生态环境学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (10): 1984-1992.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2022.10.006
张晓丽1,2( ), 王国丽1, 常芳弟1, 张宏媛1, 逄焕成1, 张建丽3, 王婧1, 冀宏杰1, 李玉义1,*(
), 王国丽1, 常芳弟1, 张宏媛1, 逄焕成1, 张建丽3, 王婧1, 冀宏杰1, 李玉义1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2021-02-24
出版日期:2022-10-18
发布日期:2022-12-09
通讯作者:
*李玉义,研究员,博士研究生导师,主要从事土壤耕作与盐碱地改良利用研究。E-mail: liyuyi@caas.cn作者简介:张晓丽(1993年生),助教,硕士,从事盐碱地改良利用研究。E-mail: 1695952120@qq.com
基金资助:
ZHANG Xiaoli1,2( ), WANG Guoli1, CHANG Fangdi1, ZHANG Hongyuan1, PANG Huancheng1, ZHANG Jianli3, WANG Jing1, JI Hongjie1, LI Yuyi1,*(
), WANG Guoli1, CHANG Fangdi1, ZHANG Hongyuan1, PANG Huancheng1, ZHANG Jianli3, WANG Jing1, JI Hongjie1, LI Yuyi1,*( )
)
Received:2021-02-24
Online:2022-10-18
Published:2022-12-09
摘要:
为明确微生物菌剂在内蒙古河套地区中度盐碱土壤改良中的作用,可为盐碱土壤质量提升提供技术支撑。采用大田随机区组试验设计方法,以空白处理(CK)为对照,设置3种微生物菌剂处理,包括丹路牌微生物菌剂(DL)、自主研发的复合微生物菌剂BZ1T/1-15(由芽孢杆菌、芽单胞菌和草炭组成),其使用量分别为570 kg·hm-2(BL1)和1140 kg·hm-2(BL2)。分析不同处理措施下的土壤盐分、养分以及细菌群落结构组成和多样性的变化特征。结果表明:施用微生物菌剂(DL、BL)均可显著降低土壤盐分和pH值,其中BL2处理对降低土壤盐分的效果最显著,与CK、DL、BL1相比分别降低了14.0%、4.2%、7.4%(P<0.05)。同时,施用BL1和BL2微生物菌剂对提高根际土壤的碱解氮、速效钾和有效磷含量有显著作用,其中BL1、BL2处理的碱解氮含量较CK和DL分别显著提高26.4%和11.67%、50.94%和33.33%,BL2处理的速效钾含量较CK、DL和BL1分别显著提高24.1%、24.7%和11.1%(P<0.05)。高通量测序结果表明,BL2处理的丰富度指数(ACE、Chao1)显著高于其他处理,还可显著提升放线菌门、厚壁菌门和蓝细菌门的优势菌群丰度,另外BL1和BL2处理显著降低了酸杆菌门、芽单胞菌门、拟杆菌门、硝化螺旋菌门和浮霉菌门细菌菌群的相对丰度(P<0.05)。相关性分析结果显示,放线菌门与土壤pH值、碱解氮分别呈显著负相关、正相关(r分别为-0.581*、0.595*);土壤速效钾与变形菌门、酸杆菌门和绿弯菌门分别呈极显著负相关、正相关和正相关(r分别为-0.753**、0.503*和0.569*)。因子分析结果表明,有机质、盐分和养分等是影响土壤细菌群落结构的主控环境因子,因为其总共解释了67.0%的群落变化;它们的贡献率依次为:土壤有机质>盐分>速效钾>pH>有效磷>碱解氮。另外,BL1和BL2菌剂的施用对提高向日葵的产量有显著作用,且作物产量与养分含量呈极显著正相关关系。因此,施用微生物菌剂不仅可以降低土壤盐分和pH值,而且还可显著提高土壤养分含量和作物产量,改善细菌菌群结构。该研究可以为微生物菌剂在内蒙古河套灌区盐碱土壤改良方面提供试验基础和参考。
中图分类号:
张晓丽, 王国丽, 常芳弟, 张宏媛, 逄焕成, 张建丽, 王婧, 冀宏杰, 李玉义. 生物菌剂对根际盐碱土壤理化性质和微生物区系的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(10): 1984-1992.
ZHANG Xiaoli, WANG Guoli, CHANG Fangdi, ZHANG Hongyuan, PANG Huancheng, ZHANG Jianli, WANG Jing, JI Hongjie, LI Yuyi. Effects of Microbial Agents on Physicochemical Properties and Microbial Flora of Rhizosphere Saline-alkali Soil[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(10): 1984-1992.
| 处理 Treatments | w(全盐 Salt)/ (g·kg-1) | pH | w(有机质Organic Matter)/ (g·kg-1) | w(碱解氮Available-N)/ (mg·kg-1) | w(有效磷Available-P)/ (mg·kg-1) | w(速效钾Available-K)/ (mg·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 2.89±0.01a | 8.90±0.15a | 11.8±0.73a | 28±0.33d | 12.3±0.24c | 238±6.96b |
| DL | 2.60±0.01b | 8.70±0.08b | 10.9±0.70a | 34±0.58c | 13.5±0.15b | 235±5.49b |
| BL1 | 2.62±0.02b | 8.76±0.29b | 12.2±0.32a | 37±0.33b | 13.2±0.18b | 279±7.64a |
| BL2 | 2.49±0.01c | 8.69±0.22b | 12.1±0.61a | 42±0.33a | 14.4±0.13a | 294±4.84a |
表1 收获后不同处理根际土壤pH及养分含量
Table 1 pH and nutrient contents in rhizosphere soil of different treatments after harvest
| 处理 Treatments | w(全盐 Salt)/ (g·kg-1) | pH | w(有机质Organic Matter)/ (g·kg-1) | w(碱解氮Available-N)/ (mg·kg-1) | w(有效磷Available-P)/ (mg·kg-1) | w(速效钾Available-K)/ (mg·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 2.89±0.01a | 8.90±0.15a | 11.8±0.73a | 28±0.33d | 12.3±0.24c | 238±6.96b |
| DL | 2.60±0.01b | 8.70±0.08b | 10.9±0.70a | 34±0.58c | 13.5±0.15b | 235±5.49b |
| BL1 | 2.62±0.02b | 8.76±0.29b | 12.2±0.32a | 37±0.33b | 13.2±0.18b | 279±7.64a |
| BL2 | 2.49±0.01c | 8.69±0.22b | 12.1±0.61a | 42±0.33a | 14.4±0.13a | 294±4.84a |
| 样品名称 Sample name | 序列 Reads | OUT数目 OUT amount | 香农指数 Shannon index | 辛普森指数 Simpson index | ACE指数 ACE index | Chao 1指数 Chao 1 index | 覆盖率 Coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 22420 | 1963±2.86c | 6.39±0.01a | 0.0040±0.0004a | 1832±18a | 1847±24a | 0.9886±0.0002a |
| DL | 22420 | 2037±4.53b | 6.44±0.01a | 0.0031±0.0001a | 1848±14a | 1857±17a | 0.9881±0.0001a |
| BL1 | 22420 | 2067±1.55a | 6.42±0.02a | 0.0032±0.0000a | 1829±19a | 1847±7a | 0.9903±0.0006a |
| BL2 | 22420 | 2076±1.61a | 6.38±0.03a | 0.0037±0.0002a | 1799±21b | 1828±31b | 0.9880±0.0017a |
表2 土壤样品基因组DNA测序数据统计及Alpha多样性分析
Table 2 Genomic DNA sequence data statistics and alpha diversity analysis for soil samples
| 样品名称 Sample name | 序列 Reads | OUT数目 OUT amount | 香农指数 Shannon index | 辛普森指数 Simpson index | ACE指数 ACE index | Chao 1指数 Chao 1 index | 覆盖率 Coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 22420 | 1963±2.86c | 6.39±0.01a | 0.0040±0.0004a | 1832±18a | 1847±24a | 0.9886±0.0002a |
| DL | 22420 | 2037±4.53b | 6.44±0.01a | 0.0031±0.0001a | 1848±14a | 1857±17a | 0.9881±0.0001a |
| BL1 | 22420 | 2067±1.55a | 6.42±0.02a | 0.0032±0.0000a | 1829±19a | 1847±7a | 0.9903±0.0006a |
| BL2 | 22420 | 2076±1.61a | 6.38±0.03a | 0.0037±0.0002a | 1799±21b | 1828±31b | 0.9880±0.0017a |
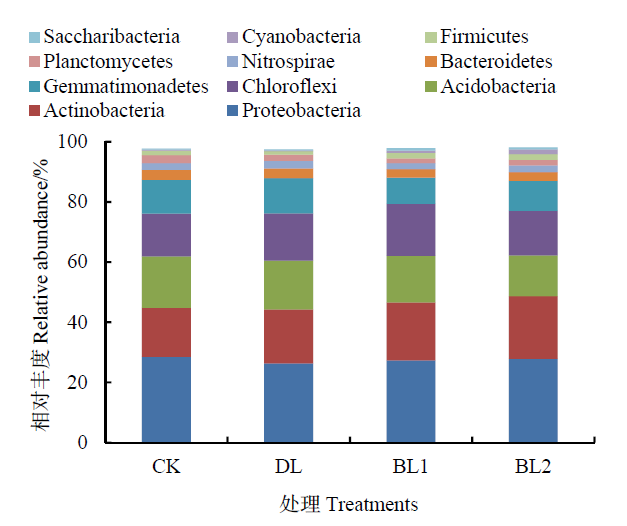
图1 门水平土壤细菌群落结构 Proteobacteria:变形菌门;Actinobacteria:放线菌门;Acidobacteria:酸杆菌门;Chloroflexi:绿弯菌门;Gemmatimonadetes:芽单胞菌门;Bacteroidetes:拟杆菌门;Nitrospirae:硝化螺旋菌门;Planctomycetes:浮霉菌门;Firmicutes:厚壁菌门;Cyanobacteria:蓝细菌门;Saccharibacteria:螺旋体菌门;Others:其他
Figure 1 Soil bacterial community at the phylum levels
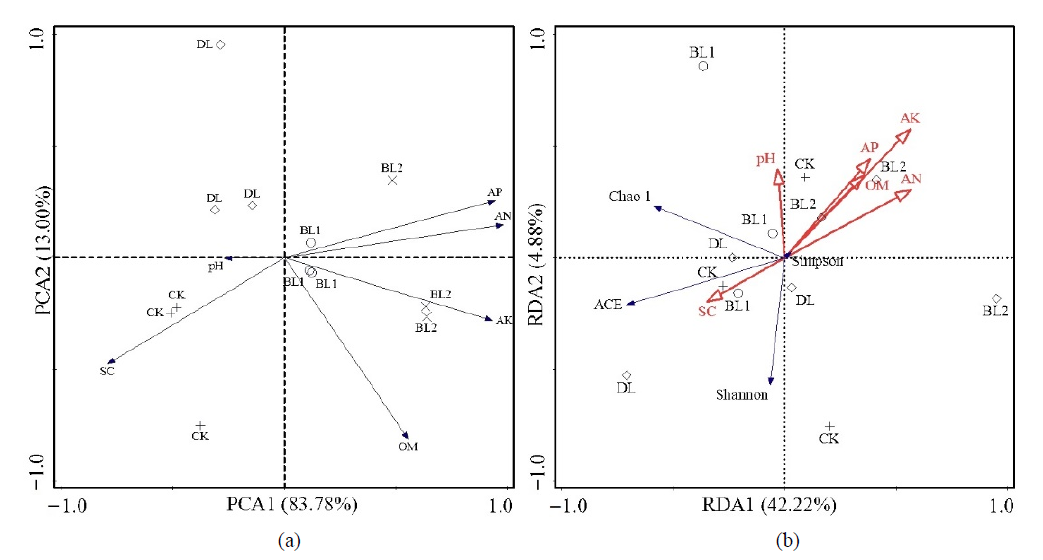
图2 土壤化学性质参数与细菌群落组成的主分量分析(a)及与细菌群落多样性的冗余分析(b) SC:盐分;OM:有机质;AN:碱解氮;AK:速效钾;CK:对照;DL:丹路菌剂;BL1:BZ1T/1-15一倍量;BL2:BZ1T/1-15二倍量;
Figure 2 Principal component analyses (PCA) of bacterial community composition in soils from different treatments (a), and redundancy analyses (RDA) of the correlations between soil parameters and bacterial community diversity (b) SC: Salt content; OM: Organic matter; AN: Soil inorganic nitrogen; AK: Available Potassium; CK: Control; DL: Danlumycin agent; BL1: BZ1T/1-15 double; BL2: BZ1T/1-15 double
| 微生物类群 | 盐分 Salt content | pH | 有机质 Organic Matter | 碱解氮 Available-N | 有效磷 Available-P | 速效钾 Available-K |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 变形菌门 Proteobacteria | 0.078 | 0.108 | -0.824** | -0.434 | -0.300 | -0.753** |
| 放线菌门 Actinobacteria | -0.283 | -0.581* | 0.058 | 0.595* | 0.192 | 0.002 |
| 酸杆菌门 Acidobacteria | 0.010 | 0.376 | 0.443 | -0.470 | 0.187 | 0.503* |
| 绿弯菌门 Chloroflexi | -0.068 | -0.299 | 0.689** | 0.151 | 0.270 | 0.569* |
| 芽单胞菌门 Gemmatimonadetes | -0.055 | 0.283 | 0.055 | -0.403 | -0.041 | 0.113 |
| 拟杆菌门 Bacteroidetes | 0.547* | 0.317 | -0.304 | -0.556* | -0.569* | -0.442 |
| 硝化螺旋菌门 NitrosPirae | -0.430 | -0.101 | -0.549* | -0.246 | 0.034 | -0.216 |
| 浮霉菌门 Planctomycetes | 0.159 | 0.618* | 0.245 | -0.494 | -0.003 | 0.291 |
| 厚壁菌门 Firmicutes | 0.263 | -0.037 | 0.081 | 0.401 | 0.012 | 0.024 |
| 蓝细菌门 Cyanobacteria | 0.288 | -0.158 | 0.040 | 0.504* | -0.151 | -0.048 |
| 螺旋体菌门 Saccharibacteria | -0.112 | -0.239 | 0.623* | 0.445 | 0.324 | 0.379 |
表3 细菌群落结构与土壤理化性质的相关性分析
Table 3 Correlation analysis among physico-chemistry characteristics and bacteria on phylum
| 微生物类群 | 盐分 Salt content | pH | 有机质 Organic Matter | 碱解氮 Available-N | 有效磷 Available-P | 速效钾 Available-K |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 变形菌门 Proteobacteria | 0.078 | 0.108 | -0.824** | -0.434 | -0.300 | -0.753** |
| 放线菌门 Actinobacteria | -0.283 | -0.581* | 0.058 | 0.595* | 0.192 | 0.002 |
| 酸杆菌门 Acidobacteria | 0.010 | 0.376 | 0.443 | -0.470 | 0.187 | 0.503* |
| 绿弯菌门 Chloroflexi | -0.068 | -0.299 | 0.689** | 0.151 | 0.270 | 0.569* |
| 芽单胞菌门 Gemmatimonadetes | -0.055 | 0.283 | 0.055 | -0.403 | -0.041 | 0.113 |
| 拟杆菌门 Bacteroidetes | 0.547* | 0.317 | -0.304 | -0.556* | -0.569* | -0.442 |
| 硝化螺旋菌门 NitrosPirae | -0.430 | -0.101 | -0.549* | -0.246 | 0.034 | -0.216 |
| 浮霉菌门 Planctomycetes | 0.159 | 0.618* | 0.245 | -0.494 | -0.003 | 0.291 |
| 厚壁菌门 Firmicutes | 0.263 | -0.037 | 0.081 | 0.401 | 0.012 | 0.024 |
| 蓝细菌门 Cyanobacteria | 0.288 | -0.158 | 0.040 | 0.504* | -0.151 | -0.048 |
| 螺旋体菌门 Saccharibacteria | -0.112 | -0.239 | 0.623* | 0.445 | 0.324 | 0.379 |
| 处理 Treatments | 花盘数 Number of faceplates/ (a·hm-2) | 植株干物质量 Plant dry mass/ (kg·hm-2) | 籽粒产量 Yield/ (kg·hm-2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 23813±364a | 538±46c | 1948±23b |
| DL | 18574±744b | 976±103c | 2129±9b |
| BL1 | 15716±1883bc | 1845±110b | 2560±45a |
| BL2 | 12859±1091c | 2460±40a | 2724±102a |
表4 不同处理对盐碱土壤向日葵生长效果的影响
Table 4 Effects on the growth of sunflower in saline-alkali soil under different treatments
| 处理 Treatments | 花盘数 Number of faceplates/ (a·hm-2) | 植株干物质量 Plant dry mass/ (kg·hm-2) | 籽粒产量 Yield/ (kg·hm-2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 23813±364a | 538±46c | 1948±23b |
| DL | 18574±744b | 976±103c | 2129±9b |
| BL1 | 15716±1883bc | 1845±110b | 2560±45a |
| BL2 | 12859±1091c | 2460±40a | 2724±102a |
| 项目 Project | 产量 Yield | 盐分 Salt content | pH | 有机质 Organic matter | 碱解氮Available-N | 速效钾 Available-K | 有效磷Available-P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 盐分 Salt content | -0.112 | 1 | |||||
| pH | -0.236 | 0.301 | 1 | ||||
| 有机质 Organic Matter | 0.623* | -0.080 | -0.145 | 1 | |||
| 碱解氮 Available-N | 0.906** | -0.816** | -0.281 | 0.482 | 1 | ||
| 速效钾 Available-K | 0.854** | -0.631* | -0.239 | 0.724** | 0.878** | 1 | |
| 有效磷 Available-P | 0.624* | -0.894** | -0.184 | 0.367 | 0.956** | 0.835** | 1 |
表5 土壤化学指标与产量的相关分析
Table 5 Correlation coefficients between yield and soil physical properties
| 项目 Project | 产量 Yield | 盐分 Salt content | pH | 有机质 Organic matter | 碱解氮Available-N | 速效钾 Available-K | 有效磷Available-P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 盐分 Salt content | -0.112 | 1 | |||||
| pH | -0.236 | 0.301 | 1 | ||||
| 有机质 Organic Matter | 0.623* | -0.080 | -0.145 | 1 | |||
| 碱解氮 Available-N | 0.906** | -0.816** | -0.281 | 0.482 | 1 | ||
| 速效钾 Available-K | 0.854** | -0.631* | -0.239 | 0.724** | 0.878** | 1 | |
| 有效磷 Available-P | 0.624* | -0.894** | -0.184 | 0.367 | 0.956** | 0.835** | 1 |
| [1] |
BARTER-LENNARD E G, 2002. Restoration of saline land though revegetation[J]. Agricultural Water Management, 53(1-3): 213-226.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
BOKULICH N A, SUBRAMANIAN S, FAITH J J, et al., 2012. Quality-filtering vastly improves diversity estimates from Illumina amplicon sequencing[J]. Nature Methods, 10(1): 57-59.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
GRIFFIYHS B S, PHILIPPOT L, 2013. Nsights into the resistance and resilience of the soil microbial community[J]. FEMS Microbiology Reviews, 37(2): 112-129.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
QADIR M, GHAFOOR A, MURTAZA G, et al., 2000. Amelioration strategies for saline soils: A review[J]. Land Degradation and Development, 11(6): 501-521.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
QUAST C, PRUESSE E, YILMAZ P, et al., 2013. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: improved data processing and web-based tools[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 41(D1): D590-D596.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
SAIT M, DAVIS K E R, JANSSEN P H, 2006. Effect of pH on isolation and distribution of members of subdivision 1 of the phylum Acidobacteria occurring insoil[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 72(3): 1852-1857.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
SCHLOSS P D, WESTCOTT S L, RYABIN T, et al., 2009. Introducing mothur: Open-source, platform-independent, community-supported software for describing and comparing microbial communities[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 75(23): 7537-7541.
DOI PMID |
| [8] |
STAFF P O, 2014. Correction: Salinity and bacterial diversity: To what extent does the concentration of salt affect the bacterial community in a saline soil[J]. Plos One, 9(9): e114658.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
ZHANG H Y, LU C, PANG H C, et al., 2020. Straw layer burial to alleviate salt stress in silty loam soils: Impacts of straw forms[J]. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 19(1): 265-276.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
ZHENG W, XIE D M, LI X Z, et al., 2017. The responses and adaptations of microbial communities to salinity in farmland soils: A molecular ecological network analysis[J]. Applied Soil Ecology, 120: 239-246.
DOI URL |
| [11] | 鲍士旦, 2005. 土壤农化分析[M]. 3版. 北京: 中国农业出版社. |
| BAO S D, 2005. Soil Agrochemical Analysis[M]. 3rd edition. Beijing: China Agriculture press. | |
| [12] | 邓松华, 梁富忠, 2018. 盐胁迫条件下微生物菌剂及助剂对土壤盐分及小白菜生长的影响[J]. 磷肥与复肥, 33(11): 37-38, 41. |
| DENG S H, LIANG F Z, 2018. Effects of microbial agents and additives on soil salinity and growth of Chinese cabbage under salt stress[J]. Phosphate and Compound Fertilizer, 33(11): 37-38, 41. | |
| [13] | 邓天天, 周士波, 胡烨, 等, 2019. 添加微生物菌剂对土壤中氮磷形态及含量的影响[J]. 江苏农业科学, 47(9): 276-280. |
| DENG T T, ZHOU S B, HU Y, et al., 2019. The effect of adding microbial agents on the form and content of nitrogen and phosphorus in soil[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 47(9): 276-280. | |
| [14] | 高圣超, 关大伟, 马鸣超, 等, 2017. 大豆连作条件下施肥对东北黑土细菌群落的影响[J]. 中国农业科学, 50(7): 1271-1281. |
| GAO S C, GUAN D W, MA M C, et al., 2017. The effect of fertilization on the bacterial community in black soil of northeast under the condition of soybean continuous cropping[J]. China Agricultural Sciences, 50(7): 1271-1281. | |
| [15] | 葛诚, 吴薇, 1994. 我国微生物肥料的生产、应用及问题[J]. 中国农学通报, 10(3): 24-28. |
| GE C, WU W, 1994. Production, application and problems of microbial fertilizers in my country[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 10(3): 24-28. | |
| [16] | 黄雅丽, 田琪, 秦光华, 等, 2018. 黄河三角洲刺槐白蜡混交对土壤细菌群落结构及多样性的影响[J]. 生态学报, 38(11): 3859-3867. |
| HUANG Y L, TIAN Q, QIN G H, et al., 2018. Effects of the mixture of Robinia pseudoacacia and white wax on soil bacterial community structure and diversity in the Yellow River Delta[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 38(11): 3859-3867. | |
| [17] | 李刚, 张乃明, 毛昆明, 等, 2004. 大棚土壤盐分累积特征与调控措施研究[J]. 农业工程学报, 20(3): 44-47. |
| LI G, ZHANG N M, MAO K M, et al., 2004. Characteristics of soil salt accumulation in plastic greenhouse and its control measures[J]. Transactions of the CSAE, 20(3): 44-47. | |
| [18] | 李新, 焦燕, 代钢, 等, 2016. 内蒙古河套灌区不同盐碱程度的土壤细菌群落多样性[J]. 中国环境科学, 36(01): 249-260. |
| LI X, JIAO Y, DAI G, et al., 2016. Diversity of soil bacterial communities with different salinity in Hetao Irrigation District, Inner Mongolia[J]. China Environmental Science, 36(1): 249-260. | |
| [19] | 李岩, 杨晓东, 秦璐, 等, 2018. 两种盐生植物根际土壤细菌多样性和群落结构[J]. 生态学报, 38(9): 3118-3131. |
| LI Y, YANG X D, QIN L, et al., 2018. Bacterial diversity and community structure in the rhizosphere soil of two halophytes[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 38(9): 3118-3131. | |
| [20] | 刘广明, 杨劲松, 吕真真, 等, 2011. 不同调控措施对轻中度盐碱土壤的改良增产效应[J]. 农业工程学报, 27(9): 164-169. |
| LIU G M, YANG J S, LÜ Z Z, et al., 2011. The improvement and yield increase effects of different control measures on mild to moderate saline-alkali soil[J]. Transactions of the CSAE, 27(9): 164-169. | |
| [21] | 刘健, 李俊, 葛诚, 2001. 微生物肥料作用机理的研究新进展[J]. 微生物学杂志, 21(1): 33-36, 46. |
| LIU J, LI J, GE C, 2001. New progress in the study of the mechanism of microbial fertilizers[J]. Journal of Microbiology, 21(1): 33-36, 46. | |
| [22] | 鲁奥, 2019. 盐碱地中纤维素降解菌的植物促生特性研究[D]. 长春: 东北师范大学. |
| LU A, 2019. Study on the plant growth promotion characteristics of cellulose degrading bacteria in saline alkali land[D]. Changchun: Northeast Normal University. | |
| [23] | 马慧媛, 黄媛媛, 刘胜尧, 等, 2020. 微生物菌剂施用对设施茄子根际土壤养分和细菌群落多样性的影响[J]. 微生物学通报, 47(1): 140-150. |
| MA H Y, HUANG Y Y, LIU S Y, et al., 2020. Effects of microbial inoculants on rhizosphere soil nutrients and bacterial community diversity in facility eggplant[J]. Bulletin of Microbiology, 47(1): 140-150. | |
| [24] | 逄焕成, 李玉义, 严慧峻, 等, 2009. 微生物菌剂对盐碱土理化和生物性状影响的研究[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 28(5): 951-955. |
| PANG H C, LI Y Y, YAN H J, et al., 2009. Study on the influence of microbial agents on the physical and chemical and biological properties of saline-alkali soil[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 28(5): 951-955. | |
| [25] | 逄焕成, 李玉义, 于天一, 等, 2011. 不同盐胁迫条件下微生物菌剂对土壤盐分及苜蓿生长的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 17(6): 1403-1408. |
| PANG H C, LI Y Y, YU T Y, et al., 2011. Effects of microbial agents on soil salinity and alfalfa growth under different salt stress conditions[J]. Journal of plant Nutrition and Fertilizer, 17(6): 1403-1408. | |
| [26] | 宋以玲, 于建, 陈士更, 等, 2019. 复合微生物菌剂对棉花生理特性及根际土壤微生物和化学性质的影响[J]. 土壤, 51(3): 477-487. |
| SONG Y L, YU J, CHEN S G, et al., 2019. Effects of compound microbial inoculants on cotton physiological characteristics and rhizosphere soil microbes and chemical properties[J]. Soil, 51(3): 477-487. | |
| [27] | 覃小红, 2013. 固氮巨大芽孢杆菌在桉树栽培上的应用初探[D]. 南宁: 广西大学. |
| QIN X H, 2013. A preliminary study on the application of Bacillus megaterium nitrogen-fixing in eucalyptus cultivation[D]. Nanning: Guangxi University. | |
| [28] | 王劲松, 戴茨华, 徐红, 等, 2012. 红壤连续施用绿肥和有机肥对玉米产量及土壤肥力的影响[J]. 中国土壤与肥料 (5): 27-30. |
| WANG J S, DAI C H, XU H, et al., 2012. Effects of continuous application of green manure and organic manure in red soil on corn yield and soil fertility[J]. China Soil and Fertilizer (5): 27-30. | |
| [29] | 王婧, 逄焕成, 李玉义, 等, 2012. 微生物菌肥对盐渍土壤微生物区系和食葵产量的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 31(11): 2186-2191. |
| WANG J, PANG H C, LI Y Y, et al., 2012. Effects of microbial fertilizer on saline soil microbial flora and sunflower yield[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 31(11): 2186-2191. | |
| [30] | 邢世和, 熊德中, 周碧青, 等, 2004. 不同土壤改良剂对土壤生化性质与烤烟产量的影响[J]. 土壤通报, 36(3): 72-75. |
| XING S H, XIONG D Z, ZHOU B Q, et al., 2004. Effects of different soil amendments on soil biochemical properties and flue-cured tobacco yield[J]. Soil Bulletin, 36(3): 72-75. | |
| [31] | 严慧峻, 逄焕成, 李玉义, 等, 2008. 微生物复混肥对盐碱土及白菜品质改良的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 24(12): 270-273. |
| YAN H J, PANG H C, LI Y Y, et al., 2008. Effects of microbial compound fertilizer on the quality improvement of saline-alkali soil and cabbage[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 24(12): 270-273. | |
| [32] | 易克, 张锦韬, 刘建峰, 等, 2019. 施用功能微生物菌剂对烤烟生长及烟叶产质量的影响[J]. 作物研究, 33(3): 215-219. |
| YI K, ZHANG J T, LIU J F, et al., 2019. Effects of application of functional microbial agents on flue-cured tobacco growth and tobacco leaf yield and quality[J]. Crop Research, 33(3): 215-219. | |
| [33] | 于占东, 宋述尧, 2003. 稻草配施生物菌剂对大棚连作土壤的改良作用[J]. 农业工程学报, 19(1): 177-179. |
| YU Z D, SONG S Y, 2003. The effect of rice straw combined with biological inoculants on soil improvement in greenhouse continuous cropping[J]. Transactions of the CSAE, 19(1): 177-179. | |
| [34] | 俞仁培, 陈德明, 1999. 我国盐渍土资源及其开发利用[J]. 土壤通报, 30(4): 158-159. |
| YU R P, CHEN D M, 1999. My country’s saline soil resources and their development and utilization[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 30(4): 158-159. | |
| [35] |
张慧敏, 郭慧娟, 侯振安, 2018. 不同盐碱胁迫对土壤细菌群落结构的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 55(6): 1074-1084.
DOI |
| ZHANG H M, GUO H J, HOU Z A, 2018. Effects of different salt-alkali stress on soil bacterial community structure[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 55(6): 1074-1084. | |
| [36] | 张金柱, 张兴, 郭春景, 等, 2007. 生物有机肥对轻度盐碱土理化性质影响的研究[J]. 生物技术, 17(6): 73-75. |
| ZHANG J Z, ZHANG X, GUO C J, et al., 2007. Research on the effect of bio-organic fertilizer on the physical and chemical properties of mild saline-alkaline soil[J]. Biotechnology, 17(6): 73-75. | |
| [37] | 赵柏霞, 潘凤荣, 王薇, 等, 2018. 生物菌剂对樱桃的促生效应及根际细菌群落的影响[J]. 沈阳农业大学学报, 49(3): 286-292. |
| ZHAO B X, PAN F R, WANG W, et al., 2018. The growth-promoting effect of cherries and the effect of rhizosphere bacterial community of biological inoculants[J]. Journal of Shenyang Agricultural University, 49(3): 286-292. |
| [1] | 董智今, 张呈春, 展秀丽, 张维福. 宁夏河东沙地生物土壤结皮及其下伏土壤养分的空间分布特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 910-919. |
| [2] | 潘昱伶, 璩向宁, 李琴, 王磊, 王筱平, 谭鹏, 崔庚, 安雨, 佟守正. 黄河宁夏段典型滩涂湿地土壤理化因子空间分布特征及其对微地形的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 668-677. |
| [3] | 赵维彬, 唐丽, 王松, 刘玲玲, 王树凤, 肖江, 陈光才. 两种生物炭对滨海盐碱土的改良效果[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 678-686. |
| [4] | 张贝儿, 吴建强, 王敏, 熊丽君, 谭娟, 沈城, 黄波涛, 黄沈发. 耕地生态保育工程的土壤健康度评价方法初探[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(2): 388-396. |
| [5] | 夏恩龙, 农珺清, 魏松坡, 刘希珍, 刘广路. 毛竹向阔叶林扩展过程中土壤养分变化特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(6): 1110-1117. |
| [6] | 朱奕豪, 李青梅, 刘晓丽, 李娜, 宋凤玲, 陈为峰. 不同土地整治类型新增耕地土壤微生物群落特征研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(5): 909-917. |
| [7] | 王英成, 姚世庭, 金鑫, 俞文政, 芦光新, 王军邦. 三江源区高寒退化草甸土壤细菌多样性的对比研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 695-703. |
| [8] | 刘红梅, 海香, 安克锐, 张海芳, 王慧, 张艳军, 王丽丽, 张贵龙, 杨殿林. 不同施肥措施对华北潮土区玉米田土壤固碳细菌群落结构多样性的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 715-722. |
| [9] | 邓晓, 武春媛, 杨桂生, 李怡, 李勤奋. 椰壳生物炭对海南滨海土壤的改良效果[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 723-731. |
| [10] | 杨贤房, 陈朝, 郑林, 万智巍, 陈永林, 王远东. 稀土矿区不同土地利用类型土壤细菌群落特征及网络分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 793-801. |
| [11] | 夏开, 邓鹏飞, 马锐豪, 王斐, 温正宇, 徐小牛. 马尾松次生林转换为湿地松和杉木林对土壤细菌群落结构和多样性的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(3): 460-469. |
| [12] | 宋秀丽, 黄瑞龙, 柯彩杰, 黄蔚, 章武, 陶波. 不同种植方式对连作土壤细菌群落结构和多样性的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(3): 487-496. |
| [13] | 杨虎, 王佩瑶, 李小伟, 王继飞, 杨君珑. 贺兰山东坡不同植被类型的土壤真菌多样性及其群落结构[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(2): 239-247. |
| [14] | 龙靖, 黄耀, 刘占锋, 简曙光, 魏丽萍, 王俊. 西沙热带珊瑚岛典型乔木叶片性状和养分再吸收特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(2): 248-256. |
| [15] | 余斐, 叶彩红, 许窕孜, 张中瑞, 朱航勇, 张耕, 华雷, 邓鉴锋, 丁晓纲. 韶关市花岗岩地区森林土壤重金属污染评价[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(2): 354-362. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
