生态环境学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (5): 907-919.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2021.05.003
周笛轩1,2,3( ), 林永标1,3, 汪雁佳1,2,3, 刘占锋1,3, 周丽霞1,3,*(
), 林永标1,3, 汪雁佳1,2,3, 刘占锋1,3, 周丽霞1,3,*( )
)
收稿日期:2020-10-03
出版日期:2021-05-18
发布日期:2021-08-06
通讯作者:
* E-mail:zhoulx@scbg.ac.cn作者简介:周笛轩(1995年生),女,硕士研究生,研究方向为恢复生态学研究。E-mail:xx512zdx@163.com
基金资助:
ZHOU Dixuan1,2,3( ), LIN Yongbiao1,3, WANG Yanjia1,2,3, LIU Zhanfeng1,3, ZHOU Lixia1,3,*(
), LIN Yongbiao1,3, WANG Yanjia1,2,3, LIU Zhanfeng1,3, ZHOU Lixia1,3,*( )
)
Received:2020-10-03
Online:2021-05-18
Published:2021-08-06
摘要:
中国南亚热带地区人口稠密,经济发展迅速,环境破坏严重,区域生态系统退化加剧。种植人工林被认为是减少水土流失、实现植被快速恢复的有效措施之一。目前对生态恢复过程中的人工林土壤养分含量、蓄水量、土壤酶活性等已开展了较多研究,但基于实测数据对不同人工林生态系统服务功能进行评估的研究较为少见。以广东鹤山10树种混交林(10 species mixed plantation,10NS)、16树种混交林(16 species mixed plantation,16NS)2种人工混交林,尾叶桉纯林(Eucalypyus urophylla monoculture,EU)、红锥纯林(Castanopsis hystrix monoculture,CM)、厚荚相思纯林(Acacia crassicaipa monoculture,AC)3种人工纯林和自然恢复的灌草坡(Shrub and herb land,SH)为研究对象,对其涵养水源、保育土壤、积累营养物质、固碳释氧、生物多样性保护等主要生态系统服务功能进行了评估,为南亚热带地区人工林合理种植和管理提供科学依据。结果表明,13林龄时,土壤保育能力为10树种混交林最强,红锥纯林最弱,尾叶桉纯林、厚荚相思纯林和灌草坡之间无显著差异;植被固碳释氧能力为10树种混交林、16树种混交林和尾叶桉纯林较高且无显著差异,红锥纯林最弱;涵养水源能力为灌草坡最强,其次为10树种混交林,尾叶桉纯林最差。研究表明,人工林改造或退化生态系统恢复时要注意结合不同人工林的生态系统服务功能进行科学种植:尾叶桉纯林土壤固碳作用和积累营养物质能力较强,宜作为用材林和碳汇林种植;厚荚相思纯林生物量较高且具有固氮作用,但抗风能力较弱,不适宜于沿海或台风多发地带种植;红锥纯林在保肥和水源涵养方面的生态服务功能相对较弱,但经济价值较高,适宜以大径材近自然林经营;10树种混交林的土壤养分含量最高且地表径流最小,林分调节水量和保育土壤功能最强,最适于生态恢复,可用作水土保持林、水源涵养林等,也可用于特种用途中的风景林建设。
中图分类号:
周笛轩, 林永标, 汪雁佳, 刘占锋, 周丽霞. 南亚热带不同人工林生态系统服务功能评估[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(5): 907-919.
ZHOU Dixuan, LIN Yongbiao, WANG Yanjia, LIU Zhanfeng, ZHOU Lixia. Assessment of Main Ecosystem Services in Subtropical Plantations[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(5): 907-919.
| 样地* Sample plot | 植被种类 Tree species | 平均高度 Mean height/ m | 平均胸径 Mean DBH/ cm | 平均盖度 Mean coverage/m2 | 主要林下植被 Main undergrowth vegetation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10树种混交林 10 species mixed plantation | 变叶榕 (Ficus variolosa)、潺槁木姜子 (Litsea glutinosa)、枫香 (Liquidambar formosana)、荷木 (Schima superba)、红锥 (Castanopsis hystrix)、华润楠 (Machilus chinensis)、灰木莲 (Manglietia glauca)、火力楠 (Michelia macclurei)、黧蒴 (Castanopsis fissa)、山苍子 (Litsea cubeba)、山矾 (Symplocos sumuntia)、深山含笑 (Michelia maudiae)、尾叶桉 (Eucalyptus urophylla)、阴香 (Cinnamomum burmannii) (14种) | 5.95±0.10 | 6.40±0.10 | 9.08±0.33 | 野牡丹 (Melastoma candidum)、桃金娘 (Rhodomyrtus tomentosa)、黄栀子 (Gardenia jasminoides)、鬼灯笼 (Clerodendrum fortunatum)、芒萁 (Dicranopteris pedata)、乌毛蕨 (Blechnum orientale) 等 |
| 16树种混交林 16 species mixed plantation | 潺槁木姜子 (Litsea glutinosa)、日本杜英 (Elaeocarpus japonicus)、山竹子 (Garcinia mangostana)、枫香 (Liquidambar formosana)、海南蒲桃 (Syzygium levinei)、红锥 (Castanopsis hystrix)、华润楠 (Machilus chinensis)、灰木莲 (Manglietia glauca)、火力楠 (Michelia macclurei)、假苹婆 (Sterculia lanceolata)、黎蒴 (Castanopsis fissa)、岭南山竹子 (Garcinia oblongifolia)、山苍子 (Litsea cubeba)、深山含笑 (Michelia maudiae)、尾叶桉(Eucalyptus urophylla)、阴香 (Cinnamomum burmannii) (16种) | 6.77±0.15 | 5.91±0.11 | 6.76±0.35 | 野牡丹 (Melastoma candidum)、桃金娘 (Rhodomyrtus tomentosa)、芒草 (Miscanthus sinensis) 等 |
| 尾叶桉纯林 Eucalypyus urophylla monoculture | 尾叶桉 (Eucalyptus urophylla) | 10.64±0.17 | 13.64±0.33 | 7.74±0.44 | 桃金娘 (Rhodomyrtus tomentosa)、梅叶冬青 (Ilex asprella)、鬼灯笼 (Clerodendrum fortunatum)、芒萁 (Dicranopteris pedata)等 |
| 红锥纯林 Castanopsis hystrix monoculture | 红锥 (Castanopsis hystrix) | 6.89±0.13 | 5.83±0.09 | 8.49±0.39 | 桃金娘 (Rhodomyrtus tomentosa)、野牡丹 (Melastoma candidum)、鬼灯笼 (Clerodendrum fortunatum)、芒萁 (Dicranopteris pedata)、乌毛蕨 (Blechnum orientale)等 |
| 厚荚相思纯林** Acacia crassicaipa monoculture | 厚荚相思 (Acacia crassicarpa) | 14.56±1.50 | 11.10±0.70 | 6.02±0.81 | ‒ |
| 灌草坡 Shrub and herb land | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ | 芒萁 (Dicranopteris pedata) |
表1 不同人工林的基本情况
Table 1 The information of different forest types
| 样地* Sample plot | 植被种类 Tree species | 平均高度 Mean height/ m | 平均胸径 Mean DBH/ cm | 平均盖度 Mean coverage/m2 | 主要林下植被 Main undergrowth vegetation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10树种混交林 10 species mixed plantation | 变叶榕 (Ficus variolosa)、潺槁木姜子 (Litsea glutinosa)、枫香 (Liquidambar formosana)、荷木 (Schima superba)、红锥 (Castanopsis hystrix)、华润楠 (Machilus chinensis)、灰木莲 (Manglietia glauca)、火力楠 (Michelia macclurei)、黧蒴 (Castanopsis fissa)、山苍子 (Litsea cubeba)、山矾 (Symplocos sumuntia)、深山含笑 (Michelia maudiae)、尾叶桉 (Eucalyptus urophylla)、阴香 (Cinnamomum burmannii) (14种) | 5.95±0.10 | 6.40±0.10 | 9.08±0.33 | 野牡丹 (Melastoma candidum)、桃金娘 (Rhodomyrtus tomentosa)、黄栀子 (Gardenia jasminoides)、鬼灯笼 (Clerodendrum fortunatum)、芒萁 (Dicranopteris pedata)、乌毛蕨 (Blechnum orientale) 等 |
| 16树种混交林 16 species mixed plantation | 潺槁木姜子 (Litsea glutinosa)、日本杜英 (Elaeocarpus japonicus)、山竹子 (Garcinia mangostana)、枫香 (Liquidambar formosana)、海南蒲桃 (Syzygium levinei)、红锥 (Castanopsis hystrix)、华润楠 (Machilus chinensis)、灰木莲 (Manglietia glauca)、火力楠 (Michelia macclurei)、假苹婆 (Sterculia lanceolata)、黎蒴 (Castanopsis fissa)、岭南山竹子 (Garcinia oblongifolia)、山苍子 (Litsea cubeba)、深山含笑 (Michelia maudiae)、尾叶桉(Eucalyptus urophylla)、阴香 (Cinnamomum burmannii) (16种) | 6.77±0.15 | 5.91±0.11 | 6.76±0.35 | 野牡丹 (Melastoma candidum)、桃金娘 (Rhodomyrtus tomentosa)、芒草 (Miscanthus sinensis) 等 |
| 尾叶桉纯林 Eucalypyus urophylla monoculture | 尾叶桉 (Eucalyptus urophylla) | 10.64±0.17 | 13.64±0.33 | 7.74±0.44 | 桃金娘 (Rhodomyrtus tomentosa)、梅叶冬青 (Ilex asprella)、鬼灯笼 (Clerodendrum fortunatum)、芒萁 (Dicranopteris pedata)等 |
| 红锥纯林 Castanopsis hystrix monoculture | 红锥 (Castanopsis hystrix) | 6.89±0.13 | 5.83±0.09 | 8.49±0.39 | 桃金娘 (Rhodomyrtus tomentosa)、野牡丹 (Melastoma candidum)、鬼灯笼 (Clerodendrum fortunatum)、芒萁 (Dicranopteris pedata)、乌毛蕨 (Blechnum orientale)等 |
| 厚荚相思纯林** Acacia crassicaipa monoculture | 厚荚相思 (Acacia crassicarpa) | 14.56±1.50 | 11.10±0.70 | 6.02±0.81 | ‒ |
| 灌草坡 Shrub and herb land | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ | 芒萁 (Dicranopteris pedata) |
| 功能类别 Functional category | 指标 Indicator | 计算公式和参数说明 Calculation formula and parameter description |
|---|---|---|
| 涵养水源 Water conservation | 调节水量 Regulating runoff | G调=10A(P-E-C);G调为林分调节水量功能,单位:m3∙a-1;P为降雨量,单位:mm∙a-1;E为林分蒸散量*,单位:mm∙a-1;C为地表径流量,单位:mm∙a-1;A为林分面积,单位:hm2 GR=10A(P-E-C); GR is the function of regulating runoff of forest (m3·a-1); P is the rainfall (mm∙a-1); E is the forest evapotranspiration (mm∙a-1)*; C is the surface runoff (mm∙a-1); A is the forest area (hm2) |
| 保育土壤 Soil conservation | 固土 Soil fixation | GN=AN(X2-X1);GP=AP(X2-X1);GN为减少的氮流失量,单位:t∙a-1;GP为减少的磷流失量,单位:t∙a-1;X1为林地土壤侵蚀模数**,单位:t∙hm-2∙a-1;X2为无林地土壤侵蚀模数,单位:t∙hm-2∙a-1;N为土壤含氮量,单位:%;P为土壤含磷量,单位:%;A为林分面积,单位:hm2 GN is the reduced nitrogen loss (t·a-1); GP is the reduced phosphorus loss (t·a-1); X1 is the soil erosion modulus in forest (t∙hm-2∙a-1)**; X2 is the soil erosion modulus without forest (t∙hm-2∙a-1); N is the soil total nitronge content (%); P is the soil total phosphorus content (%); A is the forest area (hm2) |
| 固碳释氧 Carbon fixation; oxygen released | 植被固碳 Carbon fixation by vegetation | G植被固碳=1.63R碳AB年;G植被固碳为植被年固碳量,单位t∙a-1;R碳为CO2中碳含量,为27.27%;B年为林分净生产力***,单位:t∙hm-2∙a-1;A为林分面积,单位:hm2 Gcv=1.63RcABa; Gcv is the annual carbon sequestration by forest (t∙a-1); Rc is 27.27%, representing carbon content in CO2; Ba is the forest net primary productivity (t∙hm-2∙a-1)***; A is the forest area (hm2) |
| 土壤固碳 Carbon fixation by soil | G土壤固碳=AF土壤;G土壤固碳为单位面积林分年固碳量,单位:t∙hm-2∙a-1;F土壤为单位面积林分土壤年固碳量,单位:t∙hm-2∙a-1;A为林分面积,单位:hm2 Gcs=AFs; Gcs is the per unit of annual carbon sequestration of forest (t∙hm-2∙a-1); Fs is the per unit of annual forest carbon sequestration by soil (t∙hm-2∙a-1); A is the forest area (hm2) | |
| 释氧 Oxygen released | G氧气=1.19AB年;G氧气为林分年释氧量,单位:t∙a-1;B年为林分净生产力,单位:t∙hm-2∙a-1;A为林分面积,单位:hm2 Go=1.19ABa; Go is the annual oxygen released of forest (t·a-1); Ba is the forest net primary productivity (t∙hm-2∙a-1)***; A is the forest area (hm2) | |
| 生物多样性保护 Biodiversity protection | 物种保育 Species conservation | U生物=S生****A;U生物为林分年物种保育价值,单位:yuan∙hm-2∙a-1;S生为单位面积年物种损失的机会成本,单位:yuan∙hm-2∙a-1;A为林分面积,单位:hm2 Up=Ss****A; Up is the annual forest species conservation value (yuan∙hm-2∙a-1); Ss is the annual opportunity cost of species loss in per unit area (yuan∙hm-2∙a-1)****; A is the forest area (hm2) |
表2 森林生态系统服务功能实物量评估公式及参数设置
Table 2 The formulas and parameters set for the assessment of forest ecosystem services
| 功能类别 Functional category | 指标 Indicator | 计算公式和参数说明 Calculation formula and parameter description |
|---|---|---|
| 涵养水源 Water conservation | 调节水量 Regulating runoff | G调=10A(P-E-C);G调为林分调节水量功能,单位:m3∙a-1;P为降雨量,单位:mm∙a-1;E为林分蒸散量*,单位:mm∙a-1;C为地表径流量,单位:mm∙a-1;A为林分面积,单位:hm2 GR=10A(P-E-C); GR is the function of regulating runoff of forest (m3·a-1); P is the rainfall (mm∙a-1); E is the forest evapotranspiration (mm∙a-1)*; C is the surface runoff (mm∙a-1); A is the forest area (hm2) |
| 保育土壤 Soil conservation | 固土 Soil fixation | GN=AN(X2-X1);GP=AP(X2-X1);GN为减少的氮流失量,单位:t∙a-1;GP为减少的磷流失量,单位:t∙a-1;X1为林地土壤侵蚀模数**,单位:t∙hm-2∙a-1;X2为无林地土壤侵蚀模数,单位:t∙hm-2∙a-1;N为土壤含氮量,单位:%;P为土壤含磷量,单位:%;A为林分面积,单位:hm2 GN is the reduced nitrogen loss (t·a-1); GP is the reduced phosphorus loss (t·a-1); X1 is the soil erosion modulus in forest (t∙hm-2∙a-1)**; X2 is the soil erosion modulus without forest (t∙hm-2∙a-1); N is the soil total nitronge content (%); P is the soil total phosphorus content (%); A is the forest area (hm2) |
| 固碳释氧 Carbon fixation; oxygen released | 植被固碳 Carbon fixation by vegetation | G植被固碳=1.63R碳AB年;G植被固碳为植被年固碳量,单位t∙a-1;R碳为CO2中碳含量,为27.27%;B年为林分净生产力***,单位:t∙hm-2∙a-1;A为林分面积,单位:hm2 Gcv=1.63RcABa; Gcv is the annual carbon sequestration by forest (t∙a-1); Rc is 27.27%, representing carbon content in CO2; Ba is the forest net primary productivity (t∙hm-2∙a-1)***; A is the forest area (hm2) |
| 土壤固碳 Carbon fixation by soil | G土壤固碳=AF土壤;G土壤固碳为单位面积林分年固碳量,单位:t∙hm-2∙a-1;F土壤为单位面积林分土壤年固碳量,单位:t∙hm-2∙a-1;A为林分面积,单位:hm2 Gcs=AFs; Gcs is the per unit of annual carbon sequestration of forest (t∙hm-2∙a-1); Fs is the per unit of annual forest carbon sequestration by soil (t∙hm-2∙a-1); A is the forest area (hm2) | |
| 释氧 Oxygen released | G氧气=1.19AB年;G氧气为林分年释氧量,单位:t∙a-1;B年为林分净生产力,单位:t∙hm-2∙a-1;A为林分面积,单位:hm2 Go=1.19ABa; Go is the annual oxygen released of forest (t·a-1); Ba is the forest net primary productivity (t∙hm-2∙a-1)***; A is the forest area (hm2) | |
| 生物多样性保护 Biodiversity protection | 物种保育 Species conservation | U生物=S生****A;U生物为林分年物种保育价值,单位:yuan∙hm-2∙a-1;S生为单位面积年物种损失的机会成本,单位:yuan∙hm-2∙a-1;A为林分面积,单位:hm2 Up=Ss****A; Up is the annual forest species conservation value (yuan∙hm-2∙a-1); Ss is the annual opportunity cost of species loss in per unit area (yuan∙hm-2∙a-1)****; A is the forest area (hm2) |
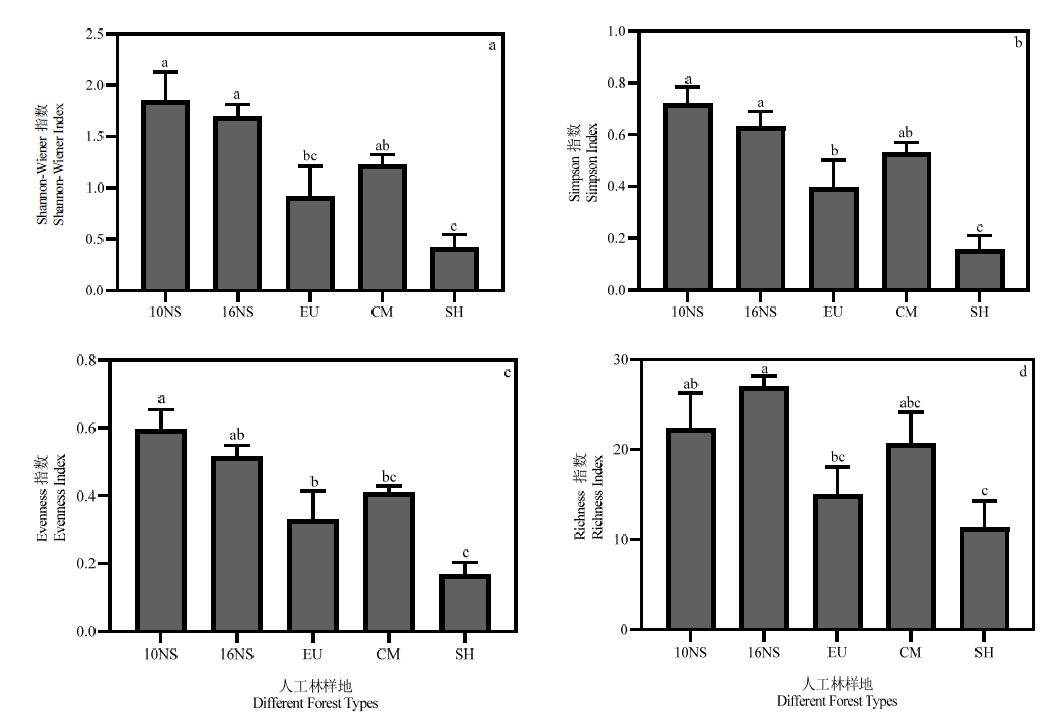
图1 不同样地生物多样性10NS:10树种混交林;16NS:16树种混交林;EU:尾叶桉纯林;CM:红锥纯林;SH:灌草坡。不同字母表示样地间差异显著(P<0.05,n=3)。下同
Fig. 1 Biodiversity in different forest types10 NS: 10 species mixed plantation; 16NS: 16 species mixed plantation; EU: Eucalypyus urophylla monoculture; CM: Castanopsis hystrix monoculture; SH: Shrub and herb land. Different letters indicate significant difference among different forest types (P<0.05,n=3). The same blow
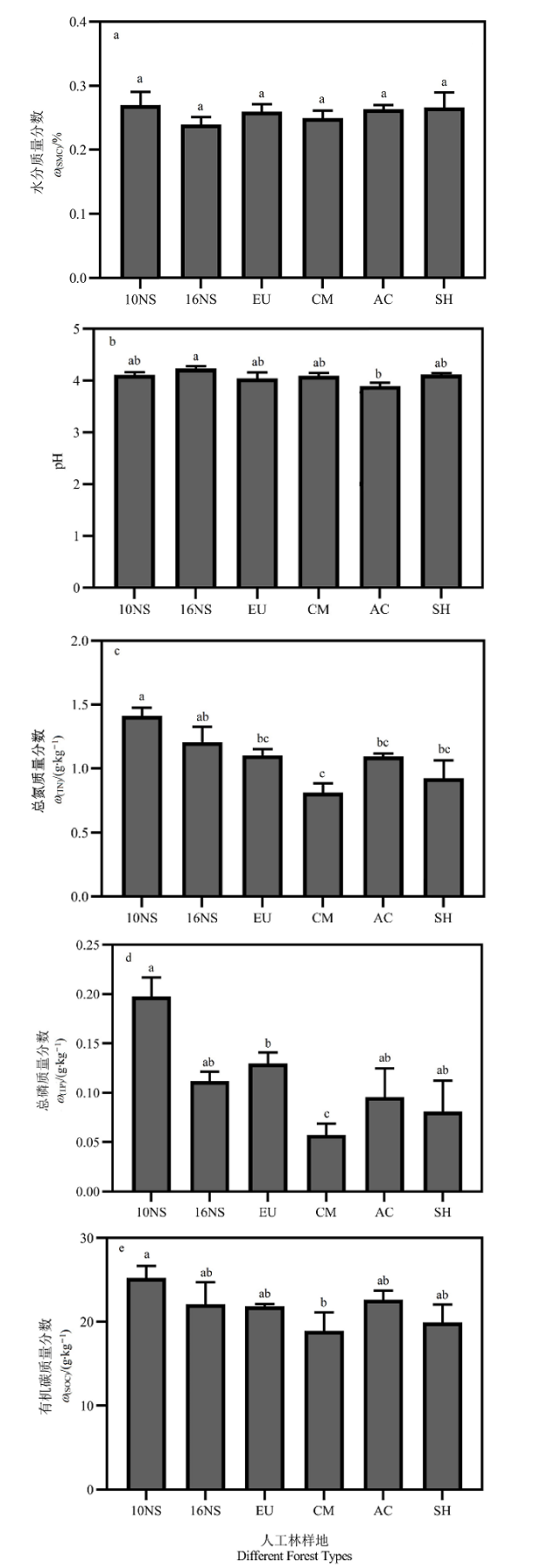
图2 不同样地土壤理化性质10NS:10树种混交林;16NS:16树种混交林;EU:尾叶桉纯林;CM:红锥纯林;AC:厚荚相思纯林;SH:灌草坡。下同
Fig. 2 Soil physicochemical properties in different forest types10NS: 10 species mixed plantation; 16NS: 16 species mixed plantation; EU: Eucalypyus urophylla monoculture; CM: Castanopsis hystrix monoculture; AC: Acacia crassicaipa monoculture; SH: Shrub and herb land. The same blow
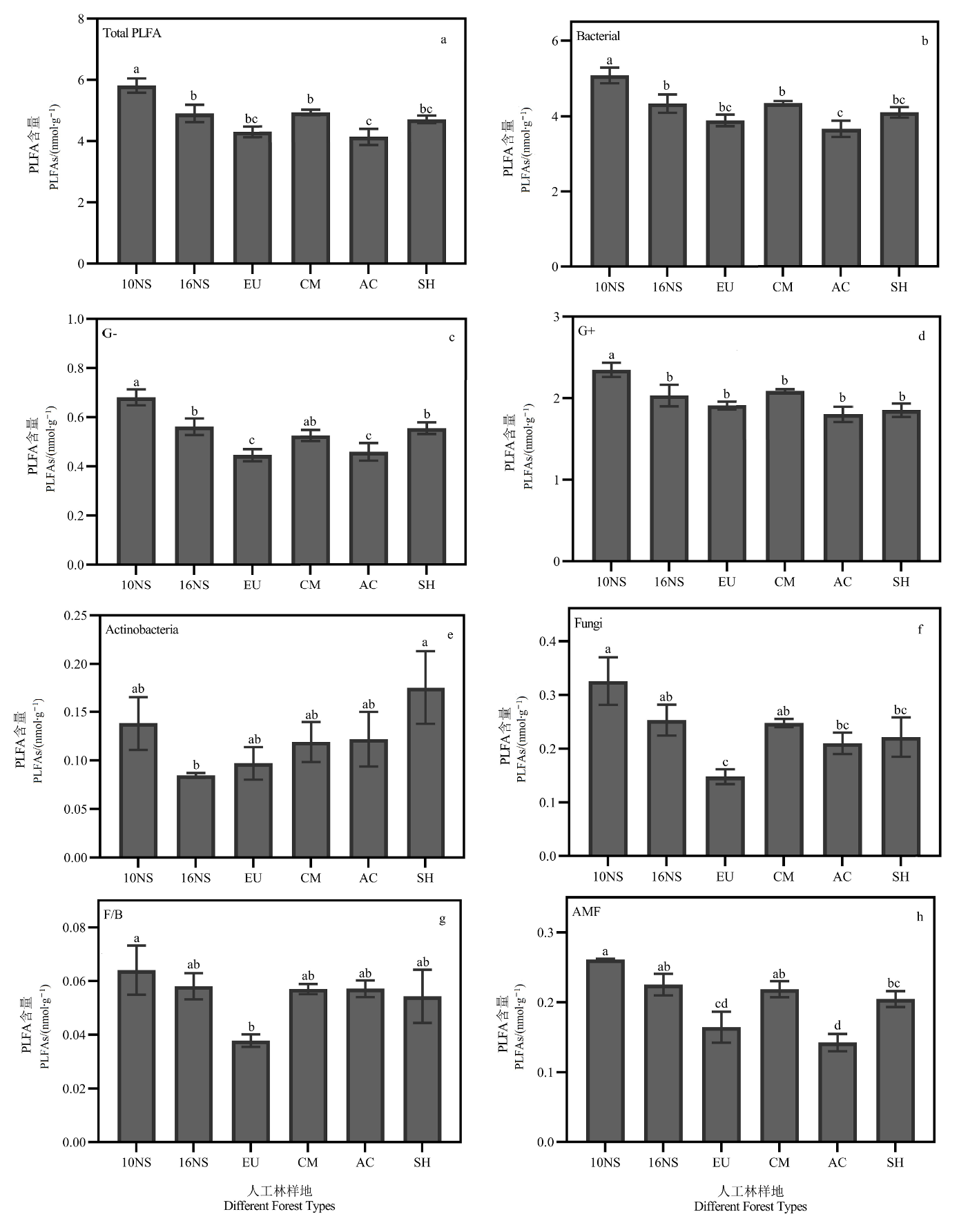
图4 不同样地土壤微生物群落特征a:PLFAs总量;b:细菌;c:革兰氏阴性菌;d:革兰氏阳性菌;e:放线菌;f:真菌;g:真细菌比;h:丛枝菌根真菌
Fig. 4 The character of soil microbial communities in different forest typesa: Total PLFAs; b: Bacteria; c: Gram-negative bacteria; d: Gram-positive bacteria; e: Actinomycetes; f: Fungi; g: Fungi: Bacteria;h: arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF)
| 样地 Sample plot | 降雨量 Rainfall/ (mm∙a-1) | 林分蒸散量 Forest evapotranspiration/ (mm∙a-1) | 地表径流量 Surface runoff/ (mm∙a-1) | 芒萁相对盖度 Dicranopteris dichotoma relative coverage | 芒萁相对密度 Dicranopteris dichotoma relative density | 林分调节 水量功能 Regulating runoff/ (m3∙a-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10树种混交林 10 species mixed plantation | 1754.83 | 767.69 | 22.21 | 0.25 | 0.30 | 9649.300 |
| 16树种混交林 16 species mixed plantation | 1754.83 | 767.69 | 43.50 | 0.27 | 0.32 | 9436.420 |
| 尾叶桉纯林 Eucalypyus urophylla monoculture | 1754.83 | 928.25 | 35.82 | 0.29 | 0.32 | 7907.579 |
| 红锥纯林 Castanopsis hystrix monoculture | 1754.83 | 767.69 | 56.38 | 0.17 | 0.27 | 9307.640 |
| 灌草坡 Shrub and herb land | 1754.83 | 435.35 | 24.63 | 0.32 | 0.32 | 12948.478 |
表3 不同样地林分调节水量功能
Table 3 Water conservation capacity in different forest types
| 样地 Sample plot | 降雨量 Rainfall/ (mm∙a-1) | 林分蒸散量 Forest evapotranspiration/ (mm∙a-1) | 地表径流量 Surface runoff/ (mm∙a-1) | 芒萁相对盖度 Dicranopteris dichotoma relative coverage | 芒萁相对密度 Dicranopteris dichotoma relative density | 林分调节 水量功能 Regulating runoff/ (m3∙a-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10树种混交林 10 species mixed plantation | 1754.83 | 767.69 | 22.21 | 0.25 | 0.30 | 9649.300 |
| 16树种混交林 16 species mixed plantation | 1754.83 | 767.69 | 43.50 | 0.27 | 0.32 | 9436.420 |
| 尾叶桉纯林 Eucalypyus urophylla monoculture | 1754.83 | 928.25 | 35.82 | 0.29 | 0.32 | 7907.579 |
| 红锥纯林 Castanopsis hystrix monoculture | 1754.83 | 767.69 | 56.38 | 0.17 | 0.27 | 9307.640 |
| 灌草坡 Shrub and herb land | 1754.83 | 435.35 | 24.63 | 0.32 | 0.32 | 12948.478 |
| 样地 Sample plot | 乔木层生物量 Arbor layer’s Biomass/ (t∙hm-2) | 灌木层生物量 Shurb layer’s Biomass/ (t∙hm-2) | 草本层生物量 Herb layer’s Biomass/ (t∙hm-2) | 总生物量 Total layer’s Biomass/ (t∙hm-2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10树种混交林 10 species mixed plantation | 60.98a | 0.82a | 2.33b | 64.13a |
| 16树种混交林 16 species mixed plantation | 54.39a | 1.42a | 2.88b | 58.69a |
| 尾叶桉纯林 Eucalypyus urophylla monoculture | 55.81a | 0.64a | 6.16a | 62.60a |
| 红锥纯林 Castanopsis hystrix monoculture | 29.20b | 1.76a | 3.39ab | 34.36b |
| 灌草坡 Shrub and herb land | 0.01c | 3.43a | 6.11a | 9.55c |
表4 不同样地乔木层生物量、灌木层生物量、草本层生物量以及总生物量
Table 4 Biomass in different levels and total Biomass in different forest types
| 样地 Sample plot | 乔木层生物量 Arbor layer’s Biomass/ (t∙hm-2) | 灌木层生物量 Shurb layer’s Biomass/ (t∙hm-2) | 草本层生物量 Herb layer’s Biomass/ (t∙hm-2) | 总生物量 Total layer’s Biomass/ (t∙hm-2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10树种混交林 10 species mixed plantation | 60.98a | 0.82a | 2.33b | 64.13a |
| 16树种混交林 16 species mixed plantation | 54.39a | 1.42a | 2.88b | 58.69a |
| 尾叶桉纯林 Eucalypyus urophylla monoculture | 55.81a | 0.64a | 6.16a | 62.60a |
| 红锥纯林 Castanopsis hystrix monoculture | 29.20b | 1.76a | 3.39ab | 34.36b |
| 灌草坡 Shrub and herb land | 0.01c | 3.43a | 6.11a | 9.55c |
| 样地 Sample plot | 净生产力 Net productivity/ (t∙hm-2∙a-1) | 植被固碳 Carbon fixation by vegetation/ (t∙a-1) | 林分释氧量 oxygen released/ (t∙a-1) | 土壤固碳 Carbon fixation by soil/ (t∙hm-2∙a-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10树种混交林 10 species mixed plantation | 24.669a | 10.965a | 29.356a | 0.339a |
| 16树种混交林 16 species mixed plantation | 22.839a | 10.152a | 27.179a | 0.315ab |
| 尾叶桉纯林 Eucalypyus urophylla monoculture | 24.156a | 10.737a | 28.745a | 0.321ab |
| 红锥纯林 Castanopsis hystrix monoculture | 14.665b | 6.519b | 17.451b | 0.248b |
| 厚荚相思纯林 Acacia crassicaipa monoculture | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ | 0.302ab |
| 灌草坡 Shrub and herb land | 6.331c | 2.814c | 7.534c | 0.303ab |
表5 不同样地固碳释氧能力
Table 5 Capability of carbon fixation and oxygen releasing in different forest types
| 样地 Sample plot | 净生产力 Net productivity/ (t∙hm-2∙a-1) | 植被固碳 Carbon fixation by vegetation/ (t∙a-1) | 林分释氧量 oxygen released/ (t∙a-1) | 土壤固碳 Carbon fixation by soil/ (t∙hm-2∙a-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10树种混交林 10 species mixed plantation | 24.669a | 10.965a | 29.356a | 0.339a |
| 16树种混交林 16 species mixed plantation | 22.839a | 10.152a | 27.179a | 0.315ab |
| 尾叶桉纯林 Eucalypyus urophylla monoculture | 24.156a | 10.737a | 28.745a | 0.321ab |
| 红锥纯林 Castanopsis hystrix monoculture | 14.665b | 6.519b | 17.451b | 0.248b |
| 厚荚相思纯林 Acacia crassicaipa monoculture | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ | 0.302ab |
| 灌草坡 Shrub and herb land | 6.331c | 2.814c | 7.534c | 0.303ab |
| 样地 Sample plot | Shannon-Wiener 指数 Shannon-Wiener index | 物种保育 Species conservation/ (yuan∙hm-2∙a-1) |
|---|---|---|
| 10树种混交林 10 species mixed plantation | 1.85 | 5000 |
| 16树种混交林 16 species mixed plantation | 1.69 | 5000 |
| 尾叶桉纯林 Eucalypyus urophylla monoculture | 0.91 | 3000 |
| 红锥纯林 Castanopsis hystrix monoculture | 1.23 | 5000 |
| 灌草坡 Shrub and herb land | 0.42 | 3000 |
表6 不同样地物种保育价值
Table 6 Species conservation in different forest types
| 样地 Sample plot | Shannon-Wiener 指数 Shannon-Wiener index | 物种保育 Species conservation/ (yuan∙hm-2∙a-1) |
|---|---|---|
| 10树种混交林 10 species mixed plantation | 1.85 | 5000 |
| 16树种混交林 16 species mixed plantation | 1.69 | 5000 |
| 尾叶桉纯林 Eucalypyus urophylla monoculture | 0.91 | 3000 |
| 红锥纯林 Castanopsis hystrix monoculture | 1.23 | 5000 |
| 灌草坡 Shrub and herb land | 0.42 | 3000 |
| 物种 | 地上生物量 | 地下生物量 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 种名 | 拉丁文名 | 回归方程 | R2 | 回归方程 | R2 | ||||||||
| 白背叶 | Mallotus apelta | y=0.1004x0.4018 | 0.759 | y=0.0364x0.3676 | 0.6466 | ||||||||
| 潺槁木姜子 | Litsea glutinosa | y=0.1518x0.7435 | 0.813 | y=0.0337x0.7913 | 0.75 | ||||||||
| 枫香 | Liquidambar formosana | y=0.2894x0.7405 | 0.8598 | y=0.1360x0.673 | 0.785 | ||||||||
| 观光木 | Tsoongiodendron odorum | y=0.1466x0.8309 | 0.9367 | y=0.0442x0.7256 | 0.8846 | ||||||||
| 鬼灯笼 | Clerodendrum fortunatum | y=0.0351x0.7675 | 0.9201 | y=0.0092x0.6673 | 0.8393 | ||||||||
| 红锥 | Castanopsis hystrix | y=0.2926x0.7162 | 0.9555 | y=0.1017x0.5941 | 0.8238 | ||||||||
| 厚荚相思 | Acacia crassicarpa | y=0.4171x0.6201 | 0.975 | y=0.0562x0.6725 | 0.9141 | ||||||||
| 华润楠 | Machilus chinensis | y=1.1447x0.582 | 0.95 | y=0.3663x0.5081 | 0.9693 | ||||||||
| 黄栀子 | Gardenia jasminoides | y=0.0556x0.9636 | 0.8814 | y=0.0295x0.5991 | 0.6635 | ||||||||
| 灰木莲 | Manglietia glauca | y=0.6355x0.4751 | 0.8123 | y=0.0635x0.6628 | 0.8994 | ||||||||
| 火力楠 | Michelia macclurei | y=0.2010x0.8013 | 0.8022 | y=0.038x0.7999 | 0.8593 | ||||||||
| 黧蒴 | Castanopsis fissa | y=0.3778x0.614 | 0.8782 | y=0.0718x0.7044 | 0.9548 | ||||||||
| 梅叶冬青 | Ilex asprella | y=0.1569x0.5899 | 0.8355 | y=0.0498x0.6248 | 0.8192 | ||||||||
| 日本杜英 | Elaeocarpus japonicus | y=0.1316x0.6959 | 0.7827 | y=0.0423x0.6827 | 0.6945 | ||||||||
| 山苍子 | Litsea cubeba | y=0.0043x1.3607 | 0.908 | y=0.0004x1.5183 | 0.7597 | ||||||||
| 深山含笑 | Michelia maudiae | y=0.1419x0.9694 | 0.9932 | y=0.0640x0.6464 | 0.7139 | ||||||||
| 湿加松 | Pinus massoniana | y=0.0245x1.0209 | 0.9711 | y=0.0126x0.9024 | 0.9685 | ||||||||
| 石斑木 | Rhaphiolepis indica | y=0.0402x0.9471 | 0.6695 | y=0.0055x1.1122 | 0.8987 | ||||||||
| 桃金娘 | Rhodomyrtus tomentosa | y=0.4571x0.7346 | 0.6964 | y=0.2144x0.8813 | 0.627 | ||||||||
| 尾叶桉 | Eucalyptus urophylla | y=0.1691x0.7472 | 0.9462 | y=0.1723x0.563 | 0.8942 | ||||||||
| 香樟 | Cinnamomum bodinieri | y=0.376x0.5171 | 0.8521 | y=0.1017x0.6883 | 0.8714 | ||||||||
| 野牡丹 | Melastoma candidum | y=0.0630x0.830 | 0.826 | y=0.0420x0.358 | 0.694 | ||||||||
| 阴香 | Cinnamomum burmannii | y=0.9665x0.3015 | 0.7535 | y=0.3376x0.2402 | 0.8446 | ||||||||
| 物种 | 树干生物量 | 树枝生物量 | 树叶生物量 | 根生物量 | |||||||||
| 种名 | 拉丁文名 | 回归方程 | R2 | 回归方程 | R2 | 回归方程 | R2 | 回归方程 | R2 | ||||
| 木荷 | Schima superba | y=0.0683x0.8504 | 0.9682 | y=0.0227x0.8516 | 0.956 | y=0.0374x0.5940 | 0.9005 | y=0.0197x0.8975 | 0.9599 | ||||
| 云南银柴 | Aporosa yunnanensis | y=0.0683x0.8504 | 0.9682 | y=0.0227x0.8516 | 0.956 | y=0.0374x0.5940 | 0.9005 | y=0.0197x0.8975 | 0.9599 | ||||
| 乌桕 | Triadica cochinchinensis | y=0.0816x0.8437 | 0.9987 | y=0.0098x1.0979 | 0.9955 | y=0.0285x0.6967 | 0.9833 | y=0.065x0.6913 | 0.9917 | ||||
| 海南蒲桃 | Syzygium levinei | y=0.0476x0.9144 | 0.9874 | y=0.0056x1.1274 | 0.9701 | y=0.2444x0.3229 | 0.9546 | y=0.0214x0.8389 | 0.9617 | ||||
| 假苹婆 | Sterculia lanceolata | y=0.0476x0.9144 | 0.9874 | y=0.0056x1.1274 | 0.9701 | y=0.2444x0.3229 | 0.9546 | y=0.0214x0.8389 | 0.9617 | ||||
| 岭南山竹子 | Garcinia oblongifolia | y=0.0163x1.0557 | 0.969 | y=0.3908x0.3725 | 0.9169 | y=0.2156x0.3596 | 0.9856 | y=0.3350x0.4598 | 0.9796 | ||||
| 变叶榕 | Ficus variolosa | y=0.0774x0.7899 | 0.9938 | y=0.0474x0.6318 | 0.9651 | y=0.0649x0.3324 | 0.9024 | y=0.0177x0.8663 | 0.9098 | ||||
| 三桠苦 | Melicope pteleifolia | y=0.0163x1.0557 | 0.969 | y=0.3908x0.3725 | 0.9169 | y=0.2156x0.3596 | 0.9856 | y=0.3350x0.4598 | 0.9796 | ||||
| 九节 | Psychotria asiatica | y=0.0774x0.7899 | 0.9938 | y=0.0474x0.6318 | 0.9651 | y=0.0649x0.3324 | 0.9024 | y=0.0177x0.8663 | 0.9098 | ||||
| 岗松 | baeckea frutescens L. | y=0.9457x0.8210 | 0.9457 | y=0.9446x0.9236 | 0.9446 | y=0.6284x0.4561 | 0.6284 | y=0.6468x0.2978 | 0.6468 | ||||
| 山黄麻 | Trema tomentosa | y=0.0103x+0.324 | 0.3078 | y=0.001x+0.0512 | 0.5979 | y=0.004x+0.1256 | 0.2217 | ||||||
| 灌木层 | Shrubs | W=0.2216x1.0018 | 0.9033 | W= -8E-06x2+ 0.0374x | 0.8058 | W=6E-06x2+ 0.0325x | 0.6843 | W= -3E-05x2+ 0.2424x | 0.7774 | ||||
表3 植被异速生长方程
表 3 Allometric regression equations of vegetation
| 物种 | 地上生物量 | 地下生物量 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 种名 | 拉丁文名 | 回归方程 | R2 | 回归方程 | R2 | ||||||||
| 白背叶 | Mallotus apelta | y=0.1004x0.4018 | 0.759 | y=0.0364x0.3676 | 0.6466 | ||||||||
| 潺槁木姜子 | Litsea glutinosa | y=0.1518x0.7435 | 0.813 | y=0.0337x0.7913 | 0.75 | ||||||||
| 枫香 | Liquidambar formosana | y=0.2894x0.7405 | 0.8598 | y=0.1360x0.673 | 0.785 | ||||||||
| 观光木 | Tsoongiodendron odorum | y=0.1466x0.8309 | 0.9367 | y=0.0442x0.7256 | 0.8846 | ||||||||
| 鬼灯笼 | Clerodendrum fortunatum | y=0.0351x0.7675 | 0.9201 | y=0.0092x0.6673 | 0.8393 | ||||||||
| 红锥 | Castanopsis hystrix | y=0.2926x0.7162 | 0.9555 | y=0.1017x0.5941 | 0.8238 | ||||||||
| 厚荚相思 | Acacia crassicarpa | y=0.4171x0.6201 | 0.975 | y=0.0562x0.6725 | 0.9141 | ||||||||
| 华润楠 | Machilus chinensis | y=1.1447x0.582 | 0.95 | y=0.3663x0.5081 | 0.9693 | ||||||||
| 黄栀子 | Gardenia jasminoides | y=0.0556x0.9636 | 0.8814 | y=0.0295x0.5991 | 0.6635 | ||||||||
| 灰木莲 | Manglietia glauca | y=0.6355x0.4751 | 0.8123 | y=0.0635x0.6628 | 0.8994 | ||||||||
| 火力楠 | Michelia macclurei | y=0.2010x0.8013 | 0.8022 | y=0.038x0.7999 | 0.8593 | ||||||||
| 黧蒴 | Castanopsis fissa | y=0.3778x0.614 | 0.8782 | y=0.0718x0.7044 | 0.9548 | ||||||||
| 梅叶冬青 | Ilex asprella | y=0.1569x0.5899 | 0.8355 | y=0.0498x0.6248 | 0.8192 | ||||||||
| 日本杜英 | Elaeocarpus japonicus | y=0.1316x0.6959 | 0.7827 | y=0.0423x0.6827 | 0.6945 | ||||||||
| 山苍子 | Litsea cubeba | y=0.0043x1.3607 | 0.908 | y=0.0004x1.5183 | 0.7597 | ||||||||
| 深山含笑 | Michelia maudiae | y=0.1419x0.9694 | 0.9932 | y=0.0640x0.6464 | 0.7139 | ||||||||
| 湿加松 | Pinus massoniana | y=0.0245x1.0209 | 0.9711 | y=0.0126x0.9024 | 0.9685 | ||||||||
| 石斑木 | Rhaphiolepis indica | y=0.0402x0.9471 | 0.6695 | y=0.0055x1.1122 | 0.8987 | ||||||||
| 桃金娘 | Rhodomyrtus tomentosa | y=0.4571x0.7346 | 0.6964 | y=0.2144x0.8813 | 0.627 | ||||||||
| 尾叶桉 | Eucalyptus urophylla | y=0.1691x0.7472 | 0.9462 | y=0.1723x0.563 | 0.8942 | ||||||||
| 香樟 | Cinnamomum bodinieri | y=0.376x0.5171 | 0.8521 | y=0.1017x0.6883 | 0.8714 | ||||||||
| 野牡丹 | Melastoma candidum | y=0.0630x0.830 | 0.826 | y=0.0420x0.358 | 0.694 | ||||||||
| 阴香 | Cinnamomum burmannii | y=0.9665x0.3015 | 0.7535 | y=0.3376x0.2402 | 0.8446 | ||||||||
| 物种 | 树干生物量 | 树枝生物量 | 树叶生物量 | 根生物量 | |||||||||
| 种名 | 拉丁文名 | 回归方程 | R2 | 回归方程 | R2 | 回归方程 | R2 | 回归方程 | R2 | ||||
| 木荷 | Schima superba | y=0.0683x0.8504 | 0.9682 | y=0.0227x0.8516 | 0.956 | y=0.0374x0.5940 | 0.9005 | y=0.0197x0.8975 | 0.9599 | ||||
| 云南银柴 | Aporosa yunnanensis | y=0.0683x0.8504 | 0.9682 | y=0.0227x0.8516 | 0.956 | y=0.0374x0.5940 | 0.9005 | y=0.0197x0.8975 | 0.9599 | ||||
| 乌桕 | Triadica cochinchinensis | y=0.0816x0.8437 | 0.9987 | y=0.0098x1.0979 | 0.9955 | y=0.0285x0.6967 | 0.9833 | y=0.065x0.6913 | 0.9917 | ||||
| 海南蒲桃 | Syzygium levinei | y=0.0476x0.9144 | 0.9874 | y=0.0056x1.1274 | 0.9701 | y=0.2444x0.3229 | 0.9546 | y=0.0214x0.8389 | 0.9617 | ||||
| 假苹婆 | Sterculia lanceolata | y=0.0476x0.9144 | 0.9874 | y=0.0056x1.1274 | 0.9701 | y=0.2444x0.3229 | 0.9546 | y=0.0214x0.8389 | 0.9617 | ||||
| 岭南山竹子 | Garcinia oblongifolia | y=0.0163x1.0557 | 0.969 | y=0.3908x0.3725 | 0.9169 | y=0.2156x0.3596 | 0.9856 | y=0.3350x0.4598 | 0.9796 | ||||
| 变叶榕 | Ficus variolosa | y=0.0774x0.7899 | 0.9938 | y=0.0474x0.6318 | 0.9651 | y=0.0649x0.3324 | 0.9024 | y=0.0177x0.8663 | 0.9098 | ||||
| 三桠苦 | Melicope pteleifolia | y=0.0163x1.0557 | 0.969 | y=0.3908x0.3725 | 0.9169 | y=0.2156x0.3596 | 0.9856 | y=0.3350x0.4598 | 0.9796 | ||||
| 九节 | Psychotria asiatica | y=0.0774x0.7899 | 0.9938 | y=0.0474x0.6318 | 0.9651 | y=0.0649x0.3324 | 0.9024 | y=0.0177x0.8663 | 0.9098 | ||||
| 岗松 | baeckea frutescens L. | y=0.9457x0.8210 | 0.9457 | y=0.9446x0.9236 | 0.9446 | y=0.6284x0.4561 | 0.6284 | y=0.6468x0.2978 | 0.6468 | ||||
| 山黄麻 | Trema tomentosa | y=0.0103x+0.324 | 0.3078 | y=0.001x+0.0512 | 0.5979 | y=0.004x+0.1256 | 0.2217 | ||||||
| 灌木层 | Shrubs | W=0.2216x1.0018 | 0.9033 | W= -8E-06x2+ 0.0374x | 0.8058 | W=6E-06x2+ 0.0325x | 0.6843 | W= -3E-05x2+ 0.2424x | 0.7774 | ||||
| [1] |
BOSSIO D A, SCOW K M, 1998. Impacts of carbon and flooding on soil microbial communities: Phospholipid fatty acid profiles and substrate utilization patterns[J]. Microbial Ecology, 35: 265-278.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
CHEN D M, ZHOU L X, WU J P, et al., 2011. Subtropical plantations are large carbon sinks: evidence from two monoculture plantations in South China[J]. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 151(9): 1214-1225.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
CHEN Y Q, LIU Z F, RAO X Q, et al., 2015. Carbon storage and allocation pattern in plant biomass among different forest plantation stands in Guangdong, China[J]. Forests, 6(3): 794-808.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
FANG X M, YU D P, ZHOU W M, et al., 2016. The effects of forest type on soil microbial activity in Changbai Mountain, Northeast China[J]. Annals of Forest Science, 73(2): 473-482.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
GETZIN S, DEAN C, HE F, et al., 2006. Spatial patterns and competition of tree species in a Douglas-fir chronosequence on Vancouver Island[J]. Ecography, 29(5): 671-682.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
KELTY M J, 2006. The role of species mixtures in plantation forestry[J]. Forest Ecology and Manage, 233(2): 195-204.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
LIU Z F, WU J P, ZHOU L X, et al., 2012. Effect of understory fern (Dicranopteris dichotoma) removal on substrate utilization patterns of culturable soil bacterial communities in subtropical Eucalyptus plantations[J]. Pedobiologia, 55(1): 7-13.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
VANCE E D, BROOKES P C, JENKINSON D S, 1987. An Extraction method for measuring soil microbial biomass C[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 19: 703-707.
DOI URL |
| [9] | WAN S Z, ZHANG C L, CHEN Y Q, et al., 2014. The understory fernDicranopteris dichotoma facilitates the overstory Eucalyptus trees in subtropical plantations[J]Ecosphere, 5(5): 51. |
| [10] |
WU J P, LIU Z F, WANG X L, et al., 2011. Effects of understory removal and tree girdling on soil microbial community composition and litter decomposition in two Eucalyptus plantations in south China[J]. Functional Ecology, 25(4): 921-931.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
ZHAO J, WAN S Z, LI Z A, et al., 2012. Dicranopteris-dominated understory as major driver of intensive forest ecosystem in humid subtropical and tropical region[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 49: 78-87.
DOI URL |
| [12] | 陈超然, 王刊, 2018. 世界森林面积正日益缩减[J]. 生态经济, 34(9): 2-5. |
| CHEN C R, WANG K, 2018. The world's forests area are shrinking[J]. Ecological Economy, 34(9): 2-5. | |
| [13] | 陈富强, 罗勇, 李清湖, 2013. 粤东地区森林灌木层优势植物生物量估算模型[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 33(2): 5-10. |
| CHEN F Q, LUO Y, LI Q H, 2013. Allometric equations for estimating biomass of dominant shurb species in subtropical forests in eastern Guangdong Province, China[J]. Jounal of Central South University of Forestry and Technology, 33(2): 5-10. | |
| [14] | 陈幸良, 巨茜, 林昆仑, 2014. 中国人工林发展现状、问题与对策[J]. 世界林业研究, 27(6): 54-59. |
| CHEN X L, JU X, LIN K L, 2014. Development status, issues and countermeasures of China’s plantation[J]. Word Forestry Research, 27(6): 54-59. | |
| [15] | 陈远其, 2015. 南亚热带典型人工林生态系统碳分配及土壤碳稳定性[D]. 广州: 华南植物园:18-19. |
| CHEN Y Q, 2015. Carbon allocation and soil carbon stability in typical subtropical plantations,South China[D]. Guang Zhou: South China Botanical Garden Chinese Academy of Science:18-19. | |
| [16] | 邓晓保, 唐建维, 2010. 中国生态系统定位观测与研究数据集—森林生态系统卷:云南西双版纳站 (1998—2006)[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社:247-256. |
| DENG X B, TANG J W, 2010. Chinese Ecosystem Localization Observation and Research Dataset-Volume on Forest Ecosystems:Xishuangbanna Yunnan (1998-2006)[M]. Beijing: China Agriculture Press:247-256. | |
| [17] | 方精云, 刘国华, 徐嵩龄, 1996. 我国森林植被的生物量和净生产量[J]. 生态学报, 16(5): 497-508. |
| FANG J Y, LIU G H, XU S L, 1996. Biomass and net Production of forest vegetation in China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 16(5): 497-508. | |
| [18] | 傅声雷, 林永标, 饶兴权, 2012. 中国生态系统定位观测与研究数据集—森林生态系统卷:广东鹤山站 (1998—2008)[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社:89-96. |
| FU S L, LIN Y B, RAO X Q, 2012. Chinese Ecosystem Localization Observation and Research Dataset-Volume on Forest Ecosystems:Heshan Guangdong (1998-2008)[M]. Beijing: China Agriculture Press:89-96. | |
| [19] | 郭雄飞, 陈璇, 黎华寿, 等, 2015. 不同林分改造模式对土壤酶活及微生物数量的影响[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 35(9): 30-34. |
| GUO X F, CHEN X, LI S H, et al., 2015. Effects of different forest stand improvement models on soil enzyme activities and microbial population[J]. Journal of Central South University of Forestry & Technology, 35(9): 30-34. | |
| [20] | 黄碧峰, 2017. 厚荚相思、火力楠和西南桦三树种生长特性与综合效益对比分析[D]. 南宁: 广西大学:45-47. |
| HUANG B F, 2017. Comparative analysis of Growth characteristics and comprehensive benefits of three species ofAcacia crassicarpa, Michelia macclurei andBetula alnoides[D]. Nanning: Guangxi University:45-47. | |
| [21] | 黄小黎, 张声才, 2002. 石门台自然保护区水资源及其利用保护[J]. 热带地理, 22(2): 121-124. |
| HUANG X L, ZHANG S C, 2002. The utilization and protection of the water resources in Shimentai Natural Reserve[J]. Tropical Geography, 22(2): 121-124. | |
| [22] | 黄钰辉, 张卫强, 甘先华, 等, 2016. 南亚热带杉木林分改造中不同树种组合模式评价[J]. 生态环境学报, 25(6): 956-964. |
| HUANG Y H, ZHANG W Q, GAN X H, et al., 2016. Evaluation of different tree species composition patterns in stand conversion of cinnamomum burmanni in southern subtropical region of China[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 25(6): 956-964. | |
| [23] | 黄志宏, 王旭, 周光益, 等, 2008. 不同理论方程模拟华南人工林蒸散量的比较[J]. 生态环境, 17(3): 1107-1111. |
| HUANG Z H, WANG X, ZHOU G Y, et al., 2008. Comparison of different theoretical equations for modelling evapotranspiration from eucalypt plantations in southern China[J]. Ecology and Environment, 17(3): 1107-1111. | |
| [24] | 李振, 李浩, 曾宪曙, 等, 2013. 广东鹤山三种南亚热带人工林的生态系统服务价值动态[J]. 生态环境学报, 22(6): 967-975. |
| LI Z, LI H, ZENG X S, et al., 2013. Dynamics in ecosystem service values of three lower subtropical forest plantations in Heshan, Guangdong Province[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 22(6): 967-975. | |
| [25] | 林友兴, 张一不, 费学海, 等, 2019. 云南不同森林生态系统蒸散特征的比较研究[J]. 云南大学学报(自然科学版), 41(1): 205-218. |
| LIN Y X, ZHANG Y B, FEI X H, et al., 2019. Comparative study of evapotranspiration characteristics over different forest ecosystems in Yunnan Province, Southwest China[J]. Journal of Yunnan University: Natural Sciences Edition, 41(1): 205-218. | |
| [26] | 刘飞鹏, 曾曙才, 莫罗坚, 等, 2013. 尾叶桉人工林改造对土壤和凋落物持水效能的影响[J]. 生态学杂志, 32(5): 1111-1117. |
| LIU F P, ZENG S C, MO L J, et al., 2013. Effects of stand transformation on the water-holding capacities of soil and litter in Eucalyptus urophylla plantations[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 32(5): 1111-1117. | |
| [27] | 刘光崧, 1996. 土壤理化分析与剖面描述[M]. 北京:中国标准出版社: 38. |
| LIU G S, 1996. Soil physical and chemical analysis and description of soil profiles[M]. Beijing: China standard Press: 38. | |
| [28] | 刘占锋, 刘国华, 傅伯杰, 等, 2007. 人工油松林 (Pinus tabulaeformis) 恢复过程中土壤微生物生物量C、N的变化特征[J]. 生态学报, 27(3): 1011-1018. |
| LIU Z F, LIU G H, FU B J, et al., 2007. Dynamics of soil microbial biomass C, N along restoration chronosequences in pine plantations[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 27(3): 1011-1018. | |
| [29] | 卢立华, 贾宏炎, 何日明, 等, 2008. 南亚热带6种人工林凋落物的初步研究[J]. 林业科学研究, 21(3): 346-352. |
| LU L H, JIA H Y, HE R M, et al., 2008. A Preliminary Study on Litter Falls of Six Kinds of Plantations in the Tropical South Asia[J]. Forest Research, 21(3): 346-352. | |
| [30] | 潘国英, 2018. 红锥人工林培育研究[J]. 现代农业 (7): 70-71. |
| PAN G Y, 2018. Study on cultivation ofCastanopsis hystrix[J]. Modern agriculture (7): 70-71. | |
| [31] | 全国绿化委员会,2020. 2019年中国国土绿化状况公报(摘要)[N]. 人民日报, 2020-03-12(014) |
| National Afforestation Environmental Protection Commission,2020. China’s circumstance of land afforestation bulletin in 2019. (Abstract)[N]. People’s Daily, 2020-03-12(014). | |
| [32] | 孙鸿烈, 汪思龙, 2012. 中国生态系统定位观测与研究数据集—森林生态系统卷:湖南会同站 (1960—2006)[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社:92-98. |
| SUN H L, WANG S L, 2012. Chinese Ecosystem Localization Observation and Research Dataset-Volume on Forest Ecosystems:Huitong Hunan (1960-2006)[M]. Beijing: China Agriculture Press:92-98. | |
| [33] | 汤松波, 习丹, 任文丹, 等, 2018. 鹤山不同植被有机碳分布特征[J]. 土壤, 50(1): 122-130. |
| TANG S B, XI D, REN W D, et al., 2018. Characteristics of soil organic carbon under different forest types in Heshan of Southern China[J]. Soils, 50(1): 122-130. | |
| [34] | 王兵, 杨锋伟, 郭浩, 等, 2008. 森林生态系统服务功能评估规范 (LY/T 1721— 2008)[M]. 北京: 中国标准出版社. |
| WANG B, YANG F W, GUO H, et al., 2008. Specifications for assessment of forest ecosystem services in China (LY/T 1721—2008)[M]. Beijing: China standard Press. | |
| [35] | 王春阳, 周建斌, 夏志敏, 等, 2011. 黄土高原区不同植物凋落物搭配对土壤微生物量碳、氮的影响[J]. 生态学报, 31(8): 2139-2147. |
| WANG C Y, ZHOU J B, XIA Z M, et al., 2011. Effects of mixed plant residues from the Loess Plateau on microbial biomass carbon and nitrogen in soil[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 31(8): 2139-2147. | |
| [36] | 王晓玲, 2011. 林下植被清除与添加对乡土树种混交林土壤呼吸和NEP的影响[D]. 广州: 华南植物园:57-58. |
| WANG X L, 2011. Impacts of understory vegetation removal and addition on soil respiration and net ecosystem production under two plantations in Southern China[D]. Guangzhou: South China Botanical Garden Chinese Academy of Science:57-58. | |
| [37] | 王永忠, 邓树剑, 韩新生, 2018. 浅谈人工林改造和管理中存在的问题及改造措施[J]. 宁夏农林科技, 59(4): 32-34. |
| WANG Y Z, DENG S J, HAN X S, 2018. Problems and improvement measures of artificial forest construction and management[J]. Ningxia Journal of Agri. and Forest Sci. & Tech., 59(4): 32-34. | |
| [38] | 徐国良, 方碧真, 周丽霞, 等, 2016. 广东鹤山南亚热带植被重建对土壤动物群落的影响(英文)[J]. 广州大学学报(自然科学版), 15(5): 56-66. |
| XU G L, FANG B Z, ZHOU L X, et al., 2016. Effects of forest rehabilitation managements on soil fauna community in southern subtropical Heshan, Guangdong of China[J]. Journal of Guangzhou University (Natural Science Edition), 15(5): 56-66. | |
| [39] | 易桂田, 王晓丽, 刘占锋, 等, 2018. 亚热带地区不同人工林配置下土壤微生物量碳及微生物墒的年际动态[J]. 生态环境学报, 27(2): 224-231. |
| YI G T, WANG X L, LIU Z F, et al., 2018. Interannual dynamics of soil microbial biomass carbon under different plantations in Subtropical China[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 27(2): 224-231. | |
| [40] | 曾小平, 蔡锡安, 赵平, 等, 2008. 南亚热带丘陵3种人工林群落的生物量及净初级生产力[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 30(6): 148-152. |
| ZENG X P, CAI X A, ZHAO P, et al., 2008. Biomass and net primary productivity of three plantation communities in hilly land of lower subtropical China[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 30(6): 148-152. | |
| [41] | 张静, 蔡静如, 许建新, 等, 2017 蕨类植物在生态修复中的应用研究进展[J]. 安徽农业科学, 45(4): 69-71, 109. |
| ZHANG J, CAI J R, XU J X, et al., 2017 Advances in the application of ferns in ecological restoration[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 45(4): 69-71, 109. | |
| [42] | 张佩霞, 2011. 广东省鹤山市林业生态规划研究[D]. 广州: 华南植物园:24-50. |
| ZHANG P X, 2011. The conception planning study on ecological forestry in Heshan City,Guangdong Province[D]. Guangzhou: South China Botanical Garden Chinese Academy of Science:24-50. | |
| [43] | 张倩媚, 2011. 中国生态系统定位观测与研究数据集-森林生态系统卷:广东鼎湖山站 (1998—2008)[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社:85-93. |
| ZHANG Q M, 2011. Chinese Ecosystem Localization Observation and Research Dataset-Volume on Forest Ecosystems:Dinghu Guangdong (1998—2008)[M]. Beijing: China Agriculture Press:85-93. | |
| [44] | 张兴国, 2019. 我国人工林面积世界第一[N]. 中国绿色时报, 2019-4-15(01) |
| ZHANG X G, 2019. China has the largest plantation area in the world[N]. China Green Times, 2019-4-15(01) | |
| [45] |
周丽霞, 丁明懋, 2007. 土壤微生物学特性对土壤健康的指示作用[J]. 生物多样性, 15(2): 162-171.
DOI |
|
ZHOU L X, DING M M, 2007. Soil microbial characteristics as bioindicators of soil health[J]. Biodiversity Science, 15(2): 162-171.
DOI URL |
|
| [46] | 邹碧, 李志安, 丁永祯, 等, 2006. 南亚热带4种人工林凋落物动态特征[J]. 生态学报, 26(03): 715-721. |
| ZOU B, LI Z A, DING Y Z, et al., 2006. Litterfall of common plantations in south subtropical China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 26(3): 715-721. |
| [1] | 王馨雨, 高灯州, 刘博林, 王斌, 郑艳玲, 李小飞, 侯立军. 长江口水体化能自养固碳过程的潮周期变化特征及影响因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 733-743. |
| [2] | 陈科屹, 王建军, 何友均, 张立文. 黑龙江大兴安岭重点国有林区森林碳储量及固碳潜力评估[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(9): 1725-1734. |
| [3] | 王礼霄, 刘晋仙, 柴宝峰. 华北亚高山土壤细菌群落及氮循环对退耕还草的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1537-1546. |
| [4] | 王超, 杨倩楠, 张池, 李祥东, 陈静, 张晓龙, 陈金洁, 刘科学. 东南湿润区典型丹霞地貌土壤有机碳组分及其敏感性研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(6): 1132-1140. |
| [5] | 喻阳华, 吴银菇, 宋燕平, 李一彤. 不同林龄顶坛花椒林地土壤微生物浓度与生物量化学计量特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(6): 1160-1168. |
| [6] | 段文军, 李达, 李冲. 5种不同林龄尾巨桉人工林林下植物多样性及其影响因素分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(5): 857-864. |
| [7] | 刘红梅, 海香, 安克锐, 张海芳, 王慧, 张艳军, 王丽丽, 张贵龙, 杨殿林. 不同施肥措施对华北潮土区玉米田土壤固碳细菌群落结构多样性的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 715-722. |
| [8] | 梁蕾, 马秀枝, 韩晓荣, 李长生, 张志杰. 模拟增温下凋落物对大青山油松人工林土壤温室气体通量的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(3): 478-486. |
| [9] | 何亚婷, 谢和生, 何友均. 不同经营模式对蒙古栎天然次生林碳储量的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(2): 215-223. |
| [10] | 宋瑞朋, 杨起帆, 郑智恒, 习丹. 3种林下植被类型对杉木人工林土壤有机碳及其组分特征的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(12): 2283-2291. |
| [11] | 肖军, 雷蕾, 曾立雄, 李肇晨, 马成功, 肖文发. 不同经营模式对华北油松人工林碳储量的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(11): 2134-2142. |
| [12] | 邓玉娇, 王捷纯, 徐杰, 吴永琪, 陈靖扬. 广东省植被固碳量时空变化及气象贡献率研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(1): 1-8. |
| [13] | 宋贤冲, 蔡雪梅, 陈韬, 潘文, 石媛媛, 唐健, 曹继钊. 不同萌芽代次桉树根际和非根际土壤养分的变化特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(9): 1814-1820. |
| [14] | 祁雪连, 葛晓敏, 钱壮壮, 张康, 郑旭, 钱琦, 丁晖, 唐罗忠. 武夷山天然针阔混交林与毛竹人工林土壤性质差异[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(8): 1599-1606. |
| [15] | 王一荃, 周璋, 李意德, 陈德祥, 张涛, 杨繁. 不同热带森林空气负离子浓度评价研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(5): 898-906. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
