生态环境学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (1): 117-130.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2022.01.014
白海锋1,3( ), 王怡睿2,4, 宋进喜1,3,4,*(
), 王怡睿2,4, 宋进喜1,3,4,*( ), 孔飞鹤1,3, 张雪仙2,4, 李琦1,3
), 孔飞鹤1,3, 张雪仙2,4, 李琦1,3
收稿日期:2021-07-28
出版日期:2022-01-18
发布日期:2022-03-10
通讯作者:
*E-mail: jinxisong@nwu.edu.cn作者简介:白海锋(1977年生),男,博士研究生,主要研究方向为河流生态学。E-mail: baihaifeng2002@126.com
基金资助:
BAI Haifeng1,3( ), WANG Yirui2,4, SONG Jinxi1,3,4,*(
), WANG Yirui2,4, SONG Jinxi1,3,4,*( ), KONG Feihe1,3, ZHANG Xuexian2,4, LI Qi1,3
), KONG Feihe1,3, ZHANG Xuexian2,4, LI Qi1,3
Received:2021-07-28
Online:2022-01-18
Published:2022-03-10
摘要:
渭河是黄河第一大支流,是黄河流域生态保护与高质量发展的重要研究区域。为了掌握渭河浮游生物组成结构及生态环境现状,于2018—2019年分两个季节在渭河开展4次水生态调查,研究分析了渭河浮游生物群落结构特征及其影响因子。调查结果显示,浮游植物有8门53种,以绿藻门和硅藻门为主,占比分别为43.4%、33.9%;浮游动物4类30种,以轮虫为主,占比为50.0%。渭河浮游生物优势种主要为梅尼小环藻(Cyclotella meneghiniana)、篦形短缝藻(Eunotia pectinalis)、小球藻(Chlorella vulgaris)、球形砂壳虫(Difflugia globulosa)、舞跃无柄轮虫(Accomorpha saltans)。种类数均呈现下游>中游>上游,春季浮游植物平均密度(2.115×106 cell∙L-1)和平均生物量(0.432 mg∙L-1)均高于秋季(1.630×106 cell∙L-1,0.352 mg∙L-1),秋季浮游动物平均密度(9.864 ind∙L-1)和平均生物量(10.219 µg∙L-1)均高于春季(4.984 ind∙L-1,3.168 µg∙L-1)。浮游生物Shannon-Weiner多样性指数(H′)、Pielou均匀度指数(J)和Margalef丰富度指数(d)均值分别为2.519、0.798、1.394。浮游生物多样性指数评价结果表明,渭河水质属于轻度污染,浮游生物群落结构趋于简单化。典范对应分析显示,海拔和水深是影响渭河浮游植物群落结构的主要环境因子,海拔、溶解氧和pH是影响渭河浮游动物群落结构的主要环境因子。河道综合治理与水体污染控制在一定程度上改变了渭河水环境质量,从而影响了浮游生物群落结构演替。该研究可为渭河河道生态修复工作提供依据,具有一定的区域指导意义。
中图分类号:
白海锋, 王怡睿, 宋进喜, 孔飞鹤, 张雪仙, 李琦. 渭河浮游生物群落结构特征及其与环境因子的关系[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(1): 117-130.
BAI Haifeng, WANG Yirui, SONG Jinxi, KONG Feihe, ZHANG Xuexian, LI Qi. Characteristics of Plankton Community Structure and Its Relation to Environmental Factors in Weihe River, China[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(1): 117-130.
| 编号 No. | 采样地点 Sampling sites | 纬度 Latitude | 经度 Longitude | 海拔 Altitude/m | 水深 Water depth/m | 类型 Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| W1 | 甘肃省渭源县五竹镇马家山 | 35.0045°N | 104.0567°E | 2512 | 0.13 | 山谷河道 |
| W2 | 陇西县文峰镇安家门 | 34.8674°N | 104.7227°E | 1599 | 0.20 | 山谷河道 |
| W3 | 武山县洛门镇石岭村 | 34.7476°N | 104.9945°E | 1399 | 0.45 | 山谷河道 |
| W4 | 甘谷县许兴镇魏家庄 | 34.7532°N | 105.3523°E | 1250 | 0.43 | 山谷河道 |
| W5 | 天水市中滩镇张白村 | 34.6750°N | 105.6970°E | 1127 | 0.45 | 平原河道 |
| W6 | 天水市麦积区伯阳村 | 34.5513°N | 106.0830°E | 1023 | 0.44 | 城市河道 |
| W7 | 陕西省宝鸡市坪头镇周川村 | 34.3974°N | 106.8788°E | 670 | 0.64 | 山谷河道 |
| W8 | 宝鸡市陈仓区姜马村 | 34.2959°N | 107.5756°E | 498 | 1.19 | 城市河道 |
| W9 | 眉县首善镇北兴村 | 34.3011°N | 107.7481°E | 470 | 0.71 | 平原河道 |
| W10 | 武功县善集镇洪寨村 | 34.2192°N | 108.2050°E | 409 | 0.52 | 平原河道 |
| W11 | 杨凌区五泉镇万家村 | 34.2321°N | 108.5135°E | 382 | 0.64 | 平原河道 |
| W12 | 西安市秦汉新城梁村 | 34.4130°N | 108.9407°E | 354 | 0.56 | 城市河道 |
| W13 | 西安市高陵区渭桥村 | 34.4677°N | 109.1021°E | 354 | 0.60 | 城市河道 |
| W14 | 渭南市临渭区淹头村 | 34.5127°N | 109.6000°E | 330 | 0.76 | 平原河道 |
| W15 | 潼关县秦东镇四枝村 | 34.6078°N | 110.2750°E | 325 | 4.04 | 平原河道 |
| W16 | 潼关县秦东镇港口村 | 34.6142°N | 110.2353°E | 316 | 0.64 | 三角洲 |
表1 渭河采样断面分布
Table 1 Distribution of sampling section in Weihe River
| 编号 No. | 采样地点 Sampling sites | 纬度 Latitude | 经度 Longitude | 海拔 Altitude/m | 水深 Water depth/m | 类型 Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| W1 | 甘肃省渭源县五竹镇马家山 | 35.0045°N | 104.0567°E | 2512 | 0.13 | 山谷河道 |
| W2 | 陇西县文峰镇安家门 | 34.8674°N | 104.7227°E | 1599 | 0.20 | 山谷河道 |
| W3 | 武山县洛门镇石岭村 | 34.7476°N | 104.9945°E | 1399 | 0.45 | 山谷河道 |
| W4 | 甘谷县许兴镇魏家庄 | 34.7532°N | 105.3523°E | 1250 | 0.43 | 山谷河道 |
| W5 | 天水市中滩镇张白村 | 34.6750°N | 105.6970°E | 1127 | 0.45 | 平原河道 |
| W6 | 天水市麦积区伯阳村 | 34.5513°N | 106.0830°E | 1023 | 0.44 | 城市河道 |
| W7 | 陕西省宝鸡市坪头镇周川村 | 34.3974°N | 106.8788°E | 670 | 0.64 | 山谷河道 |
| W8 | 宝鸡市陈仓区姜马村 | 34.2959°N | 107.5756°E | 498 | 1.19 | 城市河道 |
| W9 | 眉县首善镇北兴村 | 34.3011°N | 107.7481°E | 470 | 0.71 | 平原河道 |
| W10 | 武功县善集镇洪寨村 | 34.2192°N | 108.2050°E | 409 | 0.52 | 平原河道 |
| W11 | 杨凌区五泉镇万家村 | 34.2321°N | 108.5135°E | 382 | 0.64 | 平原河道 |
| W12 | 西安市秦汉新城梁村 | 34.4130°N | 108.9407°E | 354 | 0.56 | 城市河道 |
| W13 | 西安市高陵区渭桥村 | 34.4677°N | 109.1021°E | 354 | 0.60 | 城市河道 |
| W14 | 渭南市临渭区淹头村 | 34.5127°N | 109.6000°E | 330 | 0.76 | 平原河道 |
| W15 | 潼关县秦东镇四枝村 | 34.6078°N | 110.2750°E | 325 | 4.04 | 平原河道 |
| W16 | 潼关县秦东镇港口村 | 34.6142°N | 110.2353°E | 316 | 0.64 | 三角洲 |
| 生物多样性指数 Biodiversity index | 级别 Level | 评价状态 Evaluation of state | 水体污染程度 Degree of water pollution | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H'>3 | J>0.8 | d>6 | 丰富 | 物种种类丰富,个体分布均匀 | 清洁 |
| 3≥H'>2 | 0.8≥J>0.5 | 6≥d>4 | 较丰富 | 物种丰富度较高,个体分布比较均匀 | 轻污染 |
| 2≥H'>1 | 0.5≥J>0.3 | 4≥d>1 | 一般 | 物种丰富度较低,个体分布比较均匀 | 中污染 |
| 1≥H'>0 | 0.3≥J>0.1 | 1≥d>0 | 贫乏 | 物种丰富度低,个体分布不均匀 | 重污染 |
| H'=0 | J<0.1 | d=0 | 极贫乏 | 物种单一,多样性基本丧失 | 严重污染 |
表2 生物多样性指数水质评价标准
Table 2 List of water quality evaluation standards by plankton diversity index
| 生物多样性指数 Biodiversity index | 级别 Level | 评价状态 Evaluation of state | 水体污染程度 Degree of water pollution | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H'>3 | J>0.8 | d>6 | 丰富 | 物种种类丰富,个体分布均匀 | 清洁 |
| 3≥H'>2 | 0.8≥J>0.5 | 6≥d>4 | 较丰富 | 物种丰富度较高,个体分布比较均匀 | 轻污染 |
| 2≥H'>1 | 0.5≥J>0.3 | 4≥d>1 | 一般 | 物种丰富度较低,个体分布比较均匀 | 中污染 |
| 1≥H'>0 | 0.3≥J>0.1 | 1≥d>0 | 贫乏 | 物种丰富度低,个体分布不均匀 | 重污染 |
| H'=0 | J<0.1 | d=0 | 极贫乏 | 物种单一,多样性基本丧失 | 严重污染 |
| 参数 Parameter | 秋季 Autumn | 春季 Spring | P | 2012-2013 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 海拔 (ALT)/m | 814.00±606.42 | 813.80±607.50 | 0.999 | 1071.65 |
| 水温 (WT)/℃ | 16.00±3.08 | 17.40±5.23 | 0.368 | 14.65 |
| ρ(DO)/(mg∙L-1) | 6.67±0.71 | 8.04±1.50 | 0.003 | 9.41 |
| pH | 8.09±0.41 | 8.48±0.28 | 0.004 | 7.34 |
| 流速(CV)/(m∙s-1) | 0.52±0.16 | 0.39±0.21 | 0.063 | 0.50 |
| 水深(WD)/ m | 0.86±0.68 | 0.66±1.09 | 0.654 | 0.40 |
| ρ(TN)/(mg∙L-1) | 3.03±1.07 | 9.21±4.39 | 0.000 | 14.22 |
| ρ(TP)/(mg∙L-1) | 0.43±0.17 | 0.25±0.10 | 0.001 | 0.60 |
| ρ(NH4+-N)/(mg∙L-1) | 1.04±0.39 | 1.65±0.80 | 0.012 | 0.81 |
| ρ(CODMn)/(mg∙L-1) | 14.70±4.67 | 25.26±12.54 | 0.005 | 16.96 |
表3 渭河环境参数
Table 3 Environmental parameters of Weihe River
| 参数 Parameter | 秋季 Autumn | 春季 Spring | P | 2012-2013 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 海拔 (ALT)/m | 814.00±606.42 | 813.80±607.50 | 0.999 | 1071.65 |
| 水温 (WT)/℃ | 16.00±3.08 | 17.40±5.23 | 0.368 | 14.65 |
| ρ(DO)/(mg∙L-1) | 6.67±0.71 | 8.04±1.50 | 0.003 | 9.41 |
| pH | 8.09±0.41 | 8.48±0.28 | 0.004 | 7.34 |
| 流速(CV)/(m∙s-1) | 0.52±0.16 | 0.39±0.21 | 0.063 | 0.50 |
| 水深(WD)/ m | 0.86±0.68 | 0.66±1.09 | 0.654 | 0.40 |
| ρ(TN)/(mg∙L-1) | 3.03±1.07 | 9.21±4.39 | 0.000 | 14.22 |
| ρ(TP)/(mg∙L-1) | 0.43±0.17 | 0.25±0.10 | 0.001 | 0.60 |
| ρ(NH4+-N)/(mg∙L-1) | 1.04±0.39 | 1.65±0.80 | 0.012 | 0.81 |
| ρ(CODMn)/(mg∙L-1) | 14.70±4.67 | 25.26±12.54 | 0.005 | 16.96 |
| 浮游植物 Phytoplankton | 34. 月牙藻 Selenastrum bibraianum | 4. 似铃壳虫 Tintinnopsis sp. |
|---|---|---|
| 一. 硅藻门 Bacillariophyta | 35. 镰形纤维藻奇异变种 Ankistrodesmus falcatus var. mirabilis | 5. 中华似铃壳虫 Tintinnopsis sinensis |
| 1. 梅尼小环藻 Cyclotella meneghiniana | 36. 四足十字藻 Crucigenia tetrapedia | 6. 盘状匣壳虫 Centropyxis discoides |
| 2. 近缘桥弯藻 Cymbella aequalis | 37. 四角十字藻 Crucigenia quadrata | 7. 小口钟虫 Vorticella microstoma |
| 3. 卡里舟形藻 Navicula cari | 38. 二叉四角藻 Tetraedron bifurcattum | 8. 螺旋形扁壳虫 Lesquereusia spiralis |
| 4. 简单舟形藻 Navicula simplex | 39. 多突藻 Polyedriopsis spinulosa | 9. 巢居法帽虫 Phryganella nidulus |
| 5. 放射舟形藻 Navicula radiosa | 40. 被刺藻 Fmanceia ovalis | 10. 阔口游仆虫 Euplotes eurystomus |
| 6. 线形舟形藻 Navicula graciloides | 41. 三角四角藻小形变种 Tetraedron trigonum var. gracile | 二. 轮虫 Rotifera |
| 7. 瞳孔舟形藻Navicula pupula | 42. 单刺四星藻 Tetrastrum hastiferum | 11. 螺形龟甲轮虫 Keratella cochlearis |
| 8. 缢缩异极藻头状变种 Gomphonema constrictum var.capitatum | 43. 韦氏藻 Westella botryoides | 12. 曲腿龟甲轮虫 Keratella valga |
| 9. 尖针杆藻 Synedra acus | 44. 短鼓藻 Cosmarium abbreviatum | 13. 舞跃无柄轮虫 Ascomorpha saltans |
| 10. 状针杆藻 Synedra ulna | 45. 单角盘星藻 Pediastrum simplex | 14. 前节晶囊轮虫 Asplanchna priodonta |
| 11. 皮菱形藻 Nitzschia palea | 三. 蓝藻门 Cyanophyta | 15. 长肢多肢轮虫 Polyarthra dolichoptera |
| 12. 线形菱形藻 Nitzschia linearis | 46. 小席藻 Phormidium tenus | 16. 刺簇多肢轮虫 Polyarthra trigla |
| 13. 卵圆双壁藻 Diploneis ovalis | 47. 微小色球藻 Chroococcus minutus | 17. 污前翼轮虫 Proales sordida |
| 14. 椭圆双壁藻 Diploneis elliptica | 48. 小形色球藻 Chroococcus minor | 18. 厚实椎轮虫 Notommata pachyura |
| 15. 大羽纹藻 Pinnularia maior | 49. 弯头尖头藻 Raphidiopsis curvata | 19. 角突臂尾轮虫 Brachionus angularis |
| 16. 双头辐节藻 Stauroneis anceps | 50. 卷曲鱼腥藻 Anabaena circinalis | 20. 壶状臂尾轮虫 Brachionus urceus |
| 17. 篦形短缝藻 Eunotia pectinalis | 51. 点状平裂藻 Merismopedia punctata | 21. 萼花臂尾轮虫 Brachionus calyciflorus |
| 18. 颗粒直链藻极狭变种 Melosira granulata var. angustissima | 52. 微囊藻 Microcystis sp. | 22. 月形腔轮虫 Lecane luna |
| 19. 钝脆杆藻 Fragilaria capucina | 四. 隐藻门 Cryptophyta | 23. 长三肢轮虫 Filinia longiseta |
| 20. 尖布纹藻 Gyrosigma acuminatum | 53. 尖尾蓝隐藻 Chroomonas acuta | 24. 跃进三肢轮虫 Filinia passa |
| 二. 绿藻门 Chlorophyta | 54. 卵形隐藻 Chroomonas ovata | 25. 钩状狭甲轮虫 Colurella uncinata |
| 21. 瓜哇栅藻 Scenedesmus javaensis | 五. 裸藻门 Euglenophyta | 26. 敞水胶鞘轮虫 Collotheca pelagica |
| 22. 双对栅藻 Scenedesmus bijugatus | 55. 尾裸藻 Euglena caudata | 27. 纵长异尾轮虫 Trichocerca elongata |
| 23. 二形栅藻 Scenedesmus dimorphus | 六. 黄藻门 Xanthophyta | 28. 截头鬼轮虫 Trichotria truncata |
| 24. 被甲栅藻 Scenedesmus armatus | 56. 棕色刺棘藻 Centritractus brunneus | 三. 枝角类 Cladocera |
| 25. 裂孔栅藻 Scenedesmus perforatus | 七. 甲藻门 Pyrrophyta | 29. 老年低额溞 Simocephalus vetulus |
| 26. 斜生栅藻 Scenedesmus obliquus | 57. 光薄甲藻 Glenodinium gymnodinium | 30. 简弧象鼻溞 Bosmina coregoni |
| 27. 小球藻 Chlorella vulgaris | 八. 金藻门 Chrysophyta | 31. 透明薄皮溞 Leptodora kindti |
| 28. 狭形纤维藻 Ankistrodesmus angustus | 58. 分歧锥囊藻 Dinobryon divergens | 四. 桡足类 Copepoda |
| 29. 针形纤维藻 Ankistrodesmus acicularis | 浮游动物 Zooplankton | 32. 锯齿真剑水蚤 Eucyclops macruroides denticulatus |
| 30. 卷曲纤维藻 Ankistrodesmus convolutus | 一. 原生动物 Protozoa | 33. 毛饰拟剑水蚤 Paracyclops fimbriatus |
| 31. 四刺顶棘藻 Chodatella quadriseta | 1. 球形砂壳虫 Difflugia globulosa | 34. 无节幼体 Nauplius |
| 32. 弓形藻 Schroederia setigera | 2. 长圆砂壳虫 Difflugia oblonga | |
| 33. 硬弓形藻 Schroederia robusta | 3. 节盖虫 Opercularia articulata |
表4 渭河浮游生物物种名录
Table 4 Species of plankton in Weihe River
| 浮游植物 Phytoplankton | 34. 月牙藻 Selenastrum bibraianum | 4. 似铃壳虫 Tintinnopsis sp. |
|---|---|---|
| 一. 硅藻门 Bacillariophyta | 35. 镰形纤维藻奇异变种 Ankistrodesmus falcatus var. mirabilis | 5. 中华似铃壳虫 Tintinnopsis sinensis |
| 1. 梅尼小环藻 Cyclotella meneghiniana | 36. 四足十字藻 Crucigenia tetrapedia | 6. 盘状匣壳虫 Centropyxis discoides |
| 2. 近缘桥弯藻 Cymbella aequalis | 37. 四角十字藻 Crucigenia quadrata | 7. 小口钟虫 Vorticella microstoma |
| 3. 卡里舟形藻 Navicula cari | 38. 二叉四角藻 Tetraedron bifurcattum | 8. 螺旋形扁壳虫 Lesquereusia spiralis |
| 4. 简单舟形藻 Navicula simplex | 39. 多突藻 Polyedriopsis spinulosa | 9. 巢居法帽虫 Phryganella nidulus |
| 5. 放射舟形藻 Navicula radiosa | 40. 被刺藻 Fmanceia ovalis | 10. 阔口游仆虫 Euplotes eurystomus |
| 6. 线形舟形藻 Navicula graciloides | 41. 三角四角藻小形变种 Tetraedron trigonum var. gracile | 二. 轮虫 Rotifera |
| 7. 瞳孔舟形藻Navicula pupula | 42. 单刺四星藻 Tetrastrum hastiferum | 11. 螺形龟甲轮虫 Keratella cochlearis |
| 8. 缢缩异极藻头状变种 Gomphonema constrictum var.capitatum | 43. 韦氏藻 Westella botryoides | 12. 曲腿龟甲轮虫 Keratella valga |
| 9. 尖针杆藻 Synedra acus | 44. 短鼓藻 Cosmarium abbreviatum | 13. 舞跃无柄轮虫 Ascomorpha saltans |
| 10. 状针杆藻 Synedra ulna | 45. 单角盘星藻 Pediastrum simplex | 14. 前节晶囊轮虫 Asplanchna priodonta |
| 11. 皮菱形藻 Nitzschia palea | 三. 蓝藻门 Cyanophyta | 15. 长肢多肢轮虫 Polyarthra dolichoptera |
| 12. 线形菱形藻 Nitzschia linearis | 46. 小席藻 Phormidium tenus | 16. 刺簇多肢轮虫 Polyarthra trigla |
| 13. 卵圆双壁藻 Diploneis ovalis | 47. 微小色球藻 Chroococcus minutus | 17. 污前翼轮虫 Proales sordida |
| 14. 椭圆双壁藻 Diploneis elliptica | 48. 小形色球藻 Chroococcus minor | 18. 厚实椎轮虫 Notommata pachyura |
| 15. 大羽纹藻 Pinnularia maior | 49. 弯头尖头藻 Raphidiopsis curvata | 19. 角突臂尾轮虫 Brachionus angularis |
| 16. 双头辐节藻 Stauroneis anceps | 50. 卷曲鱼腥藻 Anabaena circinalis | 20. 壶状臂尾轮虫 Brachionus urceus |
| 17. 篦形短缝藻 Eunotia pectinalis | 51. 点状平裂藻 Merismopedia punctata | 21. 萼花臂尾轮虫 Brachionus calyciflorus |
| 18. 颗粒直链藻极狭变种 Melosira granulata var. angustissima | 52. 微囊藻 Microcystis sp. | 22. 月形腔轮虫 Lecane luna |
| 19. 钝脆杆藻 Fragilaria capucina | 四. 隐藻门 Cryptophyta | 23. 长三肢轮虫 Filinia longiseta |
| 20. 尖布纹藻 Gyrosigma acuminatum | 53. 尖尾蓝隐藻 Chroomonas acuta | 24. 跃进三肢轮虫 Filinia passa |
| 二. 绿藻门 Chlorophyta | 54. 卵形隐藻 Chroomonas ovata | 25. 钩状狭甲轮虫 Colurella uncinata |
| 21. 瓜哇栅藻 Scenedesmus javaensis | 五. 裸藻门 Euglenophyta | 26. 敞水胶鞘轮虫 Collotheca pelagica |
| 22. 双对栅藻 Scenedesmus bijugatus | 55. 尾裸藻 Euglena caudata | 27. 纵长异尾轮虫 Trichocerca elongata |
| 23. 二形栅藻 Scenedesmus dimorphus | 六. 黄藻门 Xanthophyta | 28. 截头鬼轮虫 Trichotria truncata |
| 24. 被甲栅藻 Scenedesmus armatus | 56. 棕色刺棘藻 Centritractus brunneus | 三. 枝角类 Cladocera |
| 25. 裂孔栅藻 Scenedesmus perforatus | 七. 甲藻门 Pyrrophyta | 29. 老年低额溞 Simocephalus vetulus |
| 26. 斜生栅藻 Scenedesmus obliquus | 57. 光薄甲藻 Glenodinium gymnodinium | 30. 简弧象鼻溞 Bosmina coregoni |
| 27. 小球藻 Chlorella vulgaris | 八. 金藻门 Chrysophyta | 31. 透明薄皮溞 Leptodora kindti |
| 28. 狭形纤维藻 Ankistrodesmus angustus | 58. 分歧锥囊藻 Dinobryon divergens | 四. 桡足类 Copepoda |
| 29. 针形纤维藻 Ankistrodesmus acicularis | 浮游动物 Zooplankton | 32. 锯齿真剑水蚤 Eucyclops macruroides denticulatus |
| 30. 卷曲纤维藻 Ankistrodesmus convolutus | 一. 原生动物 Protozoa | 33. 毛饰拟剑水蚤 Paracyclops fimbriatus |
| 31. 四刺顶棘藻 Chodatella quadriseta | 1. 球形砂壳虫 Difflugia globulosa | 34. 无节幼体 Nauplius |
| 32. 弓形藻 Schroederia setigera | 2. 长圆砂壳虫 Difflugia oblonga | |
| 33. 硬弓形藻 Schroederia robusta | 3. 节盖虫 Opercularia articulata |
| 优势种及编号 Dominance& number | 优势度 Dominance | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 秋季 Autumn | 春季 Spring | 上游 Upstream | 中游 Midstream | 下游 Downstream | ||||
| 浮游植物 Phytoplankton | 硅藻门Bacillariophyta | P1 | 梅尼小环藻 C. meneghiniana | 0.087 | 0.106 | 0.037 | 0.165 | 0.106 |
| P2 | 肘状针杆藻 S. ulna | 0.031 | 0.030 | |||||
| P3 | 篦形短缝藻 E. pectinalis | 0.026 | 0.022 | 0.068 | 0.028 | 0.020 | ||
| 绿藻门Chlorophyta | P4 | 瓜哇栅藻 S. sjavaensis | 0.020 | |||||
| P5 | 二形栅藻 S. dimorphus | 0.040 | 0.022 | |||||
| P6 | 小球藻 C. vulgaris | 0.026 | 0.075 | 0.086 | 0.095 | 0.068 | ||
| P7 | 狭形纤维藻 A. sangustus | 0.056 | 0.024 | 0.034 | ||||
| P8 | 卷曲纤维藻 A. sconvolutus | 0.022 | ||||||
| P9 | 弓形藻 S. setigera | 0.025 | ||||||
| P10 | 镰形纤维藻奇异变种 A. falcatus var.mirabilis | 0.035 | ||||||
| P11 | 韦氏藻 W. botryoides | 0.039 | ||||||
| 蓝藻门 Cyanophyta | P12 | 小席藻 P. tenus | 0.328 | 0.361 | 0.178 | 0.389 | ||
| P13 | 微小色球藻 C. minutus | 0.020 | 0.027 | |||||
| P14 | 小形色球藻 C. minor | 0.044 | ||||||
| 隐藻门 Cryptophyta | P15 | 尖尾蓝隐藻 C. acuta | 0.023 | 0.028 | ||||
| 浮游动物 Zooplankton | 原生动物 Protozoa | Z1 | 球形砂壳虫 D. globulosa | 0.035 | 0.091 | 0.098 | 0.177 | 0.040 |
| Z2 | 长圆砂壳虫 D. oblonga | 0.032 | 0.048 | 0.048 | ||||
| Z3 | 节盖虫 O. articulata | 0.136 | 0.033 | 0.035 | ||||
| Z4 | 小口钟虫 V. microstoma | 0.065 | 0.082 | 0.045 | 0.058 | |||
| 轮虫 Rotifer | Z5 | 螺形龟甲轮虫 K. cochlearis | 0.020 | 0.029 | ||||
| Z6 | 舞跃无柄轮虫 A. saltans | 0.028 | 0.030 | 0.058 | 0.063 | |||
| Z7 | 前节晶囊轮虫 A. priodonta | 0.042 | 0.026 | 0.031 | ||||
| Z8 | 刺簇多肢轮虫 P. trigla | 0.116 | 0.031 | |||||
| Z9 | 污前翼轮虫 P. sordida | 0.032 | 0.029 | |||||
| Z10 | 萼花臂尾轮虫 B. calyciflorus | 0.023 | 0.020 | |||||
| Z11 | 长三肢轮虫 F. longiseta | 0.026 | ||||||
| 枝角类 Cladocera | Z12 | 简弧象鼻溞 B. coregoni | 0.042 | 0.022 | 0.035 | |||
| 桡足类 Copepoda | Z13 | 毛饰拟剑水蚤 P. fimbriatus | 0.042 | 0.028 | ||||
表5 渭河浮游生物优势种分布
Table 5 Distributions of dominant phytoplankton and zooplankton species in the sampling stream
| 优势种及编号 Dominance& number | 优势度 Dominance | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 秋季 Autumn | 春季 Spring | 上游 Upstream | 中游 Midstream | 下游 Downstream | ||||
| 浮游植物 Phytoplankton | 硅藻门Bacillariophyta | P1 | 梅尼小环藻 C. meneghiniana | 0.087 | 0.106 | 0.037 | 0.165 | 0.106 |
| P2 | 肘状针杆藻 S. ulna | 0.031 | 0.030 | |||||
| P3 | 篦形短缝藻 E. pectinalis | 0.026 | 0.022 | 0.068 | 0.028 | 0.020 | ||
| 绿藻门Chlorophyta | P4 | 瓜哇栅藻 S. sjavaensis | 0.020 | |||||
| P5 | 二形栅藻 S. dimorphus | 0.040 | 0.022 | |||||
| P6 | 小球藻 C. vulgaris | 0.026 | 0.075 | 0.086 | 0.095 | 0.068 | ||
| P7 | 狭形纤维藻 A. sangustus | 0.056 | 0.024 | 0.034 | ||||
| P8 | 卷曲纤维藻 A. sconvolutus | 0.022 | ||||||
| P9 | 弓形藻 S. setigera | 0.025 | ||||||
| P10 | 镰形纤维藻奇异变种 A. falcatus var.mirabilis | 0.035 | ||||||
| P11 | 韦氏藻 W. botryoides | 0.039 | ||||||
| 蓝藻门 Cyanophyta | P12 | 小席藻 P. tenus | 0.328 | 0.361 | 0.178 | 0.389 | ||
| P13 | 微小色球藻 C. minutus | 0.020 | 0.027 | |||||
| P14 | 小形色球藻 C. minor | 0.044 | ||||||
| 隐藻门 Cryptophyta | P15 | 尖尾蓝隐藻 C. acuta | 0.023 | 0.028 | ||||
| 浮游动物 Zooplankton | 原生动物 Protozoa | Z1 | 球形砂壳虫 D. globulosa | 0.035 | 0.091 | 0.098 | 0.177 | 0.040 |
| Z2 | 长圆砂壳虫 D. oblonga | 0.032 | 0.048 | 0.048 | ||||
| Z3 | 节盖虫 O. articulata | 0.136 | 0.033 | 0.035 | ||||
| Z4 | 小口钟虫 V. microstoma | 0.065 | 0.082 | 0.045 | 0.058 | |||
| 轮虫 Rotifer | Z5 | 螺形龟甲轮虫 K. cochlearis | 0.020 | 0.029 | ||||
| Z6 | 舞跃无柄轮虫 A. saltans | 0.028 | 0.030 | 0.058 | 0.063 | |||
| Z7 | 前节晶囊轮虫 A. priodonta | 0.042 | 0.026 | 0.031 | ||||
| Z8 | 刺簇多肢轮虫 P. trigla | 0.116 | 0.031 | |||||
| Z9 | 污前翼轮虫 P. sordida | 0.032 | 0.029 | |||||
| Z10 | 萼花臂尾轮虫 B. calyciflorus | 0.023 | 0.020 | |||||
| Z11 | 长三肢轮虫 F. longiseta | 0.026 | ||||||
| 枝角类 Cladocera | Z12 | 简弧象鼻溞 B. coregoni | 0.042 | 0.022 | 0.035 | |||
| 桡足类 Copepoda | Z13 | 毛饰拟剑水蚤 P. fimbriatus | 0.042 | 0.028 | ||||
| 采样断面 Sampling sites | 浮游植物 Phytoplankton | 浮游动物 Zooplankton | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H′ | J | d | H′ | J | d | |||
| 上游 Upstrem | W1 | 0.628±0.363 | 0.224±0.114 | 0.315±0.098 | 2.362±0.321 | 0.711±0.064 | 1.119±0.076 | |
| W2 | 1.731±0.622 | 0.616±0.086 | 0.201±0.126 | 0.754±0.047 | 0.376±0.025 | 0.345±0.112 | ||
| W3 | 2.395±0.814 | 0.854±0.104 | 0.554±0.016 | 2.322±0.088 | 1.000±0.214 | 5.396±1.023 | ||
| W4 | 2.292±0.461 | 0.817±0.097 | 0.533±0.134 | 2.505±0.774 | 0.968±0.536 | 1.856±0.887 | ||
| W5 | 2.063±0.672 | 0.798±0.101 | 0.530±0.076 | 2.697±0.564 | 0.851±0.516 | 1.413±0.541 | ||
| W6 | 2.432±0.516 | 0.866±0.077 | 0.615±0.087 | 2.256±0.551 | 0.873±0.465 | 1.040±0.516 | ||
| 平均 | 1.923±0.626a | 0.696±0.227a | 0.508±0.093a | 2.149±0.640a | 0.797±0.210a | 1.862±1.644a | ||
| 中游 Midstream | W7 | 2.558±0.522 | 0.912±0.134 | 0.560±0.012 | 2.113±0.315 | 0.910±0.338 | 1.485±0.441 | |
| W8 | 1.671±0.447 | 0.596±0.116 | 0.543±0.066 | 1.917±0.652 | 0.959±0.410 | 2.227±0.714 | ||
| W9 | 3.515±0.378 | 0.777±0.047 | 1.422±0.612 | 1.923±0.522 | 0.961±0.005 | 4.047±1.365 | ||
| W10 | 3.661±1.121 | 0.821±0.096 | 1.172±0.557 | 2.917±0.104 | 0.920±0.075 | 1.141±0.884 | ||
| W11 | 2.960±0.312 | 0.740±0.254 | 0.918±0.118 | 2.724±0.089 | 0.971±0.016 | 2.227±0.056 | ||
| 平均 | 2.873±0.719ab | 0.769±0.104a | 0.923±0.342b | 2.319±0.424ab | 0.944±0.024a | 2.225±1.004a | ||
| 下游 Downstream | W12 | 3.953±0.286 | 0.852±0.058 | 1.410±0.223 | 3.335±0.241 | 0.902±0.041 | 2.016±0.771 | |
| W13 | 3.172±0.621 | 0.675±0.086 | 1.310±0.142 | 2.834±0.116 | 0.820±0.524 | 1.643±0.456 | ||
| W14 | 2.817±0.334 | 0.652±0.079 | 1.119±0.086 | 2.947±0.516 | 0.983±0.665 | 2.599±0.635 | ||
| W15 | 2.106±0.287 | 0.465±0.114 | 0.891±0.143 | 3.030±0.086 | 0.956±0.025 | 1.737±0.247 | ||
| W16 | 3.043±0.668 | 0.848±0.123 | 0.728±0.088 | 2.973±0.667 | 0.860±0.017 | 1.494±0.065 | ||
| 平均 | 3.018±0.595b | 0.698±0.144a | 1.092±0.254b | 3.024±0.168c | 0.904±0.060a | 1.898±0.390a | ||
表6 渭河浮游生物的多样性指数
Table 6 Diversity index of plankton in the Weihe River
| 采样断面 Sampling sites | 浮游植物 Phytoplankton | 浮游动物 Zooplankton | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H′ | J | d | H′ | J | d | |||
| 上游 Upstrem | W1 | 0.628±0.363 | 0.224±0.114 | 0.315±0.098 | 2.362±0.321 | 0.711±0.064 | 1.119±0.076 | |
| W2 | 1.731±0.622 | 0.616±0.086 | 0.201±0.126 | 0.754±0.047 | 0.376±0.025 | 0.345±0.112 | ||
| W3 | 2.395±0.814 | 0.854±0.104 | 0.554±0.016 | 2.322±0.088 | 1.000±0.214 | 5.396±1.023 | ||
| W4 | 2.292±0.461 | 0.817±0.097 | 0.533±0.134 | 2.505±0.774 | 0.968±0.536 | 1.856±0.887 | ||
| W5 | 2.063±0.672 | 0.798±0.101 | 0.530±0.076 | 2.697±0.564 | 0.851±0.516 | 1.413±0.541 | ||
| W6 | 2.432±0.516 | 0.866±0.077 | 0.615±0.087 | 2.256±0.551 | 0.873±0.465 | 1.040±0.516 | ||
| 平均 | 1.923±0.626a | 0.696±0.227a | 0.508±0.093a | 2.149±0.640a | 0.797±0.210a | 1.862±1.644a | ||
| 中游 Midstream | W7 | 2.558±0.522 | 0.912±0.134 | 0.560±0.012 | 2.113±0.315 | 0.910±0.338 | 1.485±0.441 | |
| W8 | 1.671±0.447 | 0.596±0.116 | 0.543±0.066 | 1.917±0.652 | 0.959±0.410 | 2.227±0.714 | ||
| W9 | 3.515±0.378 | 0.777±0.047 | 1.422±0.612 | 1.923±0.522 | 0.961±0.005 | 4.047±1.365 | ||
| W10 | 3.661±1.121 | 0.821±0.096 | 1.172±0.557 | 2.917±0.104 | 0.920±0.075 | 1.141±0.884 | ||
| W11 | 2.960±0.312 | 0.740±0.254 | 0.918±0.118 | 2.724±0.089 | 0.971±0.016 | 2.227±0.056 | ||
| 平均 | 2.873±0.719ab | 0.769±0.104a | 0.923±0.342b | 2.319±0.424ab | 0.944±0.024a | 2.225±1.004a | ||
| 下游 Downstream | W12 | 3.953±0.286 | 0.852±0.058 | 1.410±0.223 | 3.335±0.241 | 0.902±0.041 | 2.016±0.771 | |
| W13 | 3.172±0.621 | 0.675±0.086 | 1.310±0.142 | 2.834±0.116 | 0.820±0.524 | 1.643±0.456 | ||
| W14 | 2.817±0.334 | 0.652±0.079 | 1.119±0.086 | 2.947±0.516 | 0.983±0.665 | 2.599±0.635 | ||
| W15 | 2.106±0.287 | 0.465±0.114 | 0.891±0.143 | 3.030±0.086 | 0.956±0.025 | 1.737±0.247 | ||
| W16 | 3.043±0.668 | 0.848±0.123 | 0.728±0.088 | 2.973±0.667 | 0.860±0.017 | 1.494±0.065 | ||
| 平均 | 3.018±0.595b | 0.698±0.144a | 1.092±0.254b | 3.024±0.168c | 0.904±0.060a | 1.898±0.390a | ||
| 指标 Index | 浮游植物 Phytoplankton | 浮游动物 Zooplankton | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 第1轴 Axis 1 | 第2轴 Axis 2 | 第1轴 Axis 1 | 第2轴 Axis 2 | ||
| 特征值 Eigen values | 0.195 | 0.124 | 0.432 | 0.218 | |
| 种类与环境因子相关性 Species-environmental factors correlations | 0.878 | 0.916 | 0.948 | 0.949 | |
| 物种数据累计比 Cumulative percentage variance of species data | 23.4 | 38.2 | 28.6 | 43.1 | |
| 种类与环境因子相关累计比 Cumulative percentage variance of Species-environmental factors relation | 34.1 | 55.9 | 39.3 | 59.1 | |
表7 CCA前两个排序轴特征值及浮游生物种类与环境因子排序轴间的相关系数
Table 7 Eigen values and correlation coefficients of plankton species-environmental factors on the first two axis of CCA
| 指标 Index | 浮游植物 Phytoplankton | 浮游动物 Zooplankton | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 第1轴 Axis 1 | 第2轴 Axis 2 | 第1轴 Axis 1 | 第2轴 Axis 2 | ||
| 特征值 Eigen values | 0.195 | 0.124 | 0.432 | 0.218 | |
| 种类与环境因子相关性 Species-environmental factors correlations | 0.878 | 0.916 | 0.948 | 0.949 | |
| 物种数据累计比 Cumulative percentage variance of species data | 23.4 | 38.2 | 28.6 | 43.1 | |
| 种类与环境因子相关累计比 Cumulative percentage variance of Species-environmental factors relation | 34.1 | 55.9 | 39.3 | 59.1 | |
| 环境因子 Environmental factors | 与排序轴相关系数 Correlations with canonical axes | 前选所获得的因子 Forward selection of variables | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 第1轴 Axis 1 | 第2轴 Axis 2 | P值 P-value | F值 F-ratio | |||
| 浮游植物 Phytoplankton | 海拔 ALT | 0.6297 | 0.4512 | 0.005 | 2.74 | |
| 水深 WD | -0.0762 | -0.7207 | 0.047 | 2.21 | ||
| 浮游动物 Zooplankton | 海拔 ALT | 0.7344 | 0.1082 | 0.000 | 3.11 | |
| 溶解氧 DO | 0.0678 | -0.7761 | 0.041 | 1.65 | ||
| pH | -0.6109 | -0.2461 | 0.032 | 1.87 | ||
表8 浮游生物群落与环境因子CCA分析统计结果
Table 8 Statistical result of plankton community and environmental factors in CCA
| 环境因子 Environmental factors | 与排序轴相关系数 Correlations with canonical axes | 前选所获得的因子 Forward selection of variables | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 第1轴 Axis 1 | 第2轴 Axis 2 | P值 P-value | F值 F-ratio | |||
| 浮游植物 Phytoplankton | 海拔 ALT | 0.6297 | 0.4512 | 0.005 | 2.74 | |
| 水深 WD | -0.0762 | -0.7207 | 0.047 | 2.21 | ||
| 浮游动物 Zooplankton | 海拔 ALT | 0.7344 | 0.1082 | 0.000 | 3.11 | |
| 溶解氧 DO | 0.0678 | -0.7761 | 0.041 | 1.65 | ||
| pH | -0.6109 | -0.2461 | 0.032 | 1.87 | ||
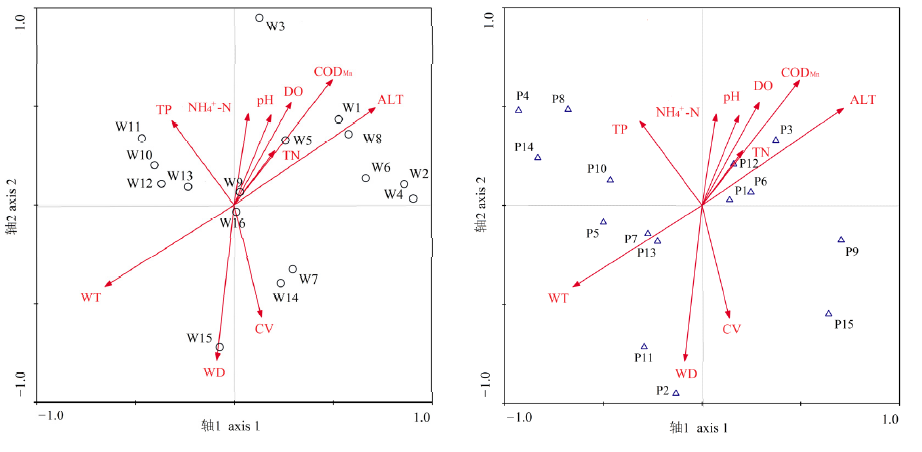
图7 浮游植物群落与环境因子的CCA排序图 ALT为海拔;WT为水温;DO为溶解氧;WD为水深;CV为流速;TN为总氮;TP为总磷;NH4+-N为铵态氮;CODMn为化学耗氧量;W1—W9为采样断面;P1—P15为浮游植物优势种(见表5)
Figure 7 CCA ordination diagram of phytoplankton community and environmental factors ALT, altitude; WT, water temperature; DO, dissolved oxygen; WD, water depth; CV, current velocity; TN, total nitrogen; TP, total phosphorus; NH4+-N; CODMn, chemical oxygen demand; W1-W9, sampling section; P1-P15, dominant species of phyplankton (shown in table 5)
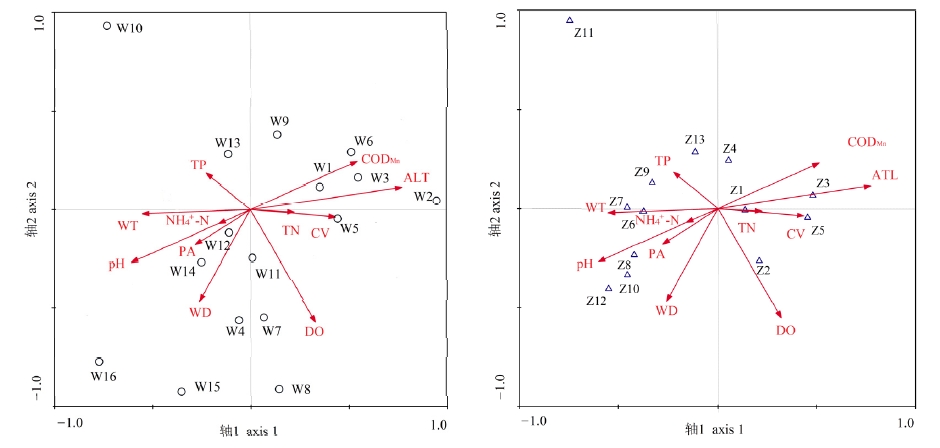
图8 浮游动物群落与环境因子的CCA排序图 PA为浮游植物丰度;Z1—Z13为浮游动物优势种(见表5);其他同上
Figure 8 CCA ordination diagram of zooplankton community and environmental factors PA, Phytoplankton abundance; Z1-Z13, dominant species of zooplankton (shown in table 5); other, the same as above
| [1] |
BARANYI C, HEIN T, HOLAREK C, et al., 2002. Zoolankton biomass and community structure in a Danube River floodplain system: Effects of hydrology[J]. Freshwater Biology, 47(3): 473-482.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
DENG W J, SONG J X, BAI H, et al., 2018. Analyzing the Impacts of Climate Variability and Land Surface Changes on the Annual Water-Energy Balance in the Weihe River Basin of China[J]. Water, 10(12): 1792-1807.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
HANSSON L, GUSTAFSSON S, RENGEFORS K, et al., 2007. Cyanobacterial chemical warfare affects zooplankton community composition[J]. Freshwater Biology, 52(7): 1290-1301.
DOI URL |
| [4] | HOFMANN W, 1977. The influence of abiotic environmental factors on population dynamics in planktonic rotifers[J]. Archiv für Hydrobiologie-Beiheft Ergebnisse der Limnologie, 8: 77-83. |
| [5] |
JACOBSEN D, SCHULTZ R, ENCALADA A, 1997. Structure and diversity of stream invertebrate assemblages: The influence of temperature with altitude and Iatitude[J]. Freshwater Biology, 38(2): 247-261.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
JAKOBSEN H, BLANDA E, STAEHR P, et al., 2015. Development of phytoplankton communities:Implications of nutrient injections on phytoplankton composition, pH and ecosystem production[J]. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology, 473: 81-89.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
KIM H, SPIVACK A J, MENDEN-DEUER S, 2013. pH alters the swimming behaviors of the raphidophyte Heterosigma akashiwo: Implications for bloom formation in an acidified ocean[J]. Harmful Algae, 26: 1-11.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
LOICK-WILDE N, WEBER S C, CONROY B J, et al., 2018. Nitrogen sources and net growth efficiency of zooplankton in three Amazon River plume food webs[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 61(2): 460-481.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
SAUNDERS J F, LEWIS JR W M, 1988. Zooplankton abundance and transport in a tropical white-water rivers[J]. Hydrobiologia, 162(2): 147-155.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
SONG J X, TANG B, ZHANG J L, et al., 2018. System dynamics simulation for optimal stream flow regulations under consideration of coordinated development of ecology and socio-economy in the Weihe River Basin, China[J]. Ecological Engineering, 124: 51-68.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
STAMPFI N C, KNILLMANN S, LIESS M, et al., 2013. Two stressors and a community-effects of hydrological disturbance and a toxicant on freshwater zooplankton[J]. Aquatic Toxicology, 127: 9-20.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
WU W, XU Z X, KENNARD M J, et al., 2016. Do human disturbance variables influence more on fish community structure and fuction than natural variables in the Weihe River basin, China?[J]. Ecological indicators, 61: 438-446.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
YIN X W, NIU C J, 2008. Effect of pH on survival, reproduction, egg viablity and growth rate of five closely related rotifer species[J]. Aquatic Ecology, 42: 607-616.
DOI URL |
| [14] | 白海锋, 李丽娟, 项珍龙, 等, 2015a. 泾河水系浮游动物群落结构及其与环境因子的关系[J]. 大连海洋大学学报, 30(3): 291-297. |
| BAI H F, LI L J, XIANG Z L, et al., 2015a. Community structure and its relationship with environmental factors in zooplankton in Jinghe River system in Northwest, China[J]. Journal of Dalian Ocean University, 30(3): 291-297. | |
| [15] | 白海锋, 王丰, 张星朗, 等, 2015b. 黄河兰州市区段秋季浮游动物群落结构特征[J]. 水生态学杂志, 36(5): 51-57. |
| BAI H F, WANG F, ZHANG X L, et al., 2015b. Characterisyics of zooplankton community structure for the Yellow River in Lanzhou city[J]. Journal of Hydroecology, 36(5): 51-57. | |
| [16] | 白海锋, 赵乃锡, 殷旭旺, 等, 2014. 渭河流域浮游动物的群落结构及其与环境因子的关系[J]. 大连海洋大学学报, 29(3): 260-266. |
| BAI H F, ZHAO N X, YIN X W, et al., 2014. Community structure and relationship with environmental factors in zooplankton in Weihe River basin, Northwest China[J]. Journal of Dalian Ocean University, 29(3): 260-266. | |
| [17] | 蔡琨, 秦春燕, 李继影, 等, 2016. 基于浮游植物生物完整性指数的湖泊生态系统评价--以2012年冬季太湖为例[J]. 生态学报, 36(5):1431-1441. |
| CAI K, QIN C Y, LI J Y, et al., 2016. Preliminary study on phytoplanktonic index of biotic integrity (P-IBI) assessment for lake ecosystem health: A case of Taihu Lake in Winter, 2012[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 36(5): 1431-1441. | |
| [18] | 董旭峰, 宋祥甫, 刘娅琴, 等, 2015. 猪场废水资源化处理系统中枝角类群落结构的周年动态[J]. 生态学杂志, 34(2): 477-482. |
| DONG X F, SONG X F, LIU Y Q, et al., 2015. Annual dynamics of cladocera community structure in swine wastewater recycling system[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 34(2): 477-482. | |
| [19] | 高宏伟, 李晓春, 陈晓霞, 等, 2015. 渭河陕西段浮游植物群落结构及水质评价[J]. 河北渔业 (11): 12-13, 77. |
| GAO H W, LI X C, CHEN X X, et al., 2015. Community structure of phytoplankton and water quality evaluation in Shaanxi section of the Weihe River[J]. Hebei Fisheries (11): 12-13, 77. | |
| [20] | 国家环境保护总局, 2002. 水和废水监测分析方法[M]. 第4版. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社. |
| State Environmental Protection Administration, 2002. Standard Methods for examination of water and wastewater[M]. 4th edition. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press. | |
| [21] | 韩茂森, 束蕴芳, 1995. 中国淡水生物图谱[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社. |
| HAN M S, SHU Y F, 1995. Atlas of freshwater biology in China[M]. Beijing: China Ocean Press. | |
| [22] | 郝媛媛, 孙国钧, 张立勋, 等, 2014. 黑河流域浮游植物群落特征与环境因子的关系[J]. 湖泊科学, 26(1): 121-130. |
|
HAO Y Y, SUN G J, ZHANG L X, et al., 2014. Relationship between community characteristics of the phytoplankton and environmental factors in Heihe River basin[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 26(1): 121-130.
DOI URL |
|
| [23] | 贺玉晓, 刘天慧, 任玉芬, 等, 2020. 北运河秋冬季浮游植物群落结构特征及影响因子分析[J]. 环境科学学报, 40(5): 1710-1720. |
| HE Y X, LIU T H, REN Y F, et al., 2020. Characteristics and influencing factors of phytoplankton community structure in autumn and winter of the North Canal, Beijing[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 40(5): 1710-1721. | |
| [24] | 洪松, 陈静生, 2002. 中国河流水生生物群落结构特征探讨[J]. 水生生物学报, 6(3): 295-305. |
| HONG S, CHEN J S, 2002. Structure characteristics of aquatic community from the main rivers in China[J]. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 6(3): 295-305. | |
| [25] | 胡鸿钧, 李尧英, 魏印心, 等, 1979. 中国淡水藻类[M]. 上海: 上海科学技术出版. |
| HU H J, LI Y Y, WEI Y X, et al., 1979. The freshwater algae of China[J]. Shanghai: Sahnghai Science and Technology Press. | |
| [26] | 胡芯, 印江平, 唐洪玉, 等, 2019. 乌杨调节坝运行初期汉丰湖浮游植物群落结构及其与环境因子的相关性分析[J]. 淡水渔业, 49(6): 48-55. |
| HU X, YIN J P, TANG H Y, et al., 2019. Phytoplankton community structure and its redundancy correlation with environmental factors in Hanfeng Lake during the early stage of the operation of Wuyang Regulating Dam[J]. Freshwater Fisheries, 49(6): 48-55. | |
| [27] | 蒋燮治, 堵南山, 1979. 中国动物志·淡水枝角类[M]. 北京: 科学出版社. |
| JIANG X Z, DU N S, 1979. The fauna of China·freshwater cladoceras[M]. Beijing: Science Press. | |
| [28] | 李静, 崔凯, 卢文轩, 等, 2015. 春季和夏季巢湖浮游生物群落组成及其动态分析[J]. 水生生物学报, 39(1): 185-192. |
| LI J, CUI K, LU W X, et al., 2015. Community dynamics of spring-summer plankton in Lake Chaohu[J]. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 39(1): 185-192. | |
| [29] | 李晓钰, 于洪贤, 马成学, 2013. 松花江哈尔滨段浮游植物群落典范对应分析及多样性分析[J]. 东北林业大学学报, 41(10): 103-107. |
| LI X Y, YU H X, MA C X, 2013. Structure of phytoplankton community based on canonical correspondence analysis and biodiversity analysis in Harbin section of Songhua River[J]. Journal of Northeast Forestry University, 41(10): 103-107. | |
| [30] | 刘峰, 冯民权, 王毅博, 2019. 汾河入黄口夏季微生物群落结构分析[J]. 微生物学通报, 46(1): 54-64. |
| LIU F, FENG M Q, WANG Y B, 2019. Microbial community structure of estuary of the Fenhe River into the Yellow Riverin summer[J]. Microbiology China, 46(1): 54-64. | |
| [31] | 刘钢, 孟云飞, 吴丹, 等, 2018. 青藏高原可鲁克湖浮游动物群落结构特征及水质评价[J]. 大连海洋大学学报, 33(6): 379-386. |
| LIU G, MENG Y F, WU D, et al., 2018. Characteristics of zooplankton community structure and water quality assessment in Keluke Lake in the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau[J]. Journal of Dalian Ocean University, 33(6): 379-386. | |
| [32] | 刘麟菲, 徐宗学, 殷旭旺, 等, 2019. 济南市不同区域水生生物与水环境因子的响应关系[J]. 湖泊科学, 31(4): 998-1011. |
|
LIU L F, XU Z X, YIN X W, et al., 2019. Response of aquatic organism richness to physiochemical factore at different regions in Ji’nan City[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 31(4): 998-1011.
DOI URL |
|
| [33] | 刘盼盼, 王龙, 王培, 等, 2018. 沙颍河流域浮游动物群落结构空间变化特征与水质评价[J]. 水生生物学报, 42(2): 373-381. |
| LIU P P, WANG L, WANG P, et al., 2018. The characteristics of zooplankton community and water quality in the Shaying River basin[J]. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 42(2): 373-381. | |
| [34] | 罗民波, 陆健健, 王云龙, 等, 2007. 东海浮游植物数量分布与优势种[J]. 生态学报, 27(12): 5076-5085. |
| LUO M B, LU J J, WANG Y L, et al., 2007. Horizontal distribution and dominant species of phytoplankton in the East China Sea[J]. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 42(2): 373-381. | |
| [35] | 马宝珊, 徐滨, 魏开金, 等, 2020. 安宁河中游浮游植物群落结构及其与环境因子的关系[J]. 生态学杂志, 39(10): 3332-3341. |
| MA B S, XU B, WEI K J, et al., 2020. Phytoplankton community structure and its relation to environmental conditions in the middle Anning River, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 39(10): 3332-3341. | |
| [36] | 闵文武, 王培培, 李丽娟, 等, 2015. 渭河流域浮游植物功能群与环境因子的关系[J]. 环境科学研究, 28(9): 1397-1406. |
| MIN W W, WANG P P, LI L J, et al., 2015. Relationship between phytoplankton functional groups and environmental factors in the Wei River Basin[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 28(9): 1397-1406. | |
| [37] | 石代军, 2017. 气候变化对地表水环境质量影响研究综述[J]. 水利水电技术, 48(11): 141-149. |
| SHI D J, 2017. A review on impact from climate change on surface water environment quality[J]. Water Resources and Hydropower Engineering, 48(11): 141-149. | |
| [38] | 宋菊梅, 白海锋, 鲁媛媛, 等, 2014. 北洛河丰水期浮游动物群落结构调查及水质初步评价[J]. 河北渔业 (7): 29-30, 50. |
| SONG J M, BAI H F, LU Y Y, et al., 2014. Investigation of zooplankton community structure and preliminary evaluation of water quality during the rainy season in Beiluo River[J]. Hebei Fisheries (7): 29-30, 50. | |
| [39] | 王家楫, 1961. 中国淡水轮虫志[M]. 北京: 科学出版社. |
| WANG J J, 1961. Freshwater rotifers of China[M]. Beijing: Science Press. | |
| [40] | 王勇, 王海军, 赵伟华, 等, 2010. 黄河干流浮游植物群落特征及其对水质的指示作用[J]. 湖泊科学, 22(5): 700-707. |
| WANG Y, WANG H J, ZHAO W H, et al., 2010. Phytoplankton assemblage characteristics and their indication of water quality in the mainstream of the Yellow River[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 22(5): 700-707. | |
| [41] | 吴利, 李源玲, 陈延松, 2015. 淮河干流浮游动物群落结构特征[J]. 湖泊科学, 27(5): 930-940. |
|
WU L, LI Y L, CHEN Y S, 2015. Characteristics of community structures of zooplankton in the mainstream Huaihe River[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 27(5): 932-940.
DOI URL |
|
| [42] | 武玮, 徐宗学, 于松延, 2013. 渭河流域水环境质量评价与分析[J]. 北京师范大学学报 (自然科学版), 49(2-3): 275-281. |
| WU W, XU Z X, YU S Y, et al., 2013. Water quality assessment and analysis for the Weihe River basin[J]. Journal of Beijing Normal University (Natural Science), 49(2-3): 275-281. | |
| [43] | 武玮, 徐宗学, 殷旭旺, 等, 2014. 渭河流域鱼类群落结构特征及其受环境因子的影响分析[J]. 环境科学学报, 34(5): 1298-1308. |
| WU W, XU Z X, YIN X W, et al., 2014. Fish community structure and the effect of environmental factors in the Wei River basin[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 34(5): 1298-1308. | |
| [44] | 徐宗学, 武玮, 殷旭旺, 2016. 渭河流域水生态系统群落结构特征及其健康评价[J]. 水利水电科技进展, 36(1): 23-30. |
| XU Z X, WU W, YIN X W, et al., 2016. Community structure characteristics and health assessment of aquatic ecosystem in Weihe basin, China[J]. Advances in Science and Technology of Water Resources, 36(1): 23-30. | |
| [45] | 杨宋琪, 祖廷勋, 王怀斌, 等, 2019. 黑河张掖段浮游植物群落结构及其与环境因子的关系[J]. 湖泊科学, 31(1): 159-170. |
|
YANG S Q, ZU T X, WANG H B, et al., 2019. Relationship between the structureof phytoplankton community and environmental factors in the Zhangye section of Heihe River[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 31(1): 159-170.
DOI URL |
|
| [46] | 杨玉珍, 关建玲, 王蕾, 等, 2012. 近10年渭河干流陕西段水质变化趋势与成因分析[J]. 安徽农业科学, 40(25): 12609-12612. |
| YANG Y Z, GUAN J L, WANG L, et al., 2012. Analysis on the changing trends of surface water quality and their causes of Weihe River in Shaanxi province during recent ten years[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Science, 40(25): 12609-12612. | |
| [47] | 殷旭旺, 李庆南, 朱美桦, 等, 2015. 渭河丰、枯水期底栖动物群落特征及综合健康评价[J]. 生态学报, 35(14): 4784-4796. |
| YIN X W, LI Q N, ZHU M H, et al., 2015. Community structure and biological integrity of macroinvertebrates in the wet and dry seasons of Wei River basin, China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 35(14): 4784-4796. | |
| [48] | 殷旭旺, 徐宗学, 高欣, 等, 2013a. 渭河流域大型底栖动物群落结构及其与环境因子的关系[J]. 应用生态学报, 24(1): 218-226. |
| YIN X W, XU Z X, GAO X, et al., 2013a. Macrobenthos community structure and its relationships with environmental factors in Weihe River basin, Northweat China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 24(1): 218-226. | |
| [49] | 殷旭旺, 徐宗学, 鄢娜, 等, 2013b. 渭河流域河流着生藻类的群落结构与生物完整性研究[J]. 环境科学学报, 33(2): 518-527. |
| YIN X W, XU Z X, YAN N, et al., 2013b. Community structure and biological integrity of periphyton in the Weihe River basin, China[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 33(2): 518-527. | |
| [50] | 袁永锋, 李引娣, 张林林, 等, 2009. 黄河中上游水生生物资源调查研究[J]. 水生态学杂志, 2(6): 15-19. |
| YUAN Y F, LI Y D, ZHANG L L, et al., 2009. Inestigation&research on hydrobios resources in the middle and upper reaches of main YellowRiver[J]. Journal of Hydroecology, 2(6): 15-19. | |
| [51] | 张军燕, 高志, 沈红保, 等, 2017. 拉萨河春季浮游生物群落结构特征研究[J]. 淡水渔业, 47(4): 23-31. |
| ZHANG J Y, GAO Z, SHENG H B, et al., 2017. Community structure characteristics of plankton in Lhasa River in spring[J]. Freshwater Fisheries, 47(4): 23-31. | |
| [52] | 张兰平, 孙亚玲, 刘进琪, 等, 2019. 渭河上游水生物河流生境状态研究[J]. 甘肃水利水电技术, 55(1): 9-12, 16. |
| ZHANG L P, SUN Y L, LIU J Q, et al., 2019. Study on river habitat status of aquatic organisms in the upper Weihe River[J]. Gansu Water Resources and Hydropower Technology, 55(1): 9-12, 16. | |
| [53] | 张世羊, 周巧红, 成水平, 等, 2009. 复合养殖系统中浮游动物种类丰度及其影响因素[J]. 中国环境科学, 29(7): 745-750. |
| ZHANG S Y, ZHOU Q H, CHENG S P, et al., 2009. Zooplankton species richness and impact factors in a compound aquaculture system[J]. China Environmental Science, 29(7): 745-750. | |
| [54] | 赵文, 2005. 水生生物学[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社. |
| ZHAO W, 2005. Hydrobiology[M]. Beijing: China Agriculture Press. | |
| [55] | 中国科学院动物研究所甲壳动物研究组, 1979. 中国动物志·淡水桡足类[M]. 北京: 科学出版社. |
| Crustacean Research Group, Institute of Zoology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 1979. The fauna of China·freshwater copepods[M]. Beijing: Science Press. | |
| [56] | 钟继承, 刘国锋, 范成新, 等, 2010. 湖泊底泥疏浚环境效应: Ⅳ. 对沉积物微生物活性与群落功能多样性的影响及其意义[J]. 湖泊科学, 22(1): 21-28. |
|
ZHONG J C, LIU G F, FAN C X, et al., 2010. Environmental effect of sediment dredging in lake: IV influence of dredging on microbial activity and functional divereity of microbial community in sediments and its significance[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 22(1): 21-28.
DOI URL |
|
| [57] | 朱宜平, 张海平, 李飞鹏, 等, 2010. 水动力对浮游生物影响的围隔研究[J]. 环境科学, 31(1): 69-75. |
| ZHU Y P, ZHANG H P, LI F P, et al., 2010. Enclosure experiments about the hydrodynamics effects on the plankton[J]. Environmental Science, 31(1): 69-75. |
| [1] | 董洁芳, 邓椿, 张仲伍. 渭河流域PM2.5时空演化及人口暴露风险[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(6): 1078-1088. |
| [2] | 巫晨煜, 许帆帆, 魏士博, 樊晶晶, 刘观鹏, 王坤. 渭河流域地表植被覆盖对气候变化的响应研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 835-844. |
| [3] | 侯晖, 颜培轩, 谢沁宓, 赵宏亮, 庞丹波, 陈林, 李学斌, 胡杨, 梁咏亮, 倪细炉. 贺兰山蒙古扁桃灌丛根际土壤AM真菌群落多样性特征研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 857-865. |
| [4] | 姜永伟, 丁振军, 袁俊斌, 张峥, 李杨, 问青春, 王业耀, 金小伟. 辽宁省主要河流底栖动物群落结构及水质评价研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 969-979. |
| [5] | 王云, 郑西来, 曹敏, 李磊, 宋晓冉, 林晓宇, 郭凯. 滨海含水层咸-淡水过渡带反硝化性能与控制因素研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 980-988. |
| [6] | 寇祝, 卿纯, 袁昌果, 李平. 西藏东北部热泉水中硫氧化菌的多样性及分布特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 989-1000. |
| [7] | 胡芳, 刘聚涛, 温春云, 韩柳, 文慧. 抚河流域浮游植物群落结构特征及其水生态状况评价[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 744-755. |
| [8] | 于菲, 曾海龙, 房怀阳, 付玲芳, 林澍, 董家豪. 典型感潮河网浮游藻类功能群时空变化特征及水质评价[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 756-765. |
| [9] | 王礼霄, 刘晋仙, 柴宝峰. 华北亚高山土壤细菌群落及氮循环对退耕还草的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1537-1546. |
| [10] | 段文军, 李达, 李冲. 5种不同林龄尾巨桉人工林林下植物多样性及其影响因素分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(5): 857-864. |
| [11] | 王英成, 姚世庭, 金鑫, 俞文政, 芦光新, 王军邦. 三江源区高寒退化草甸土壤细菌多样性的对比研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 695-703. |
| [12] | 刘红梅, 海香, 安克锐, 张海芳, 王慧, 张艳军, 王丽丽, 张贵龙, 杨殿林. 不同施肥措施对华北潮土区玉米田土壤固碳细菌群落结构多样性的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 715-722. |
| [13] | 夏开, 邓鹏飞, 马锐豪, 王斐, 温正宇, 徐小牛. 马尾松次生林转换为湿地松和杉木林对土壤细菌群落结构和多样性的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(3): 460-469. |
| [14] | 宋秀丽, 黄瑞龙, 柯彩杰, 黄蔚, 章武, 陶波. 不同种植方式对连作土壤细菌群落结构和多样性的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(3): 487-496. |
| [15] | 李聪, 吕晶花, 陆梅, 杨志东, 刘攀, 任玉连, 杜凡. 滇东南亚热带土壤细菌群落对植被垂直带变化的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(10): 1971-1983. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
