生态环境学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (10): 1634-1647.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2024.10.015
梁茂厂1,2,*( ), 郭晓华1, 张影1, 马雨萌1, 陈弈铭1, 龚复俊3
), 郭晓华1, 张影1, 马雨萌1, 陈弈铭1, 龚复俊3
收稿日期:2024-04-15
出版日期:2024-10-18
发布日期:2024-11-15
作者简介:*梁茂厂(1980年生),男,讲师,博士,研究方向为环境科学、植物生理与生态。E-mail: liangmaochang@yangtzeu.edu.cn
基金资助:
LIANG Maochang1,2,*( ), GUO Xiaohua1, ZHANG Ying1, MA Yumeng1, CHEN Yiming1, GONG Fujun3
), GUO Xiaohua1, ZHANG Ying1, MA Yumeng1, CHEN Yiming1, GONG Fujun3
Received:2024-04-15
Online:2024-10-18
Published:2024-11-15
摘要:
了解生态环境质量(EEQ)的时空演变对于理解气候变化与人类活动对生态环境的综合影响至关重要。深入分析湖北省EEQ的时空演变特征及其驱动因素,可为区域生态保护和植被恢复策略提供科学依据。该研究聚焦于海拔、气候条件及人类足迹的协同效应对EEQ演变的影响,利用2001-2020年的EEQ与土地利用数据,结合Theil-Sen Median和Mann-Kendall分析,揭示了EEQ的演变特征并预测了其未来趋势。同时,结合海拔、气候及人类足迹等多元数据,采用线性相关分析和结构方程模型,深入分析了自然与人为因素对EEQ演变的作用机制,并针对EEQ下降提出了应对措施。结果表明,EEQ指数随海拔升高而先增后减,拐点在2000-2200 m之间,这与气温条件及人类活动强度的海拔差异紧密相关。过去20年间,湖北省EEQ整体呈先升后降的趋势,区域差异显著,西部山区EEQ上升,中南部江汉平原则下降。结构方程模型进一步指出,西部山区EEQ受气温正向影响,而江汉平原EEQ则受人类足迹的负向影响与太阳辐射的正向影响的共同作用,模型解释度分别高达98%和82%。基于2011-2020年EEQ趋势与Hurst指数分析,预测西部山区EEQ将持续上升,江汉平原则可能继续下降。为此,提出加强生态环境保护,推动植被恢复,以应对EEQ下降的潜在风险。该研究不仅丰富了EEQ演变机制的理论研究,也为湖北省及类似区域的生态保护和经济可持续发展提供了实践指导和决策依据。其创新在于综合多源数据与多种分析方法,全面剖析EEQ演变的复杂成因,为生态环境研究提供了方法论参考。
中图分类号:
梁茂厂, 郭晓华, 张影, 马雨萌, 陈弈铭, 龚复俊. 湖北省生态环境质量的时空演变特征及影响因素分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(10): 1634-1647.
LIANG Maochang, GUO Xiaohua, ZHANG Ying, MA Yumeng, CHEN Yiming, GONG Fujun. Spatiotemporal Evolution Characteristics and Influencing Factors Analysis of Eco-environmental Quality in Hubei Province[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2024, 33(10): 1634-1647.
| 行政区划 | 生态环境质量指数 | 海拔/m | 年均日气温/(℃∙d−1) | 年太阳辐射量/(MJ∙m−2∙a−1) | 年降水量/(mm∙a−1) | 人类足迹指数 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 均值 (标准差) | ||||||
| 鄂州市 | 0.457 (0.052) | 31.3 (29.7) | 17.8 (0.184) | 5187 (36.4) | 1409 (19.2) | 23.0 (9.32) |
| 恩施土家族苗族自治州 | 0.681 (0.068) | 1073 (350) | 13.4 (0.982) | 4392 (187) | 1751 (179) | 10.6 (5.88) |
| 黄冈市 | 0.516 (0.105) | 177 (195) | 16.7 (0.822) | 5241 (70.7) | 1425 (111) | 17.5 (8.06) |
| 黄石市 | 0.500 (0.094) | 109 (123) | 17.5 (0.283) | 5113 (27.5) | 1477 (43.6) | 18.9 (9.48) |
| 荆门市 | 0.527 (0.098) | 121 (104) | 16.8 (0.371) | 5271 (39.6) | 1149 (79.2) | 14.0 (7.00) |
| 荆州市 | 0.499 (0.048) | 43.6 (57.4) | 17.5 (0.331) | 5097 (57.2) | 1341 (76.7) | 15.5 (7.00) |
| 潜江市 | 0.499 (0.032) | 29.8 (2.70) | 17.4 (0.062) | 5185 (17.1) | 1312 (22.7) | 17.8 (6.88) |
| 神农架林区 | 0.803 (0.052) | 1672 (463) | 10.1 (1.01) | 5001 (56.0) | 1637 (253) | 6.45 (4.39) |
| 十堰市 | 0.652 (0.127) | 733 (380) | 13.7 (1.35) | 5054 (88.8) | 1020 (199) | 11.7 (7.42) |
| 随州市 | 0.501 (0.110) | 189 (124) | 16.0 (0.381) | 5381 (29.0) | 1071 (63.9) | 17.6 (7.39) |
| 天门市 | 0.487 (0.033) | 31.2 (5.90) | 17.2 (0.071) | 5239 (14.1) | 1283 (42.5) | 15.0 (6.41) |
| 武汉市 | 0.431 (0.072) | 39.9 (43.8) | 17.4 (0.398) | 5251 (65.8) | 1382 (42.3) | 24.7 (10.8) |
| 仙桃市 | 0.483 (0.041) | 26.7 (2.43) | 17.5 (0.116) | 5182 (19.3) | 1390 (25.2) | 18.3 (7.42) |
| 咸宁市 | 0.582 (0.118) | 189 (191) | 17.1 (0.578) | 5053 (44.9) | 1574 (132) | 13.7 (7.62) |
| 襄阳市 | 0.558 (0.126) | 349 (354) | 15.4 (1.41) | 5252 (110) | 996 (101) | 15.6 (8.31) |
| 孝感市 | 0.456 (0.073) | 79.1 (83.0) | 16.8 (0.494) | 5317 (41.8) | 1241 (69.8) | 19.7 (7.96) |
| 宜昌市 | 0.651 (0.105) | 661 (503) | 14.7 (1.91) | 4896 (175) | 1352 (235) | 12.0 (7.09) |
表1 2001-2020年湖北省各地区统计数据概览
Table 1 Overview of statistical data for regions of Hubei province (2001-2020)
| 行政区划 | 生态环境质量指数 | 海拔/m | 年均日气温/(℃∙d−1) | 年太阳辐射量/(MJ∙m−2∙a−1) | 年降水量/(mm∙a−1) | 人类足迹指数 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 均值 (标准差) | ||||||
| 鄂州市 | 0.457 (0.052) | 31.3 (29.7) | 17.8 (0.184) | 5187 (36.4) | 1409 (19.2) | 23.0 (9.32) |
| 恩施土家族苗族自治州 | 0.681 (0.068) | 1073 (350) | 13.4 (0.982) | 4392 (187) | 1751 (179) | 10.6 (5.88) |
| 黄冈市 | 0.516 (0.105) | 177 (195) | 16.7 (0.822) | 5241 (70.7) | 1425 (111) | 17.5 (8.06) |
| 黄石市 | 0.500 (0.094) | 109 (123) | 17.5 (0.283) | 5113 (27.5) | 1477 (43.6) | 18.9 (9.48) |
| 荆门市 | 0.527 (0.098) | 121 (104) | 16.8 (0.371) | 5271 (39.6) | 1149 (79.2) | 14.0 (7.00) |
| 荆州市 | 0.499 (0.048) | 43.6 (57.4) | 17.5 (0.331) | 5097 (57.2) | 1341 (76.7) | 15.5 (7.00) |
| 潜江市 | 0.499 (0.032) | 29.8 (2.70) | 17.4 (0.062) | 5185 (17.1) | 1312 (22.7) | 17.8 (6.88) |
| 神农架林区 | 0.803 (0.052) | 1672 (463) | 10.1 (1.01) | 5001 (56.0) | 1637 (253) | 6.45 (4.39) |
| 十堰市 | 0.652 (0.127) | 733 (380) | 13.7 (1.35) | 5054 (88.8) | 1020 (199) | 11.7 (7.42) |
| 随州市 | 0.501 (0.110) | 189 (124) | 16.0 (0.381) | 5381 (29.0) | 1071 (63.9) | 17.6 (7.39) |
| 天门市 | 0.487 (0.033) | 31.2 (5.90) | 17.2 (0.071) | 5239 (14.1) | 1283 (42.5) | 15.0 (6.41) |
| 武汉市 | 0.431 (0.072) | 39.9 (43.8) | 17.4 (0.398) | 5251 (65.8) | 1382 (42.3) | 24.7 (10.8) |
| 仙桃市 | 0.483 (0.041) | 26.7 (2.43) | 17.5 (0.116) | 5182 (19.3) | 1390 (25.2) | 18.3 (7.42) |
| 咸宁市 | 0.582 (0.118) | 189 (191) | 17.1 (0.578) | 5053 (44.9) | 1574 (132) | 13.7 (7.62) |
| 襄阳市 | 0.558 (0.126) | 349 (354) | 15.4 (1.41) | 5252 (110) | 996 (101) | 15.6 (8.31) |
| 孝感市 | 0.456 (0.073) | 79.1 (83.0) | 16.8 (0.494) | 5317 (41.8) | 1241 (69.8) | 19.7 (7.96) |
| 宜昌市 | 0.651 (0.105) | 661 (503) | 14.7 (1.91) | 4896 (175) | 1352 (235) | 12.0 (7.09) |

图2 2001-2020年湖北省生态环境质量(EEQ)指数均值及变异系数(CV)的空间分布
Figure 2 Spatial variation of the mean eco-environmental quality (EEQ) index and coefficient of variation (CV) in Hubei province (2001-2020)
| 生态环境质量指数 | NDVI | 海拔 | 年均日气温 | 年太阳辐射量 | 年降水量 | 人类足迹指数 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NDVI | 0.824 (4.74×10−5) | 1 | |||||
| 海拔 | 0.956 (2.10×10−9) | 0.746 (5.83×10−4) | 1 | ||||
| 年均日气温 | −0.936 (3.34×10−8) | −0.798 (1.23×10−4) | −0.981 (0) | 1 | |||
| 年太阳辐射量 | −0.650 (4.73×10−3) | −0.411 (1.01×10−1) | −0.635 (6.18×10−3) | 0.515 (3.43×10−2) | 1 | ||
| 年降水量 | 0.338 (1.85×10−1) | 0.008 (9.75×10−1) | 0.378 (1.35×10−1) | −0.209 (4.20×10−1) | −0.645 (5.17×10−3) | 1 | |
| 人类足迹指数 | −0.910 (4.12×10−7) | −0.922 (1.46×10−7) | −0.802 (1.09×10−4) | 0.803 (1.03×10−4) | 0.561 (1.92×10−2) | −0.202 (4.36×10−1) | 1 |
表2 湖北省地区间各配对变量的相关关系
Table 2 Correlation analysis of paired variables across regions of Hubei province
| 生态环境质量指数 | NDVI | 海拔 | 年均日气温 | 年太阳辐射量 | 年降水量 | 人类足迹指数 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NDVI | 0.824 (4.74×10−5) | 1 | |||||
| 海拔 | 0.956 (2.10×10−9) | 0.746 (5.83×10−4) | 1 | ||||
| 年均日气温 | −0.936 (3.34×10−8) | −0.798 (1.23×10−4) | −0.981 (0) | 1 | |||
| 年太阳辐射量 | −0.650 (4.73×10−3) | −0.411 (1.01×10−1) | −0.635 (6.18×10−3) | 0.515 (3.43×10−2) | 1 | ||
| 年降水量 | 0.338 (1.85×10−1) | 0.008 (9.75×10−1) | 0.378 (1.35×10−1) | −0.209 (4.20×10−1) | −0.645 (5.17×10−3) | 1 | |
| 人类足迹指数 | −0.910 (4.12×10−7) | −0.922 (1.46×10−7) | −0.802 (1.09×10−4) | 0.803 (1.03×10−4) | 0.561 (1.92×10−2) | −0.202 (4.36×10−1) | 1 |
| 海拔高度/m | 生态环境质量指数 均值 (标准差) | 样本量 (n) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 区间 | 均值 (标准差) | ||
| (0, 200] | 72.1 (49.7) | 0.475 (0.068) | 449755 |
| (200, 400] | 288 (57.9) | 0.607 (0.104) | 92714 |
| (400, 600] | 499 (57.4) | 0.647 (0.093) | 66658 |
| (600, 800] | 699 (57.7) | 0.681 (0.067) | 64051 |
| (800, 1000] | 898 (57.2) | 0.704 (0.060) | 60858 |
| (1000, 1200] | 1100 (57.6) | 0.713 (0.066) | 49457 |
| (1 200, 1400] | 1290 (57.6) | 0.724 (0.062) | 36733 |
| (1400, 1600] | 1490 (57.4) | 0.732 (0.071) | 23686 |
| (1600, 1800] | 1690 (56.3) | 0.741 (0.083) | 13767 |
| (1800, 2000] | 1880 (56.0) | 0.773 (0.083) | 6226 |
| (2000, 2200] | 2090 (56.8) | 0.819 (0.039) | 2421 |
| (2200, 2400] | 2290 (56.4) | 0.801 (0.046) | 1275 |
| (2400, 2600] | 2490 (55.1) | 0.787 (0.060) | 643 |
| (2600, 2800] | 2680 (55.2) | 0.748 (0.079) | 242 |
| (2800, 3000] | 2860 (50.0) | 0.751 (0.056) | 61 |
表3 湖北省不同海拔高度区间的生态环境质量指数
Table 3 Eco-environmental quality index across different altitude zones in Hubei province
| 海拔高度/m | 生态环境质量指数 均值 (标准差) | 样本量 (n) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 区间 | 均值 (标准差) | ||
| (0, 200] | 72.1 (49.7) | 0.475 (0.068) | 449755 |
| (200, 400] | 288 (57.9) | 0.607 (0.104) | 92714 |
| (400, 600] | 499 (57.4) | 0.647 (0.093) | 66658 |
| (600, 800] | 699 (57.7) | 0.681 (0.067) | 64051 |
| (800, 1000] | 898 (57.2) | 0.704 (0.060) | 60858 |
| (1000, 1200] | 1100 (57.6) | 0.713 (0.066) | 49457 |
| (1 200, 1400] | 1290 (57.6) | 0.724 (0.062) | 36733 |
| (1400, 1600] | 1490 (57.4) | 0.732 (0.071) | 23686 |
| (1600, 1800] | 1690 (56.3) | 0.741 (0.083) | 13767 |
| (1800, 2000] | 1880 (56.0) | 0.773 (0.083) | 6226 |
| (2000, 2200] | 2090 (56.8) | 0.819 (0.039) | 2421 |
| (2200, 2400] | 2290 (56.4) | 0.801 (0.046) | 1275 |
| (2400, 2600] | 2490 (55.1) | 0.787 (0.060) | 643 |
| (2600, 2800] | 2680 (55.2) | 0.748 (0.079) | 242 |
| (2800, 3000] | 2860 (50.0) | 0.751 (0.056) | 61 |
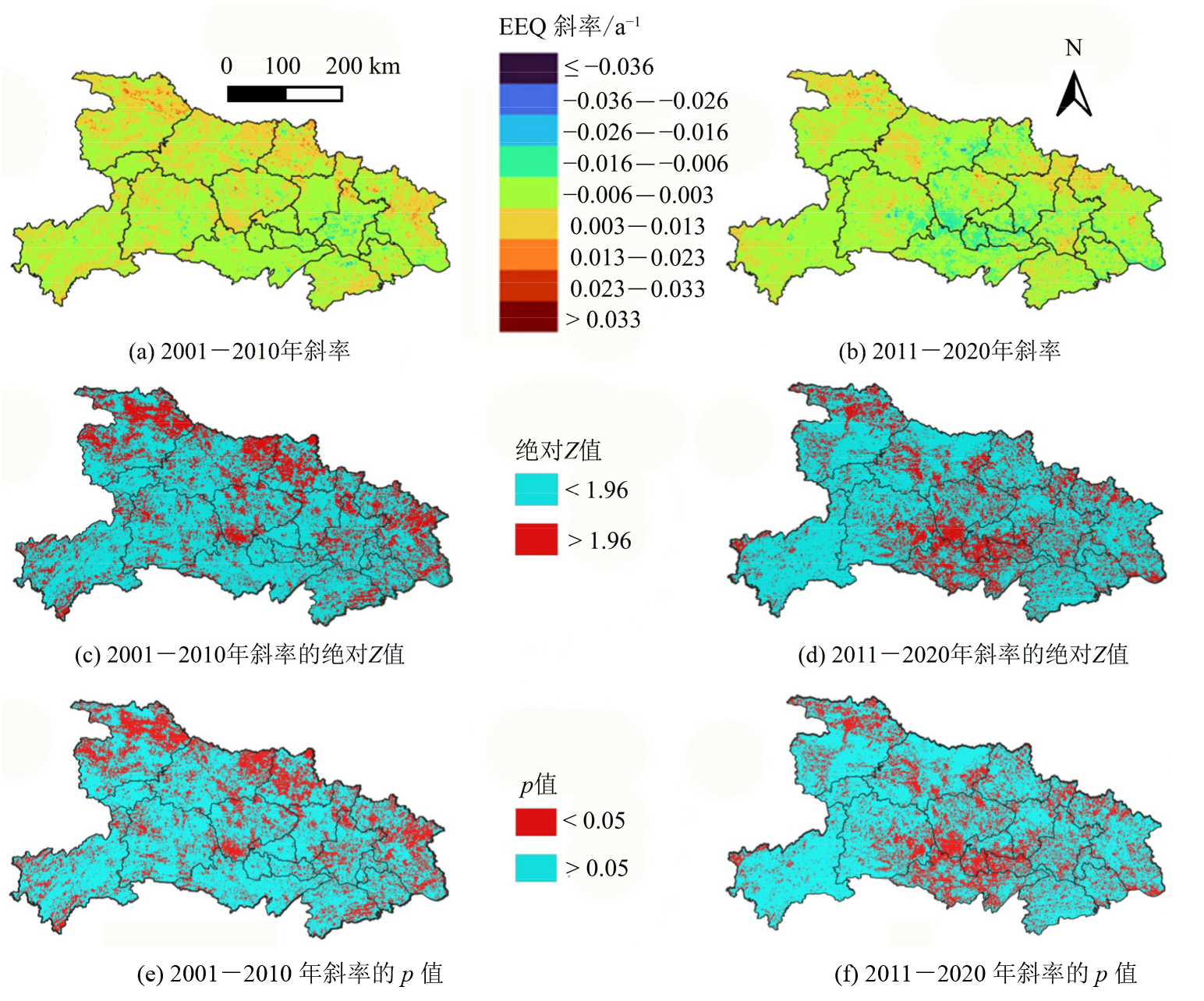
图3 湖北省生态环境质量(EEQ)时间序列趋势的斜率及其显著性检验结果
Figure 3 Trend slope and significance test results for the eco-environmental quality (EEQ) time series in Hubei province
| 时段 | 土地类型 | 耕地 | 林地 | 灌木 | 草地 | 水体 | 荒地 | 不透水面 | 总面积 | 转出 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2001-2010年 | 耕地 | 78.9 | 4.33 | 0.019 | 0.091 | 1.25 | 0.000 | 1.08 | 85.7 | 6.77 |
| 林地 | 2.75 | 84.9 | 0.029 | 0.012 | 0.005 | 0.000 | 0.032 | 87.7 | 2.83 | |
| 灌木 | 0.035 | 0.299 | 0.115 | 0.009 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.458 | 0.343 | |
| 草地 | 0.285 | 0.219 | 0.013 | 0.376 | 0.005 | 0.001 | 0.010 | 0.909 | 0.533 | |
| 水体 | 1.03 | 0.010 | 0.000 | 0.002 | 6.61 | 0.000 | 0.178 | 7.83 | 1.22 | |
| 荒地 | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.004 | 0.001 | 0.004 | 0.006 | 0.016 | 0.012 | |
| 不透水面 | 0.005 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.134 | 0.000 | 3.26 | 3.40 | 0.139 | |
| 2010-2020年 | 耕地 | 75.8 | 4.55 | 0.003 | 0.044 | 0.921 | 0.001 | 1.68 | 83.0 | 7.20 |
| 林地 | 4.19 | 85.5 | 0.024 | 0.010 | 0.007 | 0.000 | 0.073 | 89.8 | 4.30 | |
| 灌木 | 0.029 | 0.116 | 0.030 | 0.002 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.177 | 0.147 | |
| 草地 | 0.208 | 0.154 | 0.005 | 0.105 | 0.006 | 0.001 | 0.014 | 0.493 | 0.388 | |
| 水体 | 1.43 | 0.010 | 0.000 | 0.001 | 6.44 | 0.000 | 0.131 | 8.01 | 1.58 | |
| 荒地 | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.002 | 0.005 | 0.004 | |
| 不透水面 | 0.010 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.129 | 0.000 | 4.42 | 4.56 | 0.140 |
表4 2001-2020年湖北省土地利用转移矩阵
Table 4 Land-use transition matrix for Hubei province (2001-2020) 103 km2
| 时段 | 土地类型 | 耕地 | 林地 | 灌木 | 草地 | 水体 | 荒地 | 不透水面 | 总面积 | 转出 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2001-2010年 | 耕地 | 78.9 | 4.33 | 0.019 | 0.091 | 1.25 | 0.000 | 1.08 | 85.7 | 6.77 |
| 林地 | 2.75 | 84.9 | 0.029 | 0.012 | 0.005 | 0.000 | 0.032 | 87.7 | 2.83 | |
| 灌木 | 0.035 | 0.299 | 0.115 | 0.009 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.458 | 0.343 | |
| 草地 | 0.285 | 0.219 | 0.013 | 0.376 | 0.005 | 0.001 | 0.010 | 0.909 | 0.533 | |
| 水体 | 1.03 | 0.010 | 0.000 | 0.002 | 6.61 | 0.000 | 0.178 | 7.83 | 1.22 | |
| 荒地 | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.004 | 0.001 | 0.004 | 0.006 | 0.016 | 0.012 | |
| 不透水面 | 0.005 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.134 | 0.000 | 3.26 | 3.40 | 0.139 | |
| 2010-2020年 | 耕地 | 75.8 | 4.55 | 0.003 | 0.044 | 0.921 | 0.001 | 1.68 | 83.0 | 7.20 |
| 林地 | 4.19 | 85.5 | 0.024 | 0.010 | 0.007 | 0.000 | 0.073 | 89.8 | 4.30 | |
| 灌木 | 0.029 | 0.116 | 0.030 | 0.002 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.177 | 0.147 | |
| 草地 | 0.208 | 0.154 | 0.005 | 0.105 | 0.006 | 0.001 | 0.014 | 0.493 | 0.388 | |
| 水体 | 1.43 | 0.010 | 0.000 | 0.001 | 6.44 | 0.000 | 0.131 | 8.01 | 1.58 | |
| 荒地 | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.002 | 0.005 | 0.004 | |
| 不透水面 | 0.010 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.129 | 0.000 | 4.42 | 4.56 | 0.140 |

图6 湖北省生态环境质量指数与NDVI的动态变化趋势 每年的数值以平均值±标准误差表示;样本数量(n)=5;趋势线上覆盖的阴影区域代表其95%的置信区间
Figure 6 Dynamic trends of the eco-environmental quality index and normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) in Hubei province
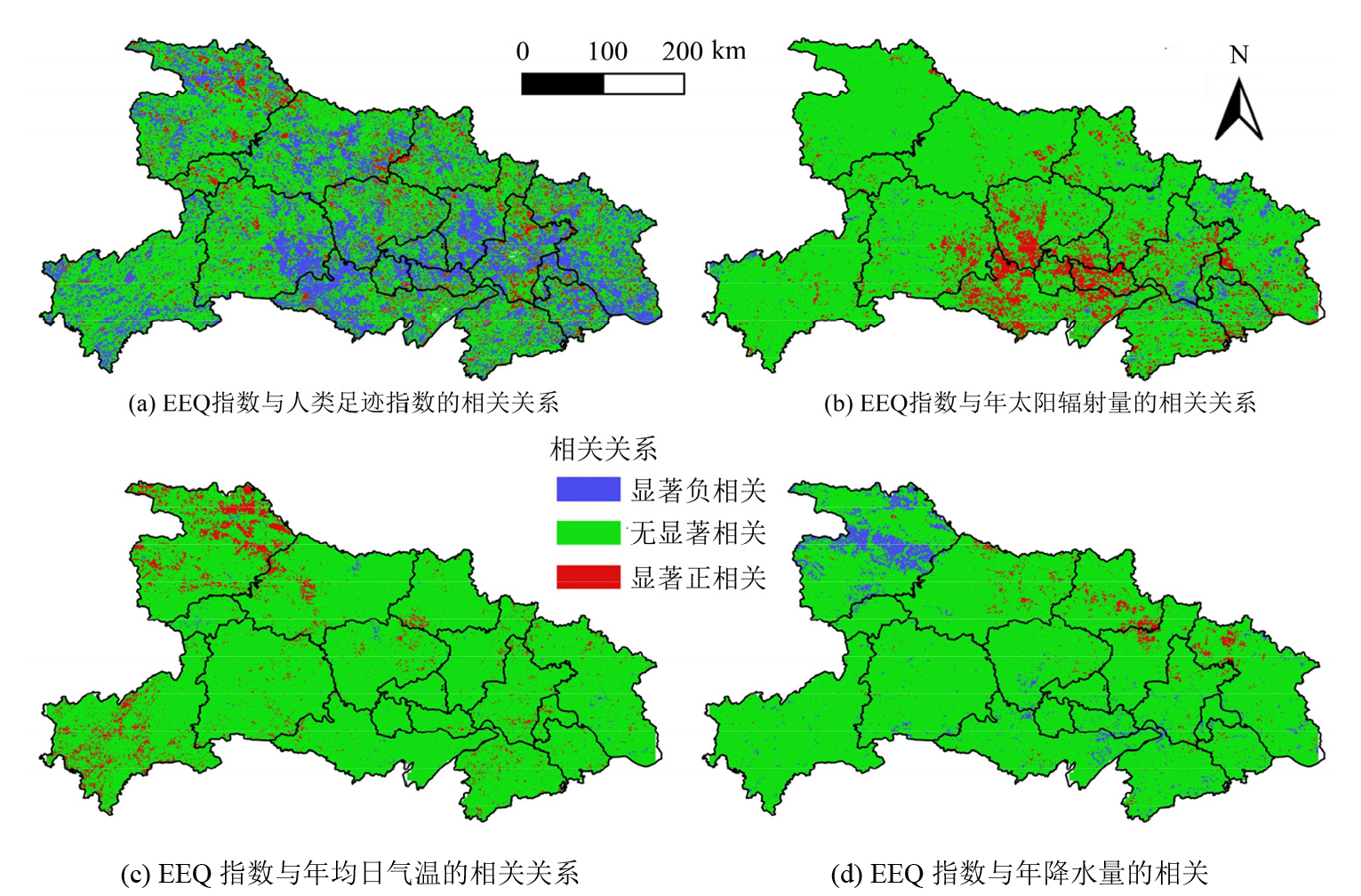
图7 EEQ与影响因子年度序列相关性的空间分布 EEQ代表生态环境质量;年度序列为2001-2020年
Figure 7 Spatial distribution of annual serial correlation between eco-environmental quality (EEQ) and impact factors
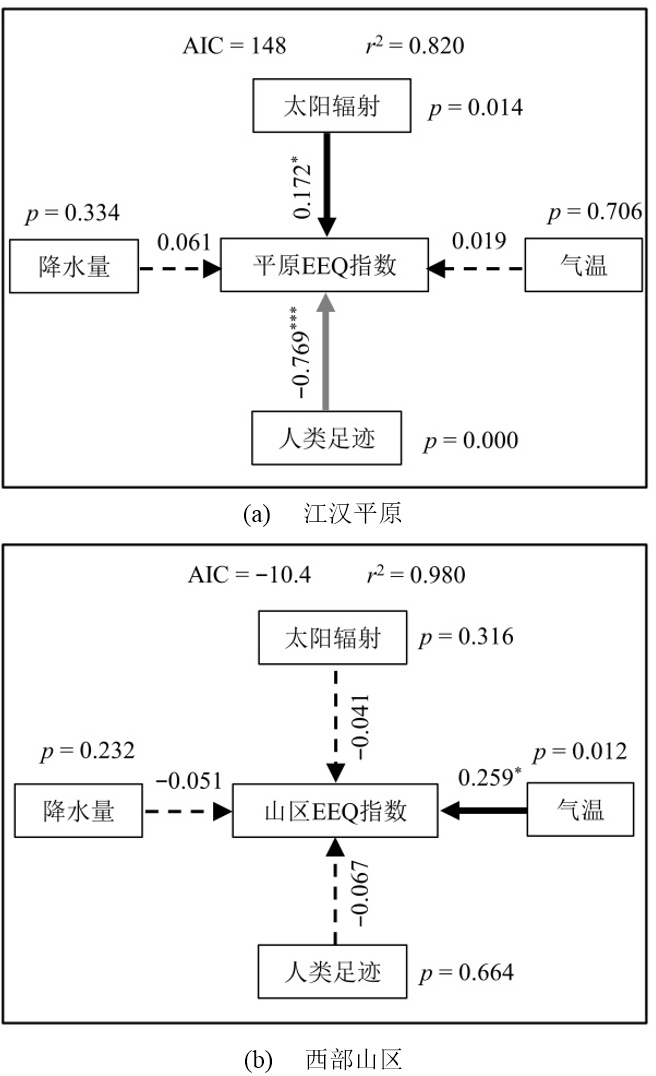
图8 湖北省各区域生态环境质量(EEQ)指数的结构方程模型构建与分析 实黑、实灰及虚线箭头分别表征路径关系的显著正向、负向及不显著性。箭头紧邻处标注的正负数值为标准化路径系数,用以量化各路径效应的强度与方向。各路径系数所对应的p值在影响因素旁标出,以评估路径关系的统计学显著性。具体而言,显著(p<0.05)、高度显著(p<0.01)和极其显著的关系(p<0.001)分别以路径系数上标1个星号、2个星号和3个星号表示。r2 值表示由模型解释的响应变量的比例。AIC:Akaike信息准则
Figure 8 Structural equation modeling and analysis for the eco-environmental quality (EEQ) index in different regions of Hubei province

图9 湖北省各区域人类足迹与气候条件动态变化趋势 每年的数值表示为平均值±标准误差;样本数量(n)=5;趋势线所覆盖的阴影区域表示其95%的置信区间
Figure 9 Dynamic trends of human footprints and climatic conditions across regions of Hubei province

图10 湖北省生态环境质量(EEQ)2011-2020年变化的Hurst指数及未来趋势预测
Figure 10 Hurst index of changes in eco-environmental quality (EEQ) in Hubei province (2011-2020) and projected future trends
| [1] | LEFCHECK J S, 2016. piecewiseSEM: Piecewise structural equation modelling in r for ecology, evolution, and systematics[J]. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 7(5): 573-579. |
| [2] | LIANG M, GONG F, JIN T, et al., 2022. Characteristics of Picea neoveitchii tree growth in mountain areas of central China: Insights from isotopic compositions and satellite-derived indices[J]. Isotopes in Environmental and Health Studies, 58(2): 121-140. |
| [3] | LIANG M, SUGIMOTO A, TEI S, et al., 2023. Arctic plant responses to summer climates and flooding events: A study of carbon and nitrogen-related larch growth and ecosystem parameters in northeastern Siberia[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Biogeosciences, 128(10): e2022JG007135. |
| [4] |
MU H W, LI X C, WEN Y N, et al., 2022. A global record of annual terrestrial Human Footprint dataset from 2000 to 2018[J]. Scientific Data, 9(1): 176.
DOI PMID |
| [5] | SEN P K, 1968. Estimates of the regression coefficient based on Kendall's tau[J]. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 63(324): 1379-1389. |
| [6] | SHAN W, JIN X B, REN J, et al., 2019. Ecological environment quality assessment based on remote sensing data for land consolidation[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 239: 118126. |
| [7] | XU D, YANG F, YU L, et al., 2021. Quantization of the coupling mechanism between eco-environmental quality and urbanization from multisource remote sensing data[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 321: 128948. |
| [8] | YANG J, HUANG X, 2021. The 30 m annual land cover dataset and its dynamics in China from 1990 to 2019[J]. Earth System Science Data, 13(8): 3907-3925. |
| [9] | ZHANG X Y, JIA W W, HE J Y, 2023. Spatial and temporal variation of ecological quality in northeastern China and analysis of influencing factors[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 423: 138650. |
| [10] | ZHENG Z, WU Z F, CHEN Y B, et al., 2020. Exploration of eco-environment and urbanization changes in coastal zones: A case study in China over the past 20 years[J]. Ecological Indicators, 119: 106847. |
| [11] | 唱彤, 郦建强, 郭旭宁, 等, 2023. 江汉平原水域空间格局时空演变特征及其驱动因素分析[J]. 水科学进展, 34(1): 21-32. |
| CHANG T, LI J Q, GUO X N, et al., 2023. The spatial-temporal characteristics and driving forces analysis of water area landscape pattern changes on the Jianghan Plain[J]. Advances in Water Science, 34(1): 21-32. | |
| [12] | 陈斌, 徐尚昭, 周阳阳, 等, 2022. 基于土地利用变化的江汉平原景观生态风险时空分异特征分析[J]. 水土保持研究, 29(5): 228-234, 243. |
| CHEN B, XU S Z, ZHOU Y Y, et al., 2022. Assessment of Landscape Ecological Risk in Jianghan Plain Area Based on Land Use Change[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 29(5): 228-234, 243. | |
| [13] |
冯自贤, 佘璐, 王秀慧, 等, 2024. 基于改进遥感生态指数的宁夏生态环境质量时空变化[J]. 生态环境学报, 33(1): 131-143.
DOI |
| FENG Z X, SHE L, WANG X H, et al., 2024. Spatial and temporal variations of ecological environment quality in Ningxia based on improved remote sensing ecological index[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 33(1): 131-143. | |
| [14] |
柯丽娜, 徐佳慧, 王楠, 等, 2022. 基于遥感生态指数的滨海湿地生态质量变化评价——以辽东湾北部区为例[J]. 生态环境学报, 31(7): 1417-1424.
DOI |
| KE L N, XU J H, WANG N, et al., 2022. Evaluation of ecological quality of coastal wetland based on remote sensing ecological index: A case study of northern Liaodong Bay[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 31(7): 1417-1424. | |
| [15] | 李婷婷, 马超, 郭增长, 2021. 基于RSEI模型的贺兰山长时序生态质量评价及影响因素分析[J]. 生态学杂志, 40(4): 1154-1165. |
|
LI T T, MA C, GUO Z C, 2021. Ecological quality evaluation and influencing factors analysis of Helan Mountain based on RSEI[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 40(4): 1154-1165.
DOI |
|
| [16] |
马丽莎, 刘殿锋, 刘耀林, 2023. 城市扩张与生态空间非线性动态耦合关系梯度分析模型[J]. 地球信息科学学报, 25(10): 1968-1985.
DOI |
| MA L S, LIU D F, LIU Y L, 2023. Modelling gradient changes of non-linear dynamic coupling relationships between urban expansion and ecological land[J]. Journal of Geo-information Science, 25(10): 1968-1985. | |
| [17] | 邵晓莉, 杨雪莹, 凌海波, 等, 2023. 加快构建 “三线一单” 助推湖北绿色发展[J]. 环境科学与技术, 46(S2): 254-258. |
| SHAO X L, YANG X Y, LING H B, et al., 2023. Speeding up the construction of “Three Lines One Permit” to boost the green development of Hubei province[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 46(S2): 254-258. | |
| [18] | 苏嘉亮, 晏晨然, 雷雨, 等, 2023. 陕西省生态环境质量长时序动态监测[J]. 生态学报, 43(2): 554-568. |
| SU J L, YAN C R, LEI Y, et al., 2023. Long time series dynamic monitoring of eco-environmental quality in Shaanxi Province[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 43(2): 554-568. | |
| [19] |
田成诗, 孙瑞欣, 2023. 长江经济带市域生态环境质量空间分异与影响因素分析——基于三生空间的土地利用转型[J]. 生态环境学报, 32(7): 1173-1184.
DOI |
| TIAN C S, SUN R X, 2023. Spatial heterogeneity and its influential factors of eco-environmental quality in the Yangtze River economic belt: Based on land use transformation of “production-living-ecological spaces”[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 32(7): 1173-1184. | |
| [20] | 田智慧, 尹传鑫, 王晓蕾, 2023. 鄱阳湖流域生态环境动态评估及驱动因子分析[J]. 环境科学, 44(2): 816-827. |
| TIAN Z H, YIN C X, WANG X L, 2023. Dynamic monitoring and driving factors analysis of ecological environment quality in Poyang Lake Basin[J]. Environmental Science, 44(2): 816-827. | |
| [21] | 王永祥, 徐园园, 杨佳嘉, 等, 2023. 基于Landsat的重庆市生态环境质量动态监测及其时空格局演变分析[J]. 生态学报, 43(15): 6278-6292. |
| WANG Y X, XU Y Y, YANG J J, et al., 2023. Dynamic monitoring and spatio-temporal pattern evolution analysis of eco-environmental quality in Chongqing based on remote sensing[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 43(15): 6278-6292. | |
| [22] |
巫晨煜, 许帆帆, 魏士博, 等, 2023. 渭河流域地表植被覆盖对气候变化的响应研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 32(5): 835-844.
DOI |
| WU C Y, XU F F, WEI S B, et al., 2023. Study on response of surface vegetation cover to climate change in Weihe River Basin[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 32(5): 835-844. | |
| [23] | 武锦辉, 张亮亮, 赵秉琨, 等, 2023. 基于临界慢化模型和GLASS LAI的植被及其恢复力遥感监测研究——以三峡库区为例[J]. 生态学报, 43(12): 5084-5095. |
| WU J H, ZHANG L L, ZHAO B K, et al., 2023. Remote sensing assessing of vegetation and its resilience based on critical slowing down model and GLASS LAI: A case study in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 43(12): 5084-5095. | |
| [24] | 徐涵秋, 2013. 城市遥感生态指数的创建及其应用[J]. 生态学报, 33(24): 7853-7862. |
| XU H Q, 2013. A remote sensing urban ecological index and its application[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 33(24): 7853-7862. | |
| [25] | 徐勇, 戴强玉, 黄雯婷, 等, 2023. 2000-2020年西南地区植被NDVI时空变化及驱动机制探究[J]. 环境科学, 44(1): 323-335. |
| XU Y, DAI Q Y, HUANG W T, et al., 2023. Spatio-temporal variation in vegetation cover and its driving mechanism exploration in Southwest China from 2000 to 2020[J]. Environmental Science, 44(1): 323-335. | |
| [26] | 杨亮洁, 秦丽双, 杨永春, 等, 2023. 城市群地区城市高质量发展与生态环境的交互协同作用——以成渝城市群为例[J]. 生态学报, 43(17): 7035-7046. |
| YANG L J, QIN L S, YANG Y C, et al., 2023. Interaction between high-quality of urban development and ecological environment in urban agglomeration areas: Taking the Chengdu-Chongqing urban agglomeration as an example[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 43(17): 7035-7046. | |
| [27] | 余慧婕, 张方敏, 马赫, 等, 2024. 基于遥感生态指数的淮河流域生态环境质量时空演化及其驱动因素分析[J]. 环境科学, 45(7): 4112-4121. |
| YU H J, ZHANG F M, MA H, et al., 2024. Spatio-temporal evolution and driving factors of ecological environment quality in the Huai River Basin based on RSEI[J]. Environmental Science, 45(7): 4112-4121. | |
| [28] | 余瑞林, 马宗良, 2018. 2000-2015年江汉平原粮食生产的时空格局及影响因素[J]. 世界地理研究, 27(3): 99-108. |
| YU R L, MA Z L, 2018. Spatio-temporal patterns and influencing factors of grain production in Jianghan Plain during 2000-2015[J]. World Regional Studies, 27(3): 99-108. | |
| [29] | 赵嘉丽, 李兴, 孙冰, 2024. 基于AWRSEI的岱海流域生态环境质量时空演变及驱动因子分析[J]. 环境科学, 45(3): 1598-1614. |
| ZHAO J L, LI X, SUN B, 2024. Spatial-temporal evolution and driving factors analysis of ecological environment quality in Daihai Basin based on AWRSEI[J]. Environmental Science, 45(3): 1598-1614. | |
| [30] | 赵体侠, 朱连奇, 王丽园, 等, 2024. 中国生态环境质量与人类活动耦合机制及其影响因子[J]. 环境科学, 45(6): 3341-3351. |
| ZHAO T X, ZHU L Q, WANG L Y, et al., 2024. Coupling mechanisms of eco-environmental quality and human activities in China and their influencing factors[J]. Environmental Science, 45(6): 3341-3351. | |
| [31] | 张萌, 杨霞, 宋蕾, 等, 2023. 湖北地方生态环境标准现状及重点建设任务分析[J]. 环境污染与防治, 45(7): 1040-1046. |
| ZHANG M, YANG X, SONG L, et al., 2023. Analysis on the status and key construction tasks of local eco-environmental standards in Hubei[J]. Environmental Pollution & Control, 45(7): 1040-1046. | |
| [32] | 张睿, 师玮一, 周靖宣, 等, 2023. 2001-2019年中国自然保护区生态环境质量时空变化特征及其驱动力[J]. 生态学报, 43(5): 2101-2113. |
| ZHANG R, SHI W Y, ZHOU J X, et al., 2023. Temporal and spatial variation characteristics and driving forces of eco-environmental quality in China’s nature reserves from 2001 to 2019[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 43(5): 2101-2113. | |
| [33] | 张妍妍, 王峥, 邱斌, 等, 2023. 长江流域湖北片区典型城市水生态环境问题解析及整治对策[J]. 环境工程技术学报, 13(1): 27-35. |
| ZHANG Y Y, WANG Z, QIU B, et al., 2023. Analysis of water eco-environmental problems and related countermeasures for typical cities in Hubei region of the Yangtze River Basin[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology, 13(1): 27-35. | |
| [34] | 张韵, 彭建东, 王晶晶, 等, 2020. 基于地学信息图谱的江汉平原土地利用时空变化分析[J]. 水土保持研究, 27(4): 85-92, 2. |
| ZHANG Y, PENG J D, WANG J J, et al., 2020. Analysis on spatial and temporal change of land use in Jianghan Plain based on Geo-information Atlas[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 27(4): 85-92, 2. | |
| [35] | 周文昌, 张维, 胡兴宜, 等, 2021. 湖北省湿地生态系统的服务价值评估[J]. 水土保持通报, 41(3): 305-311, 364. |
| ZHOU W C, ZHANG W, HU X Y, et al., 2021. Evaluation of wetland ecosystem service value in Hubei Province[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 41(3): 305-311, 364. | |
| [36] | 宗慧琳, 张晓伦, 袁希平, 等, 2024. 利用GEE进行1990-2022年小江流域生态环境质量时空格局与演变趋势分析[J]. 环境科学, 45(7): 4122-4136. |
| ZONG H L, ZHANG X L, YUAN X P, et al., 2024. Xiaojiang river basin ecological environmental quality spatiotemporal pattern and evolutionary trend analysis using GEE from 1990 to 2022[J]. Environmental Science, 45(7): 4122-4136. |
| [1] | 戴晓爱, 马佳欣, 唐艺菱, 李为乐. 甘肃省植被时空动态变化及其归因分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(8): 1163-1173. |
| [2] | 高文明, 宋芊, 张皓翔, 王士如. 基于生态系统服务功能和保护动物栖息地适宜性评价的优先保护区选取——以三江源地区为例[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(8): 1318-1328. |
| [3] | 徐佳乐, 杨兴川, 赵文吉, 杨志强, 钟一雪, 师乐颜, 马鹏飞. 气候变化背景下内蒙古中西部植被覆盖度演变特征研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(7): 1008-1018. |
| [4] | 汪东川, 李亭蓉, 王康健, 孙苗苗, 俞长锦, 杨菲, 杨琳, 张万恒, 刘云绮, 曾孔鹏. 金沙江观音岩库区植被覆盖度时空差异影响机制分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(7): 997-1007. |
| [5] | 宋小龙, 马明德, 王鹏, 李陇堂, 米文宝, 宋永永. 2000—2022年宁夏不同地理分区生长季植被覆盖度时空非平稳性特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(6): 853-868. |
| [6] | 关玉亮, 甘先华, 殷祚云, 黄钰辉, 陶玉柱, 李宽, 张卫强, 邓彩琼, 曾祥尧, 黄芳芳. 南岭自然保护区不同海拔梯度植物多样性分布格局[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(6): 877-887. |
| [7] | 卫玺玺, 晁鑫艳, 郑景明, 唐可欣, 万龙, 周金星. 贺兰山东、西侧典型植物群落物种多样性差异及其影响因子[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(4): 520-530. |
| [8] | 冯自贤, 佘璐, 王秀慧, 杨璐, 杨晨. 基于改进遥感生态指数的宁夏生态环境质量时空变化[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(1): 131-143. |
| [9] | 李佳婧, 梁咏亮, 李静尧, 李小伟, 杨君珑. 基于叶片功能性状的贺兰山西坡植物生态策略分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(1): 45-53. |
| [10] | 房园, 梁中, 张毓涛, 师庆东, 孙雪娇, 李吉玫, 李翔, 董振涛. 天山云杉森林生态系统的水源涵养能力海拔梯度变化特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(9): 1574-1584. |
| [11] | 田成诗, 孙瑞欣. 长江经济带市域生态环境质量空间分异与影响因素分析——基于三生空间的土地利用转型[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(7): 1173-1184. |
| [12] | 倪广艳. 外来植物入侵对生态系统碳循环影响的研究概述[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(7): 1325-1332. |
| [13] | 张林, 齐实, 周飘, 伍冰晨, 张岱, 张岩. 北京山区针阔混交林地土壤有机碳含量的影响因素研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 450-458. |
| [14] | 秦浩, 李蒙爱, 高劲, 陈凯龙, 张殷波, 张峰. 芦芽山不同海拔灌丛土壤细菌群落组成和多样性研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 459-468. |
| [15] | 张鐥文, 杨冉, 侯文星, 王丽丽, 刘爽, 宋汉扬, 赵文吉, 李令军. 生态补水前后永定河两岸植被覆盖度变化及驱动力分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(2): 264-273. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
