生态环境学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (5): 1047-1058.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2022.05.020
王占永1( ), 陈昕1, 胡喜生1, 何红弟2, 蔡铭3, 彭仲仁4,*(
), 陈昕1, 胡喜生1, 何红弟2, 蔡铭3, 彭仲仁4,*( )
)
收稿日期:2021-11-14
出版日期:2022-05-18
发布日期:2022-07-12
通讯作者:
* 彭仲仁(1963年生),男,教授,博士研究生导师,从事交通与环境、气候变化适应性规划等研究。E-mail: zpeng@ufl.edu作者简介:王占永(1983年生),男,讲师,博士,硕士研究生导师,从事交通污染统计学、交通减污降碳的绿地响应策略、基于无人机的空气污染智能监测技术等研究。E-mail: wangzy1026@fafu.edu.cn
基金资助:
WANG Zhanyong1( ), CHEN Xin1, HU Xisheng1, HE Hongdi2, CAI Ming3, PENG Zhongren4,*(
), CHEN Xin1, HU Xisheng1, HE Hongdi2, CAI Ming3, PENG Zhongren4,*( )
)
Received:2021-11-14
Online:2022-05-18
Published:2022-07-12
摘要:
植物屏障,一方面可以吸附沉降道路大气颗粒物,另一方面其特殊的立体结构却阻碍了颗粒物的扩散,由此导致人们对其在道路空气质量方面的影响莫衷一是。该文通过文献调研,深入分析树篱、灌木及行道树等植物屏障对路边大气颗粒物污染分布的影响机理及其研究方法,得出以下有实践指导价值的结论:(1)选择对特定环境生存力强、快速且极强滞尘的植物物种,综合考虑植物群落结构、街道形态、栽种空间等确定提高颗粒物沉降效率的绿化参数,并统一参数选择标准或标准化方法,更有利于提出普适的绿化滞尘方案;(2)基于峡谷型和开阔式道路各自流场特征及局部空间格局,同时兼顾污染防控的目标范围,确定改善污染扩散的植物群落配置及结构,才能积极引导大气颗粒物的动力学扩散过程;(3)在植物屏障调控颗粒物分布的效应评估中同时引入吸附沉降和改变扩散两种机制,并考虑微环境气象等单要素主导或多要素耦合的影响,才能使道路绿化降污策略更具实践性;(4)通过精细测算或表征动态交通排放、植物群落配置参数、微气象变量等来改进模拟方法,并发展灵活可靠且适合道路环境的立体观测技术,才能从研究方法上对植物屏障影响道路颗粒物动态过程的认识更趋真实。未来研究也亟需关注路旁植物屏障对周边大气颗粒物污染程度的响应机制,量化植物群落及与其他人工屏障的组合结构对改善周边环境污染的作用,以及考虑基于时间和空间的人群暴露评估来优化绿化配置策略。
中图分类号:
王占永, 陈昕, 胡喜生, 何红弟, 蔡铭, 彭仲仁. 植物屏障影响路边大气颗粒物分布机理及研究方法的进展[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(5): 1047-1058.
WANG Zhanyong, CHEN Xin, HU Xisheng, HE Hongdi, CAI Ming, PENG Zhongren. Mechanism and Research Methods of Roadside Green Barriers Affecting the Distribution of Atmospheric Particulate Matter: A Review[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(5): 1047-1058.
| 作者,年份 Author, year | 内容概括 Content overview |
|---|---|
| Janhäll, | 较早回顾了道路绿色设施对大气颗粒物沉降和扩散的影响,提出了可改善空气质量的植物屏障设计建议 |
| Abhijith et al., | 评述了不同种类植物对峡谷街道和开阔道路空气污染的影响,围绕植物的形态参数及配置结构提出了改善道路空气质量的绿化策略 |
| Baldauf, | 从植物的种类、形态结构、维护管理、水径流调节、交通安全等方面,回顾了植物群落对开阔道路空气污染的影响,并提及植物与固体屏障组合净污的潜力 |
| Mori et al., | 梳理了植物的种类、配置结构以及栽种方式与道路空气污染的关系,认为植物群落改善开阔道路要好于改善街道峡谷空气质量的效果 |
| Buccolieri et al., | 通过梳理案例或综述研究发现,绿地对大气颗粒物的沉降与扩散机制的相对重要性仍不清楚,特别是数值模拟的参数化过程较少考虑颗粒物再悬浮和植被热环境效应 |
| Tiwari et al., | 从宏观和微观层面回顾了考虑植物屏障的空气污染模拟方法,基于模型参数详述了植物对气态污染物和颗粒物的沉降机制,概括了模拟方法在宏观和微观层面的机理差异,以及对不同空间尺度下植物影响的模拟效果 |
| Greater London Authority, | 着眼于城市道路区域的植物群落能否减轻居民暴露于空气污染的程度和时间,认为植物不在于其去除污染的能力而在于其控制或改善空气流动和污染分布的机制 |
| Hewitt et al., | 从沉降、扩散、生物质VOC排放等视角阐述了道路植物对环境空气的影响,提出了提高空气质量改善效率的绿植栽培建议 |
| Barwise et al., | 从植物物种及叶片特性、植物屏障的物理配置和可持续管理视角出发,综述植物对空气质量的影响,归纳出适用于规划实践的植物选择策略,尤其强调基于周围环境设计植物形态结构及配置、考虑植被自身特性及利弊、比较地理区位状况等确定合适的绿地设计框架 |
| Ferrini et al., | 讨论了不同种类植物吸收和沉降颗粒物的差异及相关影响因素,发现叶片沉降捕获的颗粒物受风影响再悬浮以及受雨水冲洗污染土壤的机制尚不清楚,行道树和低矮灌木对街道空气的净化有明显差异,而在道路污染热点区域,靠近机动车排放源栽种连续低矮的灌木会起到更好的空气净化效果 |
| 胡杨等, (Hu et al., | 回顾了道路绿地对局地空气污染扩散的影响,指出未来应向拓展道路及绿带研究范畴、考虑绿地调控污染的多种生态过程、融合实地监测和数值模拟方法以及提高数据精度和丰富度等方向发展 |
表1 道路绿化影响路边空气质量的代表性综述文献
Table 1 Representative review articles of green barriers affecting roadside air quality
| 作者,年份 Author, year | 内容概括 Content overview |
|---|---|
| Janhäll, | 较早回顾了道路绿色设施对大气颗粒物沉降和扩散的影响,提出了可改善空气质量的植物屏障设计建议 |
| Abhijith et al., | 评述了不同种类植物对峡谷街道和开阔道路空气污染的影响,围绕植物的形态参数及配置结构提出了改善道路空气质量的绿化策略 |
| Baldauf, | 从植物的种类、形态结构、维护管理、水径流调节、交通安全等方面,回顾了植物群落对开阔道路空气污染的影响,并提及植物与固体屏障组合净污的潜力 |
| Mori et al., | 梳理了植物的种类、配置结构以及栽种方式与道路空气污染的关系,认为植物群落改善开阔道路要好于改善街道峡谷空气质量的效果 |
| Buccolieri et al., | 通过梳理案例或综述研究发现,绿地对大气颗粒物的沉降与扩散机制的相对重要性仍不清楚,特别是数值模拟的参数化过程较少考虑颗粒物再悬浮和植被热环境效应 |
| Tiwari et al., | 从宏观和微观层面回顾了考虑植物屏障的空气污染模拟方法,基于模型参数详述了植物对气态污染物和颗粒物的沉降机制,概括了模拟方法在宏观和微观层面的机理差异,以及对不同空间尺度下植物影响的模拟效果 |
| Greater London Authority, | 着眼于城市道路区域的植物群落能否减轻居民暴露于空气污染的程度和时间,认为植物不在于其去除污染的能力而在于其控制或改善空气流动和污染分布的机制 |
| Hewitt et al., | 从沉降、扩散、生物质VOC排放等视角阐述了道路植物对环境空气的影响,提出了提高空气质量改善效率的绿植栽培建议 |
| Barwise et al., | 从植物物种及叶片特性、植物屏障的物理配置和可持续管理视角出发,综述植物对空气质量的影响,归纳出适用于规划实践的植物选择策略,尤其强调基于周围环境设计植物形态结构及配置、考虑植被自身特性及利弊、比较地理区位状况等确定合适的绿地设计框架 |
| Ferrini et al., | 讨论了不同种类植物吸收和沉降颗粒物的差异及相关影响因素,发现叶片沉降捕获的颗粒物受风影响再悬浮以及受雨水冲洗污染土壤的机制尚不清楚,行道树和低矮灌木对街道空气的净化有明显差异,而在道路污染热点区域,靠近机动车排放源栽种连续低矮的灌木会起到更好的空气净化效果 |
| 胡杨等, (Hu et al., | 回顾了道路绿地对局地空气污染扩散的影响,指出未来应向拓展道路及绿带研究范畴、考虑绿地调控污染的多种生态过程、融合实地监测和数值模拟方法以及提高数据精度和丰富度等方向发展 |

图1 道路微环境机动车排放大气颗粒物的动力学过程示意图
Figure 1 Schematic diagram of the dynamic process of atmospheric particles emitted by motor vehicles in road microenvironment
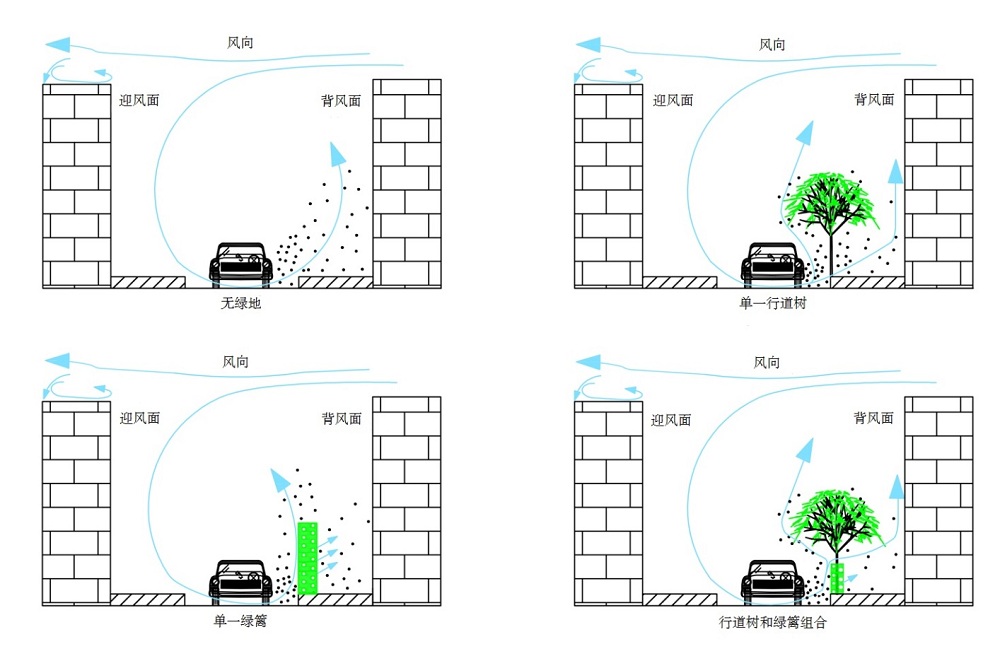
图2 街道不同绿化配置情景下风促使大气颗粒物流动的示意图
Figure 2 Schematic diagram of the wind-induced flow of atmospheric particles under different greening configurations in the street
| [1] |
ABHIJITH K V, GOKHALE S, 2015. Passive control potentials of trees and on-street parked cars in reduction of air pollution exposure in urban street canyons[J]. Environmental Pollution, 204: 99-108.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
ABHIJITH K V, KUMAR P, 2019. Field investigations for evaluating green infrastructure effects on air quality in open-road conditions[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 201: 132-147.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
ABHIJITH K V, KUMAR P, 2020. Quantifying particulate matter reduction and their deposition on the leaves of green infrastructure[J]. Environmental Pollution, 265(Part B): 114884.
DOI URL |
| [4] | ABHIJITH K V, KUMAR P, GALLAGHER J, et al., 2017. Air pollution abatement performances of green infrastructure in open road and built-up street canyon environments-A review[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 62: 71-86. |
| [5] |
AMORIM J H, RODRIGUES V, TAVARES R, et al., 2013. CFD modelling of the aerodynamic effect of trees on urban air pollution dispersion[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 461-462: 541-551.
DOI URL |
| [6] | ANTOINE A P R, BUCCOLIERI R, EDDY J, et al., 2017. Air quality affected by trees in real street canyons: The case of Marylebone neighbourhood in central London[J]. Urban Forestry & Urban Greening, 22: 41-53. |
| [7] | BALDAUF R, 2017. Roadside vegetation design characteristics that can improve local, near-road air quality[J]. Transportation Research Part D: Transport & Environment, 52(11): 354-361. |
| [8] |
BARWISE Y, KUMAP P, 2020. Designing vegetation barriers for urban air pollution abatement: a practical review for appropriate plant species selection[J]. npj Climate and Atmospheric Science, DOI: 10.1038/s41612-020-0115-3.
DOI |
| [9] |
BOWKER G E, BALDAUF R W, ISAKOV V, et al., 2007. The effects of roadside structures on the transport and dispersion of ultrafine particles from highways[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 41(37): 8128-8139.
DOI URL |
| [10] | BRUSE M, FLEER H, 1998. Simulating surface-plant-air interactions inside urban environments with a three dimensional numerical model[J]. Environmental Modelling & Software, 13(3-4): 373-384. |
| [11] |
BUCCOLIERI R, JEANJEAN A P R, GATTO E, et al., 2018b. The impact of trees on street ventilation, NOx and PM2.5 concentrations across heights in Marylebone Rd street canyon, central London[J]. Sustainable Cities and Society, 41: 227-241.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
BUCCOLIERI R, SALIM S M, LEO L S, et al., 2011. Analysis of local scale tree-atmosphere interaction on pollutant concentration in idealized street canyons and application to a real urban junction[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 45(9): 1702-1713.
DOI URL |
| [13] | BUCCOLIERI R, SANTIAGO J L, RIVAS E, et al., 2018a. Review on urban tree modelling in CFD simulations: Aerodynamic, deposition and thermal effects[J]. Urban Forestry & Urban Greening, 31: 212-220. |
| [14] |
CAI M, HUANG Y, WANG Z Y, 2020. Dynamic three-dimensional distribution of traffic pollutant at urban viaduct with the governance strategy[J]. Atmospheric Pollution Research, 11(8): 1418-1428.
DOI URL |
| [15] | CAVANAGH J E, 2006. Potential vegetation to mitigate traffic-related pollutants: Part I-Review of background information[EB/OL]. [2022-03-11]. https://niwa.co.nz/sites/niwa.co.nz/files/import/attachments/co1x0405_p05.pdf. |
| [16] |
CHEN L F, PENG S L, LIU J G, et al., 2012. Dry deposition velocity of total suspended particles and meteorological influence in four locations in Guangzhou, China[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 24(4): 632-639.
DOI URL |
| [17] | CHEN X P, PEI T T, ZHOU Z X, et al., 2015. Efficiency differences of roadside greenbelts with three configurations in removing coarse particles (PM10): A street scale investigation in Wuhan, China[J]. Urban Forestry & Urban Greening, 14(2): 354-360. |
| [18] |
DASH A, ELSINGA G E, 2018. Air pollutant sinks on noise barriers: Where do they perform the best?[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 187: 144-154.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
DENG S X, MA J, ZHANG L L, et al., 2019. Microclimate simulation and model optimization of the effect of roadway green space on atmospheric particulate matter[J]. Environmental Pollution, 246: 932-944.
DOI URL |
| [20] | DESHMUKH P, ISAKOV V, VENKATRAM A, et al., 2019. The effects of roadside vegetation characteristics on local, near-road air quality[J]. Air Quality Atmosphere & Health, 12(3): 259-20. |
| [21] | ETYEMEZIAN V, AHONEN S, NIKOLIC D, et al., 2004. Deposition and Removal of Fugitive Dust in the Arid Southwestern United States: Measurements and Model Results[J]. Journal of the Air & Waste Management Association, 54(9): 1099-1111. |
| [22] | FERRANTI E, LEVINE J, MACKENZIE R, 2019. Role of trees & other green infrastructure in urban air quality[EB/OL]. [2022-03-11]. https://www.the-ies.org/analysis/role-trees-and-other-green. |
| [23] |
FERRINI F, FINI A, MORI J, et al., 2020. Role of vegetation as a mitigating factor in the urban context[J]. Sustainability, 12(10): 1-22.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
GALLAGHER J, BALDAUF R, FULLER C H, et al., 2015. Passive methods for improving air quality in the built environment: A review of porous and solid barriers[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 120: 61-70.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
GHASEMIAN M, AMINI S, PRINCEVAC M, 2017. The influence of roadside solid and vegetation barriers on near-road air quality[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 170: 108-117.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
GOEL A, KUMAR P, 2016. Vertical and horizontal variability in airborne nanoparticles and their exposure around signalized traffic intersection[J]. Environmental Pollution, 214: 54-69.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
GOZZI F, VENTURA G D, MARCELLI A, 2016. Mobile monitoring of particulate matter: State of art and perspectives[J]. Atmospheric Pollution Research, 7(2): 228-234.
DOI URL |
| [28] | GREATER LONDON AUTHORITY, 2019. Using green infrastructure to protect people from air pollution[EB/OL]. [2022-03-11]. https://www.london.gov.uk/WHAT-WE-DO/environment/environment-publications/using-green-infrastructure-protect-people-air-pollution. |
| [29] |
GROMKE C, JAMARKATTEL N, RUCK B, 2016. Influence of roadside hedgerows on air quality in urban street canyons[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 139: 75-86.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
GROTE R, SAMSON R, ALONSO R, et al., 2016. Functional traits of urban trees: Air pollution mitigation potential[J]. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment, 14(10): 543-550.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
HAN D H, SHEN H L, DUAN W B, et al., 2020. A review on particulate matter removal capacity by urban forests at different scales[J]. Urban Forestry & Urban Greening, DOI: 10.1016/j.ufug.2019.126565.
DOI |
| [32] |
HASHAD K, YANG B, BALDAUF R W, et al., 2020. Enhancing the local air quality benefits of roadside green infrastructure using low-cost, impermeable, solid structures (LISS)[J]. Science of the Total Environment, DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.137136.
DOI |
| [33] |
HE M L, DHANIYALA S, 2012. Vertical and horizontal concentration distributions of ultrafine particles near a highway[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 46: 225-236.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
HEWITT C N, ASHWORTH K, MACKENZIE A R, 2020. Using green infrastructure to improve urban air quality (GI4AQ)[J]. Ambio: A Journal of the Human Environment, 49(1): 62-73.
DOI URL |
| [35] | HU Y, MA K M, 2021. Research progress on the effects of urban road green space on dispersion of local air pollutant[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 32(1): 349-357. |
| [36] |
HUANG Y D, LI M Z, REN S Q, et al., 2019. Impacts of tree-planting pattern and trunk height on the airflow and pollutant dispersion inside a street canyon[J]. Building and Environment, DOI: 10.1016/j.buildenv.2019.106385.
DOI |
| [37] |
JANHÄLL S, 2015. Review on urban vegetation and particle air pollution-deposition and dispersion[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 105: 130-137.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
JEANJEAN A P R, MONKS P S, LEIGH R J, 2016. Modelling the effectiveness of urban trees and grass on PM2.5 reduction via dispersion and deposition at a city scale[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 147: 1-10.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
KARTTUNEN S, KURPPA M, AUVINEN M, et al., 2020. Large-eddy simulation of the optimal street-tree layout for pedestrian-level aerosol particle concentrations-A case study from a city-boulevard[J]. Atmospheric Environment: X, DOI: 10.1016/j.aeaoa.2020.100073.
DOI |
| [40] | KATHERINE J, WILLIS G P, 2017. The natural capital of city trees[J]. Science, 356(6336): 374-376. |
| [41] |
KATUL G G, GRÖNHOLM T, LAUNIAINEN S, et al., 2011 The effects of the canopy medium on dry deposition velocities of aerosol particles in the canopy sub[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 45(5): 1203-1212.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
KUMAR P, PATTON A P, JOHN L, et al., 2018. A review of factors impacting exposure to PM2.5, ultrafine particles and black carbon in Asian transport microenvironments[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 187: 301-316.
DOI URL |
| [43] |
LEE E S, RANASINGHE D R, AHANGAR F E, et al., 2018. Field evaluation of vegetation and noise barriers for mitigation of near- freeway air pollution under variable wind conditions[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 175: 92-99.
DOI URL |
| [44] | LI B, CAO R, WANG Z Y, et al., 2019a. Use of multi-rotor unmanned aerial vehicles for fine-grained roadside air pollution monitoring[J]. Transportation Research Record Journal of the Transportation Research Board, 2673(7): 169-180. |
| [45] | LI B, LI X B, LI C, et al., 2019b. Impacts of wind fields on the distribution patterns of traffic emitted particles in urban residential areas[J]. Transportation Research Part D Transport & Environment, 68: 122-136. |
| [46] | LI Y W, LIU B, YE J H, et al., 2021. Unmanned aerial vehicle measurements of volatile organic compounds over a subtropical forest in China and implications for emission heterogeneity[J]. American Chemical Society (ACS) Earth and Space Chemistry, 5(2): 247-256. |
| [47] |
LIN X L, CHAMECKI M, KATUL G, et al., 2018. Effects of leaf area index and density on ultrafine particle deposition onto forest canopies: A LES study[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 189: 153-163.
DOI URL |
| [48] |
LITSCHKE T, KUTTLER W, 2008. On the reduction of urban particle concentration by vegetation-a review[J]. Meteorologische Zeitschrift, 17(3): 229-240.
DOI URL |
| [49] |
LIU B, WU C, MA N, et al., 2020. Vertical profiling of fine particulate matter and black carbon by using unmanned aerial vehicle in Macau, China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.136109.
DOI |
| [50] |
LU S J, WANG D, WANG Z, et al., 2019. Investigating the role of meteorological factors in the vertical variation in PM2.5 by unmanned aerial vehicle measurement[J]. Aerosol and Air Quality Research, 19(7): 1493-1507.
DOI URL |
| [51] |
MORADPOUR M, AFSHIN H, FARHANIEH B, 2016. A numerical investigation of reactive air pollutant dispersion in urban street canyons with tree planting[J]. Atmospheric Pollution Research, 8(2): 253-266.
DOI URL |
| [52] |
MORAKINYO T E, LAM Y F, 2016. Simulation study of dispersion and removal of particulate matter from traffic by road-side vegetation barrier[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 23(7): 1-14.
DOI URL |
| [53] | MORI J, FERRINI F, SAEB A, 2018. Air pollution mitigation by urban greening[J]. Italus Hortus, 25(1): 13-22. |
| [54] |
MUHAMMAD S, WUYTS K, NUYTS G, et al., 2020. Characterization of epicuticular wax structures on leaves of urban plant species and its association with leaf wettability[J]. Urban Forestry & Urban Greening, DOI: 10.1016/j.ufug.2019.126557.
DOI |
| [55] |
MUHAMMAD S, WUYTS K, SAMSON R, 2019. Atmospheric net particle accumulation on 96 plan species with contrasting morphological and anatomical leaf characteristics in a common garden experiment[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 202: 328-344.
DOI URL |
| [56] |
NEFT I, SCUNGIO M, CULVER N, et al., 2016. Simulations of aerosol filtration by vegetation: Validation of existing models with available lab data and application to near-roadway scenario[J]. Aerosol Science and Technology, 50(9): 937-946.
DOI URL |
| [57] |
NIU H H, WANG B Q, LIU B W, et al., 2018. Numerical simulations of the effect of building configurations and wind direction on fine particulate matters dispersion in a street canyon[J]. Environmental Fluid Mechanics, 18(4): 829-847.
DOI URL |
| [58] | OKE T R, 1988. Boundary Layer Climates[M]. 2nd ed. London: Routledge. |
| [59] |
OTTOSEN T B, KUMAR P, 2020. The influence of the vegetation cycle on the mitigation of air pollution by a deciduous roadside hedge[J]. Sustainable Cities and Society, DOI: 10.1016/j.scs.2019.101919.
DOI |
| [60] |
OZDEMIR H, 2019. Mitigation impact of roadside trees on fine particle pollution[J]. The Science of the Total Environment, 659: 1176-1185.
DOI URL |
| [61] | PASQUIER A, ANDRÉ M, 2017. Considering criteria related to spatial variabilities for the assessment of air pollution from traffic[J]. Transportation Research Procedia, 225: 3358-3373. |
| [62] | PENG Z R, WANG D S, WANG Z Y, et al., 2015. A study of vertical distribution patterns of PM2.5 concentrations based on ambient monitoring with unmanned aerial vehicles: a case in Hangzhou, China[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 123(Part B): 357-369. |
| [63] | POPEK R, GAWROŃSKA H, WROCHNA M, et al., 2013. Particulate Matter on Foliage of 13 Woody Species: Deposition on Surfaces and Phytostabilisation in Waxes- a 3-Year Study[J]. International Journal of Phytoremediation, 215(3): 245-256. |
| [64] |
RAMANATHAN V, CARMICHAEL G, 2008. Global and regional climate changes due to black carbon[J]. Nature Geoscience, 1(4): 221-227.
DOI URL |
| [65] |
RAMANATHAN V, RAMANA M V, ROBERTS G, et al., 2007. Warming trends in Asia amplified by brown cloud solar absorption[J]. Nature, 448(7153): 575-578.
DOI URL |
| [66] | RAWSKI K L, 2019. Greenery planning for improvement of urban air quality-A review[J]. Proceedings, 16(1): 13. |
| [67] |
ROCCO P, RÜDIGER G, 2020. Deposition and resuspension mechanisms into and from tree canopies: A study modeling particle removal of conifers and broadleaves in different cities[J]. Frontiers in Forests and Global Change, DOI: 10.3389/ffgc.2020.00026.
DOI |
| [68] | ROY S, BYRNE J, PICKERING C, 2012. A systematic quantitative review of urban tree benefits, costs, and assessment methods across cities in different climatic zones[J]. Urban Forestry & Urban Greening, 11(4): 351-363. |
| [69] |
SÆBØ A, POPEK R, NAWROT B, et al., 2012. Plant species differences in particulate matter accumulation on leaf surfaces[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 427-428: 347-354.
DOI URL |
| [70] |
SANTIAGO J L, BUCCOLIERI R, RIVAS E, et al., 2019. CFD modelling of vegetation barrier effects on the reduction of traffic-related pollutant concentration in an avenue of Pamplona, Spain[J]. Sustainable Cities and Society, DOI: 10.1016/j.scs.2019.101559.
DOI |
| [71] |
SIVARAJAH S, THOMAS S C, SMITH S M, 2020. Evaluating the ultraviolet protection factors of urban broadleaf and conifer trees in public spaces[J]. Urban Forestry & Urban Greening, DOI: 10.1016/j.ufug.2020.126679.
DOI |
| [72] | SLINN W G N, 1982. Predictions for particle deposition to vegetative canopies[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 16(7): 1785-1794. |
| [73] |
SONG Y S, MAHER B A, LI F, et al., 2015. Particulate matter deposited on leaf of five evergreen species in Beijing, China: Source identification and size distribution[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 105: 53-60.
DOI URL |
| [74] |
TIWARI A, KUMAR P, BALDAUF R, et al., 2019. Considerations for evaluating green infrastructure impacts in microscale and macroscale air pollution dispersion models[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 672: 410-426.
DOI URL |
| [75] |
TIWARY A, MORVAN H P, COLLS J J, 2006. Modelling the size-dependent collection efficiency of hedgerows for ambient aerosols[J]. Journal of Aerosol Science, 37(8): 990-1015.
DOI URL |
| [76] |
TONG Z M, BALDAUF R W, ISAKOV V, et al., 2016. Roadside vegetation barrier designs to mitigate near-road air pollution impacts[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 541: 920-927.
DOI URL |
| [77] |
TURNER M C, KREWSKI D, POPE C A, et al., 2011. Long-term ambient fine particulate matter air pollution and lung cancer in a large cohort of never-smokers[J]. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, 184(12): 1374-1381.
DOI URL |
| [78] | UNITED STATES ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION AGENCY (USEPA), 2016. Recommendations for constructing roadside vegetation barriers to improve near-road air quality[EB/OL]. [2022-03-11]. https://www.epa.gov/air-research/recommendations-constructing-roadside-vegetation-barriers-improve-near-road-air-quality. |
| [79] |
WANG D, WANG Z, PENG Z R, 2020. Using unmanned aerial vehicle to investigate the vertical distribution of fine particulate matter[J]. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 17(1): 219-230.
DOI URL |
| [80] |
WANG H, MAHER B A, AHMED I A, et al., 2019. Efficient removal of ultrafine particles from diesel exhaust by selected tree species: Implications for roadside planting for improving the quality of urban air[J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 53(12): 6906-6916.
DOI URL |
| [81] |
WANIA A, BRSE M, BLOND N, et al., 2012. Analysing the influence of different street vegetation on traffic-induced particle dispersion using microscale simulations[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 94(1): 91-101.
DOI URL |
| [82] |
WU Y, HAO J, FU L, et al., 2002. Vertical and horizontal profiles of airborne particulate matter near major roads in Macao, China[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 36(31): 4907-4918.
DOI URL |
| [83] |
XIE C K, KAN L Y, GUO J K, et al., 2018. A dynamic processes study of PM retention by trees under different wind conditions[J]. Environmental Pollution, 233: 315-322.
DOI URL |
| [84] |
XING Y, BRIMBLECOMBE P, 2020. Trees and parks as “the lungs of cities”[J]. Urban Forestry & Urban Greening, DOI: 10.1016/j.ufug.2019.126552.
DOI |
| [85] |
XUE F, LI X F, 2017. The impact of roadside trees on traffic released PM10 in urban street canyon: Aerodynamic and deposition effects[J]. Sustainable Cities and Society, 30: 195-204.
DOI URL |
| [86] |
YANG H Y, CHEN T H, LIN Y Y, et al., 2020. Integrated impacts of tree planting and street aspect ratios on CO dispersion and personal exposure in full-scale street canyons[J]. Building and Environment, DOI: 10.1016/j.buildenv.2019.106529.
DOI |
| [87] |
ZHANG L, ZHANG Z Q, MCNULTY S, et al., 2020. The mitigation strategy of automobile generated fine particle pollutants by applying vegetation configuration in a street-canyon[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, DOI: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.122941.
DOI |
| [88] |
ZHANG W K, ZHANG Z, MENG H, et al., 2018. How does leaf surface micromorphology of different trees impact their ability to capture to capture particulate matter?[J]. Forests, 9(11): 681.
DOI URL |
| [89] |
ZHANG X Y, LYU J Y, HANY J, et al., 2020. Effects of the leaf functional traits of coniferous and broadleaved trees in subtropical monsoon regions on PM2.5 dry deposition velocities[J]. Environmental pollution, 265(Pt B): 114845.
DOI URL |
| [90] |
ZHENG T, LI B, LI X B, et al., 2021. Vertical and horizontal distributions of traffic-related pollutants beside an urban arterial road based on unmanned aerial vehicle observations[J]. Building and Environment, DOI: 10.1016/j.buildenv.2020.107401.
DOI |
| [91] | 曹云擎, 王体健, 高丽波, 等, 2020. 基于无人机垂直观测的南京PM2.5污染个例研究[J]. 气候与环境研究, 25(3): 292-304. |
| CAO Y Q, WANG T J, GAO L B, et al., 2020. Pollution in Nanjing based on unmanned aerial vehicle vertical observations[J]. Climatic and Environmental Research, 25(3): 292-304. | |
| [92] | 陈小平, 肖慧玲, 周志翔, 等, 2014. 城市道路典型绿带结构对总悬浮颗粒物的净化效应[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 23(11): 1620-1626. |
| CHEN X P, XIAO H L, ZHOU Z X, et al., 2014. The purification efficiency of road greenbelts with typical structures to total suspended particulates[J]. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 23(11): 1620-1626. | |
| [93] | 高国军, 徐彦森, 莫莉, 等, 2016. 植物叶片对不同粒径颗粒物的吸附效果研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 25(2): 260-265. |
| GAO G J, XU Y S, MO L, et al., 2016. The ability of plant leaves on depositing size-fractionated particles[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 25(2): 260-265. | |
| [94] | 顾康康, 钱兆, 方云皓, 等, 2020. 基于 ENVI-met的城市道路绿地植物配置对PM2.5的影响研究[J]. 生态学报, 40(13): 4340-4350. |
| GU K K, QIAN Z, FANG Y H, et al., 2020. Influence of vegetation arrangement on PM2.5 in urban roadside based on ENVI-met[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 40(13): 4340-4350. | |
| [95] | 郭晓华, 戴菲, 殷利华, 2018. 基于ENVI-met的道路绿带规划设计对PM2.5消减作用的模拟研究[J]. 风景园林, 25(12): 75-80. |
| GUO X H, DAI F, YIN L H, 2018. A simulation study on the effect of ENVI-met-based road greenbelt planning and design on PM2.5 reduction[J]. Landscape Architecture, 25(12): 75-80. | |
| [96] | 胡杨, 马克明, 2021a. 城市道路绿地对局地空气污染扩散的影响研究进展[J]. 应用生态学报, 32(1): 349-357. |
| HU Y, MA K M, 2021a. Research progress on the effects of urban road green space on dispersion of local air pollutant[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 32(1): 349-357. | |
| [97] | 胡杨, 马克明, 2021b. 城市街道绿化对空气质量及微气候影响的综合模拟研究[J]. 生态学报, 41(4): 1314-1331. |
| HU Y, MA K M, 2021b. A comprehensive simulation study on the influence of urban street greening on air quality and microclimatee[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 41(4): 1314-1331. | |
| [98] | 蒋德海, 蒋维楣, 苗世光, 2006. 城市街道峡谷气流和污染物分布的数值模拟[J]. 环境科学研究, 19(3): 7-12. |
| JIANG D W, JIANG W M, MIAO S G, 2006. The numerical simulation of air flow and pollutant distribution in street canyons[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 19(3): 7-12. | |
| [99] | 刘文清, 陈臻懿, 刘建国, 等, 2016. 我国大气环境立体监测技术及应用[J]. 科学通报, 61(30): 3196-3207. |
| LIU W Q, CHEN Z Y, LIU J G, et al., 2016. Stereoscopic monitoring technology and applications for the atmospheric environment in China[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 61(30): 3196-3207. | |
| [100] | 马克明, 殷哲, 张育新, 2018. 绿地滞尘效应研究方法和机理评估进展[J]. 生态学报, 38(12): 4482-4491. |
| MA K M, YIN Z, ZHANG Y X, 2018. Advancement in the method and mechanism of the green space dust retention effect[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 38(12): 4482-4491. | |
| [101] | 佘欣璐, 高吉喜, 张彪, 2020. 基于城市绿地滞尘模型的上海市绿色空间滞留PM2.5功能评估[J]. 生态学报, 40(8): 2599-2608. |
| SHE X L, GAO J X, ZHANG B, 2020. PM2.5 removal service of green spaces in Shanghai based on the dust retention simulation on urban vegetation[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 40(8): 2599-2608. | |
| [102] | 李修刚, 杨晓光, 王炜, 2001. 城市开阔道路的交通排气污染实验和模拟[J]. 中国公路学报, 14(S1): 63-67. |
| LI X G, YANG X G, WANG W, 2001. The experiment and simulation of traffic exhaust pollution near urban open road[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 14(S1): 63-67. | |
| [103] | 王亚英, 李萍, 武小钢, 等, 2015. 昼间气象条件对城市道路绿化带空气净化效果的影响——以太原市为例[J]. 生态学报, 35(4): 1267-1273. |
| WANG Y Y, LI P, WU X G, et al., 2015. Effects of meteorological factors on air purification by green belts along urban roads in the daytime: A case study in Taiyuan[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 35(4): 1267-1273. | |
| [104] | 殷杉, 蔡静萍, 陈丽萍, 等, 2007. 交通绿化带植物配置对空气颗粒物的净化效益[J]. 生态学报, 27(11): 4590-4595. |
|
YIN S, CAI L P, CHEN L P, et al., 2007. Efects of vegetation status in urban green spaces on particles removal in a canyon street atmosphere[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 27(11): 4590-4595.
DOI URL |
|
| [105] | 赵晓亮, 郭猛, 吕美婷, 等, 2021. 阜新市绿化树种对大气颗粒物及重金属滞留能力研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 30(8): 1662-1671. |
| ZHAO X L, GUO M, LÜ M T, et al., 2021. Study on retention capacity of green tree species to atmospheric particulate matter and heavy metals in Fuxin[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 30(8): 1662-1671. | |
| [106] | 周姝雯, 唐荣莉, 张育新, 等, 2017. 城市街道空气污染物扩散模型综述[J]. 应用生态学报, 28(3): 1039-1048. |
| ZHOU S W, TANG R L, ZHANG Y X, et al., 2017. A review of air pollutant diffusion models for urban street[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 28(3): 1039-1048. | |
| [107] | 周姝雯, 唐荣莉, 张育新, 等, 2018. 街道峡谷绿化带设置对空气流场及污染分布的影响模拟研究[J]. 生态学报, 38(17): 6348-6357. |
| ZHOU S W, TANG R L, ZHANG Y X, et al., 2018. Simulation study on the influence of green belt settings on air-flow and pollution distribution in street canyon[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 38(17): 6348-6357. |
| [1] | 杨凯, 杨靖睿, 曹培培, 吕春华, 孙文娟, 于凌飞, 邓希. CO2浓度升高下水稻株高、茎蘖与SPAD动态响应及其模拟[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 933-942. |
| [2] | 张广毅, 张嘉涛, 王晓伟. 湖泊底泥微生物燃料电池中磷形态分布及释放研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 590-598. |
| [3] | 周世强, Vanessa HULL, 张晋东, 刘巅, 谢浩, 黄金燕, 张和民. 野生大熊猫与放牧家畜利用生境的特征比较[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(2): 309-319. |
| [4] | 张莉, 李铖, 谭皓泽, 韦家怡, 程炯, 彭桂香. 广州典型城市林地对大气颗粒物的削减效应及影响因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(2): 341-350. |
| [5] | 刘希林, 卓瑞娜. 崩岗崩积体坡面初始产流时间影响因素及其临界阈值[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 36-46. |
| [6] | 李萍, 白小明, 陈鑫, 李娟霞, 冉福, 陈辉, 杨小妮, 康瑞卿. 白三叶入侵对禾本科草坪土壤特性和植物群落的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 70-79. |
| [7] | 石文静, 周翰鹏, 孙涛, 黄金涛, 杨文焕, 李卫平. 矿区周边土壤重金属污染优先控制因子及健康风险评价研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1616-1628. |
| [8] | 查木哈, 乌云嘎, 吴琴, 马成功, 白国栋, 邰峰, 张楠. 啮齿动物对旺业甸森林不同林木种子扩散格局的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(6): 1118-1123. |
| [9] | 段文军, 李达, 李冲. 5种不同林龄尾巨桉人工林林下植物多样性及其影响因素分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(5): 857-864. |
| [10] | 李春环, 王攀, 余海龙, 李冰, 黄菊莹. 西北荒漠煤矿区降水降尘中盐基离子沉降特征及其效应研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(5): 969-978. |
| [11] | 钱学诗, 李勇, 钱壮壮, 葛晓敏, 唐罗忠. 北亚热带东部次生阔叶林降水过程中的镉、铅、砷含量变化[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(5): 979-989. |
| [12] | 梁蕾, 马秀枝, 韩晓荣, 李长生, 张志杰. 模拟增温下凋落物对大青山油松人工林土壤温室气体通量的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(3): 478-486. |
| [13] | 朱旭, 李海梅, 李彦华, 孙迎坤, 田园. 8种灌木对大气颗粒物污染的生理响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(3): 535-545. |
| [14] | 石含之, 江棋, 刘帆, 文典, 黄永东, 邓腾灏博, 王旭, 徐爱平, 李富荣, 吴志超, 李梅霞, 彭锦芬, 杜瑞英. 水稻根茬还田对土壤及稻米中镉累积的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(2): 363-369. |
| [15] | 李春环, 王攀, 韩翠, 许艺馨, 黄菊莹. 硫氮沉降下西北荒漠煤矿区周边土壤性质的变化特点[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(1): 170-180. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
