生态环境学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (6): 1111-1120.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2021.06.001
所属专题: 生物多样性专题汇编
• 研究论文 •
下一篇
收稿日期:2020-12-30
出版日期:2021-06-18
发布日期:2021-09-10
作者简介:何斌(1980年生),男,副教授,博士,主要从事森林生态学和植物生理生态学研究,E-mail: hebin23kewen@163.com
基金资助:
HE Bin( ), LI Qing, CHEN Qunli, LI Wangjun, YOU Ping
), LI Qing, CHEN Qunli, LI Wangjun, YOU Ping
Received:2020-12-30
Online:2021-06-18
Published:2021-09-10
摘要:
研究海拔高度对黄杉群落物种多样性的影响,为珍稀濒危植物黄杉的保育和喀斯特山地生物多样性的保护提供科学依据。采用样地法调查不同海拔梯度黄杉群落的物种组成,分析其区系特征,研究黄杉群落物种多样性的海拔梯度格局和维持机制。样地内共记录种子植物50科95属124种,群落内植物属的地理成分复杂、多样,具有明显的温带性质;随着海拔的增加,黄杉群落灌木层和草本层的物种丰富度指数S、Shannon-Wiener多样性指数H、Simpson优势度指数D和Pielou均匀度指数J均呈单峰格局变化趋势,且在不同海拔上存在显著差异(P<0.05),但灌木层物种的Pielou均匀度指数不显著(P≥0.05);相邻海拔间的β多样性指数变化趋势不同,灌木层物种的Sørenson指数呈双峰曲线,草本层物种的Sørenson指数呈单峰曲线,灌木层和草本层的Cody指数均呈单峰曲线;随着海拔高差的增加,黄杉群落草本层物种的Sørenson指数逐渐减小,其它均无明显变化规律。整体来看,相对海拔导致的水热条件差异是影响喀斯特山地物种多样性垂直分布格局的主要因素,其中,中海拔地带黄杉群落的物种多样性最高,这对黄杉种质资源的保护和维持具有重要意义,同时对喀斯特山地植物群落的管理和生态系统稳定的维持也具有重要指导意义。
中图分类号:
何斌, 李青, 陈群利, 李望军, 游萍. 黔西北黄杉群落物种多样性的海拔梯度格局[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(6): 1111-1120.
HE Bin, LI Qing, CHEN Qunli, LI Wangjun, YOU Ping. Altitudinal Pattern of Species Diversity of Pseudotsuga sinensis Communty in Northwestern Guizhou, China[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(6): 1111-1120.
| 海拔 Altitude/ m | 坡度 Slope/ (°) | 经纬度 Geographical coordinates | 优势种 Dominant species | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 乔木层 Arbor layer | 灌木层 Shrub layer | 草本层 Herb layer | |||
| 1904 | 30 | 26°40′55″N—104°17′45″E | 黄杉 | 荚蒾 (Viburnum dilatatum)、西南栒子、野花椒 (Zanthoxylum simulans)、薄叶鼠李 (Rhamnus leptophylla) | 半夏 (Pinellia ternate)、茜草 (Rubia cordifolia)、画眉草 (Eragrostis pilosa)、一把伞南星 (Arisaema erubescens)、香茶菜 (Isodon amethystoides) |
| 1943 | 22 | 26°40′51″N—104°12′11″E | 黄杉 | 滇榛、荚蒾、金丝桃、截叶铁扫帚 (Lespedeza cuneate)、扁刺峨眉蔷薇 (Rosa omeiensis)、锦绣杜鹃(Rhododendron×pulchrum) | 车前 (Plantago asiatica)、半夏、老鹳草 (Geranium wilfordii)、夏枯草 (Prunella vulgaris)、珠光香青 (Anaphalis margaritacea)、鸭子草 (Elsholtzia bodinieri) |
| 2075 | 25 | 26°41′44″N—104°15′26″E | 黄杉 | 滇榛、锦绣杜鹃、荚蒾、扁刺峨眉蔷薇、金丝桃、截叶铁扫帚、西南栒子 | 荩草 (Arthraxon hispidus)、翻白叶 (Potentilla griffithii)、车前、半夏、茜草、老鹳草、沿阶草 (Ophiopogon bodinieri) |
| 2140 | 28 | 26°36′08″N—103°56′46″E | 黄杉 | 矮杨梅 (Myrica nana)、扁刺峨眉蔷薇、滇榛、金丝桃、锦绣杜鹃、荚蒾、石栎 (Lithocarpus glaber)、西南栒子、截叶铁扫帚 | 半夏、车前、翻白叶、荩草、两头毛 (Incarvillea argute)、蛇莓 (Duchesnea indica)、老鹳草、灰苞蒿 (Artemisia roxburghiana)、积雪草 (Centella asiatica)、千里光 (Senecio scandens)、杏香兔儿风 (Ainsliaea fragrans)、鸭子草、银莲花 (Anemone cathayensis)、一把伞南星 |
| 2185 | 26 | 26°57′00″N—103°97′00″E | 黄杉 | 荚蒾、锦绣杜鹃、金丝桃、矮杨梅、石栎、滇榛、扁刺峨眉蔷薇、西南栒子 | 荩草、两头毛、蛇莓、千里光、沿阶草、杏香兔儿风、积雪草、茜草、香薷 |
| 2214 | 21 | 26°32′26″N—103°55′28″E | 黄杉 | 滇榛、荚蒾、锦绣杜鹃、扁刺峨眉蔷薇、金丝桃 | 两头毛、荩草、蛇莓、翻白叶 |
表1 研究区内黄杉林样地概况
Table 1 General characteristics of the sample plot of P. sinensis forest in the study area
| 海拔 Altitude/ m | 坡度 Slope/ (°) | 经纬度 Geographical coordinates | 优势种 Dominant species | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 乔木层 Arbor layer | 灌木层 Shrub layer | 草本层 Herb layer | |||
| 1904 | 30 | 26°40′55″N—104°17′45″E | 黄杉 | 荚蒾 (Viburnum dilatatum)、西南栒子、野花椒 (Zanthoxylum simulans)、薄叶鼠李 (Rhamnus leptophylla) | 半夏 (Pinellia ternate)、茜草 (Rubia cordifolia)、画眉草 (Eragrostis pilosa)、一把伞南星 (Arisaema erubescens)、香茶菜 (Isodon amethystoides) |
| 1943 | 22 | 26°40′51″N—104°12′11″E | 黄杉 | 滇榛、荚蒾、金丝桃、截叶铁扫帚 (Lespedeza cuneate)、扁刺峨眉蔷薇 (Rosa omeiensis)、锦绣杜鹃(Rhododendron×pulchrum) | 车前 (Plantago asiatica)、半夏、老鹳草 (Geranium wilfordii)、夏枯草 (Prunella vulgaris)、珠光香青 (Anaphalis margaritacea)、鸭子草 (Elsholtzia bodinieri) |
| 2075 | 25 | 26°41′44″N—104°15′26″E | 黄杉 | 滇榛、锦绣杜鹃、荚蒾、扁刺峨眉蔷薇、金丝桃、截叶铁扫帚、西南栒子 | 荩草 (Arthraxon hispidus)、翻白叶 (Potentilla griffithii)、车前、半夏、茜草、老鹳草、沿阶草 (Ophiopogon bodinieri) |
| 2140 | 28 | 26°36′08″N—103°56′46″E | 黄杉 | 矮杨梅 (Myrica nana)、扁刺峨眉蔷薇、滇榛、金丝桃、锦绣杜鹃、荚蒾、石栎 (Lithocarpus glaber)、西南栒子、截叶铁扫帚 | 半夏、车前、翻白叶、荩草、两头毛 (Incarvillea argute)、蛇莓 (Duchesnea indica)、老鹳草、灰苞蒿 (Artemisia roxburghiana)、积雪草 (Centella asiatica)、千里光 (Senecio scandens)、杏香兔儿风 (Ainsliaea fragrans)、鸭子草、银莲花 (Anemone cathayensis)、一把伞南星 |
| 2185 | 26 | 26°57′00″N—103°97′00″E | 黄杉 | 荚蒾、锦绣杜鹃、金丝桃、矮杨梅、石栎、滇榛、扁刺峨眉蔷薇、西南栒子 | 荩草、两头毛、蛇莓、千里光、沿阶草、杏香兔儿风、积雪草、茜草、香薷 |
| 2214 | 21 | 26°32′26″N—103°55′28″E | 黄杉 | 滇榛、荚蒾、锦绣杜鹃、扁刺峨眉蔷薇、金丝桃 | 两头毛、荩草、蛇莓、翻白叶 |
| 科内所含种数 Number of species in families | 种数 Number of species | 占总种数比例 Ration total species/% | 科数 Number of families | 占总科数比例 Ration total families/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ≥10 | 29 | 23.39 | 2 | 4 |
| 5‒9 | 32 | 25.805 | 5 | 10 |
| 2‒4 | 32 | 25.805 | 12 | 24 |
| 1 | 31 | 25 | 31 | 62 |
| 合计 Total | 124 | 100 | 50 | 100 |
表2 黄杉群落种子植物科内种的组成
Table 2 Composition of species in families of seed plants in the P. sinensis community
| 科内所含种数 Number of species in families | 种数 Number of species | 占总种数比例 Ration total species/% | 科数 Number of families | 占总科数比例 Ration total families/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ≥10 | 29 | 23.39 | 2 | 4 |
| 5‒9 | 32 | 25.805 | 5 | 10 |
| 2‒4 | 32 | 25.805 | 12 | 24 |
| 1 | 31 | 25 | 31 | 62 |
| 合计 Total | 124 | 100 | 50 | 100 |
| 科内所含属数 Number of genera in families | 属数 Number of genera | 占总属数比例 Ration total genera/% | 科数 Number of families | 占总科数比例 Ration total families/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ≥10 | 11 | 11.58 | 1 | 2 |
| 4‒9 | 29 | 30.53 | 5 | 10 |
| 2‒3 | 22 | 23.16 | 11 | 22 |
| 1 | 33 | 34.73 | 33 | 66 |
| 合计 Total | 95 | 100 | 50 | 100 |
表3 黄杉群落种子植物科内属的组成
Table 3 Composition of genera in families of seed plants in the P. sinensis community
| 科内所含属数 Number of genera in families | 属数 Number of genera | 占总属数比例 Ration total genera/% | 科数 Number of families | 占总科数比例 Ration total families/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ≥10 | 11 | 11.58 | 1 | 2 |
| 4‒9 | 29 | 30.53 | 5 | 10 |
| 2‒3 | 22 | 23.16 | 11 | 22 |
| 1 | 33 | 34.73 | 33 | 66 |
| 合计 Total | 95 | 100 | 50 | 100 |
| 分布区类型 Areal-type | 科数 Family | 百分比 Percentage/% | 属数 Genera | 百分比 Percentage/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. 世界分布 Cosmopolitan | 19 | 38 | 16 | 16.84 |
| 2. 泛热带分布 Pantropic | 16 | 32 | 12 | 12.63 |
| 3. 东亚 (热带、亚热带) 及热带南美间断分布 Tropical & subtropical east Asia & (south) tropical America disjuncted | 2 | 4 | 3 | 3.16 |
| 4. 旧世界热带分布 Old world Tropical | ‒ | ‒ | 3 | 3.16 |
| 5. 热带亚洲至热带大洋洲分布 Tropical Asia to tropical Australasia Oceania | ‒ | ‒ | 1 | 1.05 |
| 6. 热带亚洲至热带非洲分布 Tropic Asia to Tropic Africa | 1 | 2 | 5 | 5.26 |
| 7. 热带亚洲 (印度-马来西亚) 分布 Tropic Asia (Indo-Malesia) | 1 | 2 | 3 | 3.16 |
| 8. 北温带分布 North Temperate | 11 | 22 | 33 | 34.74 |
| 9. 东亚和北美洲间断分布 East Asia & North America disjuncted | ‒ | ‒ | 5 | 5.26 |
| 10. 旧世界温带分布 Old World Temperate | ‒ | ‒ | 4 | 4.21 |
| 11. 温带亚洲分布 Temperate Asia | ‒ | ‒ | 1 | 1.05 |
| 12. 地中海区、西亚至中亚分布 Mediterranean, West Asia to central Asia | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ |
| 13. 中亚分布 Central Asia | ‒ | ‒ | 1 | 1.05 |
| 14. 东亚分布 East Asia distribution | ‒ | ‒ | 8 | 8.42 |
| 15. 中国特有分布 Endemic to China | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ |
| 合计 Total | 50 | 100 | 95 | 100 |
表4 种子植物科、属的分布区类型
Table 4 The distribution type of families and genera in the flora of seed plants
| 分布区类型 Areal-type | 科数 Family | 百分比 Percentage/% | 属数 Genera | 百分比 Percentage/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. 世界分布 Cosmopolitan | 19 | 38 | 16 | 16.84 |
| 2. 泛热带分布 Pantropic | 16 | 32 | 12 | 12.63 |
| 3. 东亚 (热带、亚热带) 及热带南美间断分布 Tropical & subtropical east Asia & (south) tropical America disjuncted | 2 | 4 | 3 | 3.16 |
| 4. 旧世界热带分布 Old world Tropical | ‒ | ‒ | 3 | 3.16 |
| 5. 热带亚洲至热带大洋洲分布 Tropical Asia to tropical Australasia Oceania | ‒ | ‒ | 1 | 1.05 |
| 6. 热带亚洲至热带非洲分布 Tropic Asia to Tropic Africa | 1 | 2 | 5 | 5.26 |
| 7. 热带亚洲 (印度-马来西亚) 分布 Tropic Asia (Indo-Malesia) | 1 | 2 | 3 | 3.16 |
| 8. 北温带分布 North Temperate | 11 | 22 | 33 | 34.74 |
| 9. 东亚和北美洲间断分布 East Asia & North America disjuncted | ‒ | ‒ | 5 | 5.26 |
| 10. 旧世界温带分布 Old World Temperate | ‒ | ‒ | 4 | 4.21 |
| 11. 温带亚洲分布 Temperate Asia | ‒ | ‒ | 1 | 1.05 |
| 12. 地中海区、西亚至中亚分布 Mediterranean, West Asia to central Asia | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ |
| 13. 中亚分布 Central Asia | ‒ | ‒ | 1 | 1.05 |
| 14. 东亚分布 East Asia distribution | ‒ | ‒ | 8 | 8.42 |
| 15. 中国特有分布 Endemic to China | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ |
| 合计 Total | 50 | 100 | 95 | 100 |
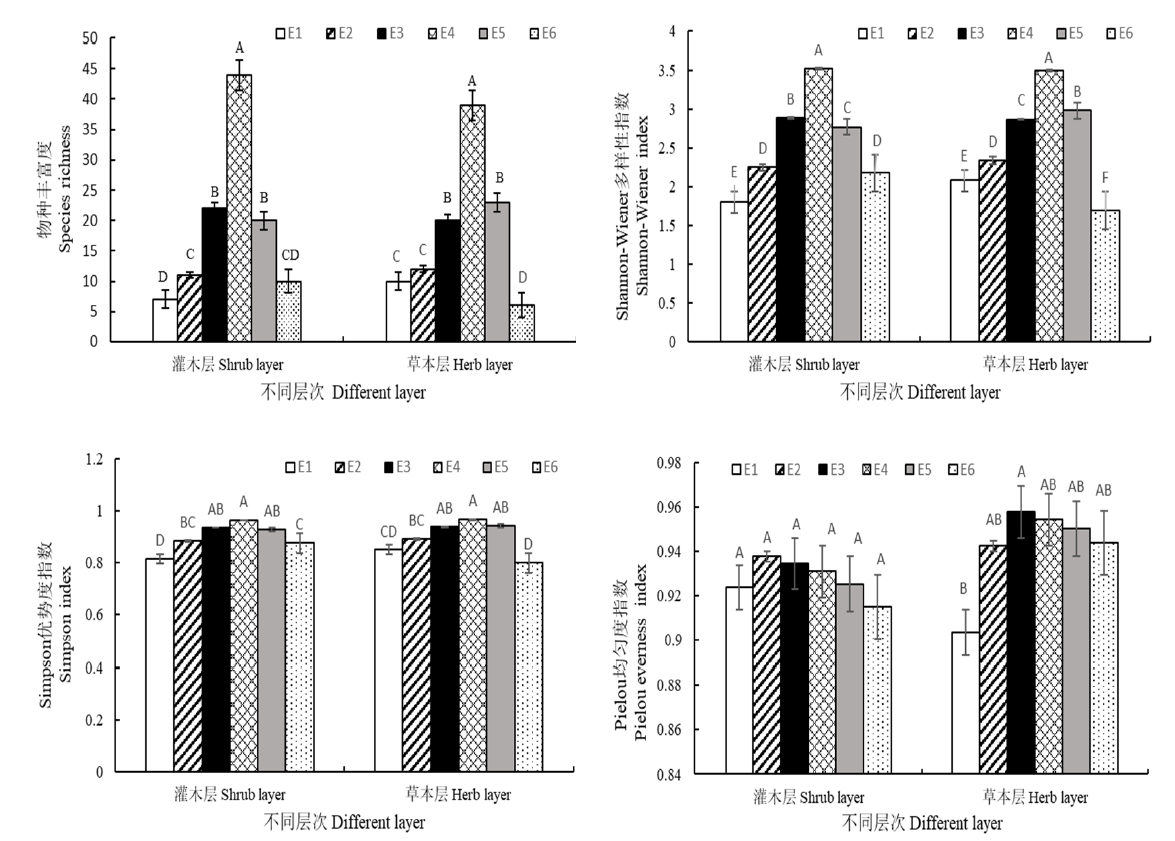
图2 不同海拔灌木层和草本层物种多样性的比较 图中E1、E2、E3、E4、E5、E6分别代表海拔1904、1943、2075、2140、2185、2214 m,不同字母表示不同海拔灌木层、草本层的多样性指数差异显著(P<0.05)
Fig. 2 Comparison of species diversity in shrub layer and herb layer at different elevation E1, E2, E3, E4, E5 and E6 represented elevation of 1904 m, 1943 m, 2075 m, 2140 m, 2185 m and 2214 m. Different letters indicated significant difference in species diversity index of shrub-layer and herb-layer among different elevation gradients at 0.05 level
| 不同层次 Different layer | 指数 Index | 物种丰富度指数S Species richness | Shannon-Wiener多样性指数H Shannon-Wiener index | Simpson优势度指数D Simpson index | Pielou均匀度指数J Pielou index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 灌木层 Shrub layer | 物种丰富度指数S Species richness | 1 | |||
| Shannon-Wiener多样性指数H Shannon-Wiener index | 0.962** | 1 | |||
| Simpson优势度指数D Simpson index | 0.856* | 0.962** | 1 | ||
| Pielou均匀度指数J Pielou index | 0.326 | 0.381 | 0.395 | 1 | |
| 草本层 Herb layer | 物种丰富度指数S Species richness | 1 | |||
| Shannon-Wiener多样性指数H Shannon-Wiener index | 0.962** | 1 | |||
| Simpson优势度指数D Simpson index | 0.879* | 0.975** | 1 | ||
| Pielou均匀度指数J Pielou index | 0.521 | 0.562 | 0.552 | 1 |
表5 植物群落α多样性指数相关性分析
Table 5 Correlation analysis of α diversity index of plant community
| 不同层次 Different layer | 指数 Index | 物种丰富度指数S Species richness | Shannon-Wiener多样性指数H Shannon-Wiener index | Simpson优势度指数D Simpson index | Pielou均匀度指数J Pielou index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 灌木层 Shrub layer | 物种丰富度指数S Species richness | 1 | |||
| Shannon-Wiener多样性指数H Shannon-Wiener index | 0.962** | 1 | |||
| Simpson优势度指数D Simpson index | 0.856* | 0.962** | 1 | ||
| Pielou均匀度指数J Pielou index | 0.326 | 0.381 | 0.395 | 1 | |
| 草本层 Herb layer | 物种丰富度指数S Species richness | 1 | |||
| Shannon-Wiener多样性指数H Shannon-Wiener index | 0.962** | 1 | |||
| Simpson优势度指数D Simpson index | 0.879* | 0.975** | 1 | ||
| Pielou均匀度指数J Pielou index | 0.521 | 0.562 | 0.552 | 1 |
| 海拔 Elevation | 1904 m | 1943 m | 2075 m | 2140 m | 2185 m | 2214 m |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1904 m | 8 | 11.5 | 22.5 | 11.5 | 5.5 | |
| 1943 m | 0.1111 | 8.5 | 20.5 | 10.5 | 5.5 | |
| 2075 m | 0.2069 | 0.4848 | 23 | 15 | 8 | |
| 2140 m | 0.1176 | 0.2545 | 0.3030 | 19 | 19 | |
| 2185 m | 0.1481 | 0.3226 | 0.2857 | 0.4063 | 10 | |
| 2214 m | 0.3529 | 0.4762 | 0.5000 | 0.2963 | 0.3333 |
表6 不同海拔灌木层的Sørenson指数和Cody指数
Table 6 The Sørenson index and Cody index of shrub layer in different elevations
| 海拔 Elevation | 1904 m | 1943 m | 2075 m | 2140 m | 2185 m | 2214 m |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1904 m | 8 | 11.5 | 22.5 | 11.5 | 5.5 | |
| 1943 m | 0.1111 | 8.5 | 20.5 | 10.5 | 5.5 | |
| 2075 m | 0.2069 | 0.4848 | 23 | 15 | 8 | |
| 2140 m | 0.1176 | 0.2545 | 0.3030 | 19 | 19 | |
| 2185 m | 0.1481 | 0.3226 | 0.2857 | 0.4063 | 10 | |
| 2214 m | 0.3529 | 0.4762 | 0.5000 | 0.2963 | 0.3333 |
| 海拔 Elevation | 1904 m | 1943 m | 2075 m | 2140 m | 2185 m | 2214 m |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1904 m | 9 | 13 | 21.5 | 15.5 | 8 | |
| 1943 m | 0.1818 | 11 | 17.5 | 17.5 | 9 | |
| 2075 m | 0.1333 | 0.3125 | 17.5 | 13.5 | 9 | |
| 2140 m | 0.1224 | 0.3137 | 0.4068 | 17 | 20.5 | |
| 2185 m | 0.0606 | 0.0000 | 0.3721 | 0.4516 | 10.5 | |
| 2214 m | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.3077 | 0.0889 | 0.2759 |
表7 不同海拔草本层的Sørenson指数和Cody指数
Table 7 The Sørenson index and Cody index of herb layer in different elevations
| 海拔 Elevation | 1904 m | 1943 m | 2075 m | 2140 m | 2185 m | 2214 m |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1904 m | 9 | 13 | 21.5 | 15.5 | 8 | |
| 1943 m | 0.1818 | 11 | 17.5 | 17.5 | 9 | |
| 2075 m | 0.1333 | 0.3125 | 17.5 | 13.5 | 9 | |
| 2140 m | 0.1224 | 0.3137 | 0.4068 | 17 | 20.5 | |
| 2185 m | 0.0606 | 0.0000 | 0.3721 | 0.4516 | 10.5 | |
| 2214 m | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.3077 | 0.0889 | 0.2759 |
| [1] |
BECK J, CHEY V K, 2008. Explaining the elevational diversity pattern of geometrid moths from borneo: A test of five hypotheses[J]. Journal of Biogeography, 35(8): 1452-1464.
DOI URL |
| [2] | BEGON M, HARPER J L, TOWNSEND C R, 1986. Ecology: Individuals, Populations and Communities [M]. Blackwell Science, Oxford, UK. |
| [3] |
BHATTARAI K R, VETAAS O R, 2003. Variation in plant species richness of different life forms along subtropical elevation gradient in the Himalayas,east Nepal[J]. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 12(4): 327-340.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
CURTIS J T, MCINTOSH R P, 1951. An upland forest continuum in the prairie-forest border region of Wisconsin[J]. Ecology, 32(3): 476-496.
DOI URL |
| [5] | DEBANO L F, SCHMIDT L J, 1990. Potential for enhancing riparian habitats in the southwest United States with watershed practices[J]. Forest Ecology and Management, 33-34: 385-403. |
| [6] |
GASTON K J, 2000. Global patterns in biodiversity[J]. Nature, 405(6783): 220-227.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
GHIMIRE S K, MAKEY D, AUMEERUDDY-THOMAS Y, 2006. Himalayan medicinal plant diversity in an ecologically complex high altitude anthropogenic landscape, Dolpo, Nepal[J]. Environmental Conservation, 33(2): 128-140.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
GRYTNES J A, VETAAS O R, 2002. Species Richness and altitude: A Comparison between null models and interpolated plant species richness along the Himalayan Altitudinal Gradient, Nepal[J]. American Naturalist, 159(3): 294-304.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
GRYTNES J A, HEEGAARD E, IHLEN P G, 2006. Species richness of vascular plants, bryophytes, and lichens along an altitudinal gradient in western Norway[J]. Acta Oecologia, 29(3): 241-246.
DOI URL |
| [10] | KITAYAMA K, 1992. An altitudinal transect study of the vegetation of Mount Kinabalu, Bomeo[J]. Vegetaio, 102(2): 149-171. |
| [11] |
LENOIR J, GRAAE B J, AARRESTAD P A, et al., 2013. Local temperatures inferred from plant communities suggest strong spatial buffering of climate warming across northern Europe[J]. Global Change Biology, 19(5): 1470-1481.
DOI URL |
| [12] | LIU Y, ZHANG Y P, HE D M, et al., 2007. Climatic control of plant species richness along elevation gradients in the Longitudinal RangeGorge Region [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 52(Supp. II):50-58. |
| [13] |
LOMOLINO M V, 2001. Elevational gradients of species-density: historical and prospective views[J]. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 10(1): 3-13.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
MACARTHUR R H, 1972. Mathematical ecology and its place among the sciences[J]. Science, 178: 389-394.
DOI URL |
| [15] | OHSAWA M, 1991. Structural comparison of tropical montane rain forests along latitudinal and altitudinal gradients in south and east Asia[J]. Vegetatio, 97: 1-10. |
| [16] |
OHSAWA M, 1995. Latitudinal comparison of altitudinal changes in forest structure, leaf-type, and species richness in humid monsoon Asia[J]. Vegetatio, 121: 3-10.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
PALMER M W, 1992. The coexistence of species in fractal landscapes[J]. American Naturalist, 139: 375-397.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
PAUSAS J G, AUSTIN M P, 2001. Patterns of plant species richness in relation to different environments: An appraisal[J]. Journal of Vegetation Science, 12: 153-166.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
QIAN H, HAO Z Q, ZHANG J, 2014. Phylogenetic structure and phylogenetic diversity of angiosperm assemblages in forests along an elevational gradient in Changbaishan, China[J]. Journal of Plant Ecology, 7(2): 154-165.
DOI URL |
| [20] | RAD J E, MANTHEY M, MATAJI A, 2009. Comparison of plant species diversity with different plant communities in deciduous forests[J]. International Journal of Environmental Science & Technology, 6(3): 389-394. |
| [21] |
RAHBEK C, 2005. The role of spatial scale and the perception of large-scale species-richness patterns[J]. Ecology Letters, 8(2): 224-239.
DOI URL |
| [22] | WANG Z H, TANG Z Y, FANG J Y, 2007. Altitudinal patterns of seed plant richness in the Gaoligong Mountains,south-east Tibet, China[J]. Diversity & Distributions, 13(6): 845-854. |
| [23] |
WHITTAKER R H, NIERING W A, 1975. Vegetation of the Santa Catalina Mountains, Arizona. V. Biomass, production, and diversity along the elevation gradient[J]. Ecology, 56(4): 771-790.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
WHITTAKER R H, 1960. Vegetation of the Siskiyou Mountains, Oregon and California[J]. Ecological Monographs, 30(3): 279-338.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
WU Y J, COLWELL R K, HAN N J, et al., 2014. Understanding historical and current patterns of species richness of babblers along a 5000 m subtropical elevational gradient[J]. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 23(11): 1167-1176.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
YADETA T, VEENENDAAL E, SYKORA K, et al., 2018. Effect of Vachellia tortilis on understory vegetation, herbaceous biomass and soil nutrients along a grazing gradient in a semi-arid African savanna[J]. Journal of Forestry Research, 29(6): 1601-1609.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
ZIMMERMAN J C, DEWALD L E, ROWLANDS P G, 1999. Vegetation diversity in an interconnected ephemeral riparian system of north-central Arizona, USA[J]. Biological Conservation, 90(3): 217-228.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
方精云, 沈泽昊, 唐志尧, 等, 2004. 中国山地植物物种多样性调查计划及若干技术规范[J]. 生物多样性, 12(1): 5-9.
DOI |
| FANG J Y, SHEN Z H, TANG Z Y, et al., 2004. The protocol for the survey plan for plant species diversity of China's mountains[J]. Biodiversity Science, 12(1): 5-9. | |
| [29] |
方精云, 2004. 探索中国山地植物多样性的分布规律[J]. 生物多样性, 12(1): 1-4.
DOI |
| FANG J Y, 2004. Exploring altitudinal patterns of plant diversity of China's mountains[J]. Biodiversity Science, 12(1): 1-4. | |
| [30] | 郝建锋, 王德艺, 李艳, 等, 2014. 海拔高度对江油地区杉木人工林群落结构和物种多样性的影响[J]. 西北植物学报, 34(12): 2544-2552. |
| HAO J F, WANG D Y, LI Y, et al., 2014. Effect of altitude on structure and species diversity of Cunninghamia lanceolate plantation in Jiangyou district, Sichuan province[J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 34(12): 2544-2552. | |
| [31] | 胡文彬, 2015. 贵州湄潭黄杉生态系统保护性评价及保护构想[J]. 福建林业科技, 42(1): 173-176. |
| HU W B, 2015. Douglas Fir Ecosystem Protective Evaluation and Idea in Meitan Guizhou[J]. Journal of Fujian Forestry Science and Technology, 42(1): 173-176. | |
| [32] | 黄鹤先, 1989. 珍稀树种黄杉在威宁已面临消失的危险[J]. 环保科技 (4): 25-26. |
| HUANG H X, 1989. The rare species of Pseudotsuga sinensis has appeared a sign of extinction in Weining[J]. Envirommental Protectlon and Technology (4): 25-26. | |
| [33] | 黄建辉, 1994. 物种多样性的空间格局及形成机制初探[J]. 生物多样性, 2(2): 103-107. |
|
HUANG J H, 1994. The spatial pattern of species diversity and its forming mechanism[J]. Biodiversity Science, 2(2): 103-107.
DOI URL |
|
| [34] | 孔祥海, 李振基, 2012. 福建梅花山常绿阔叶林植物物种多样性及其海拔梯度格局[J]. 植物分类与资源学报, 34(2): 179-186. |
|
KONG X M, LI Z J, 2012. Species Diversity and Altitudinal Gradient Patterns of Evergreen Broad-leaved Forest in Meihuashan National Natural Reserve,Fujian Province[J]. Plant Diversity and Resources, 34(2): 179-186.
DOI URL |
|
| [35] | 兰斯安, 宋敏, 曾馥平, 等, 2016. 木论喀斯特森林木本植物多样性垂直格局[J]. 生态学报, 36(22): 7374-7383. |
| LAN S A, SONG M, ZENG F P, et al., 2016. Altitudinal pattern of woody plant species diversity in the karst forest in Mulun, China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 36(22): 7374-7383. | |
| [36] | 林国俊, 黄忠良, 竺琳, 等, 2010. 鼎湖山森林群落β多样性[J]. 生态学报, 30(18): 4875-4880. |
| LIN G J, HUANG Z L, ZHU L, et al., 2010. Beta diversity of forest community on Dinghushan[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 30(18): 4875-4880. | |
| [37] | 刘维暐, 王杰, 王勇, 等, 2012. 三峡水库消落区不同海拔高度的植物群落多样性差异[J]. 生态学报, 32(17): 5454-5466. |
|
LIU W W, WANG J, WANG Y, et al., 2012. The differences of plant community diversity among the different altitudes in the Water-Level-Fluctuating zone of the Three Gorges Reservoir[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 32(17): 5454-5466.
DOI URL |
|
| [38] | 马克平, 黄建辉, 于顺利, 等, 1995. 北京东灵山地区植物群落多样性的研究Ⅱ丰富度、均匀度和物种多样性指数[J]. 生态学报, 15(3): 268-277. |
| MA K P, HUANG J H, YU S L, et al., 1995. Plant community diversity in Dongling Mountain, Beijing, China: Ⅱ. Species richness.evenness and species diversities[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 15(3): 268-277. | |
| [39] | 孟广涛, 柴勇, 方向京, 等, 2008. 滇东北黄杉种群数量动态的初步研究[J]. 西北林学院学报, 23(6):54-59. |
| MENG G T, CHAI Y, FANG X J, et al., 2008. A Preliminary Study of Population Dymamics of Pseudotsuga sinensis Population in Northeastern Yunnan[J]. Journal of Northwest Forestry University, 23(6): 54-59. | |
| [40] |
秦浩, 张殷波, 董刚, 等, 2019. 山西关帝山森林群落物种、谱系和功能多样性海拔格局[J]. 植物生态学报, 43(9): 762-773.
DOI |
|
QIN H, ZHANG Y B, DONG G, et al., 2019. Altitudinal patterns of taxonomic, phylogenetic and functional diversity of forest communitie in Mount Guandi, Shanxi, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 43(9): 762-773.
DOI URL |
|
| [41] |
沈泽昊, 刘增力, 方精云, 2004. 贡口夏山海螺沟冷杉群落物种多样性与群落结构随海拔的变化[J]. 生物多样性, 12(2): 237-244.
DOI |
| SHEN Z H, LIU Z L, FANG J Y, 2004. Altitudinal changes in species diversity and community structure of Abies fabri communities at Hailuo Valley of Mt. Congga, Sichuan[J]. Biodiversity Science, 12(2): 237-244. | |
| [42] | 苏闯, 张芯毓, 马文红, 等, 2018. 贺兰山灌丛群落物种多样性海拔格局及环境解释[J]. 山地学报, 36(5): 699-708. |
| SU C, ZHANG X Y, MA W H, et al., 2018. Altitudinal Pattern and Environmental Interpretation of Species Diversity of Scrub Communty in the Helan Mountains, China[J]. Mountain Research, 36(5): 699-708. | |
| [43] | 王飞, 屠彩芸, 曹秀文, 等, 2018. 白龙江干旱河谷不同坡向主要灌丛群落随海拔梯度变化的物种多样性研究[J]. 植物研究, 38(1): 26-36. |
| WANG F, TU C Y, CAO X W, et al., 2018. The Different Altitude Gradient Change Rules of the Main Shrub Community in Arid Valleys of the Bailongjiang River with Different Slope[J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 38(1): 26-36. | |
| [44] |
王国宏, 2002. 祁连山北坡中段植物群落多样性的垂直分布格局[J]. 生物多样性, 10(1): 7-14.
DOI |
| WANG G H, 2002. Species diversity of plant communities along an altitudinal gradient in the middle section of northern slopes of Qilian Mountains, Zhangye, Gansu, China[J]. Biodiversity Science, 10(1): 7-14. | |
| [45] | 王宇超, 王得祥, 2013. 佛坪自然保护区植物群落物种多样性和复杂性的海拔格局研究[J]. 西北植物学报, 33(1): 169-176. |
| WANG Y C, WANG D X, 2013. Study on elevational patterns of plant species diversity and community complexity in Foping natural reserve[J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 33(1): 169-176. | |
| [46] |
王志恒, 陈安平, 朴世龙, 等, 2004. 高黎贡山种子植物物种丰富度沿海拔梯度的变化[J]. 生物多样性, 12(1): 82-88.
DOI |
| WANG Z H, CHEN A P, PIAO S L, et al., 2004. Pattern of species richness along an altitudinal gradient on Gaoligong Mountains, Southwest China[J]. Biodiversity Science, 12(1): 82-88. | |
| [47] | 吴昊, 刘华, 张洋, 等, 2012. 商洛山区人工油松群落物种多样性与环境因子关系研究[J]. 西北植物学报, 32(2): 377-383. |
| WU H, LIU H, ZHANG Y, et al., 2012. Coupling relationship between species diversity of planted Chinese Pine (Pinus tabulaeformis Carr.) communities and environment factors in mountain area of Shangluo[J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 32(2): 377-383. | |
| [48] | 吴红宝, 水宏伟, 胡国铮, 等, 2019. 海拔对藏北高寒草地物种多样性和生物量的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 28(6): 1071-1079. |
| WU H B, SHUI H W, HU G Z, et al., 2019. Species diversity and biomass distribution patterns of alpine grassland along an elevation gradient in the Northern Tibetan Plateau[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 28(6): 1071-1079. | |
| [49] | 吴征镒, 周浙昆, 李德铢, 等, 2003. 世界种子植物科的分布区类型系统[J]. 云南植物研究, 25(3): 245-257. |
| WU Z Y, ZHOU Z K, LI D Z, et al., 2003. The areal-types of the world families of seed plants[J]. Acta Botanica Yunnanica, 25(3): 245-257. | |
| [50] | 吴征镒, 1991. 中国种子植物属的分布区类型[J]. 云南植物研究, 13(S4): 1-139. |
| WU Z Y, 1991. Areal-types of genera of seed plants in China[J]. Acta Botanica Yunnanica, 13(S4): 1-139. | |
| [51] | 熊斌梅, 汪正祥, 田凯, 等, 2017. 七姊妹山自然保护区黄杉林群落学特征[J]. 广西植物, 37(4): 434-441. |
| XIONG B M, WAMG Z X, TIAN K, et al., 2017. Coenological characteristics of Pseudotsuga sinensis forests in Qizimei Mountains Nature Reserve[J]. Guihaia, 37(4): 434-441. | |
| [52] | 张树斌, 王襄平, 吴鹏, 等, 2018. 吉林灌木群落物种多样性与气候及局域环境因子的关系[J]. 生态学报, 38(22): 7990-8000. |
| ZHANG S B, WAMG X P, WU P, et al., 2018. Relationship between shrub species diversity and climate and local environmental factors across Jilin[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 38(22): 7990-8000. | |
| [53] | 张晓龙, 周继华, 蔡文涛, 等, 2017. 水分梯度下黑河流域荒漠植物群落多样性特征[J]. 生态学报, 37(14): 4627-4635. |
| ZHANG X L, ZHOU J H, CAI W T, et al., 2017. Diversity characteristics of plant communities in the arid desert of the Heihe basin under different moisture gradients[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 37(14): 4627-4635. | |
| [54] | 朱珣之, 张金屯, 2005. 中国山地植物多样性的垂直变化格局[J]. 西北植物学报, 25(7): 1480-1486. |
| ZHU X Z, ZHANG J T, 2005. Altitudinal patterns of plant diversity of China Mountains[J]. Acta Botanica Boreali Occidentalia Sinica, 25(7): 1480-1486. | |
| [55] | 左家哺, 1995. 贵州西部黄杉林群落特征与天然更新的研究[J]. 贵州林业科技, 23(1): 14-21. |
| ZOU J B, 1995. The characteristics and natural regeneration of Pseudotsuga sinensis community in Western Guizhou[J]. Guizhou Forestry Science and Technology, 23(1): 14-21. |
| [1] | 秦浩, 李蒙爱, 高劲, 陈凯龙, 张殷波, 张峰. 芦芽山不同海拔灌丛土壤细菌群落组成和多样性研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 459-468. |
| [2] | 张立进, 杜虎, 曾馥平, 黄国勤, 宋敏, 宋同清. 喀斯特峰丛洼地植被恢复过程中生产力与多样性关系探讨[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 26-35. |
| [3] | 王哲, 田胜尼, 张永梅, 张和禹, 周忠泽. 巢湖派河口滩涂植物群落特征研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(9): 1823-1831. |
| [4] | 冯凌, 喻理飞, 王阳, 张丽敏, 赵庆, 李方兵. 喀斯特地区植被不同恢复阶段功能冗余和功能多样性对群落稳定性的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 670-678. |
| [5] | 陈瑶, 李云红, 邵英男, 刘玉龙, 刘延坤. 阔叶红松林物种多样性与土壤理化特征研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 679-687. |
| [6] | 胡靓达, 周海菊, 黄永珍, 姚贤宇, 叶绍明, 喻素芳. 不同杉木林分类型植物多样性及其土壤碳氮关系的研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(3): 451-459. |
| [7] | 王小娜, 徐当会, 王谢军, 方向文. 祁连山灌丛群落结构特征随海拔梯度和经度的变化[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(2): 231-238. |
| [8] | 蔡锡安, 黄娟, 吴彤, 刘菊秀, 蒋芬, 王森浩. 植物叶片排放甲烷的初步研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(9): 1842-1847. |
| [9] | 闫东锋, 张妍妍, 吕康婷, 周梦丽, 王婷, 赵宁. 太行山南麓不同海拔梯度天然林优势树种生态位特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(8): 1571-1580. |
| [10] | 洪文君, 莫罗坚, 张浩. 华南地区马占相思人工林不同改造模式对林分结构的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(7): 1360-1367. |
| [11] | 潘红丽, 李慧超, 余志祥, 蔡蕾, 李旭华, 刘兴良. 攀枝花市入侵植物马缨丹群落的物种组成与多样性研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(6): 1177-1182. |
| [12] | 张洋洋, 周清慧, 许骄阳, 魏鸣, 陈继豪, 何伟, 王鹏程, 晏召贵. 林龄对马尾松人工林林下植物与土壤种子库多样性的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(11): 2121-2129. |
| [13] | 张晓龙, 周继华, 来利明, 郑元润. 黑河下游胡杨群落多样性沿河岸距离的变化特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(10): 1952-1960. |
| [14] | 张莎莎, 李爱琴, 王会荣, 王晶晶, 徐小牛. 不同海拔杉木人工林土壤碳氮磷生态化学计量特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2020, 29(1): 97-104. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
