生态环境学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (7): 1360-1367.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2021.07.004
收稿日期:2021-02-02
出版日期:2021-07-18
发布日期:2021-10-09
通讯作者:
*张浩(1980年生),男,副教授,主要从事生态学研究。E-mail: allenzh@thei.edu.hk作者简介:洪文君(1990年生),女,工程师。E-mail: hongwenjun0827@126.com
基金资助:
HONG Wenjun1,2( ), MO Luojian3, ZHANG Hao4,*(
), MO Luojian3, ZHANG Hao4,*( )
)
Received:2021-02-02
Online:2021-07-18
Published:2021-10-09
摘要:
研究间伐强度对华南地区人工林下套种阔叶树种生长的影响,为华南地区人工林营林措施和生态功能恢复评价提供科学依据。以东莞大岭山林场马占相思(Acacia mangium)人工林为研究对象,设置了3种间伐强度处理(0、30%和60%,编号为M1、M2和M3),间伐后均匀套种乡土阔叶树种,以不间伐不套种纯林为对照。改造10 a后,分析不同间伐强度与套种改造模式群落物种组成、物种多样性及林分生长状况的影响。结果表明,间伐套种模式改造10 a后,3种改造模式均显著促进群落乔木层的物种数(22—26种),林分灌木层物种数以M1模式较高,草本层物种数差异不大(14—17种);林分中乔木层、灌木层物种的Shannon-Wiener指数均以M1林分较高,分别为2.09和2.11,Pielou指数差异不大(0.83—0.96和0.90—1.02),草本层多样性指数以CK林分最高。DCA分析结果显示,绝大多数套种树种在改造后林分生长较好,密集分布在M1林分,M2和M3林分次之;间伐或套种处理均促进了幼树的生长,M1林分乔木层树种的平均树高、平均胸径和胸高断面积均显著高于间伐M2和M3林分。该研究结果表明马占相思人工林经营模式以未间伐与套种相结合为最佳,可优化群落林冠结构,加速林分向地带性森林植被阔叶树种混交林演替。
中图分类号:
洪文君, 莫罗坚, 张浩. 华南地区马占相思人工林不同改造模式对林分结构的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(7): 1360-1367.
HONG Wenjun, MO Luojian, ZHANG Hao. Effects of Different Thinning on the Structure of Acacia mangium Plantation in South China[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(7): 1360-1367.
| 植物类群 Plant groups | M1 | M2 | M3 | CK |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 科꞉属꞉种 Families꞉ Genera꞉ Species | 科꞉属꞉种 Families꞉ Genera꞉ Species | 科꞉属꞉种 Families꞉ Genera꞉ Species | 科꞉属꞉种 Families꞉ Genera꞉ Species | |
| 蕨类植物 Pteridophytes | 6꞉5꞉6 | 4꞉4꞉4 | 4꞉4꞉5 | 6꞉6꞉7 |
| 裸子植物 Gymnosperms | 1꞉1꞉1 | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ |
| 双子叶植物 Dicotyledons | 27꞉37꞉43 | 19꞉24꞉25 | 15꞉22꞉26 | 12꞉16꞉17 |
| 单子叶植物 Monocotyledon | 1꞉2꞉2 | 3꞉4꞉4 | 3꞉3꞉3 | 2꞉4꞉4 |
| 总计 Total | 36꞉45꞉52 | 26꞉32꞉33 | 22꞉29꞉34 | 20꞉26꞉28 |
表1 不同改造模式群落物种组成比较
Table1 Comparison of species composition of communities in the four treatments
| 植物类群 Plant groups | M1 | M2 | M3 | CK |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 科꞉属꞉种 Families꞉ Genera꞉ Species | 科꞉属꞉种 Families꞉ Genera꞉ Species | 科꞉属꞉种 Families꞉ Genera꞉ Species | 科꞉属꞉种 Families꞉ Genera꞉ Species | |
| 蕨类植物 Pteridophytes | 6꞉5꞉6 | 4꞉4꞉4 | 4꞉4꞉5 | 6꞉6꞉7 |
| 裸子植物 Gymnosperms | 1꞉1꞉1 | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ |
| 双子叶植物 Dicotyledons | 27꞉37꞉43 | 19꞉24꞉25 | 15꞉22꞉26 | 12꞉16꞉17 |
| 单子叶植物 Monocotyledon | 1꞉2꞉2 | 3꞉4꞉4 | 3꞉3꞉3 | 2꞉4꞉4 |
| 总计 Total | 36꞉45꞉52 | 26꞉32꞉33 | 22꞉29꞉34 | 20꞉26꞉28 |
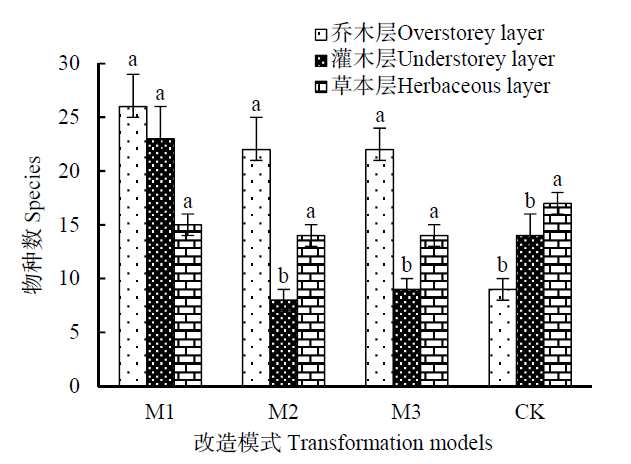
图1 不同改造模式群落各层次物种数 图中不同小写字母表示不同层次物种数在P=0.05水平上差异显著
Fig. 1 Species of different layers in different transformation treatments and the result of multiple comparison Mean values followed by the letter within a column are not significantly indicated the number of species at P=0.05 level according to the Duncan’s test
| 改造模式 Transformation models | 密度 Density/ (plant∙hm-2) | 平均树高 Mean height/ m | 平均胸径 Mean DBH/ cm | 胸高断面积 Mean basal area/ (m2∙hm-2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| M1 | 1600a | 7.60±1.87a | 12.58±3.02a | 19.88±3.28a |
| M2 | 1475b | 7.16±2.31b | 10.52±2.68b | 12.81±2369b |
| M3 | 1075b | 6.54±1.99b | 8.51±1.14b | 6.11±1.75c |
表2 不同改造模式对林分乔木层的树种生长比较
Table 2 Comparison of growth performance of tree in the four treatments
| 改造模式 Transformation models | 密度 Density/ (plant∙hm-2) | 平均树高 Mean height/ m | 平均胸径 Mean DBH/ cm | 胸高断面积 Mean basal area/ (m2∙hm-2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| M1 | 1600a | 7.60±1.87a | 12.58±3.02a | 19.88±3.28a |
| M2 | 1475b | 7.16±2.31b | 10.52±2.68b | 12.81±2369b |
| M3 | 1075b | 6.54±1.99b | 8.51±1.14b | 6.11±1.75c |
| 改造模式 Transformation models | 平均树高 Mean height/ m | 平均胸径 Mean DBH/ cm | 胸高断面积 Mean basal area/ (m2∙hm-2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| M1 | 7.83±1.28a | 15.38±2.78a | 32.01±5.34a |
| M2 | 7.16±0.96b | 10.17±2.15b | 24.11±2.87b |
| M3 | 6.54±1.52b | 8.41±1.62b | 9.85±2.14c |
| CK | 8.82±1.12a | 14.09±2.04a | 25.66±2.81b |
表3 不同改造模式对林分保留木生长的影响
Table 3 Growth performance of understorey vegetation in the four treatments
| 改造模式 Transformation models | 平均树高 Mean height/ m | 平均胸径 Mean DBH/ cm | 胸高断面积 Mean basal area/ (m2∙hm-2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| M1 | 7.83±1.28a | 15.38±2.78a | 32.01±5.34a |
| M2 | 7.16±0.96b | 10.17±2.15b | 24.11±2.87b |
| M3 | 6.54±1.52b | 8.41±1.62b | 9.85±2.14c |
| CK | 8.82±1.12a | 14.09±2.04a | 25.66±2.81b |
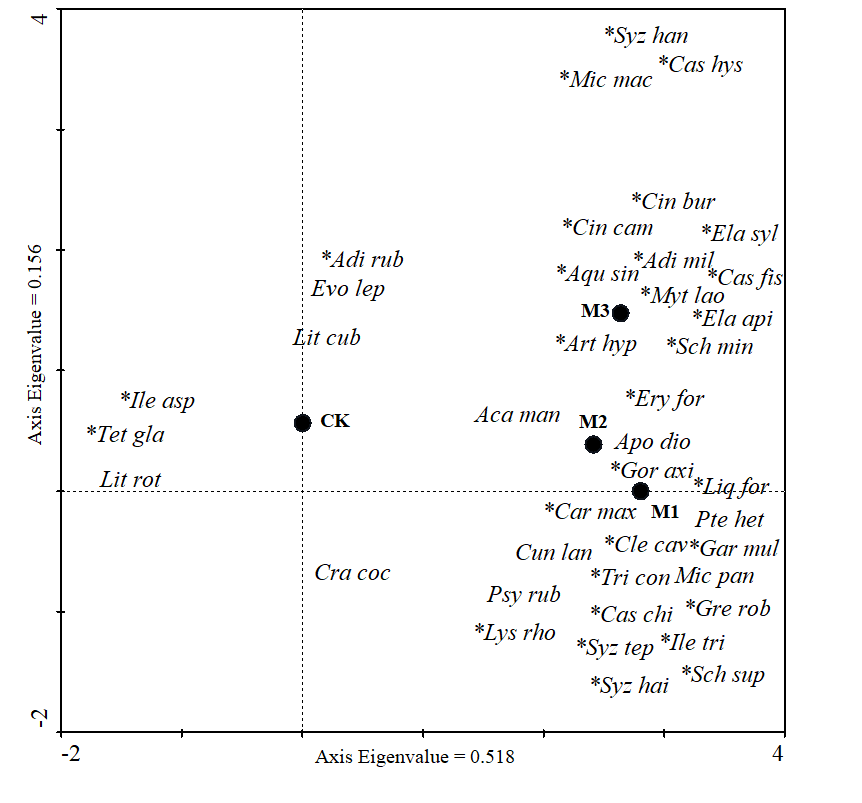
图2 不同改造模式乔木层树种DCA排序分析 图中*为套种树种。字母缩写分别表示马占相思(Aca man);水杨梅(Adi rub);杨桐(Adi mil);银柴(Apo dio);土沉香(Aqu sin);桂木(Art nit);鱼尾葵(Car och);中华锥(Cas chi);黧蒴(Cas fis);红锥(Cas hys);阴香(Cin bur);樟树(Cin cam);蝴蝶果(Cle cav);黄牛木(Cra coc);杉木(Cunlan);尖叶杜英(Ela api);山杜英(Ela syl);格木(Ery for);多花山竹子(Gar mul);岭南山竹子(Gor obl);银桦(Gre rob);梅叶冬青(Ile asp);三花冬青(Ile tri);枫香(Liq for);山苍子(Lit cub);豺皮樟(Lit rot);红胶木(Tri con);仪花(Lys rho);三叉苦(Evo lep);火力楠(Mic mac);布渣叶(Mic pan);米老排(Myt lao);大头茶(Gor axi);九节(Psy rub);翻白叶(Pte het);鸭脚木(Sch oct);荷木(Sch sup);海南蒲桃(Syz hai);红鳞蒲桃(Syz han);方枝蒲桃(Syz tep);楝叶吴茱萸(Tet gla)
Fig. 2 The first two axes of DCA ordination for different species in the tree layer on the four plots

图3 不同改造模式灌木层树种DCA排序分析 图中*为套种树种。字母缩写分别表示杨桐(Adi mil);水杨梅(Adi rub);红背山麻杆(Alc tre);银柴(Apo dio);莞香(Aqu sin);朱砂根(Ard cre);黧蒴(Cas fis);黄牛木(Cra coc);杉木(Cun lan);假鹰爪(Des chi);米碎花(Eur chi);亮叶柃(Eur loq);三叉苦(Evo lep);五指毛桃(Fic hir);银桦(Gre rob);梅叶冬青(Ile asp);三花冬青(Ile tri);桃花心木(Kha sen);山苍子(Lit cub);豺皮樟(Lit rot);仪花(Lys rho);鲫鱼胆(Mae per);破布叶(Mic pan);桂叶黄梅(Och tho);九节(Psy rub);红叶藤(Rou min);草珊瑚(Sar gla);鸭脚木(Sch oct);假苹婆(Ste lan);三棱蒲桃(Syz tep);楝叶吴茱萸(Tet gla)
Fig. 3 The first two axes of DCA ordination for different species in the understorey layer on the four plots

图4 不同改造模式草木层树种DCA排序分析 图中*为套种树种。字母缩写分别表示铁线蕨(Adi cap);扇叶铁线蕨(Adi fla);杨桐(Adi mil);水杨梅(Adi rub);银柴(Apo dio);乌毛蕨(Ble ori);黧蒴(Cas fis);金毛狗(Cib bar);杉木(Cun lan);山菅兰(Dian sif);芒萁(Dic dic);三叉苦(Evo lep);梅叶冬青(Ile asp);剑叶鳞始蕨(Lin ens);团叶鳞始蕨(Lin orb);山银花(Lon con);淡竹叶(Lop gra);海金沙(Lyg jap);布渣叶(Mic pan);蔓生莠竹(Mic vag);露籽草(Ott nod);火炭母(Pol chi);九节(Psy rub);半边旗(Pte sem);草珊瑚(Sar gla);鸭脚木(Sch oct);土茯苓(Smi gla);锡叶藤(Tet asi);两面针(Zan nit)
Fig. 4 The first two axes of the DCA ordination for different species in the herbaceous layer on the four plots
| 改造模式 Transformation models | 乔木层 Overstorey layer | 灌木层Understorey layer | 草本层Herbaceous layer | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S | H′ | J | S | H′ | J | S | H′ | J | |||
| M1 | 26a | 2.09±0.06a | 0.91±0.01a | 23a | 2.11±0.18a | 0.90±0.03a | 15a | 1.25±0.20b | 0.62±0.11b | ||
| M2 | 22a | 2.00±0.16a | 0.94±0.03a | 8b | 1.43±0.14b | 1.02±0.14a | 14a | 1.81±0.16a | 0.92±0.03a | ||
| M3 | 22a | 1.95±0.04a | 0.96±0.02a | 9b | 1.36±0.21b | 0.91±0.02a | 14a | 1.44±0.33b | 0.77±0.13b | ||
| CK | 9b | 1.45±0.04b | 0.83±0.01a | 14ab | 1.86±0.09a | 0.96±0.03a | 17a | 1.96±0.07a | 0.93±0.01a | ||
表4 不同改造模式对相思人工林物种多样性的比较
Table 4 Diversity of aboveground vegetation in the four treatments
| 改造模式 Transformation models | 乔木层 Overstorey layer | 灌木层Understorey layer | 草本层Herbaceous layer | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S | H′ | J | S | H′ | J | S | H′ | J | |||
| M1 | 26a | 2.09±0.06a | 0.91±0.01a | 23a | 2.11±0.18a | 0.90±0.03a | 15a | 1.25±0.20b | 0.62±0.11b | ||
| M2 | 22a | 2.00±0.16a | 0.94±0.03a | 8b | 1.43±0.14b | 1.02±0.14a | 14a | 1.81±0.16a | 0.92±0.03a | ||
| M3 | 22a | 1.95±0.04a | 0.96±0.02a | 9b | 1.36±0.21b | 0.91±0.02a | 14a | 1.44±0.33b | 0.77±0.13b | ||
| CK | 9b | 1.45±0.04b | 0.83±0.01a | 14ab | 1.86±0.09a | 0.96±0.03a | 17a | 1.96±0.07a | 0.93±0.01a | ||
| [1] |
ARCHER J K, MILLER D L, TANNER G W, 2007. Changes in understory vegetation and soil characteristics following silvicultural activities in a southeastern mixed pine forest[J]. Journal of the Torrey Botanical Society, 134(4): 489-504.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
BATTLES J J, SHLISKY A J, BARRETT RH, et al., 2001. The effects of forest management on plant species diversity in a Sierran conifer forest[J]. Forest Ecology and Management, 146(1-3): 211-222.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
CONNELL J H, 1978. Diversity in Tropical Rain Forests and Coral Reef[J]. Science, 199(4335): 1302-1310.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
DENG C, ZHANG S G, LU Y C, et al., 2019. Effects on the Tree Height-Diameter Allometry of Masson Pine (Pinus massoniana Lamb.)[J]. Forest, 10(12): 1129-1154.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
ERSKINE P D, LAMB D, BRISTOW M, 2006. Tree species diversity and ecosystem function: Can tropical multi-species plantations generate greater productivity?[J]. Forest Ecology and Management, 233(2-3): 205-210.
DOI URL |
| [6] | MUELLER-DOMBOIS D, ELLENBERG H, 1974. Aims and Methods of Vegetation Ecology[M]. New York: Wiley. |
| [7] |
NAGAI M, YOSHIDA T, 2006. Variation in understory structure and plant species diversity influenced by silvicultural treatments among 21-to26-year old Picea glehnii plantations[J]. Journal of Forest Research, 11(1): 1-10.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
PIELOU E C, 1966. The measurement of diversity in different types of biological collections[J]. Journal of Theoretical Biology, 13: 131-144.
DOI URL |
| [9] | SHANNON E C, WIENER W, 1963. The mathematical theory of communication[M]. Urbana, IL: University of Illinois Press. |
| [10] |
SMALL C J, MCCARTHY B C, 2005. Relationship of understory diversity to soil nitrogen, topographic variation and stand age in an eastern oak forest, USA[J]. Forest Ecology and Management, 217(2): 229-243.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
WANG Q K, WANG S L, LIN Y X, 2008. Responses to N and P fertilization in a young Eucalyptus dunnii plantation: Microbial Properties, enzyme activities and dissolved organic matter[J]. Applied Soil Ecology, 40(3): 484-490.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
XUE L, JACOBS D F, ZENG S C, et al., 2012. Relationship between aboveground biomass allocation and stand density index in Populus×euramericana stands[J]. Forestry, 85(5): 611-619.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
XUE L, PAN L, ZHANG R, et al., 2011. Growth analysis on the C-D effect of organs in self-thinning Eucalyptus urophylla stands[J]. Trees, 25(6): 1021-1031.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
ZARMORCH S J, BOCHLOLD W A, STOLTE K W, 2004. Using crown condition variables as indicators of forest health[J]. Canadian Journal of Forest Research, 34(5): 1057-1070.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
ZHANG H, ZHUANG X Y, CHU L M, 2013. Plant recruitment in early development stages on rehabilitated quarries in Hong Kong[J]. Restoration Ecology, 21(2): 166-173.
DOI URL |
| [16] | 陈贝贝, 姜俊, 陆元昌, 等, 2021. 间伐强度对马尾松人工林冠下套种树种生长的影响[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 43(1): 58-65. |
| CHEN B B, JIANG J, LU Y C, et al., 2021. Effects of thinning intensity on the growth of interplanting broadleaved trees under Pinus massoniana plantation[J]. Journal of Forestry University, 43(1): 58-65. | |
| [17] | 陈丝露, 赵敏, 李贤伟, 等, 2018. 柏木低效林不同改造模式优势草本植物多样性及其生态位[J]. 生态学报, 38(1): 143-155. |
| CHEN S L, ZHAO M, LI X W, et al., 2018. Study on plant diversity and niche characteristics of dominant herbaceous populations under different reconstruction patterns in low efficiency stands of Cupressus funebris[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 38(1): 143-155. | |
| [18] | 邓送求, 闫家锋, 王宇, 等, 2010. 间伐强度对不同林分类型下层物种多样性的短期影响[J]. 东北林业大学学报, 38(3): 31-46. |
| DENG S Q, YAN J F, WANG Y, et al., 2010. Shor-term effects of thinning intensity on species diversity of undergrowth layer in different stands[J]. Journal of Northeast Forest University, 38(3): 31-46. | |
| [19] | 段劫, 马履一, 贾黎明, 等, 2010. 抚育间伐对侧柏人工林及林下植被生长的影响[J]. 生态学报, 30(6): 1431-1441. |
| DUAN J, YAN J F, WANG Y, et al., 2010. Effect of thinning on Platycladus orientalis plantation and the diversity of undergrowth vegetation[J]. Acta Ecology Sinica, 30(6): 1431-1441. | |
| [20] | 郝建锋, 李艳, 王德艺, 等, 2015. 雅安市谢家山两种密度柳杉人工林群落结构和物种多样性研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 24(2): 217-223. |
| HAO J F, LI Y, WANG D Y, et al., 2015. Researches on Structure and Species Diversity of Cryptomeria fortunei Plantation under Two Kinds of Densities in Xiejiashan, Ya’an, Sichuan[J]. Ecology and Environment Sciences, 24(2): 217-223. | |
| [21] | 何友均, 梁星云, 覃林, 等, 2013. 南亚热带人工针叶纯林近自然改造早期对群落特征和土壤性质的影[J]. 生态学报, 33(8): 2484-2495. |
| HE Y J, LIANG X Y, QIN L, et al., 2013. Community characteristics and soil properties of coniferous plantation forest monocultures in the early stages after close-to-nature transformation management in southern subtropical China[J]. Acta Ecology Sinica, 33(8): 2484-2495. | |
| [22] | 雷相东, 陆元昌, 张会儒, 等, 2005. 抚育间伐对落叶松云冷杉混交林的影响[J]. 林业科学, 41(4):78-85. |
| LEI X D, LU Y C, ZHUANG H M, et al., 2005. Effects of thinning on mixed stands of Larix olgensis, Abies nephrolepis and Picea jazpozensis[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 41(4): 14-20. | |
| [23] | 李清湖, 庄雪影, 2012. 广东山区3种不同人工林林下植物多样性初步研究[J]. 广东林业科技, 28(2): 37-45. |
| LI Q H, ZHUANG X Y, 2012. Preliminary study on understory species diversity of three types of plantation in mountainous area of China[J]. Guangdong Forest Science and Technology, 41(4): 78-85. | |
| [24] | 刘思泽, 尹海锋, 沈逸, 等, 2020. 间伐强度对马尾松人工林间伐初期林下植被群落物种组成和多样性的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 31(9): 2866-2874. |
| LIU S Z, YIN H F, SHEN Y, et al., 2020. Effects of thinning intensity on species composition and diversity of undergrowth vegetation community in Pinus massoniana plantation at initial stage of thinning[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 31(9): 2866-2874. | |
| [25] | 罗应华, 孙冬婧, 林建勇, 等, 2013. 马尾松人工林近自然化改造对植物自然更新及物种多样性的影响[J]. 生态学报, 33(19): 6154-6162. |
|
LUO Y H, SUN D J, LIN J Y, et al., 2013. Effect of close-to-nature management on the natural regeneration and species diversity in a Pinus massomiana plantation[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 33(19): 6154-6162.
DOI URL |
|
| [26] | 马履一, 李春义, 王希群, 等, 2007. 不同强度间伐对北京山区油松生长及其林下植物多样性的影响[J]. 林业科学, 43(5): l-9. |
| MA L Y, LI C Y, WANG X Q, et al., 2007. Effects of thinning on the growth and the diversity of undergrowth of Pinus tabulaeformis plantation in Beijing Mountainous areas[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 43(5): 1-9. | |
| [27] | 毛志宏, 朱教君, 刘足根, 等, 2006. 间伐对落叶松人工林内草本植物多样性及其组成的影响[J]. 生态学杂志, 25(10): 2101-1207. |
| MAO Z H, ZHU J J, LIU Z G, et al., 2006. Effects of thinning on species diversity and composition of understorey herbs in a larch plantation[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 25(10): 1201-1207. | |
| [28] | 盛炜彤, 2014. 中国人工林及其育林体系[M]. 北京: 中国林业出版社. |
| SHENG W T, 2014. Plantation forest and their silvicature systems in China[M]. Beijing: China Forestry Publishing House. | |
| [29] | 孙冬婧, 温远光, 罗应华, 等, 2015. 近自然化改造对杉木人工林物种多样性的影响[J]. 林业科学研究, 28(2): 202-208. |
| SUN D J, WEN Y G, LUO Y H, et al., 2015. Effect of close-to-nature management on species diversity in a Cunninghamia lanceolata plantation[J]. Forest Research, 28(2): 202-208. | |
| [30] | 王晓荣, 曾立雄, 雷蕾, 等, 2019. 抚育择伐对马尾松林主要树种空间分布格局及其关联性的短期影响[J]. 生态学报, 39(12): 4421-4431. |
| WANG X R, ZENG L X, LEI L, et al., 2019. Short-term effects of selective cutting on the spatial distribution and association of dominant tree species in Pinus massoniana stands[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 39(12): 4421-4431. | |
| [31] | 王祖华, 李瑞霞, 王晓杰, 等, 2010. 间伐对杉木人工林林下植被多样性及生物量的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 19(12): 2778-2782. |
| WANG Z H, LI R X, WANG X J, et al., 2020. Effects of thinning on biomass and species diversity of understory in Chinese fir plantations[J]. Ecology and Environmental Science, 19(12): 2778-2782. | |
| [32] | 谢锦, 闫巧玲, 张婷, 2020. 间伐对日本落叶松人工林林下更新木本植物组成和生长影响的时间效应[J]. 应用生态学报, 31(8): 2481-2490. |
| XIE J, YAN Q L, ZHANG T, 2020. Temporal effects of thinning on the composition and growth of regenerated woody plants in Larix kaempferi plantations[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 31(8): 2481-2490. | |
| [33] | 薛立, 傅静丹, 2012. 影响植物竞争的因子[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 32(2): 6-15. |
| XUE L, FU J D, 2012. A review on factors affecting plant competition[J]. Journal of Central South University of Forestry and Technology, 32(2): 6-15. | |
| [34] | 张浩, 庄雪影, 黄永芳, 等, 2008. 华南乡土树种在松杉林下生长及林下植物多样性研究[J]. 林业科学研究, 21(2): 139-144. |
| ZHANG H, ZHUANG X Y, HUANG Y F, et al., 2008. Growth of some native broad-leaved trees and plant diversity in the conifers plantation of south China[J]. Forest Research, 21(2): 139-144. | |
| [35] | 庄雪影, CORLETT R T, 2000. 香港乡土树种幼苗在次生林下生长的研究[J]. 热带亚热带植物学报, 8(4): 291-300. |
| ZHUANG X Y, CORLETT R T, 2000. Survival and growth of native seedlings in secondary forest of Hong Kong[J]. Journal of Tropical and Subtropical Botany, 8(4): 291-300. |
| [1] | 张立进, 杜虎, 曾馥平, 黄国勤, 宋敏, 宋同清. 喀斯特峰丛洼地植被恢复过程中生产力与多样性关系探讨[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 26-35. |
| [2] | 肖国举, 李秀静, 郭占强, 胡延斌, 王静. 贺兰山东麓土壤有机碳对玉米生长发育及水分利用的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(9): 1754-1764. |
| [3] | 孙梦鑫, 张岳, 辛宇, 钟鼎杰, 杨存建. 川西高原近20 a植被物候变化及其对气候变化的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(7): 1326-1339. |
| [4] | 王磊, 温远光, 周晓果, 朱宏光, 孙冬婧. 尾巨桉与红锥混交对林下植被和土壤性质的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(7): 1340-1349. |
| [5] | 李程程, 张子蕤, 宋晓萱, 孔娟娟, 韩阳, 阮亚男. 臭氧胁迫对大豆抗氧化代谢与生殖生长的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(7): 1383-1392. |
| [6] | 刘宁, 刘洋, 续京平, 宋慧平, 冯政君, 程芳琴. 丛枝菌根真菌对人工湿地植物生长及水质净化的影响研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(7): 1434-1441. |
| [7] | 刘晓红, 刘柳青青, 栗敏, 刘强, 曹东东, 郑浩, 罗先香. 不同粒径的聚乙烯微塑料对玉米和黄瓜种子发芽和幼苗生长的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(6): 1263-1271. |
| [8] | 冯凌, 喻理飞, 王阳, 张丽敏, 赵庆, 李方兵. 喀斯特地区植被不同恢复阶段功能冗余和功能多样性对群落稳定性的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 670-678. |
| [9] | 陈瑶, 李云红, 邵英男, 刘玉龙, 刘延坤. 阔叶红松林物种多样性与土壤理化特征研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 679-687. |
| [10] | 魏岚, 黄连喜, 李翔, 王泽煌, 陈伟盛, 黄庆, 黄玉芬, 刘忠珍. 生物炭基质可显著地促进香蕉幼苗生长[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 732-739. |
| [11] | 李少宁, 陶雪莹, 李慧敏, 赵娜, 徐晓天, 鲁绍伟. 侧柏和垂柳释放有益BVOCs组分生长季动态变化特征研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(2): 257-264. |
| [12] | 宋瑞朋, 杨起帆, 郑智恒, 习丹. 3种林下植被类型对杉木人工林土壤有机碳及其组分特征的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(12): 2283-2291. |
| [13] | 陈赋秋雪, 唐思琪, 袁昊, 马子轩, 陈坦, 杨婷, 张冰, 刘颖. 聚苯乙烯微塑料对典型农作物种子发芽和幼苗生长的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(12): 2382-2392. |
| [14] | 丁洪, 余居华, 郑祥洲, 张玉树, 钟云峰. 中国城市污泥应用对作物产量、品质和土壤质量的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(9): 1933-1942. |
| [15] | 何斌, 李青, 陈群利, 李望军, 游萍. 黔西北黄杉群落物种多样性的海拔梯度格局[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(6): 1111-1120. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
