生态环境学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (11): 2130-2141.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2021.11.003
所属专题: 生物多样性专题汇编
林丽1( ), 代磊1, 林泽北2, 吴际通2, 颜伟2, 王志杰1,3,*(
), 代磊1, 林泽北2, 吴际通2, 颜伟2, 王志杰1,3,*( )
)
收稿日期:2021-05-26
出版日期:2021-11-18
发布日期:2021-12-29
通讯作者:
* 王志杰(1986年生),男,副教授,博士,主要从事喀斯特山地景观生态与生物多样性研究。E-mail: zjwang3@gzu.edu.cn作者简介:林丽(1993年生),女,硕士研究生,主要研究方向为修复生态。E-mail: 1292364928@qq.com
基金资助:
LIN Li1( ), DAI Lei1, LIN Zebei2, WU Jitong2, YAN Wei2, WANG Zhijie1,3,*(
), DAI Lei1, LIN Zebei2, WU Jitong2, YAN Wei2, WANG Zhijie1,3,*( )
)
Received:2021-05-26
Online:2021-11-18
Published:2021-12-29
摘要:
以贵阳市10种典型城市森林群落为研究对象,在野外抽样调查和实验室检测的基础上,采用单因素方差分析,分析了贵阳市不同城市森林群落植物多样性和土壤理化性质的差异,运用冗余分析和典范对应分析,探讨了贵阳市不同城市森林群落土壤理化性质对植物多样性及物种分布的影响,旨在为贵阳市乃至中国西南喀斯特城市森林生态保护、城市森林植物多样性维护提供重要科学依据和理论支撑。结果表明,(1)研究区有维管植物61科、107属、124种,不同类型城市森林群落不同层间重要值最高的物种不同,女贞桦木混交林物种组成丰富,马尾松林物种组成最贫乏。(2)各种城市森林群落物种Shannon-Wiener指数、丰富度指数和Pielou均匀度指数均以女贞桦木混交林最大,马尾松林最小,且二者相应的多样性指数间差异显著;灌木层与群落多样性指数变化相似,草本层Shannon-Wiener指数和丰富度指数以马尾松华山松混交林最大,Pielou均匀度指数以香樟林最大,且3个指数均以马尾松林最小,而Simpson优势度指数变化与其他3个指数变化相反。(3)不同城市森林群落的土壤pH、全磷、全钾、速效钾、速效磷、容重具有显著差异,而全氮、速效氮、有机质差异不显著,其中,土壤pH对物种分布及灌木层物种多样性有显著影响、土壤容重对物种分布及草本物种多样性有显著影响,土壤速效钾对物种分布影响不显著,但对群落物种多样性有显著影响,而土壤有机质、全磷则与之相反。
中图分类号:
林丽, 代磊, 林泽北, 吴际通, 颜伟, 王志杰. 黔中城市森林群落植物多样性及其与土壤理化性质的关系[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(11): 2130-2141.
LIN Li, DAI Lei, LIN Zebei, WU Jitong, YAN Wei, WANG Zhijie. Plant Diversity and Its Relationship with Soil Physicochemical Properties of Urban Forest Communities in Central Guizhou[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(11): 2130-2141.
| 群落号 CID | 群落类型 Community types | 海拔 Altitude/m | 经度和纬度 Longitude and Latitude | 样地 Sample plot | 坡度 Slope/(°) | 坡向 Aspect | 坡位 Slope position |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ⅰ | 马尾松华山松混交林 Pinus massoniana and Pinus armandiimixed forest | 1359 | 106°66′21.35″E 26°67′12.36″N | 1, 3 | 6, 12 | 南、西南 South, Southwest | 中坡 Middle slope |
| Ⅱ | 马尾松林 Pinus massoniana forest | 1302 | 106°66′80.27″E 26°66′80.44″N | 6, 12 | 14 | 南 South | 中坡 Middle slope |
| Ⅲ | 华山松混交林 Pinus armandii mixed forest | 1322 | 106°67′27.37″E 26°66′78.89″N | 2, 5 | 3, 8 | 西北 Northwest | 中坡 Middle slope |
| Ⅳ | 华山松林 Pinus armandii forest | 1293 | 106°66′55.36″E 26°66′53.29″N | 4 | 35 | 南 South | 中坡 Middle slope |
| Ⅴ | 女贞林 Ligustrum lucidum forest | 1174 | 106°66′52.41″E 26°66′85.28″N | 7 | 20 | 北 North | 中坡 Middle slope |
| Ⅵ | 女贞桦木混交林 Ligustrum lucidum and Betula alnoides mixed forest | 1128 | 106°66′00.70″E 26°66′18.46″N | 8 | 7 | 北 North | 上坡 Upper slope |
| Ⅶ | 桦木混交林 Betula alnoides mixed forest | 1243 | 106°69′75.56″E 26°61′30.83″N | 9 | 9 | 南 South | 下坡 lower slope |
| Ⅷ | 杉木林 Cunninghamia lanceolata forest | 1288 | 106°70′54.24″E 26°63′52.86″N | 10 | 8 | 东 East | 上坡 Upper slope |
| Ⅸ | 柳杉林 Cryptomeria japonica forest | 1210 | 106°67′43.34″E 26°64′78.75″N | 11 | 0 | 无坡向 No aspect | 平地 Flat ground |
| Ⅹ | 香樟林 Cinnamomum longepaniculatum forest | 1293 | 106°67′80.74″E 26°54′17.16″N | 13 | 1 | 无坡向 No aspect | 平地 Flat ground |
表1 样地概况
Table 1 Sample plot information of 13 typical urban forest communities
| 群落号 CID | 群落类型 Community types | 海拔 Altitude/m | 经度和纬度 Longitude and Latitude | 样地 Sample plot | 坡度 Slope/(°) | 坡向 Aspect | 坡位 Slope position |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ⅰ | 马尾松华山松混交林 Pinus massoniana and Pinus armandiimixed forest | 1359 | 106°66′21.35″E 26°67′12.36″N | 1, 3 | 6, 12 | 南、西南 South, Southwest | 中坡 Middle slope |
| Ⅱ | 马尾松林 Pinus massoniana forest | 1302 | 106°66′80.27″E 26°66′80.44″N | 6, 12 | 14 | 南 South | 中坡 Middle slope |
| Ⅲ | 华山松混交林 Pinus armandii mixed forest | 1322 | 106°67′27.37″E 26°66′78.89″N | 2, 5 | 3, 8 | 西北 Northwest | 中坡 Middle slope |
| Ⅳ | 华山松林 Pinus armandii forest | 1293 | 106°66′55.36″E 26°66′53.29″N | 4 | 35 | 南 South | 中坡 Middle slope |
| Ⅴ | 女贞林 Ligustrum lucidum forest | 1174 | 106°66′52.41″E 26°66′85.28″N | 7 | 20 | 北 North | 中坡 Middle slope |
| Ⅵ | 女贞桦木混交林 Ligustrum lucidum and Betula alnoides mixed forest | 1128 | 106°66′00.70″E 26°66′18.46″N | 8 | 7 | 北 North | 上坡 Upper slope |
| Ⅶ | 桦木混交林 Betula alnoides mixed forest | 1243 | 106°69′75.56″E 26°61′30.83″N | 9 | 9 | 南 South | 下坡 lower slope |
| Ⅷ | 杉木林 Cunninghamia lanceolata forest | 1288 | 106°70′54.24″E 26°63′52.86″N | 10 | 8 | 东 East | 上坡 Upper slope |
| Ⅸ | 柳杉林 Cryptomeria japonica forest | 1210 | 106°67′43.34″E 26°64′78.75″N | 11 | 0 | 无坡向 No aspect | 平地 Flat ground |
| Ⅹ | 香樟林 Cinnamomum longepaniculatum forest | 1293 | 106°67′80.74″E 26°54′17.16″N | 13 | 1 | 无坡向 No aspect | 平地 Flat ground |

图1 不同城市森林主要植物组成及重要值 Ⅰ:马尾松华山松混交林;Ⅱ:马尾松林;Ⅲ:华山松混交林;Ⅳ:华山松林;Ⅴ:女贞林;Ⅵ:女贞桦木混交林;Ⅶ:桦木混交林;Ⅷ:杉木林;Ⅸ:柳杉林;Ⅹ:香樟林;A:乔木层物种重要值;B:灌木层物种重要值;C:草本层物种重要值
Fig. 1 Main plant composition and importance in different urban forests Ⅰ: Pinus massoniana and Pinus armandii mixed forest; Ⅱ: Pinus massoniana forest; Ⅲ: Pinus armandii mixed forest; Ⅳ: Pinus armandii forest; Ⅴ: Ligustrum lucidum forest; Ⅵ: Ligustrum lucidum and Betula alnoides mixed forest; Ⅶ: Betula alnoides mixed forest; Ⅷ: Cunninghamia lanceolata forest; Ⅸ: Cryptomeria japonica forest; Ⅹ: Cinnamomum longepaniculatum forest; A: Importance value of tree layer species; B: Importance value of shrub layer species; C: Importance value of herb layer species
| 群落号 CID | Shannon-Wiener 指数 Shannon-Wiener index | 丰富度指数 Richness index | Simpson 指数 Simpson index | Pielou均匀度 指数 Pielou index |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ⅰ | 1.40±0.44a | 5.50±2.26a | 0.32±0.13d | 0.86±0.10a |
| Ⅱ | 0.58±0.46e | 2.18±1.22e | 0.57±0.30a | 0.60±0.44b |
| Ⅲ | 1.24±0.47abc | 4.59±2.42abc | 0.35±0.19cd | 0.86±0.23a |
| Ⅳ | 0.98±0.65abcd | 4.09±3.42abcd | 0.48±0.27abc | 0.76±0.29ab |
| Ⅴ | 1.22±0.52abc | 4.73±2.05abc | 0.38±0.24bcd | 0.84±0.20ab |
| Ⅵ | 1.45±0.33a | 5.63±2.06a | 0.29±0.13d | 0.88±0.15a |
| Ⅶ | 1.31±0.40ab | 5.00±2.05ab | 0.34±0.14cd | 0.86±0.13a |
| Ⅷ | 0.89±0.52cde | 3.55±1.75bcde | 0.52±0.24ab | 0.71±0.29ab |
| Ⅸ | 0.68±0.56de | 2.54±1.37de | 0.61±0.30a | 0.62±0.42b |
| Ⅹ | 0.91±0.43bcde | 3.09±1.22cde | 0.46±0.19abcd | 0.87±0.23ab |
表2 不同城市森林群落植物多样性指数比较
Table 2 Comparison of plant diversity indices of forest communities in different cities
| 群落号 CID | Shannon-Wiener 指数 Shannon-Wiener index | 丰富度指数 Richness index | Simpson 指数 Simpson index | Pielou均匀度 指数 Pielou index |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ⅰ | 1.40±0.44a | 5.50±2.26a | 0.32±0.13d | 0.86±0.10a |
| Ⅱ | 0.58±0.46e | 2.18±1.22e | 0.57±0.30a | 0.60±0.44b |
| Ⅲ | 1.24±0.47abc | 4.59±2.42abc | 0.35±0.19cd | 0.86±0.23a |
| Ⅳ | 0.98±0.65abcd | 4.09±3.42abcd | 0.48±0.27abc | 0.76±0.29ab |
| Ⅴ | 1.22±0.52abc | 4.73±2.05abc | 0.38±0.24bcd | 0.84±0.20ab |
| Ⅵ | 1.45±0.33a | 5.63±2.06a | 0.29±0.13d | 0.88±0.15a |
| Ⅶ | 1.31±0.40ab | 5.00±2.05ab | 0.34±0.14cd | 0.86±0.13a |
| Ⅷ | 0.89±0.52cde | 3.55±1.75bcde | 0.52±0.24ab | 0.71±0.29ab |
| Ⅸ | 0.68±0.56de | 2.54±1.37de | 0.61±0.30a | 0.62±0.42b |
| Ⅹ | 0.91±0.43bcde | 3.09±1.22cde | 0.46±0.19abcd | 0.87±0.23ab |
| 层次 Level | 群落号 CID | Shannon-Wiener指数 Shannon-Wiener index | 丰富度指数 Richness index | Simpson指数 Simpson index | Pielou均匀度指数 Pielou index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 灌木层 Shrub layer | Ⅰ | 1.31±0.43a | 4.90±0.28a | 0.34±0.14b | 0.86±0.10a |
| Ⅱ | 0.49±0.51c | 1.80±1.32d | 0.51±0.37ab | 0.52±0.54b | |
| Ⅲ | 0.98±0.46ab | 3.30±1.34bcd | 0.43±0.23b | 0.82±0.30ab | |
| Ⅳ | 0.77±0.48bc | 2.60±1.14cd | 0.53±0.28ab | 0.73±0.41ab | |
| Ⅴ | 1.19±0.67ab | 4.60±2.07abc | 0.41±0.33b | 0.70±0.41ab | |
| Ⅵ | 1.39±0.35a | 5.40±1.14a | 0.32±0.18b | 0.84±0.20ab | |
| Ⅶ | 1.30±0.50ab | 5.00±2.35ab | 0.36±0.19b | 0.83±0.18ab | |
| Ⅷ | 0.81±0.66abc | 3.20±2.28bcd | 0.56±0.28ab | 0.66±0.40ab | |
| Ⅸ | 0.36±0.35c | 1.80±0.84d | 0.77±0.23a | 0.45±0.44b | |
| Ⅹ | 0.80±0.19abc | 2.60±0.89cd | 0.48±0.07ab | 0.91±0.13a | |
| 草本层 Herb layer | Ⅰ | 1.48±0.47a | 5.80±2.97a | 0.29±0.13c | 0.89±0.08a |
| Ⅱ | 0.73±0.41b | 2.50±0.97c | 0.56±013a | 0.76±0.29b | |
| Ⅲ | 1.41±0.37a | 4.80±1.61ab | 0.28±0.10c | 0.94±0.06a | |
| Ⅳ | 1.04±0.80ab | 4.00±3.08abc | 0.48±0.30ab | 0.81±0.18ab | |
| Ⅴ | 1.27±0.46a | 4.20±1.79abc | 0.33±0.15bc | 0.94±0.02a | |
| Ⅵ | 1.43±0.32a | 5.00±2.00ab | 0.27±0.08c | 0.93±0.08a | |
| Ⅶ | 1.30±0.37a | 4.40±1.51abc | 0.32±0.12bc | 0.92±0.04a | |
| Ⅷ | 1.06±0.40ab | 3.80±1.48abc | 0.43±0.15abc | 0.82±0.06ab | |
| Ⅸ | 1.14±0.38ab | 3.60±1.14bc | 0.36±0.16bc | 0.92±0.08a | |
| Ⅹ | 1.15±0.48ab | 3.60±1.52bc | 0.36±0.18bc | 0.95±0.03a |
表3 不同城市森林群落灌木层和草本层植物多样性指数比较
Table 3 Comparison of plant diversity indices of shrub layer and herb layer in different urban forest communities
| 层次 Level | 群落号 CID | Shannon-Wiener指数 Shannon-Wiener index | 丰富度指数 Richness index | Simpson指数 Simpson index | Pielou均匀度指数 Pielou index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 灌木层 Shrub layer | Ⅰ | 1.31±0.43a | 4.90±0.28a | 0.34±0.14b | 0.86±0.10a |
| Ⅱ | 0.49±0.51c | 1.80±1.32d | 0.51±0.37ab | 0.52±0.54b | |
| Ⅲ | 0.98±0.46ab | 3.30±1.34bcd | 0.43±0.23b | 0.82±0.30ab | |
| Ⅳ | 0.77±0.48bc | 2.60±1.14cd | 0.53±0.28ab | 0.73±0.41ab | |
| Ⅴ | 1.19±0.67ab | 4.60±2.07abc | 0.41±0.33b | 0.70±0.41ab | |
| Ⅵ | 1.39±0.35a | 5.40±1.14a | 0.32±0.18b | 0.84±0.20ab | |
| Ⅶ | 1.30±0.50ab | 5.00±2.35ab | 0.36±0.19b | 0.83±0.18ab | |
| Ⅷ | 0.81±0.66abc | 3.20±2.28bcd | 0.56±0.28ab | 0.66±0.40ab | |
| Ⅸ | 0.36±0.35c | 1.80±0.84d | 0.77±0.23a | 0.45±0.44b | |
| Ⅹ | 0.80±0.19abc | 2.60±0.89cd | 0.48±0.07ab | 0.91±0.13a | |
| 草本层 Herb layer | Ⅰ | 1.48±0.47a | 5.80±2.97a | 0.29±0.13c | 0.89±0.08a |
| Ⅱ | 0.73±0.41b | 2.50±0.97c | 0.56±013a | 0.76±0.29b | |
| Ⅲ | 1.41±0.37a | 4.80±1.61ab | 0.28±0.10c | 0.94±0.06a | |
| Ⅳ | 1.04±0.80ab | 4.00±3.08abc | 0.48±0.30ab | 0.81±0.18ab | |
| Ⅴ | 1.27±0.46a | 4.20±1.79abc | 0.33±0.15bc | 0.94±0.02a | |
| Ⅵ | 1.43±0.32a | 5.00±2.00ab | 0.27±0.08c | 0.93±0.08a | |
| Ⅶ | 1.30±0.37a | 4.40±1.51abc | 0.32±0.12bc | 0.92±0.04a | |
| Ⅷ | 1.06±0.40ab | 3.80±1.48abc | 0.43±0.15abc | 0.82±0.06ab | |
| Ⅸ | 1.14±0.38ab | 3.60±1.14bc | 0.36±0.16bc | 0.92±0.08a | |
| Ⅹ | 1.15±0.48ab | 3.60±1.52bc | 0.36±0.18bc | 0.95±0.03a |
| 群落号 CID | pH | w(TN)/(g∙kg-1) | w(TP)/(g∙kg-1) | w(TK)/(g∙kg-1) | w(AN)/(mg∙kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ⅰ | 5.04±0.78cd | 2.45±0.43a | 0.59±0.14b | 20.21±5.81a | 159.68±32.40a |
| Ⅱ | 4.93±0.20cd | 2.65±1.16a | 0.99±0.45ab | 19.28±1.63a | 165.40±52.93a |
| Ⅲ | 6.13±0.27b | 3.60±0.95a | 1.15±0.19ab | 18.60±1.75a | 218.70±40.83a |
| Ⅳ | 5.81±0.23bc | 3.23±0.25a | 0.99±0.45ab | 16.16±2.01abc | 205.42±13.52a |
| Ⅴ | 7.14±0.30a | 4.02±0.97a | 1.15±0.17ab | 15.01±0.77abc | 225.87±15.89a |
| Ⅵ | 7.31±0.45a | 4.42±1.72a | 1.19±0.13ab | 17.52±2.15ab | 250.31±55.00a |
| Ⅶ | 7.22±0.63a | 2.76±1.34a | 0.79±0.11b | 11.42±0.54bc | 177.46±70.43a |
| Ⅷ | 4.62±0.04cd | 2.78±0.73a | 1.13±0.23ab | 10.24±0.46c | 191.25±33.46a |
| Ⅸ | 5.57±1.07cd | 2.93±2.10a | 1.09±0.19ab | 11.05±0.66bc | 171.53±94.65a |
| Ⅹ | 5.88±0.30bc | 2.69±0.13a | 1.69±0.71a | 15.75±2.05abc | 189.28±7.02a |
| 群落号 CID | w(AP)/(mg∙kg-1) | w(AK)/(mg∙kg-1) | w(OM)/(g∙kg-1) | w(BD)/(g∙cm-3) | |
| Ⅰ | 7.71±1.25b | 178.05±51.58a | 47.90±10.74a | 22.03±12.21ab | |
| Ⅱ | 10.47±4.32b | 163.92±19.97ab | 45.56±17.44a | 35.26±22.37ab | |
| Ⅲ | 7.21±0.34b | 164.80±54.35ab | 65.14±16.79a | 18.80±8.33ab | |
| Ⅳ | 8.75±2.38b | 163.00±29.84ab | 60.15±4.18a | 13.51±5.22b | |
| Ⅴ | 173.47±19.59a | 135.68±45.31abc | 76.83±19.03a | 61.58±30.11a | |
| Ⅵ | 198.15±43.70a | 143.35±14.28abc | 84.14±35.25a | 30.10±8.90ab | |
| Ⅶ | 178.79±64.34a | 82.37±4.53bc | 51.08±27.27a | 32.96±7.37ab | |
| Ⅷ | 9.59±1.70b | 56.36±7.10c | 53.34±15.09a | 22.23±3.55ab | |
| Ⅸ | 51.96±73.78b | 62.55±10.29bc | 53.29±39.39a | 40.08±17.62ab | |
| Ⅹ | 7.93±1.46b | 143.14±19.59abc | 46.49±2.66a | 72.89.11±4.74a |
表4 不同城市森林群落土壤理化性质比较
Table 4 Comparison of soil physical and chemical properties in different urban forest ecosystems
| 群落号 CID | pH | w(TN)/(g∙kg-1) | w(TP)/(g∙kg-1) | w(TK)/(g∙kg-1) | w(AN)/(mg∙kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ⅰ | 5.04±0.78cd | 2.45±0.43a | 0.59±0.14b | 20.21±5.81a | 159.68±32.40a |
| Ⅱ | 4.93±0.20cd | 2.65±1.16a | 0.99±0.45ab | 19.28±1.63a | 165.40±52.93a |
| Ⅲ | 6.13±0.27b | 3.60±0.95a | 1.15±0.19ab | 18.60±1.75a | 218.70±40.83a |
| Ⅳ | 5.81±0.23bc | 3.23±0.25a | 0.99±0.45ab | 16.16±2.01abc | 205.42±13.52a |
| Ⅴ | 7.14±0.30a | 4.02±0.97a | 1.15±0.17ab | 15.01±0.77abc | 225.87±15.89a |
| Ⅵ | 7.31±0.45a | 4.42±1.72a | 1.19±0.13ab | 17.52±2.15ab | 250.31±55.00a |
| Ⅶ | 7.22±0.63a | 2.76±1.34a | 0.79±0.11b | 11.42±0.54bc | 177.46±70.43a |
| Ⅷ | 4.62±0.04cd | 2.78±0.73a | 1.13±0.23ab | 10.24±0.46c | 191.25±33.46a |
| Ⅸ | 5.57±1.07cd | 2.93±2.10a | 1.09±0.19ab | 11.05±0.66bc | 171.53±94.65a |
| Ⅹ | 5.88±0.30bc | 2.69±0.13a | 1.69±0.71a | 15.75±2.05abc | 189.28±7.02a |
| 群落号 CID | w(AP)/(mg∙kg-1) | w(AK)/(mg∙kg-1) | w(OM)/(g∙kg-1) | w(BD)/(g∙cm-3) | |
| Ⅰ | 7.71±1.25b | 178.05±51.58a | 47.90±10.74a | 22.03±12.21ab | |
| Ⅱ | 10.47±4.32b | 163.92±19.97ab | 45.56±17.44a | 35.26±22.37ab | |
| Ⅲ | 7.21±0.34b | 164.80±54.35ab | 65.14±16.79a | 18.80±8.33ab | |
| Ⅳ | 8.75±2.38b | 163.00±29.84ab | 60.15±4.18a | 13.51±5.22b | |
| Ⅴ | 173.47±19.59a | 135.68±45.31abc | 76.83±19.03a | 61.58±30.11a | |
| Ⅵ | 198.15±43.70a | 143.35±14.28abc | 84.14±35.25a | 30.10±8.90ab | |
| Ⅶ | 178.79±64.34a | 82.37±4.53bc | 51.08±27.27a | 32.96±7.37ab | |
| Ⅷ | 9.59±1.70b | 56.36±7.10c | 53.34±15.09a | 22.23±3.55ab | |
| Ⅸ | 51.96±73.78b | 62.55±10.29bc | 53.29±39.39a | 40.08±17.62ab | |
| Ⅹ | 7.93±1.46b | 143.14±19.59abc | 46.49±2.66a | 72.89.11±4.74a |
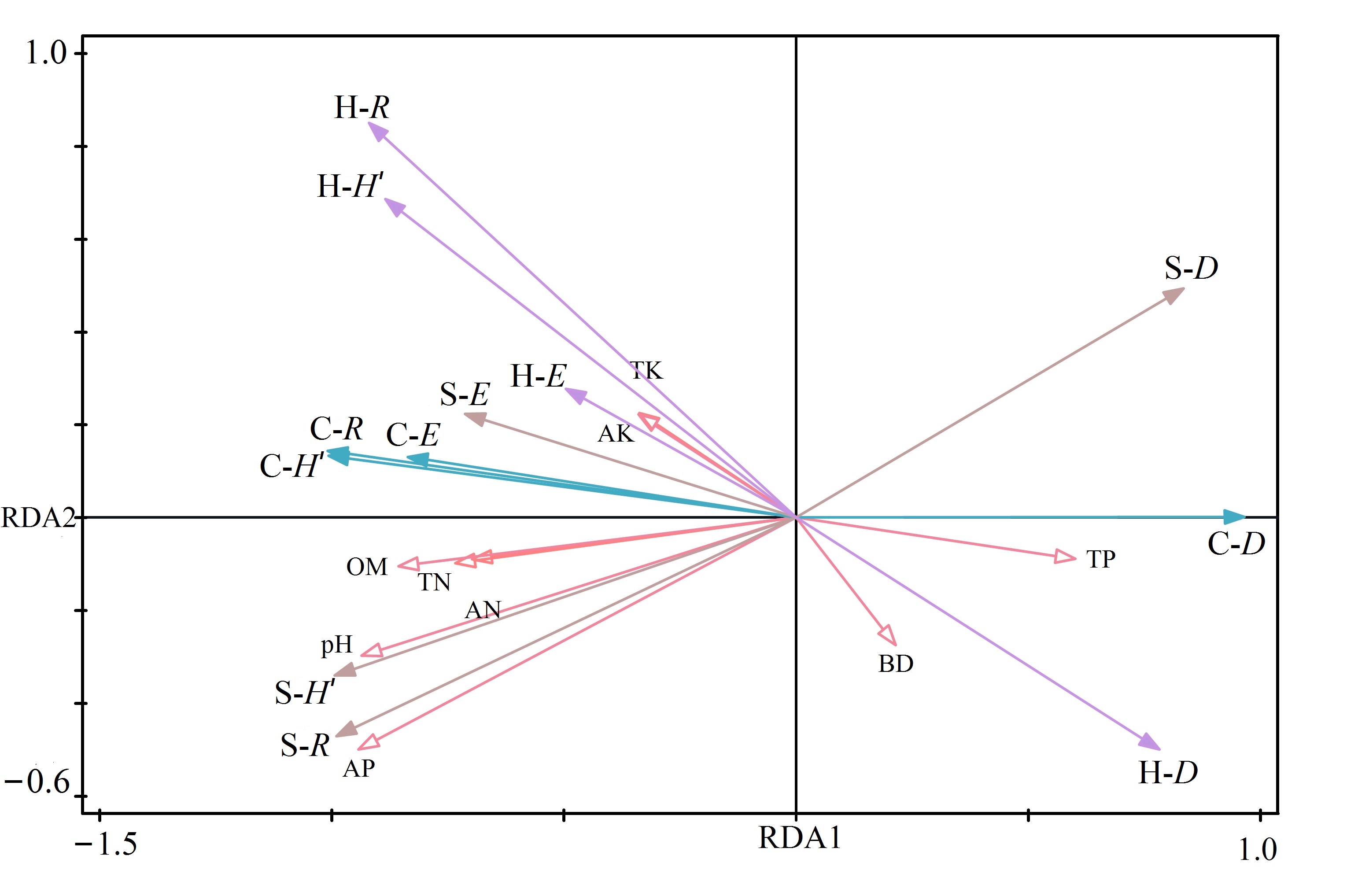
图2 植物多样性与土壤理化性质RDA排序图 C-H′:群落Shannon-Wiener指数;C-R:群落物种丰富度指数;C-D:群落Simpson指数;C-E:群落Pielou指数;BD:土壤容重;TN:全氮;TP:全磷;TN:全钾;AN:速效氮;AP:速效磷;AK:速效钾;pH;OM:有机质;S-H′:灌木层Shannon-Wiener指数;S-R:灌木层物种丰富度指数;S-D:灌木层Simpson指数;S-E:灌木层Pielou指数;H-H′:草本层Shannon-Wiener指数;H-R:草本层物种丰富度指数;H-D:草本层Simpson指数;H-E:草本层Pielou指数
Fig. 2 RDA ordination diagram of plant diversity and soil physical and chemical properties C-H′: Community Shannon-Wiener index; C-R: community species richness index; C-D: Simpson index of community; C-E: Community Pielou index; BD: soil bulk density; TN: total nitrogen; TP: total phosphorus; TN: total potassium; AN: Available nitrogen; AP: available phosphorus; AK, available potassium; pH; OM: Organic matter, S-H': Shannon-Wiener index of Shrub layer; S-R: Species richness index of shrub layer; S-D: Simpson index of shrub layer; S-E: Pielou index of shrub layer; H- H': Shannon-Wiener index of herbaceous layer; H-R: Species richness index of herbaceous layer; H-D: Simpson index of herb layer; H-E: Pielou index of herb layer
| 层次 Level | 环境因子 Environmental Factors | 解释变异量 Explain the amount of variation | 伪F统计量 Pseudo F statistic | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 群落Community | pH | 28.2 | 2.50 | 0.198 |
| w(TN)/(g∙kg-1) | 28.0 | 1.10 | 0.416 | |
| w(TP)/(g∙kg-1) | 12.0 | 2.80 | 0.120 | |
| w(TK)/(g∙kg-1) | 13.2 | 2.60 | 0.281 | |
| w(AN)/(mg∙kg-1) | 31.0 | 12.60 | 0.008 | |
| w(AP)/(mg∙kg-1) | 13.1 | 0.70 | 0.484 | |
| w(AK)/(mg∙kg-1) | 20.2 | <0.10 | 1 | |
| w(OM)/(g∙kg-1) | 32.3 | 3.80 | 0.062 | |
| w(BD)/(g∙cm-3) | 10.4 | 4.30 | 0.054 | |
| 灌木层Shrub layer | pH | 41.9 | 5.80 | 0.032 |
| w(TN)/(g∙kg-1) | 28.7 | 3.50 | 0.156 | |
| w(TP)/(g∙kg-1) | 0.6 | <0.11 | 0.123 | |
| w(TK)/(g∙kg-1) | 8.2 | 1.50 | 0.236 | |
| w(AN)/(mg∙kg-1) | 30.8 | 0.30 | 0.624 | |
| w(AP)/(mg∙kg-1) | 36.8 | 1.10 | 0.136 | |
| w(AK)/(mg∙kg-1) | 9.3 | 6.20 | 0.106 | |
| w(OM)/(g∙kg-1) | 32.7 | 3.50 | 0.156 | |
| w(BD)/(g∙cm-3) | 2.1 | 55.90 | 0.102 | |
| 草本层Herb layer | pH | 10.5 | 1.50 | 0.458 |
| w(TN)/(g∙kg-1) | 5.0 | 0.70 | 0.454 | |
| w(TP)/(g∙kg-1) | 28.2 | 3.10 | 0.011 | |
| w(TK)/(g∙kg-1) | 9.9 | 1.20 | 0.412 | |
| w(AN)/(mg∙kg-1) | 3.3 | 2.40 | 0.180 | |
| w(AP)/(mg∙kg-1) | 9.3 | 0.10 | 0.790 | |
| w(AK)/(mg∙kg-1) | 7.3 | 0.20 | 0.738 | |
| w(OM)/(g∙kg-1) | 8.9 | <0.11 | 1 | |
| w(BD)/(g∙cm-3) | 7.9 | 0.90 | 0.360 |
表5 RDA土壤理化性质对物种多样性的解释率
Table 5 Interpretation rate of RDA soil physical and chemical properties to species diversity
| 层次 Level | 环境因子 Environmental Factors | 解释变异量 Explain the amount of variation | 伪F统计量 Pseudo F statistic | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 群落Community | pH | 28.2 | 2.50 | 0.198 |
| w(TN)/(g∙kg-1) | 28.0 | 1.10 | 0.416 | |
| w(TP)/(g∙kg-1) | 12.0 | 2.80 | 0.120 | |
| w(TK)/(g∙kg-1) | 13.2 | 2.60 | 0.281 | |
| w(AN)/(mg∙kg-1) | 31.0 | 12.60 | 0.008 | |
| w(AP)/(mg∙kg-1) | 13.1 | 0.70 | 0.484 | |
| w(AK)/(mg∙kg-1) | 20.2 | <0.10 | 1 | |
| w(OM)/(g∙kg-1) | 32.3 | 3.80 | 0.062 | |
| w(BD)/(g∙cm-3) | 10.4 | 4.30 | 0.054 | |
| 灌木层Shrub layer | pH | 41.9 | 5.80 | 0.032 |
| w(TN)/(g∙kg-1) | 28.7 | 3.50 | 0.156 | |
| w(TP)/(g∙kg-1) | 0.6 | <0.11 | 0.123 | |
| w(TK)/(g∙kg-1) | 8.2 | 1.50 | 0.236 | |
| w(AN)/(mg∙kg-1) | 30.8 | 0.30 | 0.624 | |
| w(AP)/(mg∙kg-1) | 36.8 | 1.10 | 0.136 | |
| w(AK)/(mg∙kg-1) | 9.3 | 6.20 | 0.106 | |
| w(OM)/(g∙kg-1) | 32.7 | 3.50 | 0.156 | |
| w(BD)/(g∙cm-3) | 2.1 | 55.90 | 0.102 | |
| 草本层Herb layer | pH | 10.5 | 1.50 | 0.458 |
| w(TN)/(g∙kg-1) | 5.0 | 0.70 | 0.454 | |
| w(TP)/(g∙kg-1) | 28.2 | 3.10 | 0.011 | |
| w(TK)/(g∙kg-1) | 9.9 | 1.20 | 0.412 | |
| w(AN)/(mg∙kg-1) | 3.3 | 2.40 | 0.180 | |
| w(AP)/(mg∙kg-1) | 9.3 | 0.10 | 0.790 | |
| w(AK)/(mg∙kg-1) | 7.3 | 0.20 | 0.738 | |
| w(OM)/(g∙kg-1) | 8.9 | <0.11 | 1 | |
| w(BD)/(g∙cm-3) | 7.9 | 0.90 | 0.360 |
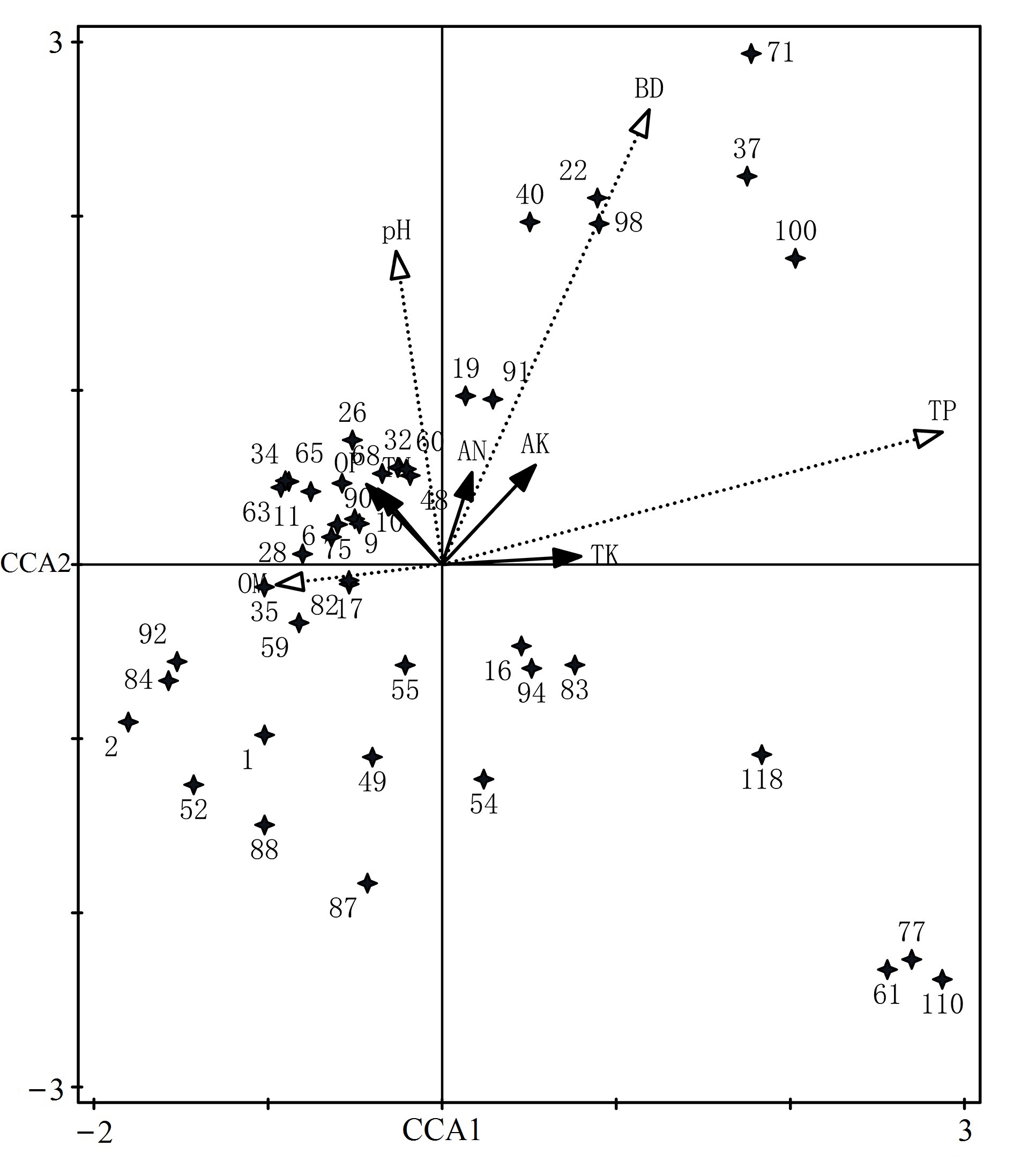
图3 物种与环境因子CCA的双序图(显示了权重为5%—100%的物种) 1:蕨类;2:川榛;6:猪屎豆;11:地果;16:路边青;17:牛膝;19:三叶木通;22:小花八角;26:冷水花;27:铁线莲;28:华中樱桃;32:臭鸡矢藤;34:长柄山蚂蝗;35:小果蔷薇;37:凤尾蕨;40:狗脊;48:铁仔;49:朴树;52:木防己;54:山莓;55:山茶;59:灯台树;60:刺楸;61:竹叶花椒;65:荚蒾;68:构树;71:蜡梅;75:旌节花;77:刺叶珊瑚冬青;82:滇鼠刺;83:桦木;84:马尾松;87:华山松;88:柳杉;90:柏木;91:楸树;92:柳杉;94:胡桃;98:中华梧桐;100:杉木;109:半夏;110:忍冬;119:侧柏
Fig. 3 The double sequence diagram of species and environmental factors CCA (weights ranging from 5% to 100%) 1: Pteridophyta; 2: Corylus heterophylla; 6: Crotalaria sessiliflora; 11: Ficus tikoua; 16: Geum aleppicum; 17: Achyranthes bidentat; 19: Akebia trifoliata; 22: Illicium micranthum; 26: Pilea notate; 27: Clematis florida; 28: Prunus conradinae; 32: Paederia cruddasiana; 34: Hylodesmum podocarpum; 35, Rosa cymosa; 37: Pteris bella; 40: Woodwardia japonica; 48: Myrsine africana; 49: Celtis sinensis; 52: Cocculus orbiculatus; 54: Rubus corchorifolius; 55: Camellia japonica; 59: Cornus controversa; 60: Kalopanax septemlobus; 61: Zanthoxylum armatum; 65: Viburnum dilatatum; 68: Broussonetia papyrifera; 71: Chimonanthus praecox; 75: Stachyurus chinensis; 77: Ilex corallina var. loeseneri; 82: Itea yunnanensis; 83: Betula alnoides; 84: Pinus massoniana; 87: Pinus armandii; 88: Cryptomeria japonica; 90: Cupressus funebris; 91: Sorbus pohuashanensis; 92: Cryptomeria japonica; 94: Juglans regia; 98: Firmiana simplex; 100: Cunninghamia lanceolata; 109: Pinellia ternata; 110: Lonicera japonica; 119: Platycladus orientalis
| [1] |
GUISAN A, ZIMMERMANN N E, et al., 2000. Predictive habitat distribution models in ecology[J]. Ecological Modelling, 135(2-3): 147-186.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
LIU L B, NI J, 2020. Variations of the biodiversity and carbon functions of Karst forests in two morphologically different sites in Southwestern China[J]. Israel Journal of Ecology and Evolution, 67(1-2): 9-16.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
PYSEK P, LEPS J, 1992. Response of a weed community to nitrogen fertilization: a multivariate analysis[J]. Journal of Vegetation Science; 2(2): 237-244.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
WEIGEL R, GILLES J, KLISZ M, et al., 2019. Forest understory vegetation is more related to soil than to climate towards the cold distribution margin of European beech[J]. Journal of Vegetation Science, 30(4): 746-755.
DOI URL |
| [5] | ROSEN Z, MICHAEL L, 1995. Species diversity in space and time Speciation[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press: 87-111. |
| [6] |
YU M, SUN O J X, 2013. Effects of forest patch type and site on herb-layer vegetation in a temperate forest ecosystem[J]. Forest Ecology and Management, 300(1): 14-20.
DOI URL |
| [7] | 安明态, 2019. 喀斯特森林土壤水分和养分格局及其植物物种多样性维持机制研究[D]. 贵阳: 贵州大学: 1-256. |
| AN M T, 2019. Studies on maintenance mechanism of plant species diversity and soil moisture and nutrient pattern in Karst forest[D]. Guiyang: Guizhou University: 1-256. | |
| [8] | 陈晓熹, 杨新东, 曾献兴, 等, 2019. 环境因子对青云山自然保护区森林群落物种分布的影响[J]. 生态学杂志, 38(12): 3642-3650. |
| CHEN X X, YANG X D, ZENG X X, et al., 2019. Influences of environmental factors on species distribution in forest community in Wengyuan Qingyunshan Nature Reserve Guangdong[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 38(12): 3642-3650. | |
| [9] | 崔宁洁, 张丹桔, 刘洋, 等, 2014. 不同林龄马尾松人工林林下植物多样性与土壤理化性质[J]. 生态学杂志, 33(10): 2610-2617. |
| CUI N J, ZHANG D J, LIU Y, et al., 2014. Plant diversity and soil physicochemical properties under different aged Pinus massoniana plantations[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 33(10): 2610-2617. | |
| [10] | 范得芳, 王得祥, 柴宗政, 等, 2016. 环境因子对秦岭锐齿栎群落物种分布及多样性的影响[J]. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 44(10): 59-67. |
| FAN D F, WANG D X, CHAI Z Z, et al., 2016. Effects of environmental factors on species distribution and diversity of Quercus aliena var. acuteserrata community in Qinling Mountains[J]. Journal of Northwest A & F University (Natural Science Edition), 44(10): 59-67. | |
| [11] | 方精云, 王襄平, 沈泽昊, 等, 2009. 植物群落清查的主要内容、方法和技术规范[J]. 生物多样性, 17(6): 533-548. |
|
FANG J Y, WANG X P, SHEN Z H, et al., 2009. Methods and protocols for plant community inventory[J]. Biodiversity Science, 17(6): 533-548.
DOI URL |
|
| [12] | 高贤明, 马克平, 陈灵芝, 等, 2001. 暖温带若干落叶阔叶林群落物种多样性及其与群落动态的关系[J]. 植物生态学报, 25(3): 283-290. |
| GAO X M, MA K P, CHEN L Z, et al., 2001. Species diversity of some deciduous broad-leaved forests in the warm-temperate zone and its relations to community stability[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 25(3): 283-290. | |
| [13] | 郭春秀, 姚拓, 马俊梅, 等, 2017. 石羊河下游不同类型荒漠草地黑果枸杞群落结构及物种多样性特征[J]. 草地学报, 25(3): 529-537. |
| GUO C X, YAO T, MA J M, et al., 2017. Characteristics and species diversity of lycium ruthenicum on different types of desert grassland in Shiyang River[J]. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 25(3): 529-537. | |
| [14] | 姜俊, 刘宪钊, 贾宏炎, 等, 2019. 杉木人工林近自然化改造对林下植被多样性和土壤理化性质的影响[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 41(5): 170-177. |
| JIANG J, LIU X Z, JIA H Y, et al., 2019. Effects of stand density on understory species diversity and soil physicochemical properties after close-to-nature transformation management of Chinese fir plantation[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 41(5): 170-177. | |
| [15] | 雷斯越, 2019. 不同地形条件下退耕草地植被恢复与土壤理化性质分异特征[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学: 1-46. |
| LEI S Y, 2019. Vegetation restoration with soil physical and chemical properties distribution characteristics of converted grassland in different topographic conditions[D]: Yangling: Northwest A & F University: 1-46. | |
| [16] | 李海梅, 何兴元, 陈玮, 等, 2004. 中国城市森林研究现状及发展趋势[J]. 生态学杂志, 23(2): 55-59. |
| LI H M, HE X Y, CHEN W, et al., 2004. Current situations and trend of investigations on urban forest in China[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology 23(2): 55-59. | |
| [17] | 李芹, 容丽, 王敏, 2019. 地形对喀斯特山地植物物种多样性及分布格局的影响[J]. 水土保持通报, 39(6): 27-34. |
| LI Q, RONG L, WANG M, 2019. Effects of topography on diversity and distribution pattern of plant species in Karst Mountains Area[J]. Bulletion of Soil and Water Conservation, 39(6): 27-34. | |
| [18] | 李婷婷, 唐永彬, 周润惠, 等, 2021. 云顶山不同人工林林下植物多样性及其与土壤理化性质的关系[J]. 生态学报, 41(3): 1168-1177. |
| LI T T, TANG Y B, ZHOU R H, et al., 2021. Understory plant diversity and its relationship with soil physicochemical properties in different plantations in Yunding Mountain[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 41(3): 1168-1177. | |
| [19] | 罗楠, 舒英格, 陈梦军, 等, 2020. 喀斯特山区不同草地土壤结构及分形特征[J]. 草业学报, 29(7): 11-22. |
| LUO N, SHU Y G, CHEN M J, et al., 2020. Soil structure and fractal characteristics of different land categories in a Karst Rocky Desertification Area[J]. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 29(7): 11-22. | |
| [20] | 罗巧玉, 王彦龙, 杜雷, 等, 2021. 黄河源区发草适生地植物群落特征及其土壤因子解释[J]. 草业学报, 30(4): 80-89. |
| LUO Q Y, WANG Y L, DU L, et al., 2021. Plant community diversity and soil factor interpretation of adaptive region of Deschampsia caespitosa in the source region of the Yellow River[J]. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 30(4): 80-89. | |
| [21] | 吕倩, 康文斯, 郭茂金, 等, 2019. 柏木人工林目标树经营初期对林下植物多样性及土壤理化性质的影响[J]. 应用与环境生物学报, 25(5): 1036-1043. |
| LV Q, KANG W S, GUO M J, et al., 2019. Early effects of target tree management on undergrowth plant diversity and soil physicochemical properties in Cupressus funebris plantations[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology, 25(5): 1036-1043. | |
| [22] | 马杰, 贾宝全, 张文, 等, 2019. 北京市六环内城市森林结构总体特征[J]. 生态学杂志, 38(8): 2318-2325. |
| MA J, JIA B Q, ZHANG W, et al., 2019. The characteristics of urban forest structure within the Sixth Ring Road of Beijing[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 38(8): 2318-2325. | |
| [23] | 郝建锋, 王德艺, 李艳, 等, 2014. 人为干扰对川西金凤山楠木次生林群落结构和物种多样性的影响[J]. 生态学报, 34(23): 6930-6942. |
| HAO J F, WANG D Y, LI Y, et al., 2014. Effects of human disturbance on species diversity of Phoebe zhennan communitis in Jinfengshan Moutain in western Sichuan[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 34(23): 6930-6942. | |
| [24] | 马天舒, 丁伟林, 肖复明, 等, 2020. 不同年龄阶段陈山红心杉人工林土壤理化性质[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 40(12): 114-124. |
| MA T S, DING W L, XIAO F M, et al., 2020. The soil physical and chemical properties in different stand ages of Chenshan red-heart Chinese fir[J]. Journal of Central South University of Forestry & Technology, 40(12): 114-124. | |
| [25] | 马志波, 肖文发, 黄清麟, 等, 2016. 森林群落多样性与空间格局研究综述[J]世界林业研究, 29(3): 35-39. |
| MA Z B, XIAO W F, HUANG Q L, et al., 2016. A Review of Diversity and Spatial Pattern of Forest Community[J]. World Forestry Research, 29(3): 35-39. | |
| [26] | 孟庆欣, 2020. 太行山植物群落多样性分布格局及其对环境因子的响应[D]. 太原: 山西大学: 1-69. |
| MENG Q X, 2020. Distribution patterns and its response to environmental factors of plant communities in Taihang Mountains[D]. Taiyuan: Shanxi university: 1-69. | |
| [27] | 秦晓佳, 丁贵杰, 2012. 低磷胁迫对不同种源马尾松幼苗氮钾吸收与利用的影响[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 32(4): 32-36. |
| QIN X J, DING G J, 2012. Effects of low phosphorus stress on absorption and utilization of nitrogen and potassium in different provenances Pinus massoniana seedlings[J]. Journal of Central South University of Forestry & Technology, 32(4): 32-36. | |
| [28] | 任学敏, 杨改河, 王得祥, 等, 2012. 环境因子对巴山冷杉-糙皮桦混交林物种分布及多样性的影响[J]. 生态学报, 32(2): 605-613. |
|
REN X M, YANG G H, WANG D X, et al., 2012. Effects of environmental factors on species distribution and diversity in an Abies fargesii-Betula utilis mixed forest[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 32(2): 605-613.
DOI URL |
|
| [29] | 戎建涛, 张晓红, 郜爱玲, 等, 2019. 不同间伐强度经营对柳杉人工林土壤理化性质的影响[J]. 西北林学院学报, 34(4): 206-211. |
| RONG J T, ZHANG X H, GAO A L, et al., 2019. Effects of different thinning intensity managements on soil physicochemical properties of cryptomeria fortunei plantations[J]. Journal of Northwest Forestry University, 34(4): 206-211. | |
| [30] | 邵方丽, 余新晓, 郑江坤, 等, 2012. 北京山区防护林优势树种分布与环境的关系[J]. 生态学报, 32(19): 6092-6099. |
|
SHAO F L, YU X X, ZHENG J K, et al., 2012. Relationships between dominant arbor species distribution and environmental factors of shelter forests in the Beijing Mountain Area[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 32(19): 6092-6099.
DOI URL |
|
| [31] | 司彬, 姚小华, 任华东, 等, 2008. 黔中喀斯特植被自然演替过程中物种组成及多样性研究--以贵州省普定县为例[J]. 林业科学研究, 21(5): 669-674. |
| SI B, YAO X H, REN H D, et al., 2008. Species composition and diversity in the process of natural succession of Karst vegetation in central Guizhou: case study of Puding country in Guizhou[J]. Forest Research, 21(5): 669-674. | |
| [32] | 孙千惠, 吴霞, 王媚臻, 等, 2018. 林分密度对马尾松林林下物种多样性和土壤理化性质的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 29(3): 732-738. |
| SUN Q H, WU X, WANG M Z, et al., 2018. Effects of stand density on understory species diversity and soil physicochemical properties of Pinus massoniana plantation[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 29(3): 732-738. | |
| [33] | 陶晓, 樊伟, 杨春, 等, 2016. 城市不同森林土壤溶解性有机碳和微生物生物量碳特征[J]. 生态学杂志, 35(12): 3191-3196. |
| TAO X, FAN W, YANG C, et al., 2016. Characteristics of soil dissolved organic carbon and microbial biomass carbon in different urban forest communities[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 35(12): 3191-3196. | |
| [34] | 汪超, 王孝安, 郭华, 等, 2006. 黄土高原马栏林区主要森林群落物种多样性研究[J]. 西北植物学报, 24(4): 791-797. |
| WANG C, WANG X A, GUO H, et al., 2006. Species diversities of major communities in Malan forest region of the Loess Plateau[J]. Acta Botanica Boredli-Occidentalia Sinica, 24(4): 791-797. | |
| [35] | 汪攀, 王霖娇, 盛茂银, 等, 2018. 西南喀斯特石漠化生态系统植物多样性、土壤生态化学计量特征及其相关性分析[J]. 南方农业学报, 49(10): 1959-1969. |
| WANG P, WANG L J, SHENG M Y, et al., 2018. Plant diversity ecological stoichiometry characteristics of soils and their correlation of the Karst rocky desertification ecosystem in southwestern China[J]. Journal of Southern Agriculture, 49(10): 1959-1969. | |
| [36] | 王凯博, 陈美玲, 秦娟, 等, 2007. 子午岭植被自然演替中植物多样性变化及其与土壤理化性质的关系[J]. 西北植物学报, 27(10): 2089-2096. |
| WANG K B, CHEN M L, QIN J, et al., 2007. Plant species diversity and the relation with soil properties in natural succession process in Ziwuling Area[J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 27(10): 2089-2096. | |
| [37] | 王玲, 2020. 林分密度对油松人工林群落结构和植物多样性的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 29(12): 2328-2336. |
| WANG L, 2020. Effects of different stand densities on community structure and species diversity of Pinus tabulaeformis plantation[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 29(12): 2328-2336. | |
| [38] | 王世雄, 王孝安, 李国庆, 等, 2010. 陕西子午岭植物群落演替过程中物种多样性变化与环境解释[J]. 生态学报, 30(6): 1638-1647. |
| WANG S X, WANG X A, LI G Q, et al., 2010. Species diversity and environmental interpretation in the process of community succession in the Ziwu Mountain of Shaanxi Province[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 30(6): 1638-1647. | |
| [39] | 王岩, 李玉灵, 石娟华, 等, 2012. 不同植被恢复模式对铁尾矿物种多样性及土壤理化性质的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 26(3): 112-117. |
| WANG Y, LI Y L, SHI J H, et al., 2012. Effect of different vegetation restoration measures on the species diversity and soil properties of Iron Tailings[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 26(3): 112-117. | |
| [40] | 魏晨辉, 沈光, 裴忠雪, 等, 2015. 不同植物种植对松嫩平原盐碱地土壤理化性质与细根生长的影响[J]. 植物研究, 35(5): 759-764. |
| WEI C H, SHEN G, PEI Z X, et al., 2015. Effects of different plants cultivation on soil physical-chemical properties and fine root growth in saline-alkaline soil in Songnen Plain, Northeastern China[J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research 35(5): 759-764. | |
| [41] | 温佩颖, 金光泽, 2019. 地形对阔叶红松林物种多样性的影响[J]. 生态学报, 39(3): 945-956. |
| WEN P Y, JIN G Z, 2019. Effects of topography on species diversity in a typical mixed broadleaved-Korean pine forest[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 39(3): 945-956. | |
| [42] | 肖德荣, 田昆, 袁华, 等, 2007. 滇西北高原典型退化湿地纳帕海植物群落景观多样性[J]. 生态学杂志, 26(8): 1171-1176. |
| XIAO D R, TIAN K, YUAN H, et al., 2007. Landscape diversity of Napahai wetland plant community in Northwest Yunnan of China[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 26(8): 1171-1176. | |
| [43] | 闫宝龙, 赵清格, 张波, 等, 2017. 不同植被类型对土壤理化性质和土壤呼吸的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 26(2): 189-195. |
| YAN B L, ZHAO Q G, ZHANG B, et al., 2017. Effects of different vegetation types on soil physicochemical properties and soil respiration[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 26(2): 189-195. | |
| [44] | 闫玮明, 孙冰, 裴男才, 等, 2019. 粤北阔叶人工林和次生林植物多样性与土壤理化性质相关性研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 28(5): 898-907. |
| YAN W M, SUN B, PEI N C, et al., 2019. Correlation analyses on plant diversity and soil physical-chemical properties between evergreen broad-leaved plantations and natural secondary forests in North Guangdong, China[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 28(5): 898-907. | |
| [45] |
杨崇曜, 李恩贵, 陈慧颖, 等, 2017. 内蒙古西部自然植被的物种多样性及其影响因素[J]. 生物多样性, 25(12): 1303-1312.
DOI |
|
YANG C Y, LI E G, CHEN H Y, et al., 2017. Biodiversity of natural vegetation and influencing factors in western Inner Mongolia[J]. Biodiversity Science, 25(12): 1303-1312.
DOI URL |
|
| [46] | 杨振奇, 秦富仓, 张晓娜, 等, 2018. 砒砂岩区不同立地类型人工沙棘林下草本物种多样性环境解释[J]. 生态学报, 38(14): 5132-5140. |
| YANG Z Q, QIN F C, ZHANG X N, et al., 2018. Environmental interpretation of herb species diversity under different site types of Hippophae rhamnoides forest in feldspathic sandstone region[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 38(14): 5132-5140. | |
| [47] | 喻理飞, 朱守谦, 叶镜中, 等, 2002. 退化喀斯特森林自然恢复过程中群落动态研究[J]. 林业科学, 38(1): 1-7. |
| YU L F, ZHU S Q, YE J Z, et al., 2002. Dynamics of a degraded Karst forest in the process of natural restoration[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 38(1): 1-7. | |
| [48] | 余飞燕, 叶鑫, 周润惠, 等, 2021. 金马河温江段河岸带不同生境植物物种多样性与土壤理化性质的动态变化[J]. 热带亚热带植物学报, 29(1): 1-8. |
| YU F Y, YE X, ZHOU R H, et al., 2021. Dynamic Changes in Plant Diversity and Soil Physical and Chemical Properties in Different Habitats in Wenjiang Section of Jinma River[J]. Journal of Tropical and Subtropical Botany, 29(1): 1-8. | |
| [49] | 张芳, 杜虎, 曾馥平, 等, 2020. 西南喀斯特峰丛洼地木本植物群落结构与多样性变化[J]. 生态学报, 40(12): 4094-4104. |
| ZHANG F, DU H, ZENG F P, et al., 2020. Changes of woody community structure and diversity in Karst peak-cluster depression in southwest China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 40(12): 4094-4104. | |
| [50] | 张涵丹, 康希睿, 邵文豪, 等, 2021. 不同类型杉木人工林林下草本植物多样性特征[J]. 生态学报, 41(6): 2118-2128. |
| ZHANG H D, KANG X R, SHAO W H, et al., 2021. Characteristics of herbaceous plant biodiversity in Cunninghamia lanceolate plantations with different community structures[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 41(6): 2118-2128. | |
| [51] | 张柳桦, 齐锦秋, 柳苹玉, 等, 2018. 林分密度对桉树人工林群落结构和物种多样性的影响[J]. 西北植物学报, 38(1): 166-175. |
| ZHANG L H, QI J Q, LIU P Y, et al., 2018. Effects of stand density on community structure and species diversity of Eucalyptus robusta plantation[J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 38(1): 166-175. | |
| [52] | 张起鹏, 2019. 地形对高寒草甸植物多样性影响的多层次分析--以合作市为例[D]. 南京: 南京师范大学: 1-135. |
| ZHANG Q P, 2019. Effects of topography on plant diversity patterns in alpine meadow using Multi-scaleanalysis: Taking Hezuo city as an example[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Normal University: 1-135. | |
| [53] | 张文, 张建利, 周玉锋, 2011. 喀斯特山地草地植物群落结构与相似性特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 20(5): 843-848. |
| ZHANG W, ZHANG J L, ZHOU Y F, 2011. The plant community structure & similarity trait of the Karst Mountain grassland[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 20(5): 843-848. | |
| [54] | 张文华, 2011. 喀斯特森林植被种群生态学与群落稳定性分析[D]. 上海: 华东师范大学: 1-191. |
| ZHANG W H, 2011. Ecological research on population and community stability in Karst forest vegetation[D]. Shanghai: East China Normal University: 1-191. | |
| [55] | 赵娜, 鲁绍伟, 李少宁, 等, 2018. 北京松山自然保护区典型植物群落物种多样性研究[J]. 西北植物学报, 38(11): 2120-2128. |
| ZHAO N, LU S W, LI S N, et al., 2018. Study on plant diversity of typical plant communities in Songshan Nature Reserve Beijing[J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 38(11): 2120-2128. | |
| [56] | 赵耀, 王百田, 2018a. 晋西黄土区不同林地植物多样性研究[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 40(9): 45-54. |
| ZHAO Y, WANG B T, 2018. Plant diversity of different forestland in the Loess region of western Shanxi Province, Northern China[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 40(9): 45-54. | |
| [57] | 赵耀, 王百田, 李萌, 等, 2018b. 晋西吕梁山区3种森林碳氮磷生态化学计量特征[J]. 应用与环境生物学报, 24(3): 518-524. |
| ZHAO Y, WANG B T, LI M, et al., 2018. Ecological stoichiometric characteristics of carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus in three forests in the Lüliang Mountainous Area of Shanxi Province[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology, 24(3): 518-524. | |
| [58] | 郑鸾, 龙翠玲, 2020. 茂兰喀斯特森林不同地形植物多样性与土壤理化特征研究[J]. 广西植物, 40(6): 792-801. |
| ZHENG L, LONG C L, 2020. Differences of plant diversity and soil physicochemical properties in Maolan Karst forest under different topographic conditions[J]. Guangxi Sciences, 40(6): 792-801. | |
| [59] | 曾亚兰, 李绍才, 孙海龙, 2021. 四川盆周山地5种典型林分土壤理化性质比较[J]. 南方农业, 15(4): 25-29. |
| ZENG Y L, LI S C, SUN H L, 2021. Comparison of soil physical and chemical properties of five typical forests in the mountainous regions around Sichuan Basin[J]. South China Agriculture, 15(4): 25-29. | |
| [60] | 朱宏光, 熊江波, 尤业民, 等, 2014. 不同更新方式巨尾桉林下植物群落变化及其环境解释[J]. 广西科学, 21(5): 469-476. |
| ZHU H G, XIONG J B, YOU Y M, et al., 2014. Changes in understory plant community of eucalyptus grandis×E. urophylla plantation in different regeneration modes and associated environment explanations[J]. Guangxi Sciences, 21(5): 469-476. | |
| [61] | 朱守谦, 杨世逸, 1987. 茂兰喀斯特森林科学考察集[M]. 贵阳: 贵州人民出版社: 210-224. |
| ZHU S Q, YANG S Y, 1987. Scientific survey of the Maolan Karst forest[M]. Guiyang: Guizhou People’s Publishing House: 210-224. |
| [1] | 杜丹丹, 高瑞忠, 房丽晶, 谢龙梅. 旱区盐湖盆地土壤重金属空间变异及对土壤理化因子的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(6): 1123-1132. |
| [2] | 李阳, 侯志勇, 陈薇, 于晓英, 谢永宏, 黄鑫, 谭佩阳, 李继承, 黎尚林, 杨辉. 大围山高山湿地植物多样性与区系组成研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 643-650. |
| [3] | 李善家, 王兴敏, 刘海锋, 孙梦格, 雷雨昕. 河西走廊荒漠植物多样性及其对环境因子的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 429-438. |
| [4] | 王哲, 田胜尼, 张永梅, 张和禹, 周忠泽. 巢湖派河口滩涂植物群落特征研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(9): 1823-1831. |
| [5] | 王礼霄, 刘晋仙, 柴宝峰. 华北亚高山土壤细菌群落及氮循环对退耕还草的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1537-1546. |
| [6] | 王磊, 温远光, 周晓果, 朱宏光, 孙冬婧. 尾巨桉与红锥混交对林下植被和土壤性质的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(7): 1340-1349. |
| [7] | 张博文, 秦娟, 任忠明, 陈子齐, 姚舜佳, 刘烨, 宋炎玉. 坡向对北亚热带区马尾松纯林及不同针阔混交林型林下植物多样性的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(6): 1091-1100. |
| [8] | 马辉英, 李昕竹, 马鑫钰, 贡璐. 新疆天山北麓中段不同植被类型下土壤有机碳组分特征及其影响因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(6): 1124-1131. |
| [9] | 段文军, 李达, 李冲. 5种不同林龄尾巨桉人工林林下植物多样性及其影响因素分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(5): 857-864. |
| [10] | 杨冲, 王春燕, 王文颖, 毛旭峰, 周华坤, 陈哲, 索南吉, 靳磊, 马华清. 青藏高原黄河源区高寒草地土壤营养特征变化及质量评价[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(5): 896-908. |
| [11] | 陈瑶, 李云红, 邵英男, 刘玉龙, 刘延坤. 阔叶红松林物种多样性与土壤理化特征研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 679-687. |
| [12] | 胡靓达, 周海菊, 黄永珍, 姚贤宇, 叶绍明, 喻素芳. 不同杉木林分类型植物多样性及其土壤碳氮关系的研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(3): 451-459. |
| [13] | 夏开, 邓鹏飞, 马锐豪, 王斐, 温正宇, 徐小牛. 马尾松次生林转换为湿地松和杉木林对土壤细菌群落结构和多样性的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(3): 460-469. |
| [14] | 玄锦, 李祖婵, 邹诚, 秦子博, 吴雅华, 黄柳菁. 江心洲景观类型和格局对植物多样性的多尺度影响——以闽江流域福州段为例[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(12): 2320-2330. |
| [15] | 韩鑫, 袁春阳, 李济宏, 洪宗文, 刘宣, 杜婷, 李晗, 游成铭, 谭波, 朱鹏, 徐振锋. 树种和土层对土壤无机氮的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(11): 2143-2151. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
