生态环境学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (11): 2150-2156.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2021.11.005
朱勇勇1,2( ), 宋秉羲3, 杨王敏3, 张宇鹏3,4, 高志红3,4, 陈晓远3,4,*(
), 宋秉羲3, 杨王敏3, 张宇鹏3,4, 高志红3,4, 陈晓远3,4,*( )
)
出版日期:2021-11-18
发布日期:2021-12-29
通讯作者:
* 陈晓远(1968年生),男,教授,博士,研究方向为作物水分养分高效利用。E-mail: chenxy2@163.com作者简介:朱勇勇(1994年生),男,硕士研究生,研究方向为作物水分高效利用。E-mail: yyongzhubio@163.com
基金资助:
ZHU Yongyong1,2( ), SONG Bingxi3, YANG Wangmin3, ZHANG Yupeng3,4, GAO Zhihong3,4, CHEN Xiaoyuan3,4,*(
), SONG Bingxi3, YANG Wangmin3, ZHANG Yupeng3,4, GAO Zhihong3,4, CHEN Xiaoyuan3,4,*( )
)
Online:2021-11-18
Published:2021-12-29
摘要:
为探讨旱作条件下减量施用氮肥对水稻生长、产量及经济收益的效应,以水稻品种美香粘为材料,设置常规淹水施氮(216 kg∙hm-2,CK)、旱作施氮(216 kg∙hm-2,H0)、旱作减氮10%(194.4 kg∙hm-2,H10)、旱作减氮20%(172.8 kg∙hm-2,H20)、旱作减氮40%(129.6 kg∙hm-2,H40)5个处理,研究不同水分条件和氮肥减施对水稻株高、叶面积、分蘖数、产量等的影响。结果表明,在旱作条件下,水稻株高随氮肥减施量的增加而降低,减施10%处理降幅最小(2.70%),差异不显著;减施40%处理降幅最大(19.92%),差异显著。氮肥减施抑制叶面积扩展,随着氮肥减施量的增加,叶面积减小,其中减施10%处理下降8.98%,差异不显著;减施40%处理下降30.32%,差异显著。氮肥减施使分蘖数明显减少,减施越多,分蘖数下降越多,其中减施10%处理下降13.86%,差异不显著,减施40%处理下降51.71%,差异显著。在氮肥不减施条件下,水稻旱作与常规淹水种植相比,产量下降2.38%,差异不显著。在旱作条件下,氮肥减施使产量降低,但减施10%和20%处理仅分别下降0.35%和1.05%,差异不显著。研究表明,水稻旱作处理的经济收益均大于常规淹水种植,在旱作条件下,与常规施氮量相比,减施10%可以获得较好的产量和经济收益。
中图分类号:
朱勇勇, 宋秉羲, 杨王敏, 张宇鹏, 高志红, 陈晓远. 旱作条件下氮肥减施对水稻生长、产量与经济收益的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(11): 2150-2156.
ZHU Yongyong, SONG Bingxi, YANG Wangmin, ZHANG Yupeng, GAO Zhihong, CHEN Xiaoyuan. Effects of Reduced Nitrogen Application on Rice Growth, Yield and Economy Profits under Dry Farming Conditions[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(11): 2150-2156.
| 项目 Item | 测定值 Measured value |
|---|---|
| pH | 5.83 |
| w(OM)/(g·kg-1) | 44.50 |
| w(NH4+-N)/(mg·kg-1) | 17.77 |
| w(NO3--N)/(mg·kg-1) | 18.84 |
| w(AN)/(mg·kg-1) | 123.48 |
| w(OP)/(mg·kg-1) | 118.95 |
| w(AK)/(mg·kg-1) | 210.80 |
表1 试验地土壤基本理化性状
Table 1 Physical and chemical properties of soil in experimental areas
| 项目 Item | 测定值 Measured value |
|---|---|
| pH | 5.83 |
| w(OM)/(g·kg-1) | 44.50 |
| w(NH4+-N)/(mg·kg-1) | 17.77 |
| w(NO3--N)/(mg·kg-1) | 18.84 |
| w(AN)/(mg·kg-1) | 123.48 |
| w(OP)/(mg·kg-1) | 118.95 |
| w(AK)/(mg·kg-1) | 210.80 |
| 处理 Treatment | N用量 N dosage/ (kg·hm-2) | P2O5用量 P2O5 dosage/ (kg·hm-2) | K2O用量 K2O dosage/ (kg·hm-2) | 种植方式 Planting mode |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 216 | 112.5 | 112.5 | 常规淹水种植 Conventional flooded planting |
| H0 | 216 | 112.5 | 112.5 | 旱作 Dry farming |
| H10 | 194.4 | 112.5 | 112.5 | 旱作 Dry farming |
| H20 | 172.8 | 112.5 | 112.5 | 旱作 Dry farming |
| H40 | 129.6 | 112.5 | 112.5 | 旱作 Dry farming |
表2 试验处理
Table 2 Treatments of the experiment
| 处理 Treatment | N用量 N dosage/ (kg·hm-2) | P2O5用量 P2O5 dosage/ (kg·hm-2) | K2O用量 K2O dosage/ (kg·hm-2) | 种植方式 Planting mode |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 216 | 112.5 | 112.5 | 常规淹水种植 Conventional flooded planting |
| H0 | 216 | 112.5 | 112.5 | 旱作 Dry farming |
| H10 | 194.4 | 112.5 | 112.5 | 旱作 Dry farming |
| H20 | 172.8 | 112.5 | 112.5 | 旱作 Dry farming |
| H40 | 129.6 | 112.5 | 112.5 | 旱作 Dry farming |
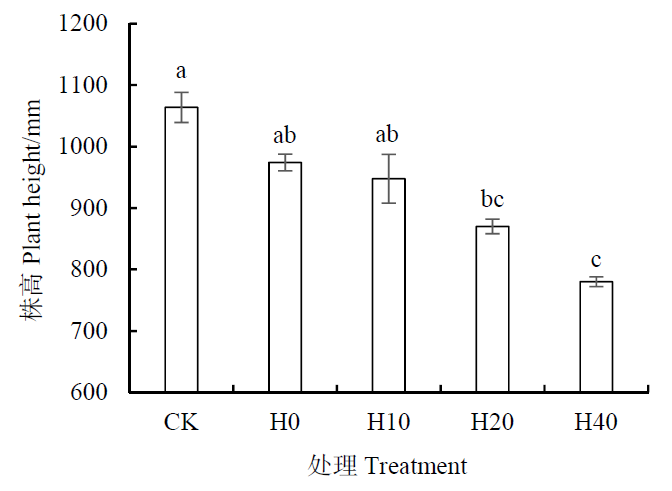
图1 不同氮肥减施处理对水稻株高的影响 CK:常规淹水施氮;H0:旱作减氮0%;H10:旱作减氮10%;H20:旱作减氮20%;H40:旱作减氮40%;不同小写字母表示不同处理间存在显著差异(P<0.05, n=3)。下同
Fig. 1 Effects of different nitrogen fertilizer reduction treatments on rice plant height CK: Conventional flooding of nitrogen; H0: Dry farming reduces nitrogen by 0%; H10: Dry farming reduces nitrogen by 10%; H20: Dry farming reduces nitrogen by 20%; H40: Dry farming reduces nitrogen by 40%; n=3; Different lowercase letters indicated that there was significant difference among different treatments (P<0.05, n=3). The same below
| 处理 Treatment | 单位面积株数 Number of plants per unit area | 有效穗数 Number of productive ear | 千粒重 1000-grainweight/g | 产量 Yield/(kg·hm-2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 40.50±2.12a | 19.00±1.41a | 24.17±1.01a | 12894.74±131.58a |
| H0 | 39.50±3.54a | 18.50±2.12ab | 23.94±0.72a | 12587.72±303.87ab |
| H10 | 37.00±1.41a | 13.00±2.83bc | 23.48±0.49a | 12543.86±151.94ab |
| H20 | 26.50±2.12b | 12.00±2.83c | 22.91±0.36ab | 12456.14±724.68ab |
| H40 | 24.50±0.71b | 11.50±0.71c | 22.15±0.63b | 12061.40±200.98b |
表3 不同氮肥减施处理对水稻产量及其构成因素的影响
Table 3 Effects of different nitrogen fertilizer reduction treatments on rice yield and its components
| 处理 Treatment | 单位面积株数 Number of plants per unit area | 有效穗数 Number of productive ear | 千粒重 1000-grainweight/g | 产量 Yield/(kg·hm-2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 40.50±2.12a | 19.00±1.41a | 24.17±1.01a | 12894.74±131.58a |
| H0 | 39.50±3.54a | 18.50±2.12ab | 23.94±0.72a | 12587.72±303.87ab |
| H10 | 37.00±1.41a | 13.00±2.83bc | 23.48±0.49a | 12543.86±151.94ab |
| H20 | 26.50±2.12b | 12.00±2.83c | 22.91±0.36ab | 12456.14±724.68ab |
| H40 | 24.50±0.71b | 11.50±0.71c | 22.15±0.63b | 12061.40±200.98b |
| 处理 Treatment | 产量 Yield/ (kg·hm-2) | 产值 Output value/ (yuan·hm-2) | 成本 Cost/ (yuan·hm-2) | 经济收益 Production profits/(yuan·hm-2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 12894.74 | 34815.798 | 6422.12 | 28393.68 |
| H0 | 12587.72 | 33986.844 | 3422.12 | 30564.72 |
| H10 | 12543.86 | 33868.422 | 3300.03 | 30568.39 |
| H20 | 12456.14 | 33631.578 | 3177.95 | 30453.63 |
| H40 | 12061.40 | 32565.78 | 2933.77 | 29632.01 |
表4 不同氮肥减施处理对水稻经济收益的影响
Table 4 Effect of different nitrogen fertilizer reduction treatments on economic profits of rice
| 处理 Treatment | 产量 Yield/ (kg·hm-2) | 产值 Output value/ (yuan·hm-2) | 成本 Cost/ (yuan·hm-2) | 经济收益 Production profits/(yuan·hm-2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 12894.74 | 34815.798 | 6422.12 | 28393.68 |
| H0 | 12587.72 | 33986.844 | 3422.12 | 30564.72 |
| H10 | 12543.86 | 33868.422 | 3300.03 | 30568.39 |
| H20 | 12456.14 | 33631.578 | 3177.95 | 30453.63 |
| H40 | 12061.40 | 32565.78 | 2933.77 | 29632.01 |
| [1] |
CHEN J, HUANG Y, TANG Y H, 2011. Quantifying economically and ecologically optimum nitrogen rates for rice production in south-eastern China[J]. Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment, 142(3-4): 195-204.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
JIN S Q, ZHOU F, 2018. Zero growth of chemical fertilizer and pesticide use: China’s objectives, progress and challenges[J]. Journal of Resources and Ecology, 9(1): 50-58.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
YU C Q, HUANG X, CHEN H, et al., 2019. Managing nitrogen to restore water quality in China[J]. Nature, 567(7749): 516-520.
DOI URL |
| [4] | 白晨阳, 姜浩, 苏庆旺, 等, 2021. 旱作条件下水稻生长指标、产量对播期的响应特征[J]. 灌溉排水学报, 40(2): 24-31. |
| BAI C Y, JIANG H, SU Q W, et al., 2021. The effects of planting date on growth traits and yield of different rice cultivars grown in dry conditions[J]. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage, 40(2): 24-31. | |
| [5] | 蔡康妮, 董新宇, 2021. 水稻旱作在铁岭市的试验应用讨论[J]. 种子科技, 39(9): 3-4. |
| CAI K N, DONG X Y, 2021. Discussion on the experiment and application of rice dry farming in Tieling city[J]. Seed Science & Technology, 39(9): 3-4. | |
| [6] | 曹志洪, 2003. 施肥与水体环境质量--论施肥对环境的影响(2)[J]. 土壤, 35(5): 2-7. |
| CAO Z H, 2003. Effect of fertilization on water quality: Effect of fertilization on environment quality (2)[J]. Soils, 35(5): 2-7. | |
| [7] | 段娜, 章尧想, 刘芳, 等, 2015. 植物氮素吸收及其转运蛋白研究进展[J]. 分子植物育种, 13(2): 461-468. |
| DUAN N, ZHANG Y X, LIU F, et al., 2015. Research progress on nitrogen uptake and transport protein in plant[J]. Molecular Plant Breeding, 13(2): 461-468. | |
| [8] | 高群山, 汤小兰, 周兴山, 等, 2015. 不同氮肥用量水平对水稻生长及产量影响[J]. 北方水稻, 45(6): 32-34, 38. |
| GAO Q S, TANG X L, ZHOU X S, et al., 2015. Effect of different amount of n fertilizer on rice growth and yield[J]. North Rice, 45(6): 32-34, 38. | |
| [9] | 高志红, 林浴霞, 张宇鹏, 等, 2021. 不同水分胁迫和氮素形态对水稻生长及木质部液流离子含量的影响[J]. 华北农学报, 36(2): 146-153. |
| GAO Z H, LIN Y X, ZHANG Y P, et al., 2021. Growth and ion content in rice seedling xylem sap under different water stresses and nitrogen forms[J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica, 36(2): 146-153. | |
| [10] | 郭琴波, 王小利, 段建军, 等, 2021. 氮肥减量配施生物炭对稻田有机碳矿化及酶活性影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 35(5): 369-374, 383. |
| GUO Q B, WANG X L, DUAN J J, et al., 2021. Effects of nitrogen reduction combined with biochar application on organic carbon mineralization and enzyme activity in paddy field[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 35(5): 369-374, 383. | |
| [11] | 巨晓棠, 张翀, 2021. 论合理施氮的原则和指标[J]. 土壤学报, 58(1): 13. |
| JU X T, ZHANG C, 2021. The principles and indicators of rational N fertilization[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 58(1): 13. | |
| [12] | 李录久, 王家嘉, 李东平, 等, 2013. 减量施氮对水稻生长和肥料利用效率的影响[J]. 安徽农业科学, 41(1): 99-100, 103. |
| LI L J, WANG J J, LI D P, et al., 2013. Effect of decreasing nitrogen application rate on rice growth and nitrogen use efficiency[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 41(1): 99-100, 103. | |
| [13] | 柳瑞, 高阳, 李恩琳, 等, 2020. 减氮配施生物炭对水稻生长发育、干物质积累及产量的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 29(5): 926-932. |
| LIU R, GAO Y, LI E L, et al., 2020. Effects of reduced nitrogen and biochar application on plant growth, dry matter accumulation and rice yield[J]. Ecology and Environment Sciences, 29(5): 926-932. | |
| [14] | 彭少兵, CHRISTIAN WITT, 黄见良, 等, 2002. 提高中国稻田氮肥利用率的研究策略[J]. 中国农业科学, 35(9): 1095-1103. |
| PENG S B, CHRISTIAN W, HUANG J L, et al., Research strategy in improving fertilizer-nitrogen use efficiency of irrigated rice in China[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 35(9): 1095-1103. | |
| [15] | 孙园园, 2010. 水分胁迫和氮素形态对不同基因型水稻生长和氮素吸收的影响及其生理机制[D]. 成都: 四川农业大学: 1-2. |
| SUN Y Y, 2010. Effects of different water stress and nitrogen forms onthe growth and nitrogen uptake of different genotypes rice and its physiological mechanism[D]. Chengdu: Sichuan Agricultural University: 1-2. | |
| [16] | 王保君, 程旺大, 陈贵, 等, 2019. 秸秆还田配合氮肥减量对稻田土壤养分、碳库及水稻产量的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 31(4): 117-123. |
| WANG B J, CHENG W D, CHEN G, et al., 2019. Effect of straw returning and nitrogen reduction on soil nutrition, carbon pool and rice yield in rice field[J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 31(4): 117-123. | |
| [17] | 王道中, 张成军, 郭熙盛, 2012. 减量施肥对水稻生长及氮素利用率的影响[J]. 土壤通报, 43(1): 161-165. |
| WANG D Z, ZHANG C J, GUO X S, 2012. Effects of lower fertilizer on rice growth and nitrogen use efficiency[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 43(1): 161-165. | |
| [18] | 王飞名, 张安宁, 刘国兰, 等, 2018. 旱种旱管对水稻产量及稻米品质的影响[J]. 中国稻米, 24(6): 73-75. |
| WANG F M, ZHANG A N, LIU G L, et al., 2018. Effects of dry seeding and drought irrigation on grain yield and quality of rice[J]. China Rice, 24(6): 73-75. | |
| [19] | 邢素丽, 邹拓, 杨军芳, 等, 2020. 节水灌溉下减施氮肥对水稻分蘖动态和产量的影响[J]. 河北农业科学, 24(4): 50-55. |
| XING S L, ZHOU T, YANG J F, et al., 2020. Effects of reducing nitrogen application on tillers development dynamics and yield of rice under water saving irrigation[J]. Journal of Hebei Agricultural Sciences, 24(4): 50-55. | |
| [20] | 许莹, 孙良杰, 杜立宇, 等, 2020. 常规田间管理条件下旱田土壤氮素淋失影响因素研究进展[J]. 土壤通报, 51(5): 1246-1254. |
| XU Y, SUN L J, DU L Y, et al., 2020. Influencing factors on soil nitrogen leaching under traditional managements of dry farmland[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 51(5): 1246-1254. | |
| [21] | 薛峰, 颜廷梅, 乔俊, 等, 2009. 太湖地区稻田减量施肥的环境效益和经济效益分析[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 25(4): 26-31. |
| XUE F, YAN T M, QIAO J, et al., 2009. Economic and environmental benefits of lower fertilizer application rate in paddy fields in Taihu area[J]. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 25(4): 26-31. | |
| [22] | 杨慧, 刘立晶, 刘忠军, 等, 2014. 我国农田化肥施用现状分析及建议[J]. 农机化研究 (9): 260-264. |
| YANG H, LIU L J, LIU Z J, et al., 2014. Analysis and suggestions of agricultural fertilizer application in China[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, (9): 260-264. | |
| [23] | 杨建昌, 王维, 王志琴, 等, 2000. 水稻旱秧大田期需水特性与节水灌溉指标研究[J]. 中国农业科学, 33(2): 34-42. |
| YANG J C, WANG W, WANG Z Q, et al., 2000. The characteristics of water requirement and water-saving irrigation indices of dry-raised rice seedlings in paddy field[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 33(2): 34-42. | |
| [24] | 杨秀霞, 燕辉, 周春火, 等, 2019. 水分胁迫下氮形态对水稻根系孔隙度及水分吸收的影响[J]. 干旱地区农业研究, 37(2): 144-149. |
| YANG X X, YAN H, ZHOU C H, et al., 2019. Effects of nitrogen forms on root porosity and water absorption of rice under drought stress[J]. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas, 37(2): 144-149. | |
| [25] | 尹钢吉, 郎景波, 侯新月, 等, 2019. 寒地水稻旱作作物需水量研究[J]. 现代农业科技 (7): 24-26. |
| YIN G J, LANG J B, HOU X Y, et al., 2019. Study on water requirement of dry farming crops in cold region[J]. Modern Agricultural Science and Technology (7): 24-26. | |
| [26] | 袁伟, 陈婉华, 王子阳, 等, 2021. 双季稻秸秆还田与减施氮肥对水稻产量和品质的影响[J]. 江西农业大学学报, 43(4): 711-720. |
| YUAN W, CHEN W H, WANG Z Y, et al., 2021. Effects of returning double-season rice straw to the field and reducing n-fertilizer on yield and quality of rice[J]. Acta Agriculturae Universitatis Jiangxiensis, 43(4): 711-720. | |
| [27] | 张美微, 屈俊峰, 张盼盼, 等, 2021. 减施氮肥对不同密度夏玉米产量和干物质积累特性的影响[J]. 玉米科学, 29(5): 145-150. |
| ZHANG M W, QU J F, ZHANG P P, et al., 2021. Effect of nitrogen fertilizer reduction on yield and dry matter accumulationin different planting densities of summer maize[J]. Journal of Maize Sciences, 29(5): 145-150. | |
| [28] | 张岩, 2019. 水稻旱作起垄夹肥技术研究[J]. 农民致富之友 (15): 170. |
| ZHANG Y, 2019. Study on the technology of ridging and adding fertilizer for rice dry farming[J]. Friends of Farmers Getting Rich (15): 170. | |
| [29] | 赵宏伟, 沙汉景, 2014. 我国稻田氮肥利用率的研究进展[J]. 东北农业大学学报, 45(2): 116-122. |
| ZHAO H W, SHA H J, 2014. Recent research of fertilizer-nitrogen use efficiency in paddy flied of China[J]. Journal of Northeast Agricultural University, 45(2): 116-122. | |
| [30] | 朱庆森, 黄丕生, 吴永祥, 等, 1995. 水稻节水栽培研究论文集[M]. 北京: 中国农业科技出版社: 11-12. |
| ZHU Q S, HUANG P S, WU Y X, et al., 1995. A collection of research papers on water-saving rice cultivation research[M]. Beijing: China Agricultural Science and Technology Press: 11-12. | |
| [31] | 朱兆良, 2003. 合理使用化肥充分利用有机肥发展环境友好的施肥体系[J]. 中国科学院院刊 (2): 15-19. |
| ZHU Z L, 2003. Fertilizer management strategies for the harmonization of agriculture development with environment protection[J]. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences (2): 15-19. |
| [1] | 胡启瑞, 吉春容, 李迎春, 王雪姣, 杨明凤, 郭燕云. 膜下滴灌棉花蕾期干旱胁迫对光合特性及产量的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(6): 1045-1052. |
| [2] | 王敬, 孟珂, 陈璇, 章家恩, 向慧敏, 钟嘉文, 石兆基. 酸雨对生菜和上海青的产量、品质及生理特性的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(6): 1098-1107. |
| [3] | 黄英梅, 钟松雄, 朱忆雯, 王向琴, 李芳柏. 单质硫抑制水稻植株甲基汞累积的效应与机制[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(6): 1115-1122. |
| [4] | 杨凯, 杨靖睿, 曹培培, 吕春华, 孙文娟, 于凌飞, 邓希. CO2浓度升高下水稻株高、茎蘖与SPAD动态响应及其模拟[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 933-942. |
| [5] | 徐敏, 许超, 余光辉, 尹力初, 张泉, 朱捍华, 朱奇宏, 张杨珠, 黄道友. 地下水位和长期秸秆还田对土壤镉有效性及稻米镉含量的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 150-157. |
| [6] | 邓天乐, 谢立勇, 张凤哲, 赵洪亮, 蒋语童. CO2浓度升高条件下稗草与水稻生长空间竞争关系研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1566-1572. |
| [7] | 董乐恒, 王旭刚, 陈曼佳, 王子豪, 孙丽蓉, 石兆勇, 吴琪琪. 光照和避光条件下石灰性水稻土Fe氧化还原与Cu活性关系研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(7): 1448-1455. |
| [8] | 徐梅华, 顾明华, 王骋臻, 雷静, 韦燕燕, 沈方科. 锰对土壤砷形态转化及水稻吸收砷的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 802-813. |
| [9] | 刘江, 朱丽杰, 张开, 王晓明, 王立为, 高西宁. 不同生育期干旱胁迫/复水对大豆光合特性及产量的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(2): 286-296. |
| [10] | 黄巧义, 于俊红, 黄建凤, 黄旭, 李苹, 付弘婷, 唐拴虎, 刘一锋, 徐培智. 广东省主要农作物秸秆养分资源量及替代化肥潜力[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(2): 297-306. |
| [11] | 石含之, 江棋, 刘帆, 文典, 黄永东, 邓腾灏博, 王旭, 徐爱平, 李富荣, 吴志超, 李梅霞, 彭锦芬, 杜瑞英. 水稻根茬还田对土壤及稻米中镉累积的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(2): 363-369. |
| [12] | 上官宇先, 尹宏亮, 徐懿, 钟红梅, 何明江, 秦鱼生, 郭松, 喻华. 不同钝化剂对水稻小麦籽粒镉吸收的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(2): 370-379. |
| [13] | 张亚平, 陈慧敏, 吴志宇, 汤佳, 谢章彰, 刘芳华. 低量水铁矿促进稻田梭菌Clostridium sp. BY-1产氢效率[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(12): 2341-2349. |
| [14] | 张开, 王立为, 高西宁, 贺明慧. 基于DNDC模型不同降水年型下氮肥管理对马铃薯田N2O减排及增产潜力影响研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(8): 1672-1682. |
| [15] | 路旭平, 李芳兰, 石亚飞, 张娟伟, 杨文伟, 罗成科, 田蕾, 李培富. 不同水稻品种幼苗响应碱胁迫的生理差异及胁迫等级构建[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(8): 1757-1768. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
