生态环境学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (4): 668-677.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2023.04.004
潘昱伶1,2,3( ), 璩向宁1,2,3, 李琴1,2,3, 王磊1,2,3,*(
), 璩向宁1,2,3, 李琴1,2,3, 王磊1,2,3,*( ), 王筱平4, 谭鹏4, 崔庚5, 安雨5, 佟守正5
), 王筱平4, 谭鹏4, 崔庚5, 安雨5, 佟守正5
收稿日期:2022-12-22
出版日期:2023-04-18
发布日期:2023-07-12
通讯作者:
*王磊,教授,主要从事为植被与生态遥感研究。E-mail: WL8999@163.com作者简介:潘昱伶(1996年生),女,硕士研究生。研究方向为生态学。E-mail:13097549806@163.com
基金资助:
PAN Yuling1,2,3( ), QU Xiangning1,2,3, LI Qing1,2,3, WANG Lei1,2,3,*(
), QU Xiangning1,2,3, LI Qing1,2,3, WANG Lei1,2,3,*( ), WANG Xiaoping4, TAN Peng4, CUI Geng5, AN Yu5, TONG Shouzheng5
), WANG Xiaoping4, TAN Peng4, CUI Geng5, AN Yu5, TONG Shouzheng5
Received:2022-12-22
Online:2023-04-18
Published:2023-07-12
摘要:
明确土壤理化因子空间分布特征及其对微地形的响应,对于黄河滩涂湿地生态系统保护、修复与适应性管理具有重要意义。以黄河宁夏段典型滩涂湿地为研究对象,根据微地形空间特征采集土壤剖面样品,对pH、全氮、全磷、全钾、碱解氮、有效磷、速效钾和有机质等指标进行地统计学分析,探究黄河典型滩涂湿地土壤理化因子空间分布特征及其对微地形的响应。结果表明,(1)黄河滩涂湿地土壤理化因子空间分布不均且丰缺程度存在一定的差异性,碱解氮、有效磷与全氮空间分布相似,分布状况垂直于黄河河道方向,随着距离的增加逐渐由低到高过渡,且它们之间呈极显著相关性(P<0.01)。全钾含量较为丰富,1级至3级水平高达86.4%。(2)根据地统计学方法得出土壤理化因子除速效钾不存在空间自相关性外,其余因子C0/(C0+C)均小于25%,表现为强烈的空间自相关性,说明其变异性主要受自然因子(微地形、水文、植被)的影响,没有过多随机因素(耕作、施肥等人为因素),为原生态区域。(3)微地形是土壤理化因子含量及其分布特征的重要影响因素,随着海拔高度的增高,全氮、碱解氮、有机质和速效钾等养分含量下降,土壤含水率降低且土壤粘粒减少,坡面曲率与碱解氮呈显著负相关(P<0.05)。该研究揭示了微地形影响下的黄河滩涂湿地土壤养分分布的空间异质性特征,由于黄河冲刷和泥沙堆积作用,距河道近的地势较高,土壤养分较少。在河岸带滩涂湿地修复中,可构建不同微地形以达到小尺度滩涂湿地的保护、植被重建、生态修复和合理利用。
中图分类号:
潘昱伶, 璩向宁, 李琴, 王磊, 王筱平, 谭鹏, 崔庚, 安雨, 佟守正. 黄河宁夏段典型滩涂湿地土壤理化因子空间分布特征及其对微地形的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 668-677.
PAN Yuling, QU Xiangning, LI Qing, WANG Lei, WANG Xiaoping, TAN Peng, CUI Geng, AN Yu, TONG Shouzheng. Spatial Distribution Characteristics of Soil Physicochemical Factors and Their Response to Microtopography in a Typical Beach Wetland of the Yellow River in Ningxia[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(4): 668-677.
| 指标 | 最小值 | 最大值 | 平均值 | 标准差 | 变异系数/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 8.26 | 9.04 | 8.71 | 0.19 | 2.16 |
| w(全氮)/(g∙kg−1) | 0.20 | 0.99 | 0.48 | 0.21 | 44.3 |
| w(全磷)/(g∙kg−1) | 0.38 | 1.07 | 0.65 | 0.18 | 27.4 |
| w(全钾)/(g∙kg−1) | 14.5 | 25.0 | 17.9 | 2.57 | 14.3 |
| w(碱解氮)/(mg∙kg−1) | 9.48 | 57.9 | 21.4 | 10.1 | 47.4 |
| w(有效磷)/(mg∙kg−1) | 1.15 | 8.23 | 4.57 | 1.80 | 39.4 |
| w(速效钾)/(mg∙kg−1) | 47.9 | 137 | 79.0 | 23.4 | 29.6 |
| w(有机质)/(g∙kg−1) | 3.25 | 17.7 | 8.13 | 4.20 | 51.6 |
表1 土壤养分基本特征统计
Table 1 Statistical table of basic characteristics of soil nutrients
| 指标 | 最小值 | 最大值 | 平均值 | 标准差 | 变异系数/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 8.26 | 9.04 | 8.71 | 0.19 | 2.16 |
| w(全氮)/(g∙kg−1) | 0.20 | 0.99 | 0.48 | 0.21 | 44.3 |
| w(全磷)/(g∙kg−1) | 0.38 | 1.07 | 0.65 | 0.18 | 27.4 |
| w(全钾)/(g∙kg−1) | 14.5 | 25.0 | 17.9 | 2.57 | 14.3 |
| w(碱解氮)/(mg∙kg−1) | 9.48 | 57.9 | 21.4 | 10.1 | 47.4 |
| w(有效磷)/(mg∙kg−1) | 1.15 | 8.23 | 4.57 | 1.80 | 39.4 |
| w(速效钾)/(mg∙kg−1) | 47.9 | 137 | 79.0 | 23.4 | 29.6 |
| w(有机质)/(g∙kg−1) | 3.25 | 17.7 | 8.13 | 4.20 | 51.6 |
| 分级标准 | 含量与比例 | 土壤指标 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| w(全氮)/(g∙kg−1) | w(全磷)/(g∙kg−1) | w(全钾)/(g∙kg−1) | w(碱解氮)/(mg∙kg−1) | w(有效磷)/(mg∙kg−1) | w(速效钾)/(mg∙kg−1) | w(有机质)/(g∙kg−1) | ||
| 一级 | 含量 | >2 | >1 | >25 | >150 | >40 | >200 | >40 |
| 比例/% | 0 | 6.82 | 2.27 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 二级 | 含量 | 1.5‒2 | 0.8‒1 | 20‒25 | 120‒150 | 20‒40 | 150‒200 | 30‒40 |
| 比例/% | 0 | 15.9 | 22.7 | 0 | 0 | 2.27 | 0 | |
| 三级 | 含量 | 1‒1.5 | 0.6‒0.8 | 15‒20 | 90‒120 | 10‒20 | 100‒150 | 20‒30 |
| 比例/% | 2.27 | 27.3 | 61.4 | 0 | 0 | 20.5 | 0 | |
| 四级 | 含量 | 0.75‒1 | 0.4‒0.6 | 10‒20 | 60‒90 | 5‒10 | 50‒100 | 10‒20 |
| 比例/% | 11.4 | 40.9 | 13.6 | 2.27 | 43.2 | 68.2 | 29.6 | |
| 五级 | 含量 | 0.5‒0.75 | 0.2‒0.4 | 5‒10 | 30‒60 | 3‒5 | 30‒50 | 6‒10 |
| 比例/% | 20.5 | 9.09 | 0 | 11.4 | 31.8 | 9.09 | 22.7 | |
| 六级 | 含量 | <0.5 | <0.2 | <5 | <30 | <3 | <30 | <6 |
| 比例/% | 65.9 | 0 | 0 | 86.4 | 25.0 | 0 | 47.7 | |
表2 土壤养分含量分级与比例
Table 2 Soil nutrient content classification and proportion statistics
| 分级标准 | 含量与比例 | 土壤指标 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| w(全氮)/(g∙kg−1) | w(全磷)/(g∙kg−1) | w(全钾)/(g∙kg−1) | w(碱解氮)/(mg∙kg−1) | w(有效磷)/(mg∙kg−1) | w(速效钾)/(mg∙kg−1) | w(有机质)/(g∙kg−1) | ||
| 一级 | 含量 | >2 | >1 | >25 | >150 | >40 | >200 | >40 |
| 比例/% | 0 | 6.82 | 2.27 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 二级 | 含量 | 1.5‒2 | 0.8‒1 | 20‒25 | 120‒150 | 20‒40 | 150‒200 | 30‒40 |
| 比例/% | 0 | 15.9 | 22.7 | 0 | 0 | 2.27 | 0 | |
| 三级 | 含量 | 1‒1.5 | 0.6‒0.8 | 15‒20 | 90‒120 | 10‒20 | 100‒150 | 20‒30 |
| 比例/% | 2.27 | 27.3 | 61.4 | 0 | 0 | 20.5 | 0 | |
| 四级 | 含量 | 0.75‒1 | 0.4‒0.6 | 10‒20 | 60‒90 | 5‒10 | 50‒100 | 10‒20 |
| 比例/% | 11.4 | 40.9 | 13.6 | 2.27 | 43.2 | 68.2 | 29.6 | |
| 五级 | 含量 | 0.5‒0.75 | 0.2‒0.4 | 5‒10 | 30‒60 | 3‒5 | 30‒50 | 6‒10 |
| 比例/% | 20.5 | 9.09 | 0 | 11.4 | 31.8 | 9.09 | 22.7 | |
| 六级 | 含量 | <0.5 | <0.2 | <5 | <30 | <3 | <30 | <6 |
| 比例/% | 65.9 | 0 | 0 | 86.4 | 25.0 | 0 | 47.7 | |
| 相关系数 | pH | w(全氮)/(g∙kg−1) | w(全磷)/(g∙kg−1) | w(全钾)/(g∙kg−1) | w(碱解氮)/(mg∙kg−1) | w(有效磷)/(mg∙kg−1) | w(速效钾)/(mg∙kg−1) | w(有机质)/(g∙kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 1 | |||||||
| w(全氮)/(g∙kg−1) | −0.189 | 1 | ||||||
| w(全磷)/(g∙kg−1) | 0.104 | 0.199 | 1 | |||||
| w(全钾)/(g∙kg−1) | 0.469* | −0.370 | 0.522* | 1 | ||||
| w(碱解氮)/(mg∙kg−1) | −0.281 | 0.717** | 0.312 | −0.270 | 1 | |||
| w(有效磷)/(mg∙kg−1) | 0.173 | 0.639** | 0.533* | 0.148 | 0.532* | 1 | ||
| w(速效钾)/(mg∙kg−1) | −0.191 | 0.550** | 0.281 | −0.140 | 0.727** | 0.407 | 1 | |
| w(有机质)/(g∙kg−1) | −0.114 | 0.986** | 0.159 | −0.357 | 0.691** | 0.630** | 0.515* | 1 |
表3 土壤指标间相关性
Table 3 Correlation analysis of soil indicators
| 相关系数 | pH | w(全氮)/(g∙kg−1) | w(全磷)/(g∙kg−1) | w(全钾)/(g∙kg−1) | w(碱解氮)/(mg∙kg−1) | w(有效磷)/(mg∙kg−1) | w(速效钾)/(mg∙kg−1) | w(有机质)/(g∙kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 1 | |||||||
| w(全氮)/(g∙kg−1) | −0.189 | 1 | ||||||
| w(全磷)/(g∙kg−1) | 0.104 | 0.199 | 1 | |||||
| w(全钾)/(g∙kg−1) | 0.469* | −0.370 | 0.522* | 1 | ||||
| w(碱解氮)/(mg∙kg−1) | −0.281 | 0.717** | 0.312 | −0.270 | 1 | |||
| w(有效磷)/(mg∙kg−1) | 0.173 | 0.639** | 0.533* | 0.148 | 0.532* | 1 | ||
| w(速效钾)/(mg∙kg−1) | −0.191 | 0.550** | 0.281 | −0.140 | 0.727** | 0.407 | 1 | |
| w(有机质)/(g∙kg−1) | −0.114 | 0.986** | 0.159 | −0.357 | 0.691** | 0.630** | 0.515* | 1 |
| 养分指标 | 理论模型 | 块金值 C0 | 基台值 (C0+C) | (块金值/基台值)/% | 变程/m | 决定系数 (R2) | 残差 (RSS) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| w(全氮)/(g∙kg−1) | 高斯 | 2.23×10−3 | 4.84×10−2 | 4.60 | 45.4 | 0.546 | 1.11×10−3 |
| w(全磷)/(g∙kg−1) | 球形 | 5.84×10−4 | 3.83×10−2 | 1.52 | 56.2 | 0.597 | 3.32×10−4 |
| w(全钾)/(g∙kg−1) | 指数 | 0.360 | 8.59 | 4.19 | 78.0 | 0.656 | 7.07 |
| w(碱解氮)/(mg∙kg−1) | 球形 | 6.50 | 150.0 | 4.33 | 258.5 | 0.811 | 4.37×103 |
| w(有效磷)/(mg∙kg−1) | 高斯 | 0.150 | 4.45 | 3.37 | 47.3 | 0.672 | 3.06 |
| w(速效钾)/(mg∙kg−1) | 高斯 | 1.0 | 793.0 | 0.13 | 62.7 | 0.676 | 2.53×105 |
| w(有机质)/(g∙kg−1) | 高斯 | 1.19 | 17.7 | 6.73 | 50.2 | 0.691 | 116.0 |
表4 土壤养分指标半方差函数模型及参数
Table 4 Semivariogram theoretical models and parameters for soil nutrients
| 养分指标 | 理论模型 | 块金值 C0 | 基台值 (C0+C) | (块金值/基台值)/% | 变程/m | 决定系数 (R2) | 残差 (RSS) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| w(全氮)/(g∙kg−1) | 高斯 | 2.23×10−3 | 4.84×10−2 | 4.60 | 45.4 | 0.546 | 1.11×10−3 |
| w(全磷)/(g∙kg−1) | 球形 | 5.84×10−4 | 3.83×10−2 | 1.52 | 56.2 | 0.597 | 3.32×10−4 |
| w(全钾)/(g∙kg−1) | 指数 | 0.360 | 8.59 | 4.19 | 78.0 | 0.656 | 7.07 |
| w(碱解氮)/(mg∙kg−1) | 球形 | 6.50 | 150.0 | 4.33 | 258.5 | 0.811 | 4.37×103 |
| w(有效磷)/(mg∙kg−1) | 高斯 | 0.150 | 4.45 | 3.37 | 47.3 | 0.672 | 3.06 |
| w(速效钾)/(mg∙kg−1) | 高斯 | 1.0 | 793.0 | 0.13 | 62.7 | 0.676 | 2.53×105 |
| w(有机质)/(g∙kg−1) | 高斯 | 1.19 | 17.7 | 6.73 | 50.2 | 0.691 | 116.0 |
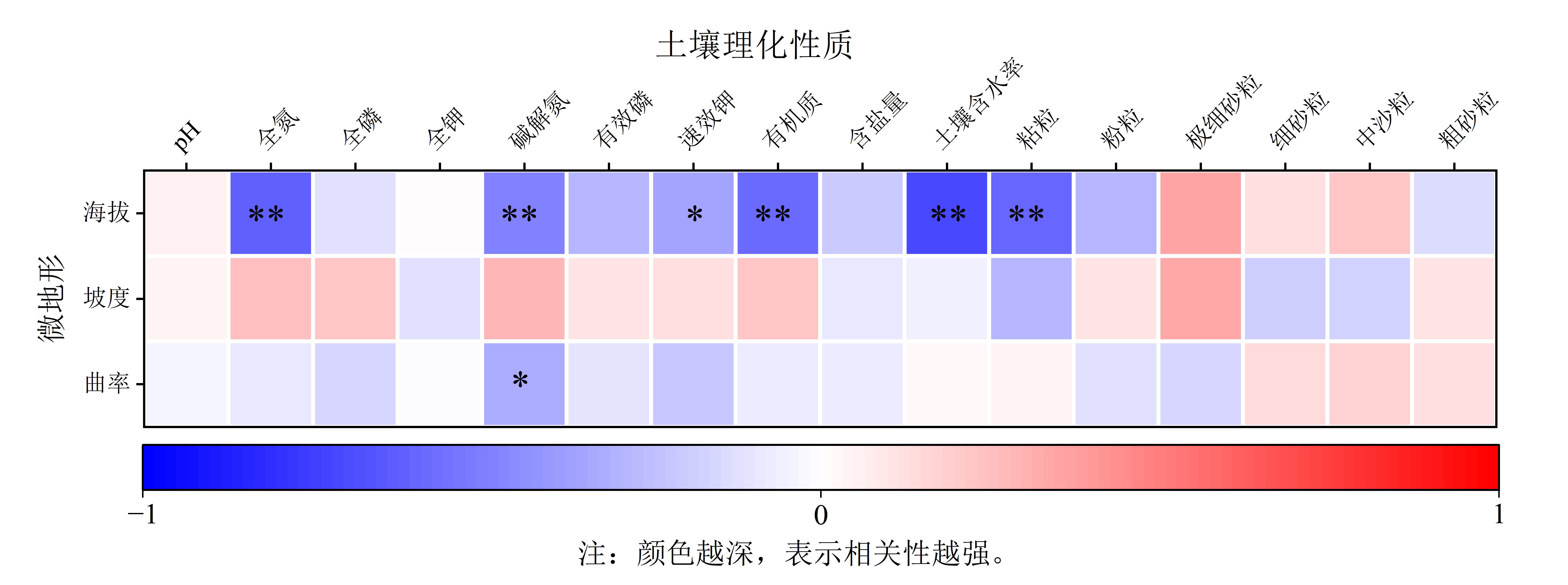
图3 土壤理化性质与微地形因子相关关系 颜色越深,表示相关性越强;**表示极显著相关(P<0.01);*表示显著相关(P<0.05)
Figure 3 Correlation of soil physicochemical properties with microtopographic factors
| 相关关系 | 盖度/% | 物种个体数 | 平均高度/m | 芦苇密度 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 海拔高度/m | 0.290 | 0.432** | −0.318* | 0.448** |
| 坡度/(°) | −0.043 | −0.240 | 0.437** | −0.146 |
| 坡面曲率 | 0.063 | 0.097 | −0.275 | 0.077 |
| pH | 0.317* | 0.145 | −0.038 | 0.205 |
| w(全氮)/(g∙kg−1) | −0.219 | −0.240 | 0.390** | −0.312* |
| w(全磷)/(g∙kg−1) | 0.044 | −0.141 | 0.136 | −0.191 |
| w(全钾)/(g∙kg−1) | 0.312* | 0.105 | −0.236 | 0.095 |
| w(碱解氮)/(mg∙kg−1) | −0.199 | −0.366* | 0.265 | −0.350* |
| w(有效磷)/(mg∙kg−1) | 0.006 | −0.249 | 0.262 | −0.246 |
| w(速效钾)/(mg∙kg−1) | 0.058 | −0.269 | 0.263 | −0.164 |
| w(有机质)/(g∙kg−1) | −0.256 | −0.241 | 0.381* | −0.311* |
| w(盐分)/% | −0.314* | −0.127 | −0.263 | −0.368* |
| w(土壤水分)/% | −0.216 | −0.395* | −0.074 | −0.456** |
表5 植被数量特征与土壤理化性质及微地形的相关关系
Table 5 The relationship between the quantitative characteristics of vegetation and soil physicochemical properties and microtopography is correlated
| 相关关系 | 盖度/% | 物种个体数 | 平均高度/m | 芦苇密度 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 海拔高度/m | 0.290 | 0.432** | −0.318* | 0.448** |
| 坡度/(°) | −0.043 | −0.240 | 0.437** | −0.146 |
| 坡面曲率 | 0.063 | 0.097 | −0.275 | 0.077 |
| pH | 0.317* | 0.145 | −0.038 | 0.205 |
| w(全氮)/(g∙kg−1) | −0.219 | −0.240 | 0.390** | −0.312* |
| w(全磷)/(g∙kg−1) | 0.044 | −0.141 | 0.136 | −0.191 |
| w(全钾)/(g∙kg−1) | 0.312* | 0.105 | −0.236 | 0.095 |
| w(碱解氮)/(mg∙kg−1) | −0.199 | −0.366* | 0.265 | −0.350* |
| w(有效磷)/(mg∙kg−1) | 0.006 | −0.249 | 0.262 | −0.246 |
| w(速效钾)/(mg∙kg−1) | 0.058 | −0.269 | 0.263 | −0.164 |
| w(有机质)/(g∙kg−1) | −0.256 | −0.241 | 0.381* | −0.311* |
| w(盐分)/% | −0.314* | −0.127 | −0.263 | −0.368* |
| w(土壤水分)/% | −0.216 | −0.395* | −0.074 | −0.456** |
| [1] |
ADHIKARI K, HARTEMINK A E, 2016. Linking soils to ecosystem services: A global review[J]. Geoderma, 262: 101-111.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
CHENG F Y, BASU N B, 2017. Biogeochemical hotspots: Role of small water bodies in landscape nutrient processing[J]. Water Resources Research, 53(6): 5038-5056.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
KEESSTRA S D, BOUMA J, WALLINGA J, et al., 2016. The significance of soils and soil science towards realization of the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals[J]. Soil, 2(2): 111-128.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
NILSSON C, SVEDMARK M, 2002. Basic principles and ecological consequences of changing water regimes: Riparian plant communities[J]. Environmental Management, 30(4): 468-480.
DOI PMID |
| [5] |
RICHARDSON S J, CLAYTON R, RANCE B D, et al., 2015. Small wetlands are critical for safeguarding rare and threatened plant species[J]. Applied Vegetation Science, 18(2): 230-241.
DOI URL |
| [6] | ROWELL D L, 2000. Agriculture, fertilizers and the environment[J]. European Journal of Soil Science, 51(3): 541-549. |
| [7] |
SUMFLETH K, DUTTMANN R, 2008. Prediction of soil property distribution in paddy soil landscapes using terrain data and satellite information as indicators[J]. Ecological Indicators, 8(5): 485-501.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
ZHANG Y G, JIANG Y, LIANG W J, et al., 2004. Vertical variation and storage of nitrogen in an aquic brown soil under different land uses[J]. Journal of Forestry Research, 15(3): 192-196.
DOI URL |
| [9] | 白军红, 余国营, 王国平, 2001. 地统计学在湿地土壤养分空间异质性研究中的应用[J]. 农业环境保护, 20(5): 311-314. |
| BAI J H, YU G Y, WANG G P, 2001. Application of geo-statistics in spatial heterogeneity of soil nutrients in wetlands[J]. Agro-environmental Protection, 20(5): 311-314. | |
| [10] |
陈桂香, 高灯州, 曾从盛, 等, 2017. 福州市农田土壤养分空间变异特征[J]. 地球信息科学学报, 19(2): 216-224.
DOI |
| CHEN G X, GAO D Z, ZENG C S, et al., 2017. Characteristics of the spatial variation of soil nutrients in farmland of Fuzhou City[J]. Journal of Geo-information Science, 19(2): 216-224. | |
| [11] | 陈正维, 朱波, 刘兴年, 2014. 不同坡度下紫色土坡耕地径流与氮素流失特征[J]. 中国农村水利水电, 384(10): 68-72. |
| CHEN Z W, ZHU B, LIU X N, 2014. Characteristics of runoff and nitrogen loss from slope cropland under different slope gradients in the hilly area of purple soil[J]. China Rural Water and Hydropower, 384(10): 68-72. | |
| [12] | 丁文雅, 2008. 庐山土壤有机质与全氮之间关系的研究[J]. 科技信息(科学教研), 257(9): 320-321. |
| DING W Y, 2008. Study on the relationship between soil organic matter and total nitrogen in Lushan Mountain[J]. Science & Technology Information, 257(9): 320-321. | |
| [13] |
杜康瑞, 段喜明, 赵晋忠, 等, 2019. 盐碱地改良剂与肥料混施对土壤pH值及玉米生长发育的影响[J]. 华北农学报, 34(3): 180-185.
DOI |
|
DU K R, DUAN X M, ZHAO J Z, et al., 2019. Effects of saline-alkali land improver and fertilizer on soil pH and Maize growth and development[J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica, 34(3): 180-185.
DOI |
|
| [14] | 段凯祥, 张松林, 赵连春, 等, 2019. 嘉峪关草湖区域土壤养分分布及与地形的关系[J]. 环境科学与技术, 42(7): 23-30. |
| DUAN K X, ZHANG S L, ZHAO L C, et al., 2019. Distribution characteristics of soil nutrients in grass lake area of Jiayuguan City and its relationship with topography[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 42(7): 23-30. | |
| [15] | 国家林业局, 1999. 森林土壤水溶性盐分分析: LY/T 1251—1999[S]. 北京:中国标准出版社:152-167. |
| NATIONAL FORESTRY ADMINISTRATION, 1999. Analysis methods of water soluble saltas of forest soil: LY/T 1251—1999[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China: 152-167. | |
| [16] | 缑倩倩, 屈建军, 王国华, 等, 2015. 中国干旱半干旱地区湿地研究进展[J]. 干旱区研究, 32(2): 213-220. |
| GOU Q Q, QU J J, WANG G H, et al., 2015. Progress of wetland researches in arid and semi-arid regions in China[J]. Arid Zone Research, 32(2): 213-220. | |
| [17] |
纪昌品, 王华, 2018. 鄱阳湖湿地植物群落分布特征及其对土壤环境因子的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 27(8): 1424-1431.
DOI URL |
| JI C P, WANG H, 2018. Response of vegetation distribution to soil environmental factors in wetlands of Poyang Lake[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 27(8): 1424-1431. | |
| [18] | 姜勇, 郝伟, 张玉革, 等, 2006. 潮棕壤不同利用方式营养元素随剖面深度的变化特征[J]. 水土保持学报, 20(3): 93-96, 122. |
| JIANG Y, HAO W, ZHANG Y G, et al., 2006. Changes in soil nutrients with profile depth in aquic brown soil under different land use[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 20(3): 93-96, 122. | |
| [19] | 寇欣, 刘华民, 王奇, 等, 2018. 锡林河中游放牧的和被围封的湿草甸土壤理化性质研究[J]. 湿地科学, 16(5): 626-634. |
| KOU X, LIU H M, WANG Q, et al., 2018. Physical and chemical properties of soils in grazing and enclosed wet meadows in the middle reaches of Xilin River[J]. Wetland Science, 16(5): 626-634. | |
| [20] | 雷志栋, 杨诗秀, 许志荣, 等, 1985. 土壤特性空间变异性初步研究[J]. 水利学报 (9): 10-21. |
| LEI Z D, YANG S X, XU Z R, et al., 1985. Preliminary investigation of the spatial variability of soil properties[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering (9): 10-21. | |
| [21] | 李伟, 崔丽娟, 赵欣胜, 等, 2014. 中国滨海湿地及其生态系统服务功能研究概述[J]. 林业调查规划, 39(4): 24-30. |
| LI W, CUI L J, ZHAO X S, et al., 2014. An overview of Chinese coastal wetland and their ecosystem services[J]. Forest Inventory and Planning, 39(4): 24-30. | |
| [22] |
李永福, 耿庆龙, 陈署晃, 等, 2021. 天山南坡农区土壤养分空间分布特征[J]. 新疆农业科学, 58(2): 324-331.
DOI |
|
LI Y F, GENG Q L, CHEN S H, et al., 2021. Spatial distribution characteristics of soil nutrients in agricultural areas on the southern slope of Tianshan Mountain[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 58(2): 324-331.
DOI |
|
| [23] | 刘万德, 苏建荣, 李帅锋, 等, 2010. 云南普洱季风常绿阔叶林演替系列植物和土壤C、N、P化学计量特征[J]. 生态学报, 30(23): 6581-6590. |
| LIU W D, SU J R, LI S F, et al., 2010. Stoichiometry study of C, N and P in plant and soil at different successional stages of monsoon evergreen broad-leaved forest in Pu'er, Yunnan Province[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 30(23): 6581-6590. | |
| [24] | 刘兴诏, 周国逸, 张德强, 等, 2010. 南亚热带森林不同演替阶段植物与土壤中N、P的化学计量特征[J]. 植物生态学报, 34(1): 64-71. |
| LIU X Z, ZHOU G Y, ZHANG D Q, et al., 2010. N and P stoichiometry of plant and soil in lower subtropical forest successional series in southern China[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 34(1): 64-71. | |
| [25] | 马耀辉, 赵永红, 张汝文, 2022. 滨州市农用地表层土壤养分的时空分布规律初探[J]. 中国农技推广, 38(7): 73-77. |
| MA Y H, ZHAO Y H, ZHANG R W, 2022. A preliminary study on the spatial and temporal distribution of soil nutrients in the surface layer of agricultural land in Binzhou City[J]. China Agricultural Technology Extension, 38(7): 73-77. | |
| [26] | 潘瑜春, 刘巧芹, 阎波杰, 等, 2010. 采样尺度对土壤养分空间变异分析的影响[J]. 土壤通报, 41(2): 257-262. |
| PAN Y C, LIU Q Q, YAN B J, et al., 2010. Effects of sampling scale on soil nutrition spatial variability analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 41(2): 257-262. | |
| [27] | 庞夙, 李廷轩, 王永东, 等, 2009. 土壤速效氮、磷、钾含量空间变异特征及其影响因子[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 15(1): 114-120. |
| PANG S, LI T X, WANG Y D, et al., 2009. Spatial variability of soil available N, P and K and influencing factors[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 15(1): 114-120. | |
| [28] | 四川省质量技术监督局, 2014. 土壤碱解氮的测定: DB51/T 1975—2014[S]. 成都: 四川省质量技术监督局: 1-3. |
| QUALITY AND TECHNICAL SUPERVISION BUREAU OF SICHUAN PROVINCE, 2014. Determination of alkali-hydrolyzed nitrogen in soil: DB51/T 1975—2014[S]. Chengdu: Quality and Technical Supervision Bureau of Sichuan Province: 1-3. | |
| [29] | 斯南雍茜, 葛继稳, 李愈, 等, 2020. 神农架大九湖亚高山典型泥炭湿地土壤养分特征分析[J]. 水土保持学报, 34(5): 321-326. |
| SINAN Y X, GE J W, LI Y, et al., 2020. Soil nutrient characteristics of typical sub-alpine peat wetland in Dajiuhu of Shennongjia[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 34(5): 321-326. | |
| [30] | 王峰, 陈玉真, 尤志明, 等, 2014. 不同类型茶园土壤团聚体组成特征及稳定性研究[J]. 茶叶科学, 34(2): 129-136. |
| WANG F, CHEN Y Z, YOU Z M, et al., 2014. Composition and stability of soil aggregates among different soil types of tea garden[J]. Journal of Tea Science, 34(2): 129-136. | |
| [31] | 王涛, 司万童, 闫瑞强, 等, 2020. 花棒 (Hedysarum scoparium) 对雅鲁藏布江中游山坡流动沙地土壤理化性质的影响[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 36(12): 1619-1625. |
| WANG T, SI W T, YAN R Q, et al., 2020. The effects of Hedysarum scoparium Restoration on physical and chemical properties of soil in hillside shifting sandy land in middle reaches of Yarlung Zangbo River, China[J]. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 36(12): 1619-1625. | |
| [32] | 王雪梅, 柴仲平, 武红旗, 2016. 典型干旱荒漠绿洲区耕层土壤养分空间变异[J]. 水土保持通报, 36(1): 51-56. |
| WANG X M, CHAI Z P, WU H Q, 2016. Spatial variation of soil nutrients in arable layer in typical arid desert oasis area[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 36(1): 51-56. | |
| [33] | 席丽, 李思瑶, 夏晓莹, 等, 2022. 天山云杉林土壤养分空间异质性及环境解释[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 42(10): 93-101, 167. |
| XI L, LI S Y, XIA X Y, et al., 2022. Spatial heterogeneity of soil nutrients and environmental interpretation in Picea schrenkiana var. tianschanica forest[J]. Journal of Central South University of Forestry & Technology, 42(10): 93-101, 167. | |
| [34] | 谢林峰, 凌晓晓, 黄圣妍, 等, 2022. 临安区山核桃林地土壤水解酶活性空间分布特征及土壤肥力评价[J]. 浙江农林大学学报, 39(3): 625-634. |
| XIE L F, LING X X, HUANG S Y, et al., 2022. Spatial distribution characteristics of soil hydrolase activities and soil fertility evaluation of Carya cathayensis forests in Lin’an District[J]. Journal of Zhejiang A & F University, 39(3): 625-634. | |
| [35] | 谢旭, 李晓文, 白军红, 等, 2021. 黄河三角洲湿地中4种典型植物地上生物量随地表高程的变化规律[J]. 湿地科学, 19(2): 226-231. |
| XIE X, LI X W, BAI J H, et al., 2021. Variations of aboveground biomass of 4 kinds of typical plants with surface elevation of wetlands in the Yellow River Delta[J]. Wetland Science, 19(2): 226-231. | |
| [36] | 杨皓, 胡继伟, 黄先飞, 等, 2015. 喀斯特地区金刺梨种植基地土壤肥力研究[J]. 水土保持研究, 22(3): 50-55. |
| YANG H, HU J W, HUANG X F, et al., 2015. Study on soil fertility of Rosa sterilis S. D. Shi planting bases located in karst areas[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 22(3): 50-55. | |
| [37] |
杨之江, 陈效民, 景峰, 等, 2018. 基于GIS和地统计学的稻田土壤养分与重金属空间变异[J]. 应用生态学报, 29(6): 1893-1901.
DOI |
| YANG Z J, CHEN X M, JING F, et al., 2018. Spatial variability of nutrients and heavy metals in paddy field soils based on GIS and Geostatistics[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 29(6): 1893-1901. | |
| [38] | 杨再梅, 谭伟, 戚玉娇, 等, 2021. 茂兰喀斯特常绿落叶阔叶林土壤养分空间分布特征[J]. 福建农林大学学报(自然科学版), 50(3): 404-412. |
| YANG Z M, TAN W, QI Y J, et al., 2021. Spatial distribution characteristics of soil nutrients in Maolan karst evergreen and deciduous broad-leaved forest[J]. Journal of Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University (Natural Science Edition), 50(3): 404-412. | |
| [39] | 姚瑶, 罗朋, 李京玲, 等, 2023. 运城市夹马口引黄灌区土壤养分空间变异特征[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 37(2): 134-141. |
| YAO Y, LUO P, LI J L, et al., 2023. Spatial variation of soil nutrients in the Jiamakou Yellow River irrigation area, Yuncheng City[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 37(2): 134-141. | |
| [40] | 张博岩, 窦森, 张笑唯, 2022. 不同种植年限榛地土壤基本理化性质及腐殖物质组成[J]. 吉林农业大学学报, 44(3): 345-351. |
| ZHANG B Y, DOU S, ZHANG X W, 2022. Basic physicochemical properties and humus composition of soil in hazelnut fields with different planting years[J]. Journal of Jilin Agricultural University, 44(3): 345-351. | |
| [41] | 张晨洋, 付双嘉, 高浩英, 等, 2023. 外生菌根真菌多样性对云杉根际土壤生化性质的影响[J]. 四川农业大学学报, 41(2): 230-239, 351. |
| ZHANG C Y, FU S J, GAO H Y, et al., 2023. Effects of ectomycorrhizal fungal diversity on biochemical properties of spruce rhizosphere soil[J]. Journal of Sichuan Agricultural University, 41(2): 230-239, 351. | |
| [42] | 张婧, 毕如田, 丁皓希, 等, 2021. 基于地形分类的黄土丘陵区土壤有机质插值方法[J]. 江苏农业科学, 49(8): 182-189. |
| ZHANG J, BI R T, DING H X, et al., 2021. Study on interpolation method of soil organic matter in loess hilly area based on terrain classification[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 49(8): 182-189. | |
| [43] | 张昆, 田昆, 吕宪国, 等, 2009. 纳帕海湖滨草甸湿地土壤氮动态对水文周期变化的响应[J]. 环境科学, 30(8): 2216-2220. |
| ZHANG K, TIAN K, LÜ X G, et al., 2009. Response of meadow soil nitrogen to hydro-periods in Napahai Plateau Wetland[J]. Environmental Science, 30(8): 2216-2220. | |
| [44] | 张淑娟, 王道杰, 梅永丽, 等, 2015. 泥石流多发区小流域土地利用方式对土壤性质的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 29(1): 257-262. |
| ZHANG S J, WANG D J, MEI Y L, et al., 2015. Effects of land use types on soil properties in a small watershed of debris flow activity region[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 29(1): 257-262. | |
| [45] | 张涛, 李素艳, 翟鹏辉, 等, 2015. 湿地土壤不同水埋深度的剖面特征——以东洞庭湖为例[J]. 中国水土保持科学, 13(4): 25-31. |
| ZHANG T, LI S Y, ZHAI P H, et al., 2015. Soil profile characteristics in wetland at different submerging depths: A case study of the East Dongting Lake[J]. Science of Soil and Water Conservation, 13(4): 25-31. | |
| [46] | 张雪, 孔范龙, 姜志翔, 2022. 基于生态功能的滨海湿地土壤质量综合评价方法构建及实证分析[J]. 环境科学, 43(5): 2709-2718. |
| ZHANG X, KONG F L, JIANG Z X, 2022. Construction and empirical analysis of a comprehensive evaluation method of coastal wetland soil quality based on ecological functions[J]. Environmental Science, 43(5): 2709-2718. | |
| [47] | 赵晖, 陈佳秋, 陈鑫, 等, 2018. 小微湿地的保护与管理[J]. 湿地科学与管理, 14(4): 22-26. |
| ZHAO H, CHEN J Q, CHEN X, et al., 2018. Conservation and management of small and micro wetlands[J]. Wetland Science & Management, 14(4): 22-26. | |
| [48] | 赵军, 张久明, 孟凯, 等, 2004. 地统计学及GIS在黑土区域土壤养分空间异质性分析中的应用——以海伦市为例[J]. 水土保持通报, 24(6): 53-57. |
| ZHAO J, ZHANG J M, MENG K, et al., 2004. Spatial heterogeneity of soil nutrients in blacksoil, China: A case study at Hailun County[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 24(6): 53-57. | |
| [49] | 赵茜宇, 于会彬, 杨芳, 等, 2023. 半干旱区湖泊湿地土壤养分与盐碱化特征研究——以岱海为例[J]. 环境工程技术学报, 13(1): 188-196. |
| ZHAO Q Y, YU H B, YANG F, et al., 2023. Study on the characteristics of soil nutrients and salinization of lake wetlands in semi-arid region: Taking Daihai Lake as an example[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology, 13(1): 188-196. | |
| [50] | 赵望龙, 郭中领, 王仁德, 等, 2016. 安固里淖干湖区土壤理化因子空间分布特征[J]. 湿地科学, 14(4): 553-560. |
| ZHAO W L, GUO Z L, WANG R D, et al., 2016. Spatial distribution of soil physical and chemical factors in the Angulinao Playa[J]. Wetland Science, 14(4): 553-560. | |
| [51] | 仲波, 孙庚, 程魏, 等, 2016. 汶川地震对森林土壤养分动态的影响[J]. 应用与环境生物学报, 22(5): 773-779. |
| ZHONG B, SUN G, CHENG W, et al., 2016. Effects of Wenchuan Earthquake on soil nutrient dynamics in forest[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology, 22(5): 773-779. | |
| [52] | 中华人民共和国农业部, 1988. 土壤全钾测定法: GB/T 9836—1988[S]. 北京:中国标准出版社: 266-270. |
| Ministry of Agriculture of the People's Republic of China, 1988. Method for determination of total potassium in soils: GB/T 9836—1988[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China: 266-270. | |
| [53] | 中华人民共和国农业部, 1988. 土壤全磷测定法: GB/T 9837—1988[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社: 150-152. |
| Ministry of Agriculture of the PEople's Republic of China, 1988. Method for detemination of soil total phosphorus: GB/T 9837—1988[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China: 150-152. | |
| [54] | 中华人民共和国农业部, 2005. 土壤速效钾和缓效钾含量的测定: NY/T 889—2004[S]. 北京: 中国农业出版社: 1-3. |
| Ministry of Agriculture of the People's Republic of China, 2005. Determination of exchangeable potassium and non-exchangeable potassium content in soil: NY/T 889—2004[S]. Beijing: China Agriculture Press: 1-3. | |
| [55] | 中华人民共和国农业部, 2006. 土壤检测第6部分: 土壤有机质的测定: NY/T 1121.6—2006[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社: 1-3. |
| Ministry of Agriculture of the People's REpublic of China, 2006. Soil testing part 6: Method for determination of soil organic matter: NY/T 1121.6—2006[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China: 1-3. | |
| [56] | 中华人民共和国农业部, 2012. 土壤检测第24部分: 土壤全氮的测定自动定氮仪法: NY/T 1121.24—2012[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社: 1-3. |
| Ministry of Agriculture of the People's Republic of China, 2012. Soil testing part 24:Determination of total nitrogen in soil. Automatic kjeldahl apparatus method: NY/T 1121.24—2012[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China: 1-3. | |
| [57] | 中华人民共和国农业部, 2015. 土壤检测第7部分: 土壤有效磷的测定: NY/T 1121.7—2014[S]. 北京: 中国农业出版社: 1-4. |
| Ministry of Agriculture of the People's Republic of China, 2015. Soil testing part 7: Method for detemination of available phosphorus in soil: NY/T 1121.7—2014[S]. Beijing: China Agriculture Press: 1-4. |
| [1] | 杜丹丹, 高瑞忠, 房丽晶, 谢龙梅. 旱区盐湖盆地土壤重金属空间变异及对土壤理化因子的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(6): 1123-1132. |
| [2] | 董智今, 张呈春, 展秀丽, 张维福. 宁夏河东沙地生物土壤结皮及其下伏土壤养分的空间分布特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 910-919. |
| [3] | 张贝儿, 吴建强, 王敏, 熊丽君, 谭娟, 沈城, 黄波涛, 黄沈发. 耕地生态保育工程的土壤健康度评价方法初探[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(2): 388-396. |
| [4] | 刘祥宏, 尹勤瑞, 辛建宝, 刘伟, 许秀泉, 黄占斌, 安如意. 生态植被自然修复及其人工促进技术研究进展与展望[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(7): 1476-1488. |
| [5] | 夏恩龙, 农珺清, 魏松坡, 刘希珍, 刘广路. 毛竹向阔叶林扩展过程中土壤养分变化特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(6): 1110-1117. |
| [6] | 龙靖, 黄耀, 刘占锋, 简曙光, 魏丽萍, 王俊. 西沙热带珊瑚岛典型乔木叶片性状和养分再吸收特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(2): 248-256. |
| [7] | 余斐, 叶彩红, 许窕孜, 张中瑞, 朱航勇, 张耕, 华雷, 邓鉴锋, 丁晓纲. 韶关市花岗岩地区森林土壤重金属污染评价[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(2): 354-362. |
| [8] | 盛基峰, 李垚, 于美佳, 韩艳英, 叶彦辉. 氮磷添加对高寒草地土壤养分和相关酶活性的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(12): 2302-2309. |
| [9] | 张晓丽, 王国丽, 常芳弟, 张宏媛, 逄焕成, 张建丽, 王婧, 冀宏杰, 李玉义. 生物菌剂对根际盐碱土壤理化性质和微生物区系的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(10): 1984-1992. |
| [10] | 宋贤冲, 蔡雪梅, 陈韬, 潘文, 石媛媛, 唐健, 曹继钊. 不同萌芽代次桉树根际和非根际土壤养分的变化特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(9): 1814-1820. |
| [11] | 廖迎春, 段洪浪, 施星星, 孟庆银, 刘文飞, 沈芳芳, 樊后保, 朱涛. 杉木(Cunninghamia lanceolate)人工林生长状况与根系生物量相关性研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(6): 1121-1128. |
| [12] | 徐文印, 张宇鹏, 段成伟, 柴瑜, 宋娴, 李希来. 黄河源不同区域退化高寒草甸土壤养分空间变异研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(10): 1968-1975. |
| [13] | 隋阳辉, 高继平, 王延波, 肖万欣, 刘晶, 史磊, 赵海岩, 张洋. 氮肥配施生物炭对旱地土壤养分和玉米根系径级分布的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(10): 2026-2032. |
| [14] | 张子璇, 牛蓓蓓, 李新举. 不同改良模式对滨海盐渍土土壤理化性质的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2020, 29(2): 275-284. |
| [15] | 张莎莎, 李爱琴, 王会荣, 王晶晶, 徐小牛. 不同海拔杉木人工林土壤碳氮磷生态化学计量特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2020, 29(1): 97-104. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
