生态环境学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (5): 710-719.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2025.05.005
林泳怡1,2( ), 周燕飞1,2, 邓金环1,2, 田纪辉1,2, 蔡昆争1,2,*(
), 周燕飞1,2, 邓金环1,2, 田纪辉1,2, 蔡昆争1,2,*( )
)
收稿日期:2024-09-29
出版日期:2025-05-18
发布日期:2025-05-16
通讯作者:
*蔡昆争。E-mail: 作者简介:林泳怡(2000年生),女,硕士研究生,主要研究方向为农业生态与作物逆境研究。E-mail: 2499723637@qq.com
基金资助:
LIN Yongyi1,2( ), ZHOU Yanfei1,2, DENG Jinhuan1,2, TIAN Jihui1,2, CAI Kunzheng1,2,*(
), ZHOU Yanfei1,2, DENG Jinhuan1,2, TIAN Jihui1,2, CAI Kunzheng1,2,*( )
)
Received:2024-09-29
Online:2025-05-18
Published:2025-05-16
摘要:
生物炭富含碳和硅,偏碱性,是酸性土壤改良的理想调理剂。土壤中硅、磷两种元素存在交互作用,在作物生长中均具有重要作用。然而,生物炭与磷对土壤硅形态转化以及作物植株硅的吸收转运机制有待进一步研究。通过盆栽试验,设置对照、单施磷、单施生物炭、磷和生物炭4个处理,探究生物炭和磷处理对赤红壤的改良效果,重点研究其对土壤硅形态及转化、有效性及大豆植株硅转运的影响。结果表明,生物炭施用显著降低土壤交换性酸,提升土壤pH(1.43-2.16个单位),提高土壤交换性盐基离子K+、Ca2+、Mg2+含量和土壤有效磷、总碳和总氮含量,而磷单独施用或者与硅的交互作用不明显。生物炭施用大幅度提高土壤有机结合态硅、铁锰氧化态硅、无定形硅及有效态硅的含量,减少无定形硅所占比例,增加土壤硅的有效性,其中有效硅含量提高7.78-11.6。生物炭处理还显著促进大豆植株对硅素养分的吸收,增加大豆茎、叶、籽粒的硅含量分别为58.8%,50.4%和149%,但显著下调大豆根部硅转运蛋白基因GmNIP2-2的表达,而磷处理无论是单独还是与生物炭协同处理则均对植株的硅吸收没有明显影响。生物炭施用能提高大豆植株的高度(8.95%-23.0%),但降低植株的干质量和产量。综上所述,生物炭对缓解土壤酸化、促进土壤硅的形态转化和植株硅吸收起重要的作用,对大豆的增产效应尚不稳定,显示其改良酸性土壤的较大潜力,而磷没有明显影响。
中图分类号:
林泳怡, 周燕飞, 邓金环, 田纪辉, 蔡昆争. 生物炭与磷添加促进赤红壤的硅形态转化和大豆植株硅吸收转运[J]. 生态环境学报, 2025, 34(5): 710-719.
LIN Yongyi, ZHOU Yanfei, DENG Jinhuan, TIAN Jihui, CAI Kunzheng. Biochar Combined with Phosphorus Promote Silicon Fraction Transformation and Si Absorption of Soybean Plant in Latosolic Red Soil[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2025, 34(5): 710-719.
| 施肥 | CK | P | B | BP |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 生物炭 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 100 |
| KH2PO4 | 0 | 0.144 | 0 | 0.144 |
| K2SO4 | 0.323 | 0.231 | 0.323 | 0.231 |
| 尿素 | 0.272 | 0.272 | 0.272 | 0.272 |
表1 生物炭及肥料施用量
Table 1 Application rate of biochar and fertilizer g·pot?1
| 施肥 | CK | P | B | BP |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 生物炭 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 100 |
| KH2PO4 | 0 | 0.144 | 0 | 0.144 |
| K2SO4 | 0.323 | 0.231 | 0.323 | 0.231 |
| 尿素 | 0.272 | 0.272 | 0.272 | 0.272 |
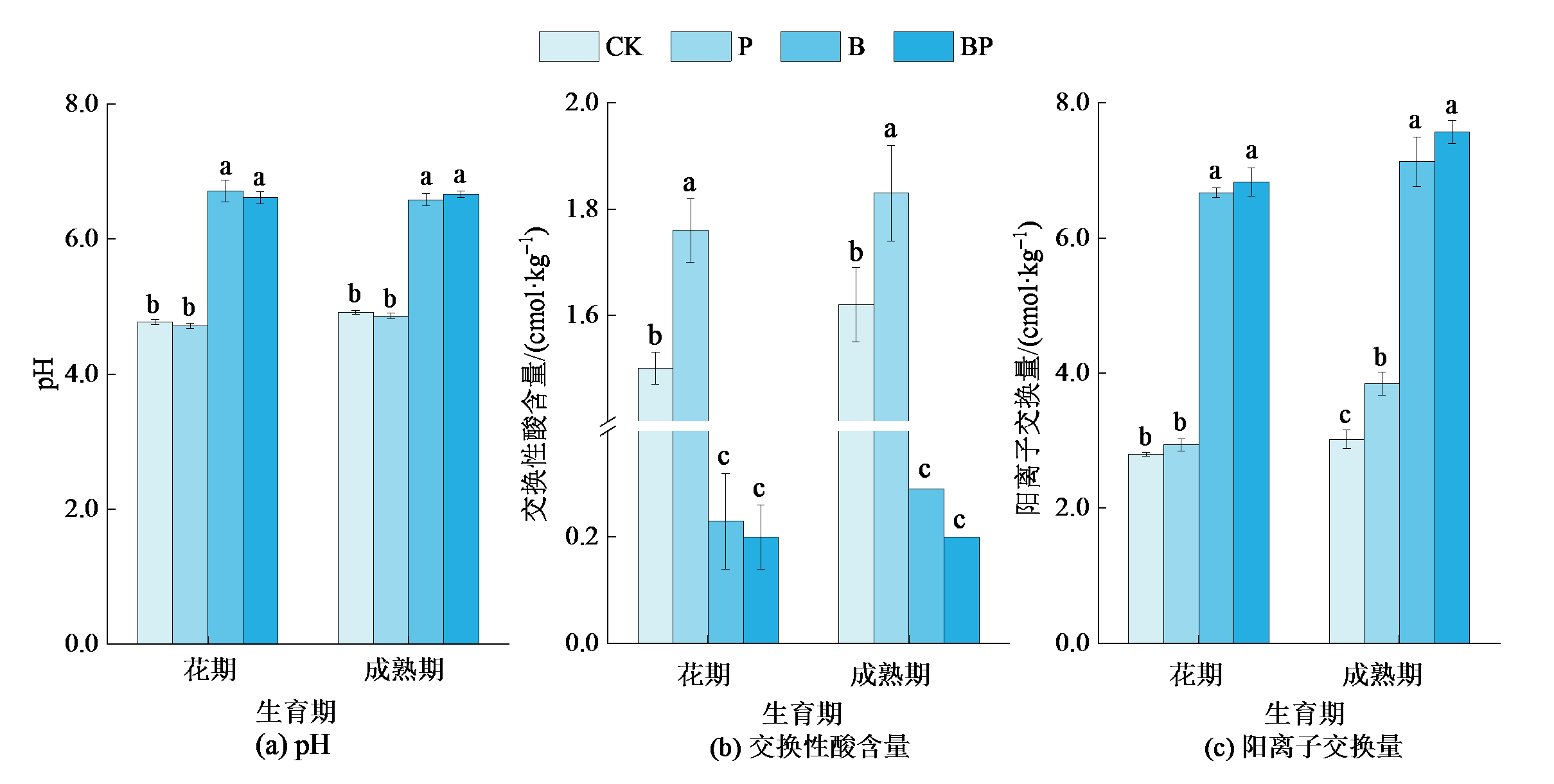
图1 生物炭和磷对土壤pH、交换性酸含量和CEC值的影响 样本重复数n=4;误差棒代表标准误;图中同一个生育时期不同处理标记的小写字母表示有显著差异(p<0.05),下同
Figure 1 Impacts of biochar and phosphorus on soil pH, exchangeable acid content and CEC
| 生育期 | 处理 | w(有效磷)/(mg·kg−1) | w(总碳)/(g·kg−1) | w(总氮)/(g·kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 花期 | CK | 5.7±0.6b | 9.7±0.2b | 1.2±0.0b |
| P | 10.1±0.9b | 10.0±0.2b | 1.2±0.0b | |
| B | 99.4±25.2a | 66.9±2.1a | 2.7±0.1a | |
| BP | 113.6±6.0a | 65.3±1.7a | 2.7±0.1a | |
| 成熟期 | CK | 5.9±0.7b | 9.8±0.2b | 1.1±0.0b |
| P | 7.9±1.2b | 10.1±0.1b | 1.2±0.0b | |
| B | 92.9±3.8a | 62.0±0.7a | 2.4±0.1a | |
| BP | 74.2±25.1a | 60.5±1.6a | 2.6±0.1a |
表2 生物炭和磷对土壤有效磷、总碳及总氮的影响
Table 2 Impacts of biochar and phosphorus on soil total carbon and total nitrogen
| 生育期 | 处理 | w(有效磷)/(mg·kg−1) | w(总碳)/(g·kg−1) | w(总氮)/(g·kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 花期 | CK | 5.7±0.6b | 9.7±0.2b | 1.2±0.0b |
| P | 10.1±0.9b | 10.0±0.2b | 1.2±0.0b | |
| B | 99.4±25.2a | 66.9±2.1a | 2.7±0.1a | |
| BP | 113.6±6.0a | 65.3±1.7a | 2.7±0.1a | |
| 成熟期 | CK | 5.9±0.7b | 9.8±0.2b | 1.1±0.0b |
| P | 7.9±1.2b | 10.1±0.1b | 1.2±0.0b | |
| B | 92.9±3.8a | 62.0±0.7a | 2.4±0.1a | |
| BP | 74.2±25.1a | 60.5±1.6a | 2.6±0.1a |
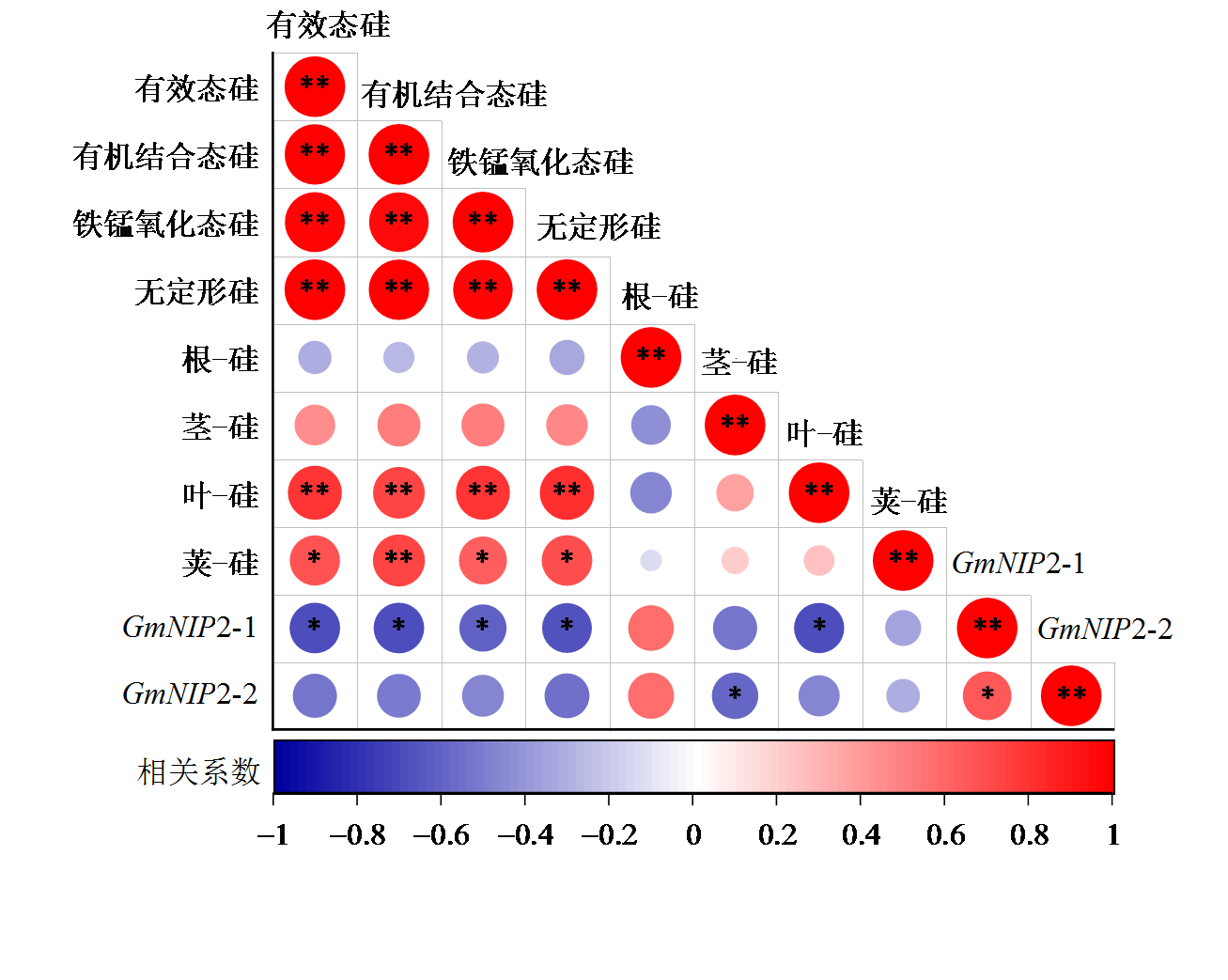
图6 土壤硅形态、大豆硅含量和大豆硅吸收转运基因相关性分析 * p£0.05, ** p£0.01
Figure 6 Redundancy analysis of soil silicon morphology and soybean silicon content and soybean silicon absorption and transport
| [1] | ARIF M, ILYAS M, RIAZ M, et al., 2017. Biochar improves phosphorus use efficiency of organic-inorganic fertilizers, maizewheat productivity and soil quality in a low fertility alkaline soil[J]. Field Crops Research, 214: 25-37. |
| [2] | BHAT J A, SHIVARAJ S, SINGH P, et al., 2019. Role of silicon in mitigation of heavy metal stresses in crop plants[J]. Plants, 8(3): 71. |
| [3] | CHEN D, WANG X B, WANG X L, et al., 2020. The mechanism of cadmium sorption by sulphur-modified wheat straw biochar and its application cadmium-contaminated soil[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 714: 136550. |
| [4] | CHEW J K, JOSEPH S, CHEN G H, et al., 2022. Biochar-based fertiliser enhances nutrient uptake and transport in rice seedlings[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 862: 154174. |
| [5] | CUI S H, PENG Y T, YANG X, et al., 2022. Comprehensive understanding of guest compound intercalated layered double hydroxides: Design and applications in removal of potentially toxic elements[J]. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 53(4): 457-482. |
| [6] | DAI Z M, ZHANG X J, TANG C, et al., 2017. Potential role of biochars in decreasing soil acidification-A critical review[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 581-582: 601-611. |
| [7] |
DESHMUKH R K, VIVANCOS J, VALÉRIE GUÉRIN, et al., 2013. Identification and functional characterization of silicon transporters in soybean using comparative genomics of major intrinsic proteins in Arabidopsis and rice[J]. Plant Molecular Biology, 83(4-5): 303-315.
DOI PMID |
| [8] |
DHIMAN P, RAJORA N, BHARDWAJ S, et al., 2021. Fascinating role of silicon to combat salinity stress in plants: An updated overview[J]. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 162: 110-123.
DOI PMID |
| [9] | EGAMBERDIEVA D, MA H, ALAYLAR B, et al., 2021. Biochar amendments improve licorice (Glycyrrhiza uralensis Fisch.) growth and nutrient uptake under salt stress[J]. Plants, 10(10): 2135. |
| [10] | FAN B B, DING S, PENG Y T, et al., 2022. Supplying amendments alleviates aluminum toxicity and regulates cadmium accumulation by spinach in strongly acidic soils[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 324: 116340. |
| [11] | GUO C X, PAN Z Y, PENG S, 2016. Effect of biochar on the growth of Poncirus trifoliata (L.) Raf. seedlings in Gannan acidic red soil[J]. Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 62(2): 194-200. |
| [12] | HU A Y, XU S N, QIN D N, et al., 2021. Role of silicon in mediating phosphorus imbalance in plants[J]. Plants, 10(1): 51. |
| [13] | HU Z W, WU D J, WU J F, et al., 2022. Silicon-rich biochar effectively increases the availability of soil silicon and rice yield in reddish paddy soil[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition, 28(8): 1421-1429. |
| [14] | HUA Y M, HEAL K V, FRIESL-HANL W, 2017. The use of red mud as an immobiliser for metal/metalloid contaminated soil: A review[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 325: 17-30. |
| [15] | IGALAVITHANA A D, OK Y S, NIAZI NK, et al., 2017. Effect of corn residue biochar on the hydraulic properties of sandy loam soil[J]. Sustainability, 9(2): 266. |
| [16] | LI X W, XU S T, NEUPANE A, et al., 2021. Coapplication of biochar and nitrogen fertilizer reduced nitrogen losses from soil[J]. PLoS One, 16(3): e0248100. |
| [17] | LI Z M, GUO F Z, CORNELIS J T, et al., 2020. Combined silicon- phosphorus fertilization affects the biomass and phytolith stock of rice plants[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 11: 67. |
| [18] | LIU X Y, LI L Q, BIAN R J, et al., 2014. Effect of biochar amendment on soil-silicon availability and rice uptake[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Soil Science, 177(1): 91-96. |
| [19] | LUO Y, DUNGAIT J A J, ZHAO X R, et al., 2018. Pyrolysis temperature during biochar production alters its subsequent utilization by microorganisms in an acid arable soil[J]. Land Degradation & Development, 29(7): 2183-2188. |
| [20] | NGUI M E, LIN Y H, WEI I L, et al., 2024. Effects of the combination of biochar and organic fertilizer on soil properties and agronomic attributes of soybean (Glycine max L.)[J]. PLoS One, 19(9): e0310221. |
| [21] | PRENDERGAST-MILLER M T, DUVALL M, SOHI S P, 2014. Biochar root interactions are mediated by biochar nutrient content and impacts on soil nutrient availability[J]. European Journal of Soil Science, 65(1): 173-185. |
| [22] | SARMA B, BORKOTOKI B, NARZARI R, et al., 2017. Organic amendments: Effect on carbon mineralization and crop productivity in acidic soil[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 152: 157-166. |
| [23] | SATTAR M, RAZA A, ALI S, et al., 2023. Integrating byproducts from bioenergy technology to improve the morphophysiological growth and yield of soybean under acidic soil[J]. Chemosphere, 327: 138424. |
| [24] |
SHEPHERD J G, JOSEPH S, SOHI S P, et al., 2017. Biochar and enhanced phosphate capture: Mapping mechanisms to functional properties[J]. Chemosphere, 179: 57-74.
DOI PMID |
| [25] |
SIGUA G C, NOVAK J M, WATTS D W, et al., 2016. Efficacies of designer biochars in improving biomass and nutrient uptake of winter wheat grown in a hard setting subsoil layer[J]. Chemosphere, 142: 176-183.
DOI PMID |
| [26] | SONG Z L, WANG H L, STRONG P J, et al., 2014. Increase of available soil silicon by Si-rich manure for sustainable rice production[J]. Agronomy for Sustainable Development, 34(4): 813-819. |
| [27] | STEINER C, TEIXEIRA W G, LEHMANN J, et al., 2007. Long term effects of manure, charcoal, and mineral fertilization on crop production and fertility on a highly weathered Central Amazonian upland soil[J]. Plant and Soil, 291(1-2): 275-290. |
| [28] | TAN Q L, GUI H P, CHENG X, et al., 2015. Differences in responses of soil microbial properties and trifoliate orange seedling to biochar derived from three feedstocks[J]. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 15(3): 541-551. |
| [29] | TAN X F, ZHU S S, WANG R P, et al., 2021. Role of biochar surface characteristics in the adsorption of aromatic compounds: Pore structure and functional groups[J]. Chinese Chemical Letters, 32(10): 2939-2946. |
| [30] | TAN Y, ZHOU X, PENG Y T, et al., 2022. Effects of phosphorus-containing material application on soil cadmium bioavailability: A meta-analysis[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 29(28): 42372-42383. |
| [31] | TRIPATHI P, NA C I, KIM Y, 2021. Effect of silicon fertilizer treatment on nodule formation and yield in soybean (Glycine max L.)[J]. European Journal of Agronomy, 122: 126172. |
| [32] | TIAN J H, KUANG X Z, TANG M T, et al., 2021. Biochar application under low phosphorus input promotes soil organic phosphorus mineralization by shifting bacterial phoD gene community composition[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 779: 146556. |
| [33] | THAKRAL V, RATURI G, SUDHAKARAN S, et al., 2024. Silicon, a quasi-essential element: Availability in soil, fertilizer regime, optimum dosage, and uptake in plants[J]. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 208: 108459. |
| [34] | WANG Y F, XIAO X, XU Y L, et al., 2019. Environmental effects of silicon within biochar (sichar) and carbon-silicon coupling mechanisms: A critical review[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 53(23): 13570-13582. |
| [35] | WROBEL-TOBISZEWSKA A, BOERSMA M, SARGISON J, et al., 2018. Nutrient changes in potting mix and Eucalyptus nitens leaf tissue under macadamia biochar amendments[J]. Journal of Forestry Research, 29(2): 383-393. |
| [36] | WU D, ZHANG W M, XIU L Q, et al., 2022. Soybean yield response of biochar-regulated soil properties and root growth strategy[J]. Agronomy, 12(6): 1412. |
| [37] | XIU L Q, ZHANG W M, SUN Y Y, et al., 2019. Effects of biochar and straw returning on the key cultivation limitations of Albic soil and soybean growth over 2 years[J]. Catena, 173: 481-493. |
| [38] | YUAN J H, XU R K, QIAN W, et al., 2011. Comparison of the ameliorating effects on an acidic ultisol between four crop straws and their biochars[J]. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 11(5): 741-750. |
| [39] | 鲍士旦, 2005. 土壤农化分析[M]. 第3版. 北京: 中国农业出版社. |
| BAO S D, 2005. Soil agrochemical analysis[M]. The 3rd edition. Beijing: China Agricultural Press. | |
| [40] | 陈心想, 何绪生, 耿增超, 等, 2013. 生物炭对不同土壤化学性质、小麦和糜子产量的影响[J]. 生态学报, 33(20): 6534-6542. |
| CHEN X X, HE X X, GENG Z C, et al., 2013. The effect of biochar on different soil chemical properties, wheat and millet yields[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 33(20): 6534-6542. | |
| [41] | 葛博浩, 耿新, 刘艳晶, 等, 2024. 植物硅转运蛋白研究进展[J]. 热带亚热带植物学报, 32(4): 562-570. |
| GE B H, GEN X, LIU Y J, et al., 2024. Research progress on plant silicon transporters[J]. Journal of Tropical and Subtropical Botany, 32(4): 562-570. | |
| [42] |
侯伟男, 刘靖愉, 邢一唱, 等, 2021. 生物炭施入量对大豆生长发育及产量的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 37(15): 14-19.
DOI |
| HOU W N, LIU J Y, XING Y C, et al., 2021. Effects of biochar application amount on growth and yield of soybean[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 37(15): 14-19. | |
| [43] |
吕波, 王宇函, 夏浩, 等, 2018. 不同改良剂对黄棕壤和红壤上白菜生长及土壤肥力影响的差异[J]. 中国农业科学, 51(22): 4306-4315.
DOI |
| LÜ B, WANG Y H, XIA H, et al., 2018. Differences in the effects of different amendments on the growth of Chinese cabbage and soil fertility on yellow brown soil and red soil[J]. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 51(22): 4306-4315. | |
| [44] | 魏永霞, 石国新, 冯超, 等, 2020. 黑土区施加生物炭对土壤综合肥力与大豆生长的影响[J]. 农业机械学报, 51(5): 285-294. |
| WEI Y X, SHI G X, FENG C, et al., 2020. The effect of applying biochar on soil comprehensive fertility and soybean growth in black soil areas[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Machinery, 51(5): 285-294. | |
| [45] | 吴昱, 赵雨森, 刘慧, 2019. 不同的生物炭施用量和施用年限对土壤结构性指标的影响[J]. 水利科学与寒区工程, 2(3): 5-11. |
| WU Y, ZHAO Y S, LIU H, 2019. The impact of different amounts and years of biochar application on soil structural indicators[J]. Hydro Science and Cold Zone Engineering, 2(3): 5-11. | |
| [46] | 吴愉萍, 王明湖, 席杰君, 等, 2019. 不同农业废弃物生物炭及施用量对土壤pH值和保水保氮能力的影响[J]. 中国土壤与肥料 (1): 87-92. |
| WU Y P, WANG M H, XI J J, et al., 2019. The effects of different agricultural waste biochar and application rates on soil pH value and water and nitrogen retention capacity[J]. Soils and Fertilizers Sciences in China (1): 87-92. | |
| [47] | 徐刚, 张友, 武玉, 等, 2016. 生物炭对土壤中氮磷有效性影响的研究进展[J]. 中国科学: 生命科学, 46(9): 1085-1090. |
| XU G, ZHANG Y, WU Y, et al., 2016. Research progress on the effects of biochar on the availability of nitrogen and phosphorus in soil[J]. Scientia Sinica (Vitae), 46(9): 1085-1090. | |
| [48] | 徐仁扣, 李九玉, 周世伟, 等, 2018. 我国农田土壤酸化调控的科学问题与技术措施[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 33(2): 160-167. |
| XU R K, LI J Y, ZHOU S W, et al., 2018. Scientific problems and technical measures of soil acidification control in farmland in China[J]. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 33(2): 160-167. | |
| [49] | 宋文涛, 宁川川, 黄美琳, 等, 2023. 秸秆生物炭对两种典型土壤的养分特性及硅的化学形态的影响[J]. 生态科学, 42(5): 123-132. |
| SONG W T, NING C C, HUANG M L, et al., 2023. The effect of straw biochar on nutrient characteristics and chemical forms of silicon in two typical soils[J]. Ecological Science, 42(5): 123-132. | |
| [50] | 张庚金, 贾露露, 索猛利, 等, 2024. 酸化与富磷影响农田土壤硅的移动性[J]. 中国土壤与肥料, (1): 51-59. |
| ZHANG G J, JIA L L, SUO M L, et al., 2024. Acidification and phosphorus enrichment affect the mobility of silicon in farmland soil[J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences, (1): 51-59. | |
| [51] | 张玲玉, 赵学强, 沈仁芳, 2019. 土壤酸化及其生态效应[J]. 生态学杂志, 38(6): 1900-1908. |
| ZHANG L Y, ZHAO X Q, SHEN R F, 2019. Soil acidification and its ecological effects[J]. Journal of Ecology, 38(6): 1900-1908. | |
| [52] | 张冉, 高宝林, 郭丽莉, 等, 2021. 贝壳类废弃物用于钝化土壤重金属的研究进展[J]. 农业资源与环境学报, 38(5): 787-796. |
| ZHANG R, GAO B L, GUO L L, et al., 2021. Research progress of shell waste for passivation of heavy metals in soil[J]. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment, 38(5): 787-796. | |
| [53] | 张伟明, 管学超, 黄玉威, 等, 2015. 玉米芯生物炭对大豆的生物学效应[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 34(2): 391-400. |
| ZHANG W M, GUAN X C, HUANG Y W, et al., 2015. Biological effects of corncob biochar on soybean[J]. Journal of Agro- Environment Science, 34(2): 391-400. | |
| [54] |
周鑫, 冯改利, 李治红, 等, 2020. 环境条件对黄瓜硅吸收分配和果面蜡粉形成的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 31(2): 501-507.
DOI |
| ZHOU X, FENG G L, LI Z H, et al., 2020. The influence of environmental conditions on the absorption and distribution of silicon in cucumber and the formation of wax powder on fruit surface[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 31(2): 501-507. |
| [1] | 梁祝, 潘树林, 郭芳成. 向家坝蓄水前后长江上游干流四川段氮磷的时空分布变化[J]. 生态环境学报, 2025, 34(4): 581-592. |
| [2] | 梅耀萍, 吴本丽, 黄龙, 吴仓仓, 陈静, 陈夏君, 何吉祥. 不同水生植物对水产养殖尾水氮磷去除效果研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2025, 34(3): 442-450. |
| [3] | 温珊, 邢思奇, 肖宇翔, 刘云, 吴旭. 基于多场耦合有限元的天福庙水库清淤过程污染物磷释放行为研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(9): 1438-1450. |
| [4] | 范贝贝, 丁帅, 张田田, 张帅, 魏露露, 陈清. 周期性淹水-落干和施用秸秆对白云石改良棕壤磷素流失风险的模拟研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(8): 1203-1213. |
| [5] | 卢聪. 生物炭负载纳米零价铁对沉积物中十溴二苯乙烷去除效果及机制[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(8): 1279-1288. |
| [6] | 陈文哲, 黄秋香, 孟凡德, 高金妍, 李敏, 张恩俊, 袁国栋. 草酸和酒石酸对稻田土壤中砷解吸行为的影响研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(8): 1298-1305. |
| [7] | 姜晓静, 谢嘉慧, 马凯, 高丽. 天鹅湖沉积物中解磷菌的解磷能力及其对硬毛藻生长的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(4): 633-644. |
| [8] | 王室苹, 李梅, 安娅, 秦好丽. 镁改性增强小麦秸秆生物炭对镉的吸附能力:表面络合模型研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(4): 617-625. |
| [9] | 肖江, 李晓刚, 赵博, 陈岩, 陈光才. 微纳富磷生物炭对土壤-苏柳系统中Cu和Pb稳定性的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(3): 439-449. |
| [10] | 刘楚天, 郭栋栋, 侯磊, 梁启斌, 王艳霞, 施艳婷, 戚艳娥. 营养调控影响滇杨幼苗镉积累的效应模型分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(3): 460-468. |
| [11] | 江润海, 温绍福, 朱城强, 张梅, 杨润玲, 王春雪, 侯秀丽. 铅污染矿区中耐铅解磷菌对玉米的促生及根际铅的固化效应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(2): 291-300. |
| [12] | 李高帆, 徐文卓, 卫昊明, 晏再生, 尤佳, 江和龙, 黄娟. 三维多孔生物炭吸附剂的制备及其对菲的吸附行为[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(2): 261-271. |
| [13] | 丛鑫, 曹平, 王晓博. 生物炭负载纳米铁活化过硫酸盐去除土壤中的五氯联苯[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(2): 282-290. |
| [14] | 梁燕, 刘家齐, 肖凡, 潘民萍, 韦凯文, 张楚雯, 段敏. 氮沉降形态对西南岩溶区森林土壤有效磷来源的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(2): 192-201. |
| [15] | 李璞君, 唐丽, 赵博, 邸东柳, 陈岩, 肖江, 陈光才. 生物炭基土壤改良剂对锑矿区土壤质量及亮叶桦生长的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(12): 1953-1963. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
