生态环境学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (5): 920-928.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2021.05.004
张乃木( ), 宋娅丽, 王克勤*, 张雨鉴, 潘禹, 郑兴蕊
), 宋娅丽, 王克勤*, 张雨鉴, 潘禹, 郑兴蕊
收稿日期:2020-09-09
出版日期:2021-05-18
发布日期:2021-08-06
通讯作者:
*作者简介:张乃木(1997年生),男(壮族),硕士研究生,研究方向为森林生态系统功能。E-mail:mg700nm@126.com
基金资助:
ZHANG Naimu( ), SONG Yali, WANG Keqin*, ZHANG Yujian, PAN Yu, ZHENG Xingrui
), SONG Yali, WANG Keqin*, ZHANG Yujian, PAN Yu, ZHENG Xingrui
Received:2020-09-09
Online:2021-05-18
Published:2021-08-06
摘要:
凋落物的养分元素释放在森林生态系统养分循环中起到了重要作用。森林生态系统受氮沉降的影响在近几十年内正显著增加,开展氮沉降背景下不同林分凋落物养分释放的研究,可为预测该区域森林生态系统养分循环及对氮沉降增加的响应提供理论依据。采用凋落物分解袋法,以滇中亚高山常绿阔叶林、高山栎(Quercus semicarpifolia)、华山松(Pinus armandii)和云南松(Pinus yunnanensis)4种林分的凋落叶和枝为研究对象,设置不同氮沉降水平,分别为对照(CK,N 0 g∙m-2∙a-1)、低氮(LN,N 5 g∙m-2∙a-1)、中氮(MN,N 15 g∙m-2∙a-1)和高氮(HN,N 30 g∙m-2∙a-1),探究4种林分凋落物营养元素释放特征、影响因素以及生态化学计量比对不同氮沉降水平的响应特征。结果表明:氮沉降12个月后,氮沉降抑制凋落叶和枝C、N元素的释放;除华山松外,氮沉降抑制其他3种林分类型P元素的释放;K元素的释放则在各林分中表现为LN促进,MN和HN抑制。各氮沉降水平降低了各林分凋落物的C/N(1.34%—37.15%)以及高山栎林和云南松林的C/P(2.29%—24.34%),LN与MN下华山松林、LN下常绿阔叶林的C/P显著提高(1.26%—7.37%)。双因素和冗余分析表明,4种林分下凋落叶和枝的元素释放受林分类型的影响最大,受施氮水平的影响次之。可见,模拟氮沉降在凋落叶和枝的分解过程中起到了抑制作用,且在不同林分间差异显著。
中图分类号:
张乃木, 宋娅丽, 王克勤, 张雨鉴, 潘禹, 郑兴蕊. 模拟氮沉降下滇中亚高山森林凋落物养分元素释放特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(5): 920-928.
ZHANG Naimu, SONG Yali, WANG Keqin, ZHANG Yujian, PAN Yu, ZHENG Xingrui. Nutrient Release Characteristics of Forest Litter under Simulated Nitrogen Deposition in the Subalpine of Central Yunnan, China[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(5): 920-928.
| 林分类型 Forest type | 林龄 Tree age/ a | 海拔 Altitude/ m | 土壤类型 Soil category | 郁闭度 Canopy density | 密度 Density/ (plant∙hm-2) | 平均胸径 Average diameter/cm | 平均树高 Average Height/m | 坡位 Slope position | 坡度 Slope gradient/(°) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 常绿阔叶林(CL) Evergreen broad-leaf forest | 15 | 2318 | 红壤 Red earth | 0.9 | 4628 | 11.3 | 14.2 | 中坡 Middle slope | 12 |
| 高山栎(GS) Quercus semicarpifolia forest | 15 | 2287 | 黄棕壤 Yellow brown earth | 0.9 | 1080 | 8.2 | 4.2 | 中坡 Middle slope | 15 |
| 华山松(HS) Pinus armandii forest | 19 | 2196 | 红壤 Red earth | 0.7 | 3466 | 19.5 | 14.0 | 中坡 Middle slope | 13 |
| 云南松(YN) Pinus yunnanensi forest | 23 | 2151 | 红壤 Red earth | 0.8 | 1437 | 11.2 | 9.5 | 中坡 Middle slope | 19 |
表1 各林分类型样地基本情况
Table 1 Basic situation of sample sites of different forest types
| 林分类型 Forest type | 林龄 Tree age/ a | 海拔 Altitude/ m | 土壤类型 Soil category | 郁闭度 Canopy density | 密度 Density/ (plant∙hm-2) | 平均胸径 Average diameter/cm | 平均树高 Average Height/m | 坡位 Slope position | 坡度 Slope gradient/(°) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 常绿阔叶林(CL) Evergreen broad-leaf forest | 15 | 2318 | 红壤 Red earth | 0.9 | 4628 | 11.3 | 14.2 | 中坡 Middle slope | 12 |
| 高山栎(GS) Quercus semicarpifolia forest | 15 | 2287 | 黄棕壤 Yellow brown earth | 0.9 | 1080 | 8.2 | 4.2 | 中坡 Middle slope | 15 |
| 华山松(HS) Pinus armandii forest | 19 | 2196 | 红壤 Red earth | 0.7 | 3466 | 19.5 | 14.0 | 中坡 Middle slope | 13 |
| 云南松(YN) Pinus yunnanensi forest | 23 | 2151 | 红壤 Red earth | 0.8 | 1437 | 11.2 | 9.5 | 中坡 Middle slope | 19 |
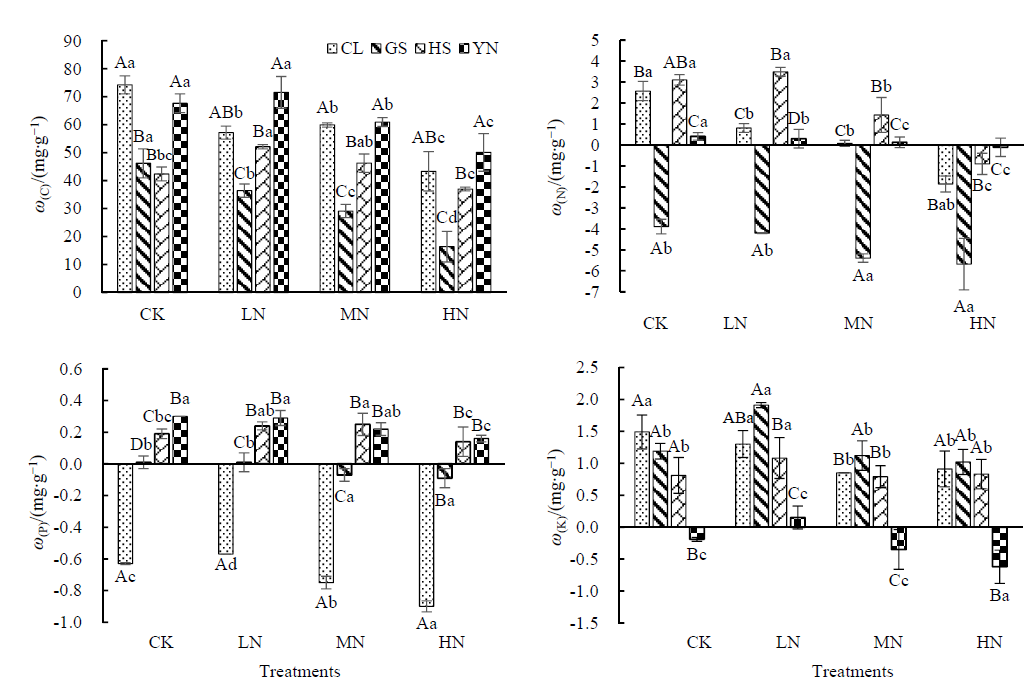
图1 不同氮处理12个月后凋落叶的养分含量特征对比CL:常绿阔叶林,GS:高山栎林,HS:华山松林,YN:云南松林;图中所示为初始元素含量与第12月元素含量之差
Fig. 1 Comparison of element contents of litter leaves under different nitrogen treatmentsCL: Evergreen broad-leaf forest, GS: Quercus semicarpifolia forest, HS: Pinus armandii forest, YN: Pinus yunnanensis forest. The difference between the initial element content and the element content in the 12th month is shown in the figure
| 林分 Forest | 元素 Element | 凋落叶 Litter leaves/% | 凋落枝 Litter branches/% | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | LN | MN | HN | CK | LN | MN | HN | ||
| CL | C | 46.09±1.37Bd | 48.83±1.27Dc | 50.56±1.11Cb | 55.32±0.96Da | 66.13±0.83Dc | 69.32±1.37Cb | 70.33±1.35Db | 72.35±0.64Da |
| N | 39.62±7.81Cc | 50.96±1.41Cb | 57.80±5.38BCb | 73.55±2.50Ba | 101.65±3.05Bb | 116.76±0.67Bab | 127.81±1.25Ba | 131.84±15.79Ba | |
| P | 103.72±4.3Ab | 104.94±3.8Ab | 128.85±10.7Aa | 144.63±9.70Aa | 73.71±1.24Abc | 75.04±9.68Ac | 72.22±1.34Aa | 65.27±10.17Aab | |
| K | 45.97±4.81Cc | 47.76±2.11Cbc | 52.75±1.37Bab | 54.97±2.19Ba | 76.03±9.98Aa | 78.98±0.55Aa | 83.25±3.03Aa | 84.59±12.09Aa | |
| GS | C | 57.77±1.32Ad | 62.41±1.11Ab | 61.55±1.47Ac | 67.92±1.10Aa | 76.83±0.59Bd | 78.53±0.99Ac | 80.52±1.27Ab | 82.12±1.19Aa |
| N | 93.97±9.16Aa | 101.58±7.18Aa | 107.64±11.28Aa | 118.07±15.23Aa | 154.79±1.85Ab | 168.31±6.58Aa | 177.24±4.9Aa | 169.02±7.05Aa | |
| P | 62.91±6.76Ba | 66.54±5.70Aa | 73.38±2.31Ba | 80.59±3.23Ba | 73.95±1.04Ca | 74.48±13.96Ba | 75.68±0.63Ba | 76.74±4.52Ba | |
| K | 56.49±1.86Ba | 54.85±2.16Ba | 58.33±5.15Ba | 63.29±5.12Ba | 73.79±0.56Aa | 71.81±4.92Aa | 78.12±4.99Aa | 79.71±12.67Aa | |
| HS | C | 59.29±1.37Ab | 55.98±0.76Cd | 57.00±1.10Bc | 60.94±1.22Ca | 79.02±1.13Aa | 75.21±1.04Bc | 77.45±1.44Bb | 79.49±1.14Ba |
| N | 46.32±2.96Cc | 42.19±0.99Dd | 54.85±0.81Cb | 71.69±2.31Ba | 78.39±21.49BCc | 104.75±2.64Cb | 92.29±3.01Cbc | 126.45±0.73Ba | |
| P | 53.06±1.85Cb | 48.33±1.17Cc | 47.62±3.37Cc | 57.52±1.40Ca | 76.1±3.40Ba | 75.11±10.75Ba | 76.90±8.18Ba | 77.65±8.37Ba | |
| K | 59.89±1.01Ba | 56.14±1.80Ba | 58.25±1.45Ba | 60.67±10.66Ba | 71.65±0.59Aab | 68.25±1.48Ab | 71.83±3.12Aab | 73.73±1.63Aa | |
| YN | C | 58.59±1.48Ac | 56.85±0.91Bc | 61.60±1.09Ab | 64.40±0.89Ba | 69.36±1.08Cc | 69.75±1.35Dd | 73.10±1.20Cb | 76.04±1.30Ca |
| N | 64.05±1.22Bb | 64.39±2.62Bb | 68.70±1.14Ba | 72.49±2.83Ba | 74.85±8.62Cc | 79.08±1.42Dc | 97.49±6.75Cb | 127.24±1.86Ba | |
| P | 51.43±4.09Ca | 51.56±7.03Ca | 57.53±8.85Ca | 61.97±5.58BCa | 41.05±3.70Dc | 42.68±6.04Cc | 49.15±1.46Cb | 58.04±1.74Ba | |
| K | 69.56±1.35Abc | 65.80±4.95Ac | 73.20±0.63Aab | 77.32±5.86Aa | 74.96±1.18Aa | 66.52±10.53Aa | 79.06±9.18Aa | 84.12±2.56Aa | |
表2 凋落叶和枝的元素残留率
Table 2 Element residue rate of leaves and branches of litter
| 林分 Forest | 元素 Element | 凋落叶 Litter leaves/% | 凋落枝 Litter branches/% | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | LN | MN | HN | CK | LN | MN | HN | ||
| CL | C | 46.09±1.37Bd | 48.83±1.27Dc | 50.56±1.11Cb | 55.32±0.96Da | 66.13±0.83Dc | 69.32±1.37Cb | 70.33±1.35Db | 72.35±0.64Da |
| N | 39.62±7.81Cc | 50.96±1.41Cb | 57.80±5.38BCb | 73.55±2.50Ba | 101.65±3.05Bb | 116.76±0.67Bab | 127.81±1.25Ba | 131.84±15.79Ba | |
| P | 103.72±4.3Ab | 104.94±3.8Ab | 128.85±10.7Aa | 144.63±9.70Aa | 73.71±1.24Abc | 75.04±9.68Ac | 72.22±1.34Aa | 65.27±10.17Aab | |
| K | 45.97±4.81Cc | 47.76±2.11Cbc | 52.75±1.37Bab | 54.97±2.19Ba | 76.03±9.98Aa | 78.98±0.55Aa | 83.25±3.03Aa | 84.59±12.09Aa | |
| GS | C | 57.77±1.32Ad | 62.41±1.11Ab | 61.55±1.47Ac | 67.92±1.10Aa | 76.83±0.59Bd | 78.53±0.99Ac | 80.52±1.27Ab | 82.12±1.19Aa |
| N | 93.97±9.16Aa | 101.58±7.18Aa | 107.64±11.28Aa | 118.07±15.23Aa | 154.79±1.85Ab | 168.31±6.58Aa | 177.24±4.9Aa | 169.02±7.05Aa | |
| P | 62.91±6.76Ba | 66.54±5.70Aa | 73.38±2.31Ba | 80.59±3.23Ba | 73.95±1.04Ca | 74.48±13.96Ba | 75.68±0.63Ba | 76.74±4.52Ba | |
| K | 56.49±1.86Ba | 54.85±2.16Ba | 58.33±5.15Ba | 63.29±5.12Ba | 73.79±0.56Aa | 71.81±4.92Aa | 78.12±4.99Aa | 79.71±12.67Aa | |
| HS | C | 59.29±1.37Ab | 55.98±0.76Cd | 57.00±1.10Bc | 60.94±1.22Ca | 79.02±1.13Aa | 75.21±1.04Bc | 77.45±1.44Bb | 79.49±1.14Ba |
| N | 46.32±2.96Cc | 42.19±0.99Dd | 54.85±0.81Cb | 71.69±2.31Ba | 78.39±21.49BCc | 104.75±2.64Cb | 92.29±3.01Cbc | 126.45±0.73Ba | |
| P | 53.06±1.85Cb | 48.33±1.17Cc | 47.62±3.37Cc | 57.52±1.40Ca | 76.1±3.40Ba | 75.11±10.75Ba | 76.90±8.18Ba | 77.65±8.37Ba | |
| K | 59.89±1.01Ba | 56.14±1.80Ba | 58.25±1.45Ba | 60.67±10.66Ba | 71.65±0.59Aab | 68.25±1.48Ab | 71.83±3.12Aab | 73.73±1.63Aa | |
| YN | C | 58.59±1.48Ac | 56.85±0.91Bc | 61.60±1.09Ab | 64.40±0.89Ba | 69.36±1.08Cc | 69.75±1.35Dd | 73.10±1.20Cb | 76.04±1.30Ca |
| N | 64.05±1.22Bb | 64.39±2.62Bb | 68.70±1.14Ba | 72.49±2.83Ba | 74.85±8.62Cc | 79.08±1.42Dc | 97.49±6.75Cb | 127.24±1.86Ba | |
| P | 51.43±4.09Ca | 51.56±7.03Ca | 57.53±8.85Ca | 61.97±5.58BCa | 41.05±3.70Dc | 42.68±6.04Cc | 49.15±1.46Cb | 58.04±1.74Ba | |
| K | 69.56±1.35Abc | 65.80±4.95Ac | 73.20±0.63Aab | 77.32±5.86Aa | 74.96±1.18Aa | 66.52±10.53Aa | 79.06±9.18Aa | 84.12±2.56Aa | |
| 状态 State | 林分 Forest | 计量比 Stoichiometric ratio | 凋落叶Litter leaves | 凋落枝Litter branches | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | LN | MN | HN | CK | LN | MN | HN | |||
| 分解前 Before decomposition | CL | C/N | 50±0.72Aa | 49±1.18Aa | 49±0.07Aa | 49±0.95Aa | 66±1.86Aa | 66±0.71Aa | 65±1.06Aa | 66±1.02Aa |
| GS | 57±1.12Aa | 57±9.17Aa | 56±6.1Aa | 56±4.76Aa | 117±2.94Aa | 114±2.81Aa | 116±0.45Aa | 115±2.92Aa | ||
| HS | 44±3.47Aa | 44±3.55Ab | 43±2.89Aa | 43±2.35Aa | 131±4.14Aa | 131±17.69Aa | 129±36.78Aa | 130±4.6Aa | ||
| YN | 70±3.1Aa | 70±2.76Aa | 69±0.27Aa | 70±1.86Aa | 209±2.76Aa | 211±6.85Aa | 204±7.91Aa | 201±2.08A | ||
| CL | C/P | 674±44.9Ab | 695±53.17Ab | 728±73.51Ab | 684±55.72Ab | 383±48.2Aa | 395±63.91Aa | 377±10.6Aa | 355±22.08Aa | |
| GS | 829±17.96Aa | 751±24.35Aa | 800±51.52Aa | 761±46.75Aa | 830±99.94Aa | 776±33.7Aa | 765±74.88Aa | 729±2.02Aa | ||
| HS | 458±47.34Aa | 453±37.87Aa | 462±79.85Aa | 437±25.63Aa | 569±79.71Aa | 597±24.8Aa | 621±38.4Aa | 508±8.43Aa | ||
| YN | 412±32.63Aa | 409±29.09Aa | 412±79.06Aa | 422±58.47Aa | 578±36.07Ab | 566±9.96Ab | 533±17.29Ab | 517±32.55Ab | ||
| 分解12个月后 After 12 months of decomposition | CL | C/N | 58±2.37Aa | 47±2.64ABa | 43±5.65Ba | 37±0.66Bb | 43±2.82Ab | 39±0.38ABb | 36±1.03Bb | 36±4.42Bb |
| GS | 35±4.06Ab | 35±3.15Ab | 32±0.11Ab | 32±6.33Ab | 58±5.08Ab | 53±5.59Ab | 53±26.57Ab | 56±3.32Ab | ||
| HS | 56±7.78Aa | 59±6.93Aa | 45±3.6Ba | 37±0.92Ba | 132±2.45Aa | 94±3.83ABb | 109±1.64ABb | 82±4.07Bb | ||
| YN | 64±3.26Aa | 63±4.02Aa | 62±1.24Aa | 62±1.81Aa | 191±39.28Aa | 183±6.57ABa | 153±16.31BCb | 120±3.29C | ||
| CL | C/P | 299±9.26Ba | 323±13.47Aa | 286±4.52Ba | 262±9.09Ca | 344±15.32Aa | 365±42.21Aa | 343±59.83Aa | 343±32.08Aa | |
| GS | 761±98.06Aa | 705±85.35Aa | 671±86.52Aa | 641±90.32Ba | 862±45.79Aa | 818±100.12Aa | 813±94.62Aa | 781±36.48Aa | ||
| HS | 512±68.18Aa | 525±38.15Aa | 553±138.19Aa | 462±12.43Aa | 591±52.71Aa | 598±61.42Aa | 626±57.6Aa | 520±29.43Aa | ||
| YN | 469±88.98Aa | 466±51.21Aa | 441±96.25Aa | 438±35.32Aa | 977±62.42Aa | 925±69.05Aa | 792±12.38Ba | 678±50.59Ba | ||
表3 分解后的凋落叶和枝化学计量比
Table 3 Stoichiometric ratio of leaf and branch of litter after decomposition
| 状态 State | 林分 Forest | 计量比 Stoichiometric ratio | 凋落叶Litter leaves | 凋落枝Litter branches | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | LN | MN | HN | CK | LN | MN | HN | |||
| 分解前 Before decomposition | CL | C/N | 50±0.72Aa | 49±1.18Aa | 49±0.07Aa | 49±0.95Aa | 66±1.86Aa | 66±0.71Aa | 65±1.06Aa | 66±1.02Aa |
| GS | 57±1.12Aa | 57±9.17Aa | 56±6.1Aa | 56±4.76Aa | 117±2.94Aa | 114±2.81Aa | 116±0.45Aa | 115±2.92Aa | ||
| HS | 44±3.47Aa | 44±3.55Ab | 43±2.89Aa | 43±2.35Aa | 131±4.14Aa | 131±17.69Aa | 129±36.78Aa | 130±4.6Aa | ||
| YN | 70±3.1Aa | 70±2.76Aa | 69±0.27Aa | 70±1.86Aa | 209±2.76Aa | 211±6.85Aa | 204±7.91Aa | 201±2.08A | ||
| CL | C/P | 674±44.9Ab | 695±53.17Ab | 728±73.51Ab | 684±55.72Ab | 383±48.2Aa | 395±63.91Aa | 377±10.6Aa | 355±22.08Aa | |
| GS | 829±17.96Aa | 751±24.35Aa | 800±51.52Aa | 761±46.75Aa | 830±99.94Aa | 776±33.7Aa | 765±74.88Aa | 729±2.02Aa | ||
| HS | 458±47.34Aa | 453±37.87Aa | 462±79.85Aa | 437±25.63Aa | 569±79.71Aa | 597±24.8Aa | 621±38.4Aa | 508±8.43Aa | ||
| YN | 412±32.63Aa | 409±29.09Aa | 412±79.06Aa | 422±58.47Aa | 578±36.07Ab | 566±9.96Ab | 533±17.29Ab | 517±32.55Ab | ||
| 分解12个月后 After 12 months of decomposition | CL | C/N | 58±2.37Aa | 47±2.64ABa | 43±5.65Ba | 37±0.66Bb | 43±2.82Ab | 39±0.38ABb | 36±1.03Bb | 36±4.42Bb |
| GS | 35±4.06Ab | 35±3.15Ab | 32±0.11Ab | 32±6.33Ab | 58±5.08Ab | 53±5.59Ab | 53±26.57Ab | 56±3.32Ab | ||
| HS | 56±7.78Aa | 59±6.93Aa | 45±3.6Ba | 37±0.92Ba | 132±2.45Aa | 94±3.83ABb | 109±1.64ABb | 82±4.07Bb | ||
| YN | 64±3.26Aa | 63±4.02Aa | 62±1.24Aa | 62±1.81Aa | 191±39.28Aa | 183±6.57ABa | 153±16.31BCb | 120±3.29C | ||
| CL | C/P | 299±9.26Ba | 323±13.47Aa | 286±4.52Ba | 262±9.09Ca | 344±15.32Aa | 365±42.21Aa | 343±59.83Aa | 343±32.08Aa | |
| GS | 761±98.06Aa | 705±85.35Aa | 671±86.52Aa | 641±90.32Ba | 862±45.79Aa | 818±100.12Aa | 813±94.62Aa | 781±36.48Aa | ||
| HS | 512±68.18Aa | 525±38.15Aa | 553±138.19Aa | 462±12.43Aa | 591±52.71Aa | 598±61.42Aa | 626±57.6Aa | 520±29.43Aa | ||
| YN | 469±88.98Aa | 466±51.21Aa | 441±96.25Aa | 438±35.32Aa | 977±62.42Aa | 925±69.05Aa | 792±12.38Ba | 678±50.59Ba | ||
| 变异类型 Variation type | 自由度 Degree of freedom | C残留率 Carbon remaining ratio | N残留率 Nitrogen remaining ratio | P残留率 Phosphorus remaining ratio | K残留率 Potassium remaining ratio | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | P | F | P | F | P | F | P | ||||||
| 凋落叶 Litter leaves | 林分类型 Forest types | 3 | 766.93 | <0.01 | 139.72 | <0.01 | 242.19 | <0.01 | 41.85 | <0.01 | |||
| 施氮水平 Nitrogen level | 3 | 233.34 | <0.01 | 24.45 | <0.01 | 15.27 | <0.01 | 6.66 | 0.001 | ||||
| 林分类型×施氮水平 Forest types×Nitrogen level | 9 | 24.25 | <0.01 | 1.69 | 0.133 | 2.99 | 0.011 | 0.55 | 0.826 | ||||
| 凋落枝 Litter branches | 林分类型 Forest types | 3 | 789.07 | <0.01 | 191.4 | <0.01 | 822.93 | <0.01 | 3.6 | 0.024 | |||
| 施氮水平 Nitrogen level | 3 | 187.57 | <0.01 | 39.92 | <0.01 | 14.5 | <0.01 | 4.04 | 0.015 | ||||
| 林分类型×施氮水平 Forest types×Nitrogen level | 9 | 29.46 | <0.01 | 5.22 | <0.01 | 5.06 | <0.01 | 0.53 | 0.844 | ||||
表4 凋落叶和枝元素残留率在林分类型和施氮水平差异的双因素方差分析
Table 4 Analysis of variance of two factors on the difference between nutrient surplus rate of leaves and branches of litter and the level of tree species and nitrogen application
| 变异类型 Variation type | 自由度 Degree of freedom | C残留率 Carbon remaining ratio | N残留率 Nitrogen remaining ratio | P残留率 Phosphorus remaining ratio | K残留率 Potassium remaining ratio | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | P | F | P | F | P | F | P | ||||||
| 凋落叶 Litter leaves | 林分类型 Forest types | 3 | 766.93 | <0.01 | 139.72 | <0.01 | 242.19 | <0.01 | 41.85 | <0.01 | |||
| 施氮水平 Nitrogen level | 3 | 233.34 | <0.01 | 24.45 | <0.01 | 15.27 | <0.01 | 6.66 | 0.001 | ||||
| 林分类型×施氮水平 Forest types×Nitrogen level | 9 | 24.25 | <0.01 | 1.69 | 0.133 | 2.99 | 0.011 | 0.55 | 0.826 | ||||
| 凋落枝 Litter branches | 林分类型 Forest types | 3 | 789.07 | <0.01 | 191.4 | <0.01 | 822.93 | <0.01 | 3.6 | 0.024 | |||
| 施氮水平 Nitrogen level | 3 | 187.57 | <0.01 | 39.92 | <0.01 | 14.5 | <0.01 | 4.04 | 0.015 | ||||
| 林分类型×施氮水平 Forest types×Nitrogen level | 9 | 29.46 | <0.01 | 5.22 | <0.01 | 5.06 | <0.01 | 0.53 | 0.844 | ||||
| 变异类型 Variation type | 凋落叶Litter leaves | 凋落枝Litter branches | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 解释量 Explains/% | 重要性 Contribution/% | 显著性 Significance | 解释量 Explains/% | 重要性 Contribution/% | 显著性 Significance | ||
| 林分类型 Forest types | 41.61 | 32.82 | 0.002 | 58.83 | 65.64 | 0.002 | |
| 施氮水平 Nitrogen level | 8.13 | 16.35 | 0.004 | 4.34 | 5.37 | 0.016 | |
表5 氮沉降和林分类型因子的解释的显著性检验结果
Table 5 Significance test results of explanation of nitrogen deposition and stand type factors
| 变异类型 Variation type | 凋落叶Litter leaves | 凋落枝Litter branches | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 解释量 Explains/% | 重要性 Contribution/% | 显著性 Significance | 解释量 Explains/% | 重要性 Contribution/% | 显著性 Significance | ||
| 林分类型 Forest types | 41.61 | 32.82 | 0.002 | 58.83 | 65.64 | 0.002 | |
| 施氮水平 Nitrogen level | 8.13 | 16.35 | 0.004 | 4.34 | 5.37 | 0.016 | |
| [1] |
ALLISON S D, HANSON C A, TRESEDER K K, 2007. Nitrogen fertilization reduces diversity and alters community structure of active fungi in boreal ecosystems[J]. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 39(8): 1878-1887.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
AUSTIN A, VIVANCO L, 2006. Plant litter decomposition in a semi-arid ecosystem controlled by photodegradation[J]. Nature, 442(7102): 555-558.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
DU E Z, JIANG Y, FANG J Y, et al., 2014. Inorganic nitrogen deposition in China's forests: Status and characteristics[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 98: 474-482.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
GALLOWAY J N, TOWNSEND A R, ERISMAN J W, et al., 2008. Transformation of the nitrogen cycle: Recent trends, questions, and potential solutions[J]. Science, 320(5878): 889-892.
DOI URL |
| [5] | KASPARI M, GARCIA M N, HARMS K E, et al., 2008. Multiple nutrients limit litterfall and decomposition in a tropical forest[J]. Ecology Letters, 11(1): 35-43. |
| [6] |
LIU X J, ZHANG Y, HAN W X, et al., 2013. Enhanced nitrogen deposition over China[J]. Nature, 494(7438): 459-462.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
MACKLON A E S, SIM A, 1994. Modifying Effects of Non-toxic Levels of Aluminium on the Uptake and Transport of Phosphate in Ryegrass[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 45(7): 887-894.
DOI URL |
| [8] | MAO Q G, LU X K, MO H, et al., 2017. Effects of simulated N deposition on foliar nutrient status, N metabolism and photosynthetic capacity of three dominant understory plant species in a mature tropical forest[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 610-611: 555-562. |
| [9] |
SALA O E, CHAPIN F S, ARMESTO J J, et al., 2000. Global Biodiversity Scenarios for the Year 2100J[J]. Science, 287(5459): 1770-1774.
DOI URL |
| [10] | VITOUSEK P M, ABER J D, HOWARTH R W, et al., 1997. Human alteration of the global nitrogen cycle: Sources and consequences[J]. Ecological Applications, 7(3): 737-750. |
| [11] |
XIA J Y, WAN S Q, 2008. Global response patterns of terrestrial plant species to nitrogen addition[J]. New Phytologist, 179(2): 428-439.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
YANG S, LIU W X, QIAO C L, et al., 2019. The decline in plant biodiversity slows down soil carbon turnover under increasingitrogen deposition in a temperate steppe[J]. Functional Ecology, 33(7): 1362-1372.
DOI URL |
| [13] | 陈美领, 陈浩, 毛庆功, 等, 2016. 氮沉降对森林土壤磷循环的影响[J]. 生态学报, 36(16): 4965-4976. |
| CHEN M L, CHEN H, MAO Q G, et al., 2016. Effect of nitrogen deposition on the soil phosphorus cycle in forest ecosystems: A review[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 36(16): 4965-4976. | |
| [14] | 陈翔, 2014. 模拟氮沉降对兴安落叶松凋落物养分释放动态的影响研究[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古农业大学. |
| CHEN X, 2014. Effects of simulated nitrogen deposition on litter decomposition of nutrient release of dynamic in larix gmelinii forest study[D]. Huhhot: Inner Mongolia Agricultural University. | |
| [15] | 邓仁菊, 杨万勤, 张健, 等, 2010. 季节性冻融期间亚高山森林凋落物的质量变化[J]. 生态学报, 30(3): 830-835. |
| DENG R J, YANG W Q, ZHANG J, et al., 2010. Changes in litter quality of subalpine forests during one freeze-thaw season[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 30(3): 830-835. | |
| [16] | 刁婵, 鲁显楷, 田静, 等, 2019. 长期氮添加对亚热带森林土壤微生物碳源代谢多样性的影响[J]. 生态学报, 39(18): 6622-6630. |
| DIAO C, LU X K, TIAN J, et al., 2019. Effects of long-term nitrogen addition on carbon metabolism diversity of soil microorganism in subtropical forest[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 39(18): 6622-6630. | |
| [17] | 葛晓改, 肖文发, 曾立雄, 等, 2014. 三峡库区马尾松林土壤-凋落物层酶活性对凋落物分解的影响[J]. 生态学报, 34(9): 2228-2237. |
| GE X G, XIAO W F, ZENG L X, et al., 2014. Eeffect of soil-litter layer enzyme activities on litter decomposition in Pinus massoniana plantation in Three Gorges Reservoir Area[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 34(9): 2228-2237. | |
| [18] | 韩雪, 王春梅, 蔺照兰, 2014. 模拟氮沉降对温带森林凋落物分解的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 23(9): 1503-1508. |
| HAN X, WANG C M, LIN Z L, 2014. Effects of simulated nitrogen deposition on temperate forest litter decomposition[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 23(9): 1503-1508. | |
| [19] | 李仁洪, 胡庭兴, 涂利华, 等, 2010. 华西雨屏区慈竹林凋落叶分解过程养分释放对模拟氮沉降的响应[J]. 林业科学, 46(8): 8-14. |
| LI R H, HU T X, TU L H, et al., 2010. Nutrient release in decomposition of leaf litter in neosinocalamus affinis stands in response to simulated nitrogen deposition in rainy area of western China[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 46(8): 8-14. | |
| [20] | 刘文飞, 樊后保, 袁颖红, 等, 2011. 氮沉降对杉木人工林凋落物大量元素归还量的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 25(1): 137-141. |
| LIU W F, FAN H B, YUAN Y H, et al., 2011. Macronutrient fluxes of the litter fall in Chinese fir plantation in response to simulated nitrogen deposition[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 25(1): 137-141. | |
| [21] | 刘文飞, 沈芳芳, 徐志鹏, 等, 2019. 氮沉降对杉木人工林凋落物叶分解过程中养分释放的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 28(4): 57-63. |
| LIU W F, SHEN F F, XU Z P, et al., 2019. Impacts of Nitrogen Deposition on Nutrient Release during Leaf Litter Decomposition in Cunninghamia lanceolata Plantations[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 28(4): 57-63. | |
| [22] | 卢广超, 邵怡若, 薛立, 2014. 氮沉降对凋落物分解的影响研究进展[J]. 世界林业研究, 27(1): 35-42. |
| LU G C, SHAO Y R, XUE L, 2014. Research progress in the effect of nitrogen deposition on litter decomposition[J]. World Forestry Research, 27(1): 35-42. | |
| [23] | 鲁显楷, 莫江明, 张炜, 等, 2019. 模拟大气氮沉降对中国森林生态系统影响的研究进展[J]. 热带亚热带植物学报, 27(5): 500-522. |
| LU X T, MO J M, ZHANG W, et al., 2019. Effects of simulated atmospheric nitrogen deposition on forest ecosystems in China: an overview[J]. Journal of Tropical and Subtropical Botany, 27(5): 500-522. | |
| [24] |
沈芳芳, 李燕燕, 刘文飞, 等, 2018. 长期氮沉降对杉木人工林叶、枝氮磷养分再吸收的影响[J]. 植物生态学报, 42(9): 926-937.
DOI |
|
SHEN F F, LI Y Y, LIU W F, et al., 2018. Responses of nitrogen and phosphorus resorption from leaves and branches to long-term nitrogen deposition in a Chinese fir plantation[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 42(9): 926-937.
DOI URL |
|
| [25] | 沈芳芳, 刘文飞, 吴建平, 等, 2019. 杉木人工林凋落物分解对氮沉降的响应[J]. 生态学报, 39(21): 8078-8090. |
| SHEN F F, LIU W F, WU J P, et al., 2019. Litter decomposition in a Chinese fir plantation in response to nitrogen deposition[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 39(21): 8078-8090. | |
| [26] | 宋学贵, 胡庭兴, 鲜骏仁, 等, 2007. 川西南常绿阔叶林凋落物分解及养分释放对模拟氮沉降的响应[J]. 应用生态学报, 18(10): 2167-2172. |
| SONG X G, HU T X, XIAN J R, et al., 2007. Responses of litter decomposition and nutrient release to simulated nitrogen deposition in an evergreen broad-leaved forest in southwestern Sichuan[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 18(10): 2167-2172. | |
| [27] | 铁烈华, 符饶, 张仕斌, 等, 2018. 模拟氮、硫沉降对华西雨屏区常绿阔叶林凋落叶分解速率的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 29(7): 2243-2250. |
| TIE L H, FU R, ZHANG S B, et al., 2018. Effects of simulated nitrogen and sulfur deposition on litter decomposition rate in an evergreen broad-leaved forest in the Rainy Area of Western China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 29(7): 2243-2250. | |
| [28] | 涂利华, 胡庭兴, 张健, 等, 2011. 模拟氮沉降对两种竹林不同凋落物组分分解过程养分释放的影响[J]. 生态学报, 31(6): 1547-1557. |
| TU L H, HU T X, ZHANG J, et al., 2011. Effect of simulated nitrogen deposition on nutrient release in decomposition of several litter fractions of two bamboo species[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 31(6): 1547-1557. | |
| [29] | 王晶苑, 张心昱, 温学发, 等, 2013. 氮沉降对森林土壤有机质和凋落物分解的影响及其微生物学机制[J]. 生态学报, 33(5): 1337-1346. |
|
WANG J Y, ZHANG X Y, WEN X F, et al., 2013. The effect of nitrogen deposition on forest soil organic matter and litter decompostion and the microbial mechanism[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 33(5): 1337-1346.
DOI URL |
|
| [30] | 吴承祯, 洪伟, 姜志林, 等, 2000. 我国森林凋落物研究进展[J]. 江西农业大学学报 (3): 405-410. |
| WU C Z, HONG W, JIANG Z L, et al., 2000. Advances in research of forest litter-fall in China[J]. Acta Agriculturae Universitatis Jiangxiensis (3): 405-410. | |
| [31] | 吴建平, 刘占锋, 2014. 环境因子对森林净生态系统生产力的影响[J]. 植物科学学报, 32(1): 97-104. |
| WU J P, LIU Z F, 2014. Effects of environmental factors on the productivity of forest net ecosystem[J]. Plant Science Journal, 32(1): 97-104. | |
| [32] | 肖银龙, 涂利华, 胡庭兴, 等, 2013. 模拟氮沉降对华西雨屏区苦竹林凋落物基质质量的影响[J]. 生态学报, 33(20): 6587-6594. |
|
XIAO Y L, TU L H, HU T X, et al., 2013. Effects of simulated nitrogen deposition on substrate quality of litterfall in aPleioblastus amarus plantation in Rainy Area of West China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 33(20): 6587-6594.
DOI URL |
|
| [33] | 杨万勤, 邓仁菊, 张健, 2007. 森林凋落物分解及其对全球气候变化的响应[J]. 应用生态学报, 18(12): 2889-2895. |
| YANG W Q, DENG R J, ZHANG J, 2007. Forest litter decomposition and its responses to global climate change[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 18(12): 2889-2895. | |
| [34] | 曾昭霞, 刘孝利, 王克林, 等, 2010. 桂西北喀斯特区原生林与次生林凋落物及养分归还特征比较[J]. 生态环境学报, 19(1): 146-151. |
| ZENG Z X, LIU X L, WANG K L, et al., 2010. Comparison of litterfall and nutrients return properties of primary and secon-dary forest ecosystems, the Karst region of Northwest Guangxi[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 19(1): 146-151. | |
| [35] | 张琴, 2014. 红松阔叶林凋落物分解特性研究[D]. 北京: 北京林业大学. |
| ZHANG Q, 2014. A study on decomposition characterics of the Korean Pine-broadleaved forest[D]. Beijing: Beijing Forestry University. | |
| [36] | 张雨鉴, 宋娅丽, 王克勤, 2019. 滇中亚高山森林乔木层各器官生态化学计量特征[J]. 生态学杂志, 38(6): 1669-1678. |
| ZHANG Y J, SONG Y L, WANG K Q, 2019. Ecological stoichiometry of various organs in the tree layer of subalpine forests in central Yunnan, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 38(6): 1669-1678. | |
| [37] | 张毓涛, 李吉玫, 李翔, 等, 2016. 模拟氮沉降对天山云杉凋落叶分解及其养分释放的影响[J]. 干旱区研究, 33(5): 966-973. |
| ZHANG Y T, LI J J, LI X, et al., 2016. Effects of simulated nitrogen deposition on decomposition and nutrient release of leaf litter of Picea schrenkiana[J]. Arid Zone Research, 33(5): 966-973. | |
| [38] | 郑世伟, 江洪, 2014. 氮沉降对森林生态系统影响的研究进展[J]. 浙江林业科技, 34(2): 56-64. |
| ZHENG S W, JIANG H, 2014. Research Progress on the effect of nitrogen deposition on forest ecosystem[J]. Journal of Zhejiang Forestry Science and Technology, 34(2): 56-64. | |
| [39] | 仲米财, 王清奎, 高洪, 等, 2013. 中亚热带主要树种凋落叶在杉木人工林中分解及氮磷释放过程[J]. 生态学杂志, 32(7): 1653-1659. |
| ZHONG M C, WANG Q K, GAO H, et al., 2013. Decomposition and nitrogen-and phosphorus release of leaf litters from main tree species in a mid-subtropical forest[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 32(7): 1653-1659. | |
| [40] | 周世兴, 肖永翔, 向元彬, 等, 2016. 模拟氮沉降对华西雨屏区天然常绿阔叶林凋落叶分解过程中基质质量的影响[J]. 生态学报, 36(22): 7428-7435. |
| ZHOU S X, XIAO Y X, XIANG Y B, et al., 2016. Effects of simulated nitrogen deposition on the substrate quality of foliar litter in a natural evergreen broad-leaved forest in the Rainy Area of Western China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 36(22): 7428-7435. |
| [1] | 肖博, 王邵军, 解玲玲, 王郑钧, 郭志鹏, 张昆凤, 张路路, 樊宇翔, 郭晓飞, 罗双, 夏佳慧, 李瑞, 兰梦杰, 杨胜秋. 蚂蚁筑巢定居活动对热带森林土壤氮库及组分分配的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(6): 1026-1036. |
| [2] | 张林, 齐实, 周飘, 伍冰晨, 张岱, 张岩. 北京山区针阔混交林地土壤有机碳含量的影响因素研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 450-458. |
| [3] | 陈治中, 昝梅, 杨雪峰, 董煜. 新疆森林植被碳储量预测研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(2): 226-234. |
| [4] | 何亚婷, 何友均, 王鹏, 谢和生. 不同经营模式对蒙古栎林土壤有机碳组分的长效性影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 11-17. |
| [5] | 宋瑞朋, 杨起帆, 郑智恒, 习丹. 3种林下植被类型对杉木人工林土壤有机碳及其组分特征的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(12): 2283-2291. |
| [6] | 杨世福, 马玲玲, 陈芸芝, 唐旭利. 鼎湖山季风常绿阔叶林演替系列土壤细菌群落的变化特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(12): 2275-2282. |
| [7] | 韩鑫, 袁春阳, 李济宏, 洪宗文, 刘宣, 杜婷, 李晗, 游成铭, 谭波, 朱鹏, 徐振锋. 树种和土层对土壤无机氮的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(11): 2143-2151. |
| [8] | 肖军, 雷蕾, 曾立雄, 李肇晨, 马成功, 肖文发. 不同经营模式对华北油松人工林碳储量的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(11): 2134-2142. |
| [9] | 刘佩伶, 刘效东, 冯英杰, 苏宇乔, 甘先华, 张卫强. 新丰江水库库区水源涵养林土壤饱和导水率特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(10): 1993-2001. |
| [10] | 李勋, 崔宁洁, 张艳, 覃宇, 张健. 马尾松与乡土阔叶树种凋落叶纤维素、总酚以及缩合单宁降解的混合效应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(9): 1813-1822. |
| [11] | 张林, 周飘, 齐实, 张岱, 伍冰晨, 崔冉冉. 侧柏人工林林分空间结构对林下草本多样性的差异性影响及其关联度[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(9): 1794-1801. |
| [12] | 秦艳培, 徐少君, 田耀武. 黄河流域河南段植被和土壤及其碳密度空间分异研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(9): 1745-1753. |
| [13] | 陈科屹, 王建军, 何友均, 张立文. 黑龙江大兴安岭重点国有林区森林碳储量及固碳潜力评估[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(9): 1725-1734. |
| [14] | 王磊, 温远光, 周晓果, 朱宏光, 孙冬婧. 尾巨桉与红锥混交对林下植被和土壤性质的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(7): 1340-1349. |
| [15] | 符裕红, 张代杰, 项蛟, 周焱, 黄宗胜, 喻理飞. 喀斯特不同地下生境剖面植物根系拓扑结构特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(5): 865-874. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
