生态环境学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (11): 2109-2120.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2021.11.001
所属专题: 生物多样性专题汇编
• 研究论文 •
下一篇
收稿日期:2021-08-13
出版日期:2021-11-18
发布日期:2021-12-29
通讯作者:
*作者简介:姜倪皓(1990年生),男(彝族),讲师,博士,主要从事种群生态及农业生态相关研究。E-mail: jnhskip@cxtc.edu.cn
基金资助:
JIANG Nihao1,*( ), ZHANG Shihan2
), ZHANG Shihan2
Received:2021-08-13
Online:2021-11-18
Published:2021-12-29
摘要:
草本植物是森林生态系统重要组成部分。对楚雄市西郊云南松(Pinus yunnanensis)林下优势草本植物间的种间联结性及其与环境因子之间的关系进行探讨,旨在为该区域云南松林生态系统的结构和功能的维持提供参考。运用生态位宽度、生态位重叠值、方差比率法、卡方检验、联结系数和M. Godron稳定性测定对8种草本优势种间的相互关系进行综合分析;运用冗余分析(redundancy analysis,RDA)方法,探讨优势草本植物分布与环境因子的关系。结果表明,(1)多数草本优势种的生态位宽度较窄,仅云南裂稃草(Schizachyrium brevifolium)具有较大的生态位宽度,多数草本优势种之间存在较小的生态位重叠。(2)云南裂稃草属于发展性物种,其他7种物种均为衰退性物种。(3)草本优势种间的总体联结性表现为显著负联结,多数种对之间联结程度不显著;群落稳定性测定坐标值为(47.42, 52.58),远离稳定坐标点(20, 80)。(4)对草本层物种分布影响显著的环境因子为:土壤pH值、坡向、土壤有机质、土壤电导率和土壤全磷。以上研究表明该地区的草本优势种间独立性较强。草本群落整体处于不稳定状态,仍处于演替的早期阶段。在今后的森林管理活动中,可根据草本优势种的种间关系、生态位特征以及影响物种分布的环境因子对林下草本植物进行调控,维持和提升草本群落的稳定性。
中图分类号:
姜倪皓, 张诗函. 楚雄市西郊云南松林下草本优势种种间联结及环境解释[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(11): 2109-2120.
JIANG Nihao, ZHANG Shihan. Interspecific Association and Environmental Interpretation of Dominant Herbaceous Species in Pinus yunnanensis Forest in the Western Suburbs of Chuxiong City[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(11): 2109-2120.
| 样地编号 Sample number | 海拔 Altitude/ m | 坡度 Slope/ (°) | 坡向 Slope aspect | 郁闭度 Canopy closure/ % | 地表凋落物厚度 Litter thickness/ cm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1853 | 15 | 1 | 0.5 | 3 |
| 2 | 1860 | 15 | 3 | 0.7 | 5 |
| 3 | 1813 | 13 | 7 | 0.7 | 5 |
| 4 | 1815 | 8 | 3 | 0.8 | 5 |
| 5 | 1910 | 22 | 3 | 0.6 | 5 |
| 6 | 1900 | 15 | 1 | 0.6 | 3 |
| 7 | 1820 | 10 | 1 | 0.8 | 3 |
| 8 | 1830 | 25 | 1 | 0.8 | 8 |
| 9 | 1820 | 11 | 1 | 0.8 | 10 |
| 10 | 1910 | 21 | 7 | 0.8 | 3 |
| 11 | 1910 | 32 | 1 | 0.5 | 3 |
| 12 | 1850 | 15 | 1 | 0.6 | 3 |
表1 样地基础信息
Table 1 General conditions of sampling transects
| 样地编号 Sample number | 海拔 Altitude/ m | 坡度 Slope/ (°) | 坡向 Slope aspect | 郁闭度 Canopy closure/ % | 地表凋落物厚度 Litter thickness/ cm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1853 | 15 | 1 | 0.5 | 3 |
| 2 | 1860 | 15 | 3 | 0.7 | 5 |
| 3 | 1813 | 13 | 7 | 0.7 | 5 |
| 4 | 1815 | 8 | 3 | 0.8 | 5 |
| 5 | 1910 | 22 | 3 | 0.6 | 5 |
| 6 | 1900 | 15 | 1 | 0.6 | 3 |
| 7 | 1820 | 10 | 1 | 0.8 | 3 |
| 8 | 1830 | 25 | 1 | 0.8 | 8 |
| 9 | 1820 | 11 | 1 | 0.8 | 10 |
| 10 | 1910 | 21 | 7 | 0.8 | 3 |
| 11 | 1910 | 32 | 1 | 0.5 | 3 |
| 12 | 1850 | 15 | 1 | 0.6 | 3 |
| 编号 No. | 物种 Species | 科 Family | 重要值 Important Value/% | 变异系数 Coefficient of Variation/% | 生态位宽度 Niche breadth | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B(sw) | B(L) | |||||
| S1 | 云南裂稃草 Schizachyrium brevifolium (Sw) Nees ex Buse | 禾本科 | 70.7 | 34.31 | 3.09 | 22.53 |
| S2 | 金丝草 Pogonatherum crinitum (Thunb.) Kunth | 禾本科 | 6.7 | 258.37 | 1.28 | 3.24 |
| S3 | 鼠曲草 Gnaphalium affine D. Don, | 菊科 | 5.8 | 209.81 | 1.56 | 4.59 |
| S4 | 芒萁 Dicranopteris dichotoma (Thunb.) Berhn. | 里白科 | 5.2 | 343.17 | 0.68 | 1.95 |
| S5 | 白茅 Imperata cylindrica (Linn.) Beauv. | 禾本科 | 4.8 | 283.16 | 1.26 | 2.88 |
| S6 | 拟金茅 Eulaliopsis binata (Retz.) C. E. Hubbard | 禾本科 | 2.3 | 282.39 | 1.06 | 2.77 |
| S7 | 皱叶狗尾草 Setaria plicata (Lam.) T. Cooke | 禾本科 | 1.0 | 442.11 | 0.32 | 1.21 |
| S8 | 浆果薹草 Carex baccans Nees | 莎草科 | 1.0 | 489.90 | 0.19 | 1.10 |
表2 草本层优势种重要值及其生态位宽度
Table 2 Importance value and niche breadth of dominant species in herbaceous layer
| 编号 No. | 物种 Species | 科 Family | 重要值 Important Value/% | 变异系数 Coefficient of Variation/% | 生态位宽度 Niche breadth | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B(sw) | B(L) | |||||
| S1 | 云南裂稃草 Schizachyrium brevifolium (Sw) Nees ex Buse | 禾本科 | 70.7 | 34.31 | 3.09 | 22.53 |
| S2 | 金丝草 Pogonatherum crinitum (Thunb.) Kunth | 禾本科 | 6.7 | 258.37 | 1.28 | 3.24 |
| S3 | 鼠曲草 Gnaphalium affine D. Don, | 菊科 | 5.8 | 209.81 | 1.56 | 4.59 |
| S4 | 芒萁 Dicranopteris dichotoma (Thunb.) Berhn. | 里白科 | 5.2 | 343.17 | 0.68 | 1.95 |
| S5 | 白茅 Imperata cylindrica (Linn.) Beauv. | 禾本科 | 4.8 | 283.16 | 1.26 | 2.88 |
| S6 | 拟金茅 Eulaliopsis binata (Retz.) C. E. Hubbard | 禾本科 | 2.3 | 282.39 | 1.06 | 2.77 |
| S7 | 皱叶狗尾草 Setaria plicata (Lam.) T. Cooke | 禾本科 | 1.0 | 442.11 | 0.32 | 1.21 |
| S8 | 浆果薹草 Carex baccans Nees | 莎草科 | 1.0 | 489.90 | 0.19 | 1.10 |
| 编号 No. | S1 | S2 | S3 | S4 | S5 | S6 | S7 | S8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 0.425 | 0.876 | 0.461 | 0.547 | 0.835 | 0.872 | 1.110 | |
| S2 | 0.061 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.301 | 0.089 | 0.149 | 0.000 | |
| S3 | 0.179 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | |
| S4 | 0.040 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | |
| S5 | 0.070 | 0.268 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.057 | 0.006 | |
| S6 | 0.103 | 0.076 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | |
| S7 | 0.047 | 0.056 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.024 | 0.000 | 0.000 | |
| S8 | 0.054 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.002 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
表3 林下草本层优势物种的生态位重叠指数
Table 3 Niche overlap of the dominant species in herbaceous layer
| 编号 No. | S1 | S2 | S3 | S4 | S5 | S6 | S7 | S8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 0.425 | 0.876 | 0.461 | 0.547 | 0.835 | 0.872 | 1.110 | |
| S2 | 0.061 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.301 | 0.089 | 0.149 | 0.000 | |
| S3 | 0.179 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | |
| S4 | 0.040 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | |
| S5 | 0.070 | 0.268 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.057 | 0.006 | |
| S6 | 0.103 | 0.076 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | |
| S7 | 0.047 | 0.056 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.024 | 0.000 | 0.000 | |
| S8 | 0.054 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.002 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| 物种 Species | | R |
|---|---|---|
| S1 | 4.57 | 4.93 |
| S2 | -0.23 | -14.45 |
| S3 | -0.69 | -6.59 |
| S4 | -0.42 | -4.64 |
| S5 | -0.47 | -6.11 |
| S6 | -0.75 | -3.73 |
| S7 | -0.95 | -1.28 |
| S8 | -1.05 | -0.96 |
表4 草本层物种发展或衰退情况
Table 4 Aggression or declining situation of dominant species in herb layer
| 物种 Species | | R |
|---|---|---|
| S1 | 4.57 | 4.93 |
| S2 | -0.23 | -14.45 |
| S3 | -0.69 | -6.59 |
| S4 | -0.42 | -4.64 |
| S5 | -0.47 | -6.11 |
| S6 | -0.75 | -3.73 |
| S7 | -0.95 | -1.28 |
| S8 | -1.05 | -0.96 |
| 林分类型 Forest type | 方差比率 Variance ratio (Rv) | 检验统计量 Test statistics (W) | χ2临界值 χ2 thershold (χ20.95, χ20.05) | 测度结果 Measurement results |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 云南松次生林 Pinus yunnanensis natural secondary forest | 0.0185 | 1.11 | (43.19, 79.08) | 显著负关联 Significantly negative correlation |
表5 草本层主要物种间的总体联结性
Table 5 Overall interspecific associations among dominant species in herb layer
| 林分类型 Forest type | 方差比率 Variance ratio (Rv) | 检验统计量 Test statistics (W) | χ2临界值 χ2 thershold (χ20.95, χ20.05) | 测度结果 Measurement results |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 云南松次生林 Pinus yunnanensis natural secondary forest | 0.0185 | 1.11 | (43.19, 79.08) | 显著负关联 Significantly negative correlation |
| 检验方法 Test methods | 联结类型 Association type | 数值范围 Value range | 测度结果 Measurement Results | 种对数 Species pair number | 百分比/% Percentage/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| χ2检验 Chi-square test | 正联结 Positive association | P≤0.01 | 极显著 Extremely significant | 0 | 0 |
| P≤0.05 | 显著 Significant | 0 | 0 | ||
| P>0.05 | 不显著 Non-significant | 3 | 10.70 | ||
| 负联结 Negative association | P≤0.01 | 极显著 Extremely significant | 3 | 10.70 | |
| P≤0.05 | 显著 Significant | 0 | 0 | ||
| P>0.05 | 不显著 Non-significant | 22 | 78.60 | ||
| 联结系数 (AC) Association coefficient | 正联结 Positive association | AC≥0.6 | 极显著 Extremely significant | 0 | 0 |
| 0.2≤AC<0.6 | 显著 Significant | 1 | 3.60 | ||
| 0.2<AC<0 | 不显著 Non-significant | 2 | 7.14 | ||
| 负联结 Negative association | AC≤-0.6 | 极显著 Extremely significant | 16 | 57.14 | |
| -0.6<AC≤-0.2 | 显著 Significant | 6 | 21.42 | ||
| -0.2<AC<0 | 不显著 Non-significant | 3 | 10.70 |
表6 草本层主要物种的χ2检验及联结系数(AC)结果比较
Table 6 Comparison of χ2-test coefficient and association coefficient among main species in herb layer
| 检验方法 Test methods | 联结类型 Association type | 数值范围 Value range | 测度结果 Measurement Results | 种对数 Species pair number | 百分比/% Percentage/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| χ2检验 Chi-square test | 正联结 Positive association | P≤0.01 | 极显著 Extremely significant | 0 | 0 |
| P≤0.05 | 显著 Significant | 0 | 0 | ||
| P>0.05 | 不显著 Non-significant | 3 | 10.70 | ||
| 负联结 Negative association | P≤0.01 | 极显著 Extremely significant | 3 | 10.70 | |
| P≤0.05 | 显著 Significant | 0 | 0 | ||
| P>0.05 | 不显著 Non-significant | 22 | 78.60 | ||
| 联结系数 (AC) Association coefficient | 正联结 Positive association | AC≥0.6 | 极显著 Extremely significant | 0 | 0 |
| 0.2≤AC<0.6 | 显著 Significant | 1 | 3.60 | ||
| 0.2<AC<0 | 不显著 Non-significant | 2 | 7.14 | ||
| 负联结 Negative association | AC≤-0.6 | 极显著 Extremely significant | 16 | 57.14 | |
| -0.6<AC≤-0.2 | 显著 Significant | 6 | 21.42 | ||
| -0.2<AC<0 | 不显著 Non-significant | 3 | 10.70 |
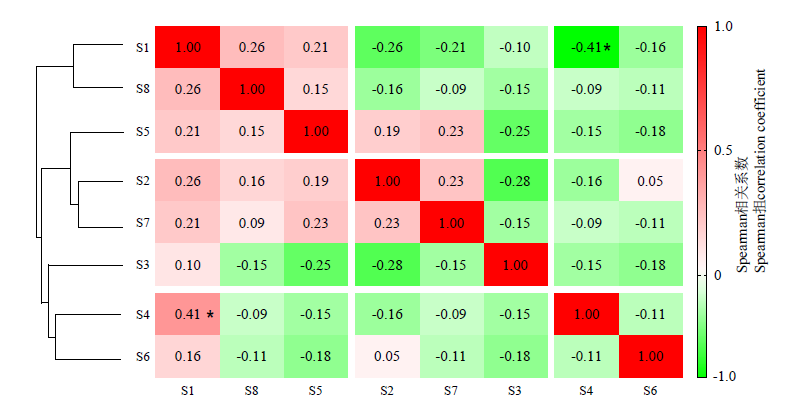
图2 草本层主要物种的Spearman秩相关检分析 注编号对应物种见表2;*P<0.05
Fig. 2 Spearman’s rank correlation coefficients of dominant herbaceous species Species numbers are shown in Table 2; *P<0.05
| 曲线类型 Type of curve | 决定系数 Determination coefficient (R2) | 交点坐标 Nodal corrdinate | 测度结果 Measurement results | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| x | y | |||
| y= -0.0049x2+ 1.6092x-12.703 | 0.9918 | 47.42 | 52.58 | 不稳定 Unstable |
表7 群落稳定性分析结果(M. Godron法)
Table 7 Results of community stability (M. Godron’s method)
| 曲线类型 Type of curve | 决定系数 Determination coefficient (R2) | 交点坐标 Nodal corrdinate | 测度结果 Measurement results | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| x | y | |||
| y= -0.0049x2+ 1.6092x-12.703 | 0.9918 | 47.42 | 52.58 | 不稳定 Unstable |
| 项目 Item | 第1轴 Axis 1 | 第2轴 Axis 2 | 第3轴 Axis 3 | 第4轴 Axis 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 特征值 Eigenvalue | 0.48 | 0.17 | 0.10 | 0.09 |
| 物种-环境相关系数 Species-environment correlation coefficient | 0.97 | 0.89 | 0.99 | 0.90 |
| 物种环境关系的累积解释 Cumulative percentage variance of species-environment relation | 47.98 | 64.72 | 75.09 | 83.89 |
| 特征值总和 Sum of eigenvalues | 1 | |||
| 典型特征值总和 Sum of canonical eigenvalues | 0.84 | |||
| 第一典范轴的显著性测验 Significant test of the first canonical axis | F=7.38, P=0.01 | |||
| 所有典范轴的显著性测验 Significant test of all canonical axes | F=4.06, P=0.004 | |||
表8 云南松林下草本植物的RDA排序
Table 8 RDA ordination of understory herbaceous in Pinus yunnanensis forests
| 项目 Item | 第1轴 Axis 1 | 第2轴 Axis 2 | 第3轴 Axis 3 | 第4轴 Axis 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 特征值 Eigenvalue | 0.48 | 0.17 | 0.10 | 0.09 |
| 物种-环境相关系数 Species-environment correlation coefficient | 0.97 | 0.89 | 0.99 | 0.90 |
| 物种环境关系的累积解释 Cumulative percentage variance of species-environment relation | 47.98 | 64.72 | 75.09 | 83.89 |
| 特征值总和 Sum of eigenvalues | 1 | |||
| 典型特征值总和 Sum of canonical eigenvalues | 0.84 | |||
| 第一典范轴的显著性测验 Significant test of the first canonical axis | F=7.38, P=0.01 | |||
| 所有典范轴的显著性测验 Significant test of all canonical axes | F=4.06, P=0.004 | |||
| 环境因子 Environment factors | 解释率 Contribution/% | F | P |
|---|---|---|---|
| pH (pH) | 17.2 | 4.8 | 0.006** |
| 坡向 Slope aspect (SA) | 9.6 | 2.9 | 0.02* |
| 电导率 Electric conductivity (EC) | 5.8 | 1.8 | 0.08* |
| 容重 Soil bulk density (SBD) | 4.5 | 1.4 | 0.22 |
| 有机质 Soil organic matter (SOM) | 8.2 | 2.8 | 0.04* |
| 全氮 Total nitrogen (TN) | 5.1 | 1.8 | 0.13 |
| 郁闭度 Canopy closure(CC) | 7.0 | 2.8 | 0.05 |
| 有效氮 Available nitrogen (AN) | 6.8 | 3.0 | 0.60 |
| 土壤含水量 Soil water content (SWC) | 3.4 | 1.6 | 0.21 |
| 凋落物厚度 Litter thickness (LT) | 4.9 | 2.5 | 0.08 |
| 有效钾 Available potassium (AK) | 3 | 1.6 | 0.21 |
| 坡度 Slope (S) | 2.5 | 1.3 | 0.26 |
| 海拔 Altitude (A) | 1.5 | 0.8 | 0.48 |
| 全磷 Total phosphorus (TP) | 6.6 | 4.7 | 0.02* |
| 全钾 Total potassium (TK) | 2.8 | 2.3 | 0.13 |
| 有效磷 Available phosphorus (AP) | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.90 |
表9 冗余分析(RDA)中环境因子对草本植物群落组成的解释率
Table 9 Contribution of significant environmental factors affecting herbaceous community composition in redundancy analysis (RDA)
| 环境因子 Environment factors | 解释率 Contribution/% | F | P |
|---|---|---|---|
| pH (pH) | 17.2 | 4.8 | 0.006** |
| 坡向 Slope aspect (SA) | 9.6 | 2.9 | 0.02* |
| 电导率 Electric conductivity (EC) | 5.8 | 1.8 | 0.08* |
| 容重 Soil bulk density (SBD) | 4.5 | 1.4 | 0.22 |
| 有机质 Soil organic matter (SOM) | 8.2 | 2.8 | 0.04* |
| 全氮 Total nitrogen (TN) | 5.1 | 1.8 | 0.13 |
| 郁闭度 Canopy closure(CC) | 7.0 | 2.8 | 0.05 |
| 有效氮 Available nitrogen (AN) | 6.8 | 3.0 | 0.60 |
| 土壤含水量 Soil water content (SWC) | 3.4 | 1.6 | 0.21 |
| 凋落物厚度 Litter thickness (LT) | 4.9 | 2.5 | 0.08 |
| 有效钾 Available potassium (AK) | 3 | 1.6 | 0.21 |
| 坡度 Slope (S) | 2.5 | 1.3 | 0.26 |
| 海拔 Altitude (A) | 1.5 | 0.8 | 0.48 |
| 全磷 Total phosphorus (TP) | 6.6 | 4.7 | 0.02* |
| 全钾 Total potassium (TK) | 2.8 | 2.3 | 0.13 |
| 有效磷 Available phosphorus (AP) | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.90 |
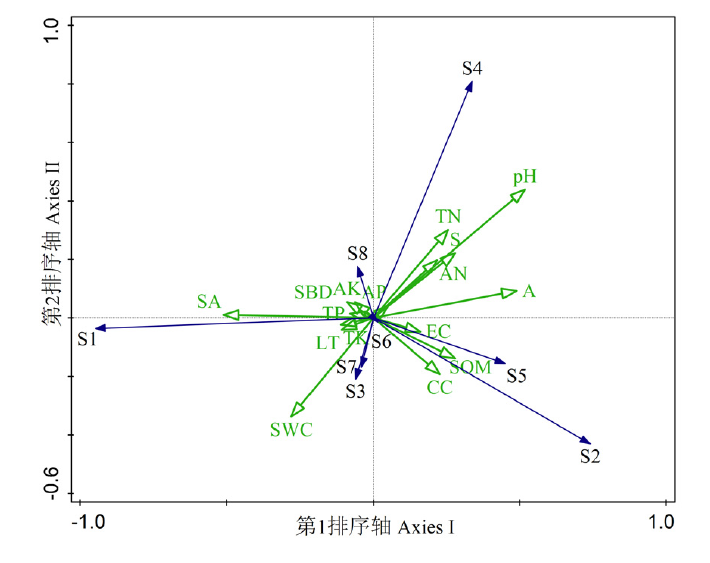
图3 草本植物与环境因子的RDA排序图 绿色箭头线段表示环境因子;编号对应物种见表2;环境因子简写详见表9
Fig. 3 RDA plot of herbaceous species and environmental factors The green arrow lines represent environmental factors. Species numbers are shown in Table 2. Abbreviation of environmental factors are the same as in Table 9
| [1] |
ÁLVAREZ-YÉPIZ J C, BÚRQUEZ A, DOVČIAK M, 2014. Ontogenetic shifts in plant-plant interactions in a rare cycad within angiosperm communities[J]. Oecologia, 175(2): 725-735.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
ARELLANO G, CALAV V, MACIA M J, 2015. Niche breadth of oligarchic species in Amazonian and Andean rain forests[J]. Journal of Vegetation Science, 25(6): 1355-1366.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
BILAL A, WANG Y H, JIA W, et al., 2018. Optimizing stand structure for trade-offs between overstory timber production and understory plant diversity: A case-study of a larch plantation in northwest China[J]. Land Degradation and Development, 29(9): 2998-3008.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
CHUDOMELOVÁ M, ZELRNY D, LI C F, 2017. Contrasting patterns of fine-scale herb layer species composition in temperate forests[J]. Acta Oecologica, 80: 24-31.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
GILLIAM F S, 2007. The ecological significance of the herbaceous layer in temperate forest ecosystems[J]. BioScience, 57: 845-858.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
HART S A, CHEN H Y, 2006. Understory vegetation dynamics of North American boreal forests[J]. Critical Reviews in Plant Sciences, 25(4): 381-397.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
HURLBERT S H, 1978. The Measurement of Niche Overlap and Some Relatives[J]. Ecology, 59(1): 67-77.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
LOMOLINO M V, 2001. Elevation gradients of species-density: Historical and prospective views[J]. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 10(1): 3-13.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
SCHLUTER D, 1984. A variance test for detecting species associations, with some example applications[J]. Ecology, 65(3): 998-1005.
DOI URL |
| [10] | SOHLBERG E H, BLISS L C, 1984. Microscale pattern of vascular plant distribution in two high arctic plant communities[J]. NRC Research Press Ottawa, Canada, 62(10): 2033-2042. |
| [11] | 蔡年辉, 李根前, 朱存福, 等, 2007. 云南松人工林与天然林群落结构的比较研究[J]. 西北林学院学报, 22(2): 1-4, 163. |
| CAI N H, LI G Q, ZHU C F, et al., 2007. A Comparison Study on the Community Structure between Artificial and Natural Forests of Pinus yunnanensis[J]. Journal of Northwest Forestry University, 22(2): 1-4, 163. | |
| [12] |
陈晓红, 万鲁河, 2013. 城市化与生态环境耦合的脆弱性与协调性作用机制研究[J]. 地理科学, 33(12): 1450-1457.
DOI |
| CHEN X H, WAN L H, 2013. The Interactive Mechanisms for the Coordination and Vulnerability Between Regional Urban and Eco- environment[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 33(12): 1450-1457. | |
| [13] |
陈玉凯, 杨琦, 莫燕妮, 等, 2014. 海南岛霸王岭国家重点保护植物的生态位研究[J]. 植物生态学报, 38(6): 576-584.
DOI |
|
CHEN Y K, YANG Q, MO Y N, et al., 2014. A study on the niches of the state's key protected plants in Bawangling, Hainan Island[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 38(6): 576-584.
DOI URL |
|
| [14] | 曹梦, 潘萍, 欧阳勋志, 等, 2018. 飞播马尾松林林下植被组成、多样性及其与环境因子的关系[J]. 生态学杂志, 37(1): 1-8. |
| CAO M, PAN P, OUYANG X Z, et al., 2018. Relationships between the composition and diversity of understory vegetation and environmental factors in aerially seeded Pinus massoniana plantations[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 37(1): 1-8. | |
| [15] | 戴开结, 沈有信, 周文君, 等, 2005. 云南松根际pH与不同磷水平下云南松幼苗根际pH变化[J]. 西北植物学报, 25(12): 2490-2494. |
| DAI K J, SHEN Y X, ZHOU W J, et al., 2005. Rhizosphere pH of Pinus yunnanensis Franch. and Rhizosphere pH of P. yunnanensis Seedlings at Different Phosphorous Rates[J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 25(12): 2490-2494. | |
| [16] | 邓喜庆, 皇宝林, 温庆忠, 等, 2013. 云南松林在云南的分布研究[J]. 云南大学学报 (自然科学版), 35(6): 843-848. |
| DENG X Q, HUANG B L, WEN Q Z, et al., 2013. A research on the distribution of Pinus yunnanensis forest in Yunnan Province[J]. Journal of Yunnan University (Natural Sciences Edition), 35(6): 843-848. | |
| [17] | 冯宜明, 陈学龙, 齐瑞, 等, 2018. 甘肃亚高山云杉人工林下植物种群生态位特征[J]. 草业科学, 35(4): 807-815. |
| FENG Y M, CHEN X L, RUI Q, et al., 2018. Niche characteristics of the primary understory populations of a Piceaasperata plantation in the subalpine region of Gansu Province[J]. Pratacultural Science, 35(4): 807-815. | |
| [18] | 郭燕, 杨邵, 沈雅飞, 等, 2018. 三峡库区消落带现存草本植物组成与生态位[J]. 应用生态学报, 29(11): 3559-3568. |
| GUO Y, YANG S, SHEN Y F, et al., 2018. Composition and niche of the existing herbaceous plants in the water-level-fluctuating zone of the Three Gorges Reservoir Area, China[J]. The Journal of Applied Ecology, 29(11): 3559-3568. | |
| [19] | 郭忠玲, 马元丹, 郑金萍, 等, 2004. 长白山落叶阔叶混交林的物种多样性、种群空间分布格局及种间关联性研究[J]. 应用生态学报, 15(11): 2013-2018. |
| GUO Z L, MA Y D, ZHENG J P, et al., 2004. Biodiversity of tree species, their populations' spatial distribution pattern and interspecific association in mixed deciduous broadleaved forest in Changbai Mountains[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 15(11): 2013-2018. | |
| [20] | 贺建林, 陈桂香, 2005. 我国生态环境恶化的理性思考[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 13(3): 199-201. |
| HE J L, CHEN G X, 2005. Analysis on the deterioration of eco-environment in our country[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 13(3): 199-201. | |
| [21] |
黄庆阳, 曹宏杰, 谢立红, 等, 2020. 五大连池火山熔岩台地草本层物种多样性及环境解释[J]. 生物多样性, 28(6): 658-667.
DOI |
|
HUANG Q Y, CAO H J, XIE L H, et al., 2020. Species diversity and environmental interpretation of herb layer in lava platform of Wudalianchi, China[J]. Biodiversity Science, 28(6): 658-667.
DOI URL |
|
| [22] | 黄秋燕, 2017. 凸显地域文化特色的城市近郊型森林公园景观规划--以肇庆市羚羊山森林公园为例[J]. 林业调查规划, 42(3): 151-156. |
| HUANG Q, 2017. Landscape Planning of Suburban Forest Park with the Emphasis of Regional Culture: A Case Study of Antelope Mountain Forest Park in Zhaoqing City[J]. Forest Inventory and Planning, 42(3): 151-156. | |
| [23] | 简尊吉, 马凡强, 郭泉水, 等, 2017. 三峡水库峡谷地貌区消落带优势植物种群生态位[J]. 生态学杂志, 36(2): 328-334. |
| JIAN Z J, MA F Q, GUO Q S, et al., 2017. Niche of dominant plant populations in the water level fluctuation zone of canyon landform area of the Three Gorges Reservoir[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 36(2): 328-334. | |
| [24] | 李小飞, 陈志彪, 陈志强, 等, 2013. 南方红壤侵蚀区芒萁生长特征及其对环境因子的响应[J]. 水土保持通报, 33(3): 33-37. |
| LI X F, CHEN Z B, CHEN Z Q, et al., 2013. Responses of Disranopteris dichotoma Growth to Environmental Factors in Eroded Red-soil Region of Southern China[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 33(3): 33-37. | |
| [25] | 李中林, 秦卫华, 周守标, 等, 2014. 围栏封育下华北半干旱草原植物生态位研究[J]. 草地学报, 22(6): 1186-1193. |
| LI Z L, QIN W H, ZHOU S B, et al., 2014. Study on Plant Niche under Fencing Measures in the Semi-arid Grassland of North China[J]. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 22(6): 1186-1193. | |
| [26] | 刘淼, 刘心茗, 董丽, 2014. 北京市郊野公园植物景观综合评价[J]. 西北林学院学报, 29(6): 245-249, 265. |
| LIU M, LIU X M, DONG L, 2014. The Synthetical Evaluation and Study on Plant Landscape of Country Parks in Beijing[J]. Journal of Northwest Forestry University, 29(6): 245-249, 265. | |
| [27] | 刘润红, 陈乐, 涂洪润, 等, 2020. 桂林岩溶石山青冈群落灌木层主要物种生态位与种间联结[J]. 生态学报, 40(6): 2057-2071. |
| LIU R H, CHEN L, XU H R, 2020. Niche and interspecific association of main species in shrub layer of Cyclobalanopsis glauca community in karst hills of Guilin, southwest China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 40(6): 2057-2071. | |
| [28] |
马程, 王晓玥, 张雅昕, 等, 2017. 北京市生态涵养区生态系统服务供给与流动的能值分析[J]. 地理学报, 72(6): 974-985.
DOI |
| CHENG M A, WANG X Y, ZHANG Y X, et al., 2017. Emergy analysis of ecosystem services supply and flow in Beijing ecological conservation area[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 72(6): 974-985. | |
| [29] | 沈会涛, 刘存歧, 2008. 白洋淀浮游植物群落及其与环境因子的典范对应分析[J]. 湖泊科学, 20(6): 773-779. |
|
SHEN H T, LIU C Q, 2008. Canonical correspondence analysis of phytoplankton community and its environmental factors in the Lake Baiyangdian[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 20(6): 773-779.
DOI URL |
|
| [30] | 谭一波, 何琴飞, 郑威, 等, 2016. 珠江流域中上游防护林冠层结构对林下植被的影响[J]. 生态学杂志, 35(12): 3148-3156. |
| TAN Y B, HE Q F, ZHENG W, et al., 2016. Effects of canopy structure on understory vegetation in shelterbelt forests along the middle and upper reaches of Pearl River[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 35(12): 3148-3156. | |
| [31] |
谭一波, 申文辉, 付孜, 等, 2019. 环境因子对桂西南蚬木林下植被物种多样性变异的解释[J]. 生物多样性, 27(9): 970-983.
DOI |
|
TAN Y B, SHEN W H, FU Z, et al., 2019. Effect of environmental factors on understory species diversity in Southwest Guangxi Excentrodendron tonkinense forests[J]. Biodiversity Science, 27(9): 970-983.
DOI URL |
|
| [32] | 唐虹, 秦飞, 2012. 城市人、环境、文化的最优协调发展模式--生态园林城市[J]. 环境科学与管理, 37(2): 131-134. |
| TANG H, QING F, 2012. Study on Ecological Landscape Garden City--Eco-garden City[J]. Environmental Science and Management, 37(2): 131-134. | |
| [33] | 王刚, 赵松岭, 张鹏云, 等, 1984. 关于生态位定义的探讨及生态位重叠计测公式改进的研究[J]. 生态学报, 4(2): 119-127. |
| WANG G, ZHAO S L, ZHANG P Y, et al., 1948. On the definition of niche and the improved formula for measuring niche overlap[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 4(2): 119-127. | |
| [34] | 王健敏, 刘娟, 陈晓鸣, 等, 2010. 云南松天然林及人工林群落结构和物种多样性比较[J]. 林业科学研究, 23(4): 515-522. |
| WANG J M, LIU J, CHEN X M, et al., 2010. Comparison of Community Structures and Species Diversity in Natural Forests and Forest Plantation of Pinus yunnanensis[J]. Forest Research, 23(4): 515-522. | |
| [35] | 王立竹, 张明如, 许焱, 等, 2018. 模拟酸雨和光强交互作用对芒萁光合生理特性的影响[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 38(10): 86-94. |
| WANG L Z, ZHANG M R, XU Y, et al., 2018. Effects of interaction of simulated acid rain and light intensity treatments on photosynthetic characteristics in Dicranopteris dichotoma. Journal of Central South University of Forestry and Technology, 38(10): 86-94. | |
| [36] | 韦宇, 杨正兵, 2015. 楚雄西山公园南坡植物群落乔木层结构特征分析[J]. 四川林业科技, 36(4): 120-124. |
| WEI Y, YANG Z B, 2015. Structure Characteristics of the Tree Layer of the Plant Community on Sunny Slope in Chuxiong Xishan Park[J]. Journal of Sichuan Forestry Science and Technology, 36(4): 120-124. | |
| [37] | 吴佳梦, 徐娜娜, 张文珺, 等, 2019. 浙江舟山定海护城河浮游植物优势种生态位与种间联结性季节性分析[J]. 湖泊科学, 31(2): 429-439. |
|
WU J M, XU N N, ZHANG W J, et al., 2019. Seasonal analysis of the niche and interspecific association of dominant species of phytoplankton in the Dinghai Moat, Zhoushan City[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 31(2): 429-439.
DOI URL |
|
| [38] | 徐满厚, 刘敏, 翟大彤, 等, 2016. 植物种间联结研究内容与方法评述[J]. 生态学报, 36(24): 8224-8233. |
| XU M H, LIU M, ZHAI D T, et al., 2016. A review of contents and methods used to analyze various aspects of plant interspecific associations[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica. 36(24): 8224-8233 | |
| [39] | 杨文云, 崔永忠, 罗香, 等, 2010. 滇中高原雕林山云南松混交林群落结构特征[J]. 林业科学研究, 23(5): 719-726. |
| YANG W Y, CUI Y Z, LUO X, 2010. Community structure of mixed yunnan pine forests in diaolinshan natural reserve, middle yunnan plateau, China[J]. Forest Research, 23(5): 719-726. | |
| [40] |
余敏, 周志勇, 康峰峰, 等, 2013. 山西灵空山小蛇沟林下草本层植物群落梯度分析及环境解释[J]. 植物生态学报, 37(5): 373-383.
DOI |
|
YU M, ZHOU Z Y, KANG F F, et al., 2013. Gradient analysis and environmental interpretation of understory herb-layer communities in Xiaoshegou of Lingkong Mountain, Shanxi, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 37(5): 373-383.
DOI URL |
|
| [41] | 袁轶男, 刘兴诏, 聂晓嘉, 等, 2019. 国际城市森林研究知识图谱--基于CiteSpace Ⅴ共被引分析[J]. 生态学报, 39(20): 7780-7787. |
| YUAN Y N, LIU X Y, NIU X J, et al., 2019. The knowledge mapping of international research about urban forest: Based on Co-citation Analysis of CiteSpace V[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 39(20): 7780-7787. | |
| [42] | 张峰, 张金屯, 2003. 历山自然保护区猪尾沟森林群落植被格局及环境解释[J]. 生态学报, 23(3): 421-427. |
| ZHANG F, ZHANG J T, 2003. Pattern of forest vegetation and its environmental interpretation in Zhuweigou, Lishan Mountain Nature Reserve[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 23(3): 421-427. | |
| [43] | 张凤成, 2012. 楚雄市城市水源地生态保护中存在的问题及对策[J]. 林业建设 (6): 24-29, 40. |
| ZHANG F C, 2012. Problem and countermeasure on ecological protection for waterhead area in Chuxiong city[J]. Forestry Construction (6): 24-29, 40. | |
| [44] | 赵娟娟, 孙小梅, 陈珊珊, 等, 2016. 城市野生草本植物种类构成的特征--以宁波市为例[J]. 生态环境学报, 25(1): 43-50. |
| ZHAO J J, SUN X M, CHEN S S, et al., 2016. Characteristics of Species Composition for Urban Spontaneous Herbs, with Ningbo, China as A Case Study[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 25(1): 43-50. | |
| [45] | 张金屯, 2018. 数量生态学[M]. 第3版. 北京: 科学出版社: 147-162. |
| ZHANG J T, 2018. Quantitative Ecology[M]. 3rd edition. Beijing: Science Press: 147-162. | |
| [46] | 赵同谦, 欧阳志云, 郑华, 等, 2004. 中国森林生态系统服务功能及其价值评价[J]. 自然资源学报, 19(4): 480-491. |
| ZHAO T Q, OUYANG Z Y, ZHENG H, et al., 2004. Forest ecosystem services and their valuation in China[J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 19(4): 480-491. | |
| [47] | 郑晓阳, 赵冲, 刘青青, 等, 2018. 成熟杉木人工林林下草本层生态位特征[J]. 生态学杂志, 37(2): 332-338. |
| ZHENG X Y, ZHAO C, LIU Q Q, et al., 2018. Niche characteristics of understory herb layer in a mature Chinese fir plantation[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 37(2): 332-338. | |
| [48] | 郑元润, 2000. 森林群落稳定性研究方法初探[J]. 林业科学, 36(5): 28-32. |
| ZHENG Y Y, 2000. Comparison of methods for studying stability of forest community[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 36(5): 28-32. |
| [1] | 杜丹丹, 高瑞忠, 房丽晶, 谢龙梅. 旱区盐湖盆地土壤重金属空间变异及对土壤理化因子的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(6): 1123-1132. |
| [2] | 李善家, 王兴敏, 刘海锋, 孙梦格, 雷雨昕. 河西走廊荒漠植物多样性及其对环境因子的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 429-438. |
| [3] | 周选博, 王晓丽, 马玉寿, 王彦龙, 罗少辉, 谢乐乐. 返青期休牧措施下高寒草甸主要植物种群的生态位变化特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1547-1555. |
| [4] | 马辉英, 李昕竹, 马鑫钰, 贡璐. 新疆天山北麓中段不同植被类型下土壤有机碳组分特征及其影响因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(6): 1124-1131. |
| [5] | 冯凌, 喻理飞, 王阳, 张丽敏, 赵庆, 李方兵. 喀斯特地区植被不同恢复阶段功能冗余和功能多样性对群落稳定性的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 670-678. |
| [6] | 陈瑶, 李云红, 邵英男, 刘玉龙, 刘延坤. 阔叶红松林物种多样性与土壤理化特征研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 679-687. |
| [7] | 玄锦, 李祖婵, 邹诚, 秦子博, 吴雅华, 黄柳菁. 江心洲景观类型和格局对植物多样性的多尺度影响——以闽江流域福州段为例[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(12): 2320-2330. |
| [8] | 薛文凯, 朱攀, 德吉, 郭小芳. 纳木措水体可培养丝状真菌优势种的时空特征研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(12): 2331-2340. |
| [9] | 韩鑫, 袁春阳, 李济宏, 洪宗文, 刘宣, 杜婷, 李晗, 游成铭, 谭波, 朱鹏, 徐振锋. 树种和土层对土壤无机氮的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(11): 2143-2151. |
| [10] | 宗宁, 石培礼, 朱军涛. 高寒草地沙化过程植物群落构成及生态位特征变化[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(8): 1561-1570. |
| [11] | 闫东锋, 张妍妍, 吕康婷, 周梦丽, 王婷, 赵宁. 太行山南麓不同海拔梯度天然林优势树种生态位特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(8): 1571-1580. |
| [12] | 郭佳琦, 陈俊辰, 黄旬, 黄佳乐, 赵丽娅, 李兆华. 喜旱莲子草入侵群落主要物种生态位和种间联结研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(8): 1607-1616. |
| [13] | 李雅男, 张峰, 赵天启, 郑佳华, 孙宇, 张彬, 赵萌莉. 刈割留茬高度对大针茅草原群落组成及物种生态位的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(7): 1386-1392. |
| [14] | 黄成, 吴月颖, 吉恒宽, 陈丽铭, 李倍莹, 符传良, 李建宏, 吴蔚东, 吴治澎. 海南典型水稻土厌氧铁还原特征对DOM分子特性的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(5): 957-967. |
| [15] | 林丽, 代磊, 林泽北, 吴际通, 颜伟, 王志杰. 黔中城市森林群落植物多样性及其与土壤理化性质的关系[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(11): 2130-2141. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
