生态环境学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (8): 1757-1768.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2021.08.023
路旭平( ), 李芳兰, 石亚飞, 张娟伟, 杨文伟, 罗成科*(
), 李芳兰, 石亚飞, 张娟伟, 杨文伟, 罗成科*( ), 田蕾, 李培富
), 田蕾, 李培富
收稿日期:2021-05-25
出版日期:2021-08-18
发布日期:2021-11-03
通讯作者:
* E-mail: chkluo2002@163.com作者简介:路旭平(1995年生),男,硕士研究生,主要从事水稻抗逆生理生态研究。E-mail: 577861974@qq.com
基金资助:
LU Xuping( ), LI Fanglan, SHI Yafei, ZHANG Juanwei, YANG Wenwei, LUO Chengke*(
), LI Fanglan, SHI Yafei, ZHANG Juanwei, YANG Wenwei, LUO Chengke*( ), TIAN Lei, LI Peifu
), TIAN Lei, LI Peifu
Received:2021-05-25
Online:2021-08-18
Published:2021-11-03
摘要:
目前关于不同耐碱水稻品种响应碱胁迫的生理差异缺乏系统性的研究,依据生理生化指标计算胁迫指数并确定胁迫等级的方法较少见。为进一步阐明水稻耐碱的生理机制、提高水稻耐碱性和明确水稻抗碱等级,以碱敏感品种“中花11”和耐碱品种“宁粳52”为材料,设3个碱浓度水平(10、20和30 mmol∙L-1)和3个pH水平(pH 8.65、pH 9.55和pH 10.50),探究碱胁迫对不同耐碱水稻品种幼苗叶片相对含水量、叶绿素(Chla、Chlb、Chl)含量、叶绿素a/b(Chla/b)、丙二醛(MDA)含量、脂氧合酶(LOX)活性、活性氧(O2∙-和H2O2)含量、渗透调节物质(Pro、SS、SP)含量、抗氧化酶(SOD、POD和CAT)活性、还原型抗坏血酸(ASA)和还原型谷胱甘肽(GSH)含量的影响,通过主成分分析提取关键生理参数并建立碱胁迫等级。结果表明,(1)在碱胁迫条件下,耐碱品种“宁粳52”能维持更高的Chla、Chlb和Chl含量、Chla/b和叶片相对含水量,保持较低的MDA含量、LOX活性、O2∙-和H2O2含量,合成更多的SOD、POD和CAT活性、Pro、SS、SP、ASA和GSH含量。(2)通过主成分分析,挑选出Chla、SOD、MDA、H2O2、SS、ASA等关键指标,并计算胁迫指数Z,将水稻受害划分为正常(0≤Z<1)、轻度(1≤Z<4)、中度(4≤Z<7)、重度(7≤Z<10)、特重度(10≤Z)5个等级。(3)与20C(碱浓度为20 mmol∙L-1、pH 10.50)相比,供试材料在30A(30 mmol∙L-1、pH 8.65)处理下MDA含量、LOX活性、活性氧含量和胁迫指数均下降,说明在碱浓度大于20 mmol∙L-1时,低碱浓度与高pH对水稻的伤害大于高碱浓度低pH。因此,在碱化土种植水稻时应考虑总盐碱浓度和pH共同对水稻生长的影响。
中图分类号:
路旭平, 李芳兰, 石亚飞, 张娟伟, 杨文伟, 罗成科, 田蕾, 李培富. 不同水稻品种幼苗响应碱胁迫的生理差异及胁迫等级构建[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(8): 1757-1768.
LU Xuping, LI Fanglan, SHI Yafei, ZHANG Juanwei, YANG Wenwei, LUO Chengke, TIAN Lei, LI Peifu. Physiological Differences of Seedlings of Different Rice Varieties in Response to Alkali Stress and Construction of Stress Levels[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(8): 1757-1768.
| 处理 Treatments | c(NaHCO3+Na2CO3)/ (mmol∙L-1) | pH | n(NaHCO3)꞉ n(Na2CO3) | c(NaHCO3)/ (mmol∙L-1) | c(Na2CO3)/ (mmol∙L-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 0 | 5.5±0.05 | ‒ | 0 | 0 |
| 10A | 10 | 8.65±0.05 | 9꞉1 | 9 | 1 |
| 10B | 9.55±0.05 | 5꞉5 | 5 | 5 | |
| 10C | 10.50±0.05 | 1꞉9 | 1 | 9 | |
| 20A | 20 | 8.65±0.05 | 9꞉1 | 18 | 2 |
| 20B | 9.55±0.05 | 5꞉5 | 10 | 10 | |
| 20C | 10.50±0.05 | 1꞉9 | 2 | 18 | |
| 30A | 30 | 8.65±0.05 | 9꞉1 | 27 | 3 |
| 30B | 9.55±0.05 | 5꞉5 | 15 | 15 | |
| 30C | 10.50±0.05 | 1꞉9 | 3 | 27 |
表1 各处理碱组成和pH
Table 1 Alkali composition and pH of each treatment
| 处理 Treatments | c(NaHCO3+Na2CO3)/ (mmol∙L-1) | pH | n(NaHCO3)꞉ n(Na2CO3) | c(NaHCO3)/ (mmol∙L-1) | c(Na2CO3)/ (mmol∙L-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 0 | 5.5±0.05 | ‒ | 0 | 0 |
| 10A | 10 | 8.65±0.05 | 9꞉1 | 9 | 1 |
| 10B | 9.55±0.05 | 5꞉5 | 5 | 5 | |
| 10C | 10.50±0.05 | 1꞉9 | 1 | 9 | |
| 20A | 20 | 8.65±0.05 | 9꞉1 | 18 | 2 |
| 20B | 9.55±0.05 | 5꞉5 | 10 | 10 | |
| 20C | 10.50±0.05 | 1꞉9 | 2 | 18 | |
| 30A | 30 | 8.65±0.05 | 9꞉1 | 27 | 3 |
| 30B | 9.55±0.05 | 5꞉5 | 15 | 15 | |
| 30C | 10.50±0.05 | 1꞉9 | 3 | 27 |
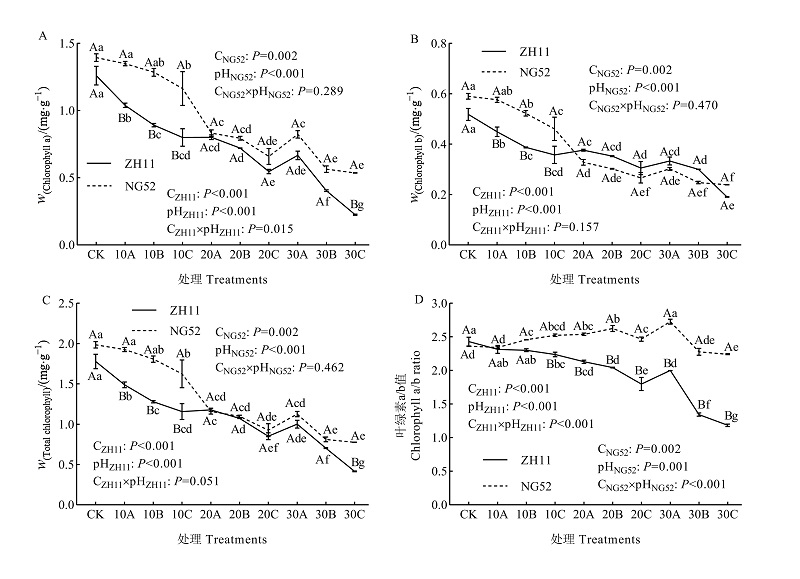
图1 碱胁迫对水稻叶片叶绿素含量的影响 n=3;10、20和30分别表示碱水平10、20和30 mmol∙L-1;A、B和C分别表示pH值8.65、9.55和10.50。不同小写字母表示同一品种在不同处理下差异显著(P<0.05);不同大写字母表示不同品种在相同处理下差异显著(P<0.05)。下同
Fig. 1 Effects of alkali stress on chlorophyll contents of rice leaves n=3; 10, 20 and 30 respectively indicate alkali application levels of 10 mmol∙L-1, 20 mmol∙L-1 and 30 mmol∙L-1; A, B and C respectively indicate pH levels of 8.65, 9.55 and 10.50. Different small letters indicate significant difference of the same rice varieties in the different treatment at 0.05 level; Different capital letters indicate significant difference of different rice varieties in the same l treatment at 0.05 level. The same as below
| 参数 Parameter | ZH11特征向量 Eigenvector | NG52特征向量 Eigenvector | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 第1主成分 PC1 | 第1主成分 PC1 | 第2主成分 PC2 | ||
| Chl a | -0.996 | -0.967 | -0.109 | |
| Chl b | -0.973 | -0.951 | -0.244 | |
| Chl | -0.994 | -0.965 | -0.150 | |
| Chl a/b | -0.937 | -0.099 | 0.968 | |
| RWC | -0.983 | -0.848 | 0.415 | |
| SOD | 0.834 | 0.966 | 0.120 | |
| POD | 0.878 | 0.912 | -0.092 | |
| CAT | 0.979 | 0.948 | 0.200 | |
| MDA | 0.957 | 0.980 | -0.030 | |
| LOX | 0.942 | 0.975 | 0.124 | |
| H2O2 | 0.983 | 0.991 | -0.091 | |
| O2·ˉ | 0.994 | 0.989 | -0.093 | |
| Pro | 0.984 | 0.995 | 0.065 | |
| SS | 0.981 | 0.995 | -0.037 | |
| SP | 0.980 | 0.989 | -0.097 | |
| ASA | 0.986 | 0.990 | -0.068 | |
| GSH | 0.985 | 0.965 | -0.031 | |
| 特征根 Eigenvalue | 15.787 | 14.901 | 1.321 | |
| 贡献率 Contribution rate/% | 92.867 | 87.653 | 7.768 | |
| 累计贡献率 Cumulative contribution rate/% | 92.867 | 87.653 | 95.422 | |
表2 两种水稻叶片生理参数的主成分分析
Table 2 Principal component analysis of physiological parameter in rice leaves
| 参数 Parameter | ZH11特征向量 Eigenvector | NG52特征向量 Eigenvector | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 第1主成分 PC1 | 第1主成分 PC1 | 第2主成分 PC2 | ||
| Chl a | -0.996 | -0.967 | -0.109 | |
| Chl b | -0.973 | -0.951 | -0.244 | |
| Chl | -0.994 | -0.965 | -0.150 | |
| Chl a/b | -0.937 | -0.099 | 0.968 | |
| RWC | -0.983 | -0.848 | 0.415 | |
| SOD | 0.834 | 0.966 | 0.120 | |
| POD | 0.878 | 0.912 | -0.092 | |
| CAT | 0.979 | 0.948 | 0.200 | |
| MDA | 0.957 | 0.980 | -0.030 | |
| LOX | 0.942 | 0.975 | 0.124 | |
| H2O2 | 0.983 | 0.991 | -0.091 | |
| O2·ˉ | 0.994 | 0.989 | -0.093 | |
| Pro | 0.984 | 0.995 | 0.065 | |
| SS | 0.981 | 0.995 | -0.037 | |
| SP | 0.980 | 0.989 | -0.097 | |
| ASA | 0.986 | 0.990 | -0.068 | |
| GSH | 0.985 | 0.965 | -0.031 | |
| 特征根 Eigenvalue | 15.787 | 14.901 | 1.321 | |
| 贡献率 Contribution rate/% | 92.867 | 87.653 | 7.768 | |
| 累计贡献率 Cumulative contribution rate/% | 92.867 | 87.653 | 95.422 | |
| 参数 Parameter | ZH11权重系数 ZH11 Weight coefficient/% | NG52权重系数 NG52 Weight coefficient/% |
|---|---|---|
| Chl a | 16.07 | 26.02 |
| SOD | 9.13 | 11.11 |
| MDA | 13.87 | 14.24 |
| H2O2 | 17.10 | 13.43 |
| SS | 23.26 | 15.43 |
| ASA | 20.58 | 19.77 |
表3 Chla、SOD、MDA、H2O2、SS和ASA的权重
Table 3 Weight coefficient of Chla, SOD, MDA, H2O2, SS and ASA
| 参数 Parameter | ZH11权重系数 ZH11 Weight coefficient/% | NG52权重系数 NG52 Weight coefficient/% |
|---|---|---|
| Chl a | 16.07 | 26.02 |
| SOD | 9.13 | 11.11 |
| MDA | 13.87 | 14.24 |
| H2O2 | 17.10 | 13.43 |
| SS | 23.26 | 15.43 |
| ASA | 20.58 | 19.77 |
| 处理 Treatments | ZH11 | NG52 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Z值 Z value | 等级 Degree | Z值 Z value | 等级 Degree | |
| CK | 0 | 正常 Normal | 0 | 正常 Normal |
| 10A | 1.949 | 轻度 Mild | 1.402 | 轻度 Mild |
| 10B | 3.029 | 轻度 Mild | 2.429 | 轻度 Mild |
| 10C | 4.343 | 中度 Moderate | 3.465 | 轻度 Mild |
| 20A | 4.534 | 中度 Moderate | 4.315 | 中度 Moderate |
| 20B | 5.928 | 中度 Moderate | 5.317 | 中度 Moderate |
| 20C | 8.069 | 重度 Severe | 6.824 | 中度 Moderate |
| 30A | 6.733 | 中度 Moderate | 5.936 | 中度 Moderate |
| 30B | 9.411 | 重度 Severe | 8.125 | 重度 Severe |
| 30C | 11.276 | 特重度 Special severe | 9.547 | 重度 Severe |
表4 碱胁迫指数在不同处理下的变化规律
Table 4 Changes of alkali stress index with different treatments
| 处理 Treatments | ZH11 | NG52 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Z值 Z value | 等级 Degree | Z值 Z value | 等级 Degree | |
| CK | 0 | 正常 Normal | 0 | 正常 Normal |
| 10A | 1.949 | 轻度 Mild | 1.402 | 轻度 Mild |
| 10B | 3.029 | 轻度 Mild | 2.429 | 轻度 Mild |
| 10C | 4.343 | 中度 Moderate | 3.465 | 轻度 Mild |
| 20A | 4.534 | 中度 Moderate | 4.315 | 中度 Moderate |
| 20B | 5.928 | 中度 Moderate | 5.317 | 中度 Moderate |
| 20C | 8.069 | 重度 Severe | 6.824 | 中度 Moderate |
| 30A | 6.733 | 中度 Moderate | 5.936 | 中度 Moderate |
| 30B | 9.411 | 重度 Severe | 8.125 | 重度 Severe |
| 30C | 11.276 | 特重度 Special severe | 9.547 | 重度 Severe |
| [1] |
APEL K, HIRT H, 2004. Reactive oxygen species: Metabolism, oxidative stress, and signal transduction[J]. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 55: 373-399.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
BAXTER A, MITTLER R, SUZUKI N, 2014. ROS as key players in plant stress signaling[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 65(5): 1229-1240.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
DEINLEIN U, STEPHAN A B, HORIE T, et al., 2014. Plant salt-tolerance mechanisms[J]. Trends in Plant Science, 19(6): 371-379.
DOI URL |
| [4] | DODERER A, KOKKELINK I, VAN DER VEEN S, et al., 1992. Purification and characterization of two lipoxygenase isoenzymes from germinating barley[J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1120(1): 97-104. |
| [5] |
FLOWERS T J, COLMER T D, 2008. Salinity tolerance in halophytes[J]. New Phytologist, 179(4): 945-963.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
SZALAI G, KELLS T, GALIBA G, et al., 2009. Glutathione as an antioxidant and regulatory molecule in plants under abiotic stress conditions[J]. Journal of Plant Growth Regulation, 28(1): 66-80.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
GUO H J, HUANG Z J, LI M Q, et al., 2020. Growth, ionic homeostasis, and physiological responses of cotton under different salt and alkali stresses[J]. Scientific Reports, DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-79045-z.
DOI |
| [8] |
GUO R, SHI L, YAN C, et al., 2017. Ionomic and metabolic responses to neutral salt or alkaline salt stresses in maize (Zea mays L.) seedlings[J]. Bmc Plant Biology, DOI: 10.1186/s12870-017-0994-6.
DOI |
| [9] |
HASANUZZAMAN M, ALAM M M, RAHMAN A, et al., 2014. Exogenous proline and glycine betaine mediated upregulation of antioxidant defense and glyoxalase systems provides better protection against salt-induced oxidative stress in two rice (Oryza sativa L.) varieties[J]. BioMed Research International, DOI: 10.1155/2014/757219.
DOI |
| [10] |
HUANG F, STUDART-WITKOWSKI C, SCHWAB W, 2010. Overexpression of hydroperoxide lyase gene in Nicotiana benthamiana using a viral vector system[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 8(7): 783-795.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
HUANG L, LI Z, PAN S, et al., 2019. Ameliorating effects of exogenous calcium on the photosynthetic physiology of honeysuckle (Lonicera japonica) under salt stress[J]. Functional Plant Biology, 46(12): 1103-1113.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
IZADI-DARBANDI E, MEHDIKHANI H, 2018. Salinity effect on some of the morphophysiological traits of three plantago species (Plantago spp.)[J]. Scientia Horticulturae, 236: 43-51.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
KUMAR S, LI G J, YANG J J, et al., 2020. Investigation of an antioxidative system for salinity tolerance in Oenanthe javanica[J]. Antioxidants, DOI: 10.3390/antiox9100940.
DOI |
| [14] |
NIU K J, MA X, LIANG G L, et al., 2017. 5-Aminolevulinic acid modulates antioxidant defense systems and mitigates drought-induced damage in Kentucky bluegrass seedlings[J]. Protoplasma, 254(6): 2083-2094.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
QIN Y, BAI J H, WANG Y Q, et al., 2018. Comparative effects of salt and alkali stress on photosynthesis and root physiology of oat at anthesis[J]. Archives of Biological Sciences, 70(2): 329-338.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
RAVIKUMAR G, MANIMARAN P, VOLETI S R, et al., 2014. Stress-inducible expression of AtDREB1A transcription factor greatly improves drought stress tolerance in transgenic indica rice[J]. Transgenic Research, 23(3): 421-439.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
TUTEJA N, GILL S S, 2010. Reactive oxygen species and antioxidant machinery in abiotic stress tolerance in crop plants[J]. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 48(12): 909-930.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
WANG P, SUN X, LI C, et al., 2013. Long-term exogenous application of melatonin delays drought-induced leaf senescence in apple[J]. Journal of Pineal Research, 54(3): 292-302.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
WANG S J, CHEN Q, LI Y, et al., 2017. Research on saline-alkali soil amelioration with FGD gypsum[J]. Resources Conservation and Recycling, 121: 82-92.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
YE T T, WANG Y P, FENG Y Q, et al., 2021. Physiological and metabolomic responses of bermudagrass (Cynodon dactylon) to alkali stress[J]. Physiologia Plantarum, 171(1): 22-33.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
ZHANG H H, LI X, CHE Y H, et al., 2020. A study on the effects of salinity and pH on PSII function in mulberry seedling leaves under saline-alkali mixed stress[J]. Trees-Structure and Function, 34(3): 693-706.
DOI URL |
| [22] | ZHANG H, LI X, NAN X, et al., 2017. Alkalinity and salinity tolerance during seed germination and early seedling stages of three alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) cultivars[J]. Legume Research, 40(5): 853-858. |
| [23] |
ZHANG H, LIU X, ZHANG R, et al., 2017. Root damage under alkaline stress is associated with reactive oxygen species accumulation in rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2017.01580.
DOI |
| [24] | 安玉艳, 梁宗锁, 2012. 植物应对干旱胁迫的阶段性策略[J]. 应用生态学报, 23(10): 2907-2915. |
| AN Y Y, LIANG Z S, 2012. Staged strategy of plants in response to drought stress[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 23(10): 2907-2915. | |
| [25] | 曹齐卫, 李利斌, 孔素萍, 等, 2015. 不同黄瓜品种幼苗对等渗Mg(NO3)2和NaCl胁迫的生理响应[J]. 应用生态学报, 26(4): 1171-1178. |
| CAO Q W, LI L B, KONG S P, et al., 2015. Physiological responses of different cucumber cultivars seedlings to iso-osmotic Mg(NO3)2 and NaCl stress[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 26(4): 1171-1178. | |
| [26] | 高立杨, 贾旭梅, 朱祖雷, 等, 2020. 盐碱复合胁迫下2种长富2号苹果砧穗组合的光合及生理特性[J]. 干旱地区农业研究, 38(2): 177-184. |
| GAO L Y, JIA X M, ZHU Z L, et al., 2020. Photosynthetic and physiological characteristics of two rootstock combinations with Changfu 2 as scion under saline-alkali stress[J]. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas, 38(2): 177-184. | |
| [27] | 黄洁, 白志刚, 钟楚, 等, 2020. 水稻耐盐生理及分子调节机制[J]. 核农学报, 34(6): 1359-1367. |
| HUANG J, BAI Z G, ZHONG C, et al., 2020. Physiological and Molecular Mechanisms of Salt Stress Tolerance in Rice[J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, 34(6): 1359-1367. | |
| [28] | 贾婷婷, 常伟, 范晓旭, 等, 2018. 盐胁迫下AM真菌对沙枣苗木光合与叶绿素荧光特性的影响[J]. 生态学报, 38(4): 1337-1347. |
| JIA T T, CHANG W, FAN X X, et al., 2018. Effects of Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on photosynthetic and chlorophyll fluorescence characteristics in Elaeagnus angustifolia seedlings under salt stress[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 38(4): 1337-1347. | |
| [29] | 贾旭梅, 朱燕芳, 王海, 等, 2019. 垂丝海棠应对盐碱复合胁迫的生理响应[J]. 生态学报, 39(17): 6349-6361. |
| JIA X M, ZHU Y F, WANG H, et al., 2019. Study on Physiological Response of Malus halliana to Saline-alkali Stress[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 39(17): 6349-6361. | |
| [30] | 罗成科, 田蕾, 毕江涛, 等, 2019. 种稻年限对盐碱土微量元素及水稻产量和品质的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 28(8): 1577-1584. |
| LUO C K, TIAN L, BI J T, et al., 2019. Effects of rice planting years on saline-alkali soil trace elements, rice yield and quality[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 28(8): 1577-1584. | |
| [31] | 冷春旭, 郑福余, 赵北平, 等, 2020. 水稻耐碱性研究进展[J]. 生物技术通报, 36(11): 103-111. |
| LENG C X, ZHENG F Y, ZHAO B P, et al., 2020. Advances on Alkaline Tolerance of Rice[J]. Biotechnology Bulletin, 36(11): 103-111. | |
| [32] | 梁银培, 孙健, 索艺宁, 等, 2017. 水稻耐盐性和耐碱性相关性状的QTL定位及环境互作分析[J]. 中国农业科学, 50(10): 1747-1762. |
| LIANG Y P, SUN J, SUO Y N, et al., 2017. QTL mapping and QTL×environment interaction analysis of salt and alkali tolerance- related traits in rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 50(10): 1747-1762. | |
| [33] | 刘建新, 刘瑞瑞, 贾海燕, 等, 2020. 外源H2S对盐碱胁迫下裸燕麦幼苗叶片渗透胁迫的调节作用[J]. 生态学杂志, 39(12): 3989-3997. |
| LIU J X, LIU R R, JIA H Y, et al., 2020. Regulation of exogenous hydrogen sulfide on osmotic stress in leaves of naked oat seedlings under saline-alkali mixed stress[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 39(12): 3989-3997. | |
| [34] | 罗姗姗, 曹昀, 纪欣圣, 等, 2019. 水深对黑藻叶绿素含量和抗氧化酶活性的影响[J]. 生态学杂志, 38(1): 221-228. |
| LUO S S, CAO Y, JI X S, et al., 2020. Effects of water depth on chlorophyll content and antioxidant enzyme activity of Hydrilla verticillata[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 38(1): 221-228. | |
| [35] | 穆阳杰, 詹玉洁, 许卫锋, 等, 2020. 高pH胁迫下拟南芥根转录组学与网络应答[J]. 土壤学报, 57(3): 691-701. |
| MU Y J, ZHAN Y J, XU W F, et al., 2020. Transcriptome and network response of arabidopsis root under high pH stress[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 57(3): 691-701. | |
| [36] | 王慧, 刘宁, 姚延梼, 等, 2017. 晋北干旱区盐碱地柽柳叶总有机碳与营养元素含量的关系[J]. 生态环境学报, 26(12): 2036-2044. |
| WANG H, LIU N, YAO Y T, et al., 2017. The Relationship between Foliar TOC of Tamarix chinensis Lour. and Nutrient Elements’ Content in Saline-alkali Soil of North Shanxi[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 26(12): 2036-2044. | |
| [37] | 徐超, 王明田, 杨再强, 等, 2021. 高温对温室草莓光合生理特性的影响及胁迫等级构建[J]. 应用生态学报, 32(1): 231-240. |
| XU C, WANG M T, YANG Z Q, et al., 2021. Effects of high temperature on photosynthetic physiological characteristics of strawberry seedlings in greenhouse and construction of stress level[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 32(1): 231-240. | |
| [38] | 徐宁, 陈冰嬬, 王明海, 等, 2017. 绿豆品种资源萌发期耐碱性鉴定[J]. 作物学报, 43(1): 112-121. |
|
XU N, CHENG B R, WANG M H, et al., 2017. Identification of Alkali Tolerance of Mungbean Germplasm Resources during Germination[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 43(1): 112-121.
DOI URL |
|
| [39] | 姚栋萍, 吴俊, 胡忠孝, 等, 2019. 水稻耐盐碱的生理机制及育种策略[J]. 杂交水稻, 34(4): 1-7. |
| YAO D P, WU J, HU Z X, et al., 2019. Physiological Mechanism and Breeding Strategy of Rice Saline-Alkaline Tolerance[J]. Hybrid Rice, 34(4): 1-7. | |
| [40] | 杨佳佳, 姜琦刚, 赵静, 等, 2011. 基于环境减灾卫星高光谱数据的盐碱地等级划分[J]. 农业工程学报, 27(10): 118-124. |
| YANG J J, JIANG Q G, ZHAO J, et al., 2011. Quantitative retrieval and classification of saline soil using HJ-1A hyperspectral data[J]. Transactions of the CSAE, 2011, 27(10): 118-124. | |
| [41] | 赵怀玉, 林鸿宣, 2020. 植物响应盐碱胁迫的分子机制[J]. 土壤与作物, 9(2): 103-113. |
| ZHAO H Y, LIN H X, 2020. Molecular mechanism of plants in responses to salt and alkali stress[J]. Soils and Crops, 9(2): 103-113. | |
| [42] | 钟嘉文, 单晓冉, 章家恩, 等, 2021. 酸雨对生菜的光合、抗氧化系统和产量的影响研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 30(3): 532-540. |
| ZHONG J W, SHAN X R, ZHANG J E, et al., 2021. Study on the effects of acid rain on the photosynthetic and antioxidant systems and yield of lettuce[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 30(3): 532-540. | |
| [43] | 邹琦, 2000. 植物生理学实验指导[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社. |
| ZOU Q, 2000. Plant physiology experiment guidance[M]. Beijing: China Agriculture Press. |
| [1] | 王敬, 孟珂, 陈璇, 章家恩, 向慧敏, 钟嘉文, 石兆基. 酸雨对生菜和上海青的产量、品质及生理特性的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(6): 1098-1107. |
| [2] | 黄英梅, 钟松雄, 朱忆雯, 王向琴, 李芳柏. 单质硫抑制水稻植株甲基汞累积的效应与机制[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(6): 1115-1122. |
| [3] | 杨凯, 杨靖睿, 曹培培, 吕春华, 孙文娟, 于凌飞, 邓希. CO2浓度升高下水稻株高、茎蘖与SPAD动态响应及其模拟[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 933-942. |
| [4] | 徐敏, 许超, 余光辉, 尹力初, 张泉, 朱捍华, 朱奇宏, 张杨珠, 黄道友. 地下水位和长期秸秆还田对土壤镉有效性及稻米镉含量的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 150-157. |
| [5] | 向兴, 满百膺, 张俊忠, 罗洋, 毛小涛, 张超, 孙丙华, 王希. 黄山土壤细菌群落及氮循环功能群的垂向分布格局[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 56-69. |
| [6] | 邓天乐, 谢立勇, 张凤哲, 赵洪亮, 蒋语童. CO2浓度升高条件下稗草与水稻生长空间竞争关系研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1566-1572. |
| [7] | 董乐恒, 王旭刚, 陈曼佳, 王子豪, 孙丽蓉, 石兆勇, 吴琪琪. 光照和避光条件下石灰性水稻土Fe氧化还原与Cu活性关系研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(7): 1448-1455. |
| [8] | 刘晓红, 刘柳青青, 栗敏, 刘强, 曹东东, 郑浩, 罗先香. 不同粒径的聚乙烯微塑料对玉米和黄瓜种子发芽和幼苗生长的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(6): 1263-1271. |
| [9] | 魏岚, 黄连喜, 李翔, 王泽煌, 陈伟盛, 黄庆, 黄玉芬, 刘忠珍. 生物炭基质可显著地促进香蕉幼苗生长[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 732-739. |
| [10] | 徐梅华, 顾明华, 王骋臻, 雷静, 韦燕燕, 沈方科. 锰对土壤砷形态转化及水稻吸收砷的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 802-813. |
| [11] | 朱旭, 李海梅, 李彦华, 孙迎坤, 田园. 8种灌木对大气颗粒物污染的生理响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(3): 535-545. |
| [12] | 石含之, 江棋, 刘帆, 文典, 黄永东, 邓腾灏博, 王旭, 徐爱平, 李富荣, 吴志超, 李梅霞, 彭锦芬, 杜瑞英. 水稻根茬还田对土壤及稻米中镉累积的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(2): 363-369. |
| [13] | 上官宇先, 尹宏亮, 徐懿, 钟红梅, 何明江, 秦鱼生, 郭松, 喻华. 不同钝化剂对水稻小麦籽粒镉吸收的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(2): 370-379. |
| [14] | 张亚平, 陈慧敏, 吴志宇, 汤佳, 谢章彰, 刘芳华. 低量水铁矿促进稻田梭菌Clostridium sp. BY-1产氢效率[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(12): 2341-2349. |
| [15] | 陈赋秋雪, 唐思琪, 袁昊, 马子轩, 陈坦, 杨婷, 张冰, 刘颖. 聚苯乙烯微塑料对典型农作物种子发芽和幼苗生长的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(12): 2382-2392. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
