生态环境学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (1): 170-180.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2022.01.019
李春环1,2( ), 王攀2, 韩翠3, 许艺馨2, 黄菊莹1,*(
), 王攀2, 韩翠3, 许艺馨2, 黄菊莹1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2021-06-24
出版日期:2022-01-18
发布日期:2022-03-10
通讯作者:
*黄菊莹(1980年生),女,研究员,主要从事全球变化生态学和生态系统生态学研究。E-mail: juyinghuang@163.com作者简介:李春环(1998年生),男,硕士研究生,主要从事大气酸沉降及其生态效应研究。E-mail: lichunhuan318@163.com
基金资助:
LI Chunhuan1,2( ), WANG Pan2, HAN Cui3, XU Yixin2, HUANG Juying1,*(
), WANG Pan2, HAN Cui3, XU Yixin2, HUANG Juying1,*( )
)
Received:2021-06-24
Online:2022-01-18
Published:2022-03-10
摘要:
近年来中国大部分区域大气硫、氮沉降速率趋于平稳甚至下降,但西北地区煤炭行业的快速发展使得硫、氮沉降速率加快。燃煤电厂作为酸前体物的主要排放源之一,在其周围开展硫、氮沉降效应研究,可为合理评价煤矿区大气污染物控制措施的实施效果提供数据支撑。该文以宁东能源化工基地3个燃煤电厂为采样点,研究了电厂周围土壤化学和生物学性质的变化特点,分析了其与降水降尘中硫、氮沉降量的关系。结果表明:研究区土壤pH变化范围分别为8.14—9.94,NO3--N质量分数、NH4+-N质量分数、速效P质量分数变化范围分别为0.34—1.32、0.37—0.67、0.18—1.18 mg∙kg-1,蔗糖酶活性变化范围为109.53—372.73 mg∙kg-1∙h-1。电导率、脲酶活性和磷酸酶活性变异系数较大,变化范围分别为51.60—3890.00 μS∙cm-1、12.36—51.80 mg∙kg-1∙h-1和13.98—77.26 mg∙kg-1∙h-1;各土壤指标在电厂间差异较大,在取样距离间差异较小,且无明显的规律性;土壤电导率、NH4+-N质量分数、速效P质量分数和磷酸酶活性与降水降尘中SO42-沉降量显著正相关(P<0.05)。土壤速效P质量分数、蔗糖酶活性和磷酸酶活性与降水降尘中NO3-沉降量显著负相关(P<0.05)。总体上,土壤pH与降水降尘中硫、氮沉降量相关性较弱。以上结果意味着,当前硫沉降强度有助于提高土壤磷酸酶活性、促进速效养分积累,氮沉降则表现出相反的效应,但二者均未对土壤pH产生明显影响。考虑到高架源大气污染物的长距离迁移性、酸沉降的时间累积性、土壤污染成分组成的复杂性等,今后还需延长取样距离,并结合土壤污染源成分分析,从较长时间尺度上深入探讨工业排放源周边硫、氮沉降的生态效应。
中图分类号:
李春环, 王攀, 韩翠, 许艺馨, 黄菊莹. 硫氮沉降下西北荒漠煤矿区周边土壤性质的变化特点[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(1): 170-180.
LI Chunhuan, WANG Pan, HAN Cui, XU Yixin, HUANG Juying. Variation Characteristics of Soil Properties Around A Northwest Desert Coal-mining Region under Sulphur and Nitrogen Deposition[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(1): 170-180.
图1 研究区采样点位置图 MLT、YYH和LW分别代表马莲台电厂、鸳鸯湖电厂和灵武电厂。下同
Figure 1 Location of the sampling points in studied area MLT, YYH, and LW represent Maliantai power plant, Yuanyanghu power plant, and Lingwu power plant, respectively. The same below
| 电厂 Power plant | SO42-沉降量 SO42- deposition/ (kg∙hm-2∙season-1) | NO3-沉降量 NO3- deposition/ (kg∙hm-2∙season-1) | NH4+沉降量 NH4+ deposition/ (kg∙hm-2∙season-1) | 无机氮沉降量 Inorganic N deposition/ (kg∙hm-2∙season-1) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 变化范围 Variation range | 平均值 Mean | 变化范围 Variation range | 平均值 Mean | 变化范围 Variation range | 平均值 Mean | 变化范围 Variation range | 平均值 Mean | ||||
| MLT | 6.33-9.64 | 8.06 | 3.18-4.27 | 3.57 | 0.58-0.84 | 0.75 | 3.89-5.05 | 4.32 | |||
| YYH | 4.69-7.81 | 6.18 | 3.50-4.53 | 3.90 | 0.50-0.75 | 0.63 | 4.11-5.14 | 4.53 | |||
| LW | 6.31-10.22 | 8.33 | 2.73-4.88 | 3.18 | 0.51-0.77 | 0.68 | 3.26-4.90 | 6.00 | |||
表1 电厂周围硫、氮季沉降量的变化特征
Table 1 Variations of seasonal sulfur and nitrogen deposition around the three studied power plants
| 电厂 Power plant | SO42-沉降量 SO42- deposition/ (kg∙hm-2∙season-1) | NO3-沉降量 NO3- deposition/ (kg∙hm-2∙season-1) | NH4+沉降量 NH4+ deposition/ (kg∙hm-2∙season-1) | 无机氮沉降量 Inorganic N deposition/ (kg∙hm-2∙season-1) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 变化范围 Variation range | 平均值 Mean | 变化范围 Variation range | 平均值 Mean | 变化范围 Variation range | 平均值 Mean | 变化范围 Variation range | 平均值 Mean | ||||
| MLT | 6.33-9.64 | 8.06 | 3.18-4.27 | 3.57 | 0.58-0.84 | 0.75 | 3.89-5.05 | 4.32 | |||
| YYH | 4.69-7.81 | 6.18 | 3.50-4.53 | 3.90 | 0.50-0.75 | 0.63 | 4.11-5.14 | 4.53 | |||
| LW | 6.31-10.22 | 8.33 | 2.73-4.88 | 3.18 | 0.51-0.77 | 0.68 | 3.26-4.90 | 6.00 | |||
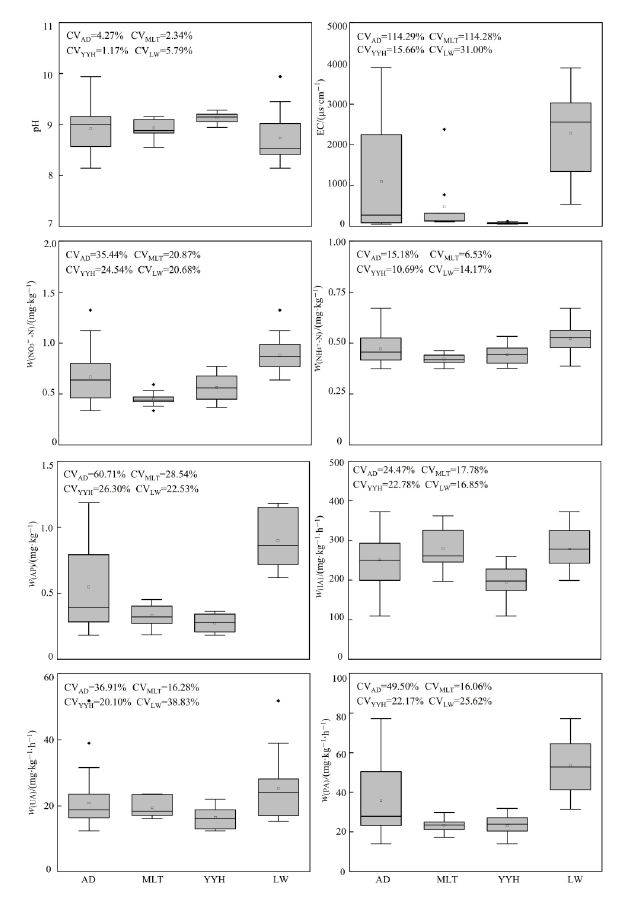
图2 研究区土壤性质的变化范围 AD代表3个电厂的所有数据(n=36)。马莲台电厂(MLT),n=9。鸳鸯湖电厂(YYH),n=12。灵武电厂(LW),n=15。pH和EC分别代表土壤pH和电导率。NO3--N、NH4+-N、AP分别代表土壤NO3--N、NH4+-N和速效P质量分数。IA、UA、PA分别代表土壤蔗糖酶、脲酶和磷酸酶活性。下同
Figure 2 The changing ranges of soil properties in studied area AD represents all data in the three studied power plants (n=36). Maliantai power plant (MLT), n=9. Yuanyanghu power plant (YYH), n=12. Lingwu power plant (LW), n=15. pH and EC represent soil pH and electrical conductivity, respectively. NO3--N, NH4+-N, and AP represent soil NO3--N, NH4+-N, and available phosphorus mass fraction, respectively. IA, UA, and PA represent soil invertase activity, urease activity, and phosphatase activity, respectively. The same below
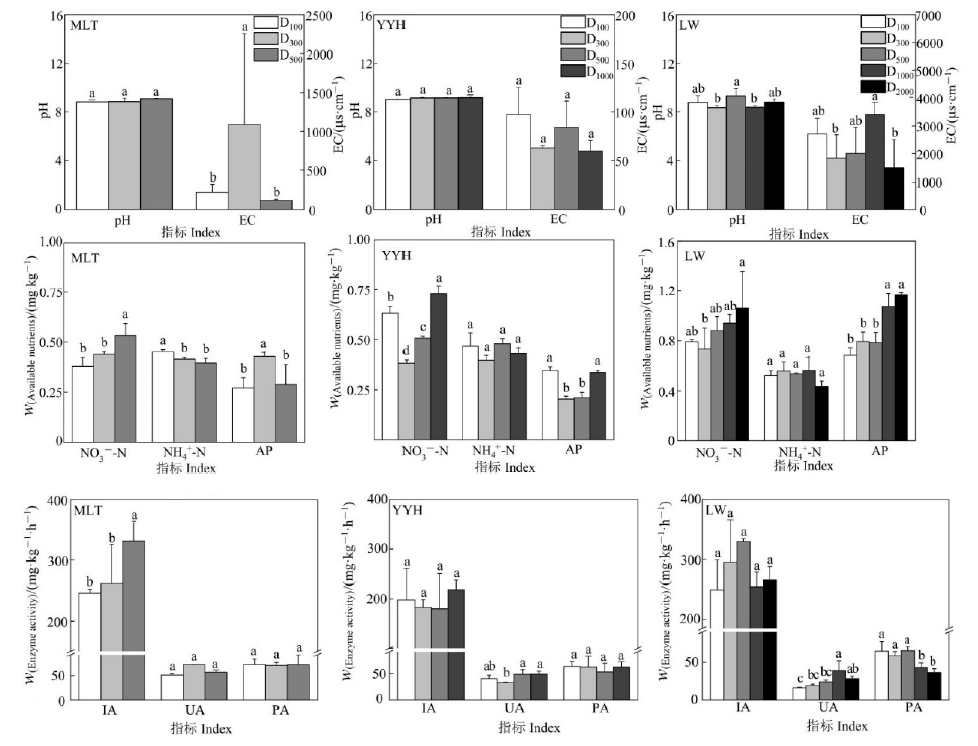
图3 取样距离间电厂周围土壤性质的差异 D100、D300、D500、D1000和D2000分别代表距离电厂围墙外100、300、500、1000和2000 m的取样距离(n=3)。不同小写字母代表3个电厂取样距离间各指标的差异显著(P<0.05)
Figure 3 The differences of soil properties among the sampling distances around the three studied power plants D100, D300, D500, D1000, and D2000 represent the sampling points are 100, 300, 500, 1000 and 2000 m far from the enclosing wall of power plants, respectively (n=3). Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences of each index among distances in the three power plants (P<0.05)
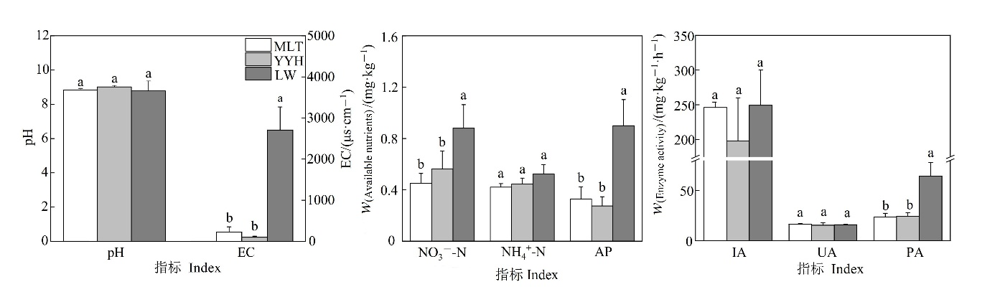
图4 3个电厂间土壤性质的差异 不同小写字母代表3个电厂间各指标的差异显著(P<0.05)
Figure 4 The differences of soil properties among the three studied power plants Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences of each index among the three power plants (P<0.05)
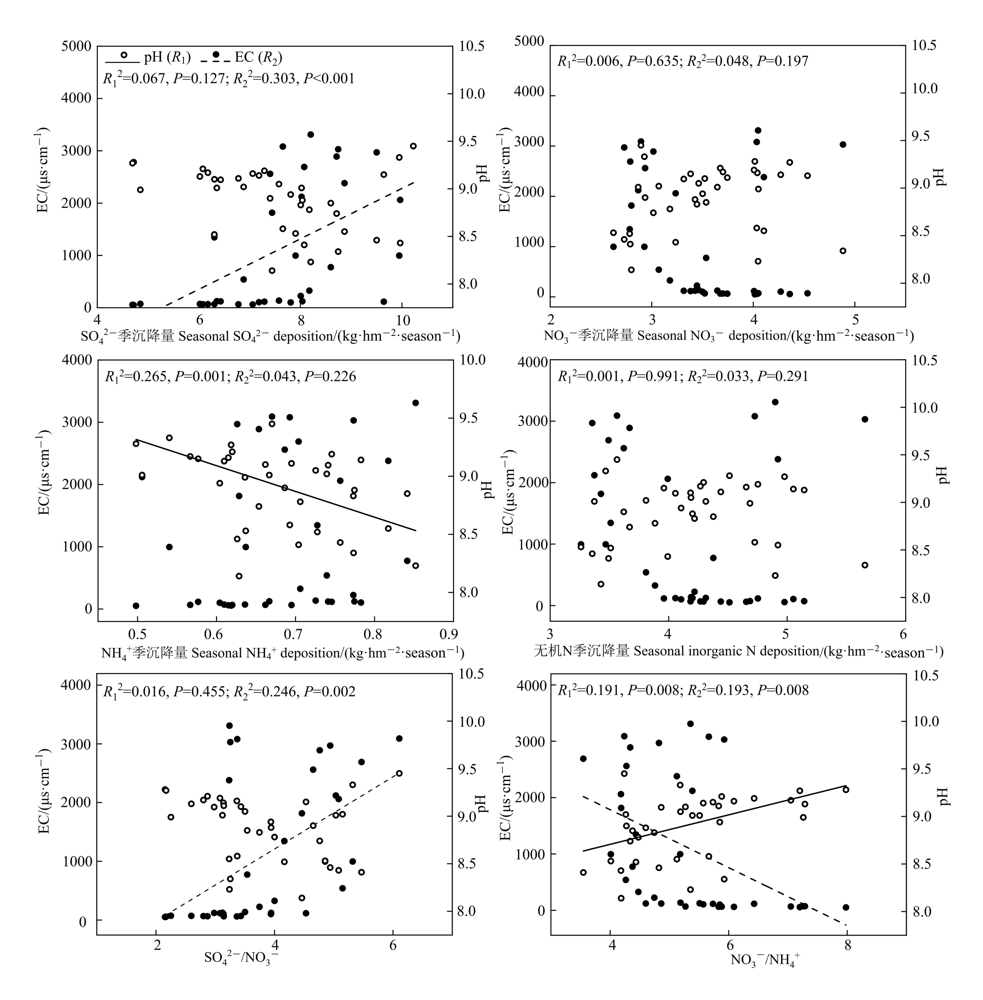
图5 土壤pH和电导率与降水降尘中硫、氮沉降的关系
Figure 5 The relationships of soil pH and electrical conductivity with the deposition of sulphur and nitrogen in precipitation and dustfall n=36. The same below
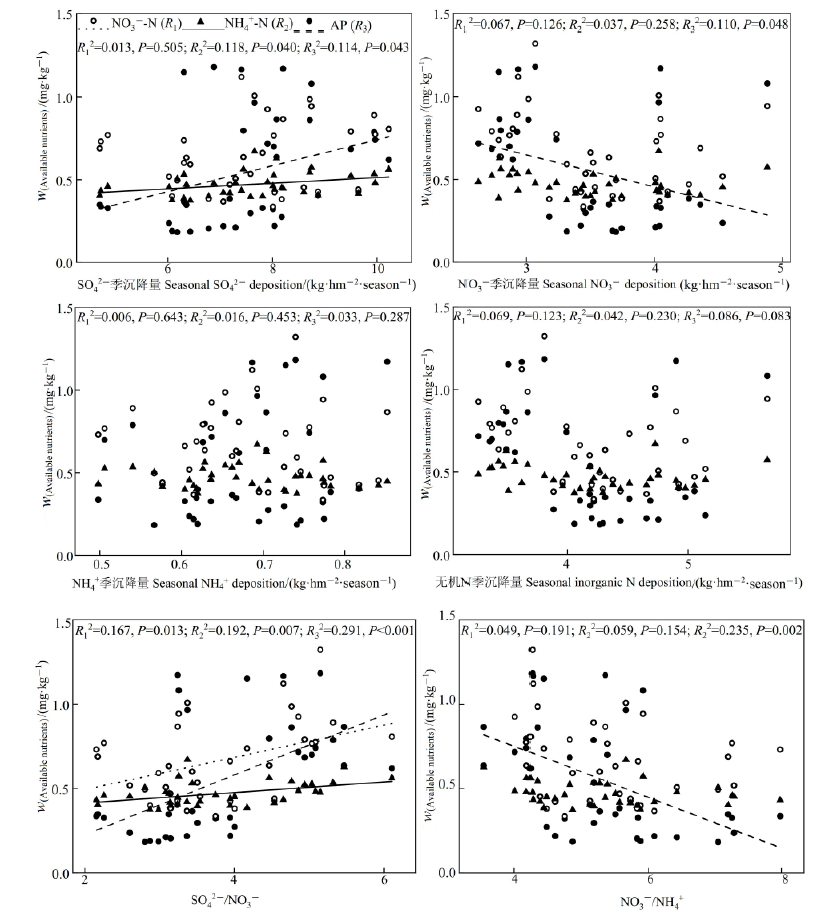
图6 土壤速效养分与降水降尘中硫、氮沉降的关系
Figure 6 The relationships of soil available nutrients with the deposition of sulphur and nitrogen in precipitation and dustfall
| [1] | BROWN L, SCHOLEFIELD D, JEWKES E C, et al., 2000. The effect of Sulphur application on the efficiency of nitrogen use in two contrasting grassland soils[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science, 135(2): 131-138. |
| [2] |
CHEN J, VAN GROENIGEN K J, HUNGATE B A, et al., 2020. Long-term nitrogen loading alleviates phosphorus limitation in terrestrial ecosystems[J]. Global Change Biology, 26(9): 5077-5086.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
FORSTNER S F, WECHSELBERGER V, STECHER S, et al., 2019. Resistant soil microbial communities show signs of increasing phosphorus limitation in two temperate forests after long-term nitrogen addition[J]. Frontiers in Forests and Global Change, DOI: 10.3389/ffgc.2019.00073.
DOI |
| [4] |
FORSIUS M, POSCH M, HOLMBERG M, et al., 2021. Assessing critical load exceedances and ecosystem impacts of anthropogenic nitrogen and sulphur deposition at unmanaged forested catchments in Europe[J]. The Science of the Total Environment, DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.141791.
DOI |
| [5] |
GAO Y, MA M Z, YANG T, et al., 2018. Global atmospheric sulfur deposition and associated impaction on nitrogen cycling in ecosystems[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 195: 1-9.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
JUNG K, KWAK J H, GILLIAM F S, et al., 2018. Simulated N and S deposition affected soil chemistry and understory plant communities in a boreal forest in western Canada[J]. Journal of Plant Ecology, 11(4): 511-523.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
KIM H, KANG H, 2011. The impacts of excessive nitrogen additions on enzyme activities and nutrient leaching in two contrasting forest soils[J]. The Journal of Microbiology, 49(3): 369-375.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
KIVLIN S N, TRESEDER K K, 2014. Soil extracellular enzyme activities correspond with abiotic factors more than fungal community composition[J]. Biogeochemistry, 117(1): 23-37.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
LUO W T, NELSON P N, LI M H, et al., 2015. Contrasting pH buffering patterns in neutral-alkaline soils along a 3600 km transect in northern China[J]. Biogeosciences, 12(23): 7047-7056.
DOI URL |
| [10] | LI R, CUI L L, ZHAO Y L, et al., 2019. Wet deposition of inorganic ions in 320 cities across China: spatiotemporal variation, source apportionment, and dominant factors[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 19(17): 11043-11070. |
| [11] |
PHOENIX G K, EMMETT B A, BRITTON A J, et al., 2012. Impacts of atmospheric nitrogen deposition: responses of multiple plant and soil parameters across contrasting ecosystems in long-term field experiments[J]. Global Change Biology, 18(4): 1197-1215.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
PERINGE G, ANNA E, MARTIN F, et al., 2020. Acid rain and air pollution: 50 years of progress in environmental science and policy[J]. Ambio: A Journal of the Human Environment, 49(33): 849-964.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
REZAPOUR S, 2014. Effect of sulfur and composted manure on SO4-S, P and micronutrient availability in a calcareous saline-sodic soil[J]. Chemistry and Ecology, 30(2): 147-155.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
TIAN D S, NIU S L, 2015. A global analysis of soil acidification caused by nitrogen addition[J]. Environmental Research Letters, 10(2): 024019.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
WEN Z, XU W, LI Q, et al., 2020. Changes of nitrogen deposition in China from 1980 to 2018 [J]. Environment International, DOI: 10.1016/j.envint.2020.106022.
DOI |
| [16] |
XIAO W, CHEN X, JING X, et al., 2018. A meta-analysis of soil extracellular enzyme activities in response to global change[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 123: 21-32.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
YU H L, HE N P, WANG Q F, et al., 2017. Development of atmospheric acid deposition in China from the 1990s to the 2010s[J]. Environmental Pollution, 231(Part 1): 182-190.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
YU G R, JIA Y L, HE N P, et al., 2019. Stabilization of atmospheric nitrogen deposition in China over the past decade[J]. Nature Geoscience, 12(6): 424-429.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
ZARFOS M R, DOVCIAK M, LAWRENCE G B, et al., 2019. Plant richness and composition in hardwood forest understories vary along an acidic deposition and soil-chemical gradient in the northeastern United States[J]. Plant and Soil, 438: 461-477.
DOI URL |
| [20] | ZHENG B, TONG D, LI M, et al., 2018. Trends in China's anthropogenic emissions since 2010 as the consequence of clean air action[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 18(19): 14095-14111. |
| [21] | 鲍士旦, 2000. 土壤农化分析[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社. |
| BAO S D, 2000. Soil and Agricultural Chemistry Analysis[M]. Beijing: China Agriculture Press. | |
| [22] | 白春华, 红梅, 韩国栋, 等, 2012. 土壤三种酶活性对温度升高和氮肥添加的响应[J]. 内蒙古大学学报(自然科学版), 43(5): 509-513. |
| BAI C H, HONG M, HAN G D, et al., 2012. Response of three kinds of enzyme activity to simulate warming and nitrogen addition[J]. Journal of Inner Mongolia University (Natural Science Edition), 43(5): 509-513. | |
| [23] | 陈向峰, 刘娟, 姜培坤, 等, 2020. 模拟氮沉降对毛竹林土壤生化特性和酶活性的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 34(5): 277-284. |
| CHEN X F, LIU J, JIANG P K, et al., 2020. Effects of nitrogen deposition on soil biochemical properties and enzymes activities in moso bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis) forest[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 34(5): 277-284. | |
| [24] | 段雷, 郝吉明, 谢绍东, 等, 2002. 用稳态法确定中国土壤的硫沉降和氮沉降临界负荷[J]. 环境科学, 23(2): 7-12. |
| DUAN L, HAO J M, XIE S D, et al., 2002. Estimating critical loads of sulfur and nitrogen for Chinese soils by steady state method[J]. Environmental Science, 23(2): 7-12. | |
| [25] | 杜锟, 张江勇, 林勇明, 等, 2015. 邓恩桉 (Eucalyptus dunnii) 人工幼龄林土壤酶活性对模拟硫、氮复合沉降的响应[J]. 热带作物学报, 36(3): 504-509. |
| DU K, ZHANG J Y, LIN Y M, et al., 2015. Responses of soil enzymes activities to simulated sulfur and nitrogen complex depositions in a young Eucalyptus dunnii plantation[J]. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops, 36(3): 504-509. | |
| [26] | 房焕英, 肖胜生, 潘萍, 等, 2019. 湿地松林土壤生化特性和酶活性对模拟硫沉降的响应[J]. 水土保持学报, 33(6): 318-325. |
| FANG H Y, XIAO S S, PAN P, et al. 2019. Effects of Sulphur deposition on soil biochemical properties and enzymes activities in Pinus elliottii plantation[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 33(6): 318-325. | |
| [27] | 付亚宁, 范秀华, 邹璐, 等, 2010. 马莲台电厂周围土壤重金属污染风险评价研究[J]. 科学技术与工程, 10(23): 5827-5830. |
| FU Y N, FAN X H, ZOU L, et al., 2010. Pollution evaluation of heavy metals in soils around Maliantai thermal power plant[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 10(23): 5827-5830. | |
| [28] | 国家环境保护总局, 国家技术监督局, 1994. 环境空气降尘标准: GB/T 15265-1994[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社: 1-4. |
| State Environmental Protection Bureau, State Bureau of Quality and Technical Supervision, 1994. Ambient Air Dust Reduction Standard: GB/T 15265-1994[S]. Beijing: China Standard Press: 1-4. | |
| [29] | 国家环境保护总局, 2004. 酸沉降监测技术规范:HJ/T 165-2004[S]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社: 1-26. |
| State Environmental Protection Bureau, 2004. Technical Specifications for Acid Deposition Monitoring: HJ/T165-2004[S]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press: 1-26. | |
| [30] | 郭平, 2016. 三峡库区酸沉降特征及其对森林土壤的影响[D]. 北京: 北京林业大学. |
| GUO P, 2016. Characteristics of acid deposition and its effects on forest soil in the Three Gorges Reservoir area[D]. Beijing: Beijing Forestry University. | |
| [31] | 姜勇, 李天鹏, 冯雪, 等, 2019. 外源硫输入对草地土壤-植物系统养分有效性的影响[J]. 生态学杂志, 38(4): 1192-1201. |
| JIANG Y, LI T P, FENG X, et al., 2019. Effects of exogenous sulfur input on nutrient availability in soil-plant system of grassland[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 38(4): 1192-1201. | |
| [32] | 刘平, 张强, 程滨, 等, 2010. 电厂煤粉尘沉降特征及其对周边土壤主要性质的影响[J]. 中国土壤与肥料 (5): 21-24. |
| LIU P, ZHANG Q, CHENG B, et al., 2010. The deposition law of coal dust from power generation plant and its effects on prosperities of the surrounding soil[J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China (5): 21-24. | |
| [33] | 刘星, 汪金松, 赵秀海, 2015. 模拟氮沉降对太岳山油松林土壤酶活性的影响[J]. 生态学报, 35(14): 4613-4624. |
| LIU X, WANG J S, ZHAO X H, 2015. Effects of simulated nitrogen deposition on the soil enzyme activities in a Pinus tabulaeformis forest at the Taiyue Mountain[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 35(14): 4613-4624. | |
| [34] | 罗成科, 张佳瑜, 肖国举, 等, 2018. 宁东基地不同燃煤电厂周边土壤5种重金属元素污染特征及生态风险[J]. 生态环境学报, 27(7): 1285-1291. |
| LUO C K, ZHANG J Y, XIAO G J, et al., 2018. Pollution characteristics and ecological assessment of heavy metals in soil around different coal-fired power plants of Ningdong Base[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 27(7): 1285-1291. | |
| [35] | 李玉平, 2010. 高架污染源的最大地面浓度及位置[J]. 安全与环境学报, 10(6): 89-91. |
| LI Y P, 2010. Maximum ground concentration and its location formed by an elevated pollution sources[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 10(6): 89-91. | |
| [36] | 李志雄, 梁美生, 姜俊杰, 2017. 火电厂周围大气环境中硫化物分布规律的探讨[J]. 环境工程学报, 11(2): 998-1002. |
| LI Z X, LIANG M S, JIANG J J, 2017. Investigation of distribution rule of sulfide located in ambient thermal power plant[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 11(2): 998-1002. | |
| [37] | 刘红梅, 周广帆, 李洁, 等, 2018. 氮沉降对贝加尔针茅草原土壤酶活性的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 27(8): 1387-1394. |
| LIU H M, ZHOU G F, LI J, et al., 2018. Effects of nitrogen deposition on soil enzyme activities of Stipa baicalensis steppe[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 27(8): 1387-1394. | |
| [38] | 梁晓雪, 2019. 我国能源金三角宁东煤化工基地大气细颗粒物的污染特征及来源解析[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学. |
| LIANG X X, 2019. Contamination characteristics and source apportionment of fine particles in Ningdong Coal Chemical Industrial Base of the Energy Golden Triangle, China[D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University. | |
| [39] | 苗琦, 孟刚, 陈敏, 等, 2020. 我国煤炭资源可供性分析及保障研究[J]. 能源与环境 (2): 6-8, 23. |
| MIAO Q, MENG G, CHEN M, et al., 2020. Study on the availability and guarantee of coal resources in China[J]. Energy and Environment (2): 6-8, 23. | |
| [40] | 裴旭倩, 2015. 基于ADMS的火电厂高架源排放二氧化硫浓度分布特征研究[D]. 太原: 太原理工大学. |
| [41] | PEI X Q, 2015. Research on concentration distribution characteristics of SO2 discharged from Coal-fired power plant elevated source based on ADMS[D]. Taiyuan: Taiyuan University of Technology. |
| [42] | 沈芳芳, 袁颖红, 樊后保, 等, 2012. 氮沉降对杉木人工林土壤有机碳矿化和土壤酶活性的影响[J]. 生态学报, 32(2): 517-527. |
|
SHEN F F, YUAN Y H, FAN H B, et al., 2012. Effects of elevated nitrogen deposition on soil organic carbon mineralization and soil enzyme activities in a Chinese fir plantation[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 32(2): 517-527.
DOI URL |
|
| [43] | 佟海, 2016. 火电厂周围土壤和水体硫化物分布规律与其排放硫的相关性探讨[D]. 太原: 太原理工大学. |
| TONG H, 2016. Investigation of the sulfides distribution charcteristics in soil and water around the thermal power plant and its relationship to sulphur emissions[D]. Taiyuan: Taiyuan University of Technology. | |
| [44] | 魏枫, 王慧娟, 邱秀文, 等, 2019. 模拟氮沉降对樟树人工林土壤酶活性的影响[J]. 江苏农业科学, 47(19): 129-133. |
| WEI F, WANG H J, QIU X W, et al., 2019. Effects of simulated nitrogen deposition on soil enzyme activities in Cinnamomum camphora plantation[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 47(19): 129-133. | |
| [45] | 王攀, 朱湾湾, 樊瑾, 等, 2020. 宁夏燃煤电厂周围降水降尘中硫氮沉降特征研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 29(6): 1189-1197. |
| WANG P, ZHU W W, FAN J, et al., 2020. Sulfur and nitrogen deposition near three coal-fired power plants in Ningxia[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 29(6): 1189-1197. | |
| [46] | 肖海兵, 李忠武, 聂小东, 等, 2016. 南方红壤丘陵区土壤侵蚀-沉积作用对土壤酶活性的影响[J]. 土壤学报, 53(4): 881-890. |
| XIAO H B, LI Z W, NIE X D, et al., 2016. Effects of soil erosion and deposition on soil enzyme activity in hilly red soil regions of south China[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 53(4): 881-890. | |
| [47] | 张艺, 王春梅, 许可, 等, 2017. 模拟氮沉降对温带森林土壤酶活性的影响[J]. 生态学报, 37(6): 1956-1965. |
| ZHANG Y, WANG C M, XU K, et al., 2017. Effect of simulated nitrogen deposition on soil enzyme activities in a temperate forest[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 37(6): 1956-1965. | |
| [48] | 周纪东, 史荣久, 赵峰, 等, 2016. 施氮频率和强度对内蒙古温带草原土壤pH及碳、氮、磷含量的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 27(8): 2467-2476. |
| ZHOU J D, SHI R J, ZHAO F, et al., 2016. Effects of the frequency and intensity of nitrogen addition on soil pH, the contents of carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus in temperate steppe in Inner Mongolia, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 27(8): 2467-2476. | |
| [49] | 周晓兵, 张元明, 2009. 干旱半干旱区氮沉降生态效应研究进展[J]. 生态学报, 29(7): 3835-3845. |
| ZHOU X B, ZHANG Y M, 2009. Review on the ecological effects of N deposition in arid and semi-arid areas[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 29(7): 3835-3845. |
| [1] | 盛美君, 李胜君, 杨昕玥, 王蕊, 李洁, 李刚, 修伟明. 华北潮土农田土壤酶活性对土地利用强度的响应特征探讨[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(2): 299-308. |
| [2] | 向兴, 满百膺, 张俊忠, 罗洋, 毛小涛, 张超, 孙丙华, 王希. 黄山土壤细菌群落及氮循环功能群的垂向分布格局[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 56-69. |
| [3] | 王瑞, 宋祥云, 柳新伟. 黄河三角洲不同植被类型土壤酶活性的季节变化[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(1): 62-69. |
| [4] | 李欣, 陈小华, 顾海蓉, 钱晓雍, 沈根祥, 赵庆节, 白玉杰. 典型农田土壤酶活性分布特征及影响因素分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(8): 1634-1641. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
