生态环境学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (10): 2070-2078.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2022.10.015
刘畅( ), 罗艳丽*(
), 罗艳丽*( ), 刘晨通, 郑玉红, 晁博, 董乐乐
), 刘晨通, 郑玉红, 晁博, 董乐乐
收稿日期:2022-06-30
出版日期:2022-10-18
发布日期:2022-12-09
通讯作者:
*罗艳丽,E-mail: luoyanlimail@sina.com作者简介:刘畅(1995年生),女,硕士研究生,研究方向为砷的迁移行为和环境效应研究。E-mail: 969070761@qq.com
基金资助:
LIU Chang( ), LUO Yanli*(
), LUO Yanli*( ), LIU Chentong, ZHENG Yuhong, CHAO Bo, DONG Lele
), LIU Chentong, ZHENG Yuhong, CHAO Bo, DONG Lele
Received:2022-06-30
Online:2022-10-18
Published:2022-12-09
摘要:
为探究典型高砷区新疆奎屯垦区地下水和农田土壤As的分布特征以及地下水灌溉对土壤As富集的影响,以新疆奎屯河下游为研究区域,地下水及其灌溉的农田土壤为研究对象,共采集50个地下水水样(以2个地表水水样为对照)和100个农田土样(各采样点分别在0—10 cm和10—20 cm取样)。采用数理统计法和GIS空间插值技术,结合标准差椭圆模型趋势性分析,研究该地区地下水和土壤As的空间分布特征,探讨地下水灌溉对土壤As累积的影响,以期为该地区合理利用地下水进行农业灌溉提供理论支撑。结果表明:研究区地下水As质量浓度范围为0.76—410.00 μg·L-1,均值为116.38 μg·L-1,有84%的地下水样品为高砷地下水;0—10、10—20 cm土层中As平均质量分数分别为12.45、10.97 mg·kg-1,分别有56%、42%的土壤样点As质量分数超出新疆土壤As元素背景值,土壤As质量分数表现为0—10 cm > 10—20 cm;地下水和土壤中As在整体水平上具有相似的空间分布特征,中部及西南方向的地下水As质量浓度较高;0—10 cm土层中,As的高值区主要集中分布于西部及中偏东北方向;10—20 cm土层中,As的分布整体呈现出由东向西方向增加的趋势;地下水As质量浓度与土壤As质量分数呈显著正相关,混灌条件下土壤As质量分数小于井灌条件下土壤As质量分数。综上,奎屯河下游区域长期受地下水灌溉的影响,农田土壤As出现一定累积现象,建议该地区利用地下水进行农业灌溉时多采用混灌方式。
中图分类号:
刘畅, 罗艳丽, 刘晨通, 郑玉红, 晁博, 董乐乐. 奎屯河下游区域地下水和农田土壤砷的空间分布特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(10): 2070-2078.
LIU Chang, LUO Yanli, LIU Chentong, ZHENG Yuhong, CHAO Bo, DONG Lele. Spatial Distribution Characteristics of Arsenic in Groundwater and Cropland Soil in the Lower Reaches of Kuitun River[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(10): 2070-2078.
| 水样类型 Water type | 样点数 Number of samples | As | pH | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 范围 Range/(μg·L-1) | 均值 Mean/(μg·L-1) | 变异系数 Coefficient of variation | 范围 Range | 均值 Mean | ||
| 地表水 Surface water | 2 | 7.07-8.57 | 7.82 | 0.14 | 8.13-8.03 | 8.08 |
| 地下水 Groundwater | 50 | 0.76-410.00 | 116.38 | 1.00 | 6.76-9.33 | 8.39 |
表1 水样中As质量浓度统计特征
Table 1 Statistical characteristics of arsenic mass concentration in water samples
| 水样类型 Water type | 样点数 Number of samples | As | pH | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 范围 Range/(μg·L-1) | 均值 Mean/(μg·L-1) | 变异系数 Coefficient of variation | 范围 Range | 均值 Mean | ||
| 地表水 Surface water | 2 | 7.07-8.57 | 7.82 | 0.14 | 8.13-8.03 | 8.08 |
| 地下水 Groundwater | 50 | 0.76-410.00 | 116.38 | 1.00 | 6.76-9.33 | 8.39 |
| 土层深度 Soil depth/cm | 样点数 Number of samples | As | pH | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 范围 Range/(mg·kg-1) | 均值 Mean/(g·kg-1) | 变异系数 Coefficient of variation | 范围 Range | 均值 Mean | ||
| 0-10 | 50 | 6.67-20.67 | 12.45 | 0.28 | 7.06-9.68 | 7.98 |
| 10-20 | 50 | 4.42-18.49 | 10.97 | 0.30 | 7.32-9.71 | 8.06 |
表2 土样中As质量分数统计特征
Table 2 Statistical characteristics of arsenic mass fraction in soil samples
| 土层深度 Soil depth/cm | 样点数 Number of samples | As | pH | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 范围 Range/(mg·kg-1) | 均值 Mean/(g·kg-1) | 变异系数 Coefficient of variation | 范围 Range | 均值 Mean | ||
| 0-10 | 50 | 6.67-20.67 | 12.45 | 0.28 | 7.06-9.68 | 7.98 |
| 10-20 | 50 | 4.42-18.49 | 10.97 | 0.30 | 7.32-9.71 | 8.06 |
| 特征椭圆 Eigenellipse | 周长 Circumference/ km | 面积 Area/km2 | 重心坐标 Barycentric coordinates | 短半轴 Semi-minor axis/ km | 长半轴 Semi-major axis/ km | 短长轴之比 Ratio of short-long axis | 方位角 Rotation/ (°) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 地下水As As in groundwater | 90.93 | 234.56 | (84°22'52″, 45°01'33″) | 3.39 | 22.02 | 0.15 | 94.98 |
| 土壤As As in soil (0-10 cm) | 97.35 | 450.82 | (84°28'03″, 45°02'22″) | 6.43 | 22.32 | 0.29 | 95.48 |
| 土壤As As in soil (10-20 cm) | 97.87 | 458.39 | (84°26'17″, 45°02'35″) | 6.51 | 22.42 | 0.29 | 95.00 |
表3 地下水和土壤As的标准差椭圆参数
Table 3 Parameters of the standard deviation ellipse of arsenic in groundwater and soil
| 特征椭圆 Eigenellipse | 周长 Circumference/ km | 面积 Area/km2 | 重心坐标 Barycentric coordinates | 短半轴 Semi-minor axis/ km | 长半轴 Semi-major axis/ km | 短长轴之比 Ratio of short-long axis | 方位角 Rotation/ (°) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 地下水As As in groundwater | 90.93 | 234.56 | (84°22'52″, 45°01'33″) | 3.39 | 22.02 | 0.15 | 94.98 |
| 土壤As As in soil (0-10 cm) | 97.35 | 450.82 | (84°28'03″, 45°02'22″) | 6.43 | 22.32 | 0.29 | 95.48 |
| 土壤As As in soil (10-20 cm) | 97.87 | 458.39 | (84°26'17″, 45°02'35″) | 6.51 | 22.42 | 0.29 | 95.00 |
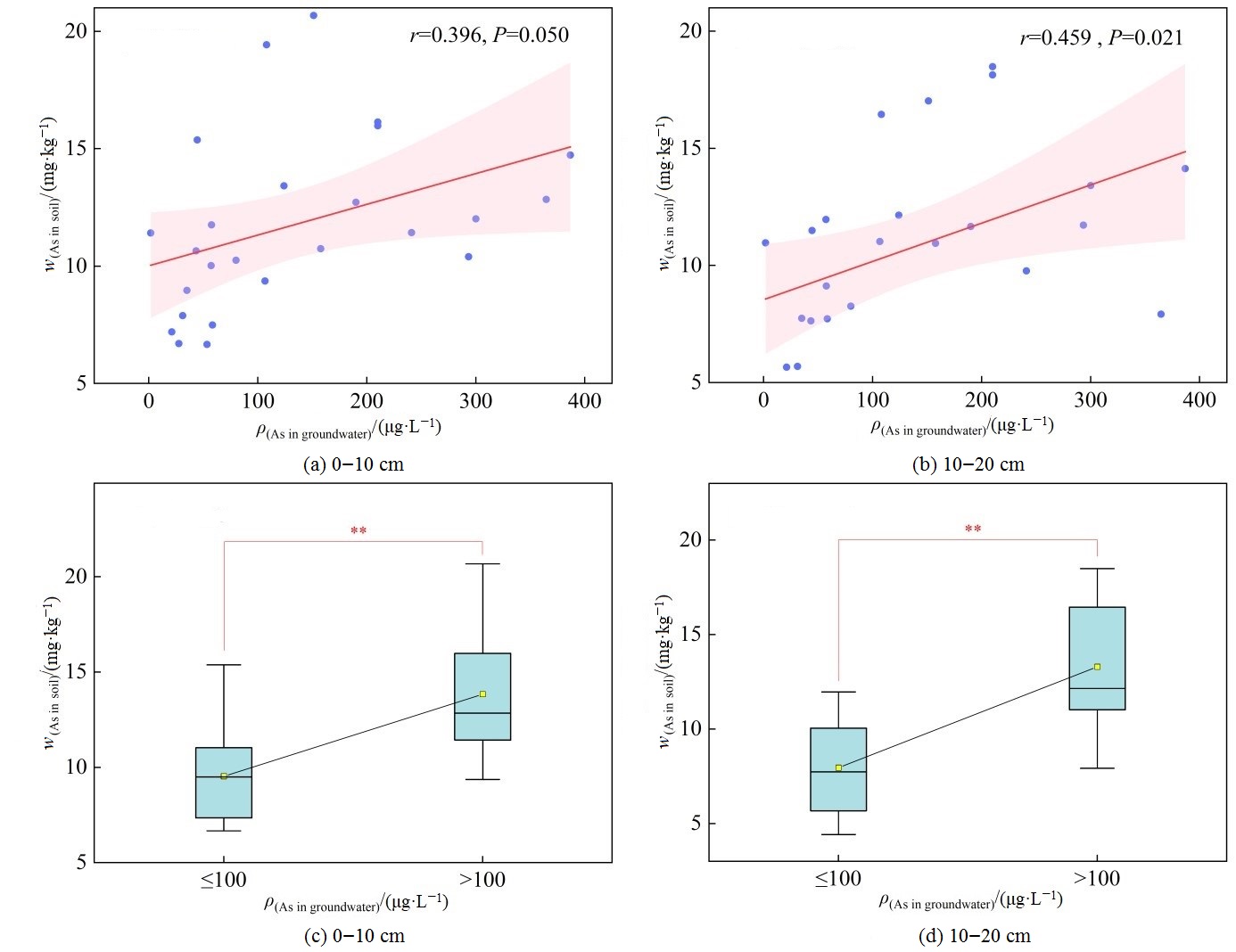
图3 土壤As质量分数与地下水As质量浓度的关系 “**”表示在0.01水平上极显著差异,n=25
Figure 3 The relationship between arsenic mass fraction in soil and arsenic mass concentration in groundwater “**” indicates highly significant differences at the 0.01 level, n=25
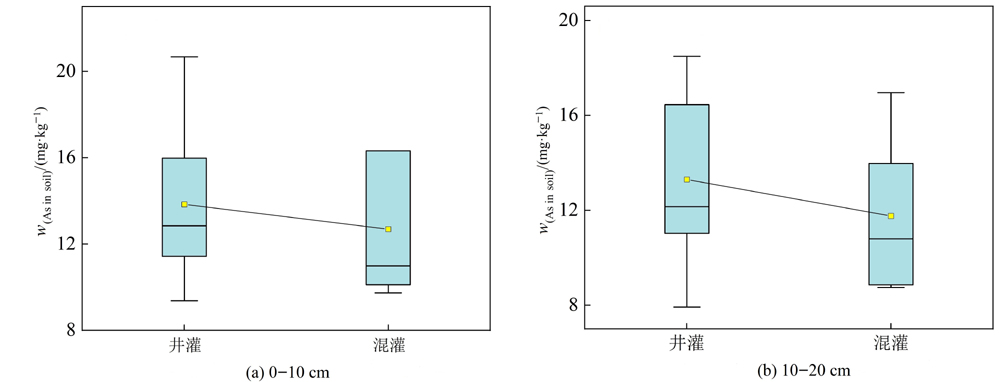
图4 不同灌溉方式下As在土壤中的质量分数 n1=13;n2=7(n1为井灌样本量;n2为混灌样本量)
Figure 4 Arsenic mass fraction in soil under different irrigation methods n1=13; n2=7 (n1 is the sample size of well irrigation; n2 is the sample size of mixed irrigation)
| [1] |
CASENTINI B, HUG S J, NIKOLAIDIS N P, 2011. Arsenic accumulation in irrigated agricultural soils in northern Greece[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 409(22): 4802-4810.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
DITTMAR J, VOEGELIN A, ROBERTS L C, et al., 2007. Spatial distribution and temporal variability of arsenic in irrigated rice fields in Bangladesh. 2. Paddy soil[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 41(17): 5967-5972.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
FAROOQ S H, CHANDRASEKHARAM D, DHANACHANDRA W, et al., 2019. Relationship of arsenic accumulation with irrigation practices and crop type in agriculture soils of Bengal Delta, India[J]. Applied Water Science, 9(5): 1-11.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
GARG N, SINGLA P, 2011. Arsenic toxicity in crop plants: physiological effects and tolerance mechanisms[J]. Environmental Chemistry Letters, 9(3): 303-321.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
GILLISPIE E C, SOWERS T D, DUCKWORTH O W, et al., 2015. Soil pollution due to irrigation with arsenic-contaminated groundwater: current state of science[J]. Current Pollution Reports, 1(1): 1-12.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
HOSSAIN M B, JAHIRUDDIN M, PANAULLAH G M, et al., 2008. Spatial variability of arsenic concentration in soils and plants, and its relationship with iron, manganese and phosphorus[J]. Environmental Pollution, 156(3): 739-744.
DOI PMID |
| [7] |
HUANG Y, MIYAUCHI K, ENDO G, et al., 2016. Arsenic contamination of groundwater and agricultural soil irrigated with the groundwater in Mekong Delta, Vietnam[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 75(9): 757.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
JAVED A, FAROOQI A, BAIG Z U, et al., 2020. Soil arsenic but not rice arsenic increasing with arsenic in irrigation water in the Punjab plains of Pakistan[J]. Plant and Soil, 450(1-2): 601-611.
DOI PMID |
| [9] |
LEFEVER D W, 1926. Measuring geographic concentration by means of the standard deviational ellipse[J]. American Journal of Sociology, 32(1): 88-94.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
MCARTHUR J M, NATH B, BANERJEE D M, et al., 2011. Palaeosol control on groundwater flow and pollutant distribution: the example of arsenic[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 45(4): 1376-1383.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
MEHARG A A, RAHMAN M M, 2003. Arsenic contamination of Bangladesh paddy field soils: implications for rice contribution to arsenic consumption[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 37(2): 229-234.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
MUKHERJEE A, KUNDU M, BASU B, et al., 2017. Arsenic load in rice ecosystem and its mitigation through deficit irrigation[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 197: 89-95.
DOI PMID |
| [13] |
QUICKSALL A N, BOSTICK B C, SAMPSON M L, 2008. Linking organic matter deposition and iron mineral transformations to groundwater arsenic levels in the Mekong delta, Cambodia[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 23(11): 3088-3098.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
SAHA G C, ALI M A, 2007. Dynamics of arsenic in agricultural soils irrigated with arsenic contaminated groundwater in Bangladesh[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 379(2-3): 180-189.
PMID |
| [15] | SHRIVASTAVA A, BARLA A, YADAV H, et al., 2014. Arsenic contamination in shallow groundwater and agricultural soil of Chakdaha block, West Bengal, India[J]. Frontiers in Environmental Science, 2(50): 1-9. |
| [16] |
SU C L, ZHU Y P, ABBAS Z, et al., 2016. Sources and controls for elevated arsenic concentrations in groundwater of Datong basin, northern China[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 75(7): 570.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
WANG Y X, LI J X, MA T, et al., 2021. Genesis of geogenic contaminated groundwater: As, F and I[J]. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 51(24): 2895-2933.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
ZHOU Y T, NIU L L, LIU K, et al., 2018. Arsenic in agricultural soils across China: Distribution pattern, accumulation trend, influencing factors, and risk assessment[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 616-617: 156-163.
DOI URL |
| [19] | 白冰, 赵作权, 张佩, 2021. 中国南北区域经济空间融合发展的趋势与布局[J]. 经济地理, 41(2): 1-10. |
|
BAI B, ZHAO Z Q, ZHANG P, 2021. Trends and layout of economic integration between north and south China[J]. Economic Geography, 41(2): 1-10.
DOI URL |
|
| [20] | 陈云飞, 周金龙, 曾妍妍, 等, 2020. 塔里木盆地东南缘绿洲区土壤砷空间分布及农作物砷富集特征[J]. 环境科学, 41(1): 438-448. |
| CHEN Y F, ZHOU J L, ZENG Y Y, et al., 2020. Spatial distribution of soil arsenic and arsenic enrichment in crops in the oasis region of the southeastern Tarim basin[J]. Environmental Science, 41(1): 438-448. | |
| [21] | 戴志鹏, 罗艳丽, 王翔, 2019. 新疆奎屯河流域高砷、高氟地下水的分布特征[J]. 环境保护科学, 45(4): 81-86. |
| DAI Z P, LUO Y L, WANG X, 2019. Distribution characteristics of high arsenic and fluorine in groundwater of Kuitun River basin in Xinjiang[J]. Environmental Protection Science, 45(4): 81-86. | |
| [22] | 邓雯文, 罗艳丽, 王翔, 等, 2021. 地下水-土壤系统中砷含量及健康风险评价[J]. 环境科学与技术, 44(4): 204-211. |
|
DENG W W, LUO Y L, WANG X, et al., 2021. Arsenic content and health risk assessment in groundwater-soil system[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 44(4): 204-211.
DOI URL |
|
| [23] | 董立宽, 方斌, 王晨歌, 2018. 基于Copula函数的茶园土壤铜锌空间协同效应研究[J]. 自然资源学报, 33(5): 867-878. |
| DONG L K, FANG B, WANG C G, 2018. Study on the spatial synergistic effect of copper and zinc in tea garden soil based on copula function[J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 33(5): 867-878. | |
| [24] |
冯子钰, 施润和, 2021. 中国近地面PM2.5浓度与排放的时空分布及其关联分析[J]. 地球信息科学学报, 23(7): 1221-1230.
DOI |
| FENG Z Y, SHI R H, 2021. Spatio-temporal features and the association of ground-level PM2.5 concentration and its emission in China[J]. Journal of Geo-Information Science, 23(7): 1221-1230. | |
| [25] | 郭华明, 郭琦, 贾永锋, 等, 2013. 中国不同区域高砷地下水化学特征及形成过程[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 35(3): 83-96. |
| GUO H M, GUO Q, JIA Y F, et al., 2013. Chemical characteristics and geochemical processes of high arsenic groundwater in different regions of China[J] Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 35(3): 83-96. | |
| [26] | 滑小赞, 程滨, 赵瑞芬, 等, 2021. 太原市农田土壤重金属污染评价与空间分布特征[J]. 灌溉排水学报, 40(3): 101-109. |
| HUA X Z, CHENG B, ZHAO R F, et al., 2021. Pollution assessment and spatial distribution of heavy metals in the farmland soils of Taiyuan city[J]. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage, 40(3): 101-109. | |
| [27] | 江军, 鲜虎胜, 李巧, 等, 2021. 奎屯河流域地下水地球化学特征及其对砷运移的影响[J]. 环境化学, 40(6): 1775-1786. |
| JIANG J, XIAN H S, LI Q, et al., 2021. Groundwater geochemistry and its implications for arsenic mobilization in Kuitun River basin, Xinjiang[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 40(6): 1775-1786. | |
| [28] | 李晶, 2016. 砷在新疆奎屯地下水中的分布及其在农田土壤中的迁移[D]. 乌鲁木齐: 新疆农业大学: 38-39. |
| LI J, 2016. Study on the distribution of arsenic in groundwater and its transport in farmland soil in Kuitun Xinjiang[D]. Urumqi: Xinjiang Agricultural University: 38-39. | |
| [29] | 鲁如坤, 2000. 土壤农业化学分析方法[M]. 北京: 中国农业科学技术出版社: 12-14. |
| LU R K, 2000. Soil agrochemical analysis methods[M]. Beijing: China Agricultural Science and Technology Press: 12-14. | |
| [30] | 罗艳丽, 蒋平安, 余艳华, 等, 2007. 新疆奎屯123团土壤砷污染研究[J]. 土壤通报, 38(3): 558-561. |
| LUO Y L, JIANG P A, YU Y H, et al., 2007. Arsenic pollution of soil in Kuitun No.123 state farm, Xinjiang[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 38(3): 558-561. | |
| [31] | 罗艳丽, 李晶, 蒋平安, 等, 2017. 新疆奎屯原生高砷地下水的分布、类型及成因分析[J]. 环境科学学报, 37(8): 2897-2903. |
| LUO Y L, LI J, JIANG P A, et al., 2017. Distribution, classification and cause analysis of geogenic high-arsenic groundwater in Kuitun, Xinjiang[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 37(8): 2897-2903. | |
| [32] | 宿彦鹏, 李巧, 陶洪飞, 等, 2022. 奎屯河流域高砷地下水砷含量空间分布异常的影响因素[J]. 长江科学院院报, 39(2): 43-49, 55. |
| SU Y P, LI Q, TAO H F, et al., 2022. Factors influencing the abnormal spatial distribution of arsenic content in groundwater in Kuitun River basin[J]. Journal of Yangtze River Scientific Research Institute, 39(2): 43-49, 55. | |
| [33] | 汪花, 刘秀明, 刘方, 等, 2019. 喀斯特地区小尺度农业土壤砷的空间分布及污染评价[J]. 环境科学, 40(6): 2895-2903. |
|
WANG H, LIU X M, LIU F, et al., 2019. Spatial distribution and pollution assessment of As at a small scale in agricultural soils of the Karst region[J]. Environmental Science, 40(6): 2895-2903.
DOI URL |
|
| [34] | 王连方, 刘鸿德, 徐训风, 等, 1983. 新疆奎屯垦区慢性地方性砷中毒调查报告[J]. 中国地方病学杂志, 2(2): 71. |
| WANG L F, LIU H D, XU X F, et al., 1983. Investigation report on chronic endemic arsenic poisoning in Kuitun reclamation area, Xinjiang[J]. Chinese Journal of Endemiology, 2(2): 71. | |
| [35] | 王翔, 2021. 奎屯河下游区域地下水中砷的释放过程研究[D]. 乌鲁木齐: 新疆农业大学:20. |
| WANG X, 2021. Mobilization processes of arsenic in groundwater of Kuitun River downsteam[D]. Urumqi: Xinjiang Agricultural University:20. | |
| [36] | 王翔, 罗艳丽, 邓雯文, 等, 2020. 新疆奎屯地区高砷地下水DOM三维荧光特征[J]. 中国环境科学, 40(11): 4974-4981. |
| WANG X, LUO Y L, DENG W W, et al., 2020. The 3D-EEM characteristics of DOM in high arsenic groundwater of Kuitun, Xinjiang[J]. China Environmental Science, 40(11): 4974-4981. | |
| [37] | 谢正苗, 1989. 砷的土壤化学[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 8(1): 36-38. |
| XIE Z M, 1989. Soil chemistry of arsenic[J]. Journal of Agro- Environment Science, 8(1): 36-38. | |
| [38] | 严怡君, 谢先军, 郑文君, 等, 2017. 灌溉活动对大同盆地表层土壤中砷迁移的影响[J]. 地质科技情报, 36(3): 235-241. |
| YAN Y J, XIE X J, ZHENG W J, et al., 2017. Influence of irrigation practices on arsenic mobilization in near-surface soil of Datong basin, northern China[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 36(3): 235-241. | |
| [39] | 袁翰卿, 李巧, 陶洪飞, 等, 2020. 新疆奎屯河流域地下水砷富集因素[J]. 环境化学, 39(2): 524-530. |
| YUAN H Q, LI Q, TAO H F, et al., 2020. Groundwater arsenic enrichment factors of Kuitun River basin, Xinjiang[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 39(2): 524-530. | |
| [40] |
张杰, 唐根年, 2018. 浙江省制造业空间分异格局及其影响因素[J]. 地理科学, 38(7): 1107-1117.
DOI |
|
ZHANG J, TANG G N, 2018. Spatial differentiation pattern of manufacturing industry in Zhejiang and its influencing factors[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 38(7): 1107-1117.
DOI |
|
| [41] | 张维, 齐丽娟, 宁钧宇, 等, 2021. 砷的健康危害评估[J]. 毒理学杂志, 35(5): 367-372, 378. |
| ZHANG W, QI L J, NING J Y, et al., 2021. Health hazard assessment of arsenic[J]. Journal of Toxicology, 35(5): 367-372, 378. | |
| [42] |
赵璐, 赵作权, 2014. 基于特征椭圆的中国经济空间分异研究[J]. 地理科学, 34(8): 979-986.
DOI |
|
ZHAO L, ZHAO Z Q, 2014. Projecting the spatial variation of economic based on the specific ellipses in China[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 34(8): 979-986.
DOI |
|
| [43] | 中国环境监测总站, 1990. 中国土壤元素背景值[M]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社:331. |
| China National Environmental Monitoring Centre, 1990. Background value of soil elements in China[M]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press:331. | |
| [44] | 中华人民共和国环境保护部, 2013. 土壤和沉积物汞、砷、硒、铋、锑的测定微波消解/原子荧光法: HJ 680—2013[S]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社. |
| Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China, 2013. Soil and sedimen-Determination of mercury, arsenic, selenium, bismuth, antimony-Microwave dissolution/Atomic Fluorescence Spectrometry: HJ 680—2013 [S]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press. | |
| [45] | 中华人民共和国生态环境部, 2018. 土壤环境质量农用地土壤污染风险管控标准 (试行): GB 15618—2018[S]. 北京: 中国环境出版集团. |
| Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China, 2018. Soil environmental quality-Risk control standard for soil contamination of agricultural land: GB 15618—2018 [S]. Beijing: China Environment Publishing Group. | |
| [46] | 中华人民共和国生态环境部, 2021. 农田灌溉水质标准: GB 5084—2021[S]. 北京: 中国环境出版集团. |
| Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China, 2021. Standard for irrigation water quality: GB 5084—2021 [S]. Beijing: China Environment Publishing Group. | |
| [47] | 左岍, 周勇, 李晴, 等, 2022. 鄂西南地区土地利用格局时空变化及轨迹特征分析[J]. 水土保持学报, 36(1): 161-169. |
| ZUO Q, ZHOU Y, LI Q, et al., 2022. Analysis of spatial and temporal changes and trajectory characteristics of land use pattern in the southwest Hubei[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 36(1): 161-169. |
| [1] | 董智今, 张呈春, 展秀丽, 张维福. 宁夏河东沙地生物土壤结皮及其下伏土壤养分的空间分布特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 910-919. |
| [2] | 杨春亮, 刘旻霞, 王千月, 苗乐乐, 肖音迪, 王敏. 单户与联户放牧经营下草玉梅与嵩草种群空间格局及其关联性[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 651-659. |
| [3] | 杨宇, 邓仁健, 隆佩, 黄中杰, 任伯帜, 王政华. 砷氧化菌Pseudomonas sp. AO-1的分离鉴定及其对As(Ⅲ)的氧化性能研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 619-626. |
| [4] | 杨秋, 曹英杰, 张宇, 陈建耀, 王诗忠, 田帝. 闭坑铅锌矿区地下水-矿坑水水化学特征及成因分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(2): 361-371. |
| [5] | 尹浩均, 龙明亮, 刘维, 倪春林, 李芳柏, 吴云当. 溶氧浓度调控嗜水气单胞菌的砷还原:效应与机制[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(2): 381-387. |
| [6] | 徐敏, 许超, 余光辉, 尹力初, 张泉, 朱捍华, 朱奇宏, 张杨珠, 黄道友. 地下水位和长期秸秆还田对土壤镉有效性及稻米镉含量的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 150-157. |
| [7] | 吴胜义, 王飞, 徐干君, 马浩, 党禹杰, 吴菲. 川西北高山峡谷区森林碳储量及空间分布研究--以四川洛须自然保护区为例[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(9): 1735-1744. |
| [8] | 李秀华, 赵玲, 滕应, 骆永明, 黄标, 刘冲, 刘本乐, 赵其国. 贵州汞矿区周边农田土壤汞镉复合污染特征空间分布及风险评估[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1629-1636. |
| [9] | 高鹏, 高品, 孙蔚旻, 孔天乐, 黄端仪, 刘华清, 孙晓旭. 蜈蚣草根际及内生微生物群落对砷污染胁迫的响应机制研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(6): 1225-1234. |
| [10] | 徐梅华, 顾明华, 王骋臻, 雷静, 韦燕燕, 沈方科. 锰对土壤砷形态转化及水稻吸收砷的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 802-813. |
| [11] | 温智峰, 魏识广, 李林, 叶万辉, 练琚愉. 南亚热带常绿阔叶林植物不同分类水平上的空间分布格局及空间关联[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(3): 440-450. |
| [12] | 刘娣, 苏超, 张红, 秦冠宇. 典型煤炭产业聚集区土壤重金属污染特征与风险评价[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(2): 391-399. |
| [13] | 张丽聪, 肖凯, 张鹏, 李海龙, 王俊坚, 李镇扬, 王芬芳, 徐华林, 郭跃华. 淤泥质潮滩重金属和溶解性有机质的潮汐变化特征及其环境影响评价[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(11): 2169-2179. |
| [14] | 张楷悦, 刘增辉, 王颜昊, 王敬宽, 崔德杰, 柳新伟. 黄河三角洲自然保护区土壤PAHs的风险评估和空间特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(11): 2198-2205. |
| [15] | 周椿富, 于锐, 王翔, 闯绍闯, 杨洪杏, 谢越. 抗生素对不同土壤中酶活性的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(11): 2234-2241. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
