生态环境学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (5): 909-917.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2022.05.006
朱奕豪1( ), 李青梅2, 刘晓丽3, 李娜2, 宋凤玲4, 陈为峰1,*(
), 李青梅2, 刘晓丽3, 李娜2, 宋凤玲4, 陈为峰1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2022-02-18
出版日期:2022-05-18
发布日期:2022-07-12
通讯作者:
* 陈为峰(1970年生),男,教授,博士研究生导师,主要研究方向为退化土壤生态治理和土地生态整治。E-mail: chwf@sdau.edu.cn作者简介:朱奕豪(1992年生),男,博士研究生,主要从事退化土壤生态治理研究。E-mail: yihao3344lin@163.com
基金资助:
ZHU Yihao1( ), LI Qingmei2, LIU Xiaoli3, LI Na2, SONG Fengling4, CHEN Weifeng1,*(
), LI Qingmei2, LIU Xiaoli3, LI Na2, SONG Fengling4, CHEN Weifeng1,*( )
)
Received:2022-02-18
Online:2022-05-18
Published:2022-07-12
摘要:
为了揭示不同土地整治类型新增耕地土壤微生物群落特征,以山东省泰安市34个土地整治项目(工矿复垦,GK;占补平衡,ZB)作为研究对象,就近选取非土地整治形成的农田作为对照,采用微生物平板计数法和高通量测序技术研究两类新增耕地与对照耕地的土壤微生物数量、多样性及群落组成等土壤微生物群落特征。结果表明,(1)与对照耕地相比,两类新增耕地土壤容重变大,有机质及氮磷钾含量降低,其中全氮和有效磷含量变化规律明显,均表现为GK<ZB<CK;两类新增耕地土壤容重最大值均出现在宁阳县,工矿复垦和占补平衡新增耕地分别比对照耕地变大了22.96%和25.19%。(2)两类新增耕地土壤细菌、放线菌数量低于对照耕地,真菌数量高于对照耕地;两类新增耕地土壤细菌数量最大值均出现在东平县,分别达到了11.89×105 cfu∙g-1和26.22×105 cfu∙g-1。(3)两类新增耕地土壤细菌Shannon指数、Ace指数和Chao1指数小于对照耕地;两类新增耕地及对照耕地的优势菌群均为放线菌门、厚壁菌门、变形菌门、绿弯菌门、酸杆菌门等;冗余分析(RDA)显示土壤有机质(SOM)是驱动土壤微生物群落变化的主要因子,该文选定的7个土壤理化性状累计解释量为82.40%,SOM单独解释量达52.00%,因此,土壤有机质成为了两类新增耕地重点调控的指标,有机质含量直接关系到新增耕地的土壤质量。该项结果将为土地整治新增耕地土壤改良指明方向。
中图分类号:
朱奕豪, 李青梅, 刘晓丽, 李娜, 宋凤玲, 陈为峰. 不同土地整治类型新增耕地土壤微生物群落特征研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(5): 909-917.
ZHU Yihao, LI Qingmei, LIU Xiaoli, LI Na, SONG Fengling, CHEN Weifeng. Characteristics of Soil Microbial Community in Newly Cultivated Land under Different Land Consolidation Types[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(5): 909-917.
| 县市区 Counties | pH | 容重 Bulk density/(g∙cm-3) | 土壤含水量 Soil moisture content/% | 有机质 w(soil organic matter)/(g∙kg-1) | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GK | ZB | CK | GK | ZB | CK | GK | ZB | CK | GK | ZB | CK | ||||||||||||||||
| 岱岳区 Daiyue district | 7.75± 0.14a | 7.85± 0.08a | 7.26± 0.62a | 1.77± 0.06a | 1.71± 0.12a | 1.48± 0.05b | 19.28± 1.57b | 21.43± 2.28b | 24.83± 0.56a | 5.72± 0.16b | 6.72± 0.65b | 10.05± 0.90a | |||||||||||||||
| 肥城市 Feicheng city | 7.97± 0.05a | 7.96± 0.18a | 7.53± 0.37a | 1.76± 0.08a | 1.63± 0.10ab | 1.50± 0.01b | 17.56± 1.50a | 19.70± 1.56a | 20.85± 1.77a | 5.86± 0.23c | 7.29± 0.39b | 11.07± 0.77a | |||||||||||||||
| 高新区 High-tech zone | 5.79± 0.58a | 5.71± 0.12a | 6.42± 0.07a | 1.74± 0.10a | 1.62± 0.15ab | 1.43± 0.01b | 15.98± 1.33b | 23.14± 4.07a | 24.09± 1.29a | 7.04± 0.38b | 6.87± 0.32b | 11.91± 0.30a | |||||||||||||||
| 新泰市 Xintai city | 7.92± 0.06a | 7.83± 0.13ab | 7.68± 0.08b | 1.60± 0.09ab | 1.69± 0.11a | 1.49± 0.04b | 15.85± 5.00a | 13.66± 1.49a | 18.07± 5.11a | 7.55± 0.37b | 5.80± 1.16c | 12.19± 0.47a | |||||||||||||||
| 宁阳县 Ningyang county | 7.64± 0.27a | 7.79± 0.02a | 7.61± 0.09a | 1.66± 0.15a | 1.69± 0.01a | 1.35± 0.10b | 18.11± 4.84a | 16.86± 4.47a | 22.30± 1.34a | 6.31± 0.34b | 6.01± 0.28b | 12.07± 1.04a | |||||||||||||||
| 东平县 Dongping county | 7.93± 0.17a | 7.58± 0.03b | 7.57± 0.06b | 1.54± 0.05b | 1.63± 0.03a | 1.40± 0.02c | 22.03± 4.04a | 21.07± 0.49a | 26.25± 3.31a | 6.83± 1.51b | 7.33± 0.02b | 13.34± 0.26a | |||||||||||||||
| 县市区 Counties | 全氮 w(total N)/(g∙kg-1) | 有效磷 w(available P)/(mg∙kg-1) | 速效钾 w(available K)/(mg∙kg-1) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| GK | ZB | CK | GK | ZB | CK | GK | ZB | CK | |||||||||||||||||||
| 岱岳区 Daiyue district | 0.75±0.04b | 0.79±0.03b | 0.92±0.01a | 12.36±2.88b | 18.54±4.05b | 34.94±1.37a | 134.67±2.52b | 130.33±10.50b | 171.17±11.37a | ||||||||||||||||||
| 肥城市 Feicheng city | 0.73±0.02c | 0.78±0.00b | 0.92±0.01a | 6.44±1.11c | 19.57±1.14b | 36.98±1.92a | 141.33±15.28a | 98.67±14.44b | 162.00±10.48a | ||||||||||||||||||
| 高新区 High-tech zone | 0.74±0.02c | 0.78±0.02b | 0.93±0.02a | 12.55±2.95b | 21.53±2.37b | 35.54±3.37a | 126.00±14.42b | 123.33±4.51b | 165.33±11.09a | ||||||||||||||||||
| 新泰市 Xintai city | 0.73±0.02c | 0.78±0.03b | 0.92±0.01a | 8.17±0.88c | 21.14±2.02b | 32.65±2.33a | 122.33±6.81c | 134.00±5.20b | 166.83±4.93a | ||||||||||||||||||
| 宁阳县 Ningyang county | 0.76±0.01b | 0.75±0.02b | 0.87±0.01a | 4.76±1.34c | 17.37±0.87b | 35.17±2.67a | 121.67±4.04b | 130.00±3.61b | 162.33±8.89a | ||||||||||||||||||
| 东平县 Dongping county | 0.74±0.02c | 0.78±0.01b | 0.89±0.02a | 5.97±1.33c | 16.79±0.04b | 36.50±1.36a | 124.67±8.50b | 126.00±4.00b | 164.00±4.77a | ||||||||||||||||||
表1 新增耕地和对照耕地土壤基本属性
Table 1 Soil basic properties of newly cultivated land and control farmland
| 县市区 Counties | pH | 容重 Bulk density/(g∙cm-3) | 土壤含水量 Soil moisture content/% | 有机质 w(soil organic matter)/(g∙kg-1) | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GK | ZB | CK | GK | ZB | CK | GK | ZB | CK | GK | ZB | CK | ||||||||||||||||
| 岱岳区 Daiyue district | 7.75± 0.14a | 7.85± 0.08a | 7.26± 0.62a | 1.77± 0.06a | 1.71± 0.12a | 1.48± 0.05b | 19.28± 1.57b | 21.43± 2.28b | 24.83± 0.56a | 5.72± 0.16b | 6.72± 0.65b | 10.05± 0.90a | |||||||||||||||
| 肥城市 Feicheng city | 7.97± 0.05a | 7.96± 0.18a | 7.53± 0.37a | 1.76± 0.08a | 1.63± 0.10ab | 1.50± 0.01b | 17.56± 1.50a | 19.70± 1.56a | 20.85± 1.77a | 5.86± 0.23c | 7.29± 0.39b | 11.07± 0.77a | |||||||||||||||
| 高新区 High-tech zone | 5.79± 0.58a | 5.71± 0.12a | 6.42± 0.07a | 1.74± 0.10a | 1.62± 0.15ab | 1.43± 0.01b | 15.98± 1.33b | 23.14± 4.07a | 24.09± 1.29a | 7.04± 0.38b | 6.87± 0.32b | 11.91± 0.30a | |||||||||||||||
| 新泰市 Xintai city | 7.92± 0.06a | 7.83± 0.13ab | 7.68± 0.08b | 1.60± 0.09ab | 1.69± 0.11a | 1.49± 0.04b | 15.85± 5.00a | 13.66± 1.49a | 18.07± 5.11a | 7.55± 0.37b | 5.80± 1.16c | 12.19± 0.47a | |||||||||||||||
| 宁阳县 Ningyang county | 7.64± 0.27a | 7.79± 0.02a | 7.61± 0.09a | 1.66± 0.15a | 1.69± 0.01a | 1.35± 0.10b | 18.11± 4.84a | 16.86± 4.47a | 22.30± 1.34a | 6.31± 0.34b | 6.01± 0.28b | 12.07± 1.04a | |||||||||||||||
| 东平县 Dongping county | 7.93± 0.17a | 7.58± 0.03b | 7.57± 0.06b | 1.54± 0.05b | 1.63± 0.03a | 1.40± 0.02c | 22.03± 4.04a | 21.07± 0.49a | 26.25± 3.31a | 6.83± 1.51b | 7.33± 0.02b | 13.34± 0.26a | |||||||||||||||
| 县市区 Counties | 全氮 w(total N)/(g∙kg-1) | 有效磷 w(available P)/(mg∙kg-1) | 速效钾 w(available K)/(mg∙kg-1) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| GK | ZB | CK | GK | ZB | CK | GK | ZB | CK | |||||||||||||||||||
| 岱岳区 Daiyue district | 0.75±0.04b | 0.79±0.03b | 0.92±0.01a | 12.36±2.88b | 18.54±4.05b | 34.94±1.37a | 134.67±2.52b | 130.33±10.50b | 171.17±11.37a | ||||||||||||||||||
| 肥城市 Feicheng city | 0.73±0.02c | 0.78±0.00b | 0.92±0.01a | 6.44±1.11c | 19.57±1.14b | 36.98±1.92a | 141.33±15.28a | 98.67±14.44b | 162.00±10.48a | ||||||||||||||||||
| 高新区 High-tech zone | 0.74±0.02c | 0.78±0.02b | 0.93±0.02a | 12.55±2.95b | 21.53±2.37b | 35.54±3.37a | 126.00±14.42b | 123.33±4.51b | 165.33±11.09a | ||||||||||||||||||
| 新泰市 Xintai city | 0.73±0.02c | 0.78±0.03b | 0.92±0.01a | 8.17±0.88c | 21.14±2.02b | 32.65±2.33a | 122.33±6.81c | 134.00±5.20b | 166.83±4.93a | ||||||||||||||||||
| 宁阳县 Ningyang county | 0.76±0.01b | 0.75±0.02b | 0.87±0.01a | 4.76±1.34c | 17.37±0.87b | 35.17±2.67a | 121.67±4.04b | 130.00±3.61b | 162.33±8.89a | ||||||||||||||||||
| 东平县 Dongping county | 0.74±0.02c | 0.78±0.01b | 0.89±0.02a | 5.97±1.33c | 16.79±0.04b | 36.50±1.36a | 124.67±8.50b | 126.00±4.00b | 164.00±4.77a | ||||||||||||||||||
| 县市区 Counties | 细菌 Bacteria/(105 cfu∙g-1) | 真菌 Fungi/(103 cfu∙g-1) | 放线菌 Actinomycetes/(104 cfu∙g-1) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GK | ZB | CK | GK | ZB | CK | GK | ZB | CK | |||
| 岱岳区 Daiyue district | 3.22±0.39b | 9.89±2.79ab | 14.61±4.47a | 15.12±6.32a | 15.89±1.92a | 10.39±2.70a | 10.11±3.47a | 9.78±2.91a | 15.56±4.79a | ||
| 肥城市 Feicheng city | 7.97±0.05a | 15.78±4.61a | 18.50±4.11a | 17.11±3.49a | 15.22±0.51a | 7.83±1.45b | 14.33±2.00ab | 9.11±2.47b | 17.78±3.64a | ||
| 高新区 High-tech zone | 8.00±1.86b | 19.33±2.00a | 22.72±4.19a | 18.00±4.55a | 12.89±2.33a | 8.72±1.36a | 4.22±0.51b | 10.78±2.15b | 20.33±3.54a | ||
| 新泰市 Xintai city | 7.33±1.93b | 16.67±4.10a | 23.28±5.91a | 12.56±2.52ab | 21.45±5.12a | 8.45±1.51b | 11.67±2.46b | 8.22±1.98b | 22.84±3.72a | ||
| 宁阳县 Ningyang county | 9.44±3.60a | 15.22±2.71a | 24.94±7.19a | 14.34±1.53ab | 17.78±5.10a | 9.56±1.11b | 12.89±3.96ab | 10.44±2.23b | 20.72±0.68a | ||
| 东平县 Dongping county | 11.89±1.95c | 26.22±0.51b | 28.67±0.33a | 24.00±5.10a | 19.78±0.51ab | 12.94±1.73b | 13.78±1.17b | 18.22±0.51b | 26.28±3.34a | ||
表2 新增耕地和对照耕地土壤微生物数量
Table 2 Number of soil microorganisms in newly cultivated land and control farmland
| 县市区 Counties | 细菌 Bacteria/(105 cfu∙g-1) | 真菌 Fungi/(103 cfu∙g-1) | 放线菌 Actinomycetes/(104 cfu∙g-1) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GK | ZB | CK | GK | ZB | CK | GK | ZB | CK | |||
| 岱岳区 Daiyue district | 3.22±0.39b | 9.89±2.79ab | 14.61±4.47a | 15.12±6.32a | 15.89±1.92a | 10.39±2.70a | 10.11±3.47a | 9.78±2.91a | 15.56±4.79a | ||
| 肥城市 Feicheng city | 7.97±0.05a | 15.78±4.61a | 18.50±4.11a | 17.11±3.49a | 15.22±0.51a | 7.83±1.45b | 14.33±2.00ab | 9.11±2.47b | 17.78±3.64a | ||
| 高新区 High-tech zone | 8.00±1.86b | 19.33±2.00a | 22.72±4.19a | 18.00±4.55a | 12.89±2.33a | 8.72±1.36a | 4.22±0.51b | 10.78±2.15b | 20.33±3.54a | ||
| 新泰市 Xintai city | 7.33±1.93b | 16.67±4.10a | 23.28±5.91a | 12.56±2.52ab | 21.45±5.12a | 8.45±1.51b | 11.67±2.46b | 8.22±1.98b | 22.84±3.72a | ||
| 宁阳县 Ningyang county | 9.44±3.60a | 15.22±2.71a | 24.94±7.19a | 14.34±1.53ab | 17.78±5.10a | 9.56±1.11b | 12.89±3.96ab | 10.44±2.23b | 20.72±0.68a | ||
| 东平县 Dongping county | 11.89±1.95c | 26.22±0.51b | 28.67±0.33a | 24.00±5.10a | 19.78±0.51ab | 12.94±1.73b | 13.78±1.17b | 18.22±0.51b | 26.28±3.34a | ||
| 微生物 Microorganism | pH | BD | SWC | SOM | TN | AP | AK |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 细菌 Bacteria | -0.123 | -0.738** | 0.513* | 0.723** | 0.665** | 0.740** | 0.480* |
| 真菌 Fungus | 0.204 | 0.597** | -0.386 | -0.735** | -0.762** | -0.701** | -0.642** |
| 放线菌 Actinomycetes | 0.152 | -0.809** | 0.602** | 0.848** | 0.737** | 0.648** | 0.739** |
表3 土壤理化性状与土壤细菌、真菌、放线菌相关性分析
Table 3 Correlation analysis between soil physio-chemical properties and soil bacteria, fungi and actinomycetes
| 微生物 Microorganism | pH | BD | SWC | SOM | TN | AP | AK |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 细菌 Bacteria | -0.123 | -0.738** | 0.513* | 0.723** | 0.665** | 0.740** | 0.480* |
| 真菌 Fungus | 0.204 | 0.597** | -0.386 | -0.735** | -0.762** | -0.701** | -0.642** |
| 放线菌 Actinomycetes | 0.152 | -0.809** | 0.602** | 0.848** | 0.737** | 0.648** | 0.739** |
| 项目区 Project area | 工矿复垦 Industrial and mining reclamation (XZ) | 占补平衡 Requisition-compensation balance (DW) | 对照耕地 Control farmland (CK) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 香农指数 Shannon index | 4.95±0.05b | 4.62±0.19c | 5.84±0.13a |
| 辛普森指数 Simpson index | 0.02±0.00ab | 0.03±0.01a | 0.01±0.00b |
| Ace指数 Ace index | 1180.33±24.57b | 990.39±10.41c | 2056.44±159.36a |
| Chao1指数 Chao1 index | 1200.24±34.60b | 980.35±29.92c | 2055.58±160.53a |
| 覆盖度 Coverage/% | 99.45±0.00a | 99.44±0.00a | 99.01±0.00b |
表4 新增耕地和对照耕地土壤细菌α多样性
Table 4 The α-diversity indexes of soil bacteria in new cultivated land and control farmland
| 项目区 Project area | 工矿复垦 Industrial and mining reclamation (XZ) | 占补平衡 Requisition-compensation balance (DW) | 对照耕地 Control farmland (CK) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 香农指数 Shannon index | 4.95±0.05b | 4.62±0.19c | 5.84±0.13a |
| 辛普森指数 Simpson index | 0.02±0.00ab | 0.03±0.01a | 0.01±0.00b |
| Ace指数 Ace index | 1180.33±24.57b | 990.39±10.41c | 2056.44±159.36a |
| Chao1指数 Chao1 index | 1200.24±34.60b | 980.35±29.92c | 2055.58±160.53a |
| 覆盖度 Coverage/% | 99.45±0.00a | 99.44±0.00a | 99.01±0.00b |
| 排序轴 Ordination axes | 特征值 Eigenvalues | 物种-环境相关系数 Species-environment correlation | 物种累积百分比变化率 Cumulative % variation of species | 物种-环境累积百分比变化率 Cumulative % variation of species-environment | 典范特征值总和 Sum of all canonical Eigenvalues |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 轴1 Axis1 | 0.585 | 0.997 | 58.5 | 71.0 | 0.824 |
| 轴2 Axis2 | 0.207 | 0.931 | 79.2 | 96.1 | |
| 轴3 Axis3 | 0.030 | 0.430 | 82.3 | 99.8 | |
| 轴4 Axis4 | 0.001 | 0.506 | 82.4 | 99.9 |
表5 冗余分析Monte Carlo置换检验结果
Table 5 Results of Monte Carlo permutation test
| 排序轴 Ordination axes | 特征值 Eigenvalues | 物种-环境相关系数 Species-environment correlation | 物种累积百分比变化率 Cumulative % variation of species | 物种-环境累积百分比变化率 Cumulative % variation of species-environment | 典范特征值总和 Sum of all canonical Eigenvalues |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 轴1 Axis1 | 0.585 | 0.997 | 58.5 | 71.0 | 0.824 |
| 轴2 Axis2 | 0.207 | 0.931 | 79.2 | 96.1 | |
| 轴3 Axis3 | 0.030 | 0.430 | 82.3 | 99.8 | |
| 轴4 Axis4 | 0.001 | 0.506 | 82.4 | 99.9 |
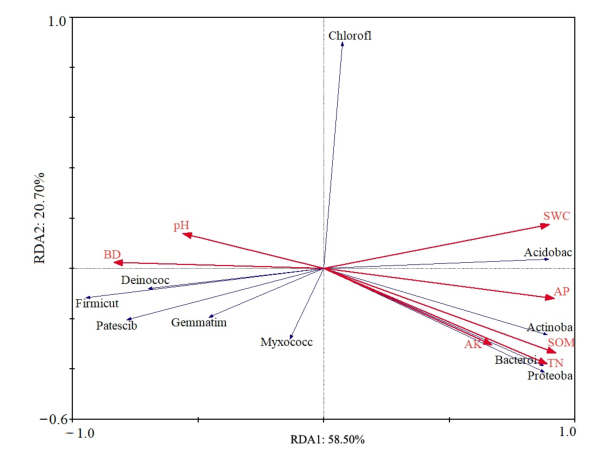
图4 土壤细菌群落与土壤理化性状冗余分析 pH、BD、SWC、SOM、TN、AP和AK分别代表两类新增耕地和对照耕地土壤的酸碱度、容重、土壤含水量、有机质、全氮、有效磷和速效钾,Acidobac、Actinoba、Bacteroi、Proteoba、Deinococ、Firmicut、Patescib、Gemmatim、Myxococc分别代表酸杆菌门、放线菌门、拟杆菌门、变形菌门、异常球菌-栖热菌门、厚壁菌门、髌骨细菌门、芽单胞菌门和粘球菌门
Figure 4 Redundancy analysis for bacterial community and soil physico-chemical pH, BD, SWC, SOM, TN, AP and AK represent the soil pH, bulk density, soil water content, soil organic matter, total nitrogen, available phosphorus and available potassium of the two types of new cultivated land and CK, respectively. Acidobac, Actinoba, Bacteroi, Proteoba, Deinococ, Firmicut, Patescib, Gemmatim, Myxococc represent Acidobacteria, Actinobacteria, Bacteroidea, Proteobacteria, Deinococcus-Thermus, Firmicutes, Patescibacteria, Gemmatimonadetes and Myxococcota, respectively
| 因子 Factors | 解释率 Explanation/% | F值 F value | P值 P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 有机质 SOM | 52.00 | 7.663 | 0.0080** |
| 土壤含水量 SWC | 15.00 | 2.579 | 0.1100 |
| 全氮 TN | 7.00 | 1.455 | 0.2680 |
| 酸碱度 pH | 3.00 | 0.559 | 0.5780 |
| 容重 BD | 2.00 | 0.222 | 0.7780 |
| 速效钾 AK | 2.00 | 0.171 | 0.7960 |
| 有效磷 AP | 1.40 | 0.108 | 0.8580 |
表6 新增耕地及对照耕地土壤细菌群落冗余分析
Table 6 Redundancy analysis of bacterial communities in newly cultivated land and control farmland
| 因子 Factors | 解释率 Explanation/% | F值 F value | P值 P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 有机质 SOM | 52.00 | 7.663 | 0.0080** |
| 土壤含水量 SWC | 15.00 | 2.579 | 0.1100 |
| 全氮 TN | 7.00 | 1.455 | 0.2680 |
| 酸碱度 pH | 3.00 | 0.559 | 0.5780 |
| 容重 BD | 2.00 | 0.222 | 0.7780 |
| 速效钾 AK | 2.00 | 0.171 | 0.7960 |
| 有效磷 AP | 1.40 | 0.108 | 0.8580 |
| [1] |
DJANIBEKOV U, FINGER R, 2018. Agricultural risks and farm land consolidation process in transition countries: The case of cotton production in Uzbekistan[J]. Agricultural Systems, 164: 223-235.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
ERTUNÇ E, ÇAY T, HAKLɪ H, 2018. Modeling of reallocation in land consolidation with a hybrid method[J]. Land Use Policy, 76: 754-761.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
LEGRAND F, PICOT A, COBO-DÍAZ J F, et al., 2018. Effect of tillage and static abiotic soil properties on microbial diversity[J]. Applied Soil Ecology, 132: 135-145.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
STAŃCZUK-GAłWIACZEK M, SOBOLEWSKA-MIKULSKA K, RITZEMA H, et al., 2018. Integration of water management and land consolidation in rural areas to adapt to climate change: Experiences from Poland and the Netherlands[J]. Land Use Policy, 77: 498-511.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
THAKUR M P, GEISEN S, 2019. Trophic regulations of the soil microbiome[J]. Trends in Microbiology, 27(9): 771-780.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
WANG H, WANG S L, ZHANG Y J, et al., 2018. Tillage system change affects soil organic carbon storage and benefits land restoration on loess soil in North China[J]. Land Degradation & Development, 29(9): 2880-2887.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
WANG X Y, LI Y, WEI Y, et al., 2020. Effects of fertilization and reclamation time on soil bacterial communities in coal mining subsidence areas[J]. Science of the Total Environment, DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.139882.
DOI |
| [8] | 鲍士旦, 2000. 土壤农化分析[M]. 第3版. 北京: 中国农业出版社. |
| BAO S D, 2000. Soil agrochemical analysis[M]. 3rd edition. Beijing: China Agricultural Press. | |
| [9] | 程分生, 尤龙辉, 余锦林, 等, 2021. 冷季型绿肥对锥栗园土壤生化性质及微生物群落的影响[J]. 草业学报, 30(11): 62-75. |
| CHENG F S, YOU L H, YU J L, et al., 2021. Effects of cold-season green manure on soil biochemical properties and the microbial community in a Castanea henryi orchard, China[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 30(11): 62-75. | |
| [10] | 陈坤秋, 龙花楼, 2020. 土地整治与乡村发展转型:互馈机理与区域调控[J]. 中国土地科学, 34(6): 1-9. |
| CHEN K Q, LONG H L, 2020. Land consolidation and rural development transformation: mutual feedback mechanism and regional regulation[J]. China Land Science, 34(6): 1-9. | |
| [11] | 丁嘉宁, 梁利宝, 冯鹏艳, 等, 2020. 施肥对采煤塌陷复垦土壤理化性状和细菌群落结构影响的研究[J]. 灌溉排水学报, 39(12): 64-70. |
| DING J N, LIANG L B, FENG P Y, et al., 2020. Effects of fertilization on physical and chemical properties and bacterial community of reclaimed soil from coal mining subsidence[J]. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage, 39(12): 64-70. | |
| [12] | 黄春萍, 吴福忠, 张健, 等, 2018. 高寒森林溪流微生物群落结构的季节性变化[J]. 生态学报, 38(1): 298-308. |
| HUANG C P, WU F Z, ZHANG J, et al., 2018. Seasonal variation of microbial community in forest streams of the high-frigid area[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 38(1): 298-308. | |
| [13] | 纪立东, 郭鑫年, 孙权, 等, 2020. 宁夏引黄灌区不同土地利用方式土壤微生物群落多样性研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 29(3): 516-524. |
| JI L D, GUO X N, SUN Q, WANG R, 2020. Soil microbial biomass and activity in different land use types in Ningxia Irrigation Area[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 29(3): 516-524. | |
| [14] | 李宏, 张青青, 江康威, 等, 2021. 山地草甸不同放牧强度对土壤细菌群落特征的影响[J]. 中国草地学报, 43(11): 37-44. |
| LI H, ZHANG Q Q, JIANG K W, et al., 2021. Effects of different grazing intensities on soil bacterial community characteristics in mountain meadow[J]. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 43(11): 37-44. | |
| [15] | 李肖肖, 骆占斌, 马静, 等, 2020. 黄土高原矿区土壤细菌群落对地表塌陷和土地复垦的响应[J]. 环境化学, 39(5): 1384-1394. |
| LI X X, LUO Z B, MA J, et al., 2020. Response of coal mining bacterial community to surface subsidence and land reclamation in the Loess Plateau[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 39(5): 1384-1394. | |
| [16] | 李肖肖, 朱凤武, 许桃元, 等, 2019. 苏南农田土壤性状和水稻长势对土地整治的短期响应[J]. 土壤学报, 56(3): 571-581. |
| LI X X, ZHU F W, XU T Y, et al., 2019. Short term response of soil properties and rice growth to land consolidation in south of Jiangsu province[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 56(3): 571-581. | |
| [17] | 李永涛, 王振猛, 李宗泰, 等, 2018. 黄河三角洲不同林龄柽柳人工林土壤养分及生物学特性研究[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 32(4): 89-94. |
| LI Y T, WANG Z M, LI Z T, et al., 2018. Soil nutrients and biological characteristics of Tamarix chinensis plantations with different ages in the Yellow River Delta[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 32(4): 89-94. | |
| [18] | 林耀奔, 叶艳妹, 吴次芳, 等, 2019. 基于微生物视角的耕地土壤质量综合评价——以A县土地整治区为例[J]. 中国土地科学, 33(6): 96-103. |
| LIN Y B, YE Y M, WU C F, et al., 2019. Comprehensive evaluation on cultivated land soil quality from the perspective of microorganism: a case study of A county[J]. China Land Science, 33(6): 96-103. | |
| [19] | 林耀奔, 叶艳妹, 杨建辉, 等, 2019. 土地整治对土壤微生物多样性的影响分析[J]. 环境科学学报, 39(8): 2644-2653. |
| LIN Y B, YE Y M, YANG J H, et al., 2019. The effect of land consolidation on soil microbial diversity[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 39(8): 2644-2653. | |
| [20] | 刘洋, 曾全超, 黄懿梅, 2016. 基于454高通量测序的黄土高原不同乔木林土壤细菌群落特征[J]. 中国环境科学, 36(11): 3487-3494. |
| LIU Y, ZENG Q C, HUANG Y M, 2016. Soil microbial communities by 454prosequencing under different arbor forests on the Loess Plateau[J]. China Environmental Science, 36(11): 3487-3494. | |
| [21] | 罗友进, 廖敦秀, 韩国辉, 等, 2020. 施用中药渣堆肥对土地整治区新改土土壤细菌多样性及群落结构的影响[J]. 南方农业学报, 51(10): 2394-2400. |
| LUO Y J, LIAO D X, HAN G H, et al., 2020. Effects of herb residue composton soil bacterial diversity and community structure of new reconstructed soil in restoration area[J]. Journal of Southern Agriculture, 51(10): 2394-2400. | |
| [22] | 马静, 卢永强, 张琦, 等, 2021. 黄土高原采煤沉陷对土壤微生物群落的影响[J]. 土壤学报, 58(5): 1278-1288. |
| MA J, LU Y Q, ZHANG Q, et al., 2021. Effects of coal mining subsidence on soil microbial community in the Loess Plateau[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 58(5): 1278-1288. | |
| [23] | 裴广廷, 孙建飞, 贺同鑫, 等, 2021. 长期人为干扰对桂西北喀斯特草地土壤微生物多样性及群落结构的影响[J]. 植物生态学报, 45(1): 74-84. |
|
PEI G T, SUN J F, HE T X, et al., 2021. Effects of long-term human disturbances on soil microbial diversity and community structure in a karst grassland ecosystem of northwestern Guangxi, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 45(1): 74-84.
DOI URL |
|
| [24] | 邵志敏, 2019. 海州露天矿生态恢复过程中土壤真菌群落演替规律研究[D]. 阜新: 辽宁工程技术大学. |
| SHAO Z M, 2019. Study on succession law of soil fungi community in the process of ecological restoration of Haizhou open-pit mine[D]. Fuxin: Liaoning Technical University. | |
| [25] | 沈晓琳, 王丽丽, 赵建宁, 等, 2021. 耕作方式对潮土土壤团聚体微生物群落结构的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 32(8): 2713-2721. |
| SHEN X L, WANG L L, ZHAO J N, et al., 2021. Effects of tillage managements on soil microbial community structure in soil aggregates of fluvo-aquic soil[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 32(8): 2713-2721. | |
| [26] | 施昊坤, 吴次芳, 张茂鑫, 等, 2020. 土地整治对工业区周边土壤微生物多样性和群落结构影响分析[J]. 环境科学学报, 40(1): 212-223. |
| SHI H K, WU C F, ZHANG M X, et al., 2020. Effects of land consolidation on soil microbial diversity and community structure around industrial zone[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 40(1): 212-223. | |
| [27] | 王军, 钟莉娜, 应凌霄, 2018. 土地整治对生态系统服务影响研究综述[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 34(9): 803-812. |
| WANG J, ZHONG L N, YING L X, 2018. Review on the study of the impacts of land consolidation on ecosystem services[J]. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 34(9): 803-812. | |
| [28] | 王蓥燕, 王子芳, 黄容, 等, 2019. 缙云山不同森林植被下土壤微生物群落结构特征研究[J]. 土壤学报, 56(5): 1210-1220. |
| WANG Y Y, WANG Z F, HUANG R, et al., 2019. Characterization of soil microbial community structure as affected by vegetation in Jinyun mountain[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 56(5): 1210-1220. | |
| [29] | 吴金水, 林启美, 黄巧云, 等, 2006. 土壤微生物生物量测定方法及其应用[M]. 北京: 气象出版社. |
| WU J S, LIN Q M, HUANG Q Y, et al., 2006. Method and application of soil microbial biomass determination[M]. Beijing: Meteorological Publishing House. | |
| [30] | 杨君珑, 刘小龙, 李帆, 等, 2018. 六盘山生态移民迁出区不同植被恢复模式土壤微生物功能多样性研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 27(12): 2193-2199. |
| YANG J L, LIU X L, LI F, et al., 2018. Effects of different vegetation restoration models on soil microbial functional diversity in eco- emigration area of Liupan mountains[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 27(12): 2193-2199. | |
| [31] | 原野, 高国卿, 高嫄, 等, 2021. 黄土区大型露天煤矿复垦24 a土壤碳氮组分特征[J]. 农业工程学报, 37(4): 167-174. |
| YUAN Y, GAO G Q, GAO Y, et al., 2021. Characteristics of soil organic carbon and nitrogen fractions after 24 years of reclamation in a large open pit coal mine in the Loess Plateau[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 37(4): 167-174. | |
| [32] | 张振佳, 曹银贵, 王舒菲, 等, 2021. 平朔黄土露天矿区复垦地表层土壤微生物与酶活性分析[J]. 生态学报, 41(1): 110-123. |
| ZHANG Z J, CAO Y G, WANG S F, et al., 2021. Characteristics and differences of surface soil microbial population and enzyme activities in opencast mining area of Pingshuo[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 41(1): 110-123. | |
| [33] | 赵瑞, 吴克宁, 陈甜倩, 2019. 面向土地整治的耕地质量评价优化[J]. 生态学杂志, 38(8): 2433-2441. |
| ZHAO R, WU K N, CHEN T Q, 2019. Optimization of cultivated land quality evaluation for land consolidation[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 38(8): 2433-2441. | |
| [34] | 郑兰香, 杨桂钦, 高礼, 等, 2021. 宁夏第三排水沟岸边带土壤微生物多样性及影响因素分析[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 35(9): 164-170. |
| ZHENG L X, YANG G Q, GAO L, et al., 2021. Analysis of soil microbial diversity and influencing factors in the riparian zone of The Third Drainage Ditch in Ningxia[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 35(9): 164-170. | |
| [35] | 郑文玲, 赵鸿彬, 韩冰, 等, 2021. 退化草原植物生长季土壤微生物群落结构与多样性变化[J]. 中国草地学报, 43(10): 46-54. |
| ZHENG W L, ZHAO H B, HAN B, et al., 2021. Changes of soil microbial community structure and diversity in plant growing season of degraded grassland[J]. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 43(10): 46-54. | |
| [36] | 周虹, 刘雲祥, 2022. 青海共和盆地人工固沙植被恢复对土壤微生物数量的影响[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 36(1): 178-185. |
| ZHOU H, LIU Y X, 2022. Effect of artificial vegetation restoration on soil microbial quantity in Gonghe Basin, Qinghai province[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 36(1): 178-185. |
| [1] | 王英成, 姚世庭, 金鑫, 俞文政, 芦光新, 王军邦. 三江源区高寒退化草甸土壤细菌多样性的对比研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 695-703. |
| [2] | 刘红梅, 海香, 安克锐, 张海芳, 王慧, 张艳军, 王丽丽, 张贵龙, 杨殿林. 不同施肥措施对华北潮土区玉米田土壤固碳细菌群落结构多样性的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 715-722. |
| [3] | 杨贤房, 陈朝, 郑林, 万智巍, 陈永林, 王远东. 稀土矿区不同土地利用类型土壤细菌群落特征及网络分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 793-801. |
| [4] | 夏开, 邓鹏飞, 马锐豪, 王斐, 温正宇, 徐小牛. 马尾松次生林转换为湿地松和杉木林对土壤细菌群落结构和多样性的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(3): 460-469. |
| [5] | 宋秀丽, 黄瑞龙, 柯彩杰, 黄蔚, 章武, 陶波. 不同种植方式对连作土壤细菌群落结构和多样性的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(3): 487-496. |
| [6] | 杨虎, 王佩瑶, 李小伟, 王继飞, 杨君珑. 贺兰山东坡不同植被类型的土壤真菌多样性及其群落结构[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(2): 239-247. |
| [7] | 张晓丽, 王国丽, 常芳弟, 张宏媛, 逄焕成, 张建丽, 王婧, 冀宏杰, 李玉义. 生物菌剂对根际盐碱土壤理化性质和微生物区系的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(10): 1984-1992. |
| [8] | 贾晨波, 郭洋, 马成莲, 苏建宇, 徐春燕. 宁杞1号枸杞健康株与根腐病患病株的土壤微生物群落和功能差异[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(9): 1831-1841. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
