生态环境学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (12): 1953-1963.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2024.12.013
李璞君1,2( ), 唐丽1, 赵博2, 邸东柳2, 陈岩2, 肖江2,*(
), 唐丽1, 赵博2, 邸东柳2, 陈岩2, 肖江2,*( ), 陈光才2
), 陈光才2
收稿日期:2024-08-16
出版日期:2024-12-18
发布日期:2024-12-31
通讯作者:
*肖江。E-mail: jiangxiao0915@caf.ac.cn作者简介:李璞君(1998年生),女,硕士研究生,主要研究方向为土壤重金属改良和植被恢复。E-mail: 3478094921@qq.com
基金资助:
LI Pujun1,2( ), TANG Li1, ZHAO Bo2, DI Dongliu2, CHEN Yan2, XIAO Jiang2,*(
), TANG Li1, ZHAO Bo2, DI Dongliu2, CHEN Yan2, XIAO Jiang2,*( ), CHEN Guangcai2
), CHEN Guangcai2
Received:2024-08-16
Online:2024-12-18
Published:2024-12-31
摘要:
土壤基质改良对改善矿区土壤质量、提升植被建成效率具有重要作用。采用贵州晴隆锑矿区污染土壤为供试土壤,并以非矿区土壤为对照,添加生物炭基土壤改良剂(BBOF,施用量0% (T1)、1% (T2)、3% (T3))研究BBOF对锑矿区污染土壤物理、化学和生物特性的改良及其对亮叶桦(Betula luminifera H. J. P. Winkl.)生长、生理和Sb、As浓度、富集与转运的影响。结果表明:添加BBOF显著改善土壤质量,其中T2处理显著增加了土壤含水率(26.00%)、孔隙度(32.42%)(p<0.05)。T3处理下,土壤pH值、有机碳质量分数分别显著提高了7.74%、31.78%(p<0.05),土壤TN、TP、TK和AN、AK、AP质量分数分别提高了38.15%、74.78%、1.41%和65.02%、336.20%、98.38%,土壤脲酶、酸性磷酸酶和β-葡萄糖苷酶活性显著增加了92.53%、41.86%和175.33%(p<0.05),亮叶桦株高、基径及地上、地下生物量分别显著增加了26.37%、39.66%、142.00%和118.62%(p<0.05),而亮叶桦根、茎、叶中锑的浓度分别下降了73.00%、25.73%和4.48%。总体而言,BBOF提高了锑矿区土壤有机碳、矿质养分质量分数以及参与碳氮磷循环土壤酶的活性;促进了亮叶桦在锑矿区污染土壤中的生长。施用1%的BBOF能有效恢复锑矿区污染土的土壤功能,促进亮叶桦在锑矿区土壤的生长,为后续锑矿区土壤改良以及植被修复提供实践参考。
中图分类号:
李璞君, 唐丽, 赵博, 邸东柳, 陈岩, 肖江, 陈光才. 生物炭基土壤改良剂对锑矿区土壤质量及亮叶桦生长的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(12): 1953-1963.
LI Pujun, TANG Li, ZHAO Bo, DI Dongliu, CHEN Yan, XIAO Jiang, CHEN Guangcai. The Amelioration of Biochar Soil Amendment on Antimony Mining Soil and Growth of Betula luminifera[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2024, 33(12): 1953-1963.
| 处理 | w(土壤水分)/% | 土壤容重/(g∙cm−3) | 土壤孔隙度/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| CK T1 T2 T3 | 0.19±0.02b 0.13±0.01a 0.16±0.01ab 0.16±0.02ab | 3.19±0.18a 2.81±0.09a 3.12±0.1a 2.86±0.16a | 0.42±0.05b 0.28±0.02a 0.37±0.02ab 0.34±0.05ab |
表1 BBOF对土壤物理性质的影响
Table 1 Effects of BBOF on the soil physical properties
| 处理 | w(土壤水分)/% | 土壤容重/(g∙cm−3) | 土壤孔隙度/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| CK T1 T2 T3 | 0.19±0.02b 0.13±0.01a 0.16±0.01ab 0.16±0.02ab | 3.19±0.18a 2.81±0.09a 3.12±0.1a 2.86±0.16a | 0.42±0.05b 0.28±0.02a 0.37±0.02ab 0.34±0.05ab |
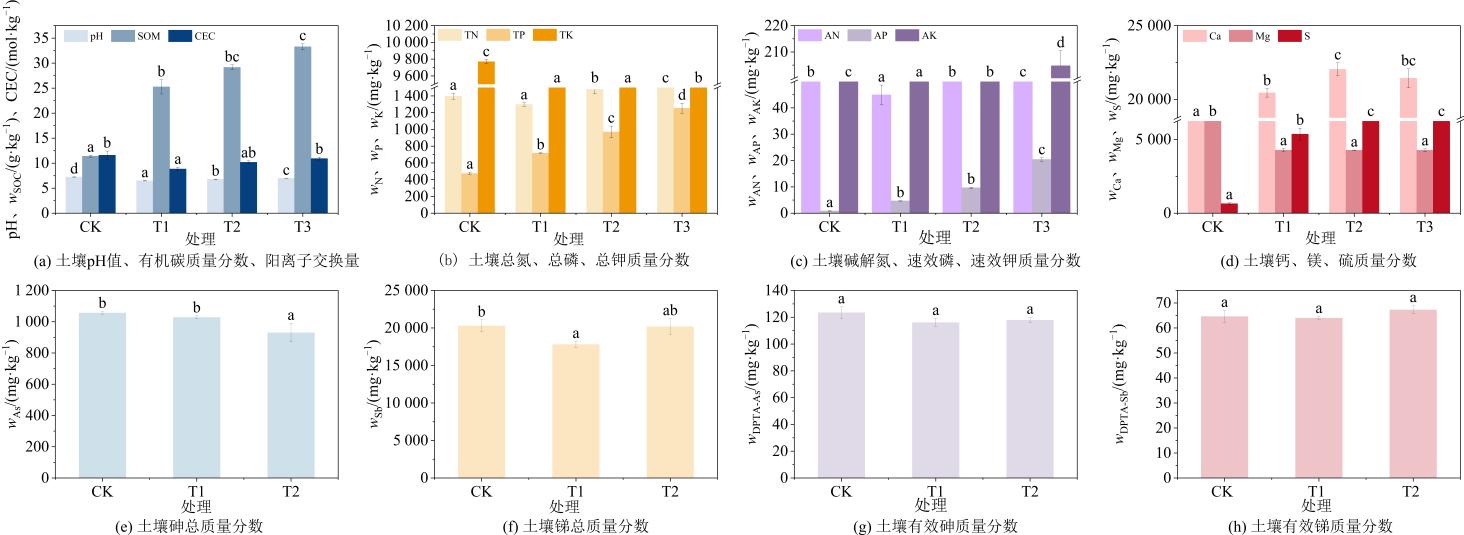
图1 BBOF对土壤主要理化性质和锑砷总量及生物有效性的影响
Figure 1 Effects of BBOF on the soil main physical and chemical propertiestotal and bioavailability contents of antimony and arsenic
| 处理 | 脲酶活性/ (μmol·g−1·d−1) | 酸性磷酸酶活性/ (μmol·g−1·d−1) | β-葡萄糖苷酶活性/ (μmol·g−1·d−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CK T1 T2 T3 | 0.48±0.015d 0.13±0.006a 0.19±0.006b 0.25±0.015c | 0.45±0.044b 0.31±0.002a 0.46±0.042b 0.43±0.068ab | 35.06±2.695b 24.65±0.888a 27.81±1.719a 34.96±2.445b |
表2 BBOF对土壤酶活性的影响
Table 2 Effects of BBOF on the soil enzyme activity
| 处理 | 脲酶活性/ (μmol·g−1·d−1) | 酸性磷酸酶活性/ (μmol·g−1·d−1) | β-葡萄糖苷酶活性/ (μmol·g−1·d−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CK T1 T2 T3 | 0.48±0.015d 0.13±0.006a 0.19±0.006b 0.25±0.015c | 0.45±0.044b 0.31±0.002a 0.46±0.042b 0.43±0.068ab | 35.06±2.695b 24.65±0.888a 27.81±1.719a 34.96±2.445b |
| 处理 | SOD (by FW)/ (U·g−1·min−1) | CAT (by FW)/ (U·g−1·min−1) | MDA (by FW)/ (μmol·g−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CK T1 T2 T3 | 2.63±0.08a 5.67±0.06d 3.57±0.11b 3.88±0.08c | 1.26±0.2a 1.52±0.11a 1.12±0.08a 1.13±0.22a | 1.56±0.02a 1.76±0.02b 1.68±0.01b 1.58±0.01a |
表3 BBOF对亮叶桦抗氧化系统的影响
Table 3 Effects of BBOF on antioxidant system of Betula luminifera
| 处理 | SOD (by FW)/ (U·g−1·min−1) | CAT (by FW)/ (U·g−1·min−1) | MDA (by FW)/ (μmol·g−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CK T1 T2 T3 | 2.63±0.08a 5.67±0.06d 3.57±0.11b 3.88±0.08c | 1.26±0.2a 1.52±0.11a 1.12±0.08a 1.13±0.22a | 1.56±0.02a 1.76±0.02b 1.68±0.01b 1.58±0.01a |
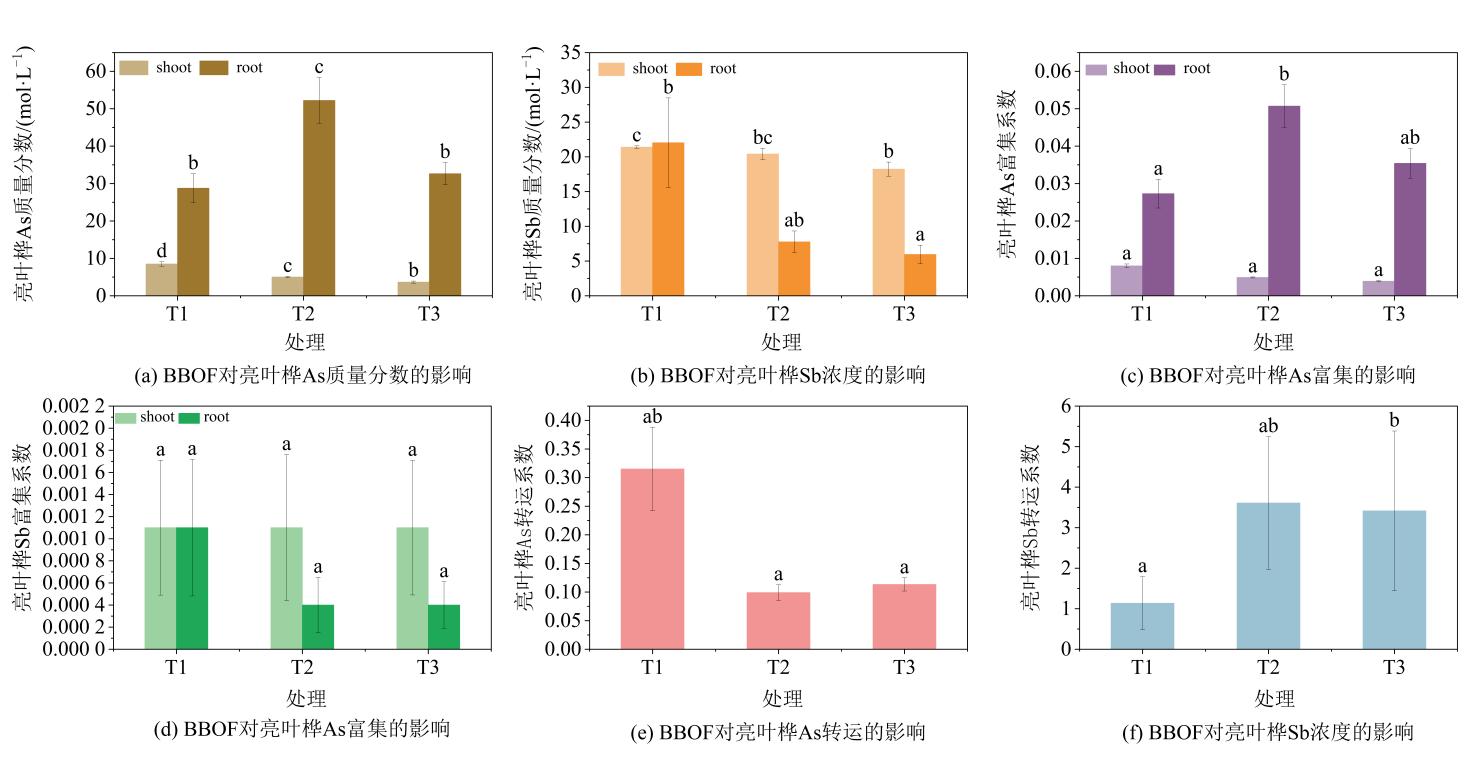
图4 BBOF对亮叶桦锑砷质量分数、生物富集系数和转运系数的影响
Figure 4 Effects of BBOF on the concentration,bioconcentration factors and translocation factor of antimony and arsenic in Betula luminifera
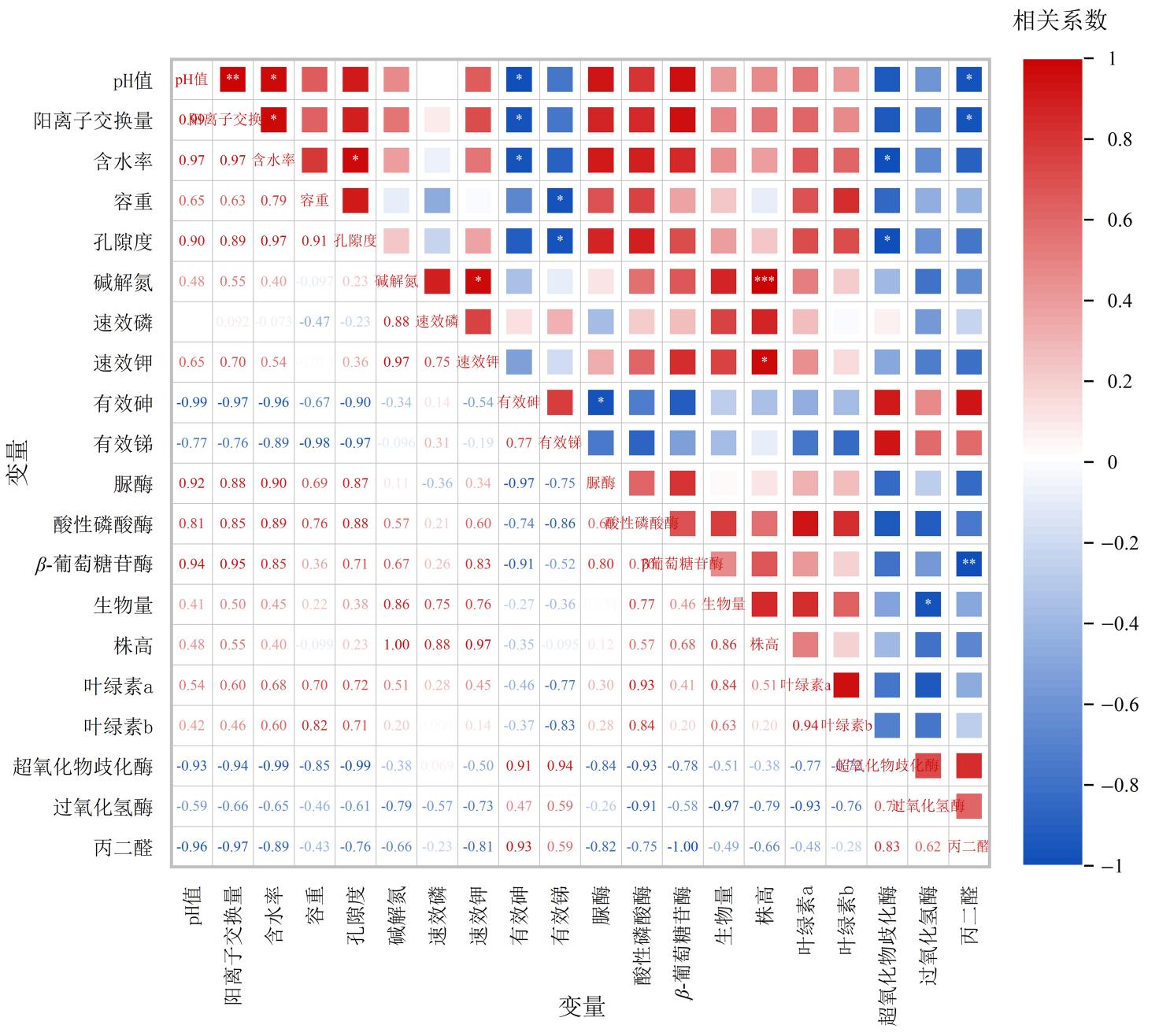
图5 BBOF处理下锑矿区土壤改良与亮叶桦生长生理及重金属积累相关性分析 *代表p≤0.05,**代表p≤0.01,***代表p≤0.001;红色代表正相关,蓝色代表负相关
Figure 5 Correlation analysis of soil improvement in antimony mine area with growth physiology and heavy metal accumulation in Betula luminifera under BBOF treatment
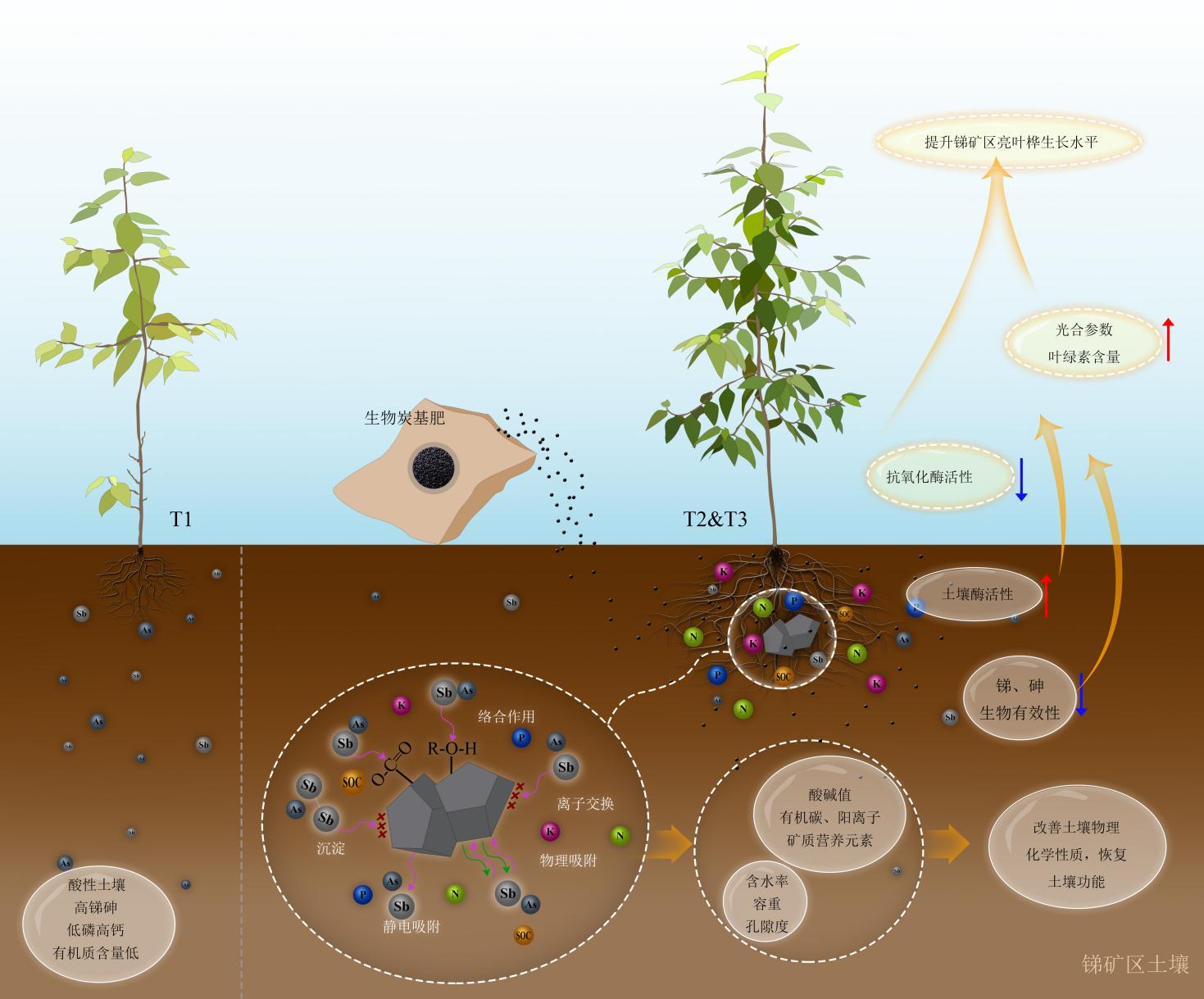
图7 BBOF对锑矿区土壤的改良及亮叶桦生长潜在影响机制
Figure 7 The potential mechanism of soil improvement and Betula luminifera growth in antimony mining area effected by BBOF
| [1] | AHMAD M, LEE S S, LEE S E, et al., 2017. Biochar-induced changes in soil properties affected immobilization/mobilization of metals/metal loids in contaminated soils[J]. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 17: 717-730. |
| [2] |
AHMAD M, LEE S S, LIM J E, et al., 2014. Speciation and phytoavailability of lead and antimony in a small arms range soil amended with mussel shell, cow bone and biochar: EXAFS spectroscopy and chemical extractions[J]. Chemosphere, 95: 433-441.
DOI PMID |
| [3] | AN Y J, KIM M, 2009. Effect of antimony on the microbial growth and the activities of soil enzymes[J]. Chemosphere, 74(5): 654-659. |
| [4] | BEESLEY L, MORENO-JIMÉNEZ E, Gomez-Eyles J L, et al., 2011. A review of biochars’ potential role in the remediation, revegetation and restoration of contaminated soils[J]. Environmental Pollution, 159(12): 3269-3282. |
| [5] | BOLAN N, KUNHIKRISHNAN A, GIBBS J, 2013. Rhizoreduction of arsenate and chromate in Australian native grass, shrub and tree vegetation[J]. Plant and Soil, 367: 615-625. |
| [6] | BOLAN N, KUNHIKRISHNAN A, THANGARAJAN R, et al., 2014. Remediation of heavy metal (loid) s contaminated soils-to mobilize or to immobilize?[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 266: 141-166. |
| [7] | CHEW J K, ZHU L L, NIELSEN S, et al., 2020. Biochar-based fertilizer: supercharging root membrane potential and biomass yield of rice[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 713: 136431. |
| [8] | DUPONT D, ARNOUT S, JONES P T, et al., 2016. Antimony recovery from end-of-life products and industrial process residues: A critical review[J]. Journal of Sustainable Metallurgy, 2(1): 79-103. |
| [9] | FENG R W, WEI C Y, TU S X, et al., 2009. Antimony accumulation and antioxidative responses in four fern plants[J]. Plant and Soil, 317: 93-101. |
| [10] | FENG R W, WEI C Y, TU S X, et al., 2013. The uptake and detoxification of antimony by plants: A review[J]. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 96: 28-34. |
| [11] | GREGORY S J, ANDERSON C W N, ARBRSTAIN M C, et al., 2014. Response of plant and soil microbes to biochar amendment of an arsenic-contaminated soil[J]. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 191: 133-141. |
| [12] | HALE B, EVANS L, LAMBERT R, 2012. Effects of cement or lime on Cd, Co, Cu, Ni, Pb, Sb and Zn mobility in field-contaminated and aged soils[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 199(15): 119-127. |
| [13] | HONG Y, LI D, XIE C, et al., 2022. Combined apatite, biochar, and organic fertilizer application for heavy metal co-contaminated soil remediation reduces heavy metal transport and alters soil microbial community structure[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 851(Part 1): 158033. |
| [14] | HU X Y, HE M C, LI S S, et al., 2017. The leaching characteristics and changes in the leached layer of antimony-bearing ores from China[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 176: 76-84. |
| [15] | JIANG L, SHI G, DING Y, et al., 2013. Differential responses of two bamboo species (Phyllostachys auresulcata ‘Spectabilis’ and Pleioblastus Chino `Hisauchii') to excess copper[J]. BioEnergy Research, 6: 1223-1229. |
| [16] |
KUPPUSAMY S, THAVAMANI P, MEGHARAJ M, et al., 2016. Agronomic and remedial benefits and risks of applying biochar to soil: Current knowledge and future research directions[J]. Environment International, 87: 1-12.
DOI PMID |
| [17] | KUZYAKOV Y, SUBBOTINA I, CHEN H, et al., 2009. Black carbon decomposition and incorporation into soil microbial biomass estimated by 14C labeling[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 41(2): 210-219. |
| [18] | LEHMANN J, RILLIGM C, THIES J, et al., 2011. Biochar effects on soil biota: A review[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 43(9): 1812-1836. |
| [19] |
LI J N, WEI Y, ZHAO L, et al., 2014. Bioaccessibility of antimony and arsenic in highly polluted soils of the mine area and health risk assessment associated with oral ingestion exposure[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 110: 308-315.
DOI PMID |
| [20] | LI Y, DEMISIE W, ZHANG M K, 2015. Digestion tests to measure heavy metal bioavailability in soils[J]. CO2 Sequestration, Biofuels and Depollution, 275-305. |
| [21] | MA C L, HE M C, ZHONG Q Y, et al., 2019. Uptake, translocation and phytotoxicity of antimonite in wheat (Triticum aestivum)[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 669: 421-430. |
| [22] | OKKENHAUG G, AMSTÄTTER K, LASSEN BUE H, et al., 2013. Antimony (Sb) contaminated shooting range soil: Sb mobility and immobilization by soil amendments[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 47(12): 6431-6439. |
| [23] | PRAPAGDEE S, TAWINTEUNG N, 2017. Effects of biochar on enhanced nutrient use efficiency of green bean, Vigna radiata L[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 24(10): 9460-9467. |
| [24] | QIAN L B, CHEN B L, 2013. Dual role of biochars as adsorbents for aluminum: The effects of oxygen-containing organic components and the scattering of silicate particles[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 47(15): 8759-8768. |
| [25] | ROUT G R, SAMANTARAY S, DAS P, 1999. Differential cadmium tolerance of mung bean and rice genotypes in hydroponic culture[J]. Acta Agriculturae Scandinavica, Section B-Plant Soil Science, 49(4): 234-241. |
| [26] | RUIZ-CHANCHO M J, LÓPEZ-SÁNCHEZ J F, SCHMEISSER E, et al., 2008. Arsenic speciation in plants growing in arsenic-contaminated sites[J]. Chemosphere, 71(8): 1522-1530. |
| [27] | SCHULZ H, DUNST G, GLASER B, 2013. Positive effects of composted biochar on plant growth and soil fertility[J]. Agronomy for Sustainable Development, 33: 817-827. |
| [28] | YAN B J, ZHANG Y P, WANG Y Z, et al., 2023. Biochar amendments combined with organic fertilizer improve maize productivity and mitigate nutrient loss by regulating the C-N-P stoichiometry of soil, microbiome, and enzymes[J]. Chemosphere, 324: 138293. |
| [29] | YANG W H, LI C J, WANG S S, et al., 2021. Influence of biochar and biochar-based fertilizer on yield, quality of tea and microbial community in an acid tea orchard soil[J]. Applied Soil Ecology, 166: 104005. |
| [30] |
YE J, ZHANG R, NIELSEN S, et al., 2016. A combination of biochar-mineral complexes and compost improves soil bacterial processes, soil quality, and plant properties[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 7: 372.
DOI PMID |
| [31] |
ZHANG J N, ZHOU S, SUN H F, et al., 2019. Three-year rice grain yield responses to coastal mudflat soil properties amended with straw biochar[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 239: 23-29.
DOI PMID |
| [32] | ZHANG Q, ZHOU W, LIANG G Q, et al., 2015. Distribution of soil nutrients, extracellular enzyme activities and microbial communities across particle-size fractions in a long-term fertilizer experiment[J]. Applied Soil Ecology, 94: 59-71. |
| [33] | ZHANG Z, JIA C X, GAN Y D, et al., 2022. Impact of biochars on the iron plaque formation and the antimony accumulation in rice seedings[J]. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 109(6): 1088-1094. |
| [34] | ZHOU C, HEAL K, TIGABU M, et al., 2020. Biochar addition to forest plantation soil enhances phosphorus availability and soil bacterial community diversity[J]. Forest Ecology and Management, 455: 117635. |
| [35] | ZHU P F, ZHU J R, PANG J Y, et al., 2020. Biochar improves the growth performance of maize seedling in response to antimony stress[J]. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 231(4): 1-12. |
| [36] | 鲍士旦, 2000. 土壤农化分析[M]. 第3版. 北京: 中国农业出版社. |
| BAO S D, 2000. Soil agricultural chemistry analysis[M]. Third edition. Beijing: China Agriculture Press. | |
| [37] | 杜忠毓, 邢文黎, 薛亮, 等, 2023. 喀斯特石漠化锑矿区植物群落主要物种生态位特征及其种间联结[J]. 生态学报, 43(7): 2865-2880. |
| DU Z Y, XING W L, XUE L, et al., 2023. Niche characteristics and interspecific association of main plant species in antimony mining sites of karst rocky desertification area Guizhou China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 43(7): 2865-2880. | |
| [38] | 关松荫, 1986. 土壤酶及其研究法[M]. 北京: 农业出版社. |
| GUAN S Y, 1986. Soil enzymes and their research methods[M]. Beijing: Agriculture Press. | |
| [39] | 李合生, 2000. 植物生理生化实验原理和技术[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社. |
| LI H S, 2000. Principles and techniques of plant physiological biochemical experiment[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press. | |
| [40] | 柳骁桐, 纪立东, 孙权, 等, 2021. 炭基肥连续两年施用对土壤质量的影响[J]. 北方园艺 (7): 96-103. |
| LIU X T, JI L D, SUN Q, et al., 2021. Effects of continuous application of carbon-based fertilizer on soil quality for two years[J]. Northern Horticulture (7): 96-103. | |
| [41] | 刘振刚, 夏宇, 孟芋含, 等, 2021. 生物质炭材料修复重金属污染土壤的研究进展: 修复机理及研究热点分析[J]. 环境工程学报, 15(4): 1140-1148. |
| LIU Z G, XIA Y, MENG Y H, et al., 2021. Research advances in biomass-based carbon materials for remediation of heavy metal contaminated soil: Immobilization mechanism and analysis of related studies[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 15(4): 1140-1148. | |
| [42] | 环境保护部, 2017. 土壤阳离子交换量的测定三氯化六氨合钴浸提-分光光度法: HJ 889—2017 [S]. 北京: 中国环境出版社. |
| Ministry of Environmental Protection. 2017. Soil quality determination of cation exchange capacity (CEC) hexamminecobalt trichloride solution-spectrophotometric method: HJ 889—2017 [S]. Beijing: China Environment Press. | |
| [43] | 马兴, 2022. 锑污染对土壤酶的作用机理及生态效应研究[D]. 咸阳: 西北农林科技大学. |
| MA X, 2022. The mechanism and ecological effect of antimony pollution on soil enzymes[D]. Xianyang: Northwest A & F University. | |
| [44] | 王友保, 2018. 土壤污染生态修复实验技术[M]. 北京: 科学出版社. |
| WANG Y B, 2018. Experimental technology for ecological remediation of soil pollution[M]. Beijing: Science Press. | |
| [45] | 沈阳农业大学, 2016. 生物炭基肥料: NY 3041—2016 [S]. 北京: 中国农业出版社. |
| Shengyang Agricultural University, 2016. Biochar-based fertilizer: NY 3041—2016 [S]. Beijing: China Agricultural Press. | |
| [46] | 施海涛, 2016. 植物逆境生理学实验指导[M]. 北京: 科学出版社. |
| SHI H T, 2016. Experimental guidance of plant stress physiology[M]. Beijing: Science Press. | |
| [47] | 宋刚练, 2018. 重金属锑污染土壤固化-稳定化修复技术研究及应用[J]. 环境与可持续发展, 43(2): 61-64. |
| SONG G L, 2018. Study and application of solidification-stabilization technology for heavy metal contaminated soil of antimony[J]. Environment and Sustainable Development, 43(2): 61-64. | |
| [48] | 张欢, 花莉, 罗婷, 2019. 锑胁迫下生物炭对番茄锑积累及生化特性的影响[J]. 生态学杂志, 38(4): 983-994. |
| ZHANG H, HUA L, LUO T, 2019. Effects of biochar on Sb accumulation and biochemical characteristics of Lycopersicum esculentum in Sb-contaminated soil[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 38(4): 983-994. | |
| [49] | 张菊梅, 刘灵飞, 龙健, 等, 2019. 土壤锑污染及其修复技术研究进展[J]. 环境科学与技术, 42(4): 61-70. |
| ZHANG J M, LIU L F, LONG J, et al., 2019. Research progress on soil antimony pollution and its remediation technology[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 42(4): 61-70. | |
| [50] | 张继宁, 周胜, 孙会峰, 等, 2018. 生物质炭在我国蔬菜地应用的研究现状与展望[J]. 农业现代化研究, 39(4): 543-550. |
| ZHANG J N, ZHOU S, SUN H F, et al., 2018. Research progress and prospects on the biochar’s application in Chinese vegetable field[J]. Research of Agricultural Modernization, 39(4): 543-550. | |
| [51] | 赵晓鹏, 杨博一, 李超, 等, 2024. 贵州晴隆锑矿区土壤中锑的形态分布和地球化学模型[J]. 环境化学, 43(3): 911-919. |
| ZHAO X P, YANG B Y, LI C, et al., 2024. Species distribution and geochemical modeling of antimony in the Qinlong antimony mining area[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 43(3): 911-919. | |
| [52] | 赵泽州, 王晓玲, 李鸿博, 等, 2021. 生物质炭基肥缓释性能及对土壤改良的研究进展[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 27(5): 886-897. |
| ZHAO Z Z, WANG X L, LI H B, et al., 2021. Slow-release property and soil remediation mechanism of biochar-based fertilizers[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 27(5): 886-897. |
| [1] | 丛鑫, 张怀迪, 张荣, 赵琛, 陈坤, 刘寒冰. 基于Meta分析的近10年中国农田土壤重金属污染特征与风险解析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(9): 1451-1459. |
| [2] | 刘东宜, 屈永华, 冯耀伟, 屈冉. 基于网格搜索优化CatBoost模型的GF-5卫星影像铬离子含量反演研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(9): 1460-1470. |
| [3] | 欧阳美凤, 尹宇莹, 张金谌, 刘清霖, 谢意南, 方平. 洞庭湖典型水域重金属含量的空间分布与来源解析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(8): 1269-1278. |
| [4] | 吴文伟, 沈城, 沙晨燕, 林匡飞, 吴健, 谢雨晴, 周璇. 城市工业地块土壤重金属污染风险评价与源解析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(5): 791-801. |
| [5] | 肖江, 李晓刚, 赵博, 陈岩, 陈光才. 微纳富磷生物炭对土壤-苏柳系统中Cu和Pb稳定性的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(3): 439-449. |
| [6] | 刘楚天, 郭栋栋, 侯磊, 梁启斌, 王艳霞, 施艳婷, 戚艳娥. 营养调控影响滇杨幼苗镉积累的效应模型分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(3): 460-468. |
| [7] | 江润海, 温绍福, 朱城强, 张梅, 杨润玲, 王春雪, 侯秀丽. 铅污染矿区中耐铅解磷菌对玉米的促生及根际铅的固化效应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(2): 291-300. |
| [8] | 李嘉惠, 童辉, 陈曼佳, 刘承帅, 姜琪, 易秀. 微氧生物亚铁氧化及其重金属固定效应研究进展[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(2): 310-320. |
| [9] | 马志伟, 张丛志, 赵占辉, 吴其聪, 赵金花, 陈卓, 李敬王, 张楠, 薛雅, 王娅茹, 陆芸萱, 张佳宝. 基于木本泥炭的土壤健康培育研究进展[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(12): 1964-1977. |
| [10] | 唐舒娅, 王春辉, 宋靖, 李刚. 环象山港区域土壤重金属污染特征及风险评估[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(11): 1768-1781. |
| [11] | 杨正桥, 邹奇, 韦行, 周凯, 陈志良. 金属尾矿微生物对尾矿环境的适应与调控机制研究进展[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(1): 156-166. |
| [12] | 王宁, 刘效东, 甘先华, 苏宇乔, 吴国章, 黄芳芳, 张卫强. 亚热带典型林分降水过程中的水质效应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(8): 1365-1375. |
| [13] | 刘炳妤, 王一佩, 姚作芳, 杨钙仁, 徐晓楠, 邓羽松, 黄钰涵. 沼液还田下不同种植模式的重金属风险评价及安全消纳量分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(8): 1507-1515. |
| [14] | 李振国, 郝星雨, 贺甜莲, 景蕊, 荣成, 顾承真, 郑新宇. 竹醋液对紫苏镉毒的缓解效应研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(7): 1313-1324. |
| [15] | 杜丹丹, 高瑞忠, 房丽晶, 谢龙梅. 旱区盐湖盆地土壤重金属空间变异及对土壤理化因子的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(6): 1123-1132. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
