生态环境学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (1): 70-79.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2023.01.008
李萍( ), 白小明(
), 白小明( ), 陈鑫, 李娟霞, 冉福, 陈辉, 杨小妮, 康瑞卿
), 陈鑫, 李娟霞, 冉福, 陈辉, 杨小妮, 康瑞卿
收稿日期:2022-08-08
出版日期:2023-01-18
发布日期:2023-04-06
通讯作者:
*白小明(1969年生),教授,博士,研究方向为草坪科学。E-mail: baixm@gsau.edu.cn作者简介:李萍(1997年生),女,硕士研究生,研究方向为草坪科学。E-mail: 1364000397@qq.com
基金资助:
LI Ping( ), BAI Xiaoming(
), BAI Xiaoming( ), CHEN Xin, LI Juanxia, RAN Fu, CHEN Hui, YANG Xiaoni, KANG Ruiqing
), CHEN Xin, LI Juanxia, RAN Fu, CHEN Hui, YANG Xiaoni, KANG Ruiqing
Received:2022-08-08
Online:2023-01-18
Published:2023-04-06
摘要:
为了明晰白三叶入侵对禾本科草坪土壤和植物群落的影响,以白三叶(Trifolium repens)入侵禾本科草坪为研究对象,探究不同入侵程度(未入侵:N;轻度入侵:L;中度入侵:M;重度入侵:H)对土壤特性和植物群落的影响,为进一步了解外来植物入侵机制及禾本科草坪的建植养护提供理论依据。结果表明,(1)白三叶重度入侵显著降低了植物群落多样性指数。(2)同一土层,随白三叶入侵程度的增加,土壤有机碳(SOC)、全氮(TN)、铵态氮(AN)、硝态氮(NN)、速效磷(AP)含量及酶活性均增加,而土壤全磷(TP)含量减少;土壤特性表聚效应明显。(3)土壤脲酶(URE)、蔗糖酶(SUC)及过氧化氢酶(CAT)活性均与SOC、TN、AN、NN及AP含量呈极显著正相关,土壤磷酸酶(ALP)活性与SOC、TN、AN、NN及AP含量呈显著正相关,土壤SUC、ALP及CAT活性均与TP含量呈显著负相关。(4)土壤性质对植物群落的影响大小顺序为:URE>CAT>SUC>AP>TN>SOC>AN>ALP>TP>NN。白三叶入侵改变了禾本科草坪土壤特性,提高了土壤养分利用率,导致土壤更有利于白三叶的生长和竞争,从而破坏入侵区草坪植物群落多样性平衡。
中图分类号:
李萍, 白小明, 陈鑫, 李娟霞, 冉福, 陈辉, 杨小妮, 康瑞卿. 白三叶入侵对禾本科草坪土壤特性和植物群落的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 70-79.
LI Ping, BAI Xiaoming, CHEN Xin, LI Juanxia, RAN Fu, CHEN Hui, YANG Xiaoni, KANG Ruiqing. Effects of Trifolium repens Invasion on Soil Properties and Plant Communities of Gramineous Turfgrass[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(1): 70-79.
| 科 | 未入侵 | 轻度入侵 | 中度入侵 | 重度入侵 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 豆科 | 白三叶 Trifolium repens (19) | 白三叶 Trifolium repens (41) | 白三叶 Trifolium repens (76) | |
| 禾本科 | 草地早熟禾 Poa pratensis (113) | 草地早熟禾 Poa pratensis (96) | 草地早熟禾 Poa pratensis (82) | 草地早熟禾 Poa pratensis (58) |
| 黑麦草 Lolium perenne (26) | 黑麦草 Lolium perenne (17) | 黑麦草 Lolium perenne (32) | ||
| 马唐Digitaria sanguinalis(20) | 马唐 Digitaria sanguinalis (32) | |||
| 稗 Echinochloa crusgalli (18) | ||||
| 牛筋草 Eleusine indica (4) | ||||
| 菊科 | 蒲公英 Taraxacum mongolicum (25) | 蒲公英 Taraxacum mongolicum (16) | 蒲公英 Taraxacum mongolicum (25) | |
| 苣荬菜 Sonchus arvensis (10) | 苣荬菜 Sonchus arvensis (20) | 苣荬菜 Sonchus arvensis (9) | ||
| 黄鹌菜 Youngia japonica (15) | ||||
| 小飞蓬 Conyza Canadensis (7) | 小飞蓬 Conyza Canadensis (18) | |||
| 旋花科 | 田旋花 Convolvulus arvensis (12) | 田旋花 Convolvulus arvensis (14) | ||
| 蓼科 | 酸模 Rumex acetosa (18) | 酸模 Rumex acetosa (25) | ||
| 合计 | 6种, 212株 | 7种, 185株 | 10种, 304株 | 4种, 147株 |
表1 白三叶入侵下禾本科草坪群落植物物种组成
Table 1 The composition of plant species in gramineous turfgrass communities under Trifolium repens invasion
| 科 | 未入侵 | 轻度入侵 | 中度入侵 | 重度入侵 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 豆科 | 白三叶 Trifolium repens (19) | 白三叶 Trifolium repens (41) | 白三叶 Trifolium repens (76) | |
| 禾本科 | 草地早熟禾 Poa pratensis (113) | 草地早熟禾 Poa pratensis (96) | 草地早熟禾 Poa pratensis (82) | 草地早熟禾 Poa pratensis (58) |
| 黑麦草 Lolium perenne (26) | 黑麦草 Lolium perenne (17) | 黑麦草 Lolium perenne (32) | ||
| 马唐Digitaria sanguinalis(20) | 马唐 Digitaria sanguinalis (32) | |||
| 稗 Echinochloa crusgalli (18) | ||||
| 牛筋草 Eleusine indica (4) | ||||
| 菊科 | 蒲公英 Taraxacum mongolicum (25) | 蒲公英 Taraxacum mongolicum (16) | 蒲公英 Taraxacum mongolicum (25) | |
| 苣荬菜 Sonchus arvensis (10) | 苣荬菜 Sonchus arvensis (20) | 苣荬菜 Sonchus arvensis (9) | ||
| 黄鹌菜 Youngia japonica (15) | ||||
| 小飞蓬 Conyza Canadensis (7) | 小飞蓬 Conyza Canadensis (18) | |||
| 旋花科 | 田旋花 Convolvulus arvensis (12) | 田旋花 Convolvulus arvensis (14) | ||
| 蓼科 | 酸模 Rumex acetosa (18) | 酸模 Rumex acetosa (25) | ||
| 合计 | 6种, 212株 | 7种, 185株 | 10种, 304株 | 4种, 147株 |
| 入侵程度 | 辛普森多样性指数 (P) | 香农-维纳多样性指数 (H) | 均匀度指数 (E) | 丰富度指数 (D) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 未入侵 | 0.66±0.03b | 1.41±0.07b | 0.79±0.04b | 0.93±0.01c |
| 轻度入侵 | 0.69±0.01b | 1.52±0.02b | 0.78±0.01b | 1.15±0.02b |
| 中度入侵 | 0.86±0.02a | 1.98±0.01a | 0.86±0.02a | 1.63±0.06a |
| 重度入侵 | 0.57±0.01c | 0.99±0.01c | 0.71±0.01c | 0.60±0.01d |
表2 白三叶入侵对禾本科草坪植物群落多样性的影响
Table 2 Effects of Trifolium repens invasion on gramineous turfgrass plant community diversity
| 入侵程度 | 辛普森多样性指数 (P) | 香农-维纳多样性指数 (H) | 均匀度指数 (E) | 丰富度指数 (D) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 未入侵 | 0.66±0.03b | 1.41±0.07b | 0.79±0.04b | 0.93±0.01c |
| 轻度入侵 | 0.69±0.01b | 1.52±0.02b | 0.78±0.01b | 1.15±0.02b |
| 中度入侵 | 0.86±0.02a | 1.98±0.01a | 0.86±0.02a | 1.63±0.06a |
| 重度入侵 | 0.57±0.01c | 0.99±0.01c | 0.71±0.01c | 0.60±0.01d |
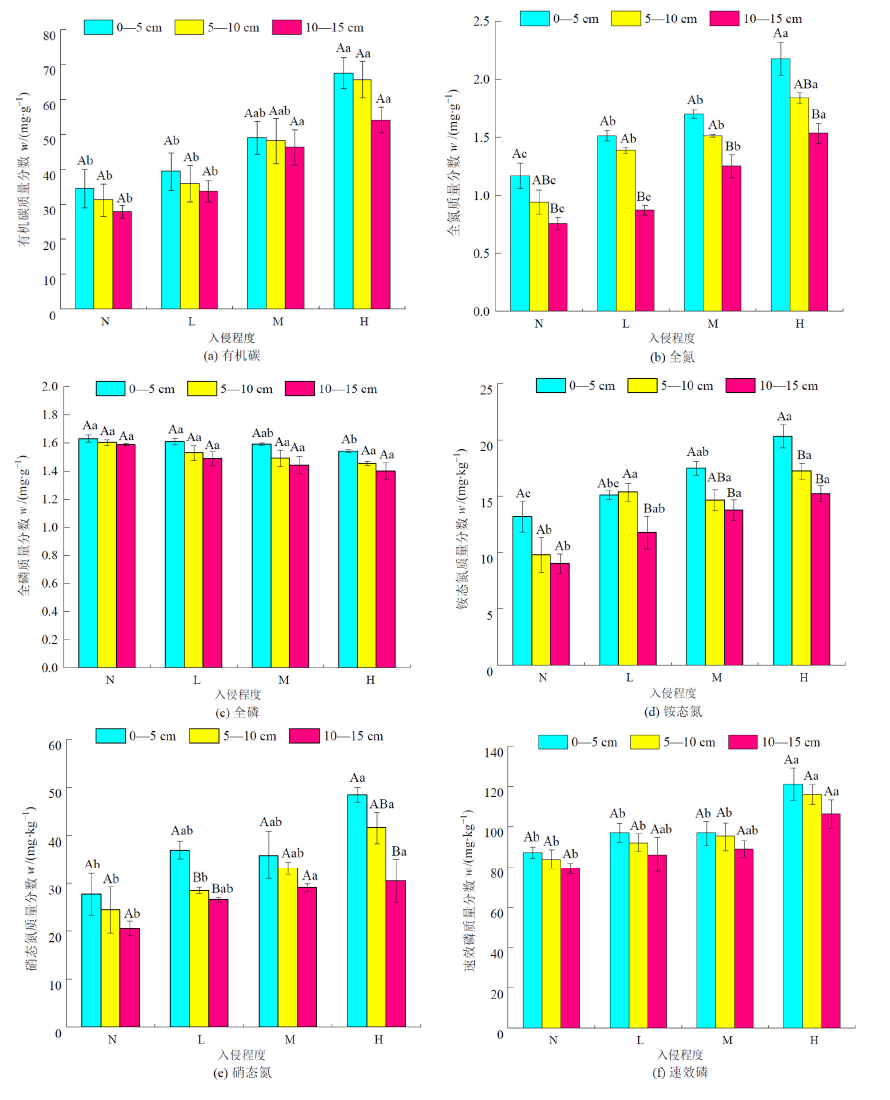
图1 白三叶入侵对禾本科草坪土壤养分的影响 平均值±标准误,n=3。不同大写字母表示同一入侵程度不同土层养分含量之间差异显著(P<0.05),不同小写字母表示同一土层不同入侵程度土壤养分含量之间差异显著(P<0.05)。下同
Figure 1 Effects of Trifolium repens invasion on gramineous turfgrass soil nutrients
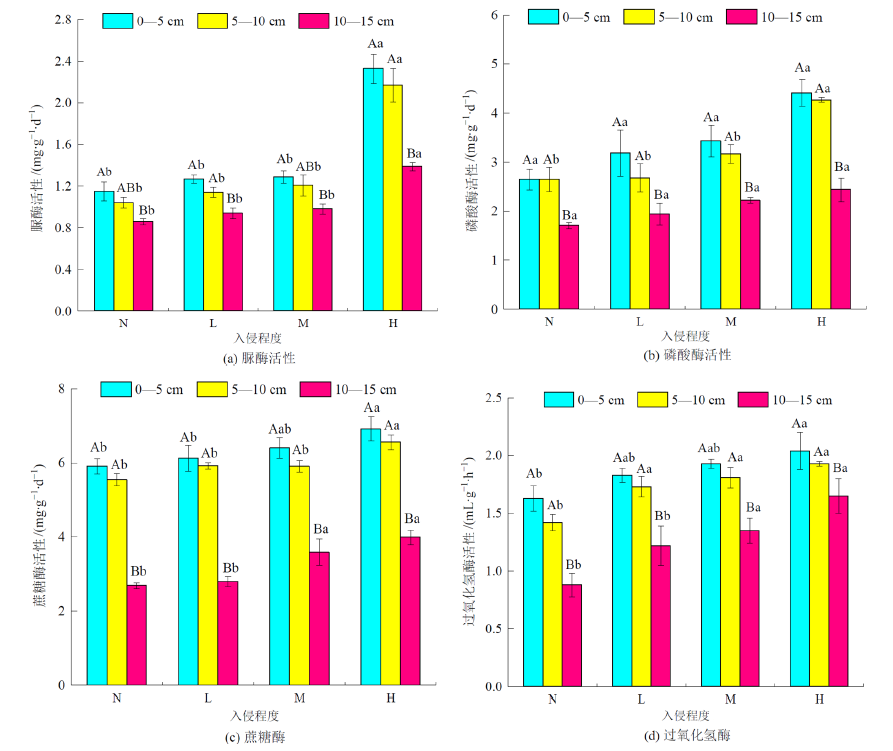
图2 白三叶入侵对禾本科草坪土壤酶活性的影响 平均值±标准误,n=3。不同小写字母表示同一土层不同入侵程度土壤酶活性之间差异显著(P<0.05),不同大写字母表示同一入侵程度不同土层土壤酶活性之间差异显著(P<0.05)
Figure 2 Effects of Trifolium repens invasion on gramineous turfgrass soil enzyme activities
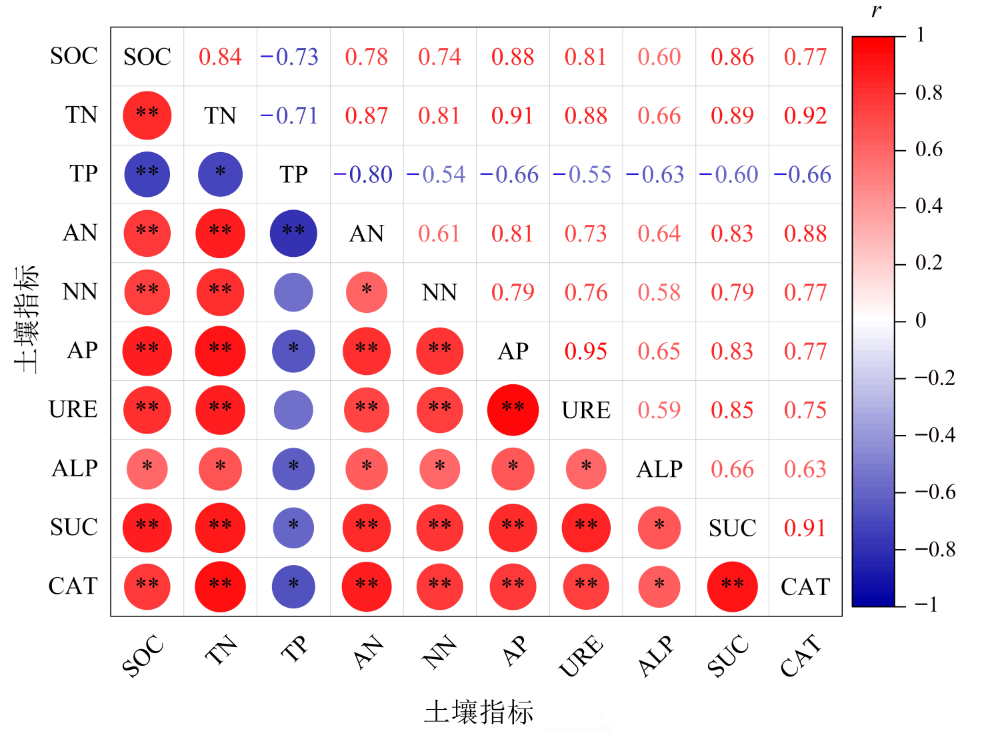
图3 土壤养分与酶活性的相关性 SOC:土壤有机碳;TN:全氮;TP:全磷;AN:铵态氮;NN:硝态氮;AP:速效磷;CAT:过氧化氢酶活性;ALP:碱性磷酸酶活性;SUC:蔗糖酶活性;URE:脲酶活性。*表示显著性相关(P<0.05);**表示极显著相关(P<0.01)。r图注表示?1—1的相关程度值,红色表示正向相关,蓝色表示负向相关,颜色越深则相应的正(负)相关性越大
Figure 3 Correlation between soil nutrients and enzyme activities
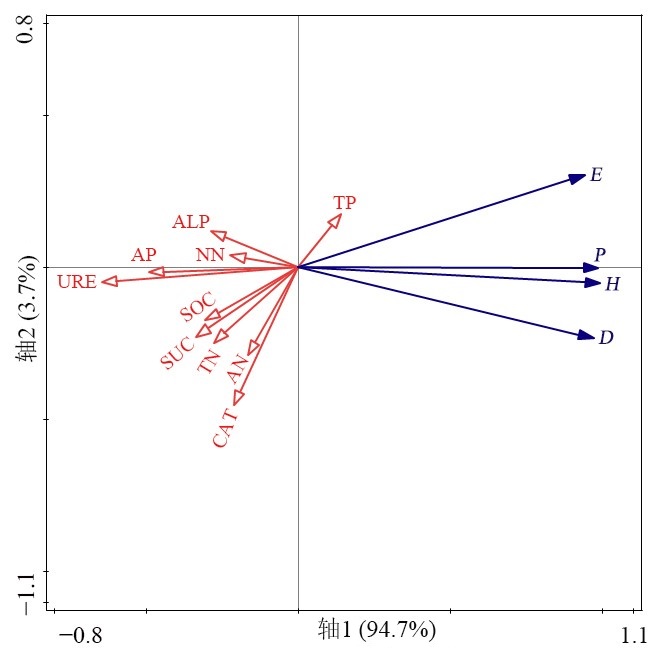
图4 土壤特性与草坪植物群落间的关系 SOC:土壤有机碳;TN:全氮;TP:全磷;AN:铵态氮;NN:硝态氮;AP:速效磷;CAT:过氧化氢酶活性;ALP:碱性磷酸酶活性;SUC:蔗糖酶活性;URE:脲酶活性;P:辛普森多样性指数;H:香农-维纳多样性指数;E:均匀度指数;D:丰富度指数
Figure 4 Relationship between soil properties and turfgrass plant communities
| [1] |
CORBIN J D, D’ANTONIO C M, 2004. Effects of exotic species on soil nitrogen cycling: Implications for restoration[J]. Weed Technology, 18(sp1): 1464-1467.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
DUDA J J, FREEMAN D C, EMLEN J M, et al., 2003. Differences in native soil ecology associated with invasion of the exotic annual chenopod, Halogeton glomeratus[J]. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 38(2): 72-77.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
EHRENFELD J G, 2003. Effects of exotic plant invasions on soil nutrient cycling processes[J]. Ecosystems, 6(6): 503-523.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
EHRENFELD J G, SCOTT N, 2001. Invasive species and the soil: effects on organisms and ecosystem processes[J]. Ecological Applications, 11(5): 1259-1260.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
GRUBB P J, 1994. Root competition in soils of different fertility: A paradox resolved[J]. Phytocoenologia, 24(2): 495-505.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
POEPLAU C, BOLINDER M A, KIRCHMANN H, et al., 2016. Phosphorus fertilisation under nitrogen limitation can deplete soil carbon stocks-evidence from Swedish meta-replicated long-term field experiments[J]. Biogeosciences, 13(4): 1119-1127.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
RICE S K, WESTERMAN B, FEDERICI R, 2004. Impacts of the exotic, nitrogen-fixing black locust (Robinia pseudoacacia) on nitrogen-cycling in a pine-oak ecosystem[J]. Plant Ecology, 174(1): 97-107.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
VALLIERE J M, ALLEN E B, 2016. Nitrogen enrichment contributes to positive responses to soil microbial communities in three invasive plant species[J]. Biological Invasions, 18(8): 1-16.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
WALKER L R, VITOUSEK P M, 1991. An invader alters germination and growth of a native dominant tree in Hawaii[J]. Ecology, 72(4): 1449-1455.
DOI URL |
| [10] | WANG C Y, JIANG K, LIU J, et al., 2018. Moderate and heavy Solidago canadensis L. invasion are associated with decreased taxonomic diversity but increased functional diversity of plant communities in East China[J]. Ecological engineering: The Journal of Ecotechnology, 112: 55-64. |
| [11] |
WU H, CARILO J, DING J Q, 2017. Species diversity and environmental determinants of aquatic and terestrial communities invaded by Alternanthera philoxeroides[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 581-582: 666-675.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
ZHANG Y R, WANG R Q, KAPLAN D, et al., 2015. Which components of plant diversity are most correlated with ecosystem properties? A case study in a restored wetland in northern China[J]. Ecological Indicators, 49(2): 228-236.
DOI URL |
| [13] | 白静, 严锦钰, 何东进, 等, 2017. 互花米草入侵对闽东滨海湿地红树林土壤理化性质和酶活性的影响[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 39(1): 70-77. |
| BAI J, YAN J Y, HE D J, et al., 2017. Effects of Spartina alterniflora invasion in eastern Fujian coastal wetland on the physicochemical properties and enzyme activities of mangrove soil[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 39(1): 70-77. | |
| [14] | 鲍士旦, 2001. 土壤农化分析[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社. |
| BAO S D, 2001. Soil agrochemical analysis[M]. Beijing: China Agriculture Press. | |
| [15] | 曹慧, 孙辉, 杨浩, 等, 2003. 土壤酶活性及其对土壤质量的指示研究进展[J]. 应用与环境生物学报, 9(1): 105-109. |
| CAO H, SUN H, YANG H, et al., 2003. A reviewosoil enzyme activity and its indication for soil quality[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology, 9(1): 105-109. | |
| [16] |
曹婧, 徐晗, 潘绪斌, 等, 2020. 中国草地外来入侵植物现状研究[J]. 草地学报, 28(1): 1-11.
DOI |
| CAO J, XU H, PAN X B, et al., 2020. Study on the status of invasive plants in Chinese grassland[J]. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 28(1): 1-11. | |
| [17] |
戴莲, 李会娜, 蒋智林, 等, 2012. 外来植物紫茎泽兰入侵对根际土壤有益功能细菌群、酶活性和肥力的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 21(2): 237-242.
DOI URL |
| DAI L, LI H N, JIANG Z L, et al., 2012. Invasive effects of Ageratina adenophora (Asteraceae) on the changes of effective functional bacteria, enzyme activity and fertility in rhizosphere soil ecosystem[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 21(2): 237-242. | |
| [18] |
邓丹丹, 刘棋, 蒋智林, 等, 2015. 紫茎泽兰与不同植物群落土壤养分及酶活性差异[J]. 生态环境学报, 24(9): 1466-1471.
DOI URL |
| DEN D D, LIU Q, JIANG Z L, et al., 2015. Differences in soil enzymatic activities and soil nutrients of Ageratina adenophora and different plant communities[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 24(9): 1466-1471. | |
| [19] | 关松荫, 1986. 土壤酶及其研究法[M]. 北京: 农业出版社. |
| GUAN S Y, 1996. Soil enzymes and their research methods[M]. Beijing: Agriculture Press. | |
| [20] | 郭传友, 王中生, 方炎明, 2003. 外来种入侵与生态安全[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 27(2): 73-78. |
| GUO C Y, WANG Z S, FANG Y M, 2003. Exotic species invasion and ecological safety[J]. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition), 27(2): 73-78. | |
| [21] | 黄玉梅, 张凯, 孙凌霞, 等, 2018. 白三叶入侵对城市草坪生态系统土壤动物的影响[J]. 生态学报, 38(23): 8489-8499. |
| HUANG Y M, ZHANG K, SUN L X, et al., 2018. Effects of Trifolium repens invasion on soil animals in an urban turf ecosystem[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 38(23): 8489-8499. | |
| [22] | 蒋智林, 刘万学, 万方浩, 等, 2009. 马缨丹入侵对草坪土壤养分特征的影响[J]. 云南农业大学学报, 24(2): 159-163, 189. |
| JIANG Z L, LIU W X, WAN F H, et al., 2009. Effects of Lantana camara invasion on lawn soil nutrient properties[J]. Journal of Yunnan Agricultural University, 24(2): 159-163, 189. | |
| [23] | 柯展鸿, 邱佩霞, 胡东雄, 等, 2013. 三裂叶蟛蜞菊入侵对土壤酶活性和理化性质的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 22(3): 432-436. |
| KE Z H, QIU P X, HU D X, et al., 2013. Effects of Wedelia trilobata invasion on soil enzyme activities and physical-chemical properties[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 22(3): 432-436. | |
| [24] | 李会娜, 2009. 三种入侵菊科植物 (紫茎泽兰、豚草、黄顶菊) 与土壤微生物的互作关系[D]. 沈阳: 沈阳农业大学. |
| LI H N, 2009. Interactions between three invasive composite plants (Ageratina adenophora, Ambrosia artemisiifolia, Flaveria bidentis) and Soil Biota[D]. Shenyang: Shenyang Agricultural University. | |
| [25] | 李剑峰, 张淑卿, 师尚礼, 等, 2008. 白三叶对禾草草坪的侵占性研究[J]. 现代农业科技 (22): 93-94, 97. |
| LI J F, ZHANG S Q, SHI S L, et al., 2008. Study on the encroachment of Trifolium repens on grass lawn[J]. Modern Agricultural Science and Technology (22): 93-94, 97. | |
| [26] |
李晶晶, 丁立人, 李志华, 等, 2017. 白三叶水浸提液对无芒稗种子萌发和幼苗生长的影响[J]. 草地学报, 25(1): 82-91.
DOI |
| LI J J, DING L R, LI Z H, et al., 2017. Effects of aqueous extracts of Trifolium repens on seed germination and seedling growth of barnyardgrass[J]. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 25(1): 82-91. | |
| [27] | 李乔, 王月, 张玉曼, 等, 2013. 意大利苍耳入侵对土壤酶活与土壤肥力的影响[J]. 河北科技师范学院学报, 27(3): 6-9. |
| LI Q, WANG Y, ZHANG Y M, et al., 2013. Effects of Xanthium italicum Moretti invasion on soil enzyme activity and fertility[J]. Journal of Hebei Normal University of Science & Technology, 27(3): 6-9. | |
| [28] |
林丽, 代磊, 林泽北, 等, 2021. 黔中城市森林群落植物多样性及其与土壤理化性质的关系[J]. 生态环境学报, 30(11): 2130-2141.
DOI URL |
| LIN L, DAI L, LIN Z B, et al., 2021. Plant diversity and its relationship with soil physicochemical properties of urban forest communities in central Guizhou[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 30(11): 2130-2141. | |
| [29] | 林秦文, 肖翠, 马金双, 2022. 中国外来植物数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 30(5): 110-117. |
| LIN Q W, XIAO C, MA J S, 2022. A dataset on catalogue of alien plants in China[J]. Biodiversity Science, 30(5): 110-117. | |
| [30] | 林玥, 郝嘉琪, 王维钰, 等, 2019. 不同耕作措施对黄土高原区域大豆根际土壤微生物量、酶活性和养分的影响[J]. 西北农业学报, 28(4): 620-630. |
| LIN Y, HAO J Q, WANG W Y, et al., 2019. Effects of different tillage measures on soil microbial biomass, enzyme activities and nutrients in rhizosphere soil of the loess plateau[J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-occidentalis Sinica, 28(4): 620-630. | |
| [31] |
刘金平, 段婧, 2012. 丝茅入侵对高羊茅根系及土壤性状的影响[J]. 草地学报, 20(5): 870-875.
DOI |
| LIU J P, DUAN J, 2012. Dynamic analysis about traits of root and soil of the young Festuca arundinacea turf infested by Imperata koenigii[J]. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 20(5): 870-875. | |
| [32] |
刘小文, 周益林, 齐成媚, 等, 2012. 入侵植物薇甘菊对土壤养分和酶活性的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 21(12): 1960-1965.
DOI URL |
| LIU X W, ZHOU Y L, QI C M, et al., 2012. Effects of Mikania micrantha invasion on soil nutrient contents and enzyme activities[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 21(12): 1960-1965. | |
| [33] | 刘兴诏, 周国逸, 张德强, 等, 2010. 南亚热带森林不同演替阶段植物与土壤中N、P的化学计量特征[J]. 植物生态学报, 34(1): 64-71. |
| LIU X Z, ZHOU G Y, ZHANG D Q, et al., 2010. N and P stoichiometry of plant and soil in lower subtropical forest successional series in southern China[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 34(1): 64-71. | |
| [34] |
陆建忠, 裘伟, 陈家宽, 等, 2005. 入侵种加拿大一枝黄花对土壤特性的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 13(4): 347-356.
DOI |
|
LU J Z, QIU W, CHEN J K, et al., 2005. Impact of invasive species on soil properties: Canadian goldenrod (Solidago canadensis) as a case study[J]. Biodiversity Science, 13(4): 347-356.
DOI URL |
|
| [35] | 吕倩, 康文斯, 郭茂金, 等, 2019. 柏木人工林目标树经营初期对林下植物多样性及土壤理化性质的影响[J]. 应用与环境生物学报, 25(5): 1036-1043. |
| LÜ Q, KANG W S, GUO M J, et al., 2019. Early effects of target tree management on undergrowth plant diversity and soil physicochemical properties in Cupressus funebris plantations[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology, 25(5): 1036-1043. | |
| [36] |
马可心, 张梅, 方馨, 等, 2020. 入侵植物曼陀罗对本地植物功能性状和土壤碳、氮、磷化学计量特征的影响[J]. 植物研究, 40(6): 867-875.
DOI |
| MA K X, ZHANG M, FANG X, et al., 2020. Effects of invasive plant Datura stramonium on the functional traits of native plants and the stoichiometric characteristics of soil carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus[J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 40(6): 867-875. | |
| [37] | 祁小旭, 张思宇, 林峰, 等, 2019. 黄顶菊对不同入侵地植物群落及土壤微生物群落的影响[J]. 生态学报, 39(22): 8472-8482. |
| QI X X, ZHANG S Y, LIN F, et al., 2019. Effect of Flaveria bidentis invasion on plant community and soil microbial community of different invaded soil[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 39(22): 8472-8482. | |
| [38] | 王进军, 2005. 紫茎泽兰[C]//万方浩, 郑小波, 郭建英. 重要农林外来入侵物种的生物学与控制. 北京: 科学出版社: 650-661. |
| WANG J J, 2005. Euphorum adenophorum[C]//Wan F H, ZHENG X B, GUO J Y. Biology and control of important alien invasive species in agriculture and forestry. Beijing: Science Press: 650-661. | |
| [39] | 王桔红, 陈文, 张燕芳, 等, 2020. 不同入侵程度的微甘菊及本土种豨莶碳氮磷化学计量特征与营养策略[J]. 生态学杂志, 39(6): 1994-2003. |
| WANG J H, CHEN W, ZHANG Y F, et al., 2020. Carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus stoichiometry and nutrition strategy of invasive species Mikania micrantha with three invasive degrees and native species Siegesbeckia orientalis[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 39(6): 1994-2003. | |
| [40] | 王伟东, 王渭玲, 徐福利, 等, 2015. 秦岭西部中幼龄华北落叶松林地土壤养分与酶活性特征研究[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 21(4): 1032-1039. |
| WANG W D, WANG W L, XU F L, et al., 2015. Characteristics of soil nutrients and enzyme activities in young and middle aged Larix principis-rupprechtii plantation in western Qinling Mountains[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 21(4): 1032-1039. | |
| [41] | 吴邦灿, 费龙, 2014. 现代环境检测技术[M]. 北京: 中国环境出版社. |
| WU B C, FEI L, 2014. Modern environmental detection technology[M]. Beijing: China Environmental Press. | |
| [42] | 吴榕, 陈雅君, 闫永庆, 等, 2014. 白三叶浸提液对四种杂草种子萌发和幼苗生理指标的影响[J]. 中国草地学报, 36(2): 104-107, 116. |
| WU R, CHEN Y J, YAN Y Q, et al., 2014. Study of allelopathy effects of Trifolium repens on the germination and seedling’s physiology of 4 kinds of weeds[J]. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 36(2): 104-107, 116. | |
| [43] | 吴天马, 丁晖, 刘志磊, 等, 2007. 外来入侵植物紫茎泽兰对土壤养分的影响[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 23(2): 94-96. |
| WU T M, DING H, LIU Z L, et al., 2007. Effects of alien invasive plant Eupatorium adenophorum on soil nutrients[J]. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 23(2): 94-96. | |
| [44] | 谢苑, 高素萍, 2008. 白三叶水浸液对高羊茅种子萌发及幼苗生长的影响[J]. 安徽农业科学, 36(9): 3616-3618. |
| XIE Y, GAO S P, 2008. Effect of Trifolium repens infusion on the seed germination and seedling growth of Festuca arundinacea[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 36(9): 3616-3618. | |
| [45] | 邢小姣, 2016. 白三叶人工种子制作技术研究[D]. 乌鲁木齐: 新疆农业大学. |
| XING X J, 2016. Study on the preparation technique on artificial seeds of Trifolium repens[D]. Urumqi: Xinjiang Agricultural University. | |
| [46] | 徐海根, 强胜, 2004. 中国外来入侵物种编目[M]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社. |
| XU H G, QIANG S, 2004. Cataloguing of invasive alien species in China[M]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press. | |
| [47] | 杨祥波, 李玉玺, 范嘉妍, 等, 2019. 不同施氮水平玉米单作和间作白三叶对白浆土腐殖质组成的影响[J]. 南京农业大学学报, 42(5): 887-894. |
| YANG X B, LI Y X, FAN J Y, et al., 2019. Effects of corn monocropping and intercropping with Trifolium repens on humus composition of Albic soil under different N levels[J]. Journal of Nanjing Agricultural University, 42(5): 887-894. | |
| [48] | 于兴军, 于丹, 卢志军, 等, 2005. 一个可能的植物入侵机制: 入侵种通过改变入侵地土壤微生物群落影响本地种的生长[J]. 科学通报, 50(9): 896-903. |
|
YU X J, YU D, LU Z J, et al., 2005. A possible mechanism of plant invasion: Invasive species by altering the soil of the invasive site microbiome influences growth of native species[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 50(9): 896-903.
DOI URL |
|
| [49] | 余婷, 2013. 白三叶根系分泌物的化感作用研究[D]. 西安: 西北农林科技大学. |
| YU T, 2013. Study on allelopathy of Trifolium repens root exudates[D]. Xi’an: North West Agriculture and Forestry University. | |
| [50] | 张桂花, 彭少麟, 李光义, 等, 2009. 外来入侵植物与地下生态系统相互影响的研究进展[J]. 中国农学通报, 25(14): 246-251. |
| ZHANG G H, PENG S L, LI G Y, et al., 2009. Recent advances in the interaction between invasive plants and below ground ecosystem[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 25(14): 246-251. | |
| [51] | 张天瑞, 皇甫超河, 白小明, 等, 2010. 黄顶菊入侵对土壤养分和酶活性的影响[J]. 生态学杂志, 29(7): 1353-1358. |
| ZHANG T R, HUNG F C H, BAI X M, et al., 2010. Effects of Flaveria bidentis invasion on soil nutrient contents and enzyme activities[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 29(7): 1353-1358. | |
| [52] | 赵晓红, 张国良, 张瑞海, 等, 2017. 刺萼龙葵入侵对不同生境土壤特征的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 26(6): 924-930. |
| ZHAO X H, ZHANG G L, ZHANG R H, et al., 2017. Effects of Solanum rostratum invasion on soil characteristics in different habitats[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 26(6): 924-930. | |
| [53] | 朱美玲, 贡璐, 张龙龙, 2015. 塔里木河上游典型绿洲土壤酶活性与环境因子相关分析[J]. 环境科学, 36(7): 2678-2685. |
| ZHU M L, GONG L, ZHANG L L, 2015. Soil enzyme activities and their relationships to environmental factors in a typical oasis in the upper reaches of the Tarim River[J]. Environmental Science, 36(7): 2678-2685. | |
| [54] |
朱珠, 包维楷, 庞学勇, 等, 2006. 旅游干扰对九寨沟冷杉林下植物种类组成及多样性的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 14(4): 284-291.
DOI |
|
ZHU Z, BAO W K, PANG X Y, et al., 2006. Tourism effect on species composition and diversity of understory plants in Abiesfargesii var. faxoniana forest in Jiuzhaigou, Sichuan[J]. Biodiversity Science, 14(4): 284-291.
DOI URL |
|
| [55] | 宗盛伟, 许嘉巍, 吴正方, 等, 2014. 长白山西坡小叶章侵入苔原带过程及影响[J]. 生态学报, 34(23): 6837-6846. |
| ZONG S W, XU J W, WU Z F, et al., 2014. Analysis of the process and impacts of Deyeuxia angustifolia invasion on the Alpine Tundra, Changbai Mountain[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 34(23): 6837-6846. |
| [1] | 刘展航, 张树岩, 侯玉平, 朱书玉, 王立冬, 施欣悦, 李培广, 韩广轩, 谢宝华. 互花米草入侵对黄河口湿地土壤碳氮磷及其生态化学计量特征的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(7): 1360-1369. |
| [2] | 姜倪皓, 张世浩, 张诗函. 哀牢山紫茎泽兰入侵群落主要物种种间联结及环境解释[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(7): 1370-1382. |
| [3] | 席辉辉, 吴丽新, 冯景秋, 殷根深. 中国大陆地区一种归化植物新记录——二十蕊商陆(Phytolacca icosandra L.)[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(8): 1555-1560. |
| [4] | 郭佳琦, 陈俊辰, 黄旬, 黄佳乐, 赵丽娅, 李兆华. 喜旱莲子草入侵群落主要物种生态位和种间联结研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(8): 1607-1616. |
| [5] | 潘红丽, 李慧超, 余志祥, 蔡蕾, 李旭华, 刘兴良. 攀枝花市入侵植物马缨丹群落的物种组成与多样性研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(6): 1177-1182. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
