生态环境学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (3): 478-486.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2022.03.006
梁蕾1( ), 马秀枝1,*(
), 马秀枝1,*( ), 韩晓荣1, 李长生2, 张志杰2
), 韩晓荣1, 李长生2, 张志杰2
收稿日期:2021-08-02
出版日期:2022-03-18
发布日期:2022-05-25
通讯作者:
*马秀枝,女,教授,研究方向为生态系统碳氮循环以及温室气体。E-mail: luckmxy@imau.edu.cn作者简介:梁蕾(1995年生),女,硕士研究生,主要研究方向为森林温室气体通量。E-mail: 578121668@qq.com
基金资助:
LIANG Lei1( ), MA Xiuzhi1,*(
), MA Xiuzhi1,*( ), HAN Xiaorong1, LI Changsheng2, ZHANG Zhijie2
), HAN Xiaorong1, LI Changsheng2, ZHANG Zhijie2
Received:2021-08-02
Online:2022-03-18
Published:2022-05-25
摘要:
大气温度的升高及凋落物的分解通过影响土壤微生物的活动,从而影响土壤呼吸。采用开顶箱式增温(Open Top Chamber,OTC),结合静态箱-气相色谱法,于2020年生长季(5—10月)野外原位观测内蒙古大青山油松(Pinus tabuliformis Carr.)人工林土壤呼吸。试验设置对照(CK)、模拟增温(W)、去除凋落物(NL)、模拟增温+凋落物去除(WNL)4个处理4次重复,同时测定了大气温湿度、土壤温湿度及土壤理化性质。结果表明,(1)增温处理1年后,大气温度、土壤5、10和20 cm处的温度分别较对照增加了1.21、0.50、0.43和0.57 ℃;土壤5、10和20 cm的含水量分别较对照降低了5.4%、7.1%和6.4%。(2)大青山油松人工林土壤CO2通量变化范围为224.19—601.15 mg∙m-2∙h-1;CH4通量范围为-28.45— -90.2 μg∙m-2∙h-1;N2O通量范围为3.94—10.78 μg∙m-2∙h-1。整个生长季4种处理下土壤均表现为CO2、N2O的排放源、CH4的吸收汇。(3)对照和模拟增温处理下土壤CO2通量与大气温度和土壤温度(0—5、5—10、10—20 cm)呈极显著正相关(P<0.01),与土壤TN(0—10 cm)呈极显著负相关(P<0.01),与土壤TN(10—20 cm)呈显著负相关(P<0.05);土壤CH4通量仅在W处理下与大气湿度呈显著负相关(P<0.05);土壤N2O通量在W处理下与土壤TN(0—10、10—20 cm)呈显著负相关(P<0.05)。由此可见,气候变化及地表凋落物层是影响森林土壤呼吸的重要因素;基于100 a时间尺度计算温室气体全球综合增温潜势,模拟增温和凋落物处理下土壤温室气体的排放对气候变暖具有正反馈作用。
中图分类号:
梁蕾, 马秀枝, 韩晓荣, 李长生, 张志杰. 模拟增温下凋落物对大青山油松人工林土壤温室气体通量的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(3): 478-486.
LIANG Lei, MA Xiuzhi, HAN Xiaorong, LI Changsheng, ZHANG Zhijie. Effects of Litter on Soil Greenhouse Gas Flux of Pinus tabulaeformis Plantation in Daqing Mountain under Simulated Warming[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(3): 478-486.
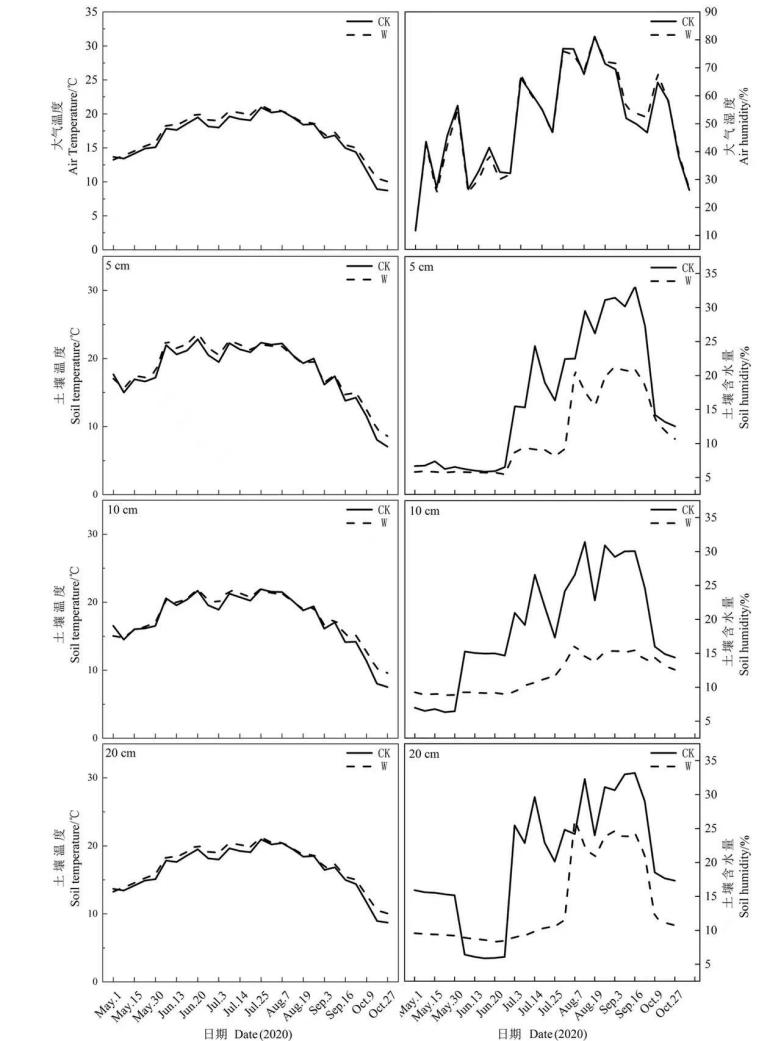
图1 模拟增温对大青山油松人工林大气及土壤温湿度的影响
Figure 1 Effects of simulated warming on air and soil temperature and humidity of Pinus tabulaeformis Plantation in Daqing Mountain
| 处理 Treatment | CO2 | CH4 | N2O | 综合增温潜势 Comprehensive warming potential |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 19.89 | -0.03 | 0.38 | 20.24 |
| W | 18.96 | -0.03 | 0.34 | 19.27 |
| NL | 17.45 | -0.03 | 0.33 | 17.75 |
| WNL | 15.69 | -0.03 | 0.30 | 15.96 |
表1 大青山油松人工林4种处理下土壤温室气体增温潜势
Table1 Warming potential of soil greenhouse gases under four treatments of Pinus tabulaeformis Plantation in Daqing Mountain t∙hm-2
| 处理 Treatment | CO2 | CH4 | N2O | 综合增温潜势 Comprehensive warming potential |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 19.89 | -0.03 | 0.38 | 20.24 |
| W | 18.96 | -0.03 | 0.34 | 19.27 |
| NL | 17.45 | -0.03 | 0.33 | 17.75 |
| WNL | 15.69 | -0.03 | 0.30 | 15.96 |
| 温室气体 Greenhouse gases | CO2 | CH4 | N2O | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 处理 Treatment | CK | W | CK | W | CK | W | |||
| 大气温度 Atmospheric temperature | 0.534** | 0.529** | -0.169 | -0.060 | 0.113 | 0.208 | |||
| 大气湿度 Atmospheric humidity | 0.746** | 0.717** | -0.313 | -0.569* | 0.020 | 0.004 | |||
| 土壤温度 Soil temperature | 0-5 cm | 0.530** | 0.505** | -0.225 | -0.117 | 0.081 | 0.220 | ||
| 5-10 cm | 0.569** | 0.606** | -0.236 | -0.165 | 0.070 | 0.221 | |||
| 10-20 cm | 0.697** | 0.702** | -0.282 | -0.188 | 0.082 | 0.212 | |||
| 土壤湿度 Soil humidity | 0-5 cm | 0.655** | 0.534** | -0.060 | 0.075 | -0.027 | -0.127 | ||
| 5-10 cm | 0.767** | 0.581** | -0.163 | 0.140 | 0.073 | -0.204 | |||
| 10-20 cm | 0.476* | 0.513** | -0.069 | 0.100 | -0.056 | -0.216 | |||
| TN | 0-10 cm | -0.852** | -0.863** | 0.349 | 0.111 | -0.419 | -0.574* | ||
| 10-20 cm | -0.762* | -0.788* | 0.413 | 0.184 | -0.295 | -0.644* | |||
| SOC | 0-10 cm | -0.675 | -0.667 | 0.630 | 0.424 | -0.398 | -0.342 | ||
| 10-20 cm | -0.345 | -0.363 | 0.565 | 0.380 | -0.433 | -0.465 | |||
表2 土壤温室气体通量与环境因子、土壤性质相关性
Table 2 Correlation of soil greenhouse gas flux with environmental factors and soil properties
| 温室气体 Greenhouse gases | CO2 | CH4 | N2O | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 处理 Treatment | CK | W | CK | W | CK | W | |||
| 大气温度 Atmospheric temperature | 0.534** | 0.529** | -0.169 | -0.060 | 0.113 | 0.208 | |||
| 大气湿度 Atmospheric humidity | 0.746** | 0.717** | -0.313 | -0.569* | 0.020 | 0.004 | |||
| 土壤温度 Soil temperature | 0-5 cm | 0.530** | 0.505** | -0.225 | -0.117 | 0.081 | 0.220 | ||
| 5-10 cm | 0.569** | 0.606** | -0.236 | -0.165 | 0.070 | 0.221 | |||
| 10-20 cm | 0.697** | 0.702** | -0.282 | -0.188 | 0.082 | 0.212 | |||
| 土壤湿度 Soil humidity | 0-5 cm | 0.655** | 0.534** | -0.060 | 0.075 | -0.027 | -0.127 | ||
| 5-10 cm | 0.767** | 0.581** | -0.163 | 0.140 | 0.073 | -0.204 | |||
| 10-20 cm | 0.476* | 0.513** | -0.069 | 0.100 | -0.056 | -0.216 | |||
| TN | 0-10 cm | -0.852** | -0.863** | 0.349 | 0.111 | -0.419 | -0.574* | ||
| 10-20 cm | -0.762* | -0.788* | 0.413 | 0.184 | -0.295 | -0.644* | |||
| SOC | 0-10 cm | -0.675 | -0.667 | 0.630 | 0.424 | -0.398 | -0.342 | ||
| 10-20 cm | -0.345 | -0.363 | 0.565 | 0.380 | -0.433 | -0.465 | |||
| [1] |
CORNELISSEN J, BODEGOM P, AERTS R, et al., 2010. Global negative vegetation feedback to climate warming responses of leaf litter decomposition rates in cold biomes[J]. Ecology Letters, 10(7): 619-627.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
DAVIDSON E A, KANTER D, 2014. Inventories and scenarios of nitrous oxide emissions[J]. Environmental Research Letters, 9(10): 105012.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
FAN J L, LUO R Y, MCCONKEY B G, et al., 2020. Effects of nitrogen deposition and litter layer management on soil CO2, N2O, and CH4 emissions in a subtropical pine forestland[J]. Entific Reports, DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-65952-8.
DOI |
| [4] |
FISHER D A, LACELLE D, POLLARD W, 2019. A model of unfrozen water content and its transport in icy permafrost soils: Effects on ground ice content and permafrost stability[J]. Permafrost and Periglacial Processes, 31(1): 184-199.
DOI URL |
| [5] | FORSTER P, RAMASWAMY V, ARTAXO P, et al., 2007. Changes in Atmospheric Constituents in Radiative Forcing[M]. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press. |
| [6] | IPCC, 2013. Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis[R]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. |
| [7] |
KANEDA S, F ROUZ J, BALDRIAN P, et al., 2013. Does the addition of leaf litter affect soil respiration in the same way as addition of macrofauna excrements (of Bibio marci Diptera larvae) produced from the same litter?[J]. Applied Soil Ecology, 72: 7-13.
DOI URL |
| [8] | LEITNER S, SAE-TUN O, KRANZINGER L, et al., 2016. Contribution of litter layer to soil greenhouse gas emissions in a temperate beech forest[J]. Plant & Soil, 403(1-2): 455-469. |
| [9] |
LI Z L, ZENG Z Q, TIAN D S, et al., 2020. Global patterns and controlling factors of soil nitrification rate[J]. Global Change Biology, 26(7): 4147-4157.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
LIU W X, ZHANG Z, WAN S Q, 2009. Predominant role of water in regulating soil and microbial respiration and their responses to climate change in a semiarid grassland[J]. Global Change Biology, 15(1): 184-195.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
MELILLO J M, FREY S D, DEANGELIS K M, et al., 2017. Long-term pattern and magnitude of soil carbon feedback to the climate system in a warming world[J]. Science, 358: 101-105.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
MELILLO J M, STEUDLER P A, ABER J D, et al., 2002. Soil warming and carbon-cycle feedbacks to the climate system[J]. Science, 298(5601): 2173-2176.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
NIINIST S M, SILVOLA J, KELLOMKI S, 2004. Soil CO2 efflux in a boreal pine forest under atmospheric CO2 enrichment and air warming[J]. Global Change Biology, 10(3): 1363-1376.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
PENG F, XU M H, YOU Q G, et al., 2015. Different Responses of soil respiration and its components to experimental warming with contrasting soil water content[J]. Arctic, Antarctic, and Alpine Research, 47(2): 359-368.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
RUSTAD L E, CAMPBELL J L, MARION G M, et al., 2001. A meta-analysis of the response of soil respiration,net nitrogen mineralization, and aboveground plant growth to experimental ecosystem warming[J]. Oecologia, 126(2): 543-562.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
SAYER E J, 2006. Using experimental manipulation to assess the roles of leaf litter in the functioning of forest ecosystems[J]. Biological Reviews, 81(1): 1-31.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
SONG C C, XU X F, SUN X X, et al., 2012. Large methane emission upon spring thaw from natural wetlands in the northern permafrost region[J]. Environmental Research Letters, DOI: 10.1088/1748-9326/7/3/034009.
DOI |
| [18] |
SONG X Y, WANG G X, RAN F, et al., 2017. Effects of topography and fire on soil CO2 and CH4 flux in boreal forest underlain by permafrost in northeast China[J]. Ecological Engineering, 106: 35-43.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
WANG Y D, WANG H M, WANG Z L, et al., 2014. Effect of litter layer on soil-atmosphere N2O flux of a subtropical pine plantation in China[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 82: 106-112.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
WU X W, ZANG S Y, MA D L, et al., 2019. Emissions of CO2, CH4, and N2O Fluxes from Forest Soil in Permafrost Region of Daxing'an Mountains, Northeast China[J]. International Journal of Environment Research and Public Health, DOI: 10.3390/ijerph16162999.
DOI |
| [21] |
YU L J, HUANG Y, ZHANG W, et al., 2017. Methane uptake in global forest and grassland soils from 1981 to 2010 [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 607-608: 1163-1172.
DOI URL |
| [22] | ZHANG J F, HAN X G, 2008. N2O emission form the semi-arid ecosystem under mineral fertilizer (urea and superphosphate) and increased precipitation in northern China[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 45(2): 291-302. |
| [23] | 党旭升, 程淑兰, 方华军, 等, 2015. 温带针阔混交林土壤碳氮气体通量的主控因子与耦合关系[J]. 生态学报, 35(19): 6530-6540. |
| DANG X S, CHENG S L, FANG H J, et al., 2015. The controlling factors and coupling of soil CO2, CH4 and N2O fluxes in a temperate needle-broadleaved mixed forest[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 35(19): 6530-6540. | |
| [24] | 段北星, 蔡体久, 宋浩, 等, 2020. 寒温带兴安落叶松林凋落物层对土壤呼吸的影响[J]. 生态学报, 40(4): 1357-1366. |
| DUAN B X, CAI T J, SONG H, et al., 2020. Effect of soil litterfall on soil respiration in cold-temperate Larch forest[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 40(4): 1357-1366. | |
| [25] |
耿元波, 罗光强, 2010. 内蒙古羊草草原呼吸的影响因素分析和区分[J]. 地理学报, 65(9): 1058-1068.
DOI |
| GENG Y B, LUO G Q, 2010. Analysis of affecting factors and partitioning of respiration in a Leymus chinensis steppe in Inner Mongolia[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 65(9): 1058-1068. | |
| [26] | 梁东丽, 同延安, Ove Emteryd, 等, 2002. 干湿交替对旱地土壤N2O气态损失的影响[J]. 干旱地区农业研究, 20(2): 28-31, 48. |
| LIANG D L, TONG Y A, OVE E, et al., 2002. The effects of wetting and drying cycles on N2O emission in dryland[J]. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas, 20(2): 28-31, 48. | |
| [27] | 梁东哲, 赵雨森, 曹杰, 等, 2019. 不同恢复方式下大兴安岭重度火烧迹地林地土壤温室气体通量[J]. 生态学报, 39(21): 7950-7959. |
| LIANG D Z, ZHAO Y S, CAO J, et al., 2019. Greenhouse gas emissions from woodland soils in a severely burned area under different restoration methods in the Greater Khingan Mountains[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 39(21): 7950-7959. | |
| [28] |
刘玲玲, 刘允芬, 温学发, 等, 2008. 千烟洲红壤丘陵区人工针叶林土壤CH4排放通量[J]. 植物生态学报, 32(2): 431-439.
DOI |
| LIU L L, LIU Y F, WEN X F, et al., 2008. CH4 emission flux from soil of pine plantations in the Qian-Yanzhou red earth hill region of China[J]. Journal of Plant Ecology, 32(2): 431-439. | |
| [29] | 李攀, 周梅, 王忠林, 等, 2012. 寒温带兴安落叶松林火烧迹地地表CO2通量研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 21(12): 1950-1954. |
| LI P, ZHOU M, WANG Z L, et al., 2012. Study on soil surface CO2 flux in burned areas of Larix gmelinii forest in the cool temperate zone[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 21(12): 1950-1954. | |
| [30] | 李伟, 刘小飞, 陈光水, 等, 2016. 凋落物对中亚热带米槠天然林和人工林土壤呼吸的影响[J]. 林业科学, 52(11): 11-18. |
| LI W, LIU X F, CHEN G S, et al., 2016. Effects of litter manipulation on soil respiration in the natural forests and plantations of Castanopsis carlesii in mid-subtropical China[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 52(11): 11-18. | |
| [31] | 马秀枝, 范雪松, 舒长禄, 等, 2016. 不同时间序列林火干扰对兴安落叶松林区土壤性质及温室气体通量的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 25(6): 939-946. |
| MA X Z, FAN X S, SHU C L, et al., 2016. Effects of forest fire disturbance in different time Series on Soil Properties and greenhouse gas flux in Larix gmelinii forest of cold-temperate zone[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 25(6): 939-946. | |
| [32] | 牟长城, 程伟, 孙晓新, 等, 2010. 小兴安岭落叶松沼泽林土壤CO2、N2O和CH4的排放规律[J]. 林业科学, 46(7): 7-15. |
| MU C C, CHENG W, SUN X X, et al., 2010. Seasonal variation of emission fluxes of CO2, N2O and CH4 from Larix gmelinii swamps soils in Xiaoxing'an mountains of China[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 46(7): 7-15. | |
| [33] | 彭少麟, 侯爱敏, 周国逸, 2000. 气候变化对陆地生态系统第一性生产力的影响研究综述[J]. 地球科学进展, 15(6): 717-722. |
| PENG S L, HOU A M, ZHOU G Y, 2000. Impact of climate change on the net primary productivity of terrestrial ecosystem[J]. Advance in Earth Sciences, 15(6): 717-722. | |
| [34] | 彭信浩, 韩海荣, 徐小芳, 等, 2018. 间伐和改变凋落物输入对华北落叶松人工林土壤呼吸的影响[J]. 生态学报, 38(15): 85-95. |
| PENG X H, HAN H R, XU X F, et al., 2018. Thinning treatment and litterfall changes influence soil respiration in a Larix principis-rupprechtii plantation[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 38(15): 85-95. | |
| [35] | 仝川, 黄佳芳, 王维奇, 等, 2012. 闽江口半咸水芦苇潮汐沼泽湿地甲烷动态[J]. 地理学报, 67(9): 1165-1180. |
| TONG C, HUANG J F, WANG W Q, et al., 2012. Methane dynamics of a brackish-water tidal Phragmites australis marsh in the Minjiang river estuary[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 67(9): 1165-1180. | |
| [36] | 王新源, 李玉霖, 赵学勇, 等, 2012. 干旱半干旱区不同环境因素对土壤呼吸影响研究进展[J]. 生态学报, 32(15): 4890-4901. |
|
WANG X Y, LI Y L, ZHAO X Y, et al., 2012. Responses of soil respiration to different environment factors in semi-arid and arid areas[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 32(15): 4890-4901.
DOI URL |
|
| [37] | 王金龙, 李艳红, 李发东, 2018. 博斯腾湖人工和天然芦苇湿地土壤CO2、CH4和N2O排放通量[J]. 生态学报, 38(2): 668-677. |
| WANG J L, LI Y H, LI F D, 2018. Emission fluxes of CO2, CH4, and N2O from artificial and natural reed wetlands in Bosten lake, China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 38(2): 668-677. | |
| [38] | 魏书精, 罗碧珍, 魏书威, 等, 2014. 森林生态系统土壤呼吸测定方法研究进展[J]. 生态环境学报, 23(3): 504-514. |
| WEI S J, LUO B Z, WEI S W, et al., 2014. Methods of measuring of soil respiration in forest ecosystems: A review[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 23(3): 504-514. | |
| [39] |
吴祥文, 臧淑英, 马大龙, 等, 2020. 大兴安岭多年冻土区森林土壤温室气体通量[J]. 地理学报, 75(11): 2319-2331.
DOI |
| WU X W, ZANG S Y, MA D L, et al., 2020. Greenhouse gas fluxes from forest soil in permafrost regions of Greater Hinggan Mountains, Northeast China[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 75(11): 2319-2331. | |
| [40] |
熊沛, 徐振锋, 林波, 等, 2010. 岷江上游华山松冬季土壤呼吸对模拟增温的短期响应[J]. 植物生态学报, 34(12): 1369-1376.
DOI |
|
XIONG P, XU Z F, LIN B, et al., 2010. Short-term response of winter soil respiration to simulated warming in a Pinus armandii plantation in the upper reaches of the Minjiang River, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 34(12): 1369-1376.
DOI |
|
| [41] | 赵昕, 张万军, 沈会涛, 等, 2014. 针阔树种人工林地表凋落物对土壤呼吸的贡献[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 22(11): 1318-1325. |
| ZHAO X, ZHANG W J, SHEN H T, et al., 2014. Contributions of aboveground litter to soil respiration in coniferous and deciduous Plantations[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 22(11): 1318-1325. | |
| [42] |
张素彦, 蒋红志, 王扬, 等, 2018. 凋落物去除和添加处理对典型草原生态系统碳通量的影响[J]. 植物生态学报, 42(3): 349-360.
DOI |
|
ZHANG S Y, JIANG H Z, WANG Y, et al., 2018. Effects of litter removal and addition on ecosystem carbon fluxes in a typical steppe[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 42(3): 349-360.
DOI URL |
|
| [43] | 张秀君, 徐慧, 陈冠雄, 2002. 影响森林土壤N2O排放和CH4吸收的主要因素[J]. 环境科学, 23(5): 8-12. |
| ZHANG X J, XU H, CHEN G X, 2002. Important factors controlling rates of N2O emission and CH4 oxidation from forest soil[J]. Environmental Science, 23(5): 8-12. |
| [1] | 韩翠, 康扬眉, 余海龙, 李冰, 黄菊莹. 荒漠草原凋落物分解过程中降水量对土壤酶活性的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(9): 1802-1812. |
| [2] | 李勋, 崔宁洁, 张艳, 覃宇, 张健. 马尾松与乡土阔叶树种凋落叶纤维素、总酚以及缩合单宁降解的混合效应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(9): 1813-1822. |
| [3] | 张涵, 唐常源, 禤映雪, 江涛, 黄品怡, 杨秋, 曹英杰. 珠江口红树林土壤甲烷和二氧化碳通量特征及其影响因素研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(5): 939-948. |
| [4] | 肖军, 雷蕾, 曾立雄, 李肇晨, 马成功, 肖文发. 不同经营模式对华北油松人工林碳储量的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(11): 2134-2142. |
| [5] | 王玄, 熊鑫, 张慧玲, 赵梦頔, 胡明慧, 褚国伟, 孟泽, 张德强. 模拟酸雨对南亚热带森林凋落物分解和土壤呼吸的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(9): 1805-1813. |
| [6] | 姚世庭, 芦光新, 邓晔, 党宁, 王英成, 张海娟, 颜珲璘. 模拟增温对土壤真菌群落组成及多样性的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(7): 1404-1411. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
