生态环境学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (1): 118-125.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2025.01.013
常春英1( ), 王刚1,2,3, 曹浩轩1,2, 邓一荣1, 陶亮2,*(
), 王刚1,2,3, 曹浩轩1,2, 邓一荣1, 陶亮2,*( )
)
收稿日期:2024-09-21
出版日期:2025-01-18
发布日期:2025-01-21
通讯作者:
* 陶亮。E-mail: taoliang@soil.gd.cn作者简介:常春英(1983年生),女,正高级工程师,博士,主要从事土壤重金属污染与控制相关研究。E-mail: xiaochong1219@163.com
基金资助:
CHANG Chunying1( ), WANG Gang1,2,3, CAO Haoxuan1,2, DENG Yirong1, TAO Liang2,*(
), WANG Gang1,2,3, CAO Haoxuan1,2, DENG Yirong1, TAO Liang2,*( )
)
Received:2024-09-21
Online:2025-01-18
Published:2025-01-21
摘要:
稳定化(固化/稳定化)技术被广泛应用于污染土壤的修复治理,但修复后的重金属会在外界复杂环境因子(淹水-落干、淋溶等)影响下改变赋存状态、缓慢释放,进而引发环境风险。选取珠三角地区典型稳定化修复后土壤为对象,研究模拟淹水、干湿交替两种情形下修复后土壤中2种重金属(Ni和Pb)的稳定性及其影响因素。结果表明,淹水可明显提高稳定化修复后土壤重金属的浸出浓度,淹水后Ni的浸出量较淹水前上升约103倍,重金属Pb浸出浓度受到淹水影响较小。淹水可促使稳定化的重金属从弱酸提取态向可氧化态和可还原态转化,淹水后Ni和Pb的弱酸提取态含量降幅分别为7.16%和19.9%。淹水通过改变土壤pH、Eh、铁锰氧化物和DOM等影响修复后重金属的稳定性,通过降低土壤pH和Eh促使体系中Mn4+、Fe3+还原,并同时耦合无定形态氧化铁的降低。干湿交替通过对水解重金属化合物的溶解解吸行为而影响重金属的稳定性,总体上干湿交替对体系中的Ni和Pb的浸出浓度、形态变化的影响相对较小。研究表明,淹水和干湿交替胁迫可以改变稳定化修复后土壤重金属的稳定性,且程度因不同重金属种类及外界胁迫强度而差异较大,短期内重金属浸出浓度远低于相关标准限值,土壤环境风险可控,但鉴于外界环境影响的长期性和多元性,实质性延长监管链条、对修复后地块实施定期回顾性评估是实现污染地块可持续安全利用的有效方式。
中图分类号:
常春英, 王刚, 曹浩轩, 邓一荣, 陶亮. 模拟干湿过程对稳定化修复土壤中重金属Ni和Pb的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2025, 34(1): 118-125.
CHANG Chunying, WANG Gang, CAO Haoxuan, DENG Yirong, TAO Liang. Impact of Simulated Dry-wet Process on Nickel (Ni) and Lead (Pb) in Stabilization Remediated Soils[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2025, 34(1): 118-125.
| 指标 | 特征参数 | |
|---|---|---|
| 土壤理化性质 | pH | 6.20 |
| Eh/mV | 47.1 | |
| 阳离子交换量(CEC)/(cmol∙kg−1) | 6.13 | |
| 游离态氧化铁(Fed)质量分数/(g∙kg−1) | 21.7 | |
| 无定形态氧化铁(Feox)质量分数/ (g∙kg−1) | 12.9 | |
| 晶体态氧化铁(Fep)质量分数/(g∙kg−1) | 8.79 | |
| 有机质质量分数/(g∙kg−1) | 14.5 | |
| 重金属质量分数/ (mg∙kg−1) | Ni | 93.5 |
| Pb | 66.0 | |
| 初始浸出质量浓度/ (μg∙L−1) | Ni | 0.0600 |
| Pb | 未检出 | |
表1 地块修复后土壤的特征参数
Table 1 Characteristics of the remediated soil
| 指标 | 特征参数 | |
|---|---|---|
| 土壤理化性质 | pH | 6.20 |
| Eh/mV | 47.1 | |
| 阳离子交换量(CEC)/(cmol∙kg−1) | 6.13 | |
| 游离态氧化铁(Fed)质量分数/(g∙kg−1) | 21.7 | |
| 无定形态氧化铁(Feox)质量分数/ (g∙kg−1) | 12.9 | |
| 晶体态氧化铁(Fep)质量分数/(g∙kg−1) | 8.79 | |
| 有机质质量分数/(g∙kg−1) | 14.5 | |
| 重金属质量分数/ (mg∙kg−1) | Ni | 93.5 |
| Pb | 66.0 | |
| 初始浸出质量浓度/ (μg∙L−1) | Ni | 0.0600 |
| Pb | 未检出 | |
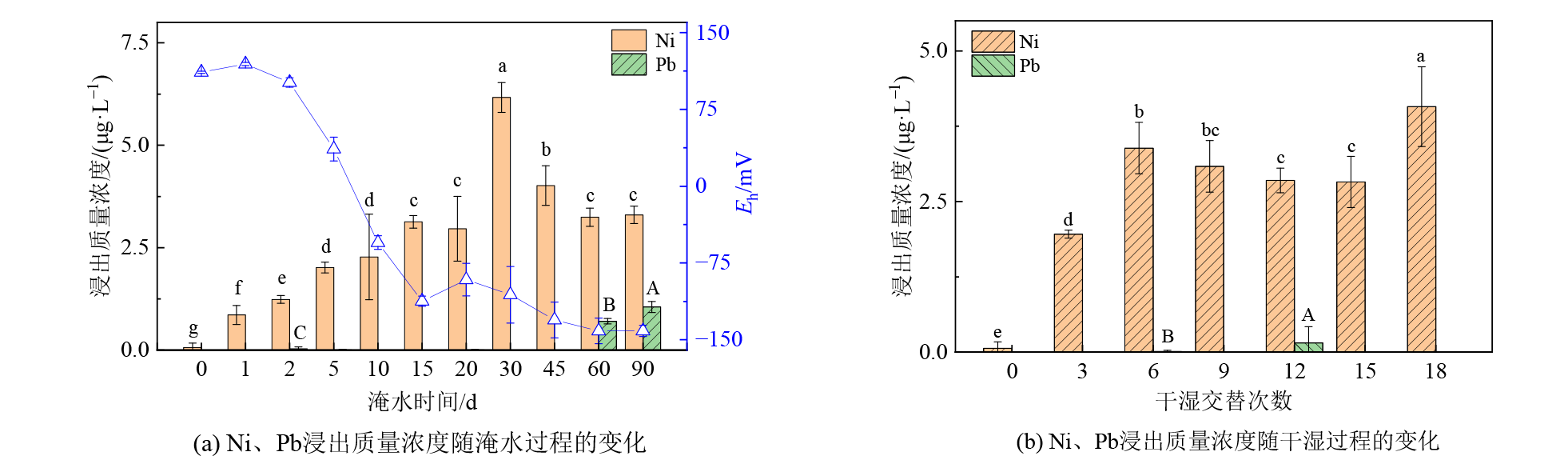
图1 稳定化后土壤Ni、Pb浸出质量浓度随淹水和干湿过程的变化 不同字母表示不同时间的显著性差异(p<0.05)
Figure 1 Leaching concentration of heavy metals of the remediated soils vs. flooding time and alternation cycles
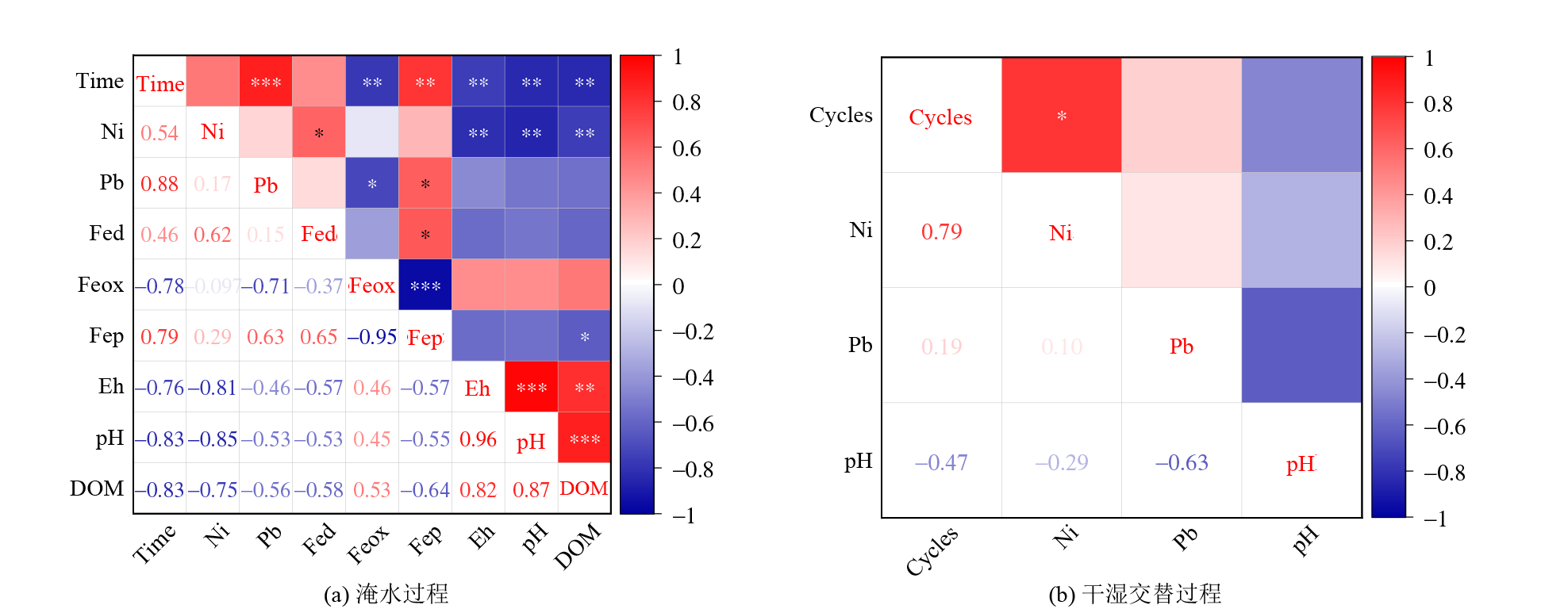
图3 两种干湿过程中修复后土壤重金属浸出浓度与特征指标的相关性分析 ***、**和*分别表示在0.001、0.01和0.05水平显著相关
Figure 3 Correlation analysis between heavy metals leaching concentration and characteristics in remediated soil during two dry-wet processes
| [1] | ALLOWAY B J, 2013. Bioavailability of elements in soil[M]. London: Springer Science+Business Media Dordrecht:351-373. |
| [2] |
CHEN Q Y, TYRER M, HILLS C D, et al., 2009. Immobilisation of heavy metal in cement-based solidification/stabilisation: A review[J]. Waste Management, 29(1):390-403.
DOI PMID |
| [3] | DENEF K, SIX J, BOSSUYT H, et al., 2001. Influence of dry-wet cycles on the interrelationship between aggregate, particulate organic matter, and microbial community dynamics[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 33(12):1599-1611. |
| [4] | FROHNE T, RINKLEBE J, DIAZ-BINE R A, et al., 2011. Controlled variation of redox conditions in a floodplain soil: Impact on metal mobilization and biomethylation of arsenic and antimony[J]. Geoderma, 160(3):414-424. |
| [5] | HOSSAM F H, AMER A R, ABDEL W H, et al., 2008. Investigation of permeability and leaching of hot mix asphalt concrete containing oil-contaminated soil[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 6(22):1239-1246. |
| [6] | JANGA J K, REDDY K R, RAVITEJA K V N S, 2023. Integrating artificial intelligence, machine learning, and deep learning approaches into remediation of contaminated sites: A review[J]. Chemosphere, 345:140476. |
| [7] | LI H K, XU D M, WAND J X, et al., 2023. The occurrence of “yellowing” phenomenon and its main driving factors after the remediation of chromium (Cr)-contaminated soils: A literature review[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 457:131698. |
| [8] | LI Z, WU L H, ZHANG H, et al., 2015. Effects of soil drying and wetting-drying cycles on the availability of heavy metals and their relationship to dissolved organic matter[J]. Journal of Soil and Sediments, 15(7):1510-1519. |
| [9] |
LYU H H, ZHAO H, TANG J C, et al., 2018. Immobilization of hexavalent chromium in contaminated soils using biochar supported nanoscale iron sulfide composite[J]. Chemosphere, 194:360-369.
DOI PMID |
| [10] | MANCEAU A, CHARLET L, BOISSET M C, et al., 1992. Sorption and speciation of heavy metals on hydrous Fe and Mn oxides. From microscopic to macroscopic[J]. Applied Clay Science, 7(1-3):201-223. |
| [11] |
MCGOWEN S L, BASTA N T, BROWN G O, 2001. Use of diammonium phosphate to reduce heavy metal solubility and transport in smelter-contaminated soil[J]. Journal of Environmental Quality, 30(2):493-500.
DOI PMID |
| [12] | PANG X H, CHEN C, SUN J, et al., 2023. Effects of complex pollution by microplastics and heavy metals on soil physicochemical properties and microbial communities under alternate wetting and drying conditions[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 458:131989. |
| [13] | US EPA, 2013. Regional Screening Levels (RSL) for chemical contaminants at superfund sites[R]. Washington DC: Office of Land and Emergency (Region 9). |
| [14] | WANG R H, ZHU X F, QIAN W, et al., 2017. Pectin adsorption on amorphous Fe/Al hydroxides and its effect on surface charge properties and Cu (II) adsorption[J]. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 17(10):2481-2489. |
| [15] | WILSON M J, HE Z L, YANG X E, 2004. The red soils of China[M]. New York: Springer Science+Business Media:35-62. |
| [16] |
YAN M Q, MA J, ZHANG C Y, et al., 2017. Optical property of dissolved organic matters (DOMs) and its link to the presence of metal ions in surface freshwaters in China[J]. Chemosphere, 188:502-509.
DOI PMID |
| [17] | ZHANG Z, SONG Z W, JIA H B, et al., 2023. Remediation of chromium(VI) in contaminated soil by schwertmannite: Leachability, long-term stability, and stabilization mechanism[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 11(2):109435. |
| [18] | ZHENG S A, ZHENG X Q, CHEN C, 2013. Transformation of metal speciation in purple soil as affected by waterlogging[J]. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 10(2):351-358. |
| [19] | 曹浩轩, 2021. 固化/稳定化修复后土壤重金属稳定性及其迁移转化研究[D]. 北京: 中国农业大学:22-31. |
| CAO H X, 2023. Study on the stability and transformation of soil heavy metals after solidification/stabilization remediation[D]. Beijing: China Agricultural University:22-31. | |
| [20] | 常春英, 曹浩轩, 陶亮, 等, 2022. 淹水和干湿交替对修复后土壤铬的稳定性影响研究[J]. 环境科学研究, 35(5):1150-1158. |
| CHANG C Y, CAO H X, TAO L, et al., 2022. Effects of flooding and dry-wet alternation on the stability of chromium (Cr) in soil after solidification/stabilization remediation[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 35(5):1150-1158. | |
| [21] | 陈承峰, 2019. 河道底泥复合重金属污染固化稳定化修复技术研究[D]. 广州: 广州大学:82-89. |
| CHEN C X, 2019. Study on solidification and stabilization technology of composite heavy metal contamination in river sediment[D]. Guangzhou: Guang Zhou University:82-89. | |
| [22] | 邓林, 李柱, 吴龙华, 等, 2014. 水分及干燥过程对土壤重金属有效性的影响[J]. 土壤, 46(6):1045-1051. |
| DENG L, LI Z, WU L H, et al., 2014. Influence of moisture and drying precess on soil heavy metal availability[J]. Soils, 46(6):1045-1051. | |
| [23] | 谷庆宝, 马福俊, 张倩, 等, 2017. 污染场地固化/稳定化修复的评价方法与标准[J]. 环境科学研究, 30(5):755-764. |
| GU Q B, MA F J, ZHANG Q, et al., 2017. Remediation of contaminates sites by solidification/stabilization: testing and performance criteria[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 30(5):755-764. | |
| [24] | 胡清, 罗培, 冯明玉, 等, 2022. 固化/稳定化修复后场地土壤中铬的环境行为与归趋[J]. 环境工程学报, 16(7):2122-2134. |
| HU Q, LUO P, FEGN M Y, et al., 2022. Environmental behavior and fate of chromium in the soils of solidification/stabilization post-remediation sites[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 16(7):2122-2134. | |
| [25] | 刘瑞平, 邹权, 宋志晓, 等, 2024. 中国污染场地修复后期管理研究[J]. 环境科学与管理, 49(3):5-9. |
| LIU R P, ZOU Q, SONG X Z, et al., 2024. Research on post remediation management of contaminated sites in China[J]. Environmental Science and Management, 49(3):5-9. | |
| [26] | 鲁如坤, 2000. 土壤农业化学分析方法[M]. 北京: 中国农业科技出版社. |
| LU R K, 2000. Soil agricultural chemical analysis methods[M]. Beijing: China Agricultural Science and Technology Press. | |
| [27] | 马妍, 董彬彬, 柳晓娟, 等, 2018. 美国制度控制在污染地块风险管控中的应用及对中国的启示[J]. 环境污染与防治, 40(1):100-103. |
| MA Y, DONG B B, LIU X J, et al., 2018. Applications of institutional for risk management of contaminated sites in America and implications for China[J]. Environmental Pollution & Control, 40(1):100-103. | |
| [28] | 毛凌晨, 叶华, 2018. 氧化还原电位对土壤中重金属环境行为的影响研究进展[J]. 环境科学研究, 31(10):1669-1676. |
| MAO L C, YE H, 2018. Influence of redox potential on heavy metal behavior in soils: A review[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 31(10):1669-1676. | |
| [29] | 彭港, 吕贻锦, 丁泽聪, 等, 2021. 干湿交替对土壤DOM特性及重金属释放的影响[J]. 环境工程学报, 15(8):2689-2700. |
| PENG G, LÜ Y J, DING Z C, et al., 2021. Effects of dry-wet cycles on the properties of soil DOM and the release of heavy metals[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 15(8):2689-2700. | |
| [30] | 史开宇, 王兴润, 范琴, 等, 2020. 不同还原药剂修复Cr(Ⅵ) 污染土壤的稳定性评估[J]. 环境工程学报, 14(2):473-479. |
| SHI K Y, WANG X R, FAN Q, et al., 2020. Stability evaluation of Cr(Ⅵ)-contaminated soils restoration eith different reducing agents[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 14(2):473-479. | |
| [31] | 闫淑兰, 赵秀红, 罗启仕, 2020. 基于文献计量的重金属固化稳定化修复技术发展动态研究[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 39(2):229-238. |
| YAN S L, ZHAO X H, LUO Q S, 2020. Bibliometrics-based development trends of solidification/stabilization technology for the remediation of sites contaminated by heavy metals[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 39(2):229-238. | |
| [32] | 于靖靖, 梁田, 罗会龙, 等, 2022. 近10年来我国污染场地再利用的案例分析与环境管理意义[J]. 环境科学研究, 35(5):1110-1119. |
| YU J J, LIANG T, LUO H L, et al., 2022. Case analysis and environmental management significance of contaminated site reuse in China from 2011 to 2021[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 35(5):1110-1119. | |
| [33] | 张素, 熊东红, 校亮, 等, 2017. 干湿交替对土壤性质影响的研究[J]. 土壤通报, 48(3):762-768. |
| ZHANG S, XIONG D H, XIAO L, et al., 2017. Influence of dry-wet cycling on soil properties[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 48(3):762-768. | |
| [34] | 张雪芹, 2017. 干湿循环作用下碱渣固化重金属污染土的稳定性研究[D]. 合肥: 合肥工业大学:33-42. |
| ZHANG X Q, 2017. Research on stability of soda residue solidified/ stabilized heavy metal contaminated soils under wetting-drying cycles[D]. Hefei: Hefei University of Technology:33-42. | |
| [35] | 赵万通, 王雨枫, 刘哲, 等, 2025. 污染水稻土淹水-落干过程土壤铁形态转化及元素生物有效性的原位监测[J]. 土壤学报, 62(1):141-152. |
| ZHAO W T, WANG Y F, LIU Z, et al., 2025. Soil iron speciation transformation and In-Situ monitoring of element bioavailability during the flooding-drainage in polluted paddy soils[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 62(1):141-152. | |
| [36] | 郑顺安, 郑向群, 张铁亮, 等, 2011. 水分条件对紫色土中铅形态转化的影响[J]. 环境化学, 30(12):2080-2085. |
| ZHENG S A, ZHENG X Q, ZHANG T L, et al., 2011. Effect of moisture regime on the fractionation of lead in purple soil[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 30(12):2080-2085. | |
| [37] | 中华人民共和国国家环境保护总局,2007. 固体废物浸出毒性浸出方法硫酸硝酸法: HJ/T 299—2007[S]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社: 1-5. |
| State Environmental Protection Administration of the People’s Republic of China,2007. Solid waste-extraction procedure for leaching toxicity-sulphuric acid & nitric acid method: HJ/T 299—2007[S]. Beijing: Beijing: China Environmental Science Press: 1-5. | |
| [38] | 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会,2010. 土壤和沉积物13个微量元素形态顺序提取程序: GB/T 25282—2010[S]. 北京:中国标准出版社: 1-5. |
| General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China, Naitonal Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China,2010. Soil and sediment sequential extraction procedure of speciation of 13 trace elements: GB/T 25282—2010[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China: 1-5. | |
| [39] | 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会,2017. 地下水质量标准: GB/T 14848—2017[S]. 北京:中国标准出版社: 2-5. |
| General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’ s Republic of China, Naitonal Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China,2017. Standard for groundwater quality: GB/T 14848―2017[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China: 2-5. | |
| [40] | 中华人民共和国环境保护部,2015. 固体废物金属元素的测定电感耦合等离子体质谱法: HJ 766—2015[S]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社: 1-11. |
| Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China,2015. Solid waste-determination of metals-Inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS): HJ 766―2015[S]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press: 1-11. | |
| [41] | 中华人民共和国环境保护部,2016. 土壤和沉积物12种金属元素的测定王水提取-电感耦合等离子体质谱法: HJ 803—2016[S]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社: 1-10. |
| Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China,2016. Soil and sediment-determination of aqua regia extracts of 12 metal elements-Inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry: HJ 803―2016[S]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press: 1-10. | |
| [42] | 中华人民共和国生态环境部,国家市场监督管理总局, 2018. 土壤环境质量建设用地土壤污染风险管控标准 (试行): GB 36600—2018[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社: 3-6. |
| Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China, State Administration for Market Regulation of the People’s Republic of China,2018. Soil environmental quality Risk control standard for soil contamination of development land: GB 36600―2018[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China: 3-6 | |
| [43] | 中华人民共和国生态环境部,2018. 污染地块风险管控与土壤修复效果评估技术导则 (试行): HJ 25.5—2018[S]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社: 8-10. |
| Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China,2018. Technical guideline for verification of risk control and soil remediation of contaminated site: HJ 25.5―2018[S]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press: 8-10. | |
| [44] | 中华人民共和国生态环境部,2019. 污染地块地下水修复和风险管控技术导则: HJ 25.6—2019[S]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社: 6-18. |
| Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China,2019. Technical guideline for groundwater remediation and risk control of contaminated sites: HJ 25.6—2019[S]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press: 6-18. | |
| [45] | 钟重, 张弛, 冯一舰, 等, 2021. 中国污染土壤再利用的环境管理思路探讨[J]. 环境污染与防治, 43(1):115-120. |
| ZHONG Z, ZHANG C, FENG Y J, et al., 2021. Thoughts on the environmental management of contaminated soil reuse in China[J]. Environmental Pollution & Control, 43(1):115-120. | |
| [46] |
周宏光, 甘艳平, 伍德权, 等, 2023. 淹水-落干条件下FeMnMg-LDH对污染底泥中砷迁移转化的调控研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 32(7):1249-1262.
DOI |
| ZHOU H G, GAN Y P, WU D Q, et al., 2023. Regulation of Arsenic Transport and Transformation in Contaminated Sediment by FeMnMg-LDH under Flooding-drying Conditions[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 32(7):1249-1262. |
| [1] | 韩军超, 郑茂坤, 涂晨, 刘颖, 曹振宇, 邢倩雯, 申卫收, 骆永明. 趋磁细菌在环境污染修复中的应用研究进展与展望[J]. 生态环境学报, 2025, 34(1): 145-155. |
| [2] | 丛鑫, 张怀迪, 张荣, 赵琛, 陈坤, 刘寒冰. 基于Meta分析的近10年中国农田土壤重金属污染特征与风险解析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(9): 1451-1459. |
| [3] | 刘东宜, 屈永华, 冯耀伟, 屈冉. 基于网格搜索优化CatBoost模型的GF-5卫星影像铬离子含量反演研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(9): 1460-1470. |
| [4] | 范贝贝, 丁帅, 张田田, 张帅, 魏露露, 陈清. 周期性淹水-落干和施用秸秆对白云石改良棕壤磷素流失风险的模拟研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(8): 1203-1213. |
| [5] | 欧阳美凤, 尹宇莹, 张金谌, 刘清霖, 谢意南, 方平. 洞庭湖典型水域重金属含量的空间分布与来源解析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(8): 1269-1278. |
| [6] | 吴文伟, 沈城, 沙晨燕, 林匡飞, 吴健, 谢雨晴, 周璇. 城市工业地块土壤重金属污染风险评价与源解析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(5): 791-801. |
| [7] | 肖江, 李晓刚, 赵博, 陈岩, 陈光才. 微纳富磷生物炭对土壤-苏柳系统中Cu和Pb稳定性的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(3): 439-449. |
| [8] | 江润海, 温绍福, 朱城强, 张梅, 杨润玲, 王春雪, 侯秀丽. 铅污染矿区中耐铅解磷菌对玉米的促生及根际铅的固化效应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(2): 291-300. |
| [9] | 李嘉惠, 童辉, 陈曼佳, 刘承帅, 姜琪, 易秀. 微氧生物亚铁氧化及其重金属固定效应研究进展[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(2): 310-320. |
| [10] | 李璞君, 唐丽, 赵博, 邸东柳, 陈岩, 肖江, 陈光才. 生物炭基土壤改良剂对锑矿区土壤质量及亮叶桦生长的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(12): 1953-1963. |
| [11] | 马志伟, 张丛志, 赵占辉, 吴其聪, 赵金花, 陈卓, 李敬王, 张楠, 薛雅, 王娅茹, 陆芸萱, 张佳宝. 基于木本泥炭的土壤健康培育研究进展[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(12): 1964-1977. |
| [12] | 唐舒娅, 王春辉, 宋靖, 李刚. 环象山港区域土壤重金属污染特征及风险评估[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(11): 1768-1781. |
| [13] | 李晴, 张梦悦, 于明乔, 李小璇, 常明, 陈立斌, 丁森. 东莞城市河流大型底栖动物群落结构及影响因子[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(1): 101-110. |
| [14] | 杨正桥, 邹奇, 韦行, 周凯, 陈志良. 金属尾矿微生物对尾矿环境的适应与调控机制研究进展[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(1): 156-166. |
| [15] | 王宁, 刘效东, 甘先华, 苏宇乔, 吴国章, 黄芳芳, 张卫强. 亚热带典型林分降水过程中的水质效应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(8): 1365-1375. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
