生态环境学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (6): 1098-1107.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2023.06.011
王敬1( ), 孟珂1, 陈璇1, 章家恩1,2,3,4,*(
), 孟珂1, 陈璇1, 章家恩1,2,3,4,*( ), 向慧敏1,2,3,4, 钟嘉文1, 石兆基1
), 向慧敏1,2,3,4, 钟嘉文1, 石兆基1
收稿日期:2022-12-27
出版日期:2023-06-18
发布日期:2023-09-01
通讯作者:
*章家恩,E-mail: jeanzh@scau.edu.cn作者简介:王敬(1997年生),女,硕士研究生,研究方向为土壤生态学。E-mail: 1535017573@qq.com
基金资助:
WANG Jing1( ), MENG Ke1, CHEN Xuan1, ZHANG Jiaen1,2,3,4,*(
), MENG Ke1, CHEN Xuan1, ZHANG Jiaen1,2,3,4,*( ), XIANG Huimin1,2,3,4, ZHONG Jiawen1, SHI Zhaoji1
), XIANG Huimin1,2,3,4, ZHONG Jiawen1, SHI Zhaoji1
Received:2022-12-27
Online:2023-06-18
Published:2023-09-01
摘要:
蔬菜在饮食结构中至关重要,维持着人体正常的生理功能。酸雨的频发会影响蔬菜正常生长,降低产量和品质。以生菜(Lactuca sativa L.)和上海青(Brassica chinensis L.)为研究对象,采用盆栽方法,以自来水(pH 7.0,CK)为对照,设计3个不同酸雨强度(pH 5.0,3.5,2.5)处理,研究不同酸雨强度对这两种叶菜产量、叶片叶绿素的荧光特性及其质量分数以及营养品质的影响。结果表明:pH 5.0酸雨对生菜和上海青的产量无显著影响,pH 3.5和pH 2.5酸雨分别引起生菜产量下降31.3%和41.6%,上海青产量下降12.2%和27.6%。在不同酸雨处理下,供试蔬菜的叶绿素荧光参数总体变化趋势为:pH 5.0>CK>pH 3.5>pH 2.5,且非光化学淬灭系数分别下降21.4%—25.3%和15.6%—19.1%,说明它们的最大光能转换效率在受到弱酸性酸雨作用时会升高,强酸性酸雨胁迫时降低。在收获期,两种叶菜的光合色素质量分数变化规律为:pH 5.0>CK, pH 3.5>pH 2.5和CK>pH 5.0>pH 3.5>pH 2.5,且pH 2.5酸雨处理时总叶绿素质量分数显著下降30.5%和10.7%。此外二者的原花青素质量分数在酸雨处理时显著下降,而可溶性蛋白、可溶性糖、游离脯氨酸、维生素C质量分数随着酸雨强度升高呈现先升高后下降的趋势,pH 5.0酸雨处理时这4个指标达到最大值,在pH 2.5酸雨胁迫时抑制作用最强,上海青的这四个指标与对照相比分别显著下降11.8%、22.7%、11.9%、16.6%,生菜下降3.68%、11.0%、17.5%、16.1%,其中可溶性蛋白质质量分数与对照相比无显著差异。综上,酸雨对蔬菜的影响与蔬菜种类和酸雨酸度有关,酸雨pH<3.5时,会严重影响蔬菜的产量和品质。研究结果可为蔬菜种植与风险防控提供相关参考。
中图分类号:
王敬, 孟珂, 陈璇, 章家恩, 向慧敏, 钟嘉文, 石兆基. 酸雨对生菜和上海青的产量、品质及生理特性的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(6): 1098-1107.
WANG Jing, MENG Ke, CHEN Xuan, ZHANG Jiaen, XIANG Huimin, ZHONG Jiawen, SHI Zhaoji. Effects of Acid Rain on Yield, Quality and Physiological Characteristics of Lettuce and Brassica chinensis L.[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(6): 1098-1107.
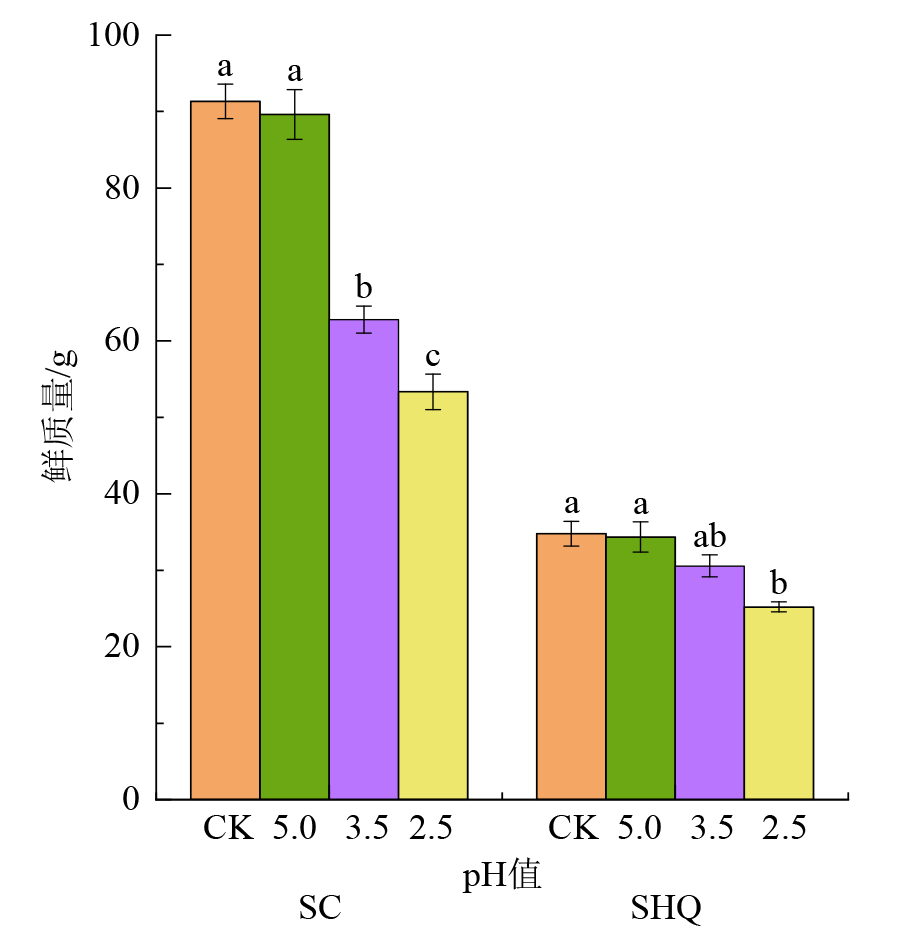
图1 不同强度酸雨处理下生菜和上海青产量 不同小写字母表示同一时间不同酸雨处理下同一种植物的差异性显著(P<0.05);SC:生菜;SHQ:上海青
Figure 1 The fresh weight of lettuce and Brassica chinensis L. under different intensity acid rain treatment
| 叶绿素荧光参数 | Fv/Fm | YII | NPQ | qL |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 蔬菜种类 | 11.225** | 654.981*** | 122.208*** | 252.035*** |
| 酸雨pH | 3.982* | 4.416** | 2.131 | 2.205 |
| 处理时长 | 6.041*** | 17.591*** | 9.062*** | 22.349*** |
| 蔬菜种类×酸雨pH | 0.391 | 2.068 | 5.061* | 1.871 |
| 蔬菜种类×处理时长 | 26.608*** | 9.74*** | 5.822** | 4.861** |
| 酸雨pH×处理时长 | 0.848 | 0.824 | 0.866 | 1.011 |
| 蔬菜种类×酸雨pH×处理时长 | 1.88 | 3.312** | 1.96 | 3.412** |
表1 不同蔬菜种类、酸雨强度以及处理时长对生菜和上海青叶绿素荧光参数的三因素方差分析
Table 1 Three-factor variance analysis of chlorophyll fluorescence parameters of lettuce and Brassica chinensis L. by different vegetable varieties, acid rain intensity and treatment duration
| 叶绿素荧光参数 | Fv/Fm | YII | NPQ | qL |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 蔬菜种类 | 11.225** | 654.981*** | 122.208*** | 252.035*** |
| 酸雨pH | 3.982* | 4.416** | 2.131 | 2.205 |
| 处理时长 | 6.041*** | 17.591*** | 9.062*** | 22.349*** |
| 蔬菜种类×酸雨pH | 0.391 | 2.068 | 5.061* | 1.871 |
| 蔬菜种类×处理时长 | 26.608*** | 9.74*** | 5.822** | 4.861** |
| 酸雨pH×处理时长 | 0.848 | 0.824 | 0.866 | 1.011 |
| 蔬菜种类×酸雨pH×处理时长 | 1.88 | 3.312** | 1.96 | 3.412** |
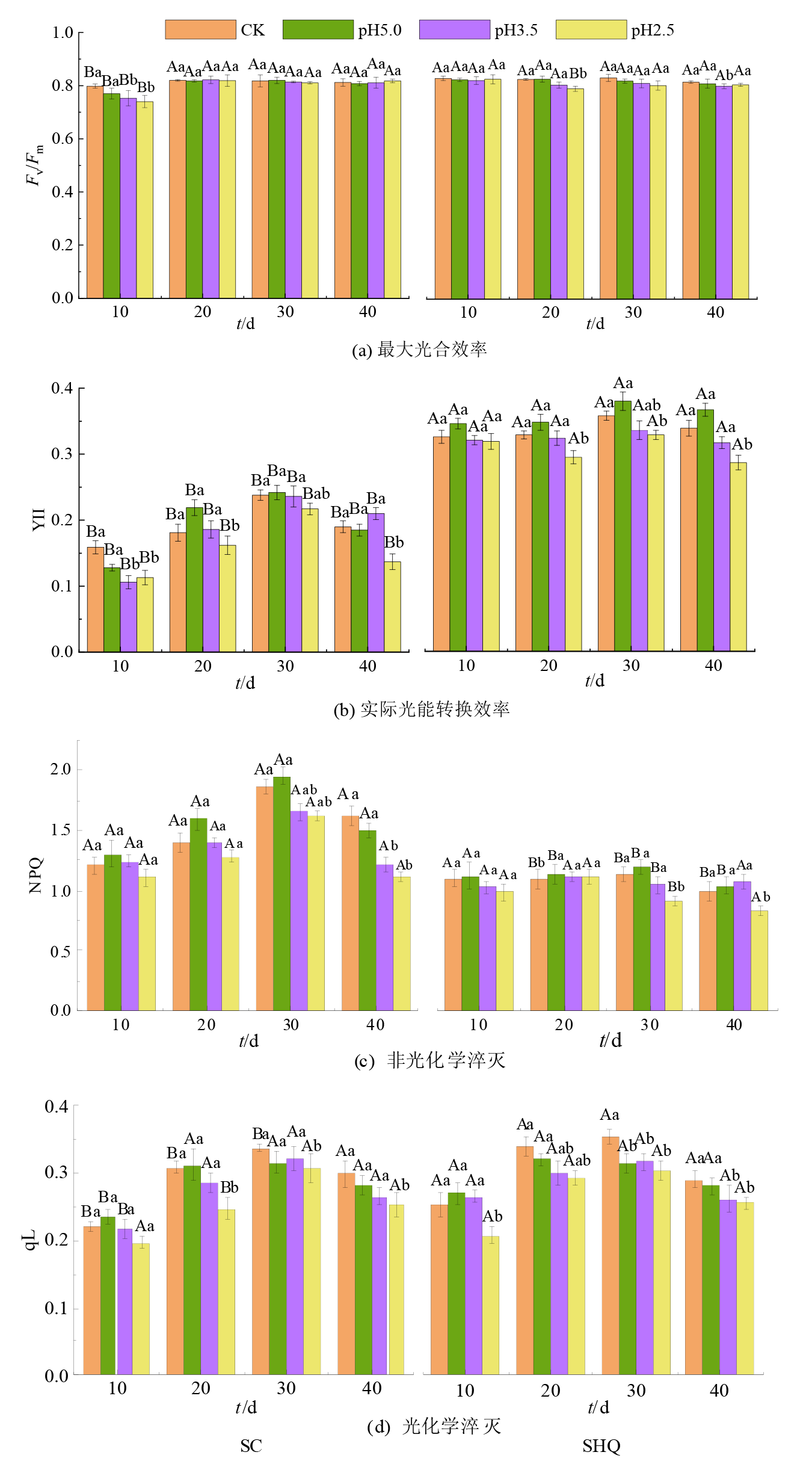
图2 不同强度酸雨处理下生菜和上海青的各个生长时期叶片的叶绿素荧光参数 不同大写字母表示同一时间相同酸雨处理下不同蔬菜的差异性显著;不同小写字母表示同一时间不同酸雨处理下同一种植物的差异性显著(P<0.05);SC:生菜;SHQ:上海青
Figure 2 Chlorophyll fluorescence parameters of lettuce and Brassica chinensis L. leaves at different periods under different intensification of acid rain
| 光合色素 | 叶绿素a | 叶绿素b | 总叶绿素 | 类胡萝卜素 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 蔬菜种类 | 1772.37*** | 2069.36*** | 2016.648*** | 8.842** |
| 酸雨pH | 25.903*** | 12.068*** | 261.08*** | 4.333* |
| 蔬菜种类×酸雨pH | 8.753** | 9.631** | 7.224** | 0.693 |
表2 不同蔬菜品种和酸雨强度对生菜和上海青光合色素的双因素方差分析
Table 2 Two-factor variance analysis of photosynthetic pigments of lettuce and Brassica chinensis L. under different vegetable varieties and acid rain intensity
| 光合色素 | 叶绿素a | 叶绿素b | 总叶绿素 | 类胡萝卜素 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 蔬菜种类 | 1772.37*** | 2069.36*** | 2016.648*** | 8.842** |
| 酸雨pH | 25.903*** | 12.068*** | 261.08*** | 4.333* |
| 蔬菜种类×酸雨pH | 8.753** | 9.631** | 7.224** | 0.693 |
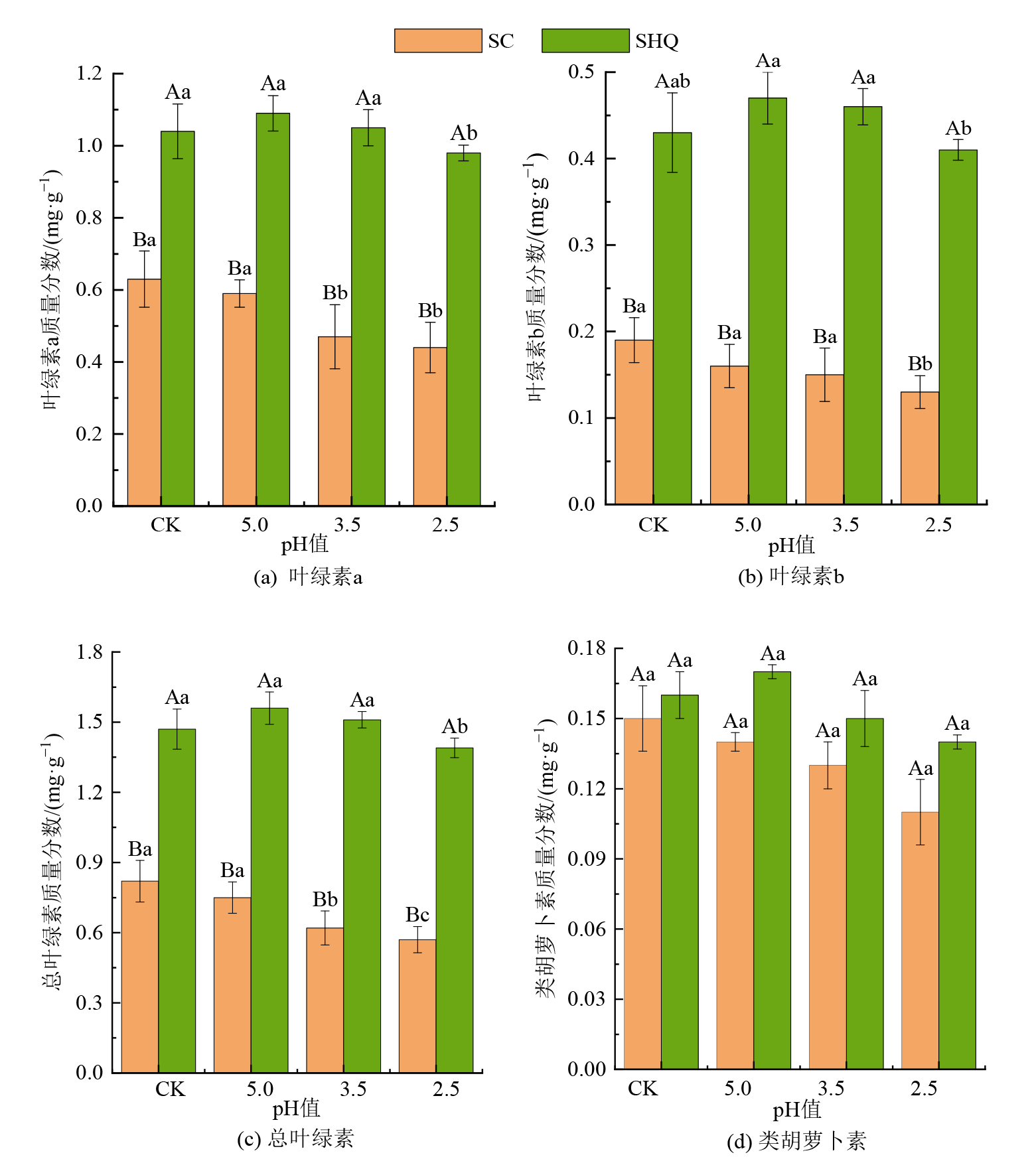
图3 不同强度酸雨处理下生菜和上海青光合色素质量分数
Figure 3 Photosynthetic pigment contents of lettuce and Brassica chinensis L. under different intensity acid rain treatment
| 营养品质 指标 | 可溶性 蛋白 | 游离脯 氨酸 | 可溶 性糖 | 原花 青素 | 还原性 抗坏血酸 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 蔬菜种类 | 79.428*** | 339.385*** | 227.218*** | 44.165*** | 117.947*** | |
| 酸雨pH | 2.667 | 71.185*** | 33.218*** | 49.680*** | 41.466*** | |
| 植物种类× 酸雨pH | 1.995 | 13.539*** | 49.302*** | 11.997*** | 17.381*** |
表3 蔬菜品种和酸雨处理对生菜和上海青营养品质的双因素方差分析
Table 3 Two-factor variance analysis of vegetable varieties and acid rain treatment on the nutritional quality of lettuce and Brassica chinensis L.
| 营养品质 指标 | 可溶性 蛋白 | 游离脯 氨酸 | 可溶 性糖 | 原花 青素 | 还原性 抗坏血酸 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 蔬菜种类 | 79.428*** | 339.385*** | 227.218*** | 44.165*** | 117.947*** | |
| 酸雨pH | 2.667 | 71.185*** | 33.218*** | 49.680*** | 41.466*** | |
| 植物种类× 酸雨pH | 1.995 | 13.539*** | 49.302*** | 11.997*** | 17.381*** |
| [1] |
AHMAD G, KHAN A A, MOHAMED H I, 2021. Changes in growth, yield, photosynthetic pigments, biochemical substances, oxidative damage, and antioxidant activities induced by treatment with different pH of artificial acid rain in pumpkin (Cucurbita Moschata)[J]. Gesunde Pflanzen, 73(4): 623-637.
DOI |
| [2] |
ANDRADE G C, CASTRO L N, DA SILVA L C, 2020. Micromorphological alterations induced by simulated acid rain on the leaf surface of Joannesia princeps Vell. (Euphorbiaceae)[J]. Ecological Indicators, 116(C): 106526.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
BISWOJIT D, MUHAMMAD I, SANGEETA M, et al., 2018. Acid rain deposition modulates photosynthesis, enzymatic and non-enzymatic antioxidant activities in tomato[J]. International Journal of Environmental Research, 12(2): 203-214.
DOI |
| [4] |
DEBNATH B, SIKDAR A, ISLAM S, et al., 2021. Physiological and molecular responses to acid rain stress in plants and the impact of melatonin, glutathione and silicon in the amendment of plant acid rain stress[J]. Molecules, 26(4): 862-862.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
HU H, HUA W, SHEN A L, et al., 2021. Photosynthetic rate and chlorophyll fluorescence of barley exposed to simulated acid rain[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 28(31): 42776-42786.
DOI |
| [6] |
HU H Q, WANG L H, LIAO C Y, et al., 2014. Combined effects of lead and acid rain on photosynthesis in soybean seedlings[J]. Biological Trace Element Research, 161(1): 136-142.
DOI PMID |
| [7] |
JAVID M, MANOJ S, KHURSHEED A W, 2018. Heavy metals in vegetables and their impact on the nutrient quality of vegetables: A review[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition, 41(13): 1744-1763.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
LI H R, XU Q Y, LI C, et al., 2022. Dual role of acid rain and pyricularia oryzae on growth, photosynthesis and chloroplast ultrastructure in rice seedlings[J]. Agronomy, 12(3): 567-567.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
NI Z Y, LU Q F, HU H Y H, et al., 2019. Estimation of chlorophyll fluorescence at different scales: A review[J]. Sensors, 19(13): 3000.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
NOREEN K, ALI N, MUHAMMAD A, et al., 2017. NPK could alleviate the adverse effects of simulated acid rain in sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.)[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition, 41(5): 584-595.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
PHAM H T, NGUYEN L N, LE T T, et al., 2022. Impact of simulated acid rain on the growth of three species Brassica integrifolia, Brassica rapa, Brassica juncea in Hanoi, Vietnam[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 29(28): 42090-42101.
DOI |
| [12] | QI Q Q, CHU M J, YU X T, et al., 2022. Anthocyanins and proanthocyanidins: Chemical structures, food sources, bioactivities, and product development[J]. Food Reviews International: 2029479. |
| [13] |
REN X Q, ZHU J Z, LIU H Y, et al., 2018. Response of antioxidative system in rice (Oryza sativa) leaves to simulated acid rain stress[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 148: 851-856.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
SUN J W, HU H Q, LI Y L, et al., 2016. Effects and mechanism of acid rain on plant chloroplast ATP synthase[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 23(18): 18296-18306.
DOI PMID |
| [15] |
SUN Z G, WANG L H, CHEN M M, et al., 2012. Interactive effects of cadmium and acid rain on photosynthetic light reaction in soybean seedlings[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 79: 62-68.
DOI PMID |
| [16] |
WANG Z Y, YANG Y C, YADAV V, et al., 2022. Drought-induced proline is mainly synthesized in leaves and transported to roots in watermelon under water deficit[J]. Horticultural Plant Journal, 8(5): 615-626.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
ZHANG Y Q, LIANG C J, 2022. Improving yield and quality of rice under acid rain stress by regulating nitrogen assimilation with exogenous Ca2+[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 30: 12085-12097.
DOI |
| [18] | 陈文胜, 出佳范, 吕再辉, 等, 2019. 模拟酸雨处理后番茄叶片叶绿素含量及叶绿素荧光参数的动态变化[J]. 植物资源与环境学报, 28(3): 108-116. |
| CHEN W S, CHU J F, LÜ Z H, et al., 2019. Dynamic changes in chlorophyll content and chlorophyll fluorescence parameters of leaf of Lycopersicon esculentum after simulated acid rain treatment[J]. Journal of Plant Resources and Environment, 28(3): 108-116. | |
| [19] | 陈雪菲, 张映雪, 黄贤燕, 等, 2020. 蕨类植物花青素和原花青素成分及含量分析[J]. 植物科学学报, 38(6): 820-830. |
| CHEN X F, ZHANG Y X, HUANG X Y, et al., 2020. Composition and content analysis of anthocyanins and proanthocyanidins in ferns[J]. Plant Science Journal, 38(6): 820-830. | |
| [20] | 董瑞霞, 李立祥, 王茜, 等, 2008. 植物中原花青素含量测定[J]. 茶业通报, 30(2): 67-69. |
| DONG R X, LI L X, WANG Q, et al., 2008. Determination of proanthocyanidin content in plants[J]. Journal of Tea Business, 30(2): 67-69. | |
| [21] | 方怡然, 薛立, 2019. 盐胁迫对植物叶绿素荧光影响的研究进展[J]. 生态科学, 38(3): 225-234. |
| FANG Y R, XUE L, 2019. Research advances in the effect of salt stress on plant chlorophyll fluorescence[J]. Ecological Science, 38(3): 225-234. | |
| [22] | 冯宗炜, 2000. 中国酸雨对陆地生态系统的影响和防治对策[J]. 中国工程科学, 2(9): 5-11, 28. |
| FENG Z W, 2000. Impacts and control strategies of acid deposition on terrestrial ecosystems in China[J]. Strategic Study of CAE, 2(9): 5-11, 28. | |
| [23] | 广东省生态环境厅, 2022. 广东省生态环境状况公报. 广东省生态环境厅公众网[EB/OL]. [2022-05-10]. http://www.gdep.gov.cn. |
| Department of ecology and environment of Guangdong province. 2022. Report on the state of Guangdong province environment[EB/OL]. [2022-05-10]. http://www.gdep.gov.cn. | |
| [24] |
李建鑫, 王文平, 胡璋健, 等, 2021. 模拟酸雨对番茄光合作用和病害发生的影响及油菜素内酯对其缓解效应[J]. 中国农业科学, 54(8): 1728-1738.
DOI |
|
LI J X, WANG W P, HU Z J, et al., 2021. Effects of simulated acid rain conditions on plant photosynthesis and disease susceptibility in tomato and its alleviation of brassinosteroid[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 54(8): 1728-1738.
DOI |
|
| [25] | 李军, 2000. 钼蓝比色法测定还原型维生素C[J]. 食品科学, 21(8):42-45. |
|
LI J, 2000. Determination of reduced vitamin C by molybdenum blue colorimetric method[J]. Food Science, 21(8): 42-45.
DOI URL |
|
| [26] | 梁骏, 麦博儒, 郑有飞, 等, 2008. 模拟酸雨对油菜 (Brassica napus L.) 生长、产量及品质的影响[J]. 生态学报, 28(1): 274-283. |
| LIANG J, MAI B R, ZHENG Y F, et al., 2008. Effects of simulated acid rain on the growth, yield and quality of rape[J]. Acta Ecological Sinica, 28(1): 274-283. | |
| [27] | 麦博儒, 郑有飞, 吴荣军, 等, 2010. 不同pH模拟酸雨对冬小麦籽粒营养品质的影响[J]. 生态学报, 30(14): 3883-3891. |
| MAI B R, ZHENG Y F, WU R J, et al., 2010. Effects of different pH simulated acid rains on nutritional quality of winter wheat grains[J]. Acta Ecological Sinica, 30(14): 3883-3891. | |
| [28] | 孟赫, 董德明, 王菊, 等, 2011. 模拟酸雨对东北地区农作物生长、生理及品质的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 41(3): 866-872. |
| MENG H, DONG D M, WANG J, et al., 2011. Effects of simulated acid rain on growth, physiology and quality of crop in northeast of China[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 41(3): 866-872. | |
| [29] | 任晓巧, 章家恩, 向慧敏, 等, 2021. 酸雨对植物地上部生理生态的影响研究进展与展望[J]. 应用与环境生物学报, 27(6): 1716-1724. |
| REN X Q, ZHANG J E, XIANG H M, et al., 2021. Research advances and prospects for effects of acid rain on aboveground physiology of plants and related alleviation countermeasures[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology, 27(6): 1716-1724. | |
| [30] | 水德聚, 王晓艳, 邵勤, 等, 2016. 模拟酸雨胁迫对油冬菜生理特性的影响[J]. 南方农业学报, 47(7): 1155-1158. |
| SHUI D J, WANG X Y, SHAO Q, et al., 2016. Effects of simulated acid rain stress on physio characteristics of Brassica chinensis L.[J]. Journal of Southern Agriculture, 47(7): 1155-1158. | |
| [31] | 苏全胜, 王爽, 孙玉强, 等, 2021. 植物原花青素生物合成及调控研究进展[J]. 中国细胞生物学学报, 43(1): 219-229. |
| SU Q S, WANG S, SUN Y Q, et al., 2021. Advances in biosynthesis and regulation of plant proanthocyanidins[J]. Chinese Journal of Cell Biology, 43(1): 219-229. | |
| [32] | 王菊, 赵秀敏, 刘禹彤, 等, 2013. 模拟酸雨对小白菜生长、生理和品质的影响[J]. 湖北农业科学, 52(16): 3791-3795. |
| WANG J, ZHAO X M, LIU Y T, et al., 2013. Effects of simulated acid rain on growth, physiology Index and quality of Brassica chinensis L.[J]. Hubei Agricultural Sciences, 52(16): 3791-3795. | |
| [33] |
王双明, 2012. 模拟酸雨胁迫对菠菜中草酸积累及营养品质的影响[J]. 核农学报, 26(4): 717-721.
DOI |
| WANG S M, 2012. Effect of simulated acid rain stress on oxalate content and nutrition quality of spinach[J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, 26(4):717-721. | |
| [34] | 吴金滢, 胡迪, 孙新, 2022. 原花青素抗衰老作用的研究进展[J]. 吉林医药学院学报, 43(6): 452-454. |
| WU J Y, HU D, SUN X, 2022. Research progress of antiaging pharmacological effects of procyanidins[J]. Journal of Jilin Medical University, 43(6): 452-454. | |
| [35] | 吴青君, 龚佑辉, 徐宝云, 2007. 西花蓟马主要寄主植物可溶性糖和蛋白质含量测定[J]. 中国蔬菜, 163(10): 20-22. |
| WU Q J, GONG Y H, XU B Y, 2007. Soluble carbohydrate and protein levels in host plants of Frankliniella occidentalis[J]. China Vegetables, 163(10): 20-22. | |
| [36] |
殷秀敏, 伊力塔, 余树全, 等, 2010. 酸雨胁迫对木荷叶片气体交换和叶绿素荧光参数的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 19(7): 1556-1562.
DOI |
| YIN X M, YI L T, YU S Q, et al., 2010. Effects of acid rain stress on gas exchange and chlorophyll fluorescence in leaves of Schima superba seedlings[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 19(7): 1556-1562. | |
| [37] | 张璐, 张伟, 陈新平, 2021. 气候变化对蔬菜品质的影响及其机制[J]. 中国生态农业学报 (中英文), 29(12): 2034-2045. |
| ZHANG L, ZHANG W, CHEN X P, 2021. Effects and mechanisms of climate change on vegetable quality[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 29(12): 2034-2045. | |
| [38] | 章家恩, 2007. 生态学常用实验研究方法与技术[M]. 化学工业出版社:74-78. |
| ZHANG J E, 2007. Common experimental research methods and techniques in ecology[M]. Chemical Industry Press:74-78. | |
| [39] | 郑有飞, 李璐, 梁骏, 2008. 模拟酸雨条件下Pb2+和Cr6+对蕹菜光合作用及品质的影响[J]. 生态学杂志, 182(9): 1580-1586. |
| ZHENG Y F, LI L, LIANG J, 2008. Impacts of Pb2+ and Cr6+ on photosynthesis and quality of Ipomoea aquatica Forsk. under simulated acid rain[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 182(9): 1580-1586. | |
| [40] |
钟嘉文, 单晓冉, 章家恩, 等, 2021. 酸雨对生菜的光合、抗氧化系统和产量的影响研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 30(3): 532-540.
DOI |
| ZHONG J W, SHAN X R, ZHANG J E, et al., 2021. Study on the effects of acid rain on the photosynthetic and antioxidant systems and yield of lettuce[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 30(3): 532-540. |
| [1] | 胡启瑞, 吉春容, 李迎春, 王雪姣, 杨明凤, 郭燕云. 膜下滴灌棉花蕾期干旱胁迫对光合特性及产量的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(6): 1045-1052. |
| [2] | 刘江, 朱丽杰, 张开, 王晓明, 王立为, 高西宁. 不同生育期干旱胁迫/复水对大豆光合特性及产量的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(2): 286-296. |
| [3] | 黄巧义, 于俊红, 黄建凤, 黄旭, 李苹, 付弘婷, 唐拴虎, 刘一锋, 徐培智. 广东省主要农作物秸秆养分资源量及替代化肥潜力[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(2): 297-306. |
| [4] | 王玄, 熊鑫, 张慧玲, 赵梦頔, 胡明慧, 褚国伟, 孟泽, 张德强. 模拟酸雨对南亚热带森林凋落物分解和土壤呼吸的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(9): 1805-1813. |
| [5] | 张开, 王立为, 高西宁, 贺明慧. 基于DNDC模型不同降水年型下氮肥管理对马铃薯田N2O减排及增产潜力影响研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(8): 1672-1682. |
| [6] | 党慧慧, 刘超, 伍翥嵘, 王圆媛, 胡正华, 李琪, 陈书涛. 不同播期粳稻稻田甲烷排放及综合效益研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(7): 1436-1446. |
| [7] | 朱勇勇, 宋秉羲, 杨王敏, 张宇鹏, 高志红, 陈晓远. 旱作条件下氮肥减施对水稻生长、产量与经济收益的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(11): 2150-2156. |
| [8] | 武岩, 靳拓, 王跃飞, 贺鹏程, 罗军, 刘宏金, 张雷, 郭晓宇, 陈瑞英. 内蒙古阴山北麓马铃薯应用PBAT/PLA全生物降解地膜可行性分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(10): 2100-2108. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
