生态环境学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (3): 590-598.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2023.03.016
收稿日期:2022-11-21
出版日期:2023-03-18
发布日期:2023-06-02
作者简介:张广毅(1985年生),男,副教授,博士,研究方向为水污染控制、微生物腐蚀、生物电化学。E-mail: Zhanggy@zzu.edu.cn
基金资助:
ZHANG Guangyi1( ), ZHANG Jiatao1, WANG Xiaowei2
), ZHANG Jiatao1, WANG Xiaowei2
Received:2022-11-21
Online:2023-03-18
Published:2023-06-02
摘要:
针对沉积物中沉积磷(P)通过微生物活动再释放,致使湖泊富营养化反复的问题,采集郑州大学眉湖上覆水和沉积物,搭建一个沉积式微生物燃料电池(Sediment Microbial Fuel Cell,SMFC)系统,研究了通过SMFC限制沉积磷向上覆水体释放的方法。实验周期内监测SMFC的电压和阳极电极电位、上覆水温度pH、沉积物磷的Standards Measurements and Testing(SMT)法分级提取;并在实验开始与结束收集阳极微生物样进行微生物群落及基因分析;首次使用氧化锆薄膜扩散梯度技术(Zr-Oxide Diffusive Gradients in Thin-films,Zr-Oxide DGT)可视化了SMFC沉积物中不稳定磷亚毫米分辨率的浓度分布。结果表明:SMFC阳极电极电位从-100 mV升至230 mV;上覆水pH从7.15升至7.46;SMFC沉积物烧失量(Loss on Ignition,LOI)从18.31%±0.7%降至13.09%±1.10%,低于对照组的14.29%±2.10%;SMFC显著促进了孔隙水磷向沉积物磷的矿化过程,在沉积物垂向方向上,NaOH-P和HCl-P出现了明显的区域性增加;根据沉积物DGT磷的二维(2D)图像,SMFC使沉积物DGT磷的浓度最低降至初始值的66%;基于京都基因与基因组百科全书(Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes,KEGG)数据库的功能基因分析,SMFC使磷相关功能基因丰度显著增加。证明SMFC对于沉积物磷和水相磷分布有显著影响,通过基质竞争、提高阳极电位等方式减弱固相磷的溶解,促进水相磷向沉积相磷的转化,可用于富营养化水体原位底泥磷稳定化。该文深入研究了SMFC固磷作用机理,为修复水体内源磷污染提供了一种新思路。
中图分类号:
张广毅, 张嘉涛, 王晓伟. 湖泊底泥微生物燃料电池中磷形态分布及释放研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 590-598.
ZHANG Guangyi, ZHANG Jiatao, WANG Xiaowei. Phosphorus Speciation Distribution and Release in Lake Sediment Microbial Fuel Cells[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(3): 590-598.
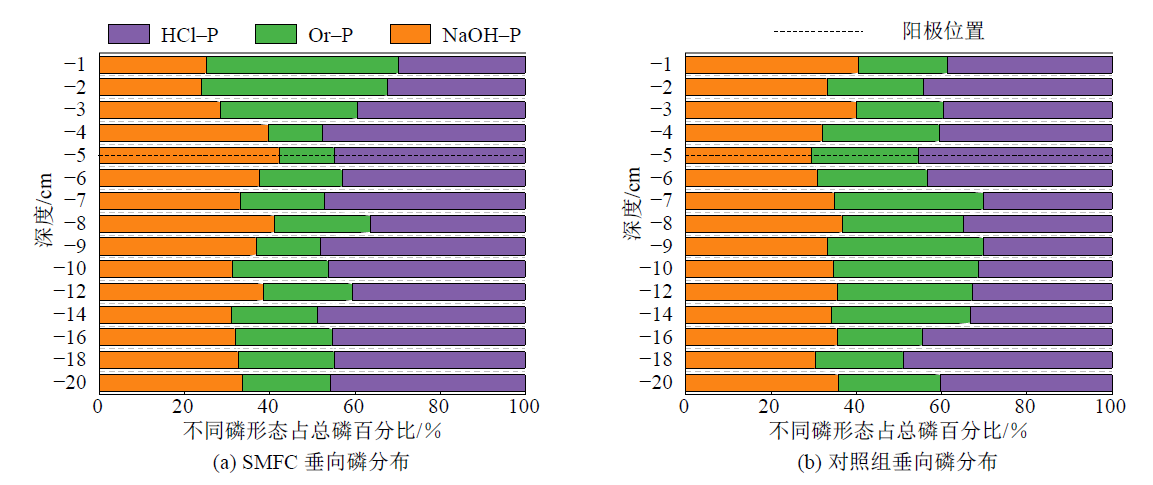
图4 实验结束时SMFC(a)和对照组(b)的沉积物垂向磷分布
Figure 4 Phosphorus fractionation in the vertical sediments of SMFC (a) and the control (b) at the end of the experiments
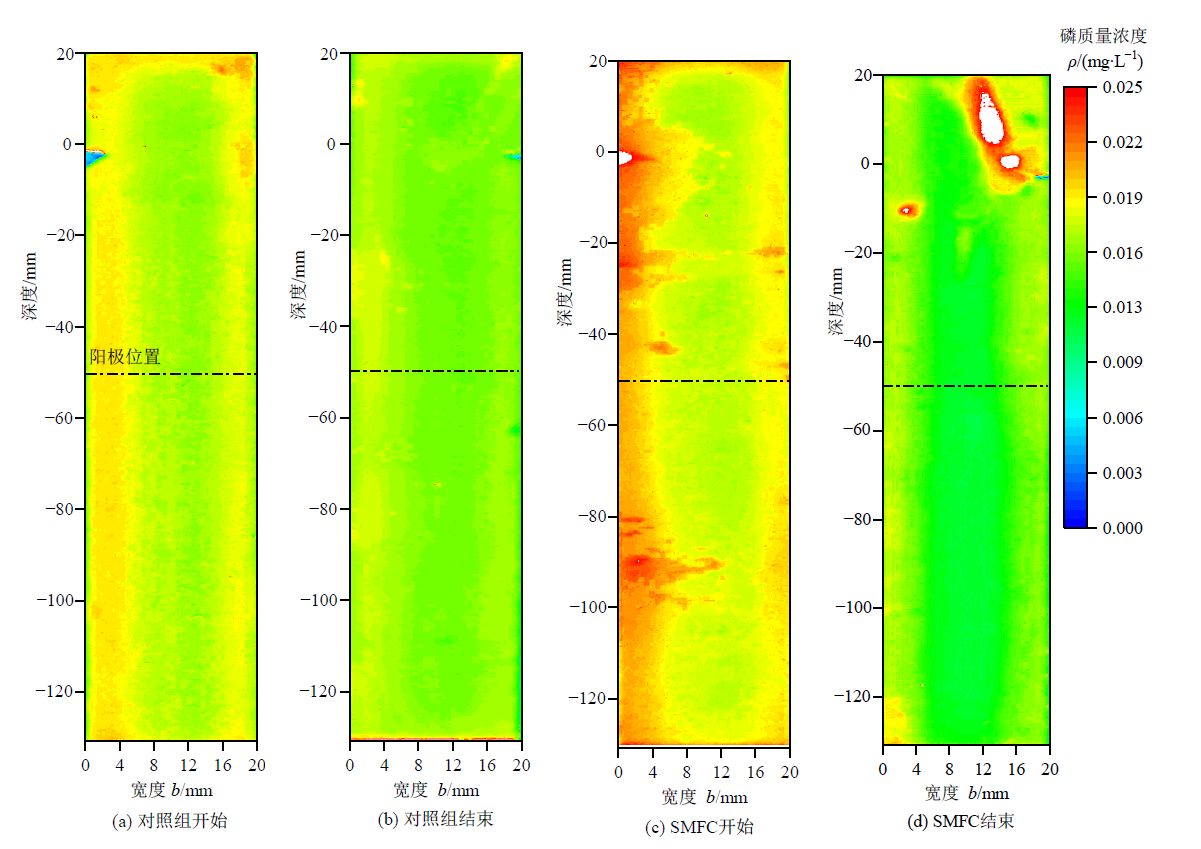
图5 实验开始和结束时SMFC和对照组沉积物的DGT磷的二维分布
Figure 5 Two-dimensional distribution of DGT-P in SMFC and control group sediment at the beginning and end of the experiment
| [1] |
AGSTAM-NORLIN O, LANNERGARD E E, FUTTER M N, et al., 2020. Optimization of aluminum treatment efficiency to control internal phosphorus loading in eutrophic lakes[J]. Water Research, 185: 116150.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
ALVARADO J N, HONG S H, LEE C G, et al., 2020. Comparison of capping and mixing of calcined dolomite and zeolite for interrupting the release of nutrients from contaminated lake sediment[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 27(13): 15045-15056.
DOI |
| [3] |
CARLTON R G, WETZEL R G, 1988. Phosphorus flux from lake-sediments: Effect of epipelic algal oxygen production[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 33(4): 562-570.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
CHEN Y, CHEN M, SHEN N, et al., 2016. H2 production by the thermoelectric microconverter coupled with microbial electrolysis cell[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 41(48): 22760-22768.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
CHOWDHURY M, BAKRI D A, 2006. Diffusive nutrient flux at the sediment-water interface in Suma Park Reservoir, Australia[J]. Hydrological Sciences Journal, 51(1): 144-156.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
CONDRON L M, NEWMAN S, 2011. Revisiting the fundamentals of phosphorus fractionation of sediments and soils[J]. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 11(5): 830-840.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
DING S M, HAN C, WANG Y P, et al., 2015. In situ, high-resolution imaging of labile phosphorus in sediments of a large eutrophic lake[J]. Water research, 74: 100-109.
DOI PMID |
| [8] |
DING S M, WANG Y, XU D, et al., 2013. Gel-based coloration technique for the submillimeter-scale imaging of labile phosphorus in sediments and soils with diffusive gradients in thin films[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 47(14): 7821-7829.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
DING S M, XU D, SUN Q, et al., 2010. Measurement of dissolved reactive phosphorus using the diffusive gradients in thin films technique with a high-capacity binding phase[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 44(21): 8169-8174.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
GILES C D, ISLES P, MANLEY T, et al., 2016. The mobility of phosphorus, iron, and manganese through the sediment-water continuum of a shallow eutrophic freshwater lake under stratified and mixed water-column conditions[J]. Biogeochemistry, 127(1): 15-34.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
GUSTAVE W, YUAN Z, LIU F, et al., 2021. Mechanisms and challenges of microbial fuel cells for soil heavy metal(loid)s remediation[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 756: 143865.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
GUSTAVE W, YUAN Z F, SEKAR R, et al., 2019. Soil organic matter amount determines the behavior of iron and arsenic in paddy soil with microbial fuel cells[J]. Chemosphere, 237: 124459.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
HAXTHAUSEN K A V, LU X, ZHANG Y, et al., 2021. Novel method to immobilize phosphate in lakes using sediment microbial fuel cells[J]. Water Research, 198: 117108.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
HONG S W, KIM H J, CHOI Y S, et al., 2008. Field experiments on bioelectricity production from lake sediment using microbial fuel cell technology[J]. Bulletin of the Korean Chemical Society, 29(11): 2189-2194.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
LI R H, CUI J L, HU J H, et al., 2020. Transformation of Fe-P complexes in bioreactors and P recovery from sludge: investigation by XANES spectroscopy[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 54(7): 4641-4650.
DOI URL |
| [16] | MARTINS G, PEIXOTO L, BRITO A G, et al., 2014. Phosphorus-iron interaction in sediments: can an electrode minimize phosphorus release from sediments?[J]. Reviews in Environmental Science and Bio-Technology, 13(3): 265-275. |
| [17] |
MARTINS G, PEIXOTO L, RIBEIRO D C, et al., 2010. Towards implementation of a benthic microbial fuel cell in lake Furnas (Azores): Phylogenetic affiliation and electrochemical activity of sediment bacteria[J]. Bioelectrochemistry, 78(1): 67-71.
DOI PMID |
| [18] |
NUR R, BATES M H, 1979. The effects of pH on the aluminum, iron and calcium phosphate fractions of lake sediments[J]. Water Research, 13(8): 813-815.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
PING Q, LU X, LI Y M, et al., 2020. Effect of complexing agents on phosphorus release from chemical-enhanced phosphorus removal sludge during anaerobic fermentation[J]. Bioresource Technology, 301: 122745.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
RUBAN V, LOPEZ-SANCHEZ J F, PARDO P, et al., 2001. Harmonized protocol and certified reference material for the determination of extractable contents of phosphorus in freshwater sediments - a synthesis of recent works[J]. Fresenius Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 370(2-3): 224-228.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
SCHINDLER D W, 2006. Recent advances in the understanding and management of eutrophication[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 51(1): 356-363.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
SCHINDLER D W, 2012. The dilemma of controlling cultural eutrophication of lakes[J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society B-Biological Sciences, 279(1746): 4322-4333.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
STOCKDALE A, DAVISON W, ZHANG H, 2009. Micro-scale biogeochemical heterogeneity in sediments: A review of available technology and observed evidence[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 92(1-2): 81-97.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
SUN Q, CHEN J, ZHANG H, et al., 2014. Improved diffusive gradients in thin films (DGT) measurement of total dissolved inorganic arsenic in waters and soils using a hydrous zirconium oxide binding layer[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 86(6): 3060-3067.
DOI PMID |
| [25] |
VAN DAEL T, DE COOMAN T, SMOLDERS E, 2020a. In-stream oxygenation to mitigate internal loading of phosphorus in lowland streams[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 590: 125536.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
VAN DAEL T, DE COOMAN T, VERBEECK M, et al., 2020b. Sediment respiration contributes to phosphate release in lowland surface waters[J]. Water Research, 168: 115168.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
WANG X, ZHI Y Y, CHEN Y, et al., 2022. Realignment of phosphorus in lake sediment induced by sediment microbial fuel cells (SMFC)[J]. Chemosphere, 291(Part 3): 132927.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
XIAO E Z, NING Z P, XIAO T F, et al., 2021. Soil bacterial community functions and distribution after mining disturbance[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 157: 108232.
DOI URL |
| [29] | XU D, WU W, DING S M, et al., 2012. A high-resolution dialysis technique for rapid determination of dissolved reactive phosphate and ferrous iron in pore water of sediments[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 421-422: 245-252. |
| [30] |
YANG Q Z, ZHAO H Z, ZHAO N N, et al., 2016. Enhanced phosphorus flux from overlying water to sediment in a bioelectrochemical system[J]. Bioresource Technology, 216: 182-187.
DOI PMID |
| [31] |
YUAN F, WEI Y D, GAO J L, et al., 2019. Water crisis, environmental regulations and location dynamics of pollution-intensive industries in China: A study of the Taihu Lake watershed[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 216: 311-322.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
ZHANG C S, DING S M, XU D, et al., 2014. Bioavailability assessment of phosphorus and metals in soils and sediments: a review of diffusive gradients in thin films (DGT)[J]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 186(11): 7367-7378.
DOI PMID |
| [33] |
ZHANG H, DAVISON W, MILLER S, et al., 1995. In-situ high-resolution measurements of fluxes of Ni, Cu, Fe, and Mn and concentrations of Zn and Cd in porewaters by DGT[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 59(20): 4181-4192.
DOI URL |
| [34] | 李向真, 刘子朋, 李娟, 等, 2012. KEGG数据库的进展及其在生物信息学中的应用[J]. 药物生物技术, 19(6): 535-539. |
| LI X Z, LIU Z P, LI J, et al., 2012. Recent progress and application of KEGG database in the research of bioinformatics[J]. Pharmaceutical Biotechnology, 19(6): 535-539. | |
| [35] | 朱梦圆, 朱广伟, 钱君龙, 等, 2012. SMT法插标分析沉积物中磷的地球化学形态[J]. 中国环境科学, 32(8): 1502-1507. |
| ZHU M Y, ZHU G W, QIAN J L, et al., 2012. SMT method for geochemical phosphorus fraction analysis in sediment by reference material inserting[J]. China Environmental Science, 32(8): 1502-1507. |
| [1] | 王家一, 孙亭亭, 沙润钰, 谌婷红, 邢冉, 秦伯强, 施文卿. 富营养化湖泊蓝藻打捞减污降碳效果模拟研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(6): 1108-1114. |
| [2] | 王超, 杨倩楠, 张池, 刘同旭, 张晓龙, 陈静, 刘科学. 丹霞山不同土地利用方式土壤磷组分特征及其有效性[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 889-897. |
| [3] | 王铁铮, 瞿心悦, 刘春香, 李有志. 东江湖水质时空变化规律及其与流域土地利用的关系[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 722-732. |
| [4] | 樊慧琳, 张佳敏, 李欢, 王艳玲. 坡耕地稻田剖面磷的储存格局与流失风险研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(2): 283-291. |
| [5] | 杨瑞, 孙蔚旻, 李永斌, 郭丽芳, 焦念元. 尾矿先锋植物根际溶磷菌的分离鉴定与其促生研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 166-174. |
| [6] | 黄伟佳, 刘春, 刘岳, 黄斌, 李定强, 袁再健. 南岭山地不同海拔土壤生态化学计量特征及影响因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 80-89. |
| [7] | 李晓晖, 艾仙斌, 李亮, 王玺洋, 辛在军, 孙小艳. 新型改性稻壳生物炭材料对镉污染土壤钝化效果的研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(9): 1901-1908. |
| [8] | 魏岚, 黄连喜, 李翔, 王泽煌, 陈伟盛, 黄庆, 黄玉芬, 刘忠珍. 生物炭基质可显著地促进香蕉幼苗生长[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 732-739. |
| [9] | 贺斌, 胡茂川. 广东省各区县农业面源污染负荷估算及特征分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 771-776. |
| [10] | 苏焱, 全妍红, 宦紫嫣, 姚佳, 苏小娟. 磷改性生物炭对云南某铅锌矿周边农田铅锌污染土壤修复效果的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(3): 593-602. |
| [11] | 崔键, 杜易, 丁程成, 李金凤, 高方述, 常雅军, 张继彪, 刘晓静, 姚东瑞. 中国湖泊水体磷的赋存形态及污染治理措施进展[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(3): 621-633. |
| [12] | 石含之, 江棋, 刘帆, 文典, 黄永东, 邓腾灏博, 王旭, 徐爱平, 李富荣, 吴志超, 李梅霞, 彭锦芬, 杜瑞英. 水稻根茬还田对土壤及稻米中镉累积的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(2): 363-369. |
| [13] | 盛基峰, 李垚, 于美佳, 韩艳英, 叶彦辉. 氮磷添加对高寒草地土壤养分和相关酶活性的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(12): 2302-2309. |
| [14] | 陈文洁, 李慧, 贺斌, 陶亮. 共存阴阳离子对针铁矿表面磷固存机制的影响研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(1): 151-159. |
| [15] | 许冬雪, 李兴, 王勇, 勾芒芒. 冰封期乌梁素海不同形态氮、磷和叶绿素a的空间分布特征及其响应关系[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(9): 1855-1864. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
