生态环境学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (11): 2169-2179.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2022.11.008
张丽聪1( ), 肖凯1,*(
), 肖凯1,*( ), 张鹏1, 李海龙1, 王俊坚1, 李镇扬2, 王芬芳3, 徐华林4, 郭跃华5
), 张鹏1, 李海龙1, 王俊坚1, 李镇扬2, 王芬芳3, 徐华林4, 郭跃华5
收稿日期:2022-06-09
出版日期:2022-11-18
发布日期:2022-12-22
通讯作者:
*肖凯(1990年生),男,副研究员,主要从事近海水质评估与滨海湿地环境保护研究。E-mail: xiaok@sustech.edu.cn作者简介:张丽聪(1998年生),女(壮族),硕士研究生,主要从事海岸带水文地质学和近海水质评价研究。E-mail: 12132234@mail.sustech.edu.cn
基金资助:
ZHANG Licong1( ), XIAO Kai1,*(
), XIAO Kai1,*( ), ZHANG Peng1, LI Hailong1, WANG Junjian1, LI Zhenyang2, WANG Fangfang3, XU Hualin4, GUO Yuehua5
), ZHANG Peng1, LI Hailong1, WANG Junjian1, LI Zhenyang2, WANG Fangfang3, XU Hualin4, GUO Yuehua5
Received:2022-06-09
Online:2022-11-18
Published:2022-12-22
摘要:
淤泥质潮滩是连接陆地和海洋生态系统的过渡带,也是海陆污染物交换的高频地带。为了解淤泥质潮滩地表水和地下水中重金属和溶解性有机质(DOM)在潮汐作用下的变化特征及环境效应,以漳江口自然保护区的淤泥质潮滩为研究场地,在一个潮汐周期内连续监测了浅层地下水动态、地表水和地下水中理化参数、重金属质量浓度和DOM光谱特征参数的时间变化特征。结合广义达西定律和Fick第一定律定量估算了重金属和有机质的向海排泄通量,最后评估了地下水和地表水中重金属污染的潜在风险。主要结论如下:(1)相比于地表水,地下水中DOM的芳香性和分子量更高,并且对pH和DO的变化更敏感。受上游淡水输入和地下水排泄的影响,潮沟地表水中重金属和DOM质量浓度均与潮汐水位相反,即在低潮期间质量浓度达到最大值,并随着潮位的增加而减少。(2)通过地表水-地下水对流作用携带的重金属和DOM通量是扩散通量的20-200倍。7种重金属在沉积物-水界面的对流通量大小顺序为:Ba (155.00 μg·m-2·d-1,单位下同)>Zn (36.60)>As (2.00)>Cu (0.33)>Cr (0.32)>Pb (0.21)>Hg (0.19),DOM的对流通量为2.57 mg·m-2·d-1。研究区所在潮滩水动力交换条件差,地表水-地下水交换未能很大程度上改变地下水的缺氧环境,导致污染物滞留在潮滩中。(3)重金属污染评价结果表明,地表水中的Hg处于中度污染水平,而地下水中的As和Hg处于轻度污染水平,其余重金属均处于清洁水平。该研究结果可为漳江口自然保护区中光滩重金属的污染防治提供科学依据。
中图分类号:
张丽聪, 肖凯, 张鹏, 李海龙, 王俊坚, 李镇扬, 王芬芳, 徐华林, 郭跃华. 淤泥质潮滩重金属和溶解性有机质的潮汐变化特征及其环境影响评价[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(11): 2169-2179.
ZHANG Licong, XIAO Kai, ZHANG Peng, LI Hailong, WANG Junjian, LI Zhenyang, WANG Fangfang, XU Hualin, GUO Yuehua. Tidal Variation Characteristics of Heavy Metals and Dissolved Organic Matter and Environmental Impact in a Silt Tidal Flat[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(11): 2169-2179.
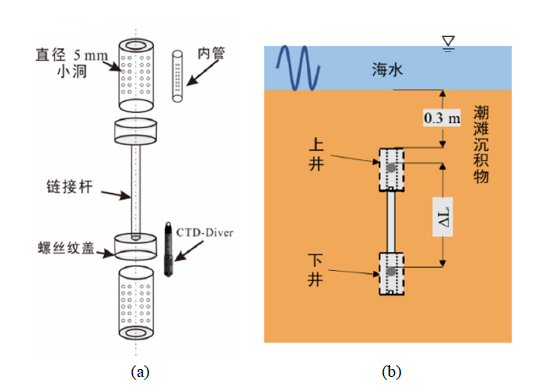
图2 对井装置的组成 (a)结构示意图;(b)场地工作示意图
Figure 2 The schematic structure diagrams showing (a) the composition of a pair-well device, and (b) field-observation scene
| 指标 Index | 缩写 Abbreviation | 单位 units | 计算方法 Computing method | 含义描述 Meaning | 参考文献 References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 单位质量有机质特定吸收 Specific ultraviolet absorbance at 254 nm per mass | SUVA254 | L·mg-1·m-1 | 单位光程下254 nm处紫外吸光度与溶解有机碳质量浓度比 | 芳香性化合物在溶解有机质中的相对贡献越高,表征芳香性,值越大芳香性越强 | 2003 |
| 吸收系数比值 Absorption coefficient ratio | E2/E3 | - | 吸光系数254 nm与365 nm比 | 指示溶解有机质中分子量, 与平均分子量大小成反比 | 2009 |
| 254 nm处的吸光系数 Absorption coefficient at 254 nm | a254 | m-1 | - | 用于计算吸收系数比值E2/E3 | |
| 350 nm处的吸光系数 Absorption coefficient at 350 nm | a350 | m-1 | - | 有色溶解有机质(CDOM)含量 | 2004 |
| 365 nm处的吸光系数 Absorption coefficient at 365 nm | a365 | m-1 | - | 用于计算吸收系数比值E2/E3 |
表1 溶解性有机质光谱特征指数含义
Table 1 Meaning of spectral characteristic index of chromophoric dissolved organic matter
| 指标 Index | 缩写 Abbreviation | 单位 units | 计算方法 Computing method | 含义描述 Meaning | 参考文献 References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 单位质量有机质特定吸收 Specific ultraviolet absorbance at 254 nm per mass | SUVA254 | L·mg-1·m-1 | 单位光程下254 nm处紫外吸光度与溶解有机碳质量浓度比 | 芳香性化合物在溶解有机质中的相对贡献越高,表征芳香性,值越大芳香性越强 | 2003 |
| 吸收系数比值 Absorption coefficient ratio | E2/E3 | - | 吸光系数254 nm与365 nm比 | 指示溶解有机质中分子量, 与平均分子量大小成反比 | 2009 |
| 254 nm处的吸光系数 Absorption coefficient at 254 nm | a254 | m-1 | - | 用于计算吸收系数比值E2/E3 | |
| 350 nm处的吸光系数 Absorption coefficient at 350 nm | a350 | m-1 | - | 有色溶解有机质(CDOM)含量 | 2004 |
| 365 nm处的吸光系数 Absorption coefficient at 365 nm | a365 | m-1 | - | 用于计算吸收系数比值E2/E3 |
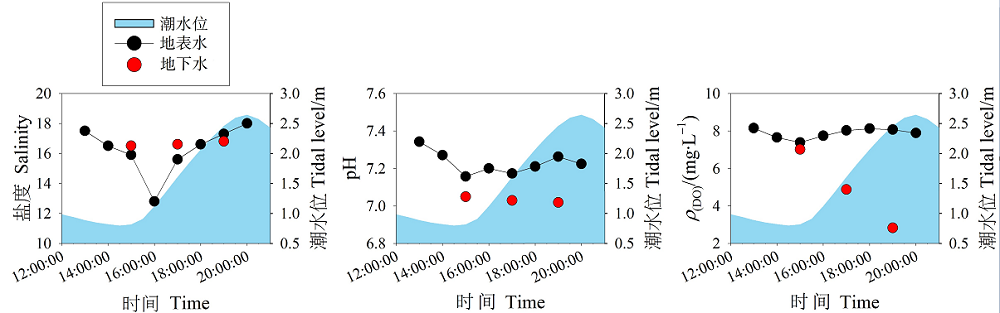
图4 潮滩地表水和地下水中理化参数(盐度,pH和DO)的潮汐变化
Figure 4 Tidal variations of physicochemicla parameters (salinity, pH and DO) in the surface water and groundwater in the tidal mudflat
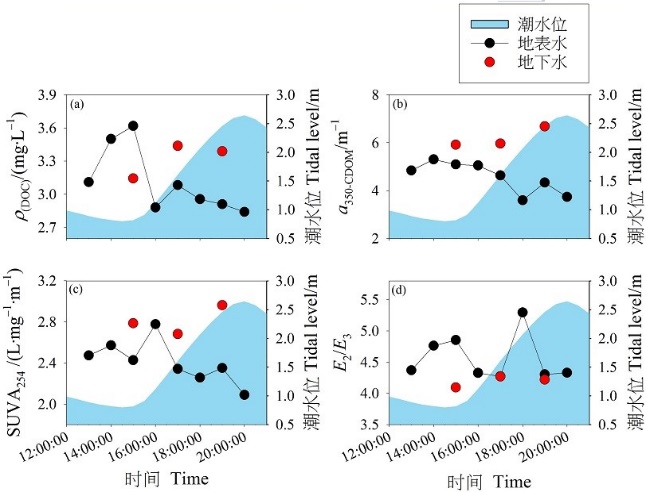
图6 潮滩地表水和地下水中DOC和CDOM光谱特征指数的潮汐变化
Figure 6 Tidal variations of the DOC and spectral characteristic indexes of CDOM in the surface water and groundwater in the tidal mudflat
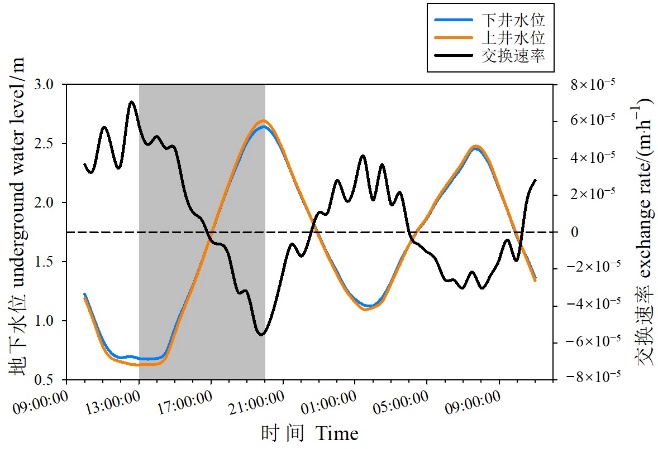
图7 监测期间地下水位和地下水-地表水交换速率 灰色背景代表取样期
Figure 7 Time series of groundwater level and groundwater-surface water exchange rates during the monitoring period The gray background represents the sampling period
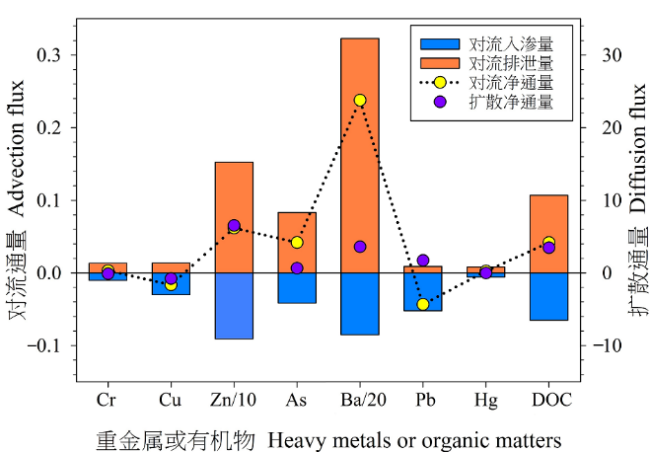
图8 重金属和DOC在沉积物-水界面的对流和扩散通量 对流通量中,重金属的单位为μg·m-2·h-1,DOC的单位为mg·m-2·h-1;扩散通量中,重金属的单位为10-3 μg·m-2·h-1,DOC的单位为10-3 mg·m-2·h-1;Zn/10和Ba/20分别表示Zn和Ba的通量除以10和20,这样更方便与其他元素在视觉上的对比
Figure 8 Calculated connective and diffusive fluxes for heavy metals and DOC The units of convective fluxes of heavy metals and DOC are μg·m-2·h-1 and mg·m-2·h-1, respectively, but 10-3 μg·m-2·h-1 and 10-3 mg·m-2·h-1 for diffusion fluxes; Zn/10 and Ba/20 represent the flux of Zn and Ba divided by 10 and 20, respectively, to facilitate visual comparison with other elements
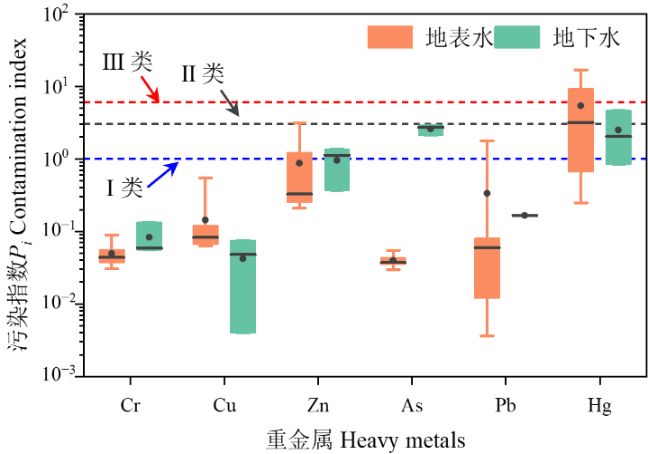
图9 地下水和地表水中重金属的污染指数 须线、水平线和点分别代表范围(最小-最大值),中位数和平均值
Figure 9 The pollution index of heavy metals in the groundwater and surface water The whiskers, horizontal lines, and points represent the range (min-max), median, and average values, respectively
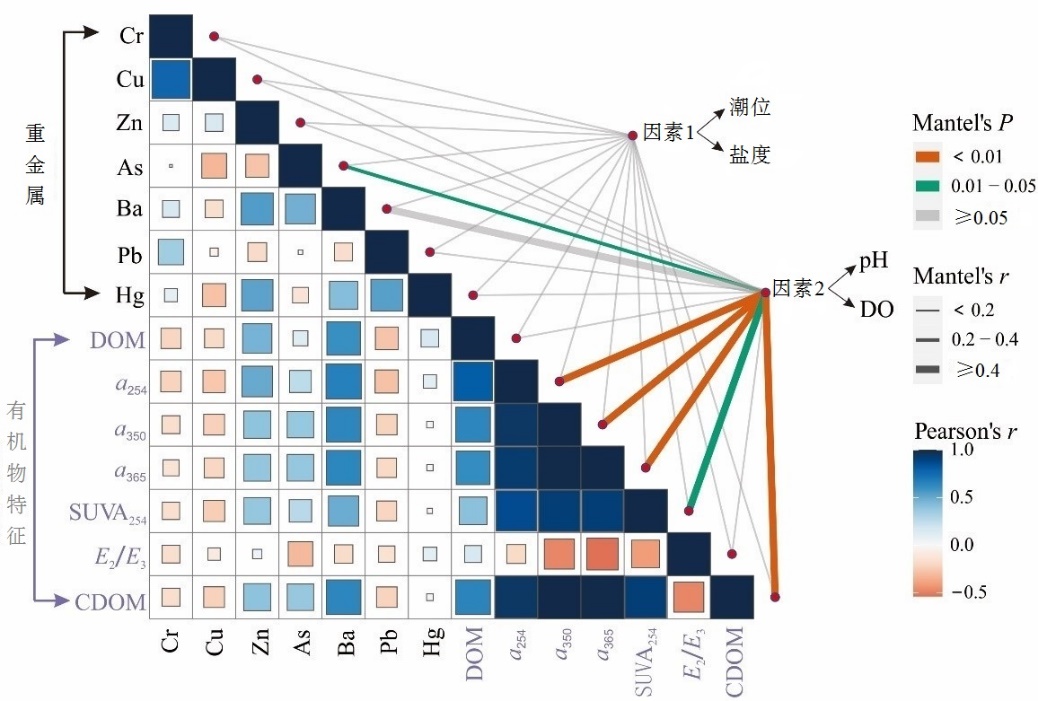
图10 环境因子的相关性 (因素1:潮汐/地下水位+盐度;因素2:DO+pH)分析。线宽对应部分Mantel’s r统计量,线色表示基于排列的统计显著性。同时对环境因素进行两两比较,用颜色梯度表示Pearson相关系数,并根据调查数据的属性将这些因素综合为两组
Figure 10 Correlations between environmental factors (Factor 1: tide/groundwater table+salinity; Factor 2: DO+pH) and heavy metal content and DOM properties by partial Mantel test. Line width corresponds to the partial Mantel’s r statistic, and line color denotes the statistical significance based on permutations. Pairwise comparisons of environmental factors are also shown, with a color gradient denoting Pearson’s correlation coefficient, and these parameters are synthesized into two groups based on attribute of data surveyed
| 地区 Area | 通量类型 Flux pattern | 溶解性重金属SGD通量 SGD flux of dissolved heavy metals/(μg·m-2·d-1) | 参考文献 Conferences | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cr | Cu | Zn | As | Ba | Pb | Hg | |||
| 漳江口淤泥质潮滩,中国福建省 Mudflat in Zhangjiang Estuary, Fujian Province, China | 对流 | 0.32 | 0.32 | 36.59 | 2.00 | 155.00 | 0.21 | 0.19 | 本研究 |
| 胶州湾砂质海滩,中国山东省 Sandy beach in Jiaozhou Bay, Shandong Province, China | 对流 | 6300 | 6200 | 840 | 210 | - | 1100 | - | 2020 |
| 胶州湾淤泥质潮滩,中国山东省 Mudflat in Jiaozhou Bay, Shandong Province, China | 对流 | 620 | 370 | 250 | 9.7 | - | 330 | - | 2020 |
| 胶州湾盐沼,中国山东省 Salt marsh in Jiaozhou Bay, Shandong Province, China | 对流 | 2.2 | 3.5 | 1.6 | 0.058 | - | 0.21 | - | 2020 |
| 胶州湾河口湿地,中国山东省 Estuarine wetland in Jiaozhou Bay, Shandong Province, China | 对流 | 56 | 57 | 26 | 3 | - | 0.01 | - | 2020 |
| 粤港澳大湾区,中国广东省 Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area, China | 对流+弥散 | 54.70 | 57.77 | 877.92 | 214.77 | - | 45.21 | - | 2022 |
| 渤海湾,中国河北省 Bohai Bay, Hebei Province, China | 对流+弥散 | 87-239 | - | 1211-3310 | - | - | - | - | 2019 |
| Coleroon River Estuary,印度 Coleroon River Estuary, Tamil Nadu, India | 对流+弥散 | 9.6-14.9 | 11-63 | 63.3-119.6 | - | 54.6-259.9 | 3.23-8.9 | - | 2021 |
| Jamaica Bay,美国 Jamaica Bay, New York, USA | 对流+弥散 | - | 2.46-11.08 | 87.5-401.3 | - | - | 0.56-2.79 | - | 2009 |
| North western Mediterranean Sea,西班牙 North western Mediterranean Sea, Spain | 对流+弥散 | - | 0.09-1.85 | 0.38-11.87 | - | - | 0.01-0.19 | - | 2016 |
表2 世界范围内对流和扩散输送的重金属通量的对比
Table 2 Comparisons of heavy metal fluxes transported by convection and diffusion globally
| 地区 Area | 通量类型 Flux pattern | 溶解性重金属SGD通量 SGD flux of dissolved heavy metals/(μg·m-2·d-1) | 参考文献 Conferences | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cr | Cu | Zn | As | Ba | Pb | Hg | |||
| 漳江口淤泥质潮滩,中国福建省 Mudflat in Zhangjiang Estuary, Fujian Province, China | 对流 | 0.32 | 0.32 | 36.59 | 2.00 | 155.00 | 0.21 | 0.19 | 本研究 |
| 胶州湾砂质海滩,中国山东省 Sandy beach in Jiaozhou Bay, Shandong Province, China | 对流 | 6300 | 6200 | 840 | 210 | - | 1100 | - | 2020 |
| 胶州湾淤泥质潮滩,中国山东省 Mudflat in Jiaozhou Bay, Shandong Province, China | 对流 | 620 | 370 | 250 | 9.7 | - | 330 | - | 2020 |
| 胶州湾盐沼,中国山东省 Salt marsh in Jiaozhou Bay, Shandong Province, China | 对流 | 2.2 | 3.5 | 1.6 | 0.058 | - | 0.21 | - | 2020 |
| 胶州湾河口湿地,中国山东省 Estuarine wetland in Jiaozhou Bay, Shandong Province, China | 对流 | 56 | 57 | 26 | 3 | - | 0.01 | - | 2020 |
| 粤港澳大湾区,中国广东省 Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area, China | 对流+弥散 | 54.70 | 57.77 | 877.92 | 214.77 | - | 45.21 | - | 2022 |
| 渤海湾,中国河北省 Bohai Bay, Hebei Province, China | 对流+弥散 | 87-239 | - | 1211-3310 | - | - | - | - | 2019 |
| Coleroon River Estuary,印度 Coleroon River Estuary, Tamil Nadu, India | 对流+弥散 | 9.6-14.9 | 11-63 | 63.3-119.6 | - | 54.6-259.9 | 3.23-8.9 | - | 2021 |
| Jamaica Bay,美国 Jamaica Bay, New York, USA | 对流+弥散 | - | 2.46-11.08 | 87.5-401.3 | - | - | 0.56-2.79 | - | 2009 |
| North western Mediterranean Sea,西班牙 North western Mediterranean Sea, Spain | 对流+弥散 | - | 0.09-1.85 | 0.38-11.87 | - | - | 0.01-0.19 | - | 2016 |
| [1] | ANDERSON D, GREGORICH E, 1984. Effect of soil erosion on soil quality and productivity[C]// Soil erosion and degradation. Processings. Annual Western Provincial Conference on Rationalization of Water and Soil Research and Manage, 105-113. |
| [2] |
BECK A J, COCHRAN J K, SANUDO-WILHELMY S A, 2009. Temporal trends of dissolved trace metals in Jamaica Bay, NY: Importance of wastewater input and submarine groundwater discharge in an urban estuary[J]. Estuaries and Coasts, 32(3): 535-550.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
BECK M, DELLWIG L, SCHNETGER B, et al., 2008. Cycling of trace metals (Mn, Fe, Mo, U, V, Cr) in deep pore waters of intertidal flat sediments[J]. Geochimica Et Cosmochimica Acta, 72(12): 2822-2840.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
BONE S E, GONNEEA M E, CHARETTE M A, 2006. Geochemical cycling of arsenic in a coastal aquifer[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 40(10): 3273-3278.
DOI URL |
| [5] | BURDIGE D J, 2006. Geochemistry of marine sediments[M]. Princeton: Princeton University Press. |
| [6] |
CHEN X G, ZHANG F F, LAO Y L, et al., 2018. Submarine groundwater discharge-derived carbon fluxes in mangroves: An important component of blue carbon budgets?[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research-Oceans, 123(9): 6962-6979.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
COX R A, CULKIN F, RILEY, J P, 1967. The electrical conductivity/chlorinity relationship in natural sea water[J]. Deep Sea Research and Oceanographic Abstracts, 14(2): 203-220.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
DHARMAPRAKASH S M, RAO P M, 1989. Diffusion-coefficient of barium ions from liesegang ring formation[J]. Journal of Materials Science Letters, 8(2): 141-143.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
DITTMAR T, PAENG J, 2009. A heat-induced molecular signature in marine dissolved organic matter[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2(3): 175-179.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
FERREIRA A M, MARQUES J C, SEIXAS S, 2017. Integrating marine ecosystem conservation and ecosystems services economic valuation: Implications for coastal zones governance[J]. Ecological Indicators, 77: 114-122.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
FICK A, 1855. Ueber diffusion[J]. Annalen der Physik, 170(1): 59-86.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
GOODWIN P M A J, ZEDLER J B, 2001. Tidal wetland restoration: An introduction[J]. Journal of Coastal Research, 27: 1-6.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
GREGORICH E G, CARTER M R, ANGERS D A, et al., 1994. Towards a minimum data set to assess soil organic matter quality in agricultural soils[J]. Canadian Journal of Soil Science, 74(4): 367-385.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
HAKANSON L, 1980. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control: A sedimentological approach[J]. Water Research, 14(8): 975-1001.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
HE R, TIAN B H, ZHANG Q Q, et al., 2015. Effect of fenton oxidation on biodegradability, biotoxicity and dissolved organic matter distribution of concentrated landfill leachate derived from a membrane process[J]. Waste Management, 38: 232-239.
DOI PMID |
| [16] |
HONG H L, ZHANG B H, LU H L., 2021. Seasonal variation and ecological risk assessment of heavy metal in an estuarine mangrove wetland[J]. Water, 13(15): 1-10.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
HOU L J, LI H L, ZHENG C M, et al., 2016. Seawater-groundwater exchange in a silty tidal flat in the south coast of Laizhou Bay, China[J]. Journal of Coastal Research, 74(sp1): 136-148.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
KALNEJAIS L H, MARTIN W R, BOTHNER M H, 2015. Porewater dynamics of silver, lead and copper in coastal sediments and implications for benthic metal fluxes[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 517: 178-194.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
KUSS J, HOLZMANN J, LUDWIG R, 2009. An elemental mercury diffusion coefficient for natural waters determined by molecular dynamics simulation[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 43(9): 3183-3186.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
LEONARDI N, GANJU N K, FAGHERAZZI S, 2016. A linear relationship between wave power and erosion determines salt-marsh resilience to violent storms and hurricanes[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 113(1): 64-68.
DOI PMID |
| [21] |
LIU Y, NOT C, JIAO J, et al., 2019. Tidal induced dynamics and geochemical reactions of trace metals (Fe, Mn, and Sr) in the salinity transition zone of an intertidal aquifer[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 664: 1133-1149.
DOI URL |
| [22] | LUO M H, ZHANG Y, LI H L, et al., 2022. Pollution assessment and sources of dissolved heavy metals in coastal water of a highly urbanized coastal area: The role of groundwater discharge[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 807(3): 1-12. |
| [23] |
MARCHAND C, FERNANDEZ J M, MORETON B, 2016. Trace metal geochemistry in mangrove sediments and their transfer to mangrove plants (New Caledonia)[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 562: 216-227.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
O′CONNOR A E, KRASK J L, CANUEL E A, et al., 2018. Seasonality of major redox constituents in a shallow subterranean estuary[J]. Geochimica Et Cosmochimica Acta, 224: 344-361.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
PAIN A J, MARTIN J B, YOUNG C R, et al., 2019. Organic matter quantity and quality across salinity gradients in conduit- vs. diffuse flow-dominated subterranean estuaries[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 64(3): 1386-1402.
DOI URL |
| [26] | PAN F, XIAO K, GUO Z R, LI H L, 2022. Effects of fiddler crab bioturbation on the geochemical migration and bioavailability of heavy metals in coastal wetlands[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 437: 1-11. |
| [27] |
POISSON A, PAPAUD A, 1983. Diffusion coefficients of major ions in seawater[J]. Marine Chemistry, 13(4): 265-280.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
PRAKASH R, SRINIVASAMOORTHY K, SUNDARAPANDIAN S M, et al., 2021. Submarine groundwater discharge from an urban estuary to Southeastern Bay of Bengal, India: Revealed by trace element fluxes[J]. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 80(1): 208-233.
DOI PMID |
| [29] |
QU W J, LI H L, HUANG H, et al., 2017. Seawater-groundwater exchange and nutrients carried by submarine groundwater discharge in different types of wetlands at Jiaozhou Bay, China[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 555: 185-197.
DOI URL |
| [30] | QU W J, WANG C Y, LUO M H, et al., 2020. Distributions, quality assessments and fluxes of heavy metals carried by submarine groundwater discharge in different types of wetlands in Jiaozhou Bay, China[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 157: 1-10. |
| [31] |
RICHARD J H, BISCHOFF C, AHRENS C G M, et al., 2016. Mercury (Ⅱ) reduction and co-precipitation of metallic mercury on hydrous ferric oxide in contaminated groundwater[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 539: 36-44.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
ROY M, MARTIN J B, SMITH C G, et al., 2011. Reactive-transport modeling of iron diagenesis and associated organic carbon remineralization in a Florida (USA) subterranean estuary[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 304(1-2): 191-201.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
SEIDEL M, BECK M, RIEDEL T, et al., 2014. Biogeochemistry of dissolved organic matter in an anoxic intertidal creek bank[J]. Geochimica Et Cosmochimica Acta, 140: 418-434.
DOI URL |
| [34] | SUN X, LI B S, LIU X L, et al., 2020. Spatial variations and potential risks of heavy metals in seawater, sediments, and living organisms in Jiuzhen Bay, China[J]. Journal of Chemistry, 2020: 1-13. |
| [35] | TANG J F, WANG W D, YANG L, et al., 2020. Seasonal variation and ecological risk assessment of dissolved organic matter in a peri-urban critical zone observatory watershed[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 707: 1-11. |
| [36] |
TREZZI G, GARCIA-ORELLANA J, RODELLAS V, et al., 2016. Submarine groundwater discharge: A significant source of dissolved trace metals to the North Western Mediterranean Sea[J]. Marine Chemistry, 186: 90-100.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
ULLMAN W J, SANDSTROM M W, 1987. Dissolved nutrient fluxes from the nearshore sediments of Bowling Green Bay, central Great Barrier Reef Lagoon (Australia)[J]. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science, 24(3): 289-303.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
VIGNUDELLI S, SANTINELLI C, MURRU E, et al., 2004. Distributions of dissolved organic carbon (DOC) and chromophoric dissolved organic matter (CDOM) in coastal of the northern Tyrrhenian Sea (Italy)[J]. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science, 60(1): 133-149.
DOI URL |
| [39] | WANG F F, XIAO K, SANTOS I R, et al., 2022. Porewater exchange drives nutrient cycling and export in a mangrove-salt marsh ecotone[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 606: 1-11. |
| [40] | WANG Q Q, LI H L, ZHANG Y, et al., 2019. Evaluations of submarine groundwater discharge and associated heavy metal fluxes in Bohai Bay, China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 695: 1-14. |
| [41] |
WANG X J, LI H L, YANG J Z, et al., 2014. Measuring in situ vertical hydraulic conductivity in tidal environments[J]. Advances in Water Resources, 70: 118-130.
DOI URL |
| [42] | WANG Y P, GAO S, JIA J J, et al., 2012. Sediment transport over an accretional intertidal flat with influences of reclamation, Jiangsu coast, China[J]. Marine Geology, 291: 147-161. |
| [43] |
WANG Y, DING S M, GONG M D, et al., 2016. Diffusion characteristics of agarose hydrogel used in diffusive gradients in thin films for measurements of cations and anions[J]. Analytica Chimica Acta, 945: 47-56.
DOI PMID |
| [44] |
WEISHAAR J L, AIKEN G R, BERGAMASCHI B A, et al., 2003. Evaluation of specific ultraviolet absorbance as an indicator of the chemical composition and reactivity of dissolved organic carbon[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 37(20): 4702-4708.
DOI URL |
| [45] | XIAO K, PAN F, SANTOS I R, et al., 2022. Crab bioturbation drives coupled iron-phosphate-sulfide cycling in mangrove and salt marsh soils[J]. Geoderma, 424: 1-12. |
| [46] |
XIAO K, WILSON A M, LI H L, et al., 2021. Large CO2 release and tidal flushing in salt marsh crab burrows reduce the potential for blue carbon sequestration[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 66(1): 14-29.
DOI URL |
| [47] | XIAO K, WU J P, LI H L, et al., 2018. Nitrogen fate in a subtropical mangrove swamp: Potential association with seawater-groundwater exchange[J]. Science of thr Total Environment, 635: 586-597. |
| [48] | YANG D, LIU J C, ZHAO W W, et al., 2020. Iron mineralogy and speciation of sediment iron-bearing minerals in mangrove forest: Case study of Zhangjiang Estuary, China[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 151: 1-9. |
| [49] |
YAO H, ZHAO Y J, LIN C J, et al., 2020. Development of a novel composite resin for dissolved divalent mercury measurement using diffusive gradients in thin films[J]. Chemosphere, DOI: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126231.
DOI |
| [50] | ZHANG X H, CAO F, HUANG Y, et al., 2022. Variability of dissolved organic matter in two coastal wetlands along the Changjiang River Estuary: Responses to tidal cycles, seasons, and degradation processes[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 807(3): 1-14. |
| [51] |
ZHOU H C, WEI S D, ZENG Q, et al., 2010. Nutrient and caloric dynamics in Avicennia marina leaves at different developmental and decay stages in Zhangjiang River Estuary, China[J]. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science, 87(1): 21-26.
DOI URL |
| [52] | 陈思明, 2018. 粉砂淤泥质潮滩表层沉积物侵蚀特性探讨[D]. 上海: 华东师范大学. |
| CHEN S M, 2018. Study on erosion charateristics of surface sediments in muddy tidal flat[D]. Shanghai: East Chaina Normal University. | |
| [53] | 李海龙, 王学静, 2015. 海底地下水排泄研究回顾与进展[J]. 地球科学进展, 30(6): 636-646. |
| LI H L, WANG X J, 2015. Submarine groundwater discharge: A review[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 30(6): 636-646. | |
| [54] | 国家标准化管理委员会, 2017. 地下水质量标准: GB/T 14848-2017[S]. |
| Standardization administration of China, 2017. Standard for groundwater quality: GB/T 14848-2017[S]. | |
| [55] | 王亚丽, 2020. 北部湾典型红树林区域海底地下水排放的碳通量及其光学特征[D]. 上海: 华东师范大学. |
| WANG Y L, 2020. Carbon fluxes by submarine groundwater diacharge and its optical charateristics in typical mangrove areas of the BeibuGulf[D]. Shanghai: East Chaina Normal University. | |
| [56] | 王颖, 1990. 中国的潮滩[J]. 第四纪研究 (4): 291-300. |
| WANG Y, 1990. Tidals of China[J]. Quaternary Science (4): 291-300. | |
| [57] | 薛博, 2007. 漳江口红树林湿地沉积物有机质来源追溯[D]. 厦门: 厦门大学. |
| XUE B, 2007. Distinguished the source of organic matter from mangrove wetland sediments in zhangjiang estuary[D]. Xiamen: Xiamen University. | |
| [58] | 杨世伦, 2003. 海岸环境和地貌过程导论[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社. |
| YANG S L, 2003. Introduction to coastal environment and geomorphic processes[M]. Beijing: Marine Press. | |
| [59] | 张耀玲, 2013. 近海环境中天然有机质的分离与表征[D]. 上海: 华东师范大学. |
| ZHANG Y L, 2013. Isolation and charaterization of natural organic matter in coastal environments[D]. Shanghai: East Chaina Normal University. | |
| [60] | 中国环境保护总局, 2002. 地表水环境质量标准(GB 3838- 2002)[S]. |
| Ministry of ecology and environment of China, 2002. Environmental quality standards for surface water (GB 3838-2002)[S]. |
| [1] | 杜丹丹, 高瑞忠, 房丽晶, 谢龙梅. 旱区盐湖盆地土壤重金属空间变异及对土壤理化因子的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(6): 1123-1132. |
| [2] | 冯树娜, 吕家珑, 何海龙. KI淋洗对黄绵土汞污染的去除效果及土壤理化性状的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 776-783. |
| [3] | 陈敏毅, 朱航海, 佘伟铎, 尹光彩, 黄祖照, 杨巧玲. 珠三角某遗留造船厂场地土壤重金属人体健康风险评估及源解析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 794-804. |
| [4] | 杨秋, 曹英杰, 张宇, 陈建耀, 王诗忠, 田帝. 闭坑铅锌矿区地下水-矿坑水水化学特征及成因分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(2): 361-371. |
| [5] | 徐敏, 许超, 余光辉, 尹力初, 张泉, 朱捍华, 朱奇宏, 张杨珠, 黄道友. 地下水位和长期秸秆还田对土壤镉有效性及稻米镉含量的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 150-157. |
| [6] | 肖洁芸, 周伟, 石佩琪. 土壤重金属含量高光谱反演[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 175-182. |
| [7] | 黄宏, 郑欣芸, 李迎东, 赵旭, 俞锦辰, 汪振华. 大陈岛海域不同年龄褐菖鲉对重金属富集作用研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(9): 1885-1891. |
| [8] | 马闯, 王雨阳, 周通, 吴龙华. 污染土壤颗粒态有机质镉锌富集特征及其解吸行为研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(9): 1892-1900. |
| [9] | 陶玲, 黄磊, 周怡蕾, 李中兴, 任珺. 污泥-凹凸棒石共热解生物炭对矿区土壤重金属生物有效性和环境风险的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1637-1646. |
| [10] | 李莹, 张洲, 杨高明, 祖艳群, 李博, 陈建军. 湿地植物根系泌氧能力和根表铁膜与根系吸收重金属的关系[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1657-1666. |
| [11] | 罗松英, 李秋霞, 邱锦坤, 邓素炎, 李一锋, 陈碧珊. 南三岛土壤-红树植物系统中重金属形态特征及迁移转化规律[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(7): 1409-1416. |
| [12] | 董乐恒, 王旭刚, 陈曼佳, 王子豪, 孙丽蓉, 石兆勇, 吴琪琪. 光照和避光条件下石灰性水稻土Fe氧化还原与Cu活性关系研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(7): 1448-1455. |
| [13] | 彭红丽, 谭海霞, 王颖, 魏建梅, 冯阳. 不同种植模式下土壤重金属形态分布差异与生态风险评价[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(6): 1235-1243. |
| [14] | 黄敏, 赵晓峰, 梁荣祥, 王鹏忠, 戴安然, 何晓曼. 3种螯合剂对Cd、Cu复合污染土壤淋洗修复的对比研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(6): 1244-1252. |
| [15] | 朱立安, 张会化, 程炯, 李婷, 林梓, 李俊杰. 珠江三角洲林业用地土壤重金属潜在生态风险格局分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(6): 1253-1262. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
