生态环境学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (2): 192-201.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2024.02.003
梁燕1,2( ), 刘家齐1,2, 肖凡3, 潘民萍1, 韦凯文1, 张楚雯1, 段敏1,2,*(
), 刘家齐1,2, 肖凡3, 潘民萍1, 韦凯文1, 张楚雯1, 段敏1,2,*( )
)
收稿日期:2023-12-12
出版日期:2024-02-18
发布日期:2024-04-03
通讯作者:
*段敏。E-mail: duanmin0517@163.com作者简介:梁燕(1999年生),女,硕士研究生,主要从事岩溶区森林土壤磷循环研究。E-mail: 1525325251@qq.com
基金资助:
LIANG Yan1,2( ), LIU Jiaqi1,2, XIAO Fan3, PAN Minping1, WEI Kaiwen1, ZHANG Chuwen1, DUAN Min1,2,*(
), LIU Jiaqi1,2, XIAO Fan3, PAN Minping1, WEI Kaiwen1, ZHANG Chuwen1, DUAN Min1,2,*( )
)
Received:2023-12-12
Online:2024-02-18
Published:2024-04-03
摘要:
森林生态系统氮和磷之间具有密切的耦合关系,阐明氮沉降形态对中国西南岩溶区森林土壤有效磷不同来源的影响,对推动全球环境变化条件下岩溶区退化森林植被恢复具有重要意义。以广西桂林岩溶区典型森林为研究对象,在野外模拟不同形态氮沉降(无氮沉降 (CK)、氧化态氮沉降 (Oxi)、还原态氮沉降 (Red) 和氧化还原态氮沉降 (RO)),在模拟氮沉降1.5 a后通过连续监测各季节凋落物、植物根系和雨水磷输入量,结合土壤全磷和有效磷的季节变化特征,探究氮沉降形态对中国西南岩溶区森林土壤有效磷不同来源的影响。结果表明:Oxi和Red处理显著提高了土壤有效磷含量,而RO处理对土壤有效磷含量的影响因季节不同而存在差异,所有氮沉降处理对土壤全磷含量的影响均不显著;CK处理凋落物磷年输入量为10.64 kg∙hm−2,植物根系磷年输入量为12.65 kg∙hm−2,雨水磷年输入量为0.78 kg∙hm−2;所有氮沉降处理均显著增加了凋落物磷年输入量,而Oxi和Red处理均显著降低了植物根系磷年输入量,RO处理对植物根系磷年输入量没有显著影响。结构方程模型表明,Oxi处理增强了季节对土壤有效磷含量的直接影响;Red处理增强了季节、凋落物磷输入量、雨水磷输入量以及土壤理化性质对土壤有效磷含量的直接影响。综上分析,中国西南岩溶区森林土壤有效磷主要来源为植物根系,其次是凋落物,雨水对土壤有效磷的贡献较小;氮沉降形态不同程度地改变了土壤磷不同来源的输入量和磷的有效性,可在一定程度上缓解森林土壤磷限制,有利于岩溶区退化森林生态系统植被恢复。
中图分类号:
梁燕, 刘家齐, 肖凡, 潘民萍, 韦凯文, 张楚雯, 段敏. 氮沉降形态对西南岩溶区森林土壤有效磷来源的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(2): 192-201.
LIANG Yan, LIU Jiaqi, XIAO Fan, PAN Minping, WEI Kaiwen, ZHANG Chuwen, DUAN Min. Effects of Nitrogen Deposition Forms on Sources of Soil Available Phosphorus in Karst Forest of Southwest China[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2024, 33(2): 192-201.
| 变异来源 | 全磷 | 有效磷 | 磷素活化系数 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | P | F | P | F | P | |||
| 氮沉降 | 1.93 | 0.145 | 27.26 | <0.001 | 31.55 | <0.001 | ||
| 季节 | 10.92 | <0.001 | 183.16 | <0.001 | 231.67 | <0.001 | ||
| 氮沉降×季节 | 4.90 | <0.001 | 10.37 | <0.001 | 13.86 | <0.001 | ||
表1 不同形态氮沉降处理和季节对土壤磷含量影响的双因素方差分析
Table 1 Two-way ANOVA for the effects of different nitrogen deposition form treatments, seasons and their interactions on soil phosphorus contents
| 变异来源 | 全磷 | 有效磷 | 磷素活化系数 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | P | F | P | F | P | |||
| 氮沉降 | 1.93 | 0.145 | 27.26 | <0.001 | 31.55 | <0.001 | ||
| 季节 | 10.92 | <0.001 | 183.16 | <0.001 | 231.67 | <0.001 | ||
| 氮沉降×季节 | 4.90 | <0.001 | 10.37 | <0.001 | 13.86 | <0.001 | ||
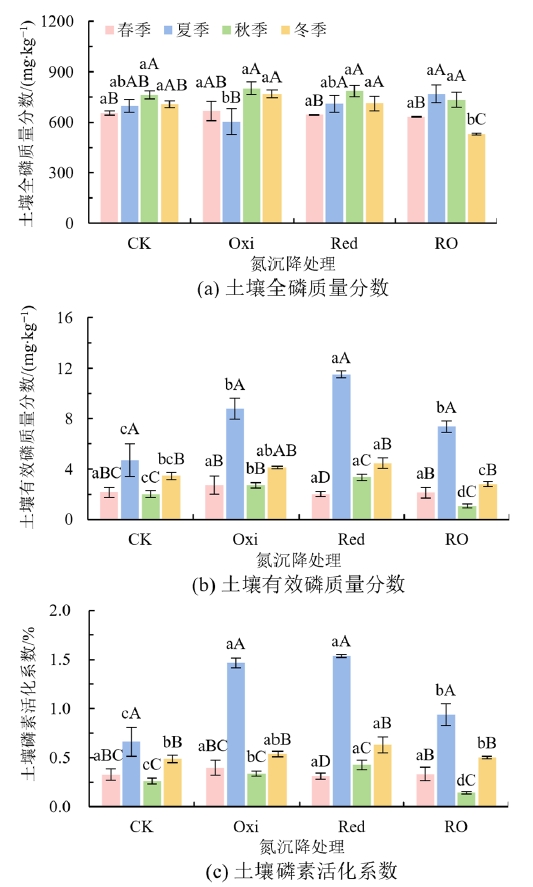
图1 不同形态氮沉降处理条件下土壤全磷(a)、有效磷(b)和磷素活化系数(c)的季节变化 CK:无氮沉降;Oxi:氧化态氮沉降;Red:还原态氮沉降;RO:氧化还原态氮沉降。图中不同小写字母表示同一季节不同氮沉降处理间差异显著(P<0.05),不同大写字母表示同一氮沉降处理不同季节间差异显著(P<0.05),下同
Figure 1 Seasonal changes of soil total phosphorus (a), available phosphorus (b) and phosphorus availability coefficient (c) in different nitrogen deposition form treatments
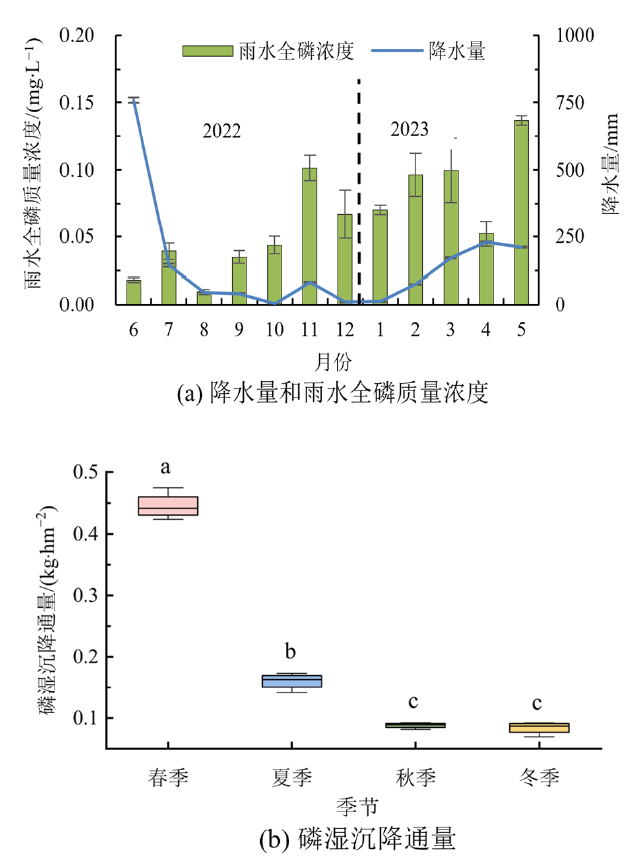
图2 研究区降水量和雨水全磷浓度月变化(a)及磷湿沉降通量(b)的季节变化 图中不同小写字母表示不同季节间差异显著(P<0.05)
Figure 2 Monthly changes of precipitation and rainfall total phosphorus concentrations (a) and seasonal changes of phosphorus wet deposition flux (b) in the study area
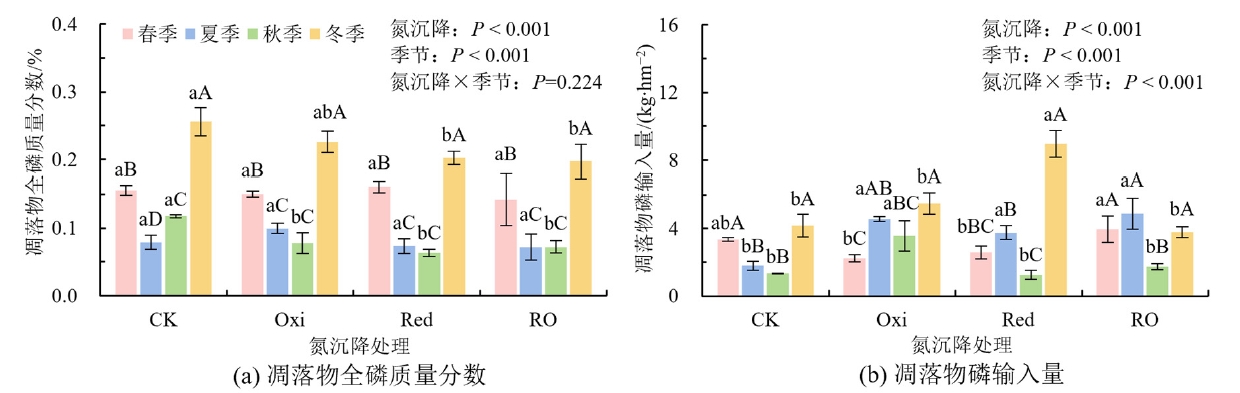
图3 不同形态氮沉降处理条件下凋落物全磷质量分数(a)和磷输入量(b)的季节变化
Figure 3 Seasonal changes of litter total phosphorus (a) and phosphorus input (b) in different nitrogen deposition form treatments
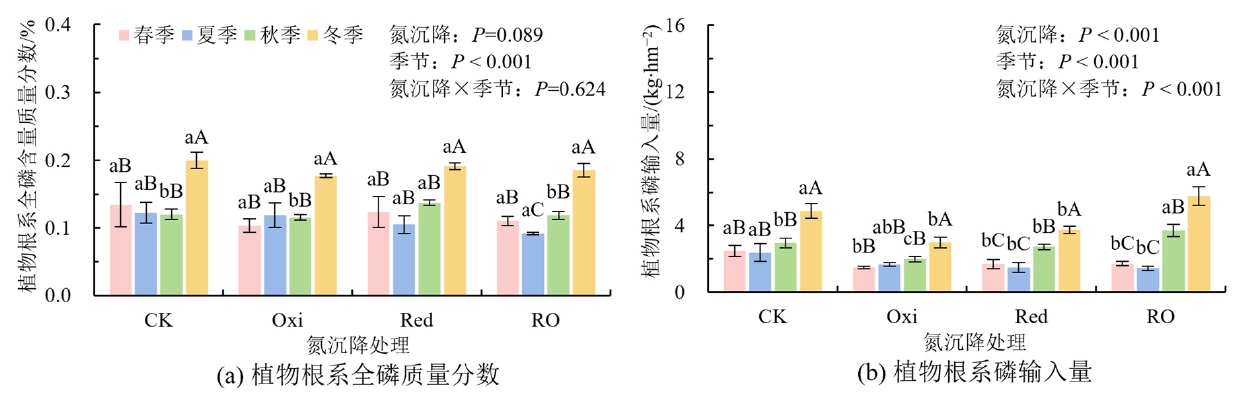
图4 不同形态氮沉降处理条件下根系全磷质量分数(a)和磷输入量(b)的季节变化
Figure 4 Season changes of plant root total phosphorus (a) and phosphorus input (b) in different nitrogen deposition form treatments

图5 不同形态氮沉降处理条件下不同磷来源、季节以及土壤理化性质对土壤AP影响的结构方程模型 图中*表示P<0.05,**表示P<0.01,***表示P<0.001,黑色虚线连接表示二者关系不显著,蓝色实线连接表示二者关系显著
Figure 5 Structural equation model of the effects of different phosphorus sources, seasons and soil physicochemical properties on soil available phosphorus in different nitrogen deposition form treatments
| [1] |
AI L, WU F Z, FAN X B, et al., 2023. Different effects of litter and root inputs on soil enzyme activities in terrestrial ecosystems[J]. Applied Soil Ecology, 183: 104764.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
AO G, FENG J G, HAN M G, et al., 2022. Responses of root and soil phosphatase activity to nutrient addition differ between primary and secondary tropical montane forests[J]. Rhizosphere, 24: 100610.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
BEIDLER K V, OH Y E, PRITCHARD S G, et al., 2021. Mycorrhizal roots slow the decay of belowground litters in a temperate hardwood forest[J]. Oecologia, 197(3): 743-755.
DOI PMID |
| [4] |
CHAVE J, NAVARRETE D, ALMEIDA S, et al., 2010. Regional and seasonal patterns of litterfall in tropical South America[J]. Biogeosciences, 7: 43-55.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
CHEN H, GURMESA GA, LIU L, et al., 2014. Effects of litter manipulation on litter decomposition in a successional gradients of tropical forests in southern China[J]. PLoS One, 9: e99018
DOI URL |
| [6] |
CUNHA H F V, ANDERSEN K M, LUGLI L F, et al., 2022. Direct evidence for phosphorus limitation on Amazon forest productivity[J]. Nature, 608: 558-562.
DOI |
| [7] |
GILL R A, JACKSON R B, 2000. Global patterns of root turnover for terrestrial ecosystems[J]. New Phytologist, 147(1): 13-31.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
HUANG W J, SPOHN M, 2015. Effects of long-term litter manipulation on soil carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus in a temperate deciduous forest[J]. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 83: 12-18.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
HUANG X L, CHEN J Z, WANG D, et al., 2021. Simulated atmospheric nitrogen deposition inhibited the leaf litter decomposition of Cinnamomum migao H. W. Li in Southwest China[J]. Scientific Reports, 11: 1748.
DOI |
| [10] |
JONARD M, FÜRST A, VERSTRAETEN A, et al., 2015. Tree mineral nutrition is deteriorating in Europe[J]. Global Change Biology, 21(1): 418-430.
DOI PMID |
| [11] |
LANG F, BAUHUS J, FROSSARD E, et al., 2016. Phosphorus in forest ecosystems: New insights from an ecosystem nutrition perspective[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Soil Science, 179(2): 129-135.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
LIU X J, DUAN L, MO J M, et al., 2011. Nitrogen deposition and its ecological impact in China: An overview[J]. Environmental Pollution, 159(10): 2251-2264.
DOI PMID |
| [13] |
LIU X J, ZHANG Y, HAN W X, et al., 2013. Enhanced nitrogen deposition over China[J]. Nature, 494: 459-462.
DOI |
| [14] |
LU X K, MO J M, GILLIAM F S, 2010. Effects of experimental nitrogen additions on plant diversity in an old-growth tropical forest[J]. Global Change Biology, 16(10): 2688-2700.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
MANNING P, SAUNDERS M, BARDGETT R D, et al., 2008. Direct and indirect effects of nitrogen deposition on litter decomposition[J]. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 40(3): 688-698.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
MARKLEIN A R, HOULTON B Z, 2012. Nitrogen inputs accelerate phosphorus cycling rates across a wide variety of terrestrial ecosystems[J]. New Phytologist, 193(3): 696-704.
DOI PMID |
| [17] |
MCGRODDY M E, SILVER W L, OLIVEIRA R C, 2004. The effect of phosphorus availability on decomposition dynamics in a seasonal lowland Amazonian forest[J]. Ecosystems, 7: 172-179.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
PATERSON E, 2003. Importance of rhizodeposition in the coupling of plant and microbial productivity[J]. European Journal of Soil Science, 54(4): 741-750.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
PEÑUELAS J, SARDANS J, RIVAS-UBACH A, et al., 2012. The human-induced imbalance between C, N and P in Earth's life system[J]. Global Change Biology, 18(1): 3-6.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
ROWLAND L, COSTA A C L, OLIVEIRA A A R, et al., 2018. Shock and stabilisation following long-term drought in tropical forest from 15 years of litterfall dynamics[J]. Journal of Ecology, 106(4): 1673-1682.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
SUHAILI N S, HATTA S M, JAMES D, et al., 2021. Soils carbon stocks and litterfall fluxes from the Bornean tropical montane forests, Sabah, Malaysia[J]. Forests, 12(12): 1621.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
SUN Z Z, LIU L L, MA Y C, et al., 2014. The effect of nitrogen addition on soil respiration from a nitrogen-limited forest soil[J]. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 197: 103-110.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
VINCENT A G, TURNER B L, TANNER E V J, 2010. Soil organic phosphorus dynamics following perturbation of litter cycling in a tropical moist forest[J]. European Journal of Soil Science, 61(1): 48-57.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
VITOUSEK P M, PORDER S, HOULTON B Z, et al., 2010. Terrestrial phosphorus limitation: mechanisms, implications, and nitrogen- phosphorus interactions[J]. Ecological Applications, 20(1): 5-15.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
WRIGHT S J, 2022. Nutrients limit carbon capture by tropical forests[J]. Nature, 608: 476-477.
DOI |
| [26] |
YANG X, WANG B R, FAKHER A, et al., 2023. Contribution of roots to soil organic carbon: From growth to decomposition experiment[J]. Catena, 231: 107317.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
YU G R, JIA Y L, HE N P, et al., 2019. Stabilization of atmospheric nitrogen deposition in China over the past decade[J]. Nature Geoscience, 12: 424-429.
DOI |
| [28] |
YUAN D X, 2001. On the karst ecosystem[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 75(3): 336-338.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
ZHU F F, GILLIAM F S, MULDER J, et al., 2022. Effects of excess nitrogen (N) on fine root growth in tropical forests of contrasting N status[J]. Forests, 13(8): 1328.
DOI URL |
| [30] | 陈立新, 乔璐, 段文标, 等, 2012. 温带森林磷沉降-水系统输出-迁移动态特征及对土壤磷影响[J]. 土壤学报, 49(3): 454-464. |
| CHEN L X, QIAO L, DUAN W B, et al., 2012. Dynamic characteristics of atmospheric deposition-output and translocation of phosphorus with water system and their effects on soil phosphorus in temperate forests[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 49(3): 454-464. | |
| [31] | 陈美领, 陈浩, 毛庆功, 等, 2016. 氮沉降对森林土壤磷循环的影响[J]. 生态学报, 36(16): 4965-4976. |
| CHEN M L, CHEN H, MAO Q G, et al., 2016. Effect of nitrogen deposition on the soil phosphorus cycle in forest ecosystems: A review[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 36(16): 4965-4976. | |
| [32] | 陈翔, 2014. 模拟氮沉降对兴安落叶松凋落物养分释放动态的影响研究[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古农业大学. |
| CHEN X, 2014. Effects of simulated nitrogen deposition on litter decomposition of nutrient release of dynamic in Larix gmelinii forest study[D]. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia Agricultural University. | |
| [33] | 邓飞, 2016. 模拟氮沉降对中亚热带常绿阔叶林细根生物量和生产量的影响研究[D]. 福州: 福建师范大学. |
| DENG F, 2016. Effects of simulated nitrogen deposition on fine root biomass and production in a mid-subtropical evergreen broadleaf forest[D]. Fuzhou: Fujian Normal University. | |
| [34] | 杜雨潭, 陈金磊, 李雷达, 等, 2020. 亚热带不同植被恢复林地凋落物层碳、氮、磷化学计量特征[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 40(2): 108-119. |
| DU Y T, CHEN J L, LI L D, et al., 2020. C, N and P stoichiometry characteristics of forest floor litter layer at different vegetation restoration stages in the mid-subtropical regions, China[J]. Journal of Central South University of Forestry & Technology, 40(2): 108-119. | |
| [35] | 广西统计局, 2022. 广西统计年鉴: 第8章资源与环境[M]. 北京: 中国统计出版社. |
| Statistics Bureau of Guangxi Province, 2022. Guangxi Statistical Yearbook: Chapter 8 Resources and Environment[M]. Beijing: China Statistical Press. | |
| [36] |
郭伟, 耿珍珍, 陈朝, 等, 2018. 模拟氮沉降增加对长白山红松和水曲柳菌根真菌群落结构及多样性的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 27(1):10-17.
DOI |
| GUO W, GENG Z Z, CHEN Z, et al., 2018. Effects of nitrogen addition on mycorrhizal fungi community structure and diversity of Pinus koraiensis and Fraxinus mandshurica in Changbai Mountain[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 27(1): 10-17. | |
| [37] | 何霄嘉, 王磊, 柯兵, 等, 2019. 中国喀斯特生态保护与修复研究进展[J]. 生态学报, 39(18): 6577-6585. |
| HE X J, WANG L, KE B, et al., 2019. Progress on ecological conservation and restoration for China karst[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 39(18): 6577-6585. | |
| [38] |
黄梓敬, 徐侠, 张惠光, 等, 2022. 根系输入对森林土壤碳库及碳循环的影响研究进展[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 46(1): 25-32.
DOI |
| HUANG Z J, XU X, ZHANG H G, et al., 2022. Advances in effects of root input on forest soil carbon pool and carbon cycle[J]. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Science Edition), 46(1): 25-32. | |
| [39] |
姜鹏, 秦美欧, 李荣平, 等, 2022. 中国典型生态系统GPP的季节变异及其影响要素[J]. 生态环境学报, 31(4): 643-651.
DOI |
| JIANG P, QIN M O, LI R P, et al., 2022. Seasonal variability of GPP and its influencing factors in the typical ecosystems in China[J] Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 31(4): 643-651. | |
| [40] | 李学敏, 张劲苗, 1994. 河北潮土磷素状态的研究[J]. 土壤通报, 25(6): 259-260. |
| LI X M, ZHANG J M, 1994. A study on the phosphorus state of Chao soil in Hebei province[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 25(6): 259-260. | |
| [41] | 廖利平, 高洪, 汪思龙, 等, 2000. 外加氮源对杉木叶凋落物分解及土壤养分淋失的影响[J]. 植物生态学报, 24(1): 34-39. |
| LIAO L P, GAO H, WANG S L, et al., 2000. The effect of nitrogen addition on soil nutrient leaching and the decomposition of Chinese fir leaf litter[J]. Acta Phytoecologica Sinica, 24(1): 34-39. | |
| [42] |
刘家齐, 梁燕, 肖凡, 等, 2023. 西南喀斯特区域不同植被恢复阶段土壤磷主要来源及其季节变化[J]. 应用生态学报, 34(12): 3313-3321.
DOI |
|
LIU J Q, LIANG Y, XIAO F, et al., 2023. Main sources of soil phosphorus and their seasonal changes across different vegetation restoration stages in karst region of southwest China. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 34(12): 3313-3321.
DOI |
|
| [43] | 刘谣, 刘金超, 宋钰珑, 等. 2023. 季节变化对川西亚高山森林土壤酶活性及化学计量特征的影响[J]. 四川农业大学学报, 41(3): 456-463. |
| LIU Y, LIU J C, SONG Y L, et al., 2023. Effects of seasonal changes on soil enzyme activities and their stoichiometric characteristics of subalpine forests in western Sichuan[J]. Journal of Sichuan Agricultural University, 41(3): 456-463. | |
| [44] | 莫江明, 薛璟花, 方运霆, 2004. 鼎湖山主要森林植物凋落物分解及其对N沉降的响应[J]. 生态学报, 24(7): 1413-1420. |
| MO J M, XUE J H, FANG Y T, 2004. Litter decomposition and its responses to simulated N deposition for the major plants of Dinghushan forests in subtropical China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 24(7): 1413-1420. | |
| [45] | 庞世龙, 欧芷阳, 申文辉, 等, 2016. 广西喀斯特地区不同植被恢复模式土壤质量综合评价[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 36(7): 60-66. |
| PANG S L, OU Z Y, SHEN W H, et al., 2016. Edaphic characteristics of different regeneration patterns in karst mountainous areas of Guangxi[J]. Journal of Central South University of Forestry & Technology, 36(7): 60-66. | |
| [46] | 任璐, 李欣, 马大龙, 等. 2021. 积雪覆盖变化对大兴安岭白桦次生林土壤微生物生物量和胞外酶活性的影响[J]. 应用与环境生物学报, 27(5): 1147-1154. |
| REN L, LI X, MA D L, et al., 2021. Effects of snow cover changes on soil microbial biomass and extracellular enzyme activities of Betula platyphylla secondary forest in the Daxing'an Mountains[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Environment Biology, 27(5): 1147-1154. | |
| [47] | 王俊丽, 张忠华, 胡刚, 等, 2020. 基于文献计量分析的喀斯特植被生态学研究态势[J]. 生态学报, 40(3): 1113-1124. |
| WANG J L, ZHANG Z H, HU G, et al., 2020. Research trend of karst vegetation ecology based on bibliometric analysis[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 40(3): 1113-1124. | |
| [48] | 王克林, 苏以荣, 曾馥平, 等, 2008. 西南喀斯特典型生态系统土壤特征与植被适应性恢复研究[J]. 农业现代化研究, 29(6): 641-645. |
| WANG K L, SU Y R, ZENG F P, et al., 2008. Ecological process and vegetation restoration in karst region of southwest China[J]. Research of Agricultural Modernization, 29(6): 641-645. | |
| [49] |
王瑞, 宋祥云, 柳新伟, 2022. 黄河三角洲不同植被类型土壤酶活性的季节变化[J]. 生态环境学报, 31(1): 62-69.
DOI |
| WANG R, SONG X Y, LIU X W, 2022. Seasonal characteristics of soil enzymes in different vegetations in the Yellow RIver Delta[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 31(1): 62-69. | |
| [50] | 王瑞丽, 程瑞梅, 肖文发, 等. 2012. 三峡库区马尾松人工林细根生产和周转[J]. 应用生态学报, 23(9): 2346-2352. |
| WANG R L, CHENG R M, XIAO W F, et al., 2012. Fine root production and turnover in Pinus massoniana plantation in Three Gorges Reservoir Area of China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 23(9): 2346-2352. | |
| [51] |
王世杰, 李阳兵, 2007. 喀斯特石漠化研究存在的问题与发展趋势[J]. 地球科学进展, 22(6): 573-582.
DOI |
|
WANG S J, LI Y B, 2007. Problems and development trends about researches on karst rocky desertification[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 22(6): 573-582.
DOI |
|
| [52] | 袁道先, 1994. 中国岩溶学[M]. 北京: 地质出版社. |
| YUAN D X, 1994. Karstiology of China[M]. Beijing: Geology Press. | |
| [53] | 苑涛, 贾亚男, 2011. 中国西南岩溶生态系统脆弱性研究进展[J]. 中国农学通报, 27(32): 175-180. |
| YUAN T, JIA Y N, 2011. Research progresses on vulnerability of karst ecological system in southwest China[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 27(32): 175-180. | |
| [54] | 张磊, 贾淑娴, 李啸灵, 等, 2022. 亚热带米槠天然林凋落物和根系输入变化对土壤磷组分的影响[J]. 生态学报, 42(2): 656-666. |
| ZHANG L, JIA S X, LI X L, et al., 2022. Effects of litter and root inputs changes on soil phosphorus fractions in a subtropical natural forest of Castanopsis carlesii[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 42(2): 656-666. | |
| [55] |
张乃木, 宋娅丽, 王克勤, 等, 2021. 模拟氮沉降下滇中亚高山森林凋落物养分元素释放特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 30(5): 920-928.
DOI |
| ZHANG N M, SONG Y L, WANG K Q, et al., 2021. Nutrient release characteristics of forest litter under simulated nitrogen deposition in the subalpine of central Yunnan, China[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 30(5): 920-928. |
| [1] | 袁茜, 傅开道, 陶雨晨, 张年, 杨丽莎. 澜沧江(云南段)水-气界面氧化亚氮释放通量时空分布特征及其影响因素研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(1): 54-61. |
| [2] | 王超, 杨倩楠, 张池, 刘同旭, 张晓龙, 陈静, 刘科学. 丹霞山不同土地利用方式土壤磷组分特征及其有效性[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 889-897. |
| [3] | 李建辉, 党争, 陈琳. 黄河几字弯都市圈PM2.5时空特征及影响因素分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 697-705. |
| [4] | 何艳虎, 龚镇杰, 吴海彬, 蔡宴朋, 杨志峰, 陈晓宏. 粤港澳大湾区城市生态效率时空演变及影响因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 469-480. |
| [5] | 郝金虎, 韦玮, 李胜男, 马牧源, 李肖夏, 杨洪国, 姜琦宇, 柴沛东. 基于GEE平台的京津冀长时序水体时空格局及其影响因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 556-566. |
| [6] | 张林, 齐实, 周飘, 伍冰晨, 张岱, 张岩. 北京山区针阔混交林地土壤有机碳含量的影响因素研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 450-458. |
| [7] | 张莉, 李铖, 谭皓泽, 韦家怡, 程炯, 彭桂香. 广州典型城市林地对大气颗粒物的削减效应及影响因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(2): 341-350. |
| [8] | 周永康, 余圣品, 李佳乐, 董一慧, 王萌, 赵齐灵, 李烨余. 土壤中抗生素的吸附行为与机理研究进展[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(11): 2072-2082. |
| [9] | 杨晓莉, 毛佳璇, 马露冉, 徐其静, 刘雪. 纳米材料固定化植酸酶的制备及其催化效率与影响因素综述[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(10): 1889-1900. |
| [10] | 李威闻, 黄金权, 齐瑜洁, 刘小岚, 刘纪根, 毛治超, 高绣纺. 土壤侵蚀条件下土壤微生物生物量碳含量变化及其影响因素的Meta分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 47-55. |
| [11] | 刘希林, 卓瑞娜. 崩岗崩积体坡面初始产流时间影响因素及其临界阈值[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 36-46. |
| [12] | 郑晓豪, 陈颖彪, 郑子豪, 郭城, 黄卓男, 周泳诗. 湖北省生态系统服务价值动态变化及其影响因素演变[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 195-206. |
| [13] | 袁林江, 李梦博, 冷钢, 钟冰冰, 夏大朋, 王景华. 厌氧环境下硫酸盐还原与氨氧化的协同作用[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 207-214. |
| [14] | 苏泳松, 宋松, 陈叶, 叶子强, 钟润菲, 王昭尧. 珠江三角洲人类活动净氮输入时空特征及其影响因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1599-1609. |
| [15] | 陈文裕, 夏丽华, 徐国良, 余世钦, 陈行, 陈金凤. 2000—2020年珠江流域NDVI动态变化及影响因素研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(7): 1306-1316. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
