生态环境学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (2): 354-362.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2022.02.016
余斐1( ), 叶彩红1,2, 许窕孜1,2, 张中瑞1, 朱航勇1, 张耕1, 华雷2, 邓鉴锋1, 丁晓纲1,*(
), 叶彩红1,2, 许窕孜1,2, 张中瑞1, 朱航勇1, 张耕1, 华雷2, 邓鉴锋1, 丁晓纲1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2021-08-05
出版日期:2022-02-18
发布日期:2022-04-14
通讯作者:
*丁晓纲(1978年生),男,教授级高级工程师,博士,主要从事森林理学研究。E-mail: 27267152@qq.com作者简介:余斐(1991年生),女,博士,研究方向为森林培育与栽培生理生态。E-mail: fishing_ok@163.com
基金资助:
YU Fei1( ), YE Caihong1,2, XU Tiaozi1,2, ZHANG Zhongrui1, ZHU Hangyong1, ZHANG Geng1, HUA Lei2, DENG Jianfeng1, DING Xiaogang1,*(
), YE Caihong1,2, XU Tiaozi1,2, ZHANG Zhongrui1, ZHU Hangyong1, ZHANG Geng1, HUA Lei2, DENG Jianfeng1, DING Xiaogang1,*( )
)
Received:2021-08-05
Online:2022-02-18
Published:2022-04-14
摘要:
探究韶关市花岗岩地区森林土壤重金属的含量分布特征并对其污染程度进行评价,探讨花岗岩地区森林土壤重金属含量的主要影响因素。以韶关市花岗岩地区森林土壤为研究对象,测定223个样地的铬、铜、铅、汞4种重金属元素含量,利用单项、内梅罗综合污染指数法和潜在生态风险指数法对研究区森林土壤重金属的污染程度和潜在生态风险进行评价,利用非参数单样本检验分析和相关性分析找出主要影响因素。4种元素的单项污染指数均小于1,污染等级为非污染;内梅罗综合污染指数小于0.7,污染等级为清洁;综合潜在生态风险指数小于150,潜在生态风险等级为轻微。森林土壤重金属受母质层(80—100 cm)、土壤养分这两种因素的影响,尤其受土壤养分影响最为显著。土壤有机碳可络合重金属,全氮、全磷会影响植被生长,植被通过吸附土壤中的重金属,从而影响森林土壤中重金属的含量。其次,土壤母质层也会影响森林土壤重金属的含量,尤其是铬、汞元素,受成土母质控制。该研究为花岗岩区森林土壤重金属含量分布特征及污染评价方法奠定了基础,也为花岗岩区森林土壤污染防控和区域生态安全保护提供了建议和意见。
中图分类号:
余斐, 叶彩红, 许窕孜, 张中瑞, 朱航勇, 张耕, 华雷, 邓鉴锋, 丁晓纲. 韶关市花岗岩地区森林土壤重金属污染评价[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(2): 354-362.
YU Fei, YE Caihong, XU Tiaozi, ZHANG Zhongrui, ZHU Hangyong, ZHANG Geng, HUA Lei, DENG Jianfeng, DING Xiaogang. Evaluation of Heavy Metal Pollution in Woodland Soil of Granite Area in Shaoguan City[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(2): 354-362.
| 统计量Statistics | 铬 Cr | 铜 Cu | 铅 Pb | 汞 Hg |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 最大值 Max/(mg∙kg-1) | 58.67 | 137.59 | 497.88 | 0.73 |
| 最小值 Min/(mg∙kg-1) | 3.00 | 0.00 | 6.14 | 0.03 |
| 平均值 Mean/(mg∙kg-1) | 16.92 | 8.96 | 48.79 | 0.15 |
| 标准差(n=223) Standard deviation (n=223) (mg∙kg-1) | 11.73 | 11.61 | 45.74 | 0.08 |
| 变异系数 Coefficient of variation | 0.69 | 1.30 | 0.94 | 0.51 |
| K-S值 Value of K-S test | 0.68 | 1.12 | 1.25 | 0.72 |
| 显著性 Significance | 0.74 | 0.16 | 0.09 | 0.68 |
| 土壤污染风险筛选值 Soil pollution risk screening value | 150 | 50 | 70 | 1.3 |
表1 森林土壤重金属描述性统计特征
Table 1 Descriptive statistical characteristics of heavy metals in forest soil
| 统计量Statistics | 铬 Cr | 铜 Cu | 铅 Pb | 汞 Hg |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 最大值 Max/(mg∙kg-1) | 58.67 | 137.59 | 497.88 | 0.73 |
| 最小值 Min/(mg∙kg-1) | 3.00 | 0.00 | 6.14 | 0.03 |
| 平均值 Mean/(mg∙kg-1) | 16.92 | 8.96 | 48.79 | 0.15 |
| 标准差(n=223) Standard deviation (n=223) (mg∙kg-1) | 11.73 | 11.61 | 45.74 | 0.08 |
| 变异系数 Coefficient of variation | 0.69 | 1.30 | 0.94 | 0.51 |
| K-S值 Value of K-S test | 0.68 | 1.12 | 1.25 | 0.72 |
| 显著性 Significance | 0.74 | 0.16 | 0.09 | 0.68 |
| 土壤污染风险筛选值 Soil pollution risk screening value | 150 | 50 | 70 | 1.3 |
| 重金属元素 Heavy metal elements | 铬Cr | 铜Cu | 铅Pb | 汞Hg |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 单项污染指数 Individual pollution index | 0.11 | 0.18 | 0.70 | 0.12 |
| 单项污染等级 Individual pollution grade | 非污染 | 非污染 | 非污染 | 非污染 |
| 内梅罗综合污染指数 Nemerow composite pollution index | 0.27 | |||
| 综合污染等级 Composite pollution grade | 清洁 | |||
表2 森林土壤重金属单项及综合污染指数评价
Table 2 Individual and Nemerow pollution index evaluation of forest soil heavy metals
| 重金属元素 Heavy metal elements | 铬Cr | 铜Cu | 铅Pb | 汞Hg |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 单项污染指数 Individual pollution index | 0.11 | 0.18 | 0.70 | 0.12 |
| 单项污染等级 Individual pollution grade | 非污染 | 非污染 | 非污染 | 非污染 |
| 内梅罗综合污染指数 Nemerow composite pollution index | 0.27 | |||
| 综合污染等级 Composite pollution grade | 清洁 | |||
| 重金属元素 Heavy metal elements | 铬Cr | 铜Cu | 铅Pb | 汞Hg |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 毒性系数 Toxic coefficient | 2 | 5 | 5 | 40 |
| 单因子生态风险指数 Single factor ecological risk index | 2.07 | 4.38 | 3.44 | 63.95 |
| 单项风险程度 Individual risk level | 轻微生态风险 | 轻微生态风险 | 轻微生态风险 | 中等生态风险 |
| 综合风险指数 Composite risk index | 73.84 | |||
| 综合风险程度 Composite risk level | 轻微生态风险 | |||
表3 森林土壤重金属潜在生态风险评价
Table 3 Potential ecological risk assessment forest soil heavy metals
| 重金属元素 Heavy metal elements | 铬Cr | 铜Cu | 铅Pb | 汞Hg |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 毒性系数 Toxic coefficient | 2 | 5 | 5 | 40 |
| 单因子生态风险指数 Single factor ecological risk index | 2.07 | 4.38 | 3.44 | 63.95 |
| 单项风险程度 Individual risk level | 轻微生态风险 | 轻微生态风险 | 轻微生态风险 | 中等生态风险 |
| 综合风险指数 Composite risk index | 73.84 | |||
| 综合风险程度 Composite risk level | 轻微生态风险 | |||
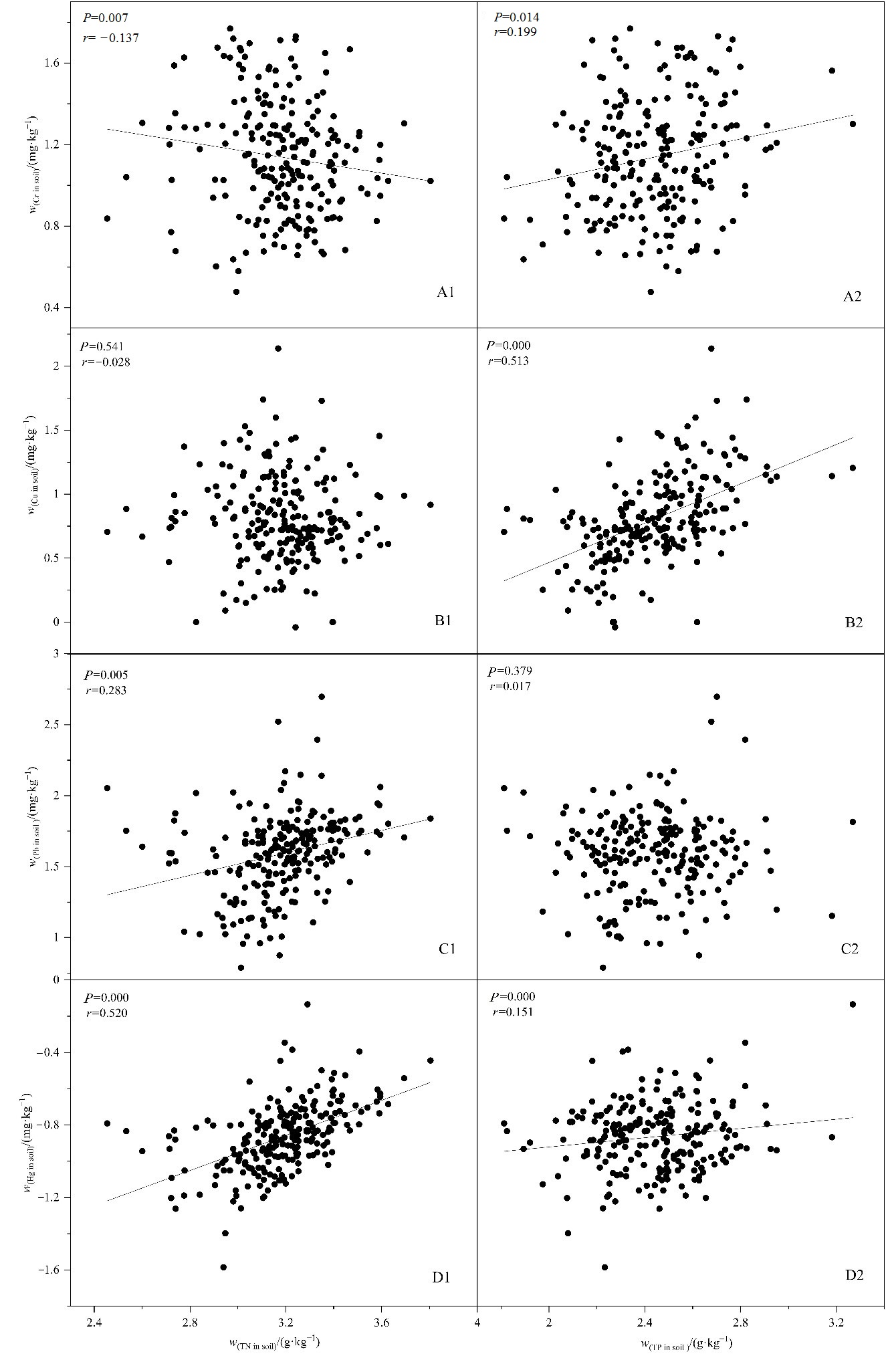
图4 土壤全氮、全磷对森林0—20 cm土壤重金属含量的影响
Figure 4 Influence of Total Nitrogen and Total Phosphorus on heavy metal content in forest soil in the depth of 0?20 cm
| [1] |
ZENG F R, SHAFAQAT A, ZHANG H T, et al., 2011. The influence of pH and organic matter content in paddy soil on heavy metal availability and their uptake by rice plants[J]. Environmental Pollution, 159(1): 84-91.
DOI URL |
| [2] | 蔡雄飞, 赵士杰, 宣斌, 等, 2021. 贵阳市城郊两处菜地土壤垂直剖面重金属迁移规律及来源解析[J]. 生态科学, 40(3): 42-50. |
| CAI X F, ZHAO S J, XUAN B, et al., 2021. Migration and source analysis of heavy metals in vertical soil profiles of the two suburban vegetable fields of Guiyang city[J]. Ecological Science, 40(3): 42-50. | |
| [3] | 车继鲁, 余树全, 刘晖, 等, 2017. 城市绿化树种香樟不同器官对土壤重金属的富集特征[J]. 应用生态学报, 28(9): 2907-2916. |
| CHE J L, YU S Q, LIU H, et al., 2017. Characteristics of heavy metal enrichment efficiency in different organs of urban green tree Cinnamomum camphora[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 28(9): 2907-2916. | |
| [4] | 陈为峰, 孙其远, 宋希亮, 等, 2019. 不同城市功能区绿地土壤重金属分布及其生态风险评价[J]. 水土保持研究, 26(3): 148-153. |
| CHEN W F, SUN Q Y, SONG X L, et al., 2019. Distribution and ecological risk assessment of heavy metal elements in soils of green spaces at different urban functional areas[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 26(3): 148-153. | |
| [5] | 陈泽华, 焦思, 余爱华, 等, 2020. 土壤重金属污染评价方法探析--以南京市为例[J]. 森林工程, 36(3): 28-36. |
| CHEN Z H, JIAO S, YU A H, et al., 2020. Analysis on evaluation methods of heavy metal pollution in soil: Taking Nanjing as an example[J]. Forest Engineering, 36(3): 28-36. | |
| [6] | 陈志彪, 朱鹤健, 2006. 不同水土流失治理模式下的土壤理化特征[J]. 福建师范大学学报(自然科学版), 22(4):5-9, 29. |
| CHEN Z B, ZHU H J, 2006. The physical and chemical characteristics of soil under the different control measures of soil and water loss[J]. Journal of Fujian Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 22(4): 5-9, 29. | |
| [7] | 陈志萍, 姜霞, 谢涛, 等, 2020. 城市森林土壤重金属的植物修复研究进展[J]. 贵州林业科技, 48(2): 42-46, 60. |
| CHEN Z P, JIANG X, XIE T, et al., 2020. Research progress on phytoremediation of soil heavy metals of urban forest[J]. Guizhou Forestry Science and Technology, 48(2): 42-46, 60. | |
| [8] | 冯慧敏, 李海渤, 2018. 粤北地区重金属污染菜地现状及土壤修复对策与建议--以韶关为例[J]. 湖南生态科学学报, 5(3): 48-56. |
| FENG H M, LI H B. 2018. Countermeasures and suggestions for remediation of heavy metal pollution in vegetable soils in northern Guangdong province: Taking Shaoguan as an example[J]. Journal of Hunan Ecological Science, 5(3): 48-56. | |
| [9] | 中华人民共和国国务院, 2016. 土壤污染防治行动计划[EB/OL].[2016-05-28]. http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/content/2016-05/31/content_5078377.htm . |
| State Council of the People's Republic of China, 2016. Action Plan for soil Pollution prevention and Control[EB/OL].[2016-05-28]. http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/content/2016-05/31/content_5078377.htm . | |
| [10] | 胡永兴, 宿虎, 张斌, 等, 2020. 土壤重金属污染及其评价方法概述[J]. 江苏农业科学, 48(17): 33-39. |
| HU Y X, SU H, ZHANG B, et al., 2020. Soil heavy metal pollution and its evaluation methods: A review[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 48(17): 33-39. | |
| [11] | 焦艳金, 陈志强, 张巧玲, 2020. 福建红壤侵蚀区土壤重金属污染特征及马尾松富集[J]. 福建师范大学学报(自然科学版), 36(3): 99-106. |
| JIAO Y J, CHEN Z Q, ZHANG Q L, 2020. Pollution characteristics of heavy metal in soil and enrichment of Masson Pine in typical red soil region of Fujian[J]. Journal of Fujian Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 36(3): 99-106. | |
| [12] | 李林, 周启星, 2014. 我国典型城市大气汞污染及对人体健康的影响[J]. 生态毒理学报, 9(5): 832-842. |
| LI L, ZHOU Q X, 2014. Atmospheric mercury pollution in typical cities of China and its influences on Human health[J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 9(5): 832-842. | |
| [13] | 骆庭川, 胡以铿, 陈海军, 1986. 广东韶关地区某些花岗岩体含矿性的地球化学研究[J]. 地球科学, 11(4): 389-395. |
| LUO T C, HU Y K, CHEN H J, 1986. The geochemical study of the ore-bearing potentiality of some granitic intrusions in the Shaoguan district, Guangdong province[J]. Earth Science, 11(4): 389-395. | |
| [14] | 区晓琳, 陈志彪, 陈志强, 等, 2016. 闽西南崩岗土壤理化性质及可蚀性分异特征[J]. 中国水土保持科学, 14(3): 84-92. |
| OU X L, CHEN Z B, CHEN Z Q, et al., 2016. Variation of soil physical-chemical property and erodibility in the area of collapse mound of southwestern Fujian[J]. Science of Soil and Water Conservation, 14(3): 84-92. | |
| [15] | 史德明, 1991. 南方花岗岩区的土壤侵蚀及其防治[J]. 水土保持学报, 5(3): 63-72. |
| SHI D M, 1991. Soil erosion and its control in the granite region of southern China[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 5(3): 63-72. | |
| [16] | 田美玲, 陆素芬, 常显志, 等, 2019. 粤北某矿业密集区土壤重金属含量特征研究[J]. 河池学院学报, 39(5): 38-43. |
| TIAN M L, LU S F, CHANG X Z, et al., 2019. Evaluation on heavy metal contamination in soils in mining intensive areas in northern Guangdong province[J]. Journal of Hechi University, 39(5): 38-43. | |
| [17] | 王文栋, 任振武, 张红英, 等, 2021. 新疆天山中部森林土壤重金属含量及其与土壤理化性质的相关性[J]. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 49(3): 47-56, 66. |
| WANG W D, REN Z W, ZHANG H Y, et al., 2021. Soil heavy metal contents and correlations with soil physical and chemical properties in central Tianshan forest, Xinjiang[J]. Journal of Northwest A & F University (Natural Science Edition), 49(3): 47-56, 66. | |
| [18] | 吴敏, 2021. 重金属铅、铬在土壤中的迁移特征--以泉州市为例[J]. 中国煤炭地质, 33(2): 68-72, 77. |
| WU M, 2021. Migration features of heavy metal Pb and Cr in soil: A case study of Quanzhou city[J]. Coal Geology of China, 33(2): 68-72, 77. | |
| [19] | 谢锦升, 杨玉盛, 解明曙, 2004. 亚热带花岗岩侵蚀红壤的生态退化与恢复技术[J]. 水土保持研究, 11(3): 154-156. |
| XIE J S, YANG Y S, XIE M S, 2004. Ecological restoration technology and degradation of eroded granite red soil in subtropical regions in China[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 11(3): 154-156. | |
| [20] | 杨皓, 范明毅, 黄先飞, 等, 2016. 喀斯特山区燃煤型电厂周边农业土壤中重金属的污染特征及评价[J]. 生态环境学报, 25(5): 893-902. |
| YANG H, FAN M Y, HAUNG X F, et al., 2016. Pollution characteristics and evaluation for agriculture soils around the coal-fired power plant located in karst mountainous area[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 25(5): 893-902. | |
| [21] | 叶俊, 任大军, 张晓晴, 等, 2020. 中国部分林地土壤重金属含量特征及污染评价[J]. 科学技术与工程, 20(6): 2507-2514. |
| YE J, REN D J, ZHANG X Q, et al., 2020. Heavy metal contents distribution and contamination assessment in some Chinese forest soils[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 20(6): 2507-2514. | |
| [22] | 曾昭婵, 李本云, 2016. 万山汞矿区土壤汞污染及其防治研究[J]. 环境科学与管理, 41(5): 115-118. |
| ZENG Z C, LI B Y, 2016. Preliminary study on soil mercury pollution and its prevention and control in Wanshan mercury mine area[J]. Environmental Science and Management, 41(5): 115-118. | |
| [23] | 张福刚, 雷国平, 2013. 黑龙江省肇源县土壤汞的空间分异研究[J]. 水土保持研究, 20(1): 273-276. |
| ZHANG F G, LEI G P, 2013. Study on spatial variability of soil mercury of Zhaoyuan county in Heilongjiang province[J]. Research on Soil and Water Conservation, 20(1): 273-276. | |
| [24] | 周曼, 徐燕, 赵玉皓, 等, 2021. N、 P添加对亚热带森林土壤重金属活性的影响[J]. 环境科学与技术, 44(4): 23-27. |
| ZHOU M, XU Y, ZHAO Y H, et al., 2021. Analysis of the activities of heavy metals in forest soil under N and P addition[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 44(4): 23-27. | |
| [25] | 朱立安, 殷爱华, 林兰稳, 等, 2021. 佛山城市森林公园表层土壤重金属累积特征、影响因素及其评价[J]. 生态环境学报, 30(4): 849-856. |
| ZHU L A, YIN A H, LIN L W, et al., 2021. Accumulation characteristics, influencing factors and evaluation of heavy metals in surface soil in urban forest park of Foshan[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 30(4): 849-856. |
| [1] | 杜丹丹, 高瑞忠, 房丽晶, 谢龙梅. 旱区盐湖盆地土壤重金属空间变异及对土壤理化因子的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(6): 1123-1132. |
| [2] | 董智今, 张呈春, 展秀丽, 张维福. 宁夏河东沙地生物土壤结皮及其下伏土壤养分的空间分布特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 910-919. |
| [3] | 潘昱伶, 璩向宁, 李琴, 王磊, 王筱平, 谭鹏, 崔庚, 安雨, 佟守正. 黄河宁夏段典型滩涂湿地土壤理化因子空间分布特征及其对微地形的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 668-677. |
| [4] | 冯树娜, 吕家珑, 何海龙. KI淋洗对黄绵土汞污染的去除效果及土壤理化性状的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 776-783. |
| [5] | 陈敏毅, 朱航海, 佘伟铎, 尹光彩, 黄祖照, 杨巧玲. 珠三角某遗留造船厂场地土壤重金属人体健康风险评估及源解析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 794-804. |
| [6] | 张贝儿, 吴建强, 王敏, 熊丽君, 谭娟, 沈城, 黄波涛, 黄沈发. 耕地生态保育工程的土壤健康度评价方法初探[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(2): 388-396. |
| [7] | 肖洁芸, 周伟, 石佩琪. 土壤重金属含量高光谱反演[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 175-182. |
| [8] | 黄宏, 郑欣芸, 李迎东, 赵旭, 俞锦辰, 汪振华. 大陈岛海域不同年龄褐菖鲉对重金属富集作用研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(9): 1885-1891. |
| [9] | 马闯, 王雨阳, 周通, 吴龙华. 污染土壤颗粒态有机质镉锌富集特征及其解吸行为研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(9): 1892-1900. |
| [10] | 陶玲, 黄磊, 周怡蕾, 李中兴, 任珺. 污泥-凹凸棒石共热解生物炭对矿区土壤重金属生物有效性和环境风险的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1637-1646. |
| [11] | 李莹, 张洲, 杨高明, 祖艳群, 李博, 陈建军. 湿地植物根系泌氧能力和根表铁膜与根系吸收重金属的关系[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1657-1666. |
| [12] | 罗松英, 李秋霞, 邱锦坤, 邓素炎, 李一锋, 陈碧珊. 南三岛土壤-红树植物系统中重金属形态特征及迁移转化规律[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(7): 1409-1416. |
| [13] | 董乐恒, 王旭刚, 陈曼佳, 王子豪, 孙丽蓉, 石兆勇, 吴琪琪. 光照和避光条件下石灰性水稻土Fe氧化还原与Cu活性关系研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(7): 1448-1455. |
| [14] | 夏恩龙, 农珺清, 魏松坡, 刘希珍, 刘广路. 毛竹向阔叶林扩展过程中土壤养分变化特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(6): 1110-1117. |
| [15] | 彭红丽, 谭海霞, 王颖, 魏建梅, 冯阳. 不同种植模式下土壤重金属形态分布差异与生态风险评价[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(6): 1235-1243. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
