生态环境学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (8): 1561-1570.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2021.08.002
所属专题: 生物多样性专题汇编
收稿日期:2021-04-07
出版日期:2021-08-18
发布日期:2021-11-03
通讯作者:
* 朱军涛(1981年生),男,副研究员,博士,主要从事生态系统与全球变化生态学。E-mail: zhujt@igsnrr.ac.cn作者简介:宗宁(1987年生),男,副研究员,博士,主要从事高原生态学研究。E-mail: zongning@igsnrr.ac.cn
基金资助:
ZONG Ning1( ), SHI Peili1,2, ZHU Juntao1,*(
), SHI Peili1,2, ZHU Juntao1,*( )
)
Received:2021-04-07
Online:2021-08-18
Published:2021-11-03
摘要:
草地沙化是目前面临的重要环境问题,会对草原地区牧草生产与居民生活环境产生影响。目前对沙化草地的研究主要集中在植被与土壤性质的变化,对物种之间关系的变化并未进行深入探究。基于经典的生态位理论,利用空间代替时间序列的方法,通过调查高寒草地沿沙化梯度的植物群落变化特征,分析沙化演替过程中高寒草原植物群落构成、生态位宽度以及生态位重叠(O)的变化,探索沙化过程植物种群的资源利用状况及生态适应能力,以期为青藏高原高寒草原植物多样性维持机制与沙化草地植被恢复提供参考依据。结果发现,随着沙化程度的加重,群落盖度和地上生物量呈现逐渐降低的趋势。不同的是,物种丰富度、辛普森指数和香农-维纳指数的最大值出现在轻度沙化梯度,而后呈显著降低趋势(P<0.001),但Pielou指数在各沙化梯度间差异不显著(P=0.634)。通过计算重要值发现,沙化梯度之间群落结构变异较大。相关性分析发现,沙化过程物种生态位宽度与重要值呈饱和曲线关系。随着沙化程度的加重,生态位高度重叠(>0.9)和部分重叠(0.5<O≤0.9)的植物种对数逐渐降低,而中度重叠以下(≤0.5)的植物种对数则变化不大,这说明沙化程度加深导致的物种数减少会降低种群间资源利用的竞争。沙化程度的加重伴随土壤养分的减少,为降低对有限资源的竞争,植物种群间的资源利用呈现多样化。
中图分类号:
宗宁, 石培礼, 朱军涛. 高寒草地沙化过程植物群落构成及生态位特征变化[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(8): 1561-1570.
ZONG Ning, SHI Peili, ZHU Juntao. Changes of Plant Community Composition and Niche Characteristics during Desertification Process in An Alpine Steppe[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(8): 1561-1570.
| 沙化梯度Desertification gradient | 潜在沙化 Potential desertification | 轻度沙化 Light desertification | 中度沙化 Moderate desertification | 重度沙化 Heavy desertification | 极重度沙化 Severely heavy desertification |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 植被覆盖度 Vegetation cover | >50% | >30% | 10%‒30% | 5%‒10% | <5% |
| 裸地面积 Proportion of bare land | <10% | <20% | 20%‒30% | 30%‒50% | >50% |
| 优势物种 Dominant species | 紫花针茅 (Stipa purpurea)、多裂委陵菜 (Potentilla multifida)、 微孔草 (Microula sikkimensis) | 窄叶苔草 (Carex montis-everestii)、多裂委陵菜、羊茅 (Festuca ovina) | 紫花针茅、多裂委陵菜、冷地早熟禾 (Poa crymophila) | 紫花针茅、纤杆蒿(Artemisia demissa)、窄叶苔草 | 微孔草、平卧轴藜(Axyris prostrata) |
表1 不同沙化梯度高寒草地植物群落特征
Table 1 Characteristics of plant community in alpine grasslands with different desertification gradients
| 沙化梯度Desertification gradient | 潜在沙化 Potential desertification | 轻度沙化 Light desertification | 中度沙化 Moderate desertification | 重度沙化 Heavy desertification | 极重度沙化 Severely heavy desertification |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 植被覆盖度 Vegetation cover | >50% | >30% | 10%‒30% | 5%‒10% | <5% |
| 裸地面积 Proportion of bare land | <10% | <20% | 20%‒30% | 30%‒50% | >50% |
| 优势物种 Dominant species | 紫花针茅 (Stipa purpurea)、多裂委陵菜 (Potentilla multifida)、 微孔草 (Microula sikkimensis) | 窄叶苔草 (Carex montis-everestii)、多裂委陵菜、羊茅 (Festuca ovina) | 紫花针茅、多裂委陵菜、冷地早熟禾 (Poa crymophila) | 紫花针茅、纤杆蒿(Artemisia demissa)、窄叶苔草 | 微孔草、平卧轴藜(Axyris prostrata) |
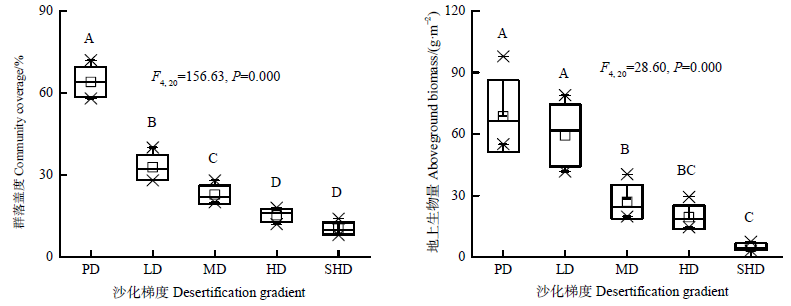
图1 沙化过程植被群落盖度与地上生物量的变化 n=5;图中不同大写字母代表沙化梯度间差异显著;横坐标PD、LD、MD、HD、SHD分别代表潜在、轻度、中度、重度和极重度沙化高寒草地;下同
Fig. 1 Variations of plant community coverage and aboveground biomass under different desertification gradients n=5; Different capital letters indicate significant differences between different desertification gradients. The abscissas PD, LD, MD, HD, and SHD represent native, mild, moderate, heavy and extremely heavy desertification gradients in alpine grasslands, respectively; similarly for the following figures
| 科 Family | 序号 No. | 植物种 Plant species | 重要值 Importance value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 潜在沙化Potential desertification | 轻度沙化Light desertification | 中度沙化Moderate desertification | 重度沙化Heavy desertification | 极重度沙化Severely heavy desertification | |||
| 禾本科 Gramineae | S1 | 紫花针茅 Stipa purpurea | 25.45 | 1.40 | 51.92 | 37.51 | 1.31 |
| S2 | 冷地早熟禾 Poa crymophila | 7.44 | 4.36 | 10.90 | 2.22 | ‒ | |
| S3 | 羊茅 Festuca ovina | 6.73 | 12.47 | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ | |
| S4 | 穗三毛 Trisetum spicatum | 5.32 | ‒ | ‒ | 3.80 | ‒ | |
| 莎草科 Cyperaceae | S5 | 窄叶苔草 Carex montis-everestii | 4.95 | 25.22 | 2.49 | 13.52 | ‒ |
| 豆科 Leguminosae | S6 | 丛生黄耆 Astragalus confertus | 1.85 | 3.35 | ‒ | 6.56 | ‒ |
| 蔷薇科 Rosaceae | S7 | 多裂委陵菜 Potentilla multifida | 22.96 | 24.15 | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ |
| S8 | 二裂委陵菜 Potentilla bifurca | 4.82 | 5.04 | 13.67 | ‒ | ‒ | |
| 菊科 Asteraceae | S9 | 青藏狗娃花 Heteropappus bowerii | 0.54 | ‒ | 10.45 | 4.49 | ‒ |
| S10 | 纤杆蒿 Artemisia demissa | 0.98 | 3.05 | 7.32 | 26.78 | ‒ | |
| S11 | 弱小火绒草 Leontopodium pusillum | 1.07 | 1.85 | ‒ | 0.64 | ‒ | |
| 龙胆科 Gentianaceae | S12 | 线叶龙胆 Gentiana farreri | 2.79 | 10.49 | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ |
| 紫草科 Boraginaceae | S13 | 微孔草 Microula sikkimensis | 12.88 | 4.38 | 2.96 | 4.47 | 54.24 |
| 景天科 Crassulaceae | S14 | 藏布红景天 Rhodiola sangpo-tibetana | 1.19 | 3.65 | 0.31 | ‒ | ‒ |
| 石竹科 Caryophyllaceae | S15 | 高山雪灵芝 Arenaria kansuensis | ‒ | 0.40 | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ |
| 伞形科 Umbelliferae | S16 | 棱子芹 Pleurospermum camtschaticum | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ |
| 藜科 Chenopodiaceae | S17 | 平卧轴藜 Axyris prostrata | 1.05 | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ | 44.45 |
表2 不同沙化梯度主要植物种重要值
Table 2 Importance value of plant species under different desertification gradients in alpine grasslands
| 科 Family | 序号 No. | 植物种 Plant species | 重要值 Importance value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 潜在沙化Potential desertification | 轻度沙化Light desertification | 中度沙化Moderate desertification | 重度沙化Heavy desertification | 极重度沙化Severely heavy desertification | |||
| 禾本科 Gramineae | S1 | 紫花针茅 Stipa purpurea | 25.45 | 1.40 | 51.92 | 37.51 | 1.31 |
| S2 | 冷地早熟禾 Poa crymophila | 7.44 | 4.36 | 10.90 | 2.22 | ‒ | |
| S3 | 羊茅 Festuca ovina | 6.73 | 12.47 | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ | |
| S4 | 穗三毛 Trisetum spicatum | 5.32 | ‒ | ‒ | 3.80 | ‒ | |
| 莎草科 Cyperaceae | S5 | 窄叶苔草 Carex montis-everestii | 4.95 | 25.22 | 2.49 | 13.52 | ‒ |
| 豆科 Leguminosae | S6 | 丛生黄耆 Astragalus confertus | 1.85 | 3.35 | ‒ | 6.56 | ‒ |
| 蔷薇科 Rosaceae | S7 | 多裂委陵菜 Potentilla multifida | 22.96 | 24.15 | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ |
| S8 | 二裂委陵菜 Potentilla bifurca | 4.82 | 5.04 | 13.67 | ‒ | ‒ | |
| 菊科 Asteraceae | S9 | 青藏狗娃花 Heteropappus bowerii | 0.54 | ‒ | 10.45 | 4.49 | ‒ |
| S10 | 纤杆蒿 Artemisia demissa | 0.98 | 3.05 | 7.32 | 26.78 | ‒ | |
| S11 | 弱小火绒草 Leontopodium pusillum | 1.07 | 1.85 | ‒ | 0.64 | ‒ | |
| 龙胆科 Gentianaceae | S12 | 线叶龙胆 Gentiana farreri | 2.79 | 10.49 | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ |
| 紫草科 Boraginaceae | S13 | 微孔草 Microula sikkimensis | 12.88 | 4.38 | 2.96 | 4.47 | 54.24 |
| 景天科 Crassulaceae | S14 | 藏布红景天 Rhodiola sangpo-tibetana | 1.19 | 3.65 | 0.31 | ‒ | ‒ |
| 石竹科 Caryophyllaceae | S15 | 高山雪灵芝 Arenaria kansuensis | ‒ | 0.40 | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ |
| 伞形科 Umbelliferae | S16 | 棱子芹 Pleurospermum camtschaticum | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ |
| 藜科 Chenopodiaceae | S17 | 平卧轴藜 Axyris prostrata | 1.05 | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ | 44.45 |
| 科 Family | 序号 No. | 植物种 Plant species | 生态位Niche breadth | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 潜在沙化Potential desertification | 轻度沙化 Light desertification | 中度沙化Moderate desertification | 重度沙化 Heavy desertification | 极重度沙化Severely heavy desertification | |||
| 禾本科 Gramineae | S1 | 紫花针茅 Stipa purpurea | 0.898 | 0.398 | 0.975 | 0.963 | 0.200 |
| S2 | 冷地早熟禾 Poa crymophila | 0.695 | 0.713 | 0.947 | 0.358 | ‒ | |
| S3 | 羊茅 Festuca ovina | 0.567 | 0.799 | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ | |
| S4 | 穗三毛 Trisetum spicatum | 0.394 | ‒ | ‒ | 0.394 | ‒ | |
| 莎草科 Cyperaceae | S5 | 窄叶苔草 Carex montis-everestii | 0.552 | 0.938 | 0.584 | 0.785 | ‒ |
| 豆科 Leguminosae | S6 | 丛生黄耆 Astragalus confertus | 0.336 | 0.384 | ‒ | 0.226 | ‒ |
| 蔷薇科 Rosaceae | S7 | 多裂委陵菜 Potentilla multifida | 0.851 | 0.924 | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ |
| S8 | 二裂委陵菜 Potentilla bifurca | 0.295 | 0.595 | 0.623 | ‒ | ‒ | |
| 菊科 Asteraceae | S9 | 青藏狗娃花 Heteropappus bowerii | 0.200 | ‒ | 0.790 | 0.384 | ‒ |
| S10 | 纤杆蒿 Artemisia demissa | 0.400 | 0.763 | 0.700 | 0.780 | ‒ | |
| S11 | 弱小火绒草 Leontopodium pusillum | 0.309 | 0.270 | ‒ | 0.200 | ‒ | |
| 龙胆科 Gentianaceae | S12 | 线叶龙胆 Gentiana farreri | 0.458 | 0.837 | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ |
| 紫草科 Boraginaceae | S13 | 微孔草 Microula sikkimensis | 0.638 | 0.506 | 0.375 | 0.526 | 0.971 |
| 景天科 Crassulaceae | S14 | 藏布红景天 Rhodiola sangpo-tibetana | 0.506 | 0.779 | 0.200 | ‒ | ‒ |
| 石竹科 Caryophyllaceae | S15 | 高山雪灵芝 Arenaria kansuensis | ‒ | 0.400 | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ |
| 伞形科 Umbelliferae | S16 | 棱子芹 Pleurospermum camtschaticum | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ |
| 藜科 Chenopodiaceae | S17 | 平卧轴藜 Axyris prostrata | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ | 0.950 |
表3 不同沙化梯度主要植物种类生态位宽度
Table 3 Niche breadth of plant species under different desertification gradients in alpine grasslands
| 科 Family | 序号 No. | 植物种 Plant species | 生态位Niche breadth | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 潜在沙化Potential desertification | 轻度沙化 Light desertification | 中度沙化Moderate desertification | 重度沙化 Heavy desertification | 极重度沙化Severely heavy desertification | |||
| 禾本科 Gramineae | S1 | 紫花针茅 Stipa purpurea | 0.898 | 0.398 | 0.975 | 0.963 | 0.200 |
| S2 | 冷地早熟禾 Poa crymophila | 0.695 | 0.713 | 0.947 | 0.358 | ‒ | |
| S3 | 羊茅 Festuca ovina | 0.567 | 0.799 | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ | |
| S4 | 穗三毛 Trisetum spicatum | 0.394 | ‒ | ‒ | 0.394 | ‒ | |
| 莎草科 Cyperaceae | S5 | 窄叶苔草 Carex montis-everestii | 0.552 | 0.938 | 0.584 | 0.785 | ‒ |
| 豆科 Leguminosae | S6 | 丛生黄耆 Astragalus confertus | 0.336 | 0.384 | ‒ | 0.226 | ‒ |
| 蔷薇科 Rosaceae | S7 | 多裂委陵菜 Potentilla multifida | 0.851 | 0.924 | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ |
| S8 | 二裂委陵菜 Potentilla bifurca | 0.295 | 0.595 | 0.623 | ‒ | ‒ | |
| 菊科 Asteraceae | S9 | 青藏狗娃花 Heteropappus bowerii | 0.200 | ‒ | 0.790 | 0.384 | ‒ |
| S10 | 纤杆蒿 Artemisia demissa | 0.400 | 0.763 | 0.700 | 0.780 | ‒ | |
| S11 | 弱小火绒草 Leontopodium pusillum | 0.309 | 0.270 | ‒ | 0.200 | ‒ | |
| 龙胆科 Gentianaceae | S12 | 线叶龙胆 Gentiana farreri | 0.458 | 0.837 | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ |
| 紫草科 Boraginaceae | S13 | 微孔草 Microula sikkimensis | 0.638 | 0.506 | 0.375 | 0.526 | 0.971 |
| 景天科 Crassulaceae | S14 | 藏布红景天 Rhodiola sangpo-tibetana | 0.506 | 0.779 | 0.200 | ‒ | ‒ |
| 石竹科 Caryophyllaceae | S15 | 高山雪灵芝 Arenaria kansuensis | ‒ | 0.400 | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ |
| 伞形科 Umbelliferae | S16 | 棱子芹 Pleurospermum camtschaticum | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ |
| 藜科 Chenopodiaceae | S17 | 平卧轴藜 Axyris prostrata | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ | 0.950 |
| 植物种 Plant species | S1 | S2 | S3 | S4 | S5 | S6 | S7 | S8 | S9 | S10 | S11 | S12 | S13 | S14 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | ‒ | 0.685 | 0.660 | 0.718 | 0.530 | 0.609 | 0.811 | 0.410 | 0.657 | 0.607 | 0.660 | 0.818 | 0.669 | 0.517 |
| S2 | 0.542 | ‒ | 0.838 | 0.206 | 0.875 | 0.454 | 0.973 | 0.222 | 0.174 | 0.623 | 0.625 | 0.430 | 0.698 | 0.655 |
| S3 | 0.748 | 0.913 | ‒ | 0 | 0.590 | 0.791 | 0.895 | 0.147 | 0 | 0.761 | 0.371 | 0.922 | 0.250 | 0.961 |
| S4 | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ | 0.250 | 0 | 0.120 | 0.610 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.426 | 0 |
| S5 | 0.488 | 0.795 | 0.778 | ‒ | ‒ | 0.285 | 0.820 | 0.459 | 0 | 0.566 | 0.747 | 0.400 | 0.445 | 0.460 |
| S6 | 0.045 | 0.221 | 0.303 | ‒ | 0.714 | ‒ | 0.590 | 0.096 | 0 | 0.906 | 0.351 | 0.964 | 0.142 | 0.926 |
| S7 | 0.597 | 0.684 | 0.757 | ‒ | 0.968 | 0.743 | ‒ | 0.315 | 0.251 | 0.689 | 0.603 | 0.739 | 0.541 | 0.798 |
| S8 | 0.406 | 0.983 | 0.854 | ‒ | 0.741 | 0.455 | 0.595 | ‒ | 0 | 0.071 | 0 | 0.126 | 0.721 | 0.135 |
| S9 | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ | 0 | 0.285 | 0 | 0.674 | 0 |
| S10 | 0.301 | 0.816 | 0.670 | ‒ | 0.951 | 0.774 | 0.852 | 0.799 | ‒ | ‒ | 0.696 | 0.872 | 0.140 | 0.848 |
| S11 | 0.641 | 0.335 | 0.647 | ‒ | 0.312 | 0.161 | 0.445 | 0.221 | ‒ | 0.065 | ‒ | 0.336 | 0.266 | 0.344 |
| S12 | 0.705 | 0.803 | 0.869 | ‒ | 0.825 | 0.454 | 0.846 | 0.694 | ‒ | 0.726 | 0.856 | ‒ | 0.196 | 0.992 |
| S13 | 0.456 | 0.471 | 0.730 | ‒ | 0.592 | 0.675 | 0.658 | 0.421 | ‒ | 0.372 | 0.811 | 0.623 | ‒ | 0.216 |
| S14 | 0.511 | 0.723 | 0.666 | ‒ | 0.906 | 0.585 | 0.894 | 0.631 | ‒ | 0.889 | 0.581 | 0.370 | 0.682 | ‒ |
表4 植物物种间生态位重叠
Table 4 Plant niche overlap in potential and light desertification grasslands
| 植物种 Plant species | S1 | S2 | S3 | S4 | S5 | S6 | S7 | S8 | S9 | S10 | S11 | S12 | S13 | S14 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | ‒ | 0.685 | 0.660 | 0.718 | 0.530 | 0.609 | 0.811 | 0.410 | 0.657 | 0.607 | 0.660 | 0.818 | 0.669 | 0.517 |
| S2 | 0.542 | ‒ | 0.838 | 0.206 | 0.875 | 0.454 | 0.973 | 0.222 | 0.174 | 0.623 | 0.625 | 0.430 | 0.698 | 0.655 |
| S3 | 0.748 | 0.913 | ‒ | 0 | 0.590 | 0.791 | 0.895 | 0.147 | 0 | 0.761 | 0.371 | 0.922 | 0.250 | 0.961 |
| S4 | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ | 0.250 | 0 | 0.120 | 0.610 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.426 | 0 |
| S5 | 0.488 | 0.795 | 0.778 | ‒ | ‒ | 0.285 | 0.820 | 0.459 | 0 | 0.566 | 0.747 | 0.400 | 0.445 | 0.460 |
| S6 | 0.045 | 0.221 | 0.303 | ‒ | 0.714 | ‒ | 0.590 | 0.096 | 0 | 0.906 | 0.351 | 0.964 | 0.142 | 0.926 |
| S7 | 0.597 | 0.684 | 0.757 | ‒ | 0.968 | 0.743 | ‒ | 0.315 | 0.251 | 0.689 | 0.603 | 0.739 | 0.541 | 0.798 |
| S8 | 0.406 | 0.983 | 0.854 | ‒ | 0.741 | 0.455 | 0.595 | ‒ | 0 | 0.071 | 0 | 0.126 | 0.721 | 0.135 |
| S9 | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ | 0 | 0.285 | 0 | 0.674 | 0 |
| S10 | 0.301 | 0.816 | 0.670 | ‒ | 0.951 | 0.774 | 0.852 | 0.799 | ‒ | ‒ | 0.696 | 0.872 | 0.140 | 0.848 |
| S11 | 0.641 | 0.335 | 0.647 | ‒ | 0.312 | 0.161 | 0.445 | 0.221 | ‒ | 0.065 | ‒ | 0.336 | 0.266 | 0.344 |
| S12 | 0.705 | 0.803 | 0.869 | ‒ | 0.825 | 0.454 | 0.846 | 0.694 | ‒ | 0.726 | 0.856 | ‒ | 0.196 | 0.992 |
| S13 | 0.456 | 0.471 | 0.730 | ‒ | 0.592 | 0.675 | 0.658 | 0.421 | ‒ | 0.372 | 0.811 | 0.623 | ‒ | 0.216 |
| S14 | 0.511 | 0.723 | 0.666 | ‒ | 0.906 | 0.585 | 0.894 | 0.631 | ‒ | 0.889 | 0.581 | 0.370 | 0.682 | ‒ |
| 植物种 Plant species | S1 | S2 | S4 | S5 | S6 | S8 | S9 | S10 | S11 | S13 | S14 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | ‒ | 0.967 | ‒ | 0.709 | ‒ | 0.686 | 0.940 | 0.746 | ‒ | 0.666 | 0.503 |
| S2 | 0.476 | ‒ | ‒ | 0.670 | ‒ | 0.710 | 0.884 | 0.767 | ‒ | 0.700 | 0.466 |
| S4 | 0.642 | 0.271 | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ |
| S5 | 0.806 | 0.604 | 0.654 | ‒ | ‒ | 0.854 | 0.450 | 0.901 | ‒ | 0.005 | 0.577 |
| S6 | 0.384 | 0.898 | 0 | 0.433 | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ |
| S8 | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ | 0.449 | 0.988 | ‒ | 0.158 | 0.163 |
| S9 | 0.519 | 0.497 | 0 | 0.748 | 0.552 | ‒ | ‒ | 0.511 | ‒ | 0.786 | 0.420 |
| S10 | 0.910 | 0.237 | 0.627 | 0.720 | 0.039 | ‒ | 0 | ‒ | ‒ | 0.170 | 0.309 |
| S11 | 0.370 | 0.440 | 0.616 | 0.488 | 0 | ‒ | 0 | 0.539 | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ |
| S13 | 0.772 | 0.534 | 0.212 | 0.379 | 0.643 | ‒ | 0.136 | 0 | 0.432 | ‒ | 0.226 |
| S14 | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ |
表5 植物物种间生态位重叠
Table 5 Plant niche overlap in moderate and heavy desertification grasslands
| 植物种 Plant species | S1 | S2 | S4 | S5 | S6 | S8 | S9 | S10 | S11 | S13 | S14 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | ‒ | 0.967 | ‒ | 0.709 | ‒ | 0.686 | 0.940 | 0.746 | ‒ | 0.666 | 0.503 |
| S2 | 0.476 | ‒ | ‒ | 0.670 | ‒ | 0.710 | 0.884 | 0.767 | ‒ | 0.700 | 0.466 |
| S4 | 0.642 | 0.271 | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ |
| S5 | 0.806 | 0.604 | 0.654 | ‒ | ‒ | 0.854 | 0.450 | 0.901 | ‒ | 0.005 | 0.577 |
| S6 | 0.384 | 0.898 | 0 | 0.433 | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ |
| S8 | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ | 0.449 | 0.988 | ‒ | 0.158 | 0.163 |
| S9 | 0.519 | 0.497 | 0 | 0.748 | 0.552 | ‒ | ‒ | 0.511 | ‒ | 0.786 | 0.420 |
| S10 | 0.910 | 0.237 | 0.627 | 0.720 | 0.039 | ‒ | 0 | ‒ | ‒ | 0.170 | 0.309 |
| S11 | 0.370 | 0.440 | 0.616 | 0.488 | 0 | ‒ | 0 | 0.539 | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ |
| S13 | 0.772 | 0.534 | 0.212 | 0.379 | 0.643 | ‒ | 0.136 | 0 | 0.432 | ‒ | 0.226 |
| S14 | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ |
| 植物种 Plant species | S1 | S13 | S17 |
|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | ‒ | 0.443 | 0.380 |
| S13 | ‒ | ‒ | 0.927 |
| S17 | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ |
表6 极重度沙化草地植物生态位重叠
Table 6 Plant niche overlap in severely heavy desertification grassland
| 植物种 Plant species | S1 | S13 | S17 |
|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | ‒ | 0.443 | 0.380 |
| S13 | ‒ | ‒ | 0.927 |
| S17 | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ |
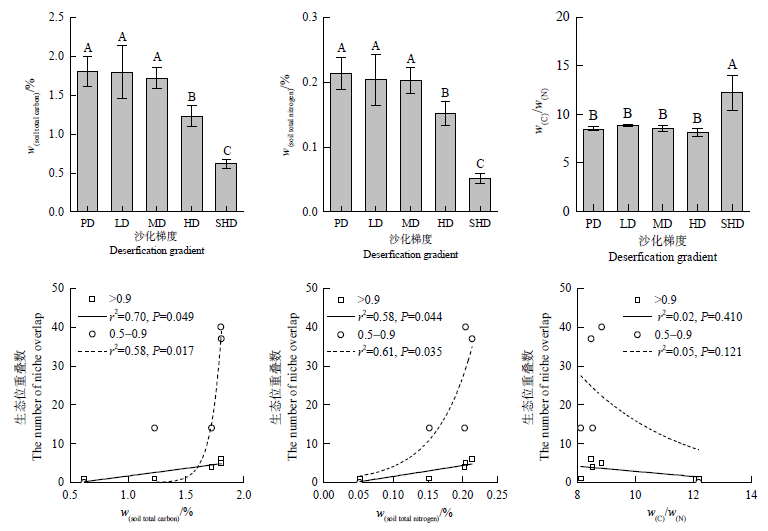
图4 土壤全碳、全氮含量以及碳氮比(n=5)与物种生态位重叠的关系
Fig. 4 Soil total carbon, total nitrogen content, carbon-nitrogen ratio (n=5) and the relationships with species niche overlap
| [1] |
BUCKLEY R, 1987. The effect of sparse vegetation on the transport of dune sand by wind[J]. Nature, 325(6103): 426-428.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
CHESSON P, 2000. Mechanisms of maintenance of species diversity[J]. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics, 31: 343-366.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
DONG J, CUI X, WANG S, et al., 2016. Changes in biomass and quality of alpine steppe in response to N & P fertilization in the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Plos One, 11(5): e0156146.
DOI URL |
| [4] | DREGNE H E, 1994. Land degradation in the worlds arid zones[C]// In Soil and water science: Key to understanding our global environment, Symposium on Soil and Water Science-Key to Understanding Our Global Environment. Cincinnati, OH: SOIL SCI SOC AMER: 53-58. |
| [5] |
GRINNELL J, 1917. Field tests of theories concerning distributional control[J]. American Naturalist, 51: 115-128.
DOI URL |
| [6] | LEVINS R, 1968. Evolution in Changing Environments - Some Theoretical Explorations[M]. Princeton: Princeton University Press. |
| [7] |
MA L, WANG Q, SHEN S T, et al., 2020. Heterogeneity of soil structure and fertility during desertification of alpine grassland in northwest Sichuan[J]. Ecosphere, DOI: 10.1002/ecs2.3161.
DOI |
| [8] |
PENG F, XUE X, YOU Q G, et al., 2020. Change in the trade-off between aboveground and belowground biomass of alpine grassland: Implications for the land degradation process[J]. Land Degradation and Development, 31(1): 105-117.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
ZONG N, SHI P, 2020. Soil properties rather than plant production strongly impact soil bacterial community diversity along a desertification gradient on the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Grassland Science, 66(4): 197-206.
DOI URL |
| [10] | 陈林, 辛佳宁, 苏莹, 等, 2019. 异质生境对荒漠草原植物群落组成和种群生态位的影响[J]. 生态学报, 39(17): 6187-6205. |
| CHEN L, XIN J N, SU Y, et al., 2019. Effects of heterogeneous habitats on community composition and niche characteristics of different plant populations in the desert steppe of China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 39(17): 6187-6205. | |
| [11] | 陈文业, 张瑾, 戚登臣, 等, 2013. 黄河首曲-玛曲县高寒草甸沙化动态演变趋势及其驱动因子定量分析[J]. 草业学报, 22(2): 11-21. |
| CHEN W Y, ZHANG J, QI D C, et al., 2013. Desertification dynamic change trend and quantitative analysis of driving factors of alpine meadow in Maqu County in the first meander of the Yellow River[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 22(2): 11-21. | |
| [12] | 程中秋, 张克斌, 常进, 等, 2010. 宁夏盐池不同封育措施下的植物生态位研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 19(7): 1537-1542. |
| CHENG Z Q, ZHANG K B, CHANG J, et al., 2010. Vegetable niche of different enclosure measures in Yanchi county, Ningxia[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 19(7): 1537-1542. | |
| [13] | 段敏杰, 高清竹, 万运帆, 等, 2010. 放牧对藏北紫花针茅高寒草原植物群落特征的影响[J]. 生态学报, 30(14): 3892-3900. |
| DUAN M J, GAO Q Z, WAN Y F, et al., 2010. Effect of grazing on community characteristics and species diversity of Stipa purpurea alpine grassland in Northern Tibet[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 30(14): 3892-3900. | |
| [14] | 国家林业局, 2015. 第五次中国荒漠化和沙化状况公报[R/OL].(2015.12.29) [2021-8-20]. http://www.forestry.gov.cn/main/58/content-832363.html. |
| National Forestry Administration, 2015. The 5th China Desertification and Desertification Communiqué[R/OL].(2015.12.29) [2021-8-20]. http://www.forestry.gov.cn/main/58/content-832363.html. | |
| [15] | 韩光中, 屈建军, 俎瑞平, 2014. 安多县沙漠化过程中土壤理化性质的演变特征[J]. 土壤通报, 45(5): 1032-1037. |
| HAN G Z, QU J J, ZU R P, 2014. Evolution characteristics of soil properties during desertification progress in Amdo County[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 45(5): 1032-1037. | |
| [16] | 何芳兰, 金红喜, 王锁民, 等, 2016. 沙化对玛曲高寒草甸土壤微生物数量及土壤酶活性的影响[J]. 生态学报, 36(18): 5876-5883. |
| HE F L, JIN H X, WANG S M, et al., 2016. Effect of desertification on soil microbial biomass and enzyme activities in Maqu alpine meadow[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 36(18): 5876-5883. | |
| [17] | 金红喜, 何芳兰, 李昌龙, 等, 2015. 玛曲沙化高寒草甸植被、土壤理化性质及土壤微生物数量研究[J]. 草业学报, 24(11): 20-28. |
| JIN H X, HE F L, LI C L, et al., 2015. Vegetation characteristics, abundance of soil microbes, and soil physico-chemical properties in desertified alpine meadows of Maqu[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 24(11): 20-28. | |
| [18] | 李昌龙, 徐先英, 金红喜, 等, 2014. 玛曲高寒草甸沙化过程中群落结构与植物多样性[J]. 生态学报, 34(14): 3953-3961. |
| LI C L, XU X Y, JIN H X, et al., 2014. Community structures and plant diversities in the desertification process of Maqu Alpine Meadow in Gansu[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 34(14): 3953-3961. | |
| [19] | 李军玲, 张金屯, 2006. 太行山中段植物群落优势种生态位研究[J]. 植物研究, 26(2): 2156-2162. |
| LI J L, ZHANG J T, 2006. Niche of dominant species in the Midst of Taihang Mountain[J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 26(2): 156-162. | |
| [20] | 李森, 杨萍, 高尚玉, 等, 2004. 近10年西藏高原土地沙漠化动态变化与发展态势[J]. 地球科学进展, 19(1): 63-70. |
| LI S, YANG P, GAO S Y, et al., 2004. Dynamic changes and developmental trends of the land desertification in Tibetan Plateau over the past 10 years[J]. Advance in Earth Sciences, 19(1): 63-70. | |
| [21] | 李中林, 秦卫华, 周守标, 等, 2014. 围栏封育下华北半干旱草原植物生态位研究[J]. 草地学报, 22(6): 1186-1193. |
| LI Z L, QIN W H, ZHOU S B, et al., 2014. Study on plant niche under fencing measures in the semi-arid grassland of North China[J]. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 22(6): 1186-1193. | |
| [22] | 聂莹莹, 徐丽君, 辛晓平, 等, 2020. 围栏封育对温性草甸草原植物群落构成及生态位特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 29(11): 11-22. |
| NIE Y Y, XU L J, XIN X P, et al., 2020. Effects of fence enclosure on the plant community composition and niche characteristics in a temperate meadow steppe[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 29(11): 11-22. | |
| [23] | 牛翠娟, 娄安如, 孙儒泳, 2015. 基础生态学[M]. 第3版. 北京: 高等教育出版社. |
| NIU C J, LOU A R, SUN R Y, 2015. Foundations in Ecology[M]. Beijing: 3 rd Edition. Higher Education Press. | |
| [24] | 牛叔文, 马利邦, 曾明明, 2008. 过牧对玛曲草地沙化的影响[J]. 生态学报, 28(1): 145-153. |
| NIU S W, MA L B, ZENG M M, 2008. Effect of overgrazing on grassland desertification in Maqu County[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 28(1): 145-153. | |
| [25] | 彭文俊, 王晓鸣, 2016. 生态位概念和内涵的发展及其在生态学中的定位[J]. 应用生态学报, 27(1): 327-334. |
| PENG W J, WANG X M, 2016, Concept and connotation development of niche and its ecological orientation[J]. The Journal of Applied Ecology, 27(1): 327-334. | |
| [26] | 戚登臣, 陈文业, 刘振恒, 等, 2011. 黄河首曲-玛曲县高寒草甸沙化演替进程中群落结构及种群生态位特征[J]. 西北植物学报, 31(12): 2522-2531. |
| QI D C, CHEN W Y, LIU Z H, et al., 2011. Population structure and niche dynamics characteristics of plants communities in the sandy succession of Maqu alpine meadow in first meander of Yellow River[J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 31(12): 2522-2531. | |
| [27] | 舒向阳, 胡玉福, 蒋双龙, 等, 2016. 川西北沙化草地植被群落、土壤有机碳及微生物特征[J]. 草业学报, 25(4): 45-54. |
| SHU X Y, HU Y F, JIANG S L, et al., 2016. Plant community characteristics, soil organic carbon and soil biological properties of grassland desertification sites in Northwest Sichuan[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 25(4): 45-54. | |
| [28] |
孙鸿烈, 郑度, 姚檀栋, 等, 2012. 青藏高原国家生态安全屏障保护与建设[J]. 地理学报, 67(1): 3-12.
DOI |
| SUN H L, ZHENG D, YAO T D, et al., 2012. Protection and construction of the national ecological security shelter zone on Tibetan Plateau[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 67(1): 3-12. | |
| [29] | 王兮之, 李森, 何巧如, 等, 2009. 西藏沙漠化土地退化程度动态分析及其评价[J]. 中国水土保持 (7): 25-28. |
| WANG X Z, LI S, HE Q R, et al., 2009. Dynamic analysis and evaluation of the degree of desertification land in Tibet[J]. Soil and Water Conservation In China (7): 25-28. | |
| [30] | 魏兴琥, 李森, 杨萍, 等, 2007. 藏北高山嵩草草甸植被和多样性在沙漠化过程中的变化[J]. 中国沙漠, 27(5): 750-757. |
| WEI X H, LI S, YANG P, et al., 2007. Changes of vegetation and diversity of alpine Kobresia (Kobresia pygmaea) steppe meadow in desertification process in Northern Tibet Plateau[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 27(5): 750-757. | |
| [31] | 魏兴琥, 杨萍, 李森, 等, 2005. 西藏沙漠化典型分布区沙漠化过程中的生物生产力和物种多样性变化[J]. 中国沙漠, 25(5): 663-667. |
| WEI X H, YANG P, LI S, et al., 2005. Changes of bio-productivity and species diversity in process of desertification in typical desertified land, Tibet[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 25(5): 663-667. | |
| [32] | 郑度, 赵东升, 2017. 青藏高原的自然环境特征[J]. 科技导报, 35(6): 13-22. |
|
ZHENG D, ZHAO D S, 2017. Characteristics of natural environment of the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Science and Technology Review, 35(6): 13-22.
DOI URL |
|
| [33] | 朱灵, 李易, 杨婉秋, 等, 2021. 沙化对高寒草地土壤碳、氮、酶活性及细菌多样性的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 35(3): 350-358. |
| ZHU L, LI Y, YANG W Q, et al., 2021. Effect of desertification on soil carbon and nitrogen,enzyme activity and bacterial diversity in alpine grassland[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 35(3): 350-358. | |
| [34] | 字洪标, 阿的鲁骥, 刘敏, 等, 2016. 高寒草甸不同类型草地群落特征及优势种植物生态位差异[J]. 应用与环境生物学报, 22(4): 546-554. |
| ZI H B, ADE L J, LIU M, et al., 2016. Difference of community characteristics and niche of dominant species in different grassland types of alpine meadow[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology, 22(4): 546-554. | |
| [35] | 宗宁, 石培礼, 牛犇, 等, 2014. 氮磷配施对藏北退化高寒草甸群落结构和生产力的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 25(12): 3458-3468. |
| ZONG N, SHI P L, NIU B, et al., 2014. Effects of nitrogen and phosphorous fertilization on community structure and productivity of degraded alpine meadows in northern Tibet, China[J]. The Journal of Applied Ecology, 25(12): 3458-3468. | |
| [36] | 宗宁, 石培礼, 孙建, 2020. 高寒草地沙化过程植被与土壤特征变化的生态阈值估算[J]. 干旱区研究, 37(6): 1580-1589. |
| ZONG N, SHI P L, SUN J, 2020. Estimation of ecological thresholds in plant and soil properties during desertification in an alpine grassland[J]. Arid Zone Research, 37(6): 1580-1589. |
| [1] | 李海鹏, 黄月华, 孙晓东, 曹启民, 符芳兴, 孙楚涵. 海南农田不同质地砖红壤及其细菌群落与番茄青枯病发生的关联分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(6): 1062-1069. |
| [2] | 陈俊芳, 吴宪, 刘啸林, 刘娟, 杨佳绒, 刘宇. 不同土壤水分下元素化学计量对微生物多样性的塑造特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 898-909. |
| [3] | 姜永伟, 丁振军, 袁俊斌, 张峥, 李杨, 问青春, 王业耀, 金小伟. 辽宁省主要河流底栖动物群落结构及水质评价研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 969-979. |
| [4] | 李阳, 侯志勇, 陈薇, 于晓英, 谢永宏, 黄鑫, 谭佩阳, 李继承, 黎尚林, 杨辉. 大围山高山湿地植物多样性与区系组成研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 643-650. |
| [5] | 周沁苑, 董全民, 王芳草, 刘玉祯, 冯斌, 杨晓霞, 俞旸, 张春平, 曹铨, 刘文亭. 放牧方式对高寒草地瑞香狼毒根际土壤团聚体及有机碳特征的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 660-667. |
| [6] | 李善家, 王兴敏, 刘海锋, 孙梦格, 雷雨昕. 河西走廊荒漠植物多样性及其对环境因子的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 429-438. |
| [7] | 宋志斌, 周佳诚, 谭路, 唐涛. 高原河流着生藻类群落沿海拔梯度的变化特征--以西藏黑曲、雪曲为例[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(2): 274-282. |
| [8] | 张立进, 杜虎, 曾馥平, 黄国勤, 宋敏, 宋同清. 喀斯特峰丛洼地植被恢复过程中生产力与多样性关系探讨[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 26-35. |
| [9] | 李萍, 白小明, 陈鑫, 李娟霞, 冉福, 陈辉, 杨小妮, 康瑞卿. 白三叶入侵对禾本科草坪土壤特性和植物群落的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 70-79. |
| [10] | 王洁, 单燕, 马兰, 宋延静, 王向誉. 秸秆/生物质炭协同还田措施对黄河三角洲盐碱土壤的改良效果研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 90-98. |
| [11] | 张林, 周飘, 齐实, 张岱, 伍冰晨, 崔冉冉. 侧柏人工林林分空间结构对林下草本多样性的差异性影响及其关联度[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(9): 1794-1801. |
| [12] | 王哲, 田胜尼, 张永梅, 张和禹, 周忠泽. 巢湖派河口滩涂植物群落特征研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(9): 1823-1831. |
| [13] | 陈乐, 卫伟. 西北旱区典型流域土地利用与生境质量的时空演变特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(9): 1909-1918. |
| [14] | 王礼霄, 刘晋仙, 柴宝峰. 华北亚高山土壤细菌群落及氮循环对退耕还草的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1537-1546. |
| [15] | 周选博, 王晓丽, 马玉寿, 王彦龙, 罗少辉, 谢乐乐. 返青期休牧措施下高寒草甸主要植物种群的生态位变化特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1547-1555. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
