Y, CAO X Y, et al., 2012. Effect of air-drying and flooding on phosphorus sorption behavior of soils and sediments along the aquatic-terrestrial ecotone of Lake Chaohu[J]. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 21(S2): 10-17. | |
| [54] | 周岩, 靳嘉雯, 邬刚, 等, 2023. 施用氰氨化钙和秸秆对淹水设施土壤磷释放动态特征的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 42(5): 1100-1108. |
| ZHOU Y, JIN J W, WU G, et al., 2023. Dynamic characteristics of soil phosphorus release in a flooded greenhouse soil after calcium cyanamide and or straw addition[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 42(5): 1100-1108. |
| [1] | 蒋云峰, 严婷, 刘俊男, 马丙增, 王海萌, 窦笑萌. 黑土区农田中型土壤动物群落对免耕玉米秸秆覆盖频率的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(5): 699-707. |
| [2] | 唐志伟, 翁颖, 朱夏童, 蔡洪梅, 代雯慈, 王捧娜, 郑宝强, 李金才, 陈翔. 秸秆还田下中国农田土壤微生物生物量碳变化及其影响因素的Meta分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(9): 1552-1562. |
| [3] | 刘晨, 白雪冬, 赵海超, 黄智鸿, 刘松涛, 卢海博, 刘子刚, 刘雪玲. 寒旱区春玉米秸秆还田方式对土壤DOM光谱特征的影响机制[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(8): 1419-1432. |
| [4] | 周宏光, 甘艳平, 伍德权, 杨延梅, 张扬, 王璐瑶. 淹水-落干条件下FeMnMg-LDH对污染底泥中砷迁移转化的调控研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(7): 1249-1262. |
| [5] | 宫亮, 金丹丹, 牛世伟, 王娜, 邹晓锦, 张鑫, 隋世江, 解占军, 韩瑛祚. 辽宁省水稻田固碳减排潜力分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(7): 1226-1236. |
| [6] | 徐敏, 许超, 余光辉, 尹力初, 张泉, 朱捍华, 朱奇宏, 张杨珠, 黄道友. 地下水位和长期秸秆还田对土壤镉有效性及稻米镉含量的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 150-157. |
| [7] | 郝小雨, 王晓军, 高洪生, 毛明艳, 孙磊, 马星竹, 周宝库, 迟凤琴, 李伟群. 松嫩平原不同秸秆还田方式下农田温室气体排放及碳足迹估算[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(2): 318-325. |
| [8] | 邹晨怡, 丁洪, 王亚萨, 张玉树, 余居华, 郑祥洲. 秸秆对尿素氮在土壤中转化的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(6): 1213-1219. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
