生态环境学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (10): 2033-2041.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2021.10.010
佘延娣1,5( ), 周华坤1, 张中华1,5, 马丽1,5, 周秉荣2, 宋明华3, 孙建3, 邓艳芳4, 徐文华1, 王芳1, 姚步青1, 马真1, 黄小涛1,*(
), 周华坤1, 张中华1,5, 马丽1,5, 周秉荣2, 宋明华3, 孙建3, 邓艳芳4, 徐文华1, 王芳1, 姚步青1, 马真1, 黄小涛1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2021-03-02
出版日期:2021-10-18
发布日期:2021-12-21
通讯作者:
* 黄小涛(1983年生),男,助理研究员,主要从事遥感生态学研究。E-mail: xthuang@nwipb.cas.cn作者简介:佘延娣(1997年生),女,硕士研究生,主要从事恢复生态学研究。E-mail: sheyandi@nwipb.cas.cn
基金资助:
SHE Yandi1,5( ), ZHOU Huakun1, ZHANG Zhonghua1,5, MA Li1,5, ZHOU Bingrong2, SONG Minghua3, SUN Jian3, DENG Yanfang4, XU Wenhua1, WANG Fang1, YAO Buqing1, MA Zhen1, HUANG Xiaotao1,*(
), ZHOU Huakun1, ZHANG Zhonghua1,5, MA Li1,5, ZHOU Bingrong2, SONG Minghua3, SUN Jian3, DENG Yanfang4, XU Wenhua1, WANG Fang1, YAO Buqing1, MA Zhen1, HUANG Xiaotao1,*( )
)
Received:2021-03-02
Online:2021-10-18
Published:2021-12-21
摘要:
羌活(Notopterygium incisum)是重要的药用资源和濒危物种,明确其适宜分布情况对其可持续利用至关重要。基于三江源18个羌活分布点数据,利用最大熵模型(MaxEnt)和地理信息系统(GIS)技术预测了气候变化背景下羌活在三江源的适宜分布情况,并筛选出影响其分布的主要环境因子。结果表明:当前羌活适宜分布面积为146.43×103 km2,占三江源区域的26.67%,且主要集中在三江源区的东部和南部;影响羌活分布主要的环境因子有6个,按贡献率由大到小分别是:海拔(37.1%)、年平均气温(15.9%)、坡向(12.2%)、最湿季降水量(11.4%)、最冷季平均气温(9.6%)、气温季节性变动系数(5.4%);未来羌活在不同CO2浓度情景下的适宜分布面积由大到小为:RCP2.6(126.92×103 km2)、RCP4.5(95.32×103 km2)、RCP6.0(25.53×103 km2)、RCP8.0(22.13×103 km2),未来不同CO2浓度情景下羌活的适宜分布面积均小于当前羌活适宜分布,且未来高CO2浓度情景下的羌活适宜分布面积小于低CO2浓度情景。当前及未来不同CO2浓度情景下三江源国家公园中羌活的适宜分布面积分别为:当前(22.60×103 km2)、RCP2.6(16.64×103 km2)、RCP4.5(4.79×103 km2)、RCP6.0(0.43×103 km2)、RCP8.0(0.27×103 km2),羌活在三江源国家公园的适宜分布面积相对较小。该研究对于理解三江源区羌活野生资源生长环境具有重要意义,并有利于实现这一野生药用植物资源的科学保护与合理利用。
中图分类号:
佘延娣, 周华坤, 张中华, 马丽, 周秉荣, 宋明华, 孙建, 邓艳芳, 徐文华, 王芳, 姚步青, 马真, 黄小涛. 气候变化背景下羌活在三江源的适宜分布[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(10): 2033-2041.
SHE Yandi, ZHOU Huakun, ZHANG Zhonghua, MA Li, ZHOU Bingrong, SONG Minghua, SUN Jian, DENG Yanfang, XU Wenhua, WANG Fang, YAO Buqing, MA Zhen, HUANG Xiaotao. Suitable Distribution of Notopterygium incisum in the Three Rivers Headwater Region under Climate Change[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(10): 2033-2041.
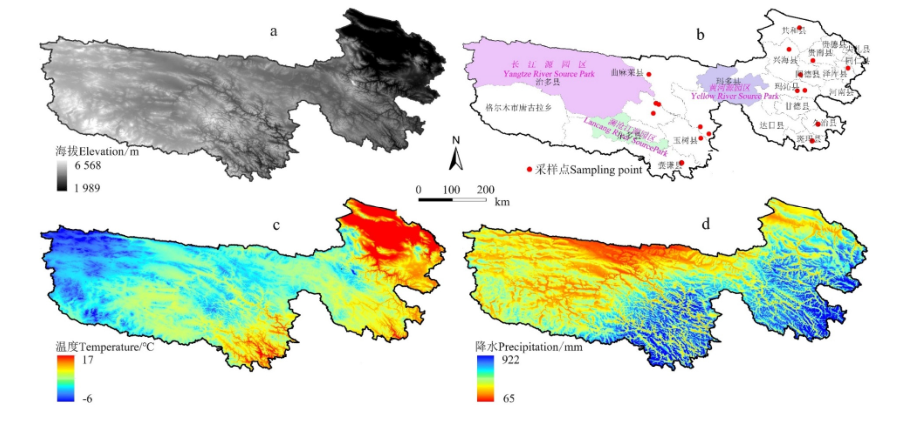
图1 三江源概况 (a)海拔;(b)行政区划;(c)生长季均温;(d)生长季降水
Fig. 1 Overview of the Three Rivers Headwater Region (a) Altitude; (b) Administrative division; (c) Growing season average temperature; (d) Growing season precipitation
| 数据简称 Code | 中文名称 Chinese name | 英文名称 English name |
|---|---|---|
| Bio1 | 年平均气温 | Annual mean air temperature |
| Bio2 | 平均气温日较差 (平均每月最高气温—平均每月最低气温) | Mean diurnal air temperature range (Mean of monthly (maximum air temperature-minimum air temperature)) |
| Bio3 | 等温性 | Isothermality |
| Bio4 | 气温季节性变动系数 | Air temperature seasonality |
| Bio5 | 最热月的最高气温 | Max air temperature of the warmest month |
| Bio6 | 最冷月的最低气温 | Min air temperature of the coldest month |
| Bio7 | 气温年较差 | Air temperature annual range |
| Bio8 | 最湿季平均气温 | Mean air temperature of the wettest quarter |
| Bio9 | 最干季平均气温 | Mean air temperature of the driest quarter |
| Bio10 | 最热季平均气温 | Mean air temperature of the warmest quarter |
| Bio11 | 最冷季平均气温 | Mean air temperature of the coldest quarter |
| Bio12 | 年降水量 | Annual precipitation |
| Bio13 | 最湿月降水量 | Precipitation of the wettest month |
| Bio14 | 最干月降水量 | Precipitation of the driest month |
| Bio15 | 降水量的季节性变化(变异系数) | Precipitation seasonality (coefficient of variation) |
| Bio16 | 最干季降水量 | Precipitation of the driest quarter |
| Bio17 | 最湿季降水量 | Precipitation of the wettest quarter |
| Bio18 | 最热季降水量 | Precipitation of the warmest quarter |
| Bio19 | 最冷季降水量 | Precipitation of the coldest quarter |
| ATG | 生长期平均气温* | Average air temperature of growth period * |
| PG | 生长期降水量* | Precipitation of growth period |
| DEM | 海拔 | Digital Elevation Model |
| slope | 坡度 | slope |
| aspect | 坡向 | aspect |
表1 羌活潜在适生区分布环境因子
Table 1 Distribution of environmental factors in potential suitable areas for Notopterygium incisum
| 数据简称 Code | 中文名称 Chinese name | 英文名称 English name |
|---|---|---|
| Bio1 | 年平均气温 | Annual mean air temperature |
| Bio2 | 平均气温日较差 (平均每月最高气温—平均每月最低气温) | Mean diurnal air temperature range (Mean of monthly (maximum air temperature-minimum air temperature)) |
| Bio3 | 等温性 | Isothermality |
| Bio4 | 气温季节性变动系数 | Air temperature seasonality |
| Bio5 | 最热月的最高气温 | Max air temperature of the warmest month |
| Bio6 | 最冷月的最低气温 | Min air temperature of the coldest month |
| Bio7 | 气温年较差 | Air temperature annual range |
| Bio8 | 最湿季平均气温 | Mean air temperature of the wettest quarter |
| Bio9 | 最干季平均气温 | Mean air temperature of the driest quarter |
| Bio10 | 最热季平均气温 | Mean air temperature of the warmest quarter |
| Bio11 | 最冷季平均气温 | Mean air temperature of the coldest quarter |
| Bio12 | 年降水量 | Annual precipitation |
| Bio13 | 最湿月降水量 | Precipitation of the wettest month |
| Bio14 | 最干月降水量 | Precipitation of the driest month |
| Bio15 | 降水量的季节性变化(变异系数) | Precipitation seasonality (coefficient of variation) |
| Bio16 | 最干季降水量 | Precipitation of the driest quarter |
| Bio17 | 最湿季降水量 | Precipitation of the wettest quarter |
| Bio18 | 最热季降水量 | Precipitation of the warmest quarter |
| Bio19 | 最冷季降水量 | Precipitation of the coldest quarter |
| ATG | 生长期平均气温* | Average air temperature of growth period * |
| PG | 生长期降水量* | Precipitation of growth period |
| DEM | 海拔 | Digital Elevation Model |
| slope | 坡度 | slope |
| aspect | 坡向 | aspect |
| 简称 Code | 环境变量 Variables | 贡献率 Percent contribution/% |
|---|---|---|
| dem | 海拔 Digital Elevation Model | 37.1 |
| bio_01 | 年平均气温 Annual mean air temerature | 15.9 |
| aspect | 坡向 Aspect | 12.2 |
| bio_17 | 最湿季降水量 Precipitation of the wettest quarter | 11.4 |
| bio_11 | 最冷季平均气温 Mean air temperature of the coldest quarter | 9.6 |
| bio_04 | 气温季节性变动系数 Air temperature seasonality | 5.4 |
| bio_03 | 等温性 Isothermality | 5 |
| bio_07 | 气温年较差 Air temperature annual range | 2.4 |
| bio_19 | 最冷季降水量 Precipitation of the coldest quarter | 0.7 |
| bio_14 | 最干月降水量 Precipitation of the driest month | 0.1 |
| bio_02 | 平均气温日较差 Mean diurnal air temperature range | 0.1 |
| bio_06 | 最冷月的最低气温 Min air temperature of the coldest month | 0.1 |
表2 影响羌活分布的主要环境要素及其贡献率
Table 2 Main environmental factors affecting the distribution of Notopterygium incisum and their contribution rate
| 简称 Code | 环境变量 Variables | 贡献率 Percent contribution/% |
|---|---|---|
| dem | 海拔 Digital Elevation Model | 37.1 |
| bio_01 | 年平均气温 Annual mean air temerature | 15.9 |
| aspect | 坡向 Aspect | 12.2 |
| bio_17 | 最湿季降水量 Precipitation of the wettest quarter | 11.4 |
| bio_11 | 最冷季平均气温 Mean air temperature of the coldest quarter | 9.6 |
| bio_04 | 气温季节性变动系数 Air temperature seasonality | 5.4 |
| bio_03 | 等温性 Isothermality | 5 |
| bio_07 | 气温年较差 Air temperature annual range | 2.4 |
| bio_19 | 最冷季降水量 Precipitation of the coldest quarter | 0.7 |
| bio_14 | 最干月降水量 Precipitation of the driest month | 0.1 |
| bio_02 | 平均气温日较差 Mean diurnal air temperature range | 0.1 |
| bio_06 | 最冷月的最低气温 Min air temperature of the coldest month | 0.1 |
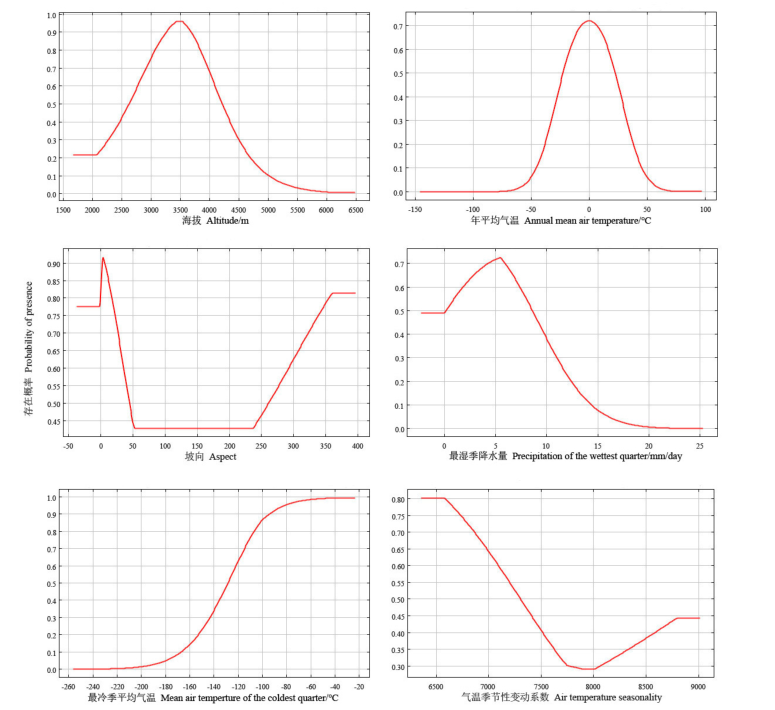
图4 影响羌活生存的主要环境因子响应曲线 年平均气温响应曲线的横坐标是10×实际摄氏度(℃);最冷季平均气温响应曲线的横坐标是10×实际摄氏度(℃)
Fig. 4 Response curve of main environmental factors affecting the survival of Notopterygium incisum The abscissa of the annual average temperature response curve is 10 × actual degrees Celsius (℃); the abscissa of the average temperature response curve in the coldest season is 10 × actual degrees Celsius (℃)
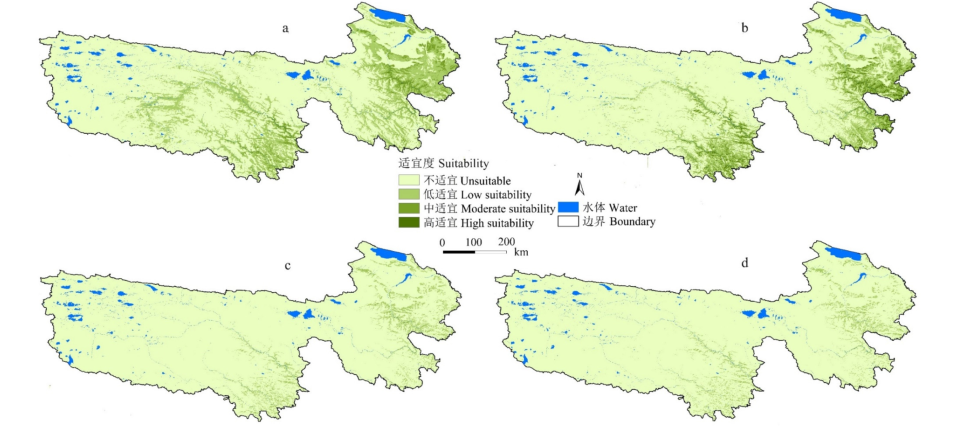
图5 未来不同情景下羌活在三江源的适宜分布 a为三江源区羌活在RCP2.6情景下的适生区分布;b为三江源区羌活在RCP4.5情景下的适生区分布;c为三江源区羌活在RCP6.0情景下的适生区分布;d为三江源区羌活在RCP8.0情景下的适生区分布
Fig. 5 Appropriate distribution of Notopterygium incisum under different scenarios in the Three Rivers Headwater Region in the future a is the distribution of suitable areas for Notopterygium incisum in the RCP2.6 scenario in the three rivers region; b is the distribution of suitable areas for Notopterygium incisum in the RCP4.5 scenario in the three rivers region; c is the distribution of suitable areas for Notopterygium incisum in the RCP6.0 scenario in the three rivers region; d is the distribution of suitable areas for Notopterygium incisum in the RCP8.0 scenario in the three rivers region
| [1] | IPCC, 2013. Climate change 2013: The physical science basis [M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. |
| [2] |
PHILLIPS S J, ANDERSON R P, SCHAPIRE R E, 2006. Maximum entropy modeling of species geographic distributions[J]. Ecological Modelling, 190(3):231-259.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
PHILLIPS S J, MIROSLAV D, 2008. Modeling of species distributions with Maxent: New extensions and a comprehensive evaluation[J]. Ecography, 31(2):161-175.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
ZHAO Z F, GUO Y L, WEI H Y, et al., 2020. Potential distribution of Notopterygium incisum Ting ex H. T. chang and its predicted responses to climate change based on a comprehensive habitat suitability model[J]. Ecology and Evolution, 10(6):3004-3016.
DOI URL |
| [5] | 曹策, 蒋昕, 2017. 植物分布对气候变化的响应[J]. 绿色科技 (16):111-113. |
| CAO C, JIANG X, 2017. Response of plant distribution to climate change[J]. Journal of Green Science and Technology (16):111-113. | |
| [6] | 陈陆丹, 胡菀, 李单琦, 等, 2019. 珍稀濒危植物野生莲的适生分布区预测[J]. 植物科学学报, 37(6):731-740. |
| CHEN L D, HU W, LI D Q, et al., 2019. Prediction of suitable distribution areas of the endangered plant wild Nelumbo nucifera Gaertn. in China[J]. Plant Science Journal, 37(6):731-740. | |
| [7] | 陈小玮, 2020. 三江源国家公园: 美丽中国建设的生态范本[J]. 新西部 (Z4):13-20. |
| CHEN X W, 2020. Sanjiangyuan National Park: an ecological model for building a beautiful China[J]. New West (Z4):13-20. | |
| [8] | 陈衍如, 谢慧敏, 罗火林, 等, 2019. 气候变化对寒兰分布的影响及其分布格局模拟[J]. 应用生态学报, 30(10):3419-3425. |
| CHEN Y R, XIE H M, LUO H L, et al., 2019. Impacts of climate change on the distribution of Cymbidium kanran and the simulation of distribution pattern[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 30(10):3419-3425. | |
| [9] | 郭斌, 王珊, 陈超, 等, 2019. 气候变化背景下川西北高原多年生垂穗披碱草种植适生区分布预测[J]. 草地学报, 27(6):1596-1606. |
| GUO B, WANG S, CHEN C, et al., 2019. Distribution prediction of suitable growth area of Perennial Elymus nutans in the Northwest Plateau of Sichuan Province under climate change[J]. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 27(6):1596-1606. | |
| [10] | 景鹏飞, 武坤毅, 龚晔, 等, 2015. 药用植物细辛在中国的潜在适生区分布[J]. 植物分类与资源学报, 37(3):349-356. |
| JING P F, WU K Y, GONG Y, et al., 2019. Prediction of potential geological distribution of Asarum in China by Maxent Model[J]. Plant Diversity and Resources, 37(3):349-356. | |
| [11] | 李国庆, 刘长成, 刘玉国, 等, 2013. 物种分布模型理论研究进展[J]. 生态学报, 33(16):4827-4835. |
| LI G Q, LIU C C, LIU Y G, et al., 2013. Advances in theoretical issues of species distribution models[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 33(16):4827-4835. | |
| [12] |
李茂华, 都金康, 李皖彤, 等, 2020. 1982—2015年全球植被变化及其与温度和降水的关系[J]. 地理科学, 40(5):823-832.
DOI |
| LI M H, DU J K, LI W T, et al., 2020. Global vegetation change and its relationship with temperature and precipitation from 1982 to 2015[J]. Geoscience, 40(5):823-832. | |
| [13] | 李响, 张成福, 贺帅, 等, 2020. MaxEnt模型综合应用研究进展分析[J]. 绿色科技 (14):14-17. |
| LI X, ZHANG C F, HE S, et al., 2020. Research progress of comprehensive application of MaxEnt model[J]. Green Technology (14):14-17. | |
| [14] | 厉静文, 郭浩, 王雨生, 等, 2019. 基于MaxEnt模型的胡杨潜在适生区预测[J]. 林业科学, 55(12):133-139. |
| LI J W, GUO H, WANG Y S, et al., 2019. Identification of potential distribution area for Populus euphratica by the MaxEnt ecologic niche model[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 55(12):133-139. | |
| [15] | 梁红艳, 姜效雷, 孔玉华, 等, 2018. 气候变暖背景下春兰和蕙兰的适生区分布预测[J]. 生态学报, 38(23):8345-8353. |
| LIANG H Y, JIANG X L, KONG Y H, et al., 2018. Prediction of the potent distribution of Cymbidium goeringii and C. faberi under the background of global warming[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 38(23):8345-8353. | |
| [16] | 林丽, 晋玲, 王振恒, 等, 2017. 气候变化背景下藏药黑果枸杞的潜在适生区分布预测[J]. 中国中药杂志, 42(14):2659-2669. |
| LIN L, JIN L, WANG Z H, et al., 2017. Prediction of the potential distribution of Tibetan medicinalLycium ruthenicum in context of climate change[J]. Chinese Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 42(14):2659-2669. | |
| [17] |
刘晓彤, 袁泉, 倪健, 2019. 中国植物分布模拟研究现状[J]. 植物生态学报, 43(4):273-283.
DOI |
| LIU X T, YUAN Q, NI J, 2019. Research advances in modelling plant species distribution in China[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 43(4):273-283. | |
| [18] | 吕佳佳, 2009. 气候变化对我国主要珍稀濒危物种分布影响及其适应对策研究[D]. 北京: 中国环境科学研究院. |
| LV J J, 2009. Effects of climate change on distribution of rare and endangered species in China and its adaptation countermeasures[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Environmental Sciences. | |
| [19] | 马士彬, 安裕伦, 杨广斌, 等, 2019. 不同地形梯度上的植被变化趋势及原因分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 28(5):857-864. |
| MA S B, AN Y L, YANG G B, et al., 2019. The analysis of distribution characteristics and reasons of NDVI change trends along the terrain gradient[J]. Journal of Ecological Environment, 28(5):857-864. | |
| [20] | 牛书丽, 万师强, 马克平, 2009. 陆地生态系统及生物多样性对气候变化的适应与减缓[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 24(4):421-427. |
| NIU S L, WAN S Q, MA K P, 2009. Acclimation and mitigation of terrestrial ecosystem and biodiversity to climate change[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, 24(4):421-427. | |
| [21] | 欧阳林男, 陈少雄, 张维耀, 等, 2019. 细叶桉在中国的潜在适生区预测[J]. 桉树科技, 36(3):1-7. |
| OUYANG L N, CHEN S X, ZHANG W Y, et al., 2019. Potential Suitable Area of Eucalyptus tereticornis in China[J]. Eucalypt Science & Technology, 36(3):1-7. | |
| [22] | 秦大河, 2014. 三江源区生态保护与可持续发展[M]. 北京: 科学出版社. |
| QIN D H, 2014. Ecological protection and sustainable development in the headwaters of the Three Rivers [M]. Beijing: Science Press. | |
| [23] | 青海省人民政府, 2017. 青海省人民政府关于公布青海省第二批重点保护野生植物名录的通知[J]. 青海草业, 26(1):63-65. |
| Qinghai Provincial Peoples Government, 2017. Notice of Qinghai Provincial Peoples Government on publishing the second batch of list of key protected wild plants in Qinghai Province[J]. Qinghai Prataculture, 26(1):63-65. | |
| [24] | 尚雪, 董丽君, 文路军, 等, 2015. 基于遥感与GIS技术的四川省羌活资源适宜性分布研究[J]. 中国中药杂志, 40(13):2553-2558. |
| SHANG X, DONG L J, WEN L J, et al., 2018. Study on the suitability distribution of Notopterygium incisum resources in Sichuan Province based on Remote Sensing and GIS technology[J]. Chinese Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 40(13):2553-2558. | |
| [25] | 尚忠慧, 2016. 基于MaxEnt的物种空间分布预测不确定性分析[D]. 西安: 陕西师范大学. |
| SHANG Z H, 2016. Uncertainty analysis of species spatial distribution prediction based on MaxEnt [D]. Xi’an: Shaanxi Normal University. | |
| [26] | 孙洪兵, 孙辉, 蒋舜媛, 等, 2015. 基于3S技术的羌活区划研究I.基于MaxEnt和ArcGIS的羌活生长适宜性分析及评价[J]. 中国中药杂志, 40(5):853-862. |
| SUN H B, SUN H, JIANG S Y, et al., 2015. Study on division of Notopterygium incisum based on 3S Technology I. growth suitability analysis and evaluation of Notopterygium incisum based on Maxent and ArcGIS[J]. Chinese Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 40(5):853-862. | |
| [27] | 孙辉, 蒋舜媛, 陈士林, 等, 2009. 高寒山区濒危药用植物羌活产地适宜性及生产区划分析[J]. 中国中药杂志, 34(5):535-538. |
| SUN H, JIANG S Y, CHEN S L, et al., 2009. Origin suitability and production zoning of Notopterygium incisum, an endangered medicinal plant in alpine mountainous areas[J]. Chinese Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 34(5):535-538. | |
| [28] | 孙辉, 蒋舜媛, 周毅, 等, 2004. 药用植物羌活现状及其民族植物学调查[J]. 世界科技研究与发展, 26(6):42-47. |
| SUN H, JIANG S Y, ZHOU Y, et al., 2004. Status and ethnobotanical investigation of medicinal plant Notopterygium[J]. World Science and Technology Research and Development, 26(6):42-47. | |
| [29] | 汪松, 解焱, 2004. 中国物种红色名录[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社. |
| WANG S, XIE Y, 2004. Red List of Species in China [M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press. | |
| [30] | 王明宁, 马金祥, 胡琳, 等, 2006. 三江源区植物多样性与保护[J]. 青海草业, 15(2):24-27. |
| WANG M N, MA J X, HU L, et al., 2006. Plant diversity and protection in the headwaters of the Three Rivers[J]. Qinghai Prataculture, 15(2):24-27. | |
| [31] | 王瑞, 万方浩, 2010. 外来入侵植物意大利苍耳在我国适生区预测[J]. 草业学报, 19(6):222-230. |
| WANG R, WAN F H, 2010. Prediction of the potential survival area of Xanthium italicum in China[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 19(6):222-230. | |
| [32] | 王幼平, 溥发鼎, 王萍莉, 等, 1996. 中国特有属——羌活属的系统分类研究[J]. 云南植物研究, 18(4):64-70, 129. |
| WANG Y P, PU F D, WANG P L, et al., 1996. A systematic taxonomic study on the genus Notopterygium endemic to China[J]. Yunnan Plant Research, 18(4):64-70, 129. | |
| [33] | 吴建国, 吕佳佳, 艾丽, 2009. 气候变化对生物多样性的影响: 脆弱性和适应[J]. 生态环境学报, 18(2):693-703. |
| WU J G, LV J J, AI L, 2009. The impacts of climate change on the biodiversity: Vulnerability and adaptation[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 18(2):693-703. | |
| [34] | 武自念, 侯向阳, 任卫波, 等, 2018. 气候变化背景下我国扁蓿豆潜在适生区预测[J]. 草地学报, 26(4):898-906. |
| WU Z N, HOU X Y, REN W B, et al., 2018. Prediction of the potential distribution of Medicago ruthenicain China under climate change[J]. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 26(4):898-906. | |
| [35] | 徐佳, 2019. 气候变化对我国植被影响的观测证据集成分析[D]. 杭州: 浙江师范大学. |
| XU J, 2019. Integrated analysis of observational evidence on the impact of climate change on vegetation in China [D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang Normal University. | |
| [36] | 赵琪, 2015. 气候变化威胁生物多样性[N]. 中国社会科学报, 2015-04-01(A03). |
| ZHAO Q, 2015. Climate change threatens biodiversity [N]. China Social Science Journal, 2015-04-01(A03). | |
| [37] | 赵泽芳, 2018. 气候变化下物种分布模型建构与模型比较[D]. 西安: 陕西师范大学. |
| ZHAO Z F, 2018. Construction and comparison of species distribution models under climate change[D]. Xi’an: Shaanxi Normal University. | |
| [38] |
周贵尧, 周灵燕, 邵钧炯, 等, 2020. 极端干旱对陆地生态系统的影响:进展与展望[J]. 植物生态学报, 44(5):515-525.
DOI |
| ZHOU G Y, ZHOU L Y, SHAO J J, et al., 2020. Effects of extreme drought on terrestrial ecosystems: Review and prospects[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 44(5):515-525. | |
| [39] | 张路, 2015. MAXENT最大熵模型在预测物种潜在分布范围方面的应用[J]. 生物学通报, 50(11):9-12. |
| ZHANG L, 2015. Application of Maxent maximum entropy model in predicting potential range of species distribution[J]. Biology Bulletin, 50(11):9-12. |
| [1] | 王雪梅, 杨雪峰, 赵枫, 安柏耸, 黄晓宇. 基于机器学习算法的干旱区绿洲地上生物量估算[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(6): 1007-1015. |
| [2] | 陈科屹, 林田苗, 王建军, 何友均, 张立文. 天保工程20年对黑龙江大兴安岭国有林区森林碳库的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(6): 1016-1025. |
| [3] | 张兴旺, 谢艳萍, 吴晓敏, 李垚, 肖书平. 福建省明溪县极小种群野生植物喜树种群结构与动态特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(6): 1037-1044. |
| [4] | 杜彩艳, 杨鹏, 蜂述先, 毛妍婷, 陶琼, 此主拉姆, 彭慧娉, 和建美, 李卫林. 不同生态区维西糯山药品质与生态因子相关性研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(6): 1053-1061. |
| [5] | 翁升恒, 张玉琴, 姜冬昕, 潘卫华, 李丽纯, 张方敏. 福建省森林植被NEP时空变化及影响因子分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 845-856. |
| [6] | 巫晨煜, 许帆帆, 魏士博, 樊晶晶, 刘观鹏, 王坤. 渭河流域地表植被覆盖对气候变化的响应研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 835-844. |
| [7] | 郝蕾, 翟涌光, 戚文超, 兰穹穹. 2001-2020年内蒙古植被碳源/碳汇时空动态及对气候因子的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 825-834. |
| [8] | 李阳, 侯志勇, 陈薇, 于晓英, 谢永宏, 黄鑫, 谭佩阳, 李继承, 黎尚林, 杨辉. 大围山高山湿地植物多样性与区系组成研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 643-650. |
| [9] | 胡芳, 刘聚涛, 温春云, 韩柳, 文慧. 抚河流域浮游植物群落结构特征及其水生态状况评价[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 744-755. |
| [10] | 李善家, 王兴敏, 刘海锋, 孙梦格, 雷雨昕. 河西走廊荒漠植物多样性及其对环境因子的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 429-438. |
| [11] | 李晖, 李必龙, 葛黎黎, 韩琛惠, 杨倩, 张岳军. 2000-2021年汾河流域植被时空演变特征及地形效应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 439-449. |
| [12] | 徐晨, 裴顺祥, 吴莎, 郭慧, 马淑敏, 吴迪, 章尧想, 法蕾. 北京九龙山不同林型林间大气主要BVOCs组成研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(2): 245-255. |
| [13] | 张鐥文, 杨冉, 侯文星, 王丽丽, 刘爽, 宋汉扬, 赵文吉, 李令军. 生态补水前后永定河两岸植被覆盖度变化及驱动力分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(2): 264-273. |
| [14] | 宋志斌, 周佳诚, 谭路, 唐涛. 高原河流着生藻类群落沿海拔梯度的变化特征--以西藏黑曲、雪曲为例[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(2): 274-282. |
| [15] | 贾志峰, 刘鹏程, 刘宇, 吴博博, 陈丹姿, 张向飞. 气候变化和人类活动对松辽流域植被覆盖的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 1-10. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
